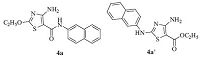
In our previous work,we found a new method by chance for the synthesis of thiazole derivatives with diversified substitutes on 2- and 5-positions of the thiazole scaffold which was published in Chinese Chemical Letters [2014,Vol. 25 p. 411]. The structures were identified by 1H NMR,13C NMR and HRMS as 2-alkoxy-4-amino-N-arylthiazole- 5-carboxamides,exemplified by compound 4a (Fig. 1). However,in our continuous research work,we found that the reported structure of compound 4a was not corrected. It was reconfirmed as the structure of ethyl 4-amino-2-(naphthalene- 2-ylamino) thiazole-5-carboxylate (4a',Fig. 1). Herein,we described the results of the structure rectification.
|
Download:
|
| Fig. 1.Structures of compounds 4a and 4a' . | |
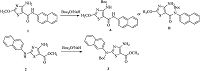
In our lab,we tried to use compound 1 (Scheme 1),the methoxyl analog of 4a prepared using the previously reported method,as a chemical intermediate to synthesize novel thiazole derivatives as Pin1 inhibitors. When compound 1 was reacted with (Boc)2O,a new compound was produced with high yield. The structure was assumed as compound B rather than the desired compound A due to a broad single peak appearing at 5.54 ppm (designating as a NH2 group) in 1H NMR spectra. However,the Xray crystal data showed that the product was structure 3,methyl 4- amino-2-(tert-butoxycarbonyl(naphthalene-2-yl)amino)thiazole- 5-carboxylate (Fig. 2 and Figs. S1-S4 in Supporting information). Therefore,the starting material was supposed to be compound 2. At this point,we speculated that the structures (compounds 4a- 4r) in our previous report might be incorrect.
|
Download:
|
| Scheme 1.Introduction of a Boc group. | |
|
Download:
|
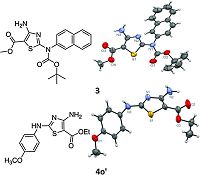
| Fig. 2.The crystal structures of compounds 3 and 4o' . | |
|
Download:
|
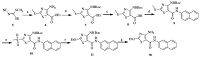
| Scheme 2.Reagents and conditions: (a) Ethyl bromoacetate, triethylamine, ethanol, 93%; (b) NaH, (Boc)2O, THF, 90%; (c) NaOH, THF, H2O, 45 8C, 90%; (d) β-naphthylamine, EDC, HOAT, DMAP, DIEA, DCM, DMF, 50%; (e) mCPBA, CHCl3, reflux, 51%; (f) EtOH, NaH, DMF, 79%; (g) TFA, DCM, 67%. | |
|
Download:
|
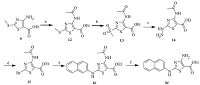
| Scheme 3.Reagents and conditions: (a) Acetyl chloride, MW, 94%; (b) m-CPBA, CHCl3, reflux, 89%; (c) N2H4·H2O, EtOH, 83%; (d) CuBr2, HOAc, H2O, 49%; (e) β-naphthylamine, Pd2(dba)3, Davephos, K3PO4, PhMe, H2O, 57%; (f) LiOH, EtOH, THF, H2O, 52%. | |
|
Download:
|
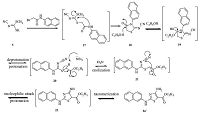
| Scheme 4.A plausible mechanism proposed for the formation of 4-amino-2-(arylamino)thiazole-5-carboxylic ester (4a' ). | |
In order to validate the structures of our previously reported compounds (compounds 4a-4r) to be 4-amino-2-(arylamino)thiazole- 5-carboxylic esters,we carried out chemical synthesis and single crystal X-ray structure analysis. The detailed experimental results were shown below.
The synthesis of compound 4a was outlined in Scheme 2. The mixture of potassium methyl cyanimidodithiocarbonate 5,ethyl bromoacetate and triethylamine in ethanol was heated to give rise to the key thiazole scaffold 6 in high yield. Upon subsequent Boc protection,hydrolysis of the ester,condensation with naphthylamine,and oxidation of methylthio group,compound 6 was converted into compound 10 smoothly. In the presence of NaH in ethanol,compound 11 was prepared by the nucleophilic substitution reaction,which further generated target compound 4a by removal of the Boc group with trifluoroacetic acid.
4-Amino-2-ethoxy-N-(naphthalen-2-yl)thiazole-5-carboxamide (4a): 1H NMR (400 MHz,DMSO-d6): δ 9.30 (s,1H),8.24 (s,1H),7.77-7.83 (m,3H),7.72 (d,1H,J = 8.8 Hz),7.45 (t,1H,J = 7.6 Hz),7.38 (t,1H,J = 7.2 Hz),7.24 (brs,2H),4.45 (q,2H,J = 6.8 Hz),1.38 (t,J = 6.8 Hz,3H);HRMS (ESI) Calcd. forC16H16N3O2S[M+H]+: 314.0954; found: 314.0958.
The synthetic route of compound 4a' was outlined in Scheme 3. Starting from compound 6,the key intermediate 15 was synthesized by acetylation,oxidation,hydrazinolysis and bromination reaction in four steps. The palladium catalyzed coupling reaction between compound 15 and β-naphthylamine afforded compound 16,which was subsequently transformed into target compound 4a' by hydrolysis.
Ethyl 4-amino-2-(naphthalen-2-ylamino) thiazole-5-carboxylate (4a’): 1H NMR (400 MHz,DMSO-d6): δ 10.78 (s,1H),8.26 (s,1H),7.79-7.88 (m,3H),7.59 (d,1H,J = 8.8 Hz),7.48 (t,1H,J = 7.2 Hz),7.39 (t,1H,J = 7.6 Hz),6.95 (brs,2H),4.14 (q,2H,J = 7.2 Hz),1.22 (t,3H,J = 7.2 Hz),HRMS (ESI) Calcd. for C16H16N3O2S [M+H]+: 314.0953; found: 314.0958.
Comparing the data of compounds 4a and 4a',we found that both of them have the same molecular weight (314.0958) as ESIHRMS indicated. However,there are slight differences in their 1H NMR spectra. The signals of ethyl group in compound 4a appeared at δ 4.45 ppm (q,2H,J = 6.8 Hz) and δ 1.38 ppm (t,3H,J = 6.8 Hz); while the signals of ethyl group in compound 4a' resonated at δ 4.14 ppm (q,2H,J = 7.2 Hz) and 1.22 ppm (t,3H,J = 7.2 Hz). In addition,the splitting pattern of the signals δ 7.83-7.77 ppm in compound 4a and δ 7.88-7.79 ppm in compound 4a' is different (1H NMR spectra shown in the Supporting information,Figs. S10- S12). Furthermore,the crystal structure of compound 4o' ,which was prepared by our pubished method,was also obtained and shown in Fig. 2 (the details shown in the Supporting information,Figs. S5-S9). It was further confirmed that the chemical structures of the title compounds in our priviously published article are aryl thiazole amines,instead of alkyl thiazole ethers.
Based on the corrected structures of the titled compounds,the reaction mechanism was proposed as illustrated in Scheme 4. In the presence of triethylamine,ethanol attacks on the electrophilic carbonyl group of the amide bond in compound 18,followed by the intramolecular ring opening of 19 to provide the key intermediate 20. After deprotonation of 20 with Et3N,the resulted 21 underwent an intramolecular cyclization by attacking cyano group to afford 22,which was finally tautomerized into the desired compound 4a' with the assistance of Et3N. In this mechanism ethanol was proposed to attack on the carbonyl group of the amide bond in compound 18; while in our previously published work ethanol was assumed to attack at the carbon of N-cyanamide in compound 18.
In conclusion,the structures of thiazole derivatives reported previously by our group were confirmed by the single crystal X-ray diffraction method to be 4-amino-2-(arylamino)thiazole-5-carboxylic esters rather than 2-alkoxy-4-amino-N-arylthiazole- 5-carboxamides.
Appendix A. Supplementary dataSupplementarymaterial related to this article canbe found,inthe online version,at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2015.11.006.
 2016, Vol.27
2016, Vol.27 


