文章信息
- 刘玄华, 朱秋映, 孟琴, 沈智勇, 阮玉华, 吴秀玲, 周信娟, 黄精华, 唐帅, 杨文敏.
- Liu Xuanhua, Zhu Qiuying, Meng Qin, Shen Zhiyong, Ruan Yuhua, Wu Xiuling, Zhou Xinjuan, Huang Jinghua, Tang Shuai, Yang Wenmin
- 广西壮族自治区2015-2018年新报告非婚非商业异性性传播HIV/AIDS特征分析
- Characteristics of newly reported HIV/AIDS cases with non-marital or non-commercial heterosexual transmission in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 2015-2018
- 中华流行病学杂志, 2020, 41(4): 537-541
- Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 2020, 41(4): 537-541
- http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20190625-00467
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2019-06-25
2. 中国疾病预防控制中心性病艾滋病预防控制中心, 北京 102206;
3. 广西壮族自治区疾病预防控制中心, 南宁 530028
2. National Center for AIDS/STD Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing 102206, China;
3. Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Center for Disease Prevention and Control, Nanning 530028, China
异性性传播已成为我国艾滋病流行的最主要传播途径[1],广西壮族自治区(广西)新报告HIV/AIDS异性性传播构成比明显高于全国平均水平,是造成广西艾滋病疫情快速增长的重要因素之一[2]。国内多项研究表明,非婚非商业异性性传播(非婚非商性传播)已成为异性性传播HIV的主要途径[3-6]。本研究分析2015-2018年广西新报告非婚非商性传播HIV/AIDS的流行病学特征及相关影响因素,为广西控制异性性传播HIV提供参考依据。
资料与方法1.资料来源:中国疾病预防控制信息系统艾滋病防治基本信息系统,下载2015年1月1日至2018年12月31日广西新报告HIV/AIDS数据。
2.研究对象:纳入标准:①2015-2018年新报告HIV/AIDS;②现住址为广西;③≥18岁。排除标准:查无此人或既往报告HIV/AIDS。
3.相关定义:
(1)非婚非商性传播:与非配偶发生的婚前或婚外、或与非固定性伴发生的异性性行为,且不以换取金钱或其他财物为目的。
(2)婚姻状况:①已婚/有固定性伴:已婚,或者未婚有固定性伴、离异有固定性伴、丧偶有固定性伴;②未婚/离异/丧偶:未婚无固定性伴、离异无固定性伴、丧偶无固定性伴。
4.研究方法及内容:采用横断面研究方法,分析广西2015-2018年新报告HIV/AIDS数据,收集研究对象的性别、年龄、职业、婚姻状况、文化程度、民族、户籍地、现住址、报告年份等基本特征,比较不同特征新报告非婚非商性传播HIV/AIDS与其他传播途径(商业性传播、配偶/固定性伴传播、男男性行为传播、注射毒品等)的传播风险差异。
5.统计学分析:应用SPSS 23.0软件整理数据和统计分析。采用χ2检验比较不同特征研究对象的非婚非商性传播构成的差异;利用单因素、多因素logistic回归模型,以非婚非商性传播作为因变量,以基本特征作为自变量,将单因素分析有统计学意义的自变量纳入多因素模型,分析相关因素对非婚非商性传播风险的影响。双侧检验,检验水准α=0.05。
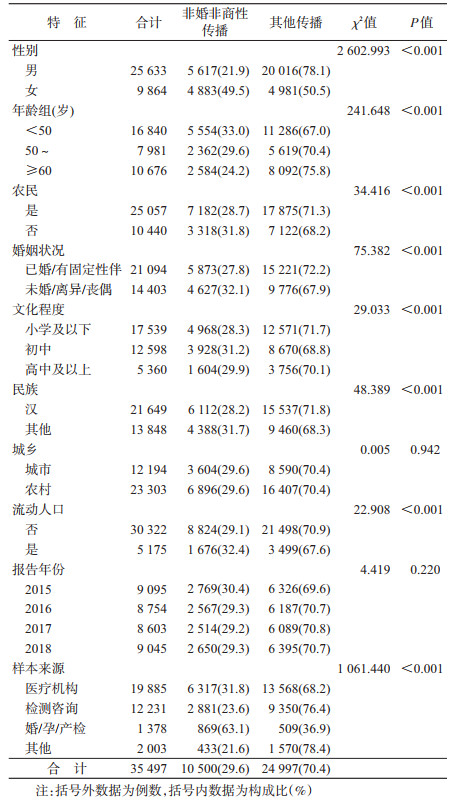
结果1.新报告HIV/AIDS基本特征:2015-2018年广西≥18岁新报告HIV/AIDS 35 497例,异性性传播32 648例(占92.0%),非婚非商性传播10 500例,占新报告HIV/AIDS的29.6%(10 500/35 497),占异性性传播的32.2%(10 500/32 648);其中男性5 617例(占53.5%,5 617/10 500),女性4 883例(占46.5%,4 883/10 500),男女性别比为1.2:1;汉族6 112例(占58.2%,6 112/10 500);年龄(49.5±15.0)岁;已婚/有固定性伴5 873例(占55.9%,5 873/10 500)。见表 1。
2.非婚非商性传播的HIV/AIDS基本特征:男性和女性中,非婚非商性传播的构成比分别为21.9%(5 617/25 633)和49.5%(4 883/9 864)。非婚非商性传播构成比在性别、年龄、是否为农民、婚姻状况、文化程度、民族、样本来源、是否为流动人口的差异有统计学意义,女性高于男性,随着年龄增长而下降,<50岁组高于50~岁组,50~岁组高于≥60岁组;未婚/离异/丧偶高于已婚/有固定性伴;初中以上文化程度高于小学及以下;流动人口高于常住人口。见表 1。
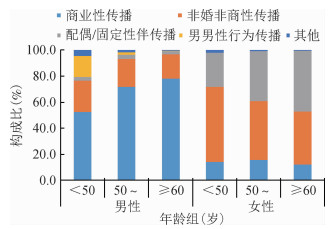
3.新报告HIV/AIDS不同性别与年龄组的感染方式:男性以商业性传播为主(64.4%,16 516/25 633),女性以非婚非商性传播为主(49.5%,4 883/9 864),差异有统计学意义(χ2=12 703.170,P<0.001)。男性的商业性传播构成比随年龄增加而增加(趋势χ2=2 284.673,P<0.001),女性的非婚非商性传播构成比随年龄增加而减少,而配偶/固定性伴传播构成比随年龄增加而增加(趋势χ2=104.380,P<0.001)。见图 1。
|
| 图 1 2015-2018年广西壮族自治区新报告HIV/AIDS不同性别与年龄组的感染方式 |
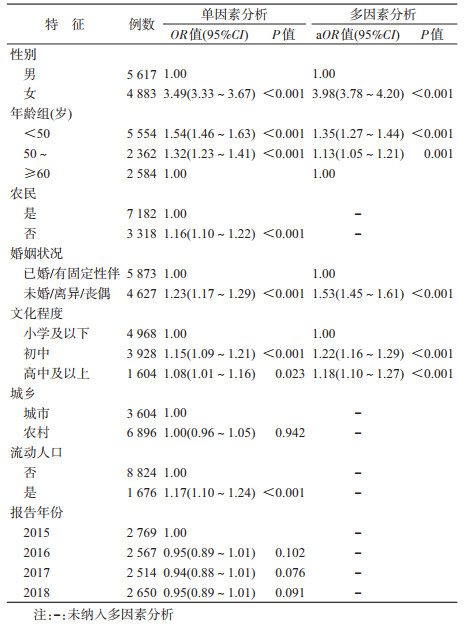
4.非婚非商性传播HIV/AIDS感染HIV影响因素:单因素logistic回归分析结果显示,性别、年龄、是否为农民、婚姻状况、文化程度、是否为流动人口等自变量有统计学意义,纳入多因素logistic回归分析结果显示,女性非婚非商性传播的HIV感染风险是男性的3.98倍,<50、50~59岁组分别是≥60岁组的1.35、1.13倍,未婚/离异/丧偶是已婚/有固定性伴的1.53倍,初中、高中及以上文化程度分别是小学及以下的1.22、1.18倍。见表 2。
2015-2018年广西新报告HIV/AIDS的非婚非商性传播构成比为29.6%,接近2014年上半年全国的32.1%[3],低于2015-2017年杭州市的46.6%[4]、2016年广东省的44.0%[5]以及2017年北京市男性的75.25%、女性的70.10%水平[6]。近年来社会性观念日益开放,尤其随着网络交友方式的兴起和普及,与暗娼、嫖客等高危人群相比,非婚非商性传播人群更具隐蔽性、多样性,分布更为广泛,给艾滋病干预工作带来较大挑战。
本研究发现,不同性别、年龄、婚姻状况、文化程度的人群非婚非商性传播HIV构成比存在差异。非婚非商性传播HIV的危险因素包括女性、<60岁、未婚/离异/丧偶和初中及以上文化程度,女性HIV/AIDS的非婚非商性传播构成比为49.5%,远高于男性HIV/AIDS的21.9%。未婚/离异/丧偶者的非婚非商性传播构成比高于已婚/有固定性伴人群,与2015-2017年杭州市未婚或已婚者高于离异/丧偶者的研究结果不同[4]。随着文化程度的提高,非婚非商性传播的HIV感染风险有所增加。随着年龄增长,非婚非商性传播HIV构成比逐渐下降,<50岁组高于50~岁组,50~岁组高于≥60岁组。
目前商业性传播是广西艾滋病异性性传播的主要感染方式,其次为非婚非商性传播。国内多数预防干预研究和哨点监测的对象主要为暗娼、嫖客等商业性传播的高危人群[7-11],非婚非商性传播人群是当前艾滋病干预的薄弱环节。需摸清广西非婚非商性传播的人群规模和分布特征,开展针对性监测,明确非婚非商性行为的来源和传播链,探索非婚非商性传播HIV的防控措施。
本研究存在不足,数据缺少HIV/AIDS非婚非商性传播接触史、发生高危性行为的详细信息,可能存在漏报、误分或误报,对结果的解释、结论的外推需谨慎。
综上所述,2015-2018年广西新报告HIV/AIDS中,非婚非商性传播的构成比接近30.0%,非婚非商性传播HIV的危险因素包括女性、<60岁、未婚/离异/丧偶和初中及以上文化程度,应采取精准的防控措施。
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
| [1] |
中国疾病预防控制中心性病艾滋病预防控制中心性病控制中心. 2018年第3季度全国艾滋病性病疫情[J]. 中国艾滋病性病, 2018, 24(11): 1075. NCAIDS, NCSTD, China CDC. Update on the AIDS/STD epidemic in China the third quarter of 2018[J]. Chin J AIDS STD, 2018, 24(11): 1075. DOI:10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2018.11.01 |
| [2] |
葛宪民, 杨文敏, 朱秋映, 等. 广西壮族自治区2010-2017年艾滋病流行病学特征分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2019, 40(3): 315-321. Ge XM, Yang WM, Zhu QY, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of HIV/AIDS in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, 2010-2017[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2019, 40(3): 315-321. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2019.03.011 |
| [3] |
陈方方, 郭巍, 王丽艳, 等. 我国部分地区艾滋病非婚异性性传播病例感染方式构成及特征分析[J]. 中国艾滋病性病, 2015, 21(7): 550-553. Chen FF, Guo W, Wang LY, et al. Characteristics of HIV/AIDS cases with extra-marital heterosexual transmission in some regions in China[J]. Chin J AIDS STD, 2015, 21(7): 550-553. DOI:10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2015.07.02 |
| [4] |
陈珺芳, 吴虹, 张兴亮, 等. 杭州市2015-2017年非婚非商业的异性性传播新报告艾滋病病毒感染者特征分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2018, 39(12): 1602-1606. Chen JF, Wu H, Zhang XL, et al. Characteristics of newly reported HIV/AIDS cases with non-marital but non-commercial heterosexual transmission in Hangzhou, 2015-2017[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2018, 39(12): 1602-1606. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.12.012 |
| [5] |
林梓铭, 李艳, 付笑冰, 等. 广东省2015-2016年新报告HIV/AIDS病人异性性途径传播方式分析[J]. 中国艾滋病性病, 2017, 23(11): 1002-1005. Lin ZM, Li Y, Fu XB, et al. Study on modes of HIV transmission through heterosexual contact in Guangdong province, 2015-2016[J]. Chin J AIDS STD, 2017, 23(11): 1002-1005. DOI:10.13419/j.cnki.aids.2017.11.08 |
| [6] |
王娟, 贺淑芳, 李洋, 等. 2017年北京市艾滋病流行特征分析[J]. 首都公共卫生, 2018, 12(6): 282-284. Wang J, He SF, Li Y, et al. Analysis of epidemiological characteristics of HIV/AIDS in Beijing, 2017[J]. Cap J Public Health, 2018, 12(6): 282-284. DOI:10.16760/j.cnki.sdggws.2018.06.002 |
| [7] |
孙坤, 卢珊, 郭巍, 等. 暗娼商业性行为中安全套使用的影响因素研究进展[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2018, 39(8): 1135-1142. Sun K, Lu S, Guo W, et al. Progress of research on influencing factors of condom use among female sex workers[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2018, 39(8): 1135-1142. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.08.024 |
| [8] |
李培龙, 李东民, 葛琳, 等. 四川省雅安市嫖客HIV和梅毒感染状况及相关行为调查[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2018, 39(3): 329-332. Li PL, Li DM, Ge L, et al. Prevalence of HIV infection and syphilis and related behaviors in clients in Ya'an of Sichuan province[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2018, 39(3): 329-332. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.03.015 |
| [9] |
胡婷, 董丽芳, 丁正伟, 等. 西安市和咸阳市性病门诊男性就诊者HIV/STD感染及相关行为特征比较[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(12): 1634-1637. Hu T, Dong LF, Ding ZW, et al. HIV/STD prevalence and related behaviors among male STD clinic attendees in Xi'an and Xianyang cities, Shaanxi province[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(12): 1634-1637. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.12.010 |
| [10] |
陆华湘, 唐振柱, 沈智勇, 等. 广西中部地区中老年嫖客使用助性药西地那非的相关危险因素研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2014, 35(11): 1218-1222. Lu HX, Tang ZZ, Shen ZY, et al. Sildenafil use and relevant risk factors among middle-aged or elderly male clients of female commercial sex workers in the central areas of Guangxi, China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2014, 35(11): 1218-1222. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2014.11.009 |
| [11] |
韦所苏, 邹云锋, 吴腾燕, 等. 广西女性性工作者暴露前药物预防HIV感染接受意愿及其影响因素研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2011, 32(11): 1091-1094. Wei SS, Zou YF, Wu TY, et al. Acceptability and influencing factors on pre-exposure prophylaxis programs among female sex workers in Guangxi, China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2011, 32(11): 1091-1094. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2011.11.008 |
 2020, Vol. 41
2020, Vol. 41