文章信息
- 刘然, 张桂林, 孙响, 郑重, 刘晓明, 赵焱, 刘栓奎, 党荣理, 赵彤言. 2014.
- Liu Ran, Zhang Guilin, Sun Xiang, Zheng Zhong, Liu Xiaoming, Zhao Yan, Liu Shuankui, Dang Rongli, Zhao Tongyan. 2014.
- 新疆艾比湖布尼亚病毒的分离与分子生物学鉴定
- Isolation and molecular characterization on Abbey Lake Orthobunyavirus (Bunyaviridae) in Xinjiang,China
- 中华流行病学杂志, 2014, 35(8): 939-942
- Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 2014, 35(8): 939-942
- http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2014.08.014
-
文章历史
- 投稿日期:2014-2-14
新疆艾比湖湿地国家级自然保护区位于准噶尔盆地西南,是典型的湿地荒漠生态景观。湿地内栖息有鸟类、啮齿动物等160多种脊椎动物,夏秋季节蚊虫大量孳生,具备蚊传病毒(mosquito-borne virus)传播、蓄存的天然条件。本课题组曾利用高通量测序分析技术从当地库蚊种群中检测出高丰度的布尼亚科(Bunyaviridae)病毒RNA读序(reads),提示该地区蚊虫可能携带某种布尼亚科病毒。为验证上述结果,本研究试对该种病毒进行分离培养,最终从凶小库蚊(Culex modestus)中分离获得1株新型布尼亚病毒。 材料与方法
1. 材料:
(1)蚊标本:于2012年8月在艾比湖湿地保护区(东经82°33′47″~83°53′21″,北纬44°31′05″~45°09′35″)苇丛、静水附近设置CO2诱蚊灯于当日20:00至次日06:00采集蚊虫样品。经蚊虫分类鉴定后,每100只库蚊为1份,置于冻存管中液氮冻存,共采集50份库蚊标本。
(2)实验动物与细胞:地鼠肾细胞系BHK-21(Baby hamster kidney-21)由军事医学科学院微生物流行病研究所病毒学专业实验室提供。2~3日龄昆明种乳鼠由新疆医科大学实验动物中心提供。
(3)试剂:Trizol试剂为Invitrogen公司产品;琼脂糖凝胶纯化试剂盒QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit为Qiagen公司产品;AMV一步法RT-PCR试剂盒、分子Marker 2000为TaKaRa公司产品;DMEM细胞培养基与胎牛血清为Life technology公司产品;0.22 μm滤器为Millipore公司产品。
(4)引物:布亚韦拉血清群病毒核酸鉴定使用Lambert和Lanciotti[1]文献提供的Bun引物对序列,5′-CTG CTA ACA CCA GCA GTA CTT TTG AC-3′与5′-TGG AGG GTA AGA CCA TCG TCA GGA ACT G-3′。艾比湖布尼亚病毒基因组S节段扩增引物NP-F/R:5′-CTT GGC TTT TAA ATG TTG GAG TTG G-3′与5′-TAG CCC GAT TAA TGC ACT TCT CTG-3′,M基因节段扩增M-1F/2R:5′-CAC TGT TGA TTG TTG CCC TTC TAA-3′与5′-ATT ATT TCT GCA TTT GCT GGT GTG-3′。上述扩增产物预期长度为651 bp与980 bp。引物合成与测序工作均由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司完成。
2. 病毒分离及鉴定:
(1)病毒空斑试验:将库蚊样本经磷酸盐缓冲液漂洗3次,加入2 ml DMEM细胞培养液反复研磨,3 000 r/min离心5 min,离心上清液经0.22 μm滤过后,取1 ml接种25 cm2细胞培养瓶分种的BHK-21细胞,37 ℃吸附1 h后弃上清,加入含有2%胎牛血清(v/v)的DMEM细胞培养液5 ml,置5% CO2孵箱培养3 d以上,利用Olympus IX51显微镜每日观察细胞病变现象。取病毒上清液1 ml按10倍稀释至10-6,取每个稀释度下病毒悬液1 ml接种分种于12空板中的BHK-21细胞,吸附结束后弃上清并用含有1.5%(m/v)低熔点琼脂糖的DMEM培养液覆盖,37 ℃培养3 d至空斑形成,最后用0.1%(m/v)结晶紫-甲醇溶液染色观察。
(2)病毒核酸提取与扩增:吸取病毒细胞培养上清液210 μl移入灭菌1.5 ml eppendorf管中,然后加入490 μl Trizol试剂混匀,室温静止15 min,再加入700 μl无水乙醇。13 000 r/min 4 ℃离心10 min,弃上清,待沉淀晾干后,加入100 μl 无核酸酶去离子水溶解。利用一步法RT-PCR对布尼亚病毒科成员进行核酸检测。正布尼亚病毒属(Orthobunyavirus)通用引物BUN按Lambert等方法扩增。病毒基因组S、M节段RT-PCR扩增方法:反转录条件为50 ℃反应30 min,95 ℃热变性10 min;PCR反应条件为95 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸45 s,共35个循环,72 ℃最终延伸5 min。RT-PCR阳性扩增产物经1.5%(m/v)琼脂糖凝胶纯化后,交生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行Sanger法双向测序。
(3)病毒基因组序列比对分析:利用Mega 6.0软件对扩增产物序列与布亚韦拉(Bunyamwera)血清群病毒序列进行Blast比对。采用邻位相连法(neighbor-joining),分别构建病毒基因组S与M节段序列的系统发育树,确信限度估计设为1 000 Bootstrap。将加州脑炎(California encephalitis)复合群中Tahyna virus设为组外对照(表 1)。
1. 蚊虫分类及病毒分离:艾比湖湿地蚊虫包括伊蚊属6种、库蚊属2种及脉毛蚊属、曼蚊属、按蚊属各1种,共计5属11种。其中赫坎按蚊(Anophele hyrcanus)和凶小库蚊为优势种,分别占蚊虫种群数量的52.4%和36.6%。一组凶小库蚊样品接种BHK-21和Vero细胞,3 d后即能产生细胞圆缩、脱落等病变现象(图 1)。连传3代以上,细胞病变现象逐渐加强,病变出现时间缩短至2 d(图 2)。表明从艾比湖库蚊中分离获得一种能对哺乳动物细胞具有致病性的病毒,暂定名为艾比湖布尼亚病毒(Abbey Lake bunyavirus,Ab-BUNV)。
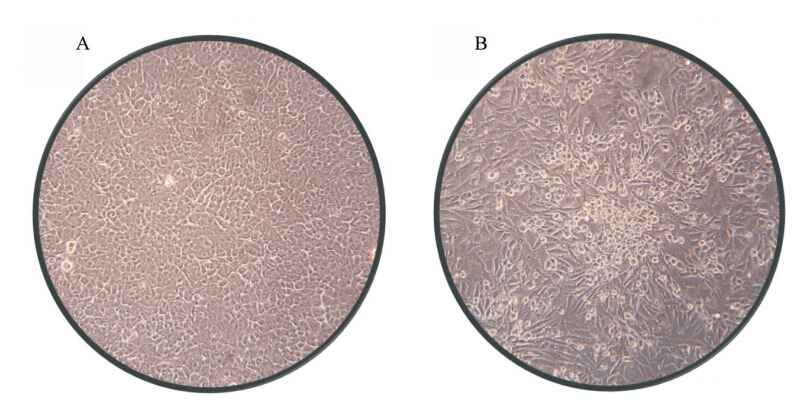 |
| 注:A. BHK-21正常对照; B. Ab-BUNV感染引起的BHK-21病变(20×)图 1 Ab-BUNV的BHK-21细胞毒力试验结果 |
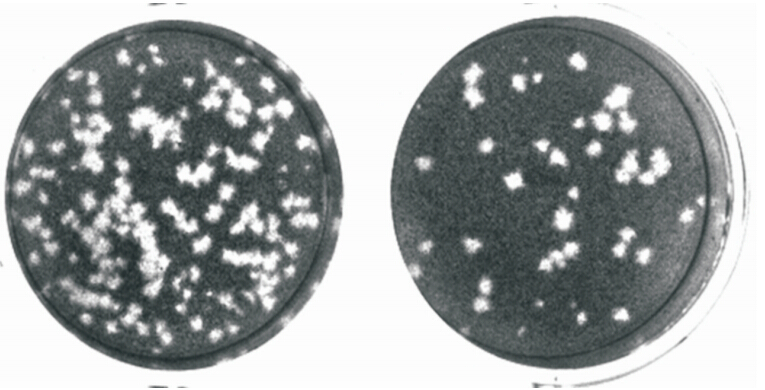 |
| 图 2 Ab-BUNV在BHK-21上形成的空斑形态观察(4×) |
2. 病毒基因组鉴定:为鉴定Ab-BUNV分子生物学特征,首先利用RT-PCR对病毒核酸进行扩增并获得长度为255 bp的正布尼亚病毒属特异性产物,而黄病毒属、甲病毒属病毒检测结果均为阴性。序列比对结果初步表明Ab-BUNV属布尼亚病毒科正布尼亚病毒属成员,归入布亚韦拉病毒血清复合群。根据布尼亚属病毒保守序列设计引物,通过扩增分别获得病毒基因组S和M节段的较长片段,分别为651 bp与980 bp,GenBank登录号分别为KJ412986和KJ412987。Ab-BUNV的S、M节段序列与同群病毒的比对结果进一步显示,Ab-BUNV在进化亲缘关系上仅与非洲Germiston布尼亚病毒最为接近(图 3)。S节段核苷酸序列同源性为90.6%, 氨基酸序列同源性为95.0%;M节段核苷酸序列同源性为78.6%,氨基酸序列同源性为86.1%。Ab-BUNV的S、M节段与Germiston病毒同源,表明病毒基因组节段间未出现重排现象。L节段基因序列尚不清楚。表明分离自我国新疆北部的Ab-BUNV是布亚韦拉血清群病毒中的新成员。 讨 论
布尼亚病毒科成员是一大群带有包膜的负链RNA病毒,共分为5个属(Bunyavirus、Nairovirus、Hantavirus、Phlebovirus和Tospovirus)。其中布尼亚病毒属(Bunyavirus)成员数量多达160余种,包括18个血清群。例如分离自新疆喀什地区的Tahyna病毒属于加州脑炎血清群[2]。而此次分离获得的Ab-BUNV与分离自云南地区的Batai病毒同属布亚韦拉血清型[3]。
布尼亚病毒基因组由L、M和S三个节段组成,分别编码病毒的RNA聚合酶、包膜糖蛋白(Gn/Gc)及核衣壳蛋白。其中M节段核苷酸序列变异性高,也是布尼亚病毒属形成众多血清群的遗传基础。Ab-BUNV的M节段序列与亲缘关系最近的Germiston病毒的氨基酸序列同源性也未超过90%[4, 5],提示Ab-BUNV是一种新发现的布尼亚病毒。 从Ab-BUNV与其他布尼亚病毒的进化亲缘关系[6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15],以及引起细胞病变现象均提示该病毒对人类具有潜在致病性。而目前对Ab-BUNV的生物学特性及其传播流行的规律还知之甚少,且缺乏当地人群抗体阳性率检测数据。该病毒的主要媒介——凶小库蚊多栖息于伊犁河、额尔齐斯河及额敏河流域为主的盐渍性荒漠生态景观中[16],按蚊、库蚊和伊蚊等蚊种均可能作为布尼亚病毒的媒介生物。由此推测Ab-BUNV在新疆地区的分布范围可能不仅限定于艾比湖及其周边区域,应对新疆地区蚊媒病毒开展监测。
| [1] Lambert AJ, Lanciotti RS. Consensus amplification and novel multiplex sequencing method for S segment species identification of 47 viruses of the Orthobunyavirus,Phlebovirus,and Nairovirus genera of the family Bunyaviridae[J]. J Clin Microbiol,2009,47(8):2398-2404. |
| [2] Lu Z, Lu XJ, Fu SH,et al. Tahyna virus and human infection,China[J]. Emerg Infect Dis,2009,15(2):306-309. |
| [3] Fu SH,Sun XH,Wang HY,et al. Molecular biological identification of Batai virus isolated in China[J]. Chin J Exp Clin Virol,2005,19:331-334.(in Chinese)付士红,孙肖红,王环宇,等. 我国首次分离巴泰病毒的分子生物学鉴定[J]. 中华实验和临床病毒学杂志,2005,19:331-334. |
| [4] Kokernot RH, Smithburn KC,Paterson HE,et al. Isolation of Germiston virus,a hitherto unknown agent,from culicine mosquitoes,and a report of infection in two laboratory workers[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg,1960,9:62-69. |
| [5] Okuno T. Immunological studies relating two recently isolated viruses,Germiston virus from South Africa and Ilesha virus from West Africa,to the Bunyamwera group[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg,1961,10:223-226. |
| [6] Briese T,Bird B,Kapoor V,et al. Batai and Ngari viruses:M segment reassortment and association with severe febrile disease outbreaks in East Africa[J]. J Virol,2006,80(11):5627-5630. |
| [7] Gerrard SR, Li L, Barrett AD, et al. Ngari virus is a Bunyamwera virus reassortant that can be associated with large outbreaks of hemorrhagic fever in Africa[J]. J Virol,2004,78(16):8922-8926. |
| [8] Pachler K,Ruzek D,Nowotny N. Molecular characterization of the African ortho- bunyavirus Ilesha virus[J]. Infect Genet Evol,2013,20:124-130. |
| [9] Dilcher M, Sall AA, Hufert FT, et al. Clarifying Bunyamwera virus riddles of the past[J]. Virus Genes,2013,47(1):160-163. |
| [10] Elliott RM. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the small (S) RNA segment of Bunyamwera virus,the prototype of the family Bunyaviridae[J]. J Gen Virol,1989,70 ( Pt 5):1281-1285. |
| [11] Watts SL,Garcia-Maruniak A,Maruniak JE. Tensaw virus genome sequence and its relation to other Bunyaviridae[J]. Virus Genes,2009,39(3):309-318. |
| [12] Nguyen NL,Zhao G,Hull R,et al. Cache valley virus in a patient diagnosed with aseptic meningitis[J]. J Clin Microbiol,2013,51(6):1966-1969. |
| [13] Farfan-Ale JA,Lorono-Pino MA,Garcia-Rejon JE,et al. Detection of RNA from a novel West Nile-like virus and high prevalence of an insect-specific flavivirus in mosquitoes in the Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg,2009,80(1):85-95. |
| [14] Yandoko EN,Gribaldo S,Finance C,et al. Molecular characterization of African Ortho-bunyaviruses[J]. J Gen Virol,2007,88(Pt 6):1761-1766. |
| [15] Lambert AJ,Lanciotti RS. Molecular characterization of medically important viruses of the genus Ortho-bunyavirus[J]. J Gen Virol,2008,89(Pt 10):2580-2585. |
| [16] Zhang GL,Zheng Z,Dong YD,et al. Research on the population composition of mosquitoes and method of mosquitoes surveying in Beiwan area of Xinjiang, China[J]. Acta Parasitol Med Entomol Sinica,2011,18(2):95-98.(in Chinese)张桂林,郑重,董言德,等. 新疆额尔齐斯河下游北湾地区蚊虫种群组成及调查方法的研究[J]. 寄生虫与医学昆虫学报,2011,18(2):95-98. |
 2014, Vol. 35
2014, Vol. 35