2. 诸暨市联系数学研究所,浙江 诸暨 311800
2. Institute of Zhuji Connection Mathematics, Zhuji 311800, China
语言是思维的表达。智能决策是人们基于确定性与不确定性对立统一思维的一类不确定性决策,用自然语言或者把自然语言与数学语言相结合进行决策是智能决策的一个特点。集对分析作为处理事物确定性与不确定性关系的一种系统数学理论,把人们对事物的确定性与不确定性关系的辩证认识转换成一个具体的数学工具——联系数,使得集对分析自赵克勤于1989年提出以来[1-4],在不同领域得到广泛应用[5-50]。其中有关不确定性决策方面的专著有2部[6, 13],在中国知网用主题词“集对分析−决策”查到的文献270多篇。从智能决策的角度看,这些应用大致分8个方面:1)纯自然语言智能决策[51],2)自然语言与数学混合智能决策[52-53],3)区间模糊决策和直觉模糊决策[54-67],4)应用赵森烽−克勤概率的风险决策与贝叶斯决策[68-70],5)借助偏联系数的前瞻性决策[71-72],6)集对分析粗糙决策[13,73],7)集对分析与马尔可夫链相结合的动态决策[74],8)集对分析与灰色、云模型等其他方法同异反综合集成智能决策[75-76]等。集对分析在这8类不确定性决策中的主要应用途径是建立基于联系数的决策模型同时展开不确定性分析;常用的有二元联系数决策模型[4, 77]、三元联系数决策模型[48, 78-79]、四元联系数决策模型[80-83]、五元联系数决策模型[84-91],六元以上联系数决策模型较为少见[74, 92-95],还有多维联系数模型[96-98],以及粗糙集对决策[99],累积前景理论与集对分析相结合的决策[100],基于偏联系数的系统演化趋势决策[101]等。当然,理论上存在基于无穷多元联系数的决策模型,以便遍历决策空间中的任意一个决策点作出决策建议。本文试用文献资料法综述以上工作,但限于篇幅仅举3个应用实例,并在讨论中指出,基于集对分析的不确定性决策,是一种立足于全局的智能决策,其物理意义在于把蕴藏在决策系统中的信息能转换成智能。
1 集对分析及其联系数由文献[1-2]可知,集对这个概念由赵克勤在解读集合论罗素悖论时给出,联系数是集对的特征函数,也是集对分析的主要数学工具,有不同的表达形式,决策中常用到二元、三元、四元、五元归一化联系数:
| $u = a + bi$ |
| $ u = a + bi + cj $ |
| $ u = a + bi + cj + dk $ |
| $u = a + bi + cj + dk + el$ |
式中:a、b、c、d、e统称为联系数
| $ a + b = 1, $ |
| $a + b + c = 1,$ |
| $a + b + c + d = 1,$ |
| $a + b + c + d + e = 1,$ |
归一化约束。i、j、k、l是示性系数,表示相关联系分量的不确定性或确定性。
联系数是一种结构函数,具有不同的伴随函数,偏联系数是联系数的一种伴随函数,有偏正联系数、偏负联系数、全偏联系数、一阶至多阶偏联系数之分,研究表明,三元联系数有二阶全偏联系数。一个
人类的自然语言是人类思维和智慧的表达。利用自然语言决策是一类常见的智能决策。这是因为,无论是普通人的日常决策,还是关键人物在紧要关头作重大决策,不少情况下很难用数字表示决策者的意见,使用定性的自然语言对事物进行评价和决策显得方便、快捷、明确。如指标值高或低、方案可行与不可行等。评价的语意可以是二等级语意,如“好坏”;也可以用三等级语意,如“好中差”;或四等级语意,如“优良中差”;或五等级语意,如“非常满意、很满意、满意、不满意、极不满意”;甚至更多级语意,如“极差、很差、差、一般、好、很好、极好”;或用“非常重要、很重要、重要、一般、差、很差、非常差”7等级语意,
人类自然语言的一大特点是语意的模糊性,理解时的歧义性。因此,对纯自然语言决策问题,1)把自然语言用模糊数表示;2)把模糊数转换成联系数;3)建立基于联系数的决策模型;4)对模型作出计算;5)对计算结果作不确定性分析;6)根据计算和分析结果提出决策建议。
2.3 实例本实例取自文献[51]。
例1 已知作战仿真系统中生成了4套指挥方案
| 表 1 决策者给出的方案各属性的语言表示 Tab.1 Language representation of each attribute of the scheme given by the decision maker |
已知3名决策者权重为
| $ {{{w}}_1} = {(0.328,0.329,0.343)}, $ |
| $ {{{w}}_2} = {(0.278,0.401,0.321)}, $ |
| $ {{{w}}_3} = {(0.339,0.332,0.329)}, $ |
试选出最优方案。决策步骤如下:
| 表 2 方案的语言表示转换为直觉模糊数的决策矩阵 Tab.2 Decision matrix for conversion of language representation of scheme to intuitive fuzzy number |
2)把表2中的模糊数转换成三元联系数,得表3。转换方法:直觉模糊数
| 表 3 用三元联系数表示各方案属性的决策矩阵 Tab.3 Decision matrices representing the attributes of each scheme by the number of ternary connections |
3)按照数(属性权重)与多项式(属性三元联系数)相乘的法则,计算每一个决策者关于方案的综合联系数。
第1位决策者的4个方案的综合联系数
| $u_1^{(1)} = 0.603\;3 + 0.067\;15i + 0.329\;55j$ |
| $u_2^{(1)} = 0.538\;8 + 0.049\;95i + 0.411\;25j$ |
| $u_3^{(1)} = 0.565\;9 + 0.098\;5i + 0.335\;6j$ |
| $ u_4^{(1)} = 0.603 + 0.165\;7i + 0.231\;3j。$ |
第2位决策者的4个方案的综合联系数分别为
| $u_1^{(2)} = 0.652\;4 + 0.104\;3i + 0.243\;3j$ |
| $u_2^{(2)} = 0.391\;4 + 0.167\;9i + 0.440\;7j$ |
| $u_3^{(2)} = 0.577 + 0.047\;9i + 0.375\;11j$ |
| $u_4^{(2)} = 0.519\;3 + 0.079\;9i + 0.400\;8j$ |
第3位决策者的4个方案的综合联系数分别为
| $u_1^{(3)} = 0.668\;4 + 0.132\;9i + 0.197\;8j$ |
| $u_2^{(3)} = 0.264\;8 + 0.050\;15i + 0.685\;05j$ |
| $u_3^{(3)} = 0.533\;6 + 0.2i + 0.266\;4j$ |
| $u_4^{(3)} = 0.598\;4 + 0.082\;85i + 0.318\;75j$ |
4)按照3位决策者各自的权重,计算决策群体关于每个方案的综合联系数
| ${u_1} = 0.642\;5 + 0.101\;7i + 0.255\;8j$ |
| ${u_2} = 0.397\;6 + 0.097\;3i + 0.505\;1j$ |
| ${u_3} = 0.560\;7 + 0.108\;7i + 0.330\;6j$ |
| ${u_4} = 0.568\;1 + 0.106\;5i + 0.325\;4j$ |
5)对每个方案的综合联系数
| ${e_1} = 0.715\;2,{e_2} = 0.440\;5$ |
| ${e_3} = 0.629\;1,{e_4} = 0.635\;8$ |
由此知,根据
6)计算每个方案综合联系数
其中,二阶偏正为
| ${\partial ^{2 \pm }}{u_1} = - 0.087\;5,{\partial ^{2 \pm }}{u_2} = 0.022\;5$ |
| ${\partial ^{2 \pm }}{u_3} = - 0.050\;6,{\partial ^{2 \pm }}{u_4} = - 0.053\;3$ |
由此知,根据
7)对每个方案的综合联系数作不确定性分析。分析情况见表4,为简便计,仅考虑
| 表 4 4个方案的不确定性分析 Tab.4 Uncertainty analysis of 4 schemes |
由表4看出,当方案
还可以看出,当方案
综合以上可知,S1、S2、S3、S4 4个方案都可以是最优方案,这一事实似乎看起来让人们难以理解,其实,上述计算和不确定性分析的价值恰恰在于指出了在哪些具体的条件下哪个方案最优,而这是最重要的,例如在忽略不计4个方案联系数中
自然语言和数学语言混合的不确定性智能决策也简称混合智能决策,这也是一类常见的智能决策,基于集对分析的混合智能决策步骤总体上与基于集对分析的纯自然语言智能决策步骤相同,为节约篇幅,下面用一个实例[52]说明具体决策步骤。
3.2 实例例2 电力系统黑启动是电力系统在出现大面积停电事故情况下的一种应急启动,作出应急启动的决策是一种带有诸多不确定性因素的多属性决策,通常由应急启动专家委员会根据电力系统的有关参数和专家经验,在若干个应急预案中筛选出最优黑启动方案和次优黑启动方案并付诸实施。原始数据见表5。
| 表 5 6个候选方案的属性与属性值 Tab.5 Properties and attribute values of 6 candidate schemes |
属性说明:需要选取最优启动方案(机组),其中机组的额定容量和机组爬坡速率是效益型属性,机组启动需要的电能和变电站个数是成本型属性;对于机组所处状态,极热态比热态更容易启动,热态比温态更容易启动,温态比冷态更容易启动。当按“冷−热”次序依次赋“小−大”值时,该属性是效益型属性。
决策步骤如下:
1)把表5中的语言变量用区间数表示,按照“冷−热”语言变量在
| 表 6 6个候选方案的区间数属性值 Tab.6 Interval number attribute values for 6 candidate schemes |
2)把表6中的各区间数(属性值和权重)联系数化,转换为二元联系数,对区间数
| 表 7 6个候选方案转换后的属性值联系数 Tab.7 Converted attribute value connection number of 6 candidate schemes |
3)把表7中的各数据作规范化处理(去量纲),对于效益型属性值联系数,规范化处理后所得联系数
对于成本型属性联系数,规范化后所得联系数
6个候选方案的规范化属性值联系数见表8。
| 表 8 6个候选方案的规范化属性值联系数 Tab.8 Normative attribute value connection number for 6 candidate schemes |
4)把表8中的各属性规范化联系数计入属性权重运用多项式乘法规则,并求和,用以下模型计算:
| $ \begin{array}{c} {u_k} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{t = 1}^n {w{'_t}u{'_{kt}}} = {A_{kt}} + {B_{kt}}i\\ \left( {k = 1,2, \cdots ,6,\;t = 1,2, \cdots ,5} \right) \end{array} $ |
式中:
| 表 9 6个候选方案的决策联系数及主值 Tab.9 Decision connections number and main values of 6 candidate schemes |
5)根据集对分析理论,把表9中的各方案决策值联系数还原成归一化三元决策联系数,并按
根据表10可知,6个方案的排序为
| ${S_5} \succ {S_6} \succ {S_2} \succ S_3 \succ {S_1} \succ S_4$ |
6)利用例1中6)中的计算二阶全偏联系数公式,计算表10中的三元决策联系数的二阶全偏联系数
| 表 10 6个候选方案的归一化三元决策联系数 Tab.10 Normalized ternary three-element connection number for decision for 6 candidate schemes |
| 表 11 6个候选方案三元决策联系数的二阶全偏联系数 Tab.11 Second order full partial coefficients of the triple decision relation numbers of 6 candidate schemes |
根据表11可知,这时6个方案的排序为
| ${S_4} \succ S_1 \succ {S_3} \succ S_2 \succ {S_6} \succ {S_5}$ |
7)不确定性分析。
对表10中的各个方案的三元决策联系数计算
| 表 12 6个候选方案的不确定性分析 Tab.12 Uncertainty analysis of 6 candidate schemes |
从表12看出,当
由此可知,在不同的条件下,
区间数是一种最大、最小边界值确定,边界内取值不确定的实数。区间数可以客观地表示某些决策参数的边界范围确定,边界内取值不确定的智能决策问题。基于区间数不确定性智能决策分为属性值用区间数表示但属性权重是点实数,以及属性与属性权重都用区间数表示两类,这里给出属于后者的一个实例加以说明,因为后者包含前者。
4.2 实例例3 图书馆的空调系统选择问题。在该决策问题中,有5个备选方案S1 、S2、S3、S4、S5,有4个属性,分别是运营成本
| 表 13 空调系统选择的区间数决策矩阵 Tab.13 Interval decision matrix of air conditioning system selection |
各属性权重信息为不完全形式,其中
这一实例引自文献[99],该文献是利用MATLAB6.5软件求解二次线性规划问题得到的权重向量
采用本文前2节的方法,决策过程如下:
1)对表13数据进行规范化处理,方法见参考文献[6],得规范化区间数决策矩阵:
| $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {[0.609,0.712]}&{[0.8,1.0]}&{[0.3,0.5]}&{[0.6,0.8]} \\ {[0.737,0.894]}&{[0.4,0.6]}&{[0.3,0.5]}&{[0.4,0.6]} \\ {[0.808,1.000]}&{[0.4,0.6]}&{[0.7,0.9]}&{[0.5,0.7]} \\ {[0.764,0.933]}&{[0.7,0.9]}&{[0.8,1.0]}&{[0.7,0.9]} \\ {[0.700,0.840]}&{[0.6,0.8]}&{[0.5,0.7]}&{[0.8,1.0]} \end{array}} \right]$ |
2)用三元联系数表示用规范化处理得到的上述矩阵,例如化区间数[0.609,0.712]为0.609+0.103
| 表 14 三元联系数决策矩阵 Tab.14 Decision matrix of three-element connection number |
3)用区间数表示各属性权重得
4)把各属性权重区间数改写成三元联系数,得
| ${u_{{{\tilde w}_1}}} = 0.25 + 0.15i + 0.60j$ |
| ${u_{{{\tilde w}_2}}} = 0.22 + 0.08i + 0.70j$ |
| ${u_{{{\tilde w}_3}}} = 0.00 + 0.10i + 0.90j$ |
| ${u_{{{\tilde w}_4}}} = 0.20 + 0.10i + 0.70j$ |
5)按普通多项式相乘规则得到各属性加权联系数,见表15。
| 表 15 三元联系数加权决策矩阵 Tab.15 Weighting decision matrix of three-element connection number |
6)计算每个方案的综合联系数
转化后为
对这些三元联系数作归一(四舍五入保留4位小数),得
7)按
由此知,根据
8)仿照例1的6)的方法,计算方案决策联系数的二阶全偏联系数
| ${\partial ^{2 \pm }}u'{'_1} = 0.013\;3$ |
| ${\partial ^{2 \pm }}u'{'_2} = 0.000\;9$ |
| ${\partial ^{2 \pm }}u'{'_3} = 0.014\;4$ |
| ${\partial ^{2 \pm }}u'{'_4} = 0.012\;1$ |
| ${\partial ^{2 \pm }}u'{'_5} = 0.019\;0$ |
由此,根据决策联系数的二阶全偏联系数的值得到方案的排序为
9)作方案的不确定性分析。仅考虑
从表16中看出,如果方案
| 表 16 5个方案的不确定性分析 Tab.16 Uncertainty analysis of 5 scheme |
1)本文对两个三元联系数a+bi+cj作乘积运算采用普通的多项式乘法规则,在运算结果中出现了i、j项和
2)决策总是在一定条件下做出。条件变化,决策也随之变化,简称为条件决策。条件决策的特点就是在决策的时候充分考虑条件的不确定性。
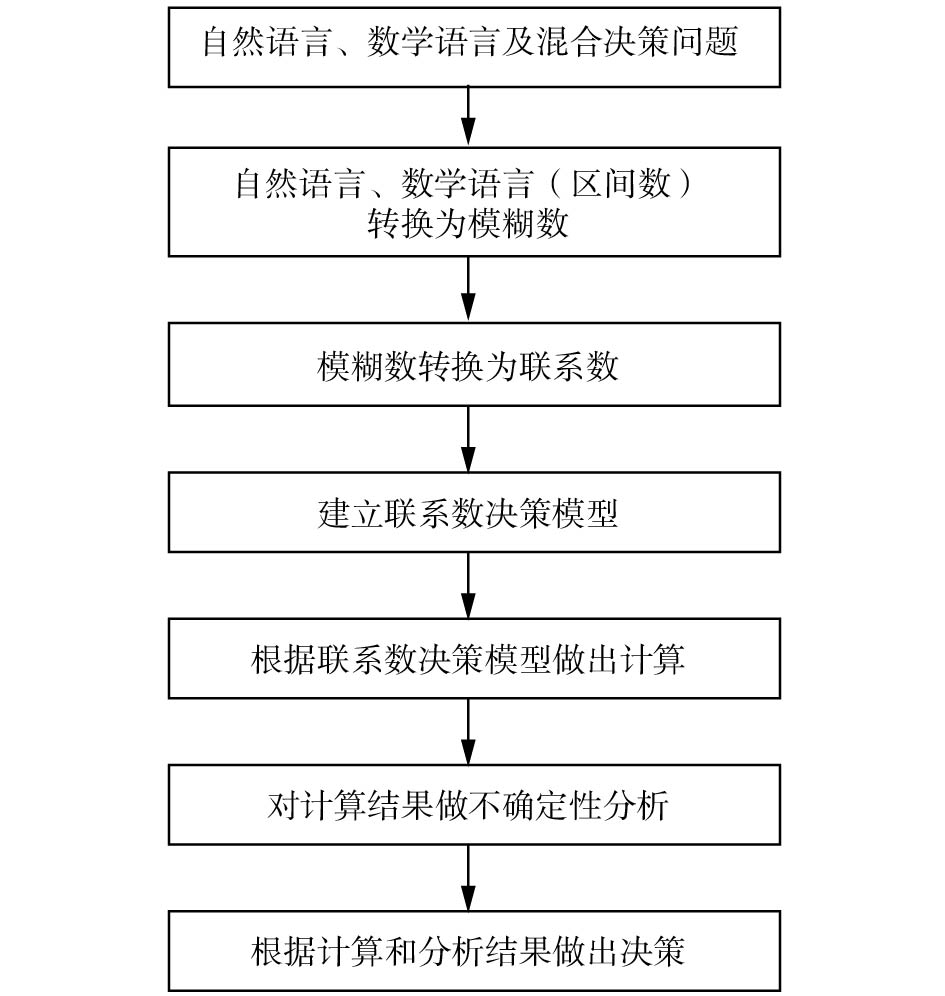
3)关于纯自然语言、自然语言与数学语言混合和区间数决策问题的决策程序。通过上述讨论,发现纯自然语言、自然语言与数学语言混合和区间数决策3种类型的决策模型具有统一的形式和统一的决策步骤,用框图表示如图1所示。
|
Download:
|
| 图 1 不确定性智能决策框图 Fig. 1 Intelligent decision block for uncertainty | |
4)关于同异反集成决策。有二层意思,一是把“同异反”看作是“正常(同),异常(异)”,反常(反)的代名词,由于决策环境通常处于开放状态,科学的决策就需要全方位地考虑到决策环境的“正常(同),异常(异)”,反常(反);二是在决策建模上,建同(同类型模型)异(不同类型模型)反(逆向模型)三类模型的组合模型,以提高决策的科学性与实用性,从效用的角度实现最优化决策。
5)在真实世界中,任何一个不确定性决策系统都是动态变化着的系统。为此,我们在文献[61]中提出既确定又有不确定性的D-U决策空间,D-U空间与虚实结合的复空间叠加,从而存在不同的层次,这样,即使在宏观层次上看来是静止的决策系统,在微观层次上依然处在变化之中,利用宏观层次上的状态联系数的偏联系数计算,可以判断出该决策系统在微观层次上的趋势,以便洞察秋毫、随机决策。
6)立足全局的智能决策。把前述的条件决策、同异反组合模型决策、基于不确定性的决策和基于层次的决策以及这些决策的算法统一性等内容加以归纳,可以看出基于集对分析的不确定性智能决策是一种立足全局的智能决策。其物理意义则在于把蕴藏在决策系统中的信息能转换成智能。因为从信息能的角度看,从给定的一组看上去处于静态的决策条件连同这组条件所在的决策环境在某个决策子空间中作出最优决策,实现既定目标,本质上实现了决策系统中的信息能向智能的转换。本文前面所综述的不确定性决策模型和阐述的决策步骤,就是在决策空间中把决策系统中的信息能转换成智能的过程,但转换机制需要深入研究。
6 结束语集对分析用于决策研究已有众多文献,本文仅限于集对分析理论用于不确定性智能决策作一综述,基本思路是试图给出一种通用的决策模式,利用这种模式能给出一个不确定性智能决策问题在某个决策子空间的不确定性环境中,给出不同条件的决策建议,文中把这些条件归成3类:1)利用例1中 5)的贴近度公式,忽略不计不确定性得到方案排序;2)利用偏联系数规避宏观层次上的不确定性,得到各方案在微观层次上的演化趋势判断,3)经不确定性分析得到方案排序。同一批方案在上述不同条件下有不同的优劣排序,从而给出不同层次条件下的决策建议和立足于全局的决策建议。但由于决策问题的多样性,决策系统中的信息能转换成智能的具体途径和转换机制也具有多样性,这种多样性又决定了决策模型和决策算法的多样性;因此,这种立足全局的集对分析智能决策是一个需要作深入研究的课题。
| [1] |
赵克勤. 集对分析对不确定性的描述和处理[J]. 信息与控制, 1995, 24(3): 162-166. ZHAO Keqin. Disposal and description of uncertainties based on the set pair analysis[J]. Information and control, 1995, 24(3): 162-166. (  0) 0)
|
| [2] |
赵克勤, 宣爱理. 集对论——一种新的不确定性理论方法与应用[J]. 系统工程, 1996, 14(1): 18-23, 72. ZHAO Keqin, XUAN Aili. Set pair theory——A new theory method of non-define and its applications[J]. Systems engineering, 1996, 14(1): 18-23, 72. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.1996.01.003 (  0) 0)
|
| [3] |
赵克勤. 集对分析及其初步应用[M]. 杭州: 浙江科学技术出版社, 2000.
( 0) 0)
|
| [4] |
赵克勤. 二元联系数A+Bi的理论基础与基本算法及在人工智能中的应用
[J]. 智能系统学报, 2008, 3(6): 476-486. ZHAO Keqin. The theoretical basis and basic algorithm of binary connection A+Bi and its application in AI [J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2008, 3(6): 476-486. (  0) 0)
|
| [5] |
王文圣, 李跃清, 金菊良, 等. 水文水资源集对分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010.
( 0) 0)
|
| [6] |
刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 区间数决策集对分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.
( 0) 0)
|
| [7] |
蒋云良, 赵克勤, 刘以安, 等. 信息处理集对分析[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015.
( 0) 0)
|
| [8] |
蒋云良, 赵克勤. 集对分析在人工智能中的应用与进展[J]. 智能系统学报, 2019, 14(1): 28-43. JIANG Yunliang, ZHAO Keqin. Application and development of set pair analysis in artificial intelligence: a survey[J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2019, 14(1): 28-43. (  0) 0)
|
| [9] |
金菊良, 张浩宇, 宁少尉, 等. 效应全偏联系数及其在区域水资源承载力评价中的应用[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 40(1): 1-8. JIN Juliang, ZHANG Haoyu, NING Shaowei, et al. Effect full partial connection number and its application in evaluation of regional water resources carrying capacity[J]. Journal of North China university of water resources and electric power (natural science edition), 2019, 40(1): 1-8. (  0) 0)
|
| [10] |
沈定珠. 体育用联系数学[M]. 北京: 中国教育文化出版社, 2007.
( 0) 0)
|
| [11] |
汪明武, 金菊良, 周玉良. 集对分析耦合方法与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.
( 0) 0)
|
| [12] |
潘争伟, 吴成国, 金菊良. 水资源系统评价与预测的集对分析方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.
( 0) 0)
|
| [13] |
刘保相. 粗糙集对分析理论与决策模型[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010.
( 0) 0)
|
| [14] |
王万军, 晏燕. 不确定信息处理的集对分析研究与应用[M]. 兰州: 兰州大学出版社, 2015.
( 0) 0)
|
| [15] |
蒋云良, 赵克勤. 人工智能集对分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.
( 0) 0)
|
| [16] |
赵克勤, 米红. 非传统安全与集对分析[M]. 北京: 知识产权出版社, 2010.
( 0) 0)
|
| [17] |
蒋云良, 徐从富. 集对分析理论及其应用研究进展[J]. 计算机科学, 2006, 33(1): 205-209. JIANG Yunliang, XU Congfu. Advances in set pair analysis theory and its applications[J]. Computer science, 2006, 33(1): 205-209. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2006.01.057 (  0) 0)
|
| [18] |
赵克勤. 集对分析的不确定性系统理论在AI中的应用[J]. 智能系统学报, 2006, 1(2): 16-25. ZHAO Keqin. The application of uncertainty systems theory of set pair analysis (SPU)in the artificial intelligence[J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2006, 1(2): 16-25. (  0) 0)
|
| [19] |
赵克勤, 赵森烽. 奇妙的联系数[M]. 北京: 知识产权出版社, 2014.
( 0) 0)
|
| [20] |
赵克勤. 成对原理及其在集对分析(SPA)中的作用与意义[J]. 大自然探索, 1998, 17(4): 90. ZHAO Keqin. The function and meaning of pair principle in the set pair analysis[J]. Exploration of nature, 1998, 17(4): 90. (  0) 0)
|
| [21] |
赵克勤. SPA的同异反系统理论在人工智能研究中的应用[J]. 智能系统学报, 2007, 2(5): 20-35. ZHAO Keqin. The application of SPA-based identical-discrepancy-contrary system theory in artificial intelligence research[J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2007, 2(5): 20-35. (  0) 0)
|
| [22] |
PAN Zhengwei, WANG Yanhua, JIN Juliang, et al. Set pair analysis method for coordination evaluation in water resources utilizing conflict[J]. Physics and chemistry of the earth, parts A/B/C, 2017, 101: 149-156. DOI:10.1016/j.pce.2017.05.009 ( 0) 0)
|
| [23] |
YU Furong, QU Jihong, LI Zhiping, et al. Application of set pair analysis based on the improved five-element connectivity in the evaluation of groundwater quality in Xuchang, Henan Province, China[J]. Water science & technology: water supply, 2017(3): 632-642. ( 0) 0)
|
| [24] |
YAN Fang, XU Kaili. Application of a cloud model-set pair analysis in hazard assessment for biomass gasification stations[J]. PLoS one, 2017, 12(1): e0170012. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0170012 ( 0) 0)
|
| [25] |
YAN Fang, XU Kaili, LI Deshun, et al. Hazard Assessment for biomass gasification station using general set pair analysis[J]. Bioresources, 2016, 11(4): 8307-8324. ( 0) 0)
|
| [26] |
TAN Chong, SONG Yi, CHE H. Application of set pair analysis method on occupational hazard of coal mining[J]. Safety science, 2017, 92: 10-16. DOI:10.1016/j.ssci.2016.09.005 ( 0) 0)
|
| [27] |
LI Chunhui, SUN Lian, JIA Junxiang, et al. Risk assessment of water pollution sources based on an integrated k-means clustering and set pair analysis method in the region of Shiyan, China
[J]. Science of the total environment, 2016, 557-558: 307-316. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.069 ( 0) 0)
|
| [28] |
WANG Ya, ZHOU Lihua. Assessment of the coordination ability of sustainable social-ecological systems development based on a set pair analysis: a case study in Yanchi County, China[J]. Sustainability, 2016, 8(8): 733. DOI:10.3390/su8080733 ( 0) 0)
|
| [29] |
( 0) 0)
|
| [30] |
ZHANG Jian, YANG Xiaohua, LI Yuqi. A refined rank set pair analysis model based on wavelet analysis for predicting temperature series[J]. International journal of numerical methods for heat & fluid flow, 2015, 25(5): 974-985. ( 0) 0)
|
| [31] |
YANG Xiaohua, SUN Boyang, ZHANG Jian, et al. Hierarchy evaluation of water resources vulnerability under climate change in Beijing, China[J]. Natural hazards, 2016, 84(S1): 63-76. DOI:10.1007/s11069-015-1932-2 ( 0) 0)
|
| [32] |
Science. Deemed university details findings in science (an advanced study on operations of connection number based on set pair analysis)[J]. Science letter, 2019. ( 0) 0)
|
| [33] |
WEI Chao, DAI Xiaoyan, YE Shufeng, et al. Prediction analysis model of integrated carrying capacity using set pair analysis[J]. Ocean & coastal management, 2016, 120: 39-48. ( 0) 0)
|
| [34] |
BAO Danwen, ZHANG Xiaoling. Measurement methods and influencing mechanisms for the resilience of large airports under emergency events[J]. Transportmetrica a: transport science, 2018, 14(10): 855-880. DOI:10.1080/23249935.2018.1448016 ( 0) 0)
|
| [35] |
GARG H, KUMAR K. An advanced study on the similarity measures of intuitionistic fuzzy sets based on the set pair analysis theory and their application in decision making[J]. Soft computing, 2018, 22(15): 4959-4970. DOI:10.1007/s00500-018-3202-1 ( 0) 0)
|
| [36] |
YAN Fang, XU Kaili. A set pair analysis based layer of protection analysis and its application in quantitative risk assessment[J]. Journal of loss prevention in the process industries, 2018, 55: 313-319. DOI:10.1016/j.jlp.2018.07.007 ( 0) 0)
|
| [37] |
LI Peiyue, QIAN Hui, WU Jianhua. Application of set pair analysis method based on entropy weight in groundwater quality assessment -a case study in Dongsheng city, northwest China[J]. Journal of chemistry, 2011, 8: 879683. DOI:10.1155/2011/879683 ( 0) 0)
|
| [38] |
ZENG Jiajun, HUANG Guoru. Set pair analysis for karst waterlogging risk assessment based on AHP and entropy weight[J]. Hydrology research, 2018, 49(4): 1143-1155. DOI:10.2166/nh.2017.265 ( 0) 0)
|
| [39] |
KUMAR K, GARG H. Connection number of set pair analysis based TOPSIS method on intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their application to decision making[J]. Applied intelligence, 2018, 48(8): 2112-2119. DOI:10.1007/s10489-017-1067-0 ( 0) 0)
|
| [40] |
GARG H, KUMAR K. Some aggregation operators for linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy set and its application to group decision-making process using the set pair analysis[J]. Arabian journal for science and engineering, 2018, 43(6): 3213-3227. DOI:10.1007/s13369-017-2986-0 ( 0) 0)
|
| [41] |
FENG Yixiong, LU Runjie, GAO Yicong, et al. Multi-objective optimization of VBHF in sheet metal deep-drawing using Kriging, MOABC, and set pair analysis[J]. The international journal of advanced manufacturing technology, 2018, 96(9-12): 3127-3138. DOI:10.1007/s00170-017-1506-4 ( 0) 0)
|
| [42] |
赵克勤. 偏联系数[C]//中国人工智能进展2005论文集. 北京: 北京邮电大学出版社, 2005: 884−885. ZHAO Keqin. Partial connection number[C]//Proceedings of Chinese artificial intelligence 2005. Beijing: Beijing university of posts and telecommunications publishing house, 2005: 884−885. (  0) 0)
|
| [43] |
施志坚, 王华伟, 王祥. 基于多元联系数集对分析的航空维修风险态势评估[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2016, 38(3): 588-594. SHI Zhijian, WANG Huawei, WANG Xiang. Risk state evaluation of aviation maintenance based on multiple connection number set pair analysis[J]. Systems engineering and electronics, 2016, 38(3): 588-594. (  0) 0)
|
| [44] |
李聪, 陈建宏, 杨珊, 等. 五元联系数在地铁施工风险综合评价中的应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2013, 23(10): 21-26. LI Cong, CHEN Jianhong, YANG Shan, et al. Application of five-element connection number to comprehensive evaluation of risks involved with subway construction[J]. China safety science journal, 2013, 23(10): 21-26. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2013.10.004 (  0) 0)
|
| [45] |
谢红涛, 李波, 赵云胜. 基于联系数的地铁隧道施工邻近建筑物风险评价[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2014, 44(7): 16-19. XIE Hongtao, LI Bo, ZHAO Yunsheng. Risk assessment of neighboring building in metro tunneling construction based on connection number[J]. Industrial safety and environmental protection, 2014, 44(7): 16-19. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2014.07.006 (  0) 0)
|
| [46] |
XIE Xuecai, GUO Deyong. Human factors risk assessment and management: process safety in engineering[J]. Process safety and environmental protection, 2018, 113: 467-482. DOI:10.1016/j.psep.2017.11.018 ( 0) 0)
|
| [47] |
马成正, 王洪德. 联系数在地铁车站火灾安全风险评价中的应用[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 37(1): 26-31. MA Chengzheng, WANG Hongde. Application of connection number to safety risk evaluation of fire accident in subway station[J]. Journal of liaoning technical university (natural science edition), 2015, 37(1): 26-31. (  0) 0)
|
| [48] |
赵金楼, 高宏玉, 成俊会. 基于三元联系数的网络舆情传播中主体参与意愿演化评价方法[J]. 情报科学, 2017, 35(8): 118-120, 140. ZHAO Jinlou, GAO Hongyu, CHENG Junhui. Research on evolution of participation willingness in network public opinion: based on three-element connection number[J]. Information science, 2017, 35(8): 118-120, 140. (  0) 0)
|
| [49] |
赵克勤. 反偏联系数[C]//中国人工智能学会第12届全国学术年会论文汇编. 哈尔滨: 中国人工智能学会, 2007: 66−67. ZHAO Keqin, Inverse correlation number[C]//Advances in Artificial Intelligence in China. Harbin: Chinese association for artificial intelligence, 2007: 66−67. (  0) 0)
|
| [50] |
刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 基于联系数复运算的区间数多属性决策方法及应用[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2008, 38(23): 57-64. LIU Xiumei, ZHAO Keqin. Multiple attribute decision making and its applications based on complex number arithmetic operation of connection number with interval numbers[J]. Mathematics in practice and theory, 2008, 38(23): 57-64. (  0) 0)
|
| [51] |
张肃. 基于集对分析和直觉模糊集的语言型多属性群决策方法[J]. 科技导报, 2008, 26(12): 67-69. ZHANG Su. Method for multiple attribute decision making with linguistic assessment information based on set pair analysis and intuitionistic fuzzy set[J]. Science & technology review, 2008, 26(12): 67-69. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-7857.2008.12.013 (  0) 0)
|
| [52] |
金卫雄, 刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 基于联系数的定性定量混合多属性区间数决策[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2014, 44(16): 166-173. JIN Weixiong, LIU Xiumei, ZHAO Keqin. Multiple attribute decision-making with the interval number and with the hybrid qualitative and quantitative based on the connection number[J]. Mathematics in practice and theory, 2014, 44(16): 166-173. (  0) 0)
|
| [53] |
刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 区间数伴语言变量的混合多属性决策[J]. 模糊系统与数学, 2014, 28(1): 113-118. LIU Xiumei, ZHAO Keqin. On studying hybrid multi-attribute decision-making with interval number and linguistic value[J]. Fuzzy systems and mathematics, 2014, 28(1): 113-118. (  0) 0)
|
| [54] |
刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 基于联系数不确定性分析的区间数多属性决策[J]. 模糊系统与数学, 2010, 24(5): 141-148. LIU Xiumei, ZHAO Keqin. Multiple attributes decision-making of intervals based on analysis of the uncertainty of connection number[J]. Fuzzy systems and mathematics, 2010, 24(5): 141-148. (  0) 0)
|
| [55] |
刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 基于区间数确定性与不确定性相互作用点的多属性决策[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2009, 39(8): 68-75. LIU Xiumei, ZHAO Keqin. Multiple attribute decision making based on the interval numbers certainty and the uncertainty interact on each other[J]. Mathematics in practice and theory, 2009, 39(8): 68-75. (  0) 0)
|
| [56] |
刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 基于二次联系数的区间数多属性决策方法及应用[J]. 模糊系统与数学, 2011, 25(5): 115-121. LIU Xiumei, ZHAO Keqin. Quadratic-connection-number-based method and its applications for multiple attributes decision-making with interval numbers[J]. Fuzzy systems and mathematics, 2011, 25(5): 115-121. (  0) 0)
|
| [57] |
刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 基于联系数的不确定空情意图识别[J]. 智能系统学报, 2012, 7(5): 450-456. LIU Xiumei, ZHAO Keqin. Inference method on intention with uncertain aerial information based on the connection number[J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2012, 7(5): 450-456. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4785.201206016 (  0) 0)
|
| [58] |
吴维煊, 刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 区间数特性集对分析及在多指标决策中的应用[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2012, 42(24): 66-71. WU Weixuan, LIU Xiumei, ZHAO Keqin. The application of interval number character set in analysis and multiple attribute decision making[J]. Mathematics in practice and theory, 2012, 42(24): 66-71. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2012.24.009 (  0) 0)
|
| [59] |
吴维煊. 基于区间数正态分布假设的多属性决策集对分析[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2013, 43(3): 260-264. WU Weixuan. Multi-attribute decision-making and set pair analysis based on normal distribution hypothesis interval number[J]. Mathematics in practice and theory, 2013, 43(3): 260-264. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2013.03.038 (  0) 0)
|
| [60] |
刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 基于联系数的属性权重未知的区间数多属性决策研究[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2013, 49(3): 143-148. LIU Xiumei, ZHAO Keqin. Interval multi-attribute decision making with the attribute weight unknown based on connection number[J]. Mathematics in practice and theory, 2013, 49(3): 143-148. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2013.03.019 (  0) 0)
|
| [61] |
刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 基于SPA的D-U空间的区间数多属性决策模型及应用[J]. 模糊系统与数学, 2009, 23(2): 167-174. LIU Xiumei, ZHAO Keqin. Multiple attribute decision making and its applications with interval numbers based on D-U space of SPA[J]. Fuzzy systems and mathematics, 2009, 23(2): 167-174. (  0) 0)
|
| [62] |
吴维煊. 联系数在梯形模糊数多属性决策中的应用[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2013, 43(1): 160-166. WU Weixuan. The utilization of interval number in multi-attribute decision-making of trapezoidal fuzzy number[J]. Mathematics in practice and theory, 2013, 43(1): 160-166. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2013.01.022 (  0) 0)
|
| [63] |
徐泽水. 直觉模糊偏好信息下的多属性决策途径[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2007, 27(11): 62-71. XU Zeshui. Approaches to multiple attribute decision making with intuitionistic fuzzy preference information[J]. Systems engineering-theory & practice, 2007, 27(11): 62-71. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-6788.2007.11.009 (  0) 0)
|
| [64] |
施丽娟, 黄天民, 翟秀枝. 基于集对分析的区间直觉模糊多属性决策方法[J]. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 35(3): 468-471. SHI Lijuan, HUANG Tianmin, ZHAI Xiuzhi. Approach to interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy set multiple attribute decision making based on set pair analysis[J]. Journal of southwest university for nationalities (natural science edition), 2009, 35(3): 468-471. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-2843.2009.03.020 (  0) 0)
|
| [65] |
叶跃祥, 糜仲春, 王宏宇, 等. 一种基于集对分析的区间数多属性决策方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2006, 28(9): 1344-1347. YE Yuexiang, MI Zhongchun, WANG Hongyu, et al. Set-pair-analysis-based method for multiple attributes decision-making with intervals[J]. Systems engineering and electronics, 2006, 28(9): 1344-1347. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2006.09.016 (  0) 0)
|
| [66] |
刘秀梅, 赵克勤. 属性等级和属性值均为区间数的多属性决策集对分析[J]. 模糊系统与数学, 2012, 26(6): 124-131. LIU Xiumei, ZHAO Keqin. Set-pair-analysis-based method for uncertain multi-attributes decision-making with intervals of the attribute grades and the attribute values[J]. Fuzzy systems and mathematics, 2012, 26(6): 124-131. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-7402.2012.06.018 (  0) 0)
|
| [67] |
张传芳, 杨春玲. 区间型联系数及其在多属性决策中的应用[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2012, 42(13): 61-67. ZHANG Chuanfang, YANG Chunling. Interval connection number and application on multiple attribute decision-making model[J]. Mathematics in practice and theory, 2012, 42(13): 61-67. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2012.13.008 (  0) 0)
|
| [68] |
赵森烽, 赵克勤. 概率联系数化的原理及其在概率推理中的应用[J]. 智能系统学报, 2012, 7(3): 200-205. ZHAO Senfeng, ZHAO Keqin. The principle of a connection number in probability and its application in probabilistic reasoning[J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2012, 7(3): 200-205. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4785.201112014 (  0) 0)
|
| [69] |
赵森烽, 赵克勤. 联系概率的由来及其在风险决策中的应用[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2013, 43(4): 165-171. ZHAO Senfeng, ZHAO Keqin. The contact probability in risk decision-making medium application[J]. Mathematics in practice and theory, 2013, 43(4): 165-171. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2013.04.024 (  0) 0)
|
| [70] |
赵克勤, 赵森烽. 贝叶斯概率向赵森烽-克勤概率的转换与应用[J]. 智能系统学报, 2015, 10(1): 51-61. ZHAO Keqin, ZHAO Senfeng. Bayes probability transition to Zhao Senfeng-Keqin probability and its application[J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2015, 10(1): 51-61. (  0) 0)
|
| [71] |
张萌萌, 刘以安, 宋萍. 偏联系聚类和RF算法在雷达信号分选中的应用[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(06): 236-243. Zhang Mengmeng, Liu Yian, Song Ping. Application of partial connection clustering and random forest in radar signal sorting[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics progress, 2019, 56(06): 236-243. (  0) 0)
|
| [72] |
王万军. 一种基于集对决策的偏联系数方法[J]. 甘肃联合大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 23(3): 43-45. WANG Wanjun. A decision method in parital connection number based on SPA[J]. Journal of Gansu Lianhe university (natural sciences edition), 2009, 23(3): 43-45. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-691X.2009.03.013 (  0) 0)
|
| [73] |
赵克勤. 集对分析与同异反决策[J]. 决策探索, 1992(2): 14-15. ZHAO Keqin. Set pair analysis and identical-discrepancy-contrary decision[J]. Policy research & exploration, 1992(2): 14-15. (  0) 0)
|
| [74] |
杨红梅. 基于二元联系数的三角模糊数直觉模糊集多属性决策[J]. 山西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 29(2): 13-19. YANG Hongmei. Multiple attribute decision making of triangular fuzzy number intuition fuzzy set based on two-element connection number[J]. Journal of Shanxi normal university (natural science edition), 2015, 29(2): 13-19. (  0) 0)
|
| [75] |
杨亚锋, 张春英, 李丽红. 粗糙集对分析方法及其在属性约简中的应用[J]. 模糊系统与数学, 2013, 27(6): 176-181. YANG Yafeng, ZHANG Chunying, LI Lihong. Rough set pair method and its application in the attribute reduction[J]. Fuzzy systems and mathematics, 2013, 27(6): 176-181. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-7402.2013.06.027 (  0) 0)
|
| [76] |
常志朋, 刘小弟, 张世涛. 基于高阶Markov链的重大决策社会风险变权集对预测模型[J]. 决策与控制, 2018, 33(12): 2243-2250. CHANG Zhipeng, LIU Xiaodi, ZHANG Shitao. Set pair prediction model for social risk from major decision-making based on variable weight and higher-order Markov chain[J]. Control and decision, 2018, 33(12): 2243-2250. (  0) 0)
|
| [77] |
汪新凡, 王坚强, 杨恶恶. 基于二元联系数集结算子的多准则群决策方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2013, 28(11): 1630-1636. WANG Xinfan, WANG Jianqiang, YANG Wue. Multiple criteria group decision making method based on binary connection number aggregation operators[J]. Control and decision, 2013, 28(11): 1630-1636. (  0) 0)
|
| [78] |
汪新凡. 基于三元联系数的不确定多属性决策方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2007, 29(12): 2068-2071. WANG Xinfan. Uncertain multiple attribute decision making methods based on three-unit connection number[J]. Systems engineering and electronics, 2007, 29(12): 2068-2071. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-506x.2007.12.017 (  0) 0)
|
| [79] |
王万军. 一种基于三元联系数的语言区间信息集结方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2014, 51(17): 219-222. WANG Wanjun. Linguistic interval information aggregation method based on three element connection numbers[J]. Computer engineering and applications, 2014, 51(17): 219-222. DOI:10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1310-0021 (  0) 0)
|
| [80] |
许逊哲, 茹意, 蒯仂, 等. 四元联系数在土槐菝葜汤治疗血热型银屑病疗效研究中的应用[J]. 中国中西医结合皮肤性病学杂志, 2018, 17(6): 489-492. XU Xunzhe, RU Yi, KUAI Le, et al. Four-element connection number in the study of tuhuai-smilax decoction in treating psoriasis vulgaris[J]. Chinese journal of dermatovenerology of integrated traditional and western medicine, 2018, 17(6): 489-492. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-0709.2018.06.003 (  0) 0)
|
| [81] |
王冰洁. 四元联系数在2型糖尿病住院患者抑郁发生影响因子分析中的应用[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2011, 41(17): 101-105. WANG Bingjie. The application of four unit relation number in the analysis of influencing factors of depression on type 2 diabetes patients in hospital[J]. Mathematics in practice and theory, 2011, 41(17): 101-105. (  0) 0)
|
| [82] |
王霞. 联系范数为4与6的四元联系数系统态势数值排序及应用[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2004, 34(7): 107-112. WANG Xia. The perrmutation and use of four unit relation number systems situation numer ical value of relation model number 4 and 6[J]. Mathematics in practice and theory, 2004, 34(7): 107-112. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0984.2004.07.019 (  0) 0)
|
| [83] |
刘双跃, 王娟, 何发龙. 四元联系数对煤矿安全质量标准化的优化研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2012, 8(12): 32-37. LIU Shuangyue, WANG Juan, HE Falong. Optimization research of coal mine safety quality standardization based on four-element connection number model[J]. Journal of safety science and technology, 2012, 8(12): 32-37. (  0) 0)
|
| [84] |
张林凤. 基于五元联系数的浙江省国民体质态势分析[J]. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 26(4): 402-405. ZHANG Linfeng. A situation-oriented order analysis of people′s constitution in Zhejiang on five-element connection number[J]. Journal of Zhejiang normal university (natural sciences edition), 2003, 26(4): 402-405. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5051.2003.04.019 (  0) 0)
|
| [85] |
周兴慧, 张吉军. 基于五元联系数的风险综合评价方法及其应用[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2013, 33(8): 2169-2176. ZHOU Xinghui, ZHANG Jijun. Risk comprehensive evaluation method and its application based on the five-element connection number[J]. Systems engineering —theory & practice, 2013, 33(8): 2169-2176. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6788.2013.08.035 (  0) 0)
|
| [86] |
祁云清, 姚安林, 黄亮亮, 等. 五元联系数在LNG接收站失效可能性评价中的应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2014, 24(12): 130-136. QI Yunqing, YAO Anlin, HUANG Liangliang, et al. Application of five-element connection number to failure possibility assessment of LNG terminal[J]. China safety science journal, 2014, 24(12): 130-136. (  0) 0)
|
| [87] |
冯东梅, 徐雨函, 贾崇. 基于五元联系数的PPP项目风险评价研究[J]. 工程管理学报, 2017, 31(6): 77-82. FENG Dongmei, XU Yuhan, JIA Chong. A risk assessment of PPP projects based on five-element connection number[J]. Journal of engineering management, 2017, 31(6): 77-82. (  0) 0)
|
| [88] |
袁乐平, 蔡月茹, 崔振新. 基于五元联系数法的进近管制员压力评价模型[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(2): 573-577. YUAN Leping, CAI Yueru, CUI Zhenxin. An appreciation model for the controller's pressure based on the five-element connection number[J]. Journal of safety and environment, 2017, 17(2): 573-577. (  0) 0)
|
| [89] |
刘晗, 赵修茗, 赵鑫, 等. 基于五元联系数的古建筑火灾风险评价[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2018, 38(6): 901-909. LIU Han, ZHAO Xiuming, ZHAO Xin, et al. Fire risk assessment of the ancient buildings based on five-element connection number[J]. Journal of Xi'an university of science and technology, 2018, 38(6): 901-909. (  0) 0)
|
| [90] |
王红瑞, 巩书鑫, 邓彩云, 等. 基于五元联系数的水资源承载力评价[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 49(2): 211-218. WANG Hongrui, GONG Shuxin, DENG Caiyun, et al. Research on water resources carrying capacity based on five-element connection number[J]. Journal of northwest university (natural science edition), 2019, 49(2): 211-218. (  0) 0)
|
| [91] |
陈光怡, 吕大为. 基于五元联系数的集对分析模型在围岩稳定性评价中的应用[J]. 湖南工程学院学报, 2019, 29(2): 79-82, 94. CHEN Guangyi, LYU Dawei. Application of set pair analysis model based on five-element connection number in surrounding rock stability evaluation[J]. Journal of Hunan institute of engineering, 2019, 29(2): 79-82, 94. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-119X.2019.02.016 (  0) 0)
|
| [92] |
冯莉莉, 高军省. 基于六元联系数的水质综合评价模型[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2011, 30(1): 121-124. FENG Lili, GAO Junsheng. Water quality assessment model based on six-element connection number[J]. Journal of irrigation and drainage, 2011, 30(1): 121-124. (  0) 0)
|
| [93] |
高苏蒂, 潘争伟, 刘巧红. 淮河干流水质评价的集对分析模型[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(2): 962-963, 989. GAO Sudi, PAN Zhengwei, LIU Qiaohong. Set pair analysis model for evaluating water quality of huaihe river mainstream[J]. Journal of Anhui agricultural sciences, 2012, 40(2): 962-963, 989. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.02.128 (  0) 0)
|
| [94] |
盛祥, 王恩. 单一供水模式下城市供水风险评价[J]. 淮阴工学院学报, 2015, 24(3): 83-88. SHENG Xiang, WANG En. Urban water supply risk assessment under single supply mode[J]. Journal of Huaiyin institute of technology, 2015, 24(3): 83-88. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-7961.2015.03.018 (  0) 0)
|
| [95] |
张清河. 多元联系数在地基处理方案模糊选优中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2005, 32(6): 112-115. ZHANG Qinghe. Application of multivariate connection number in the fuzzy optimizing of foundation treatment plan[J]. Hydrogeology and engineering geology, 2005, 32(6): 112-115. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.06.027 (  0) 0)
|
| [96] |
胡启洲, 吴娟. 基于多维联系数的城市交通安全态势监控模型[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2011, 21(10): 16-22. HU Qizhou, WU Juan. A monitoring and controlling model for urban traffic safety state based on multi-dimension connection number[J]. China safety science journal, 2011, 21(10): 16-22. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2011.10.003 (  0) 0)
|
| [97] |
李军, 李海玉, 陈波, 等. 基于多维联系数的城轨交通车站安全态势理解模型研究[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2014, 58(9): 129-134. LI Jun, LI Haiyu, CHEN Bo, et al. Security situation comprehension model of urban rail transit station based on multi-dimension connection number[J]. Railway standard design, 2014, 58(9): 129-134. (  0) 0)
|
| [98] |
胡启洲, 孙煦. 基于多维联系数的城市路网交通拥堵态势监控模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26(6): 143-149. HU Qizhou, SUN Xu. Model for traffic congestion state monitor in urban road network based on multi-dimension connection number[J]. China journal of highway and transport, 2013, 26(6): 143-149. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2013.06.020 (  0) 0)
|
| [99] |
胡军华, 杨柳, 刘咏梅. 基于累积前景理论的动态随机多准则决策方法[J]. 软科学, 2012, 26(2): 132-135. HU Junhua, YANG Liu, LIU Yongmei. Dynamic stochastic multi-criteria decision making method based on cumulative prospect theory[J]. Soft science, 2012, 26(2): 132-135. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-8409.2012.02.028 (  0) 0)
|
| [100] |
樊治平, 尤天慧, 张尧. 属性权重信息不完全的区间数多属性决策方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 26(8): 798-800. FAN Zhiping, YOU Tianhui ZHANG Yao. Method for Interval multiple attribute decision-making problem with incomplete attribute weights[J]. Journal of northeastern university (natural science edition), 2005, 26(8): 798-800. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2005.08.023 (  0) 0)
|
| [101] |
杨红梅, 赵克勤. 偏联系数的计算与应用研究[J]. 智能系统学报, 2019, 14(5): 865-876. YANG Hongmei, ZHAO Keqin. The calculation and application of partial connection numbers[J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2019, 14(5): 865-876. (  0) 0)
|
 2020, Vol. 15
2020, Vol. 15


