2. 青岛大学 自动化工程学院,山东 青岛 266071
2. School of Automation Engineering, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, China
多智能体系统的一致性问题作为多智能体系统协作控制的基本问题,因具有重要的理论和现实意义受到国内外研究人员的广泛关注[1-9]。一致性是指随着时间的变化,系统中智能体通过合作或竞争的方式调节各自的目标与行为,最终使智能个体的部分或全部状态(如:位置、速度等)都收敛到某个共同的值。目前多智能体系统在许多领域中得到广泛应用,如机器人系统的编队控制、无人机的协作控制、卫星簇的姿态调整、传感器网络的目标跟踪等。
然而随着系统规模的增加和复杂度的提高,单一平衡点不能满足控制的要求,因此有学者提出了分组一致性的概念,即同一子系统中所有智能体收敛至一个状态,不同子系统中智能体收敛至不同状态[10-12]。以上的研究成果都是针对具有非负连接权重的多智能体系统获得的,在很多情况下系统中还存在着一种特殊的“共识”现象,即所有的智能体最终能达到大小相同,符号相反的状态。可以理解为,不同智能体之间有的具有合作关系,有的具有敌对关系[13-16]。2013年,Altafini[13]在对具有敌对关系的多智能体系统的研究中,给出了系统达到二分一致性的定义。杜明骏等[14]研究了具有敌对关系且含通讯时滞的多智能体系统的二分一致性。上述文献研究的都是由具有相同动态方程的智能体构成的同质多智能体系统。而实际上,受到各种因素的限制,自然界的个体和人造工程在功能和结构上都存在差异,发生耦合的每个智能体的动态方程可能不同,导致其系统描述的是混合多种动态方程的复杂系统。因此研究具有一阶和二阶智能体组成的异质多智能体系统是很有必要的[17-19]。刘聪等[17]讨论了具有有向生成树的离散时间异质多智能体系统的一致性,但对控制增益的要求为
基于上面的研究,本文考虑具有包含一棵有向生成树和结构平衡拓扑结构的由一阶和二阶多智能体混合而成的多智能体系统的二分一致性问题,对连续和离散系统均进行了讨论。
1 预备知识本文中使用有向图表示多智能体系统中智能体之间形成的网络拓扑。用
定义1 (结构平衡)[13] 图
1)
2)
| $ {a_{ij}} \leqslant 0,\forall {v_i} \in {V_q},{v_j} \in {V_r},q \ne r(q,r \in \{ 1,2\} ) 。$ |
定义2 (规范变换)[13] 借助正交矩阵
记
引理1[2] 给定矩阵
考虑由
假设1 本文考虑的拓扑结构,按如下分组满足结构平衡关系,设指标集
首先,考虑连续多智能体系统,其个体的动态方程为
| $\left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{{\dot x}_i}(t) = {v_i}(t),\;\;{{\dot v}_i}(t) = {u_i}(t),\;\;i \in {I_1}} \\ {{{\dot x}_i}(t) = {u_i}(t),\;\;i \in {I_2}} \end{array}} \right.$ | (1) |
式中:
基于假设1设计如下的二分一致性协议:
| $\left\{ \begin{array}{l} {u_i}(t) = - \alpha {v_i}(t) + {\alpha ^2}\left[\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i1}}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_j}(t) - {y_i}(t)) - \right. \\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \left. \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i2}}} \mid {a_{ij}}\mid ({y_i}(t) + {x_j}(t))\right],\;\;i \in {I_1} \\ {u_i}(t) = \alpha \left[\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i2}}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_j}(t) - {x_i}(t)) - \right. \\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \left. \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i1}}} \mid {a_{ij}}\mid ({x_i}(t) + {x_j}(t))\right],\;\;i \in {I_2} \\ \end{array} \right.$ | (2) |
式中:
其次,考虑离散多智能体系统,其个体的动态方程为
| $\left\{ \begin{array}{l} {x_i}(k + 1) = {x_i}(k) + T{v_i}(k),i \in {I_1} \\ {v_i}(k + 1) = {v_i}(k) + T{u_i}(k),i \in {I_1} \\ {x_i}(k + 1) = {x_i}(k) + T{u_i}(k),i \in {I_2} \\ \end{array} \right.$ | (3) |
式中:
在文献[19]中,针对系统(3)设计的二分一致性协议为
| $\left\{ \begin{array}{l} {u_i}(k) = - \alpha {v_i}(k) + {\alpha ^2}\left[\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i1}}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_j}(k) - {x_i}(k)) + \right. \\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \left. \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i2}}} {{a_{ij}}} {x_j}(k)\right],\;\;\;i \in {I_1} \\ {u_i}(k) = \alpha \left[\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i2}}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_j}(k) - {x_i}(k)) + \right. \\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \left. \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i1}}} {{a_{ij}}} {x_j}(k)\right],\;\;\;\;i \in {I_2} \\ \end{array} \right.$ | (4) |
其中
假定1
假定2 除去两个单的零特征值外,图
在本文中,基于假设1,删除了对上述两条假定的要求并设计了如下的二分一致性协议:
| $\left\{ \begin{array}{l} {u_i}(k) = - \alpha {v_i}(k) + {\alpha ^2}\left[\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i1}}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_j}(k) - {y_i}(k)) - \right. \\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \left. \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i2}}} \mid {a_{ij}}\mid ({y_i}(k) + {x_j}(k))\right],\;\;i \in {I_1} \\ {u_i}(k) = \alpha \left[\displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i2}}} {{a_{ij}}} ({x_j}(k) - {x_i}(k)) - \right. \\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \left. \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j \in {N_{i1}}} \mid {a_{ij}}\mid ({x_i}(k) + {x_j}(k))\right],\;i \in {I_2} \\ \end{array} \right.$ | (5) |
式中:
注释1 在式(4)协议作用下,式(3)系统虽然能够实现二分一致性,但是两组最终的收敛状态没有任何关系。而在式(5)协议作用下,式(3)系统最终实现二分一致性,并且两组的收敛值互为相反数,这样的收敛状态具有更好的应用价值。
定义3 如果对于式(1)系统的任何初始条件满足:
| $\left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {\mathop {\lim }\limits_{t \to \infty } \Bigg| {x_i}(t) - \dfrac{{| {a_{ij}}| }}{{{a_{ij}}}}{x_j}(t)\Bigg| = 0,}&{\forall i \in {I_1},j \in I}\\ {\mathop {\lim }\limits_{t \to \infty } | {v_i}(t)| = 0,}\quad{\forall i \in {I_1}}\\ {\mathop {\lim }\limits_{t \to \infty } \Bigg| {x_i}(t) - \dfrac{{| {a_{ij}}| }}{{{a_{ij}}}}{x_j}(t)\Bigg| = 0,}&{\forall i \in {I_2},j \in I} \end{array}} \right.$ | (6) |
则称式(1)系统渐近实现了二分一致性。
如果对于式(3)系统的任何初始条件满足:
| $\left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {\mathop {\lim }\limits_{k \to \infty } \Bigg| {x_i}(k) - \dfrac{{| {a_{ij}}| }}{{{a_{ij}}}}{x_j}(k)\Bigg| = 0,}&{\forall i \in {I_1},j \in I}\\ {\mathop {\lim }\limits_{k \to \infty } | {v_i}(k)| = 0,\;}\quad{\forall i \in {I_1}}\\ {\mathop {\lim }\limits_{k \to \infty } \Bigg| {x_i}(k) - \dfrac{{| {a_{ij}}| }}{{{a_{ij}}}}{x_j}(k)\Bigg| = 0,}&{\forall i \in {I_2},j \in I} \end{array}} \right.$ | (7) |
则称式(3)系统渐近实现了二分一致性。
3 一致性分析基于所考虑多智能体系统的分组,将图
| ${{A}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{{A}}_1}}&{{{{A}}_2}} \\ {{{{A}}_3}}&{{{{A}}_4}} \end{array}} \right]$ | (8) |
式中:
对连续式(1)系统,令
| $\dot \xi = - {\bar{ L}}\xi $ | (9) |
其中
| ${\bar{ L}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\alpha {{{I}_m}}}&{ - \alpha {{{I}}_m}}&{{{0}}} \\ { - \alpha {{\tilde{{A}}}_1}}&{\alpha ({{{\varLambda}} _1} + {{{\varLambda}} _2})}&{\alpha {{\tilde{{A}}}_{\rm{2}}}} \\ {\alpha {{\tilde{{A}}}_{\rm{3}}}}&{{{0}}}&{ - \alpha {{\tilde{{A}}}_{\rm{4}}} + \alpha {{{\varLambda}} _3} + \alpha {{{\varLambda}} _4}} \end{array}} \right]$ | (10) |
式中:
根据假设
| ${\dot{\hat{\xi}}} = - {\hat{ L}}{\hat{\xi}} ,$ | (11) |
其中
| ${\hat{ L}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\alpha {{{I}}_m}}&{ - \alpha {{{I}}_m}}&{\bf 0} \\ { - \alpha {{{\tilde{ A}}}_1}}&{\alpha ({{{\varLambda}} _1} + {{{\varLambda}} _2})}&{ - \alpha {{{\tilde{ A}}}_{\rm{2}}}} \\ { - \alpha {{{\tilde{ A}}}_3}}&{\bf 0}&{ - \alpha {{{\tilde{ A}}}_4} + \alpha {{{\varLambda}} _3} + \alpha {{{\varLambda}} _4}} \end{array}} \right]$ |
易知
引理2 假定假设1成立,图
文献[18]中针对切换有向拓扑给出了该引理的证明。针对固定拓扑,本文运用将图
证明 对
| $\begin{gathered} {\hat{ L}} \to \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\alpha {{{I}}_m}}&{\bf 0} \\ {\bf 0}&{\alpha ({{{\varLambda}} _1} + {{{\varLambda}} _2}) - \alpha {{{\tilde{ A}}}_1}} \\ {\bf 0}&{ - \alpha {{{\tilde{ A}}}_3}} \end{array}} \right.\left. {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\bf 0} \\ { - \alpha {{{\tilde{ A}}}_2}} \\ { - \alpha {{{\tilde{ A}}}_4} + \alpha {{{\varLambda}} _3} + \alpha {{{\varLambda}} _4}} \end{array}} \right] \;\;\;\; \buildrel \Delta \over = \alpha \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{{I}}_m}}&{\bf{0}} \\ {\bf{0}}&{{L}} \end{array}} \right] \\ \end{gathered} $ |
从而
通过针对式(9)系统的规范变换,我们实现了系统连接权重符号的改变,将具有敌对关系的式(9)系统转换为具有非负连接权重的式(11)系统。根据系统渐近实现一致性的定义,容易得出下面的引理。
引理3 式(1)系统在式(2)协议作用下渐近实现二分一致性;当且仅当式(11)系统能够渐近实现一致性。
针对一般一致性问题,文献[2]中有如下引理:
引理4[2] 在固定拓扑下,连续时间多智能体系统
下面给出保证式(1)系统二分一致性成立的一个定理。
定理1 假定假设1成立。式(1)系统在式(2)协议作用下渐近实现二分一致性的充要条件是图
证明 在假设1成立的条件下,由引理3,式(1)系统在式(2)协议作用下渐近实现二分一致性等价于式(11)系统能够渐近实现一致性。由引理4,式(11)系统能够渐近实现一致性当且仅当图
对离散式(3)系统,令
| $\left\{ \begin{gathered} {{{x}}_m}(k + 1) = (1 - \alpha T){{{x}}_m}(k) + \alpha T{{{y}}_m}(k) \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \\ {{{y}}_m}(k + 1) = {{{I}}_m}{{{y}}_m}(k) + \alpha T[{{{A}}_1}{{{x}}_m}(k) - {{{\varLambda}} _1}{{{y}}_m}(k) +\;\; \\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; {{{A}}_2}{{{x}}_f}(k) - {{{\varLambda}} _2}{{{y}}_m}(k)] \\ {{{x}}_f}(k + 1) = {{{I}}_{n - m}}{{{x}}_f}(k) + \alpha T[{{{A}}_4}{{{x}}_f}(k) - {{{\varLambda}} _4}{{{x}}_f}(k) +\\ \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; {{{A}}_3}{{{x}}_m}(k) - {{{\varLambda}} _3}{{{x}}_f}(k)] \\ \end{gathered} \right.$ | (12) |
式中:
令
| ${ z}(k + {\rm{1}}) = { U}{ z}(k)$ | (13) |
其中
| $ \begin{gathered} {{U}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {(1 - \alpha T){{{I}}_m}}&{\alpha T{{{I}}_m}} \\ {\alpha T{{{\tilde{ A}}}_1}}&{{{{I}}_m} - \alpha T({{{\varLambda}} _1} + {{{\varLambda}} _2})} \\ { - \alpha T{{{\tilde{ A}}}_3}}&{\bf 0} \end{array} \begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\bf 0} \\ { - \alpha T{{{\tilde{ A}}}_2}} \\ {{{{I}}_{n - m}} + \alpha T({{{\tilde{ A}}}_4} - {{{\varLambda}} _3} - {{{\varLambda}} _4})} \end{array}} \right] \\ \end{gathered} $ |
基于假设1,令
| ${\tilde{ z}}(k + 1) = {\tilde{ U}} {\tilde{ z}}(k)$ | (14) |
其中
| $\begin{gathered} {\tilde{ U}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {(1 - \alpha T){{{I}}_m}}&{\alpha T{{{I}}_m}} \\ {\alpha T{{{\tilde{ A}}}_1}}&{{{{I}}_m} - \alpha T({{{\varLambda}} _1} + {{{\varLambda}} _2})} \\ {\alpha T{{{\tilde{ A}}}_3}}&{\bf 0} \end{array}\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\bf 0} \\ {\alpha T{{{\tilde{ A}}}_2}} \\ {{{{I}}_{n - m}} + \alpha T({{{\tilde{ A}}}_4} - {{{\varLambda}} _3} - {{{\varLambda}} _4})} \end{array}} \right] \\ \end{gathered} $ |
对矩阵
| $ \begin{array}{l} {\tilde{ U}} \to \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {(1 - \alpha T){{{I}}_m}}&{\bf 0} \\ {\alpha T{{{\tilde{ A}}}_3}}&{{{{I}}_{n - m}} + \alpha T({{{\tilde{ A}}}_4} - {{{\varLambda}} _3} - {{{\varLambda}} _4})} \\ {\alpha T{{{\tilde{ A}}}_1}}&{\alpha T{{{\tilde{ A}}}_2}} \end{array}\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\alpha T{{{I}}_m}} \\ {\bf 0} \\ {{{{I}}_m} - \alpha T({{{\varLambda}} _1} + {{{\varLambda}} _2})} \end{array}} \right] {\rm{ }} \triangleq {\hat{ U}} \\ \end{array} $ |
易知
| ${\hat{ z}}(k + 1) = {\hat{ U}}{\hat{ z}}(k)$ | (15) |
式中:
可将矩阵
| ${{V}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{{I}}_m}}&{\bf 0}&{ - {{{I}}_m}} \\ { - {{{\tilde{ A}}}_3}}&{ - {{{\tilde{ A}}}_4} + {{{\varLambda}} _3} + {{{\varLambda}} _4}}&{\bf{0}} \\ { - {{{\tilde{ A}}}_1}}&{ - {{{\tilde{ A}}}_2}}&{{{{\varLambda}} _1} + {{{\varLambda}} _2}} \end{array}} \right]$ |
显然地,
类似于引理3,通过针对式(13)系统的规范变换,容易得出下面的引理。
引理5 式(3)系统在式(5)协议作用下渐近实现二分一致性,当且仅当式(15)系统能够渐近实现一致性。
引理6 假定假设1成立且图
证明 充分性:由于
必要性:记
定理2 假定假设1成立且图G包含一棵有向生成树。式(3)系统在式(5)协议作用下渐近实现二分一致性当且仅当αT满足
证明 根据引理6,定理2等价于:式(3)系统在式(5)协议作用下渐近实现二分一致性当且仅当矩阵
由于假设1成立且图
| $ \begin{gathered} { P} = [{{{\varphi}} _{r1}},{{{\varphi}} _{r2}}, \cdots ,{{{\varphi}} _{r(n + m)}}] \in {{ R}^{(n + m) \times (n + m)}}\\ {{ P}^{ - 1}} = {[{{\varphi}} _{l1}^{\rm{T}},{{\varphi}} _{l2}^{\rm{T}}, \cdots ,{{\varphi}} _{l(n + m)}^{\rm{T}}]^{\rm{T}}} \in {{ R}^{(n + m) \times (n + m)}} \end{gathered} $ |
式中:
充分性:因为矩阵
| $ {\hat{{\textit{z}}}}(k)={\hat{ U}} {\hat{{\textit{z}}}}(k - 1) = {{\hat{ U}}^2} {\hat{{\textit{z}}}}(k - 2)= \cdots ={{\hat{ U}}^k} {\hat{{\textit{z}}}}(0) $ |
则
| $\mathop {\lim }\limits_{k \to \infty } {\hat{ z}}(k) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{k \to \infty } \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{{\hat{ x}}}_n}(k)} \\ {{{{\hat{ y}}}_m}(k)} \end{array}} \right] = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{k \to \infty } {{\hat{ U}}^k}{\hat{ z}}(0) = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{{\textit{1}}}_n}{{\varphi}} _{l1}^{\rm{T}}{\hat{ z}}(0)} \\ {{{{\textit{1}}}_m}{{\varphi}} _{l1}^{\rm{T}}{\hat{ z}}(0)} \end{array}} \right]$ |
其中
必要性:由引理5,式(3)系统渐近实现二分一致性等价于式(15)系统渐近实现一致性,即
考虑由
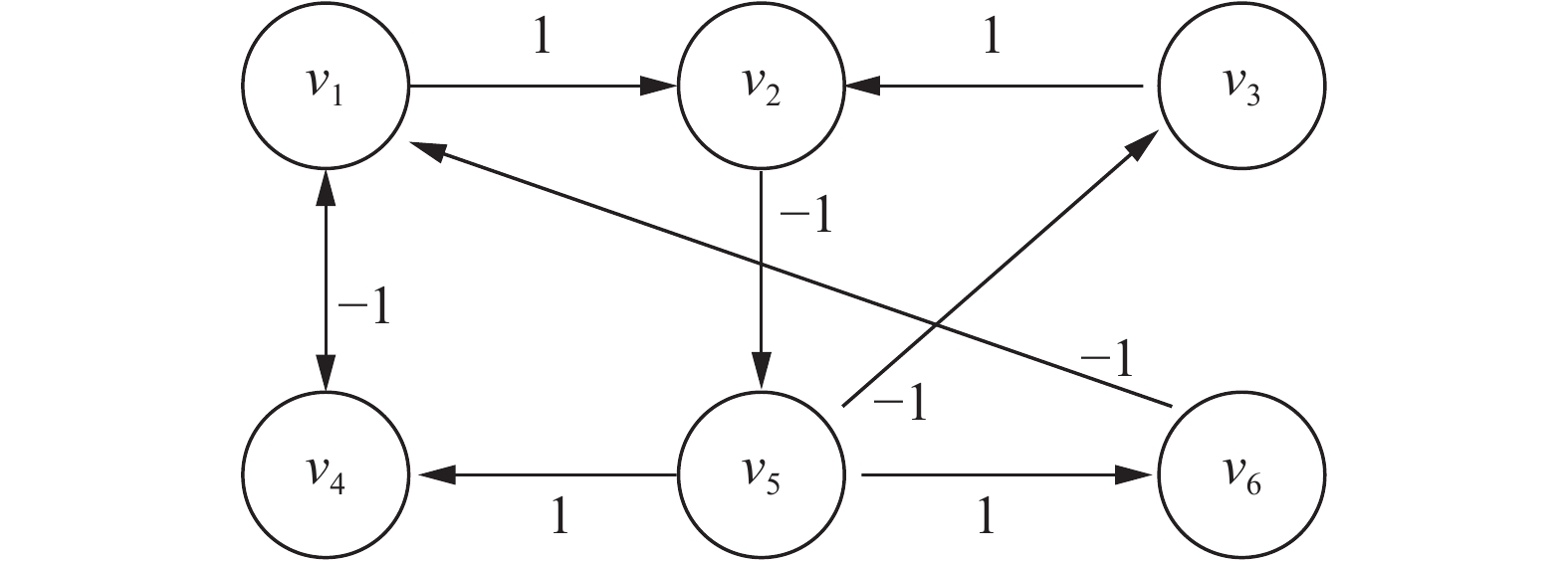
|
Download:
|
| 图 1 有向拓扑图−包含一棵有向生成树 Fig. 1 Directed topology which contains a directed spanning tree | |

|
Download:
|
| 图 2 系统 (1) 中每个智能体的位置 Fig. 2 Position of each agent of system (1) | |
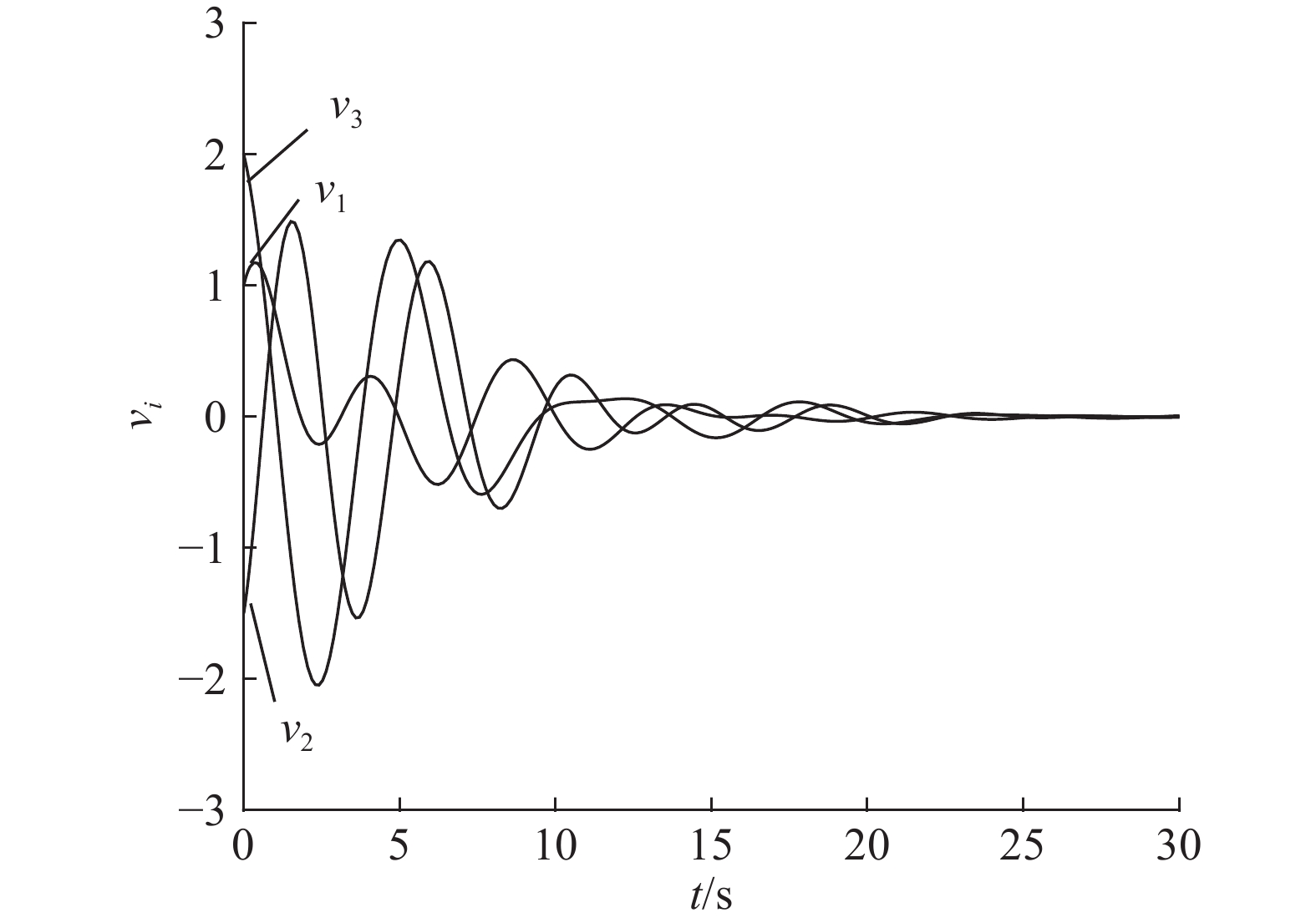
|
Download:
|
|
图 3 系统 (1) 分组
|
|
选取
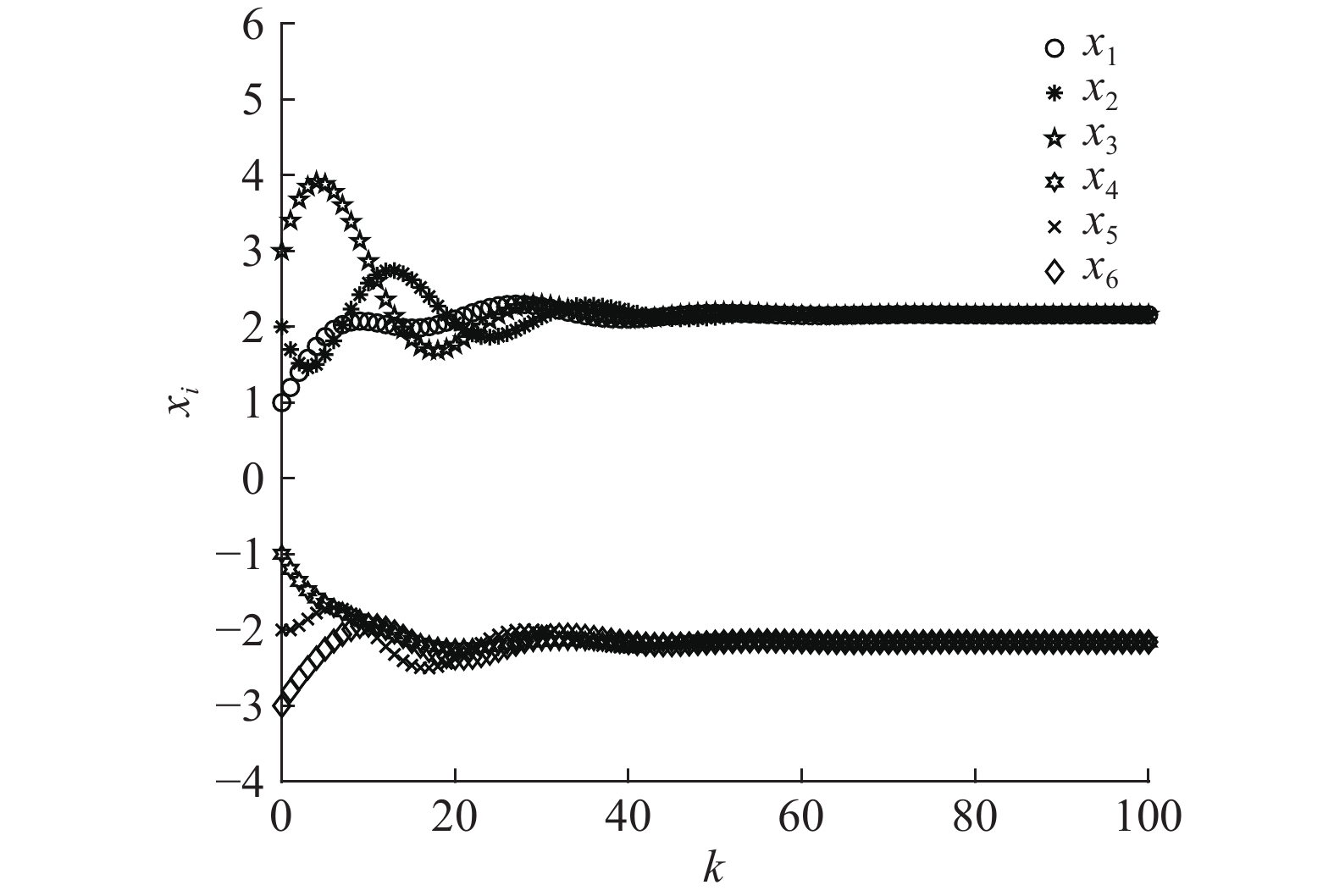
|
Download:
|
|
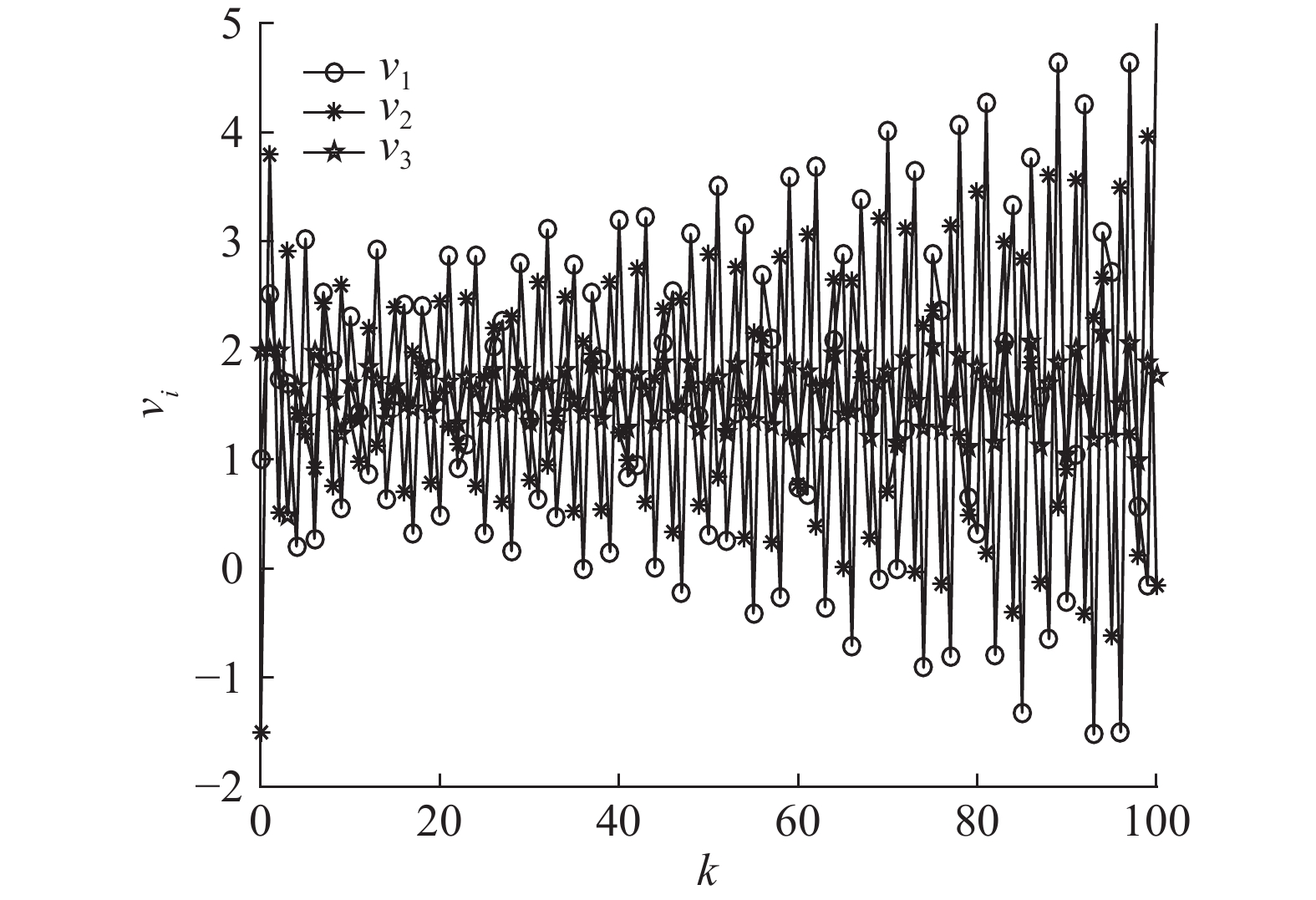
图 4 系统 (3) 中每个智能体的位置 (
|
|
|
Download:
|
|
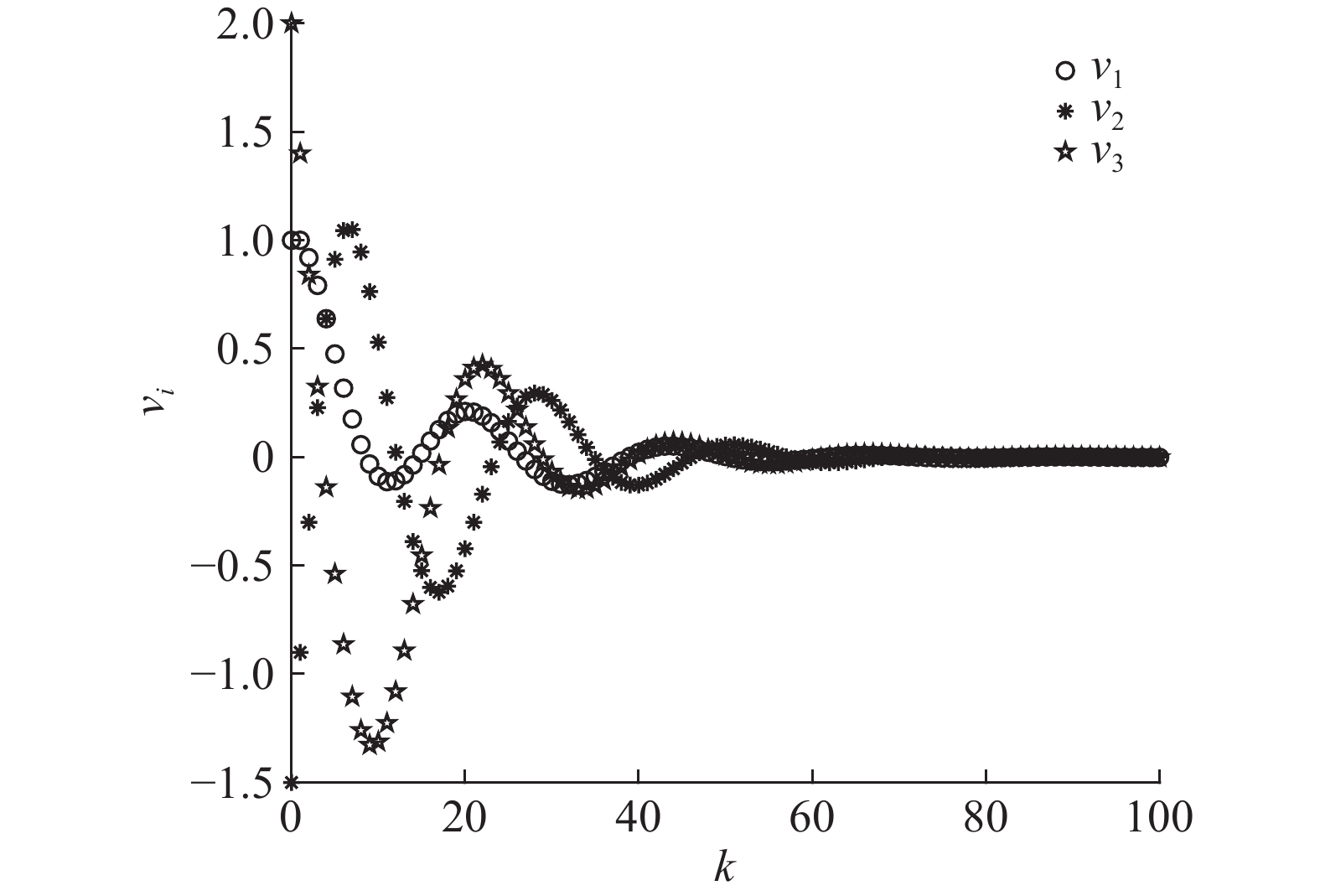
图 5 系统 (3) 分组
|
|
|
Download:
|
|
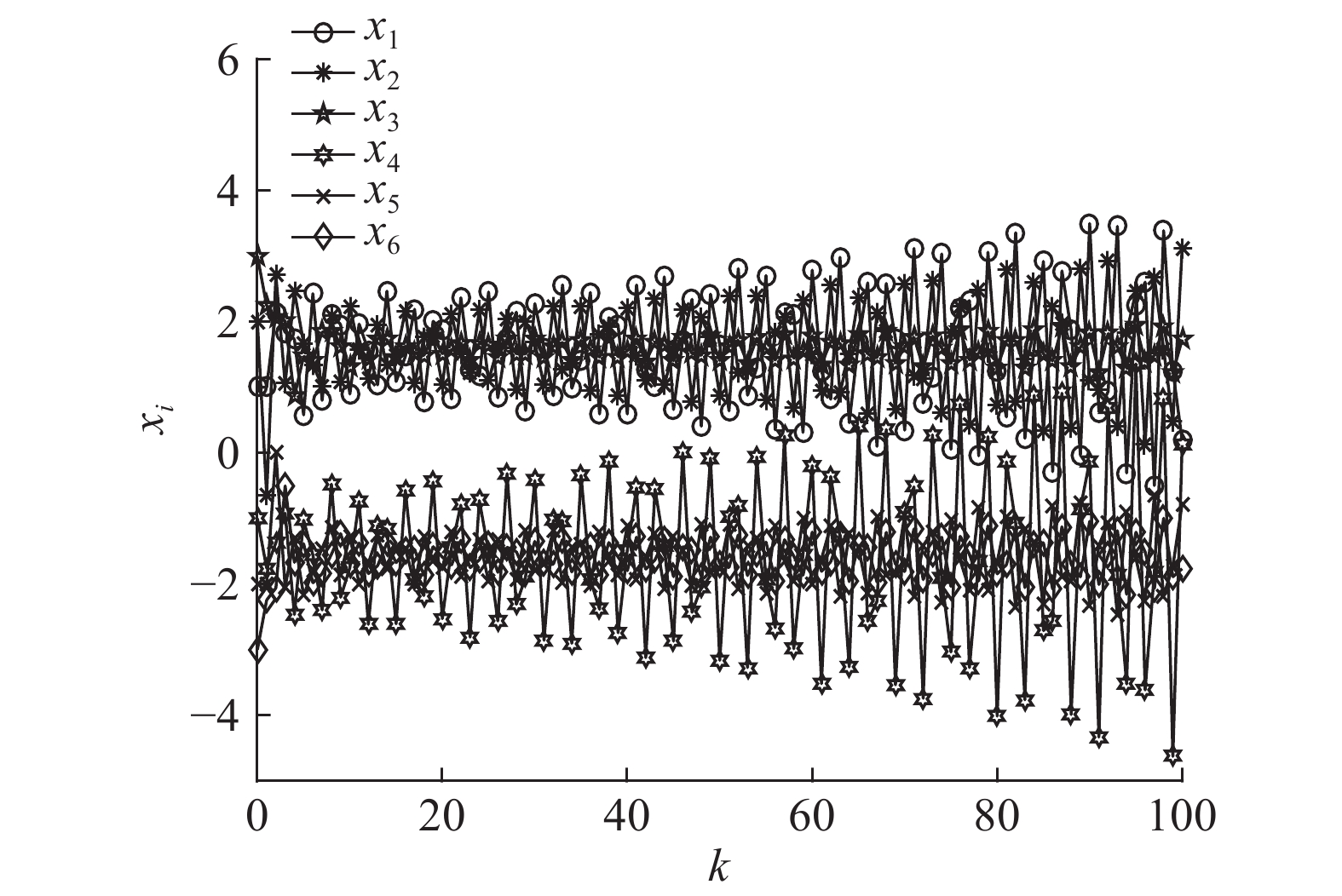
图 6 系统 (3) 中每个智能体的位置 (
|
|
|
Download:
|
|
图 7 系统(3)分组
|
|
本文研究了由一阶和二阶智能体混合而成的异质多智能体系统的二分一致性问题。研究的系统具有包含有向生成树和结构平衡的拓扑结构。在设计的二分一致性协议中利用了特殊变量
| [1] |
OLFATI-SABER R, MURRAY R M. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays[J]. IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2004, 49(9): 1520-1533. DOI:10.1109/TAC.2004.834113 ( 0) 0)
|
| [2] |
REN Wei, BEARD R W. Consensus seeking in multiagent systems under dynamically changing interaction topologies[J]. IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2005, 50(5): 655-661. DOI:10.1109/TAC.2005.846556 ( 0) 0)
|
| [3] |
REN Wei, ATKINS E. Distributed multi-vehicle coordinated control via local information exchange
[J]. International journal of robust and nonlinear control, 2007, 17(10/11): 1002-1033. ( 0) 0)
|
| [4] |
XIE Guangming, WANG Long. Consensus control for a class of networks of dynamic agents[J]. International journal of robust and nonlinear control, 2007, 17(10/11): 941-959. ( 0) 0)
|
| [5] |
LIU Kaien, XIE Guangming, REN Wei, et al. Consensus for multi-agent systems with inherent nonlinear dynamics under directed topologies[J]. Systems & control letters, 2013, 62(2): 152-162. ( 0) 0)
|
| [6] |
LIU Kaien, JI Zhijian, REN Wei. Necessary and sufficient conditions for consensus of second-order multiagent systems under directed topologies without global gain dependency[J]. IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 2017, 47(8): 2089-2098. DOI:10.1109/TCYB.2016.2616020 ( 0) 0)
|
| [7] |
LIU Kaien, JI Zhijian. Consensus of multi-agent systems with time delay based on periodic sample and event hybrid control[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 270: 11-17. DOI:10.1016/j.neucom.2016.12.106 ( 0) 0)
|
| [8] |
夏倩倩, 刘开恩, 纪志坚. 基于二阶邻居事件触发多智能体系统的一致性[J]. 智能系统学报, 2017, 12(6): 833-840. XIA Qianqian, LIU Kaien, JI Zhijian. Event-triggered consensus of multi-agent systems based on second-order neighbors[J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2017, 12(6): 833-840. DOI:10.11992/tis.201702008 (  0) 0)
|
| [9] |
GAO Yanping, LIU Bo, YU Junyan, et al. Consensus of first-order multi-agent systems with intermittent interaction[J]. Neurocomputing, 2014, 129: 273-278. DOI:10.1016/j.neucom.2013.09.031 ( 0) 0)
|
| [10] |
YU Junyan, WANG Long. Group consensus in multi-agent systems with switching topologies and communication delays[J]. Systems & control letters, 2010, 59(6): 340-348. ( 0) 0)
|
| [11] |
YU Junyan, WANG Long. Group consensus of multi-agent systems with directed information exchange[J]. International journal of systems science, 2012, 43(2): 334-348. DOI:10.1080/00207721.2010.496056 ( 0) 0)
|
| [12] |
HAN Guangsong, HE Dingxin, GUAN Zhihong, et al. Multi-consensus of multi-agent systems with various intelligences using switched impulsive protocols[J]. Information sciences, 2016, 349-350: 188-198. DOI:10.1016/j.ins.2016.02.038 ( 0) 0)
|
| [13] |
ALTAFINI C. Consensus problems on networks with antagonistic interactions[J]. IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2013, 58(4): 935-946. DOI:10.1109/TAC.2012.2224251 ( 0) 0)
|
| [14] |
杜明骏, 孟德元. 具有正负混合连接权重及通讯时滞的多智能体系统一致性[C]//第33届中国控制会议论文集. 南京, 2014: 1075–1088. DU Mingjun, MENG Deyuan. Consensus of multi-agent systems with antagonistic interactions and communication delays[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd Chinese Control Conference. Nanjing, 2014: 1075–1088. (  0) 0)
|
| [15] |
张晓丹, 刘开恩, 纪志坚. 具有时变时滞多智能体系统二分一致性[J]. 系统科学与数学, 2018, 38(8): 841-851. ZHANG Xiaodan, LIU Kaien, JI Zhijian. Bipartite consensus of multi-agent systems with time-varying delays[J]. Journal of systems science and mathematical sciences, 2018, 38(8): 841-851. (  0) 0)
|
| [16] |
VALCHER M E, MISRA P. On the consensus and bipartite consensus in high-order multi-agent dynamical systems with antagonistic interactions[J]. Systems & control letters, 2014, 66: 94-103. ( 0) 0)
|
| [17] |
刘聪, 周强, 胡晓光. 离散时间异质多智能体系统的一致性控制[J]. 工程科学学报, 2016, 38(1): 143-148. LIU Cong, ZHOU Qiang, HU Xiaoguang. Consensus control of discrete-time heterogeneous multi-agent systems[J]. Chinese journal of engineering, 2016, 38(1): 143-148. (  0) 0)
|
| [18] |
LIU Kaien, JI Zhijian, XIE Guangming, et al. Consensus for heterogeneous multi-agent systems under fixed and switching topologies[J]. Journal of the franklin institute, 2015, 352(9): 3670-3683. DOI:10.1016/j.jfranklin.2015.03.009 ( 0) 0)
|
| [19] |
修言彬, 刘聪, 刘亚斌. 离散异质多智能体系统的分组一致性控制[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2015, 23(12): 4034-4037. XIU Yanbin, LIU Cong, LIU Yabin. Group consensus control of discrete heterogeneous multi-agent system[J]. Computer measurement & control, 2015, 23(12): 4034-4037. (  0) 0)
|
 2020, Vol. 15
2020, Vol. 15


