b School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Chongqing Key Laboratory of Chemical Theory and Mechanism, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400030, China
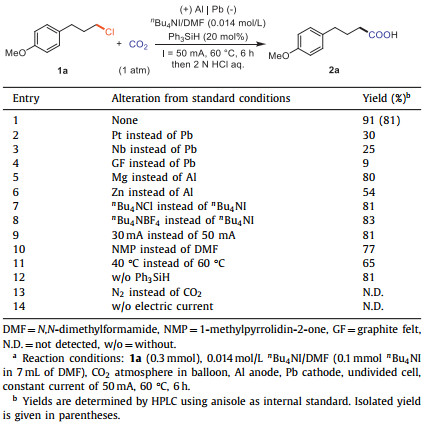
It is highly desirable to synthesize useful and sought-after compounds from readily available starting materials under mild conditions with ease of operation. Various investigations have shown that the production of valuable carboxylic acids using carbon dioxide (CO2) as C1 source is an attractive strategy due to the abundance, availability, sustainability, and non-toxicity of CO2 [1–23]. Among diverse methods to produce carboxylic acids, carboxylation of organo halides with CO2 is considered as one of the most attractive and practical approaches [24–31]. One representative strategy is conversion of organo halides to organometallic reagents, including Grignard, organolithium and organozinc reagents, which could react with CO2 to give carboxylic acids [32–47]. However, the practical application of this method is limited by the preparation, storage and use of the air and moisture-sensitive organometallic reagents. Meanwhile, transition metal-promoted or -catalyzed carboxylation of organo halides with CO2 has emerged as an efficient and highly promising strategy to generate a variety of valuable carboxylic acids [48–59]. Compared with the widely investigated carboxylation of alkyl bromines and iodinates with CO2, those transformations with unactivated alkyl chlorides, which are more readily available and inexpensive, were much less investigated due to the higher bond energy of C(sp3)—Cl cleavage. Notably, Martin reported a leading work in this field on nickel-catalyzed carboxylation of alkyl chlorides with CO2 under mild reaction conditions (Scheme 1A) [60]. However, excess of Mn powder was used as reductant, which might cause safety issue in large-scale synthesis. Therefore, it is still highly desirable to develop other sustainable strategies to realize safe and user-friendly carboxylation of unactivated alkyl chlorides.
|
Download:
|
| Scheme 1. Carboxylation of C(sp3)—Cl bonds with CO2. | |
As well-known, electrosynthesis has proven to be an efficient and environmentally friendly method and is increasingly pursued as a sustainable synthetic technology [61–102]. The direct electro-reductive or the integration of electrochemistry with transition-metal catalysis has been developed as an effective strategy to realize the carboxylation reactions [103–129], including those of activated C(sp3)—Cl bonds in benzyl chlorides and allyl chlorides (Scheme 1B) [130–142]. However, despite recent advances, the electro-reductive carboxylation of unactivated alkyl chlorides remains challenging. In addition to the high bond dissociation energy (~350 kJ/mol) of the C(sp3)—Cl bonds, many side reactions, such as radical involved dehydrochlorination [143], radical-radical coupling, and reductive protonation [144-145], might occur to result in low selectivity. To the best of our knowledge, there is only one isolated example for carboxylation of unactivated C—Cl bonds to give 25% yield of carboxylation products via successive single-electron reduction (Scheme 1C) [146]. With our continuous interest in carboxylation with CO2 [147–151], especially electrochemical carboxylation [152–157], herein we report an electro-reductive carboxylation of unactivated alkyl chlorides with CO2, offering an efficient and practical approach for the functionalization of inert alkyl chlorides and polyvinyl chloride (Scheme 1D).
We initiated our studies by investigating the electrochemical carboxylation of 1-(3-chloropropyl)−4-methoxybenzene 1a with CO2 to generate alkyl carboxylic acid derivative 2a. After systematic optimization of this reaction conditions (please see Supporting information for details), the desired product 2a was obtained in 81% isolated yield by employing Pb as the cathode and Al as the anode (Table 1, entry 1). A variety of cathode electrode materials were tested (entries 2–4) to give lower yields than lead (Pb), which has been widely used in electroreductive industrial processes and the detrimental corrosion should be paid attention to [158]. Among the tested anodes, aluminum proved to be the best choice (entries 5 and 6). Furthermore, when nBu4NCl or nBu4NBF4 was employed as an electrolyte in the reaction, it resulted in lower yield of 2a (entries 7 and 8). In addition, an attempt to decrease the current resulted in a slightly decrease in yield (entry 9). This reaction could also be carried out with polar solvents, such as N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), but with a lower yield (entry 10). The yield was decreases drastically to 65% when the reaction temperature was elevated to 40 ℃ (entry 11). Control experiments demonstrated that catalytic amounts of silane have a significant contribution to this reaction (entry 12), both CO2 (entry13) and electric current (entry 14) played an important role in this conversion.
|
|
Table 1 Optimization of the reaction conditions.a |
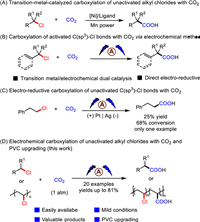
With the optimized conditions in hand (Table 1, entry 12), the scope of unactivated alkyl chlorides was then examined (Scheme 2). This transformation could proceed smoothly for unactivated alkyl chlorides with different chain lengths. For example, (3-chloropropyl)bezene derivatives bearing methoxy (1b, 1c), alkyl (1d), phenyl (1e) or fluorine (1f) delivered the corresponding products 2a-2f in good yields. Moreover, high value-added alkyl carboxylic acids could be successfully obtained from alkyl chlorides with longer carbon chain (1g-1j). In addition, alkyl chlorides in the presence of branched substituents also give the target products (2k) in moderate yields. The universality of our method was further illustrated by the tolerance of ether (2l, 2m), thiol ether (2n), amides (2o, 2p), heterocycles (2q) and ester (2r) groups. To our delight, secondary alkyl chlorides (1s, 1t) were also suitable substrates.
|
Download:
|
| Scheme 2. Substrate scope of unactivated alkyl chlorides. The same reaction conditions as Table 1, entry 1. Isolated yields. | |
Based on the success in carboxylation of unactivated alkyl chlorides, we posed the question of whether this strategy could be applied to the upcycling of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which is the world's fourth most popular general-purpose plastic [159]. Obviously, maximizing the amount of PVC upgrade to other functional materials is attractive [160,161]. However, currently, waste PVC materials upgrading lack green treatment methods due to their chemical inertness. We envision the possibility of achieving post-carboxylation of C—Cl bonds in PVC with CO2 to treat this problem. Therefore, we treated a commercial PVC tube under 0.1 mmol TBAI and 10 mol% DEHP [bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate] in DMF using a Pb cathode and Al anode at 60 ℃ under 50 mA CCE for 10 h. Then, a carboxyl-modified PVC was obtained after easily precipitation in MeOH. Attenuated total reflection flourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy showed a stretching frequency at 1760 cm−1, indicating the successful introduction of the carboxyl group. Furthermore, element analyser analysis showed that the proportions of C, H, and O elements in modified PVC were 47.74%, 6.22%, and 7.36%, respectively. Therefore, the carboxyl group content in modified PVC is around 14%, and the dechlorination protonation content is 4.8%. Additionally, water contact angle testing showed the water contact angle of PVC changed from 97.8° to 74.3° due to the modification, indicating that hydrophobic PVC can be modified to hydrophilic PVC through the introduction of carboxyl groups (Scheme 3).
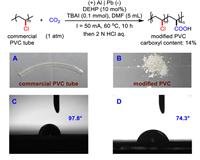
|
Download:
|
| Scheme 3. Carboxylation of PVC. (A) The photo of commercial PVC tube. (B) The photo of modified PVC. (C) Contact angle test image of commercial PVC tube. (D) Contact angle test image of modified PVC. | |
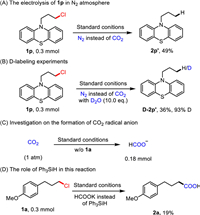
To further understand the mechanism of this reaction, some control experiments were conducted (Scheme 4, see more details in Supporting information). The experiment in absence of CO2 under the standard conditions provided the reductive protonation product 2p' in 49% yield (Scheme 4A). When 10 equiv. of D2O was subject to the reaction, we obtained the reductive deuteration product d in 36% isolated yield with 93% deuterium incorporation, which suggested that the alkyl anion might exist in this reaction. Additionally, the detection of formate when conducting experiment in the absence of 1a verified CO2 radical anion might be generated via reduction of CO2 at the cathode. According to previous work [162], the reaction of hydrosilance, carboxylates, and CO2 could give a mixture of formate and silanolate. When we conducted the control experiment of 1a using formate instead of Ph3SiH, we found the yield of 2a was decreases drastically to 19%, which indicates that the role of silanes is not to provide formate. Further control experiment validates the role of silanes in our laboratory.
|
Download:
|
| Scheme 4. Mechanistic investigation. | |
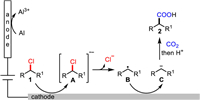
On the basis of the experimental results and previous reports [145], we proposed the following plausible mechanism for this electro-reductive carboxylation (Scheme 5). First, at the cathode, single-electron transfer (SET) reduction of 1 takes place to generate the corresponding radical anion A, which further undergoes C—Cl bond cleavage to release chloride anion and the alkyl radical B. Further SET reduction of B at the cathode forms the alkyl carbanion C, which reacts with CO2 to give the corresponding carboxylate. At this stage, the single-electron reduction of 1 by CO2 radical anion to give A [163] and direct radical coupling of B with CO2 radical anion cannot be excluded.
|
Download:
|
| Scheme 5. Proposed reaction mechanism. | |
In conclusion, we have developed an efficient and practical strategy for electrochemical carboxylation of unactivated alkyl chlorides with CO2 via C—Cl bond cleavage. Both primary and secondary alkyl chlorides could undergo selective carboxylation with CO2. This method features mild reaction conditions, low electrolyte concentration, broad substrate scope and good functional group tolerance. Notably, this strategy is a promising and feasible method to recycle and reuse waste PVC, which could convert the PVC into hydrophilic functional products containing carboxylate groups. The preliminary mechanistic studies indicate that alkyl radical and alkyl anion might be involved in this reaction.
Declaration of competing interestThe authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
CRediT authorship contribution statementLi Li: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation. Zhi-Xin Yan: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation. Chuan-Kun Ran: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation. Yi Liu: Investigation. Shuo Zhang: Investigation. Tian-Yu Gao: Methodology, Investigation. Long-Fei Dai: Methodology. Li-Li Liao: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Conceptualization. Jian-Heng Ye: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. Da-Gang Yu: Writing – review & editing, Validation, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization.
AcknowledgmentsFinancial support was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22225106, 22201027) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. We thank Xiaoyan Wang from the Analysis and Testing Center of Sichuan University as well as Jing Li, Qinfang Zhang and Dongyan Deng from College of Chemistry at Sichuan University for compound testing. We also thank the comprehensive training platform of the Specialized Laboratory in the College of Chemistry at Sichuan University and the collaborative innovation center for eco-friendly and fire-safety polymeric materials for polymer characterization.
Supplementary materialsSupplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2024.110104.
| [1] |
M. Aresta, Carbon Dioxide as Chemical Feedstock, WileyVCH, Germany, 2010.
|
| [2] |
K. Huang, C.L. Sun, Z.J. Shi, Chem. Soc. Rev. 40 (2012) 2435-2452. |
| [3] |
L. Ackermann, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50 (2011) 3842-3844. DOI:10.1002/anie.201007883 |
| [4] |
W. Zhang, X.B. Lu, Chin. J. Catal. 33 (2012) 745-756. DOI:10.1016/S1872-2067(11)60390-2 |
| [5] |
L. Zhang, Z. Hou, Chem. Sci. 4 (2013) 3395-3403. DOI:10.1039/c3sc51070k |
| [6] |
M. Aresta, A. Dibenedetto, A. Angelini, Chem. Rev. 114 (2014) 1709-1742. DOI:10.1021/cr4002758 |
| [7] |
Q. Liu, L. Wu, R. Jackstell, M. Beller, Nat. Commun. 6 (2015) 5933. DOI:10.1038/ncomms6933 |
| [8] |
Q.W. Song, Z.H. Zhou, L.N. He, Green Chem. 19 (2017) 3707-3728. DOI:10.1039/C7GC00199A |
| [9] |
A. Tortajada, F. Juliá-Hernández, M. Börjesson, T. Moragas, R. Martin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57 (2018) 15948-15982. DOI:10.1002/anie.201803186 |
| [10] |
Y.G. Chen, X.T. Xu, K. Zhang, et al., Synthesis 50 (2018) 35-48. DOI:10.1055/s-0036-1590908 |
| [11] |
J. Hou, J.S. Li, J. Wu, Asian J. Org. Chem. 7 (2018) 1439-1447. DOI:10.1002/ajoc.201800226 |
| [12] |
C.S. Yeung, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58 (2019) 5492-5502. DOI:10.1002/anie.201806285 |
| [13] |
Y. Yang, J.W. Lee, Chem. Sci. 10 (2019) 3905-3926. DOI:10.1039/C8SC05539D |
| [14] |
M.D. Burkart, N. Hazari, C.L. Tway, E.L. Zeitler, ACS Catal. 9 (2019) 7937-7956. DOI:10.1021/acscatal.9b02113 |
| [15] |
S. Wang, C. Xi, Chem. Soc. Rev. 48 (2019) 382-404. DOI:10.1039/C8CS00281A |
| [16] |
L. Zhang, Z. Li, M. Takimoto, Z. Hou, Chem. Rec. 20 (2019) 494-512. |
| [17] |
B. Cai, H.W. Cheo, T. Liu, J. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60 (2021) 18950-18980. DOI:10.1002/anie.202010710 |
| [18] |
G. Bertuzzi, A. Cerveri, L. Lombardi, M. Bandini, Chin. J. Chem. 39 (2021) 3116-3126. DOI:10.1002/cjoc.202100450 |
| [19] |
Y. Yi, W. Hang, C. Xi, Chin. J. Org. Chem. 41 (2021) 80-93. DOI:10.6023/cjoc202007013 |
| [20] |
G. Zhang, Y. Cheng, M. Beller, F. Chen, Adv. Synth. Catal. 363 (2021) 1583-1596. DOI:10.1002/adsc.202001280 |
| [21] |
L. Wang, C. Qi, W. Xiong, H. Jiang, Chin. J. Catal. 43 (2022) 1598-1617. DOI:10.1016/S1872-2067(21)64029-9 |
| [22] |
N. Iwasawa, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 96 (2021) 824. |
| [23] |
K. Shimomaki, K. Murata, R. Martin, N. Iwasawa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139 (2017) 9467-9470. DOI:10.1021/jacs.7b04838 |
| [24] |
Q. Wang, Y. Wang, M. Liu, G. Chu, Y. Qiu, Chin. J. Chem. 42 (2024) 2249-2266. DOI:10.1002/cjoc.202400008 |
| [25] |
Q.Y. Meng, S. Wang, B. König, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56 (2017) 13426-13430. DOI:10.1002/anie.201706724 |
| [26] |
B. Sahoo, P. Bellotti, F. Juli ′ α-Hernández, et al., Chem. Eur. J. 25 (2019) 9001-9005. DOI:10.1002/chem.201902095 |
| [27] |
C. Zhu, Y.F. Zhang, Z.Y. Liu, et al., Chem. Sci. 10 (2019) 6721-6726. DOI:10.1039/C9SC01336A |
| [28] |
S.S. Yan, S.H. Liu, L. Chen, et al., Chem 7 (2021) 3099-3113. DOI:10.1016/j.chempr.2021.08.004 |
| [29] |
Z.Y. Bo, S.S. Yan, T.Y. Gao, et al., Chin. J. Catal. 43 (2022) 2388-2394. DOI:10.1016/S1872-2067(22)64140-8 |
| [30] |
K. Jing, M.K. Wei, S.S. Yan, et al., Chin. J. Catal. 43 (2022) 1667-1673. DOI:10.1016/S1872-2067(21)63859-7 |
| [31] |
J. Davies, J.R. Lyonnet, B. Carvalho, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146 (2024) 1753-1759. DOI:10.1021/jacs.3c11205 |
| [32] |
L.N. Mander, S.P. Sethi, Tetrahedron. Lett. 24 (1983) 5425-5428. DOI:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)87886-7 |
| [33] |
M. Shi, K.M. Nicholas, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119 (1997) 5057-5058. DOI:10.1021/ja9639832 |
| [34] |
I. Mutule, E. Suna, Tetrahedron 61 (2005) 11168-11176. DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2005.09.022 |
| [35] |
K. Ukai, M. Aoki, J. Takaya, N. Iwasawa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128 (2006) 8706-8707. DOI:10.1021/ja061232m |
| [36] |
C.S. Yeung, V. Dong, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130 (2008) 7826-7827. DOI:10.1021/ja803435w |
| [37] |
H. Ochiai, M. Jang, K. Hirano, H. Yorimitsu, K. Oshima, Org. Lett. 10 (2008) 2681-2683. DOI:10.1021/ol800764u |
| [38] |
T. Ohishi, M. Nishiura, Z. Hou, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47 (2008) 5792-5795. DOI:10.1002/anie.200801857 |
| [39] |
J. Wu, N. Hazari, Chem. Coumun. 47 (2011) 1069-1071. DOI:10.1039/C0CC03191G |
| [40] |
M. Takimoto, Z. Hou, Chem. Eur. J. 19 (2013) 11439-11445. DOI:10.1002/chem.201301456 |
| [41] |
X. Feng, A. Sun, S. Zhang, X. Yu, M. Bao, Org. Lett. 15 (2013) 108-111. DOI:10.1021/ol303135e |
| [42] |
A. Ueno, M. Takimoto, W.N.O. Wylie, et al., Chem. Asian J. 10 (2015) 1010-1016. DOI:10.1002/asia.201403247 |
| [43] |
S. Wang, P. Shao, C. Chem, C. Xi, Org. Lett. 17 (2015) 5112-5115. DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b02619 |
| [44] |
B. Miao, S. Ma, Org. Chem. Front. 2 (2015) 65-68. DOI:10.1039/C4QO00300D |
| [45] |
B. Miao, G. Li, S. Ma, Chem. Eur. J. 21 (2015) 17224-17228. DOI:10.1002/chem.201503494 |
| [46] |
P. Shao, S. Wang, C. Chen, C. Xi, Org. Lett. 18 (2016) 2050-2053. DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.6b00665 |
| [47] |
W. Hang, Y. Yi, C. Xi, Organometallics 39 (2020) 1476-1479. DOI:10.1021/acs.organomet.9b00712 |
| [48] |
A. Correa, R. Martin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 (2009) 15974-15975. DOI:10.1021/ja905264a |
| [49] |
T. Fujihara, K. Nogi, T. Xu, J. Terao, Y. Tsuji, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123 (2012) 9106-9109. |
| [50] |
T. León, A. Correa, R. Martin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (2013) 1221-1224. DOI:10.1021/ja311045f |
| [51] |
H. Tran-Vu, O. Daugulis, ACS Catal. 3 (2013) 2417-2420. DOI:10.1021/cs400443p |
| [52] |
B. Miao, S. Ma, Chem. Commun. 50 (2014) 3285-3287. DOI:10.1039/c4cc00148f |
| [53] |
S. Zhang, W.Q. Chen, A. Yu, L.N. He, ChemCatChem 7 (2015) 3972-3977. DOI:10.1002/cctc.201500724 |
| [54] |
F. Juliá-Hernández, T. Moragas, J. Cornella, R. Martin, Nature 545 (2017) 84-88. DOI:10.1038/nature22316 |
| [55] |
S.L. Xie, X.Y. Cui, X.T. Gao, et al., Org. Chem. Front. 6 (2019) 3678-3682. DOI:10.1039/C9QO00923J |
| [56] |
S.S. Yan, D.S. Wu, J.H. Ye, et al., ACS Catal. 9 (2019) 6987-6992. DOI:10.1021/acscatal.9b02351 |
| [57] |
R.J. Somerville, C. Odena, M.F. Obst, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142 (2020) 10936-10941. DOI:10.1021/jacs.0c04695 |
| [58] |
L. Wang, T. Li, S. Perveen, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61 (2022) e202213943. DOI:10.1002/anie.202213943 |
| [59] |
D. Li, L. Wei, C. Qi, et al., J. Org. Chem. 88 (2023) 5205-5211. DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.2c01808 |
| [60] |
M. Börjesson, T. Moragas, R. Martin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138 (2016) 7504-7507. DOI:10.1021/jacs.6b04088 |
| [61] |
R.D. Little, K.D. Moeller, Electrochem. Soc. Interface 11 (2002) 36. DOI:10.1149/2.F06024IF |
| [62] |
M. Yan, Y. Kawanata, P.S. Baran, Chem. Rev. 117 (2017) 13230-13319. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00397 |
| [63] |
Y. Jiang, K. Xu, C. Zeng, Chem. Rev. 118 (2018) 4485-4540. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00271 |
| [64] |
D. Pletcher, R.A. Green, R.C.D. Brown, Chem. Rev. 118 (2018) 4573-4591. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00360 |
| [65] |
J.I. Yoshida, A. Shimizu, R. Hayashi, Chem. Rev. 118 (2018) 4702-4730. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00475 |
| [66] |
K.D. Moeller, Chem. Rev. 118 (2018) 4817-4833. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00656 |
| [67] |
J.E. Nutting, M. Rafiee, S.S. Stahl, Chem. Rev. 118 (2018) 4834-4885. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00763 |
| [68] |
M.D. Kärkäs, Chem. Soc. Rev. 47 (2018) 5786-5865. DOI:10.1039/C7CS00619E |
| [69] |
S.R. Waldvogel, S. Lips, M. Selt, B. Riehl, C.J. Kampf, Chem. Rev. 118 (2018) 6706-6765. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00233 |
| [70] |
P. Xiong, H.C. Xu, Acc. Chem. Res. 52 (2019) 3339-3350. DOI:10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00472 |
| [71] |
J.C. Siu, N. Fu, S. Lin, Acc. Chem. Res. 53 (2020) 547-560. DOI:10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00529 |
| [72] |
K.J. Jiao, Y.K. Xing, Q.L. Yang, H. Qiu, T.S. Mei, Acc. Chem. Res. 53 (2020) 300-310. DOI:10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00603 |
| [73] |
T.H. Meyer, I. Choi, C. Tian, L. Ackermann, Chem 6 (2020) 2484-2496. DOI:10.1016/j.chempr.2020.08.025 |
| [74] |
Y. Yuan, J. Yang, A. Lei, Chem. Soc. Rev. 50 (2021) 10058-10086. DOI:10.1039/D1CS00150G |
| [75] |
C. Ma, P. Fang, Z.R. Liu, et al., Sci. Bull. 66 (2021) 2412-2429. DOI:10.1016/j.scib.2021.07.011 |
| [76] |
L.F.T. Novaes, J. Liu, Y. Shen, et al., Chem. Soc. Rev. 50 (2021) 7941-8002. DOI:10.1039/D1CS00223F |
| [77] |
C.A. Malapit, M.B. Prater, J.R. Cabrera-Pardo, et al., Chem. Rev. 122 (2022) 3180-3218. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00614 |
| [78] |
X. Cheng, A. Lei, T.S. Mei, et al., CCS Chem. 4 (2022) 1120-1152. DOI:10.31635/ccschem.021.202101451 |
| [79] |
Y. Zhang, Z. Cai, S. Warratz, C. Ma, L. Ackermann, Sci. China Chem. 66 (2023) 703-717. DOI:10.1007/s11430-022-1071-4 |
| [80] |
Y. Wang, S. Dana, H. Long, et al., Chem. Rev. 123 (2023) 11269-11335. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00158 |
| [81] |
J. Rein, S.B. Zacate, K. Mao, S. Lin, Chem. Soc. Rev. 52 (2023) 8106-8125. DOI:10.1039/D3CS00511A |
| [82] |
M. Ju, Z. Lu, L.F.T. Novaes, J.I.M. Alvarado, S. Lin, J. Am. Soc. Chem. 145 (2023) 19478-19489. DOI:10.1021/jacs.3c07070 |
| [83] |
X. Wang, S. Wu, Y. Zhong, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 34 (2023) 107537. DOI:10.1016/j.cclet.2022.05.051 |
| [84] |
J. Jiang, K.L. Wang, X. Li, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 34 (2023) 108699. DOI:10.1016/j.cclet.2023.108699 |
| [85] |
H.T. Ji, J. Jiang, W.B. He, et al., J. Org. Chem. 89 (2024) 4113-4119. DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.3c02946 |
| [86] |
H.Y. Song, J. Jiang, Y.H. Song, et al., Chin. Chem. Lett. 35 (2024) 109246. DOI:10.1016/j.cclet.2023.109246 |
| [87] |
C.H. Ou, Y.M. Pan, H.T. Tang, Sci. China Chem. 65 (2022) 1873-1878. DOI:10.1007/s11426-022-1360-3 |
| [88] |
X. Yan, S. Wang, Z. Liu, et al., Sci. China Chem. 65 (2022) 762-770. DOI:10.1007/s11426-021-1210-y |
| [89] |
Z. Chang, J. Wang, X. Lu, Y. Fu, Chin. J. Org. Chem. 42 (2022) 147-159. DOI:10.6023/cjoc202108006 |
| [90] |
W. Xie, X. Chen, Y. Li, et al., Chin. J. Org. Chem. 42 (2022) 1286-1306. DOI:10.6023/cjoc202110028 |
| [91] |
L. Du, B. Zhang, S. Ji, H. Cai, H. Zhang, Sci. China Chem. 66 (2023) 534-539. DOI:10.1007/s11426-022-1470-8 |
| [92] |
Y.K. Xing, Z.H. Wang, P. Fangm, C. Ma, T.S. Mei, Sci. China Chem. 66 (2023) 2863-2870. DOI:10.1007/s11426-023-1603-9 |
| [93] |
G. Zhong, Y. Huang, L. He, Chem. Synth. 3 (2023) 19. |
| [94] |
H.Y. Zhou, H.T. Tang, W.M. He, Chin. J. Catal. 46 (2023) 4-10. DOI:10.1016/S1872-2067(22)64197-4 |
| [95] |
Z. Guan, D. Yang, Z. Liu, et al., Chin. J. Catal. 52 (2023) 144-153. DOI:10.1016/S1872-2067(23)64510-3 |
| [96] |
L. Zeng, J.H. Qin, G.F. Lv, et al., Chin. J. Chem. 41 (2023) 1921-1930. DOI:10.1002/cjoc.202300174 |
| [97] |
F. Lian, F. Luo, M. Wang, K. Xu, C. Zeng, Chin. J. Chem. 41 (2023) 1583-1588. DOI:10.1002/cjoc.202200825 |
| [98] |
H. Yue, C. Zhu, M. Rueping, Sci. Bull. 68 (2023) 1730-1732. DOI:10.1016/j.scib.2023.07.028 |
| [99] |
B. Sun, Z.H. Wang, Y.Z. Wang, et al., Sci. Bull. 68 (2023) 2033-2041. DOI:10.1016/j.scib.2023.07.007 |
| [100] |
Z. Tan, Zhang H, K. Xu, C. Zeng, Sci. China Chem. 67 (2024) 450-470. |
| [101] |
Y. Zhang, X. Zhao, G. Qing, Chem. Synth. 4 (2024) 16. |
| [102] |
D. Lehnherr, L. Chen, Org. Process Res. Dev. 28 (2024) 338-366. DOI:10.1021/acs.oprd.3c00340 |
| [103] |
R. Matthessen, J. Fransaer, K. Binnemans, D.E. De Vos, Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 10 (2014) 2484-2500. DOI:10.3762/bjoc.10.260 |
| [104] |
L. Rossi, Curr. Green Chem. 2 (2015) 77-89. DOI:10.2174/2213346101666140804222344 |
| [105] |
H. Senboku, A. Katayama, Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 3 (2017) 50. DOI:10.1016/j.cogsc.2016.10.003 |
| [106] |
Y. Cao, X. He, N. Wang, H.R. Li, L.N. He, Chin. J. Chem. 36 (2018) 644-659. DOI:10.1002/cjoc.201700742 |
| [107] |
N.W. Kinzel, C. Werlé, W. Leitner, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60 (2021) 11628-11686. DOI:10.1002/anie.202006988 |
| [108] |
H. Senboku, Chem. Rec. 21 (2021) 2354-2374. DOI:10.1002/tcr.202100081 |
| [109] |
Z. Yang, Y. Yu, L. Lai, et al., Green Synth. Catal. 2 (2021) 19-26. DOI:10.1016/j.gresc.2021.01.009 |
| [110] |
S. Wang, T. Feng, Y. Wang, Y. Qiu, Chem. Asian J. 17 (2022) e202200543. DOI:10.1002/asia.202200543 |
| [111] |
X.F. Liu, K. Zhang, L. Tao, X.B. Lu, W.Z. Zhang, Green Chem. Eng. 3 (2022) 125-137. DOI:10.1016/j.gce.2021.12.001 |
| [112] |
S. Jia, X. Ma, X. Sun, B. Han, CCS Chem. 4 (2022) 3213-3229. DOI:10.31635/ccschem.022.202202094 |
| [113] |
G.Q. Yuan, L. Li, H. Jiang, C. Qi, F. Xie, Chin. J. Chem. 28 (2010) 1983-1988. DOI:10.1002/cjoc.201090331 |
| [114] |
A. Alkayal, V. Tabas, S. Montanaro, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142 (2020) 1780-1785. DOI:10.1021/jacs.9b13305 |
| [115] |
Y. Kim, G.D. Park, M. Balamurugan, et al., Adv. Sci. 7 (2020) 1900137. DOI:10.1002/advs.201900137 |
| [116] |
W. Zhang, S. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142 (2020) 20661-20670. DOI:10.1021/jacs.0c08532 |
| [117] |
X.T. Gao, Z. Zhang, X. Wang, et al., Chem. Sci. 11 (2020) 10414-10420. DOI:10.1039/D0SC04091F |
| [118] |
A.M. Sheta, M.A. Mashaly, S.B. Said, et al., Chem. Sci. 11 (2020) 9109-9114. DOI:10.1039/D0SC03148H |
| [119] |
A.M. Sheta, A. Alkayal, M.A. Mashaly, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60 (2021) 21832-21837. DOI:10.1002/anie.202105490 |
| [120] |
Y. You, W. Kanna, H. Takano, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144 (2022) 3685-3695. DOI:10.1021/jacs.1c13032 |
| [121] |
H. Senboku, K. Yoneda, S. Hara, Tetrahedron Lett. 56 (2022) 6772-6776. |
| [122] |
K.J. Jiao, Z.M. Li, X.T. Xu, et al., Org. Chem. Front. 5 (2018) 2244-2248. DOI:10.1039/C8QO00507A |
| [123] |
D.T. Yang, M. Zhu, Z.J. Schiffer, et al., ACS Catal. 9 (2019) 4699-4750. DOI:10.1021/acscatal.9b00818 |
| [124] |
J.S. Zhong, Z.X. Yang, C.L. Ding, et al., J. Org. Chem. 86 (2021) 16162-16170. DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.1c01261 |
| [125] |
Y. Wang, S. Tang, G. Yang, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61 (2022) e202207746. DOI:10.1002/anie.202207746 |
| [126] |
K. Zhang, B.H. Ren, X.F. Liu, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61 (2022) e202207660. DOI:10.1002/anie.202207660 |
| [127] |
Z. Zhao, Y. Liu, S. Wang, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62 (2023) e202214710. DOI:10.1002/anie.202214710 |
| [128] |
M. Surke, R. Zhao, L. Ackermann, Sci. China Chem. 66 (2023) 1549-1550. DOI:10.1007/s11426-023-1585-6 |
| [129] |
L. Li, N. Fu, Chem 9 (2023) 556-558. DOI:10.1016/j.chempr.2023.02.001 |
| [130] |
O. Sock, M. Troupel, J. Perichon, Tetrahedrn Lett. 26 (1985) 1509-1512. DOI:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)98538-1 |
| [131] |
A.A. Isse, A. Gennaro, E. Vianello, J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. (1996) 1613-1618. |
| [132] |
W.H. Chung, P. Guo, K.Y. Wong, C.P. Lau, J. Electroanal. Chem. 486 (2000) 32-39. DOI:10.1016/S0022-0728(00)00125-X |
| [133] |
A. Gennaro, A.A. Isse, F. Maran, J. Electroanal. Chem. 507 (2001) 124-134. DOI:10.1016/S0022-0728(01)00373-4 |
| [134] |
A.A. Isse, M.G. Ferlin, A. Gennaro, J. Electroanal. Chem. 581 (2005) 38-45. DOI:10.1016/j.jelechem.2005.04.007 |
| [135] |
D.F. Niu, L.P. Xiao, A.J. Zhang, et al., Tetrahedron 64 (2008) 10517. DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2008.08.093 |
| [136] |
Y. Hiejima, M. Hayashi, A. Uda, et al., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 12 (2010) 1953-1957. DOI:10.1039/b920413j |
| [137] |
B.L. Chen, H.W. Zhu, Y. Xiao, et al., Electrochem. Commun. 42 (2014) 55-59. DOI:10.1016/j.elecom.2014.02.009 |
| [138] |
H. Senboku, K. Nagakura, T. Fukuhara, S. Hara, Tetrahedron 71 (2015) 3850-3856. DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2015.04.020 |
| [139] |
H. Yang, L. Wu, H. Wang, J. Lu, Chin. J. Catal. 37 (2016) 994-998. DOI:10.1016/S1872-2067(15)61075-0 |
| [140] |
L.X. Wu, Y.G. Zhao, Y.B. Guan, et al., RSC Adv. 9 (2019) 32628-32633. DOI:10.1039/C9RA05253D |
| [141] |
N.W.J. Ang, J.C.A. Oliveira, L. Ackermann, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59 (2020) 12842-12847. DOI:10.1002/anie.202003218 |
| [142] |
L.X. Wu, F.J. Deng, L. Wu, et al., New J. Chem. 45 (2021) 13137-13141. DOI:10.1039/D1NJ02006D |
| [143] |
M.A. Keane, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 82 (2007) 787-795. DOI:10.1002/jctb.1757 |
| [144] |
L. Dai, Z.F. Zhang, X.Y. Chen, Sci. China Chem. 67 (2024) 471-481. DOI:10.1007/s11426-023-1787-3 |
| [145] |
P. Li, C. Guo, S. Wang, et al., Nat. Commun. 13 (2022) 3774. DOI:10.1038/s41467-022-31435-9 |
| [146] |
N. Corbin, D.T. Yang, N. Lazouski, K. Steinberg, K. Manthiram, Chem. Sci. 12 (2021) 12365-12376. DOI:10.1039/D1SC02413B |
| [147] |
C.K. Ran, X.W. Chen, Y.Y. Gui, et al., Sci. China Chem. 63 (2020) 1336-1351. DOI:10.1007/s11426-020-9788-2 |
| [148] |
J.H. Ye, T. Ju, H. Huang, L.L. Liao, D.G. Yu, Acc. Chem. Res. 54 (2020) 2518-2531. |
| [149] |
C.K. Ran, L.L. Liao, T.Y. Gao, Y.Y. Gui, D.G. Yu, Cur. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 32 (2021) 100525. DOI:10.1016/j.cogsc.2021.100525 |
| [150] |
C.K. Ran, H.Z. Xiao, L.L. Liao, et al., Natl. Sci. Open 2 (2023) 20220024. DOI:10.1360/nso/20220024 |
| [151] |
Y.Y. Gui, S.S. Yan, W. Wang, et al., Sci. Bull. 68 (2023) 3124-3128. DOI:10.1016/j.scib.2023.11.018 |
| [152] |
G.Q. Sun, W. Zhang, L.L. Liao, Nat. Commun. 12 (2021) 7086. DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-27437-8 |
| [153] |
L.L. Liao, Z.H. Wang, K.G. Cao, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144 (2022) 2062-2068. DOI:10.1021/jacs.1c12071 |
| [154] |
W. Zhang, L.L. Liao, L. Li, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62 (2023) e202301892. DOI:10.1002/anie.202301892 |
| [155] |
G.Q. Sun, P. Yu, W. Zhang, et al., Nature 615 (2023) 67-72. DOI:10.1038/s41586-022-05667-0 |
| [156] |
C.K. Ran, Q. Qu, Y.Y. Tao, et al., Sci. China Chem. 67 (2024) 3366-3372. DOI:10.1007/s11426-024-2075-6 |
| [157] |
Q. Hu, B. Wei, M. Wang, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146 (2024) 14864-14874. DOI:10.1021/jacs.4c04211 |
| [158] |
T. Wirtanen, T. Prenzel, J.P. Tessonnier, S.R. Waldvogel, Chem. Rev. 121 (2021) 10241-10270. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00148 |
| [159] |
B. Feng, Y. Guo, X. Liu, Y. Wang, Green Chem. 25 (2023) 8505-8509. DOI:10.1039/D3GC03063F |
| [160] |
S. Xu, Z. Han, K. Yuan, et al., Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 3 (2023) 44. DOI:10.1038/s43586-023-00227-w |
| [161] |
L. Lu, W. Li, Y. Cheng, M. Liu, Waste Manage. 166 (2023) 245-258. DOI:10.1016/j.wasman.2023.05.012 |
| [162] |
X.F. Liu, C. Qiao, X.Y. Li, L.N. He, Green Chem. 19 (2017) 1726-1731. DOI:10.1039/C7GC00484B |
| [163] |
C.M. Hendy, G.C. Smith, Z. Xu, T. Lian, N.T. Jui, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143 (2021) 8987-8992. DOI:10.1021/jacs.1c04427 |
 2024, Vol. 35
2024, Vol. 35