文章信息
- 伍俊锋, 林李嵩, 陈法, 刘凤琼, 鄢灵君, 包晓丹, 汪靖, 王瑞, 林亮坤, 邱宇, 郑晓燕, 胡志坚, 蔡琳, 何保昌.
- Wu Junfeng, Lin Lisong, Chen Fa, Liu Fengqiong, Yan Lingjun, Bao Xiaodan, Wang Jing, Wang Rui, Lin Liangkun, Qiu Yu, Zheng Xiaoyan, Hu Zhijian, Cai Lin, He Baochang.
- 福建省口腔鳞状细胞癌预后指数构建
- A novel prognostic index for oral cancer in Fujian province
- 中华流行病学杂志, 2018, 39(6): 841-846
- Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 2018, 39(6): 841-846
- http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.06.028
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2017-09-15
2. 350004 福州, 福建医科大学附属第一医院口腔颌面外科
2. Department of Stomatology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350004, China
口腔癌主要病理类型为鳞状细胞癌(oral squamous cell carcinoma,OSCC)[1]。近年来OSCC患者的死亡率略有下降,但5年生存率仍徘徊在50%[2]。有研究显示,临床病理特征、治疗方式、吸烟、饮酒、口腔卫生、HPV感染等均为影响OSCC患者的主要预后因素[3-6],由于个体差异、预后因素暴露不同等情况,影响OSCC患者预后的评价,因而构建一个OSCC患者的预后综合指标尤为重要。目前国内外学者提出的预后指数模型得到广泛关注[7-8],但在OSCC患者中构建预后指数的研究鲜有报道。本研究针对福建地区OSCC患者开展大样本的预后随访调查,在Cox比例风险模型分析的基础上构建预后指数(prognostic index,PI),并验证模型检验效能,旨在为OSCC患者个体化治疗和改善预后提供科学依据。
对象与方法1.研究对象:收集2004年1月至2016年6月福建医科大学附属第一医院口腔颌面外科确诊的634例OSCC患者,其中男性408例,女性226例,年龄中位数57(18~90)岁。纳入标准:①手术或活检标本经病理确诊的原发性OSCC;②均经手术治疗;③在福建省本地居住>10年;④排除其他继发性OSCC、伴有其他口腔相关疾病和病情危重不能清晰回答问题者。通过计算机产生随机数字,以1 : 1的比例将纳入的调查对象随机分为建立模型组(建模组)和验证模型组(验证组),其中建模组318(男性206、女性112)例,验证组316(男性202、女性114)例。本研究通过福建医科大学伦理委员会批准[批号:(2012)福医伦理审字第(120)号]。
2.研究方法:
(1)问卷调查:采用统一编制的调查问卷,经患者知情同意,在入院后进行面访调查。包括一般情况(年龄、性别、文化程度、身高、体重等)、吸烟史、饮酒史、口腔卫生状况、肿瘤家族史等。登记患者诊治情况表,主要包括诊断情况(OSCC确诊时间、肿瘤部位、TNM分期、组织学分级等)和治疗情况(手术、放疗、化疗等)。
(2)随访调查:2004年1月1日至2017年7月采用电话随访。每6个月收集1次随访信息,以1周内连续3次不同时间随访失败定为失访。失访、死于其他原因或随访截止时仍存活者视为删失,作截尾处理。随访截止时共收集634例,截尾数据398例(62.78%),其中失访88例(13.88%),死于其他疾病13例(2.05%),终止297例(46.85%),完全数据者236例(37.22%)。共随访22 319.567人月。
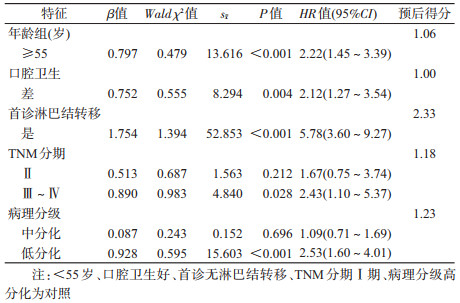
3.相关定义:①吸烟:累计吸烟>100支[9];②饮酒:每周至少1次,持续>6个月[10-12];③TNM分期:口腔癌分期按2002年AJCC唇及口腔癌分期方案进行确定[13];④口腔卫生:根据简化软垢指数(debris index-simplified)进行评定,得分为0~1分为口腔卫生好,2~3分为口腔卫生差[14-16];⑤PI[17]:利用多因素模型中有意义变量的回归系数β值构建PI模型。PI=β1/β最小+β2/β最小…+βn/β最小。
4.统计学分析:采用EpiData 3.1软件建立数据库,进行数据双录入。应用χ2检验比较组间差异;log-rank检验比较生存差别;采用Cox比例风险回归模型对影响生存时间的因素进行单因素分析,纳入所有因素(性别、年龄、BMI、文化程度、职业、居住地、肿瘤家族史、治疗前吸烟、治疗前饮酒、口腔卫生、TNM分期、组织分化程度、治疗方式、首诊淋巴结转移)进入多因素Cox比例风险回归模型,并做共线性诊断判断纳入因素是否存在多重共线性,使用逐步回归分析法对变量进行筛选,变量进入模型的入选标准为0.05,剔除标准为0.10。以多因素模型中每个有统计学意义的预测变量的β值构建预后指数PI。采用三分位数确定PI的截断点,将患者按PI值划分为不同的亚组,采用Kaplan-Meier法计算生存率并绘制生存曲线。运用赤池信息准则(Akaike information criterion,AIC)和Harrell一致性指数(Harrell’s c-statistic,C)在验证组中反映预后指数模型的预测效能[18]。统计学分析采用Stata 13.0软件,P值均为双侧概率检验,检验水准α=0.05。
结果1.一般特征:建模组318例,1、3、5年生存率为73.29%、63.48%、56.93%,中位随访时间为34.33个月;验证组316例,1、3、5年生存率为76.96%、63.14%、56.40%,中位随访时间为35.72个月。经log-rank检验,两组OSCC患者生存率的差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.42,P=0.518)。此外两组患者性别、年龄、BMI、文化程度、职业、居住地和肿瘤家族史分布的差异均无统计学意义(表 1)。
2. OSCC预后影响因素:单因素分析显示建模组人群中年龄、TNM分期、N分期、组织病理分级、治疗方式、首诊淋巴结转移均为口腔癌预后的影响因素(P<0.05)(表 2)。纳入所有影响因素(共线性诊断提示不存在多重共线性,所有纳入变量VIF<3)进入Cox比例风险回归模型,采用逐步回归分析法进行多因素分析,结果显示年龄、口腔卫生、首诊淋巴结转移、TNM分期和病理学分级是影响OSCC患者预后的因素(表 3)。
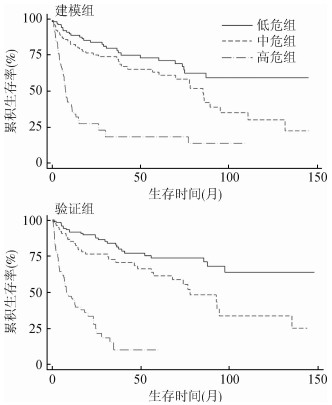
3.建模组与验证组PI、生存曲线比较:根据多因素有意义的β值计算PI,按三分位将PI分为低危、中危和高危组,经单因素Cox风险比例回归模型得出中危组和高危组相对于低危组可增加口腔癌死亡风险,且趋势性χ2检验提示差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。在验证组中检验其预测效能,结果显示检验效能较好(AIC=1 150.470,C=0.737 3)(表 4)。建模组以低危组为对照组,结果显示中危组和高危组预后情况较差,并在验证组中得到验证(图 1)。
|
| 图 1 建模组和验证组口腔鳞状细胞癌预后指数生存曲线 |
本研究在福建地区开展大样本OSCC预后随访调查,通过Cox风险比例模型筛选出OSCC相关的预后因素。结果发现年龄、口腔卫生、首诊淋巴结转移、TNM分期和组织病理学分级是OSCC预后影响因素,并构建PI模型验证其效能,显示可较好反映OSCC患者的生存状况。
肿瘤病理学分级是反映肿瘤细胞破坏性和增殖速度的指标[19],影响患者预后。本研究结果显示,相对于OSCC高分化的患者,低分化可增加患者死亡风险。肿瘤TNM分期同样严重影响预后。本研究发现,TNM分期为Ⅲ~Ⅳ期相对于Ⅰ期可增加OSCC的死亡风险(调整HR=2.43),与Gao等[20]的报道一致。此外,手术联合放化疗并未比单纯手术有更好的预后(HR=1.73),其原因可能与患者的TNM分期有关[21]。但此结果在多因素Cox模型中无统计学意义,可能是由于同时进行手术合并放化疗的例数较少,有待扩大样本进一步研究。肿瘤患者若出现淋巴结转移及复发,其预后不良[22-24],与本研究OSCC患者首诊淋巴结转移可增加死亡风险的结果一致。口腔卫生是影响OSCC预后的主要因素之一。本研究结果显示较差的口腔卫生状况可增加患者的死亡风险。较差的口腔卫生可增加口腔内牙周病相关菌群,从而导致癌症的发生,并在患者术后康复的过程中引起手术切缘炎症反应的发生,从而影响患者的预后[4]。此外,研究中还发现年龄≥55岁可增加OSCC死亡的风险,高龄口腔癌患者由于年龄的增加,机体对突变细胞的免疫监视减弱,对肿瘤的免疫效应降低[25]。OSCC是常见的口腔恶性肿瘤,在一些亚洲地区,其占所有恶性肿瘤病例的10%以上[26],其预后差,是患者死亡的主要原因之一。
本文通过Cox风险比例模型筛选出OSCC预后影响因素,通过最小β权重法构建PI模型,并根据PI三分位数将患者分为低危组、中危组和高危组,在验证组中验证其效能,对OSCC患者生存情况进行评估。结果显示高危组相对于低危组其口腔癌死亡风险更高,且其检验效能良好(AIC和C值分别为1 150.47和0.737 3),与Chen等[27]研究结果一致。提示在OSCC患者的治疗中可计算PI得分,在不进行生化检测情况下,根据患者年龄、口腔卫生、首诊淋巴结转移、TNM分期和组织病理学分级等信息预测其生存情况,并根据患者的危险分组实施针对性治疗方案。
利益冲突: 无
| [1] | Warnakulasuriya S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer[J]. Oral Oncol, 2009, 45(4/5): 309–316. DOI:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2008.06.002 |
| [2] | Patmanathan SN, Johnson SP, Lai SL, et al. Aberrant expression of the S1P regulating enzymes, SPHK1 and SGPL1, contributes to a migratory phenotype in OSCC mediated through S1PR2[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 25650. DOI:10.1038/srep25650 |
| [3] | Bu JQ, Bu X, Liu B, et al. Increased expression of tissue/salivary transgelin mRNA predicts poor prognosis in patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC)[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2015, 21: 2275–2281. DOI:10.12659/MSM.893925 |
| [4] | Sato J, Goto J, Harahashi A, et al. Oral health care reduces the risk of postoperative surgical site infection in inpatients with oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2011, 19(3): 409–416. DOI:10.1007/s00520-010-0853-6 |
| [5] | Grimm M. Prognostic value of clinicopathological parameters and outcome in 484 patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma:microvascular invasion (V+) is an independent prognostic factor for OSCC[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2012, 14(11): 870–880. DOI:10.1007/s12094-012-0867-2 |
| [6] | Zhang M, Rose B, Lee CS, et al. In vitro 3-dimensional tumor model for radiosensitivity of HPV positive OSCC cell lines[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2015, 16(8): 1231–1240. DOI:10.1080/15384047.2015.1056410 |
| [7] | Zhou Z, Sehn LH, Rademaker AW, et al. An enhanced International Prognostic Index (NCCN-IPI) for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated in the rituximab era[J]. Blood, 2014, 123(6): 837–842. DOI:10.1182/blood-2013-09-524108 |
| [8] | Sposito C, Di Sandro S, Brunero F, et al. Development of a prognostic scoring system for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(36): 8194–8202. DOI:10.3748/wjg.v22.i36.8194 |
| [9] | World Health Organization.Guidelines for controlling and monitoring the tobacco epidemic[M]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1998. |
| [10] | Yan LJ, Chen F, He BC, et al. A novel environmental exposure index and its interaction with familial susceptibility on oral cancer in non-smokers and non-drinkers:a case-control study[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 274(4): 1945–1950. DOI:10.1007/s00405-016-4427-1 |
| [11] |
张林峰, 赵连成, 周北凡, 等. 男性饮酒与缺血性脑卒中发病关系的研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2004, 25(11): 954–957.
Zhang LF, Zhao LC, Zhou BF, et al. Alcohol consumption and incidence of ischemic stroke in male Chinese[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2004, 25(11): 954–957. DOI:10.3760/j.issn:0254-6450.2004.11.009 |
| [12] | World Health Organization.International guide for monitoring alcohol consumption and related harm[M]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2000. |
| [13] | Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, et al.AJCC cancer staging handbook[M]. 6th ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2002: 47–60. |
| [14] | Llena-Puy C. The rôle of saliva in maintaining oral health and as an aid to diagnosis[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2006, 11(5): E449–E455. |
| [15] | Greene JG, Vermillion JR. The simplified oral hygiene index[J]. J Am Dent Assoc, 1964, 68(1): 7–13. DOI:10.14219/jada.archive.1964.0034 |
| [16] | Greene JC. Oral hygiene and periodontal disease[J]. Am J Public Health Nations Health, 1963, 53(6): 913–922. DOI:10.2105/AJPH.53.6.913 |
| [17] | Bower M, Gazzard B, Mandalia S, et al. A prognostic index for systemic AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma treated in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2005, 143(4): 265–273. DOI:10.7326/0003-4819-143-4-200508160-00007 |
| [18] | Lee CC, Ho HC, Su YC, et al. The prognostic ability of log odds of positive lymph nodes in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Medicine, 2015, 94(27): e1069. DOI:10.1097/MD.0000000000001069 |
| [19] |
黄江峰, 王靖雯, 何保昌, 等. 口腔鳞状细胞癌患者生存影响因素研究[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2016, 50(10): 880–886.
Huang JF, Wang JW, He BC, et al. Study of survival factors of oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2016, 50(10): 880–886. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2016.10.009 |
| [20] | Gao CH, Wang ZJ, Li C, et al. A functional polymorphism (rs10817938) in the XPA promoter region is associated with poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma in a Chinese Han population[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(9): e0160801. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0160801 |
| [21] | Goldstein M, Kastan MB. The DNA damage response:implications for tumor responses to radiation and chemotherapy[J]. Annu Rev Med, 2015, 66: 129–143. DOI:10.1146/annurev-med-081313-121208 |
| [22] | Vázquez-Mahía I, Seoane J, Varela-Centelles P, et al. Predictors for tumor recurrence after primary definitive surgery for oral cancer[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2012, 70(7): 1724–1732. DOI:10.1016/j.joms.2011.06.228 |
| [23] | Zhang YY, Wang DC, Su JZ, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and outcomes of squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue in different age groups[J]. Head Neck, 2017, 39(11): 2276–2282. DOI:10.1002/hed.24898 |
| [24] | Cadoni G, Giraldi L, Petrelli L, et al. Prognostic factors in head and neck cancer:a 10-year retrospective analysis in a single-institution in Italy[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2017, 37(6): 458–466. DOI:10.14639/0392-100X-1246 |
| [25] |
刘善廷, 吴俊福, 郑荣寿, 等. 2009年中国口腔癌和咽喉癌发病与死亡情况分析[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2013, 47(7): 586–591.
Liu ST, Wu JF, Zheng RS, et al. Incidence and mortality of oralcavity and pharyngeal cancer in China, 2009[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2013, 47(7): 586–591. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2013.07.003 |
| [26] | Zhang W, Gao CH, Zhang SH, et al. Serum annexin A2 level is associated with diagnosis and prognosis in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 75(5): 1081–1087. DOI:10.1016/j.joms.2016.10.032 |
| [27] | Chen F, Cao YJ, Huang JF, et al. A novel prognostic index for oral squamous cell carcinoma patients with surgically treated[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(33): 55525–55533. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.14821 |
 2018, Vol. 39
2018, Vol. 39