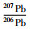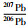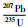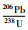2. 中国地质大学(北京)地球科学与资源学院, 北京 10008;
3. 内蒙古第三地质矿产勘查开发有限责任公司, 呼和浩特 010010;
4. 中煤地质集团有限公司, 北京 100040;
5. 山东省水土保持与环境保育重点实验室, 临沂大学资源环境学院, 临沂 276005
2. School of Earth Science and Resources, China University of Geosciences(Beijing), Beijing 10008;
3. No.3 Geology Mineral Resources Exploration and Development Co., Ltd. of Inner Mongolia, Huhhot 010010, China;
4. China Coal Geology Group Co., Ltd., Beijing 100040, China;
5. Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Water and Soil Conservation and Environmental Protection, School of Resources and Environment, Linyi University, Linyi 276005, China
二道河银铅锌矿是近年来新发现的一处大型矽卡岩型矿床,地处大兴安岭中段柴河-塔尔气地区,为接触交代矽卡岩型矿床,矿体的分布与矽卡岩密切相关(Chen et al., 2021; He et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2021; 衮民汕等, 2021)。已查明其保有资源储量分别为:锌134万t,平均品位5.19%;铅35万t,平均品位1.51%;银0.16万t,平均品位121.38×10-6,矿床规模为大型(内蒙古第三地质矿产勘查开发有限责任公司, 2017①; Guo et al., 2021)。以往在该区未发现大型规模有色金属矿产,该矿床的发现使得这一地区实现找矿重大突破(崔学武等, 2015)。目前,对于该矿床的研究成果主要集中于矿床类型、物化探特征、控矿构造、流体包裹体以及稳定同位素等,由于矿区内发育多期次的岩浆活动,而矿床的形成究竟与何种性质的岩浆存在密切联系还存在较大的争议,矿区发育的各期次的岩浆活动通过不同的研究手段都被认为与成矿关系密切:例如王忠等(2012)、郑萍等(2013)根据区域多金属矿化特征和燕山期岩浆活动特征推测成矿年龄为116Ma左右,成矿岩体未明确;杨发亭(2016)认为与成矿相关的地质体是最晚期侵入的花岗斑岩,其年龄为127~134Ma;张璟等(2017)根据矿床同位素特征结合矿体与地质体空间关系,推断成矿物质来源于145Ma左右的细粒闪长岩或隐伏侵入体;杨发亭(2018)、Guo et al.(2021)根据岩体与矿体之间的接触关系认为成矿地质体为闪长岩,年龄为145~139Ma;衮民汕等(2021)根据硫同位素特征对比认为矿体的形成与花岗斑岩或闪长岩关系密切;郭向国(2020)测得黄铁矿Re-Os等时线年龄为145Ma,认为与闪长岩有关;而Chen et al.(2021)测得闪锌矿Rb-Sr等时线年龄为130.5±1.9Ma,认为与花岗斑岩有关;内蒙古第三地质公司(2017)根据大量勘探结果和区域地质特征,认为矿体形成与矿区广泛分布的石炭纪碎裂状花岗闪长岩关系密切,而早白垩世闪长岩和花岗斑岩等为成矿后期岩浆活动产物,穿切矿体及矽卡岩。这些相互冲突的结论表明二道河银铅锌矿的形成可能涉及多期次矿化的复杂过程,需要厘清矿区究竟发育几期岩浆作用,以及与矿体形成之间的关系,成矿过程等。作为矽卡岩型矿床中重要的赋矿岩石,矽卡岩内矿物组成及地球化学特征对理解二道河银铅锌矿床的成因具有重要的意义(赵一鸣等, 1990; Meinert et al., 2005; 彭惠娟等, 2014; 赵超等, 2017)。因此,通过二道河银铅锌矿矿区典型矽卡岩矿物的化学分析,矿物学研究,结合野外地质调查可有效揭示矽卡岩矿床的成矿过程(Meinert et al., 2005)。鉴于此,本文通过对二道河银铅锌矿矿区钻孔进行取样,对与矿体密切相关的岩体中锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素分析以及矽卡岩中石榴子石成分特征研究,揭示二道河银铅锌矿床的成矿过程,并对成矿构造背景进行探讨,以期为该区进一步的找矿勘查方向提供一定的依据。
① 内蒙古第三地质矿产勘查开发有限责任公司(后文简称内蒙古第三地质公司).2017. 内蒙古自治区扎兰屯市二道河矿区锌多金属矿生产勘探报告
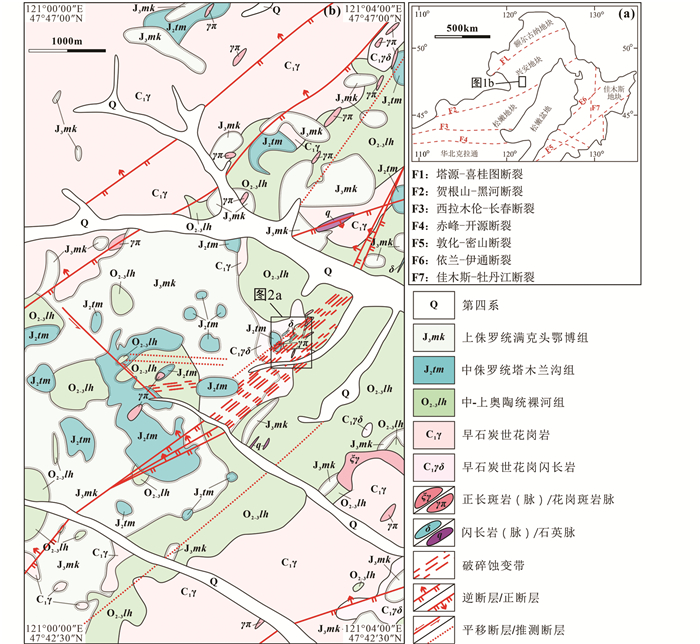
1 地质背景二道河银铅锌矿位于中亚造山带东缘(兴蒙造山带)的兴安地块中段(Şengör et al., 1993),以贺根山-黑河断裂为界,东南紧邻松嫩地块,以塔源-喜桂图断裂为界,北西侧为额尔古纳地块(Liu et al., 2017; 图 1a)。中亚造山带在古生代-中生代期间叠加了蒙古-鄂霍茨克构造体系的改造,该大洋板块在晚古生代晚期经历了向南俯冲(Tang et al., 2014, 2016; Li et al., 2017)、闭合(李宇等, 2015),以及后期的伸展作用(Wu et al., 2011; 崔芳华等, 2013; Tang et al., 2015),对中亚造山带进行了强烈的改造(许文良等, 2019),中生代期间又经历了古太平洋板块向西的俯冲叠加与改造(李益龙等, 2012; Xu et al., 2013; 许文良等, 2019),这些过程都伴随了大规模的构造-岩浆-成矿作用,形成许多大型-超大型矽卡岩型、斑岩型、热液型矿床(Zeng et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2015; 秦克章等, 2017; Guo et al., 2021)。
2 矿区及矿床地质特征 2.1 地层、岩浆岩及构造二道河矿区内出露最老的地层为中-上奥陶统裸河组(O2-3lh),为一套浅海相变质砂板岩夹砂质灰岩的沉积组合,含腕足、三叶虫、珊瑚及介形虫等化石(邵积东等, 2011),被中侏罗统塔木兰沟组(J2tm)和上侏罗统满克头鄂博组(J3mk)不整合覆盖。塔木兰沟组以安山玄武岩、碳酸盐化安山岩为主,向满克头鄂博组逐渐过渡为流纹质凝灰岩。第四系全新统以现代河床冲积物(Qhal)、残坡积物(Qhspl)为主,覆盖在古生代和中生代地层之上。矿区内岩浆活动频繁,具有多阶段多期次喷发和侵入的特点,岩石类型为中基性-中酸性,主要为中石炭-早白垩世侵入岩,其次为潜火山岩。侵入岩多以岩株、岩枝、岩脉形式产出,主要包括花岗岩、花岗闪长岩、闪长岩、花岗斑岩等。区内构造极为发育,北东向构造和北西向构造构成了矿区的总体构造格架。北东向断裂构造控制了矿体和岩体的分布,其派生的小构造又对矿床的形成有着直接的控制作用(王忠等, 2012; 和静等, 2019; 图 1b)。
|
图 1 东北大地构造图(a,据Li et al., 2017)及二道河地区地质简图(b,据中煤地质集团有限公司, 2016①;张璟等, 2017修改) Fig. 1 Tectonic map of northeastern China (a, after Li et al., 2017) and geological sketch map of the Erdaohe area (b, modified after Zhang et al., 2017) |
① 中煤地质集团有限公司. 2016. 内蒙古自治区扎兰屯市五一林场南铜多金属矿预查报告
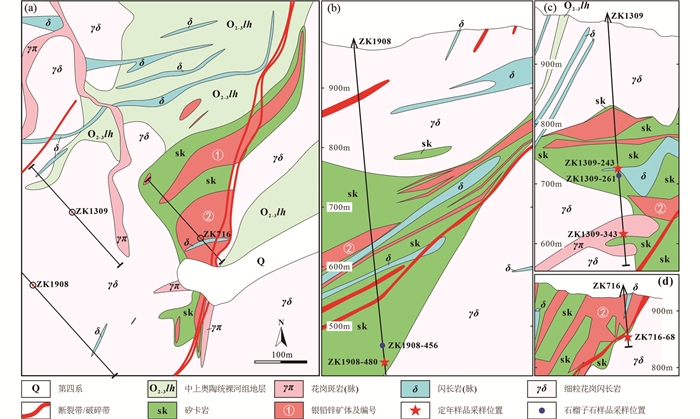
2.2 矿体和矿石二道河银铅锌矿矿体主要赋存于矽卡岩或大理岩内,其次赋存于碎裂状细粒花岗闪长岩内,在矿区其它地质体中也均可见矿体的产出(图 2、图 3),共计39条,大部分为地表出露矿体,部分为隐伏矿体,主要的矿体有①号和②号矿体,其中①号矿体通过钻孔和探槽控制长度625m,斜深控制432m,埋深0~264m。矿体呈似层状-不规则脉状产出,平均厚度23.21m,走向42°,倾向312°,平均倾角32°,Pb平均品位1.55%,Zn平均品位5.12%,Ag平均品位118.35×10-6;②号矿体通过钻孔和探槽控制长度475m,斜深控制506m,埋深0~260m。矿体呈似层状-不规则脉状产出,平均厚度26.63m,走向25°,倾向295°,平均倾角30°,Pb平均品位1.39%,Zn平均品位5.52%,Ag平均品位136.55×10-6(内蒙古第三地质公司, 2017; 图 2)。
|
图 2 二道河矿区平面及剖面地质图(据内蒙古第三地质公司, 2017) (a)二道河矿床地质简图;(b)19号勘探线剖面图;(c)13号勘探线剖面图;(d)7号勘探线剖面图 Fig. 2 Geological sketch map of the Erdaohe deposit (a) and geological sections of exploration line 19 (b), 13 (c) and 7 (d) |
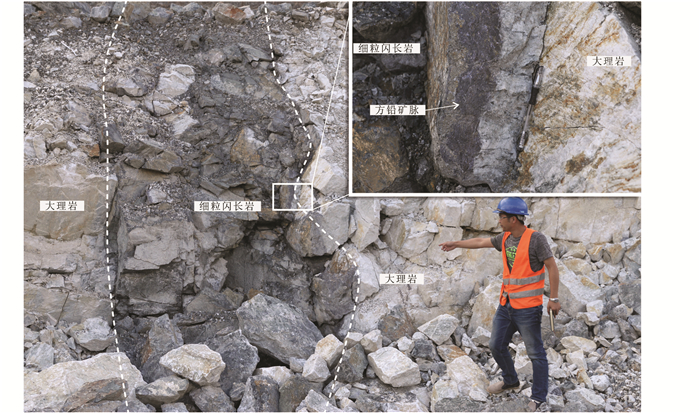

|
图 3 细粒闪长岩脉与大理岩接触带一侧发育闪锌矿和方铅矿 Fig. 3 Sphalerite and galena developing on one side of the contact zone between fine-grained diorites and marble |
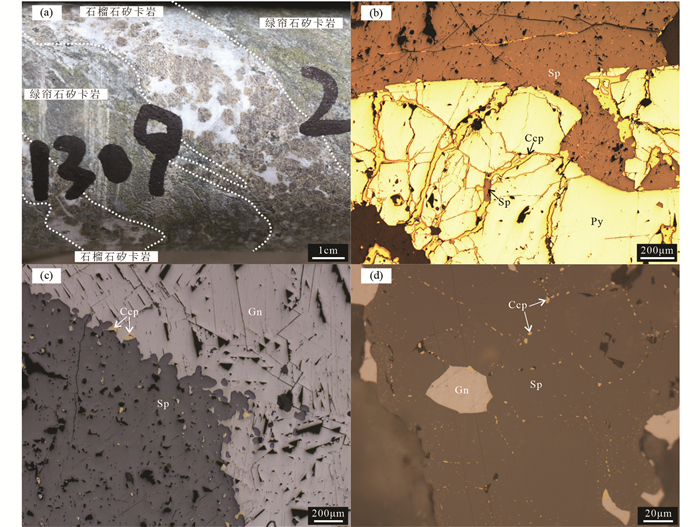
矿石矿物包括闪锌矿、方铅矿、黄铁矿和黄铜矿。闪锌矿为褐色、浅棕色,呈他形粒状产出,晶体较纯,局部见乳滴状黄铜矿,大部分晶体组成致密状集合体分布,集合体呈块状、细网脉状和不均匀稠密浸染状分布于矿脉中,粒度0.1~10mm。闪锌矿与方铅矿互为包裹共生关系,局部见两者沿黄铁矿边部分布,或以交代的形式填充于黄铁矿裂隙中(图 4b)。方铅矿为铅灰色,半自形-自形粒状,可见黑三角孔,大小不一,粒径在0.01~10mm之间,集合体呈团块状、粒状、浸染状、斑杂状分布(图 4c, d)。黄铁矿为浅黄色,自形(立方体)-半自形,粒状,晶体呈斑杂状、星散状、脉状分布,粒度大小不等,一般为0.1~5mm(图 4b)。黄铜矿为铜黄色,他形粒状,多在闪锌矿中呈包裹体、乳滴状形式出现(图 4b-d)。
|
图 4 二道河矿床代表性矽卡岩及矿石特征 (a)石榴石矽卡岩与绿帘石矽卡岩相互穿插;(b)闪锌矿与黄铜矿沿裂隙充填交代黄铁矿;(c)闪锌矿与方铅矿相互交代呈港湾状;(d)闪锌矿颗粒间隙发育乳滴状黄铜矿,方铅矿交代闪锌矿呈星状结构. Sp-闪锌矿;Gn-方铅矿;Ccp-黄铜矿;Py-黄铁矿 Fig. 4 Characteristics of representative skarns and ores in the Erdaohe deposit (a) garnet skarn and epidote skarn interspersed with each other; (b) sphalerite and chalcopyrite filling and replacing pyrite along fissures; (c) mutual metasomatism between sphalerite and galena, showing an embayment pattern; (d) chalcopyrite appearing as emulsion drops among sphalerite crystals, which have been locally replaced with starlike galena. Sp-sphalerite; Gn-galena; Ccp-chalcopyrite; Py-pyrite |
二道河银铅锌矿围岩蚀变以矽卡岩化为主,岩石类型主要为绿帘石矽卡岩、石榴石矽卡岩,常相互穿插(图 4a),脉石矿物主要为绿帘石、石榴子石、石英、方解石以及透辉石、绿泥石等,并伴随有黄铁矿化、黄铜矿化、方铅矿化、闪锌矿化等。围岩蚀变还可见硅化、绿帘石化、碳酸盐化、绿泥石化以及绢云母化等,分带不明显。
3 样品及分析方法 3.1 样品特征与采集本文样品均取自二道河银铅锌矿钻孔内,采样位置如图 2所示。样品编号以“钻孔号-采样深度”表示,例如ZK716-68表示样品位于ZK716钻孔的68m深度。选取4件样品进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素定年以及Hf同位素分析,分别是紧邻矽卡岩带的绿帘石化细粒花岗闪长岩(ZK716-68),穿插于矽卡岩内的绿帘石化细粒闪长岩(ZK1309-243),花岗斑岩(ZK1309-343)以及石榴石矽卡岩(ZK1908-480)。选取2件样品进行石榴子石电子探针分析,分别是矽卡岩带中部石榴石矽卡岩(ZK1309-261)和矽卡岩带边部石榴石矽卡岩(ZK1908-456)。
绿帘石化细粒花岗闪长岩(ZK716-68,图 5a, b),细粒结构,块状构造,钾长石(20%)呈半自形-他形板状,条纹结构发育,粒径为0.2~2mm;斜长石(50%)半自形板柱状,粒径为0.2~2mm;石英(25%)他形粒状,粒径为1~2mm;可见少量角闪石、黑云母。副矿物为磁铁矿、锆石、榍石,绿帘石呈粒状、放射状呈脉状产出或穿插于矿物颗粒之间。
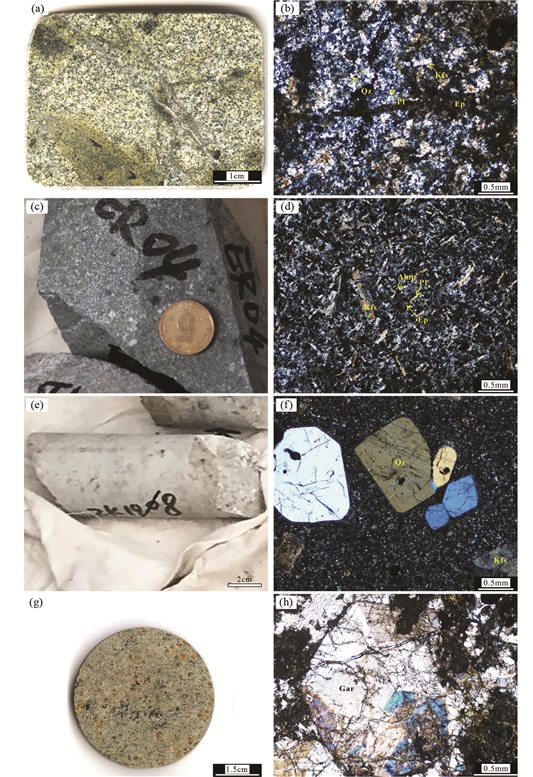

|
图 5 二道河矿床代表性岩体手标本及显微岩相特征 (a、b)绿帘石化细粒花岗闪长岩;(c、d)细粒闪长岩;(e、f)花岗斑岩和(g、h)石榴石矽卡岩. Qz-石英;Kfs-钾长石;Pl-斜长石;Amp-角闪石;Ep-绿帘石;Gar-石榴子石 Fig. 5 Photos of hand specimens and microscopic lithofacies characteristics of representative intrusions in the Erdaohe deposit (a, b) epidotized fine-grained granodiorites; (c, d) fine-grained granodiorite; (e, f) granite porphyry and (g, h) garnet skarn. Qz-quartz; Kfs-K-feldspar; Pl-plagioclase; Amp-amphibole; Ep-epidote; Gar-garnet |
绿帘石化细粒闪长岩(ZK1390-243,图 5c, d),细粒结构,块状构造,斜长石(65%)自形-半自形板状,粒径为0.1~1mm;角闪石(25%)自形-半自形柱状,粒径为0.1~1mm。副矿物为少量磁铁矿、磷灰石、锆石等,绿帘石呈粒状、放射状集合体呈脉状、团块状分布于岩石中。
花岗斑岩(ZK1309-343,图 5e, f),斑状结构,块状构造,石英斑晶(10%)自形-半自形粒状,粒径为2~4mm;钾长石斑晶(10%)自形-半自形板状,常具卡式双晶,粒径为2~3mm;基质以霏细状长英质为主,含量为80%。副矿物为少量锆石、磁铁矿等。
石榴石矽卡岩(ZK1309-261、ZK1908-456和ZK1908-480,图 5g, h),粒状变晶结构,块状构造。石榴子石(40%~65%),自形-半自形粒状,粒径为0.1~10mm,玻璃光泽,环带结构发育,多呈集合体形态产出;透辉石(10%)半自形-他形柱状,粒径为0.1~2mm;石英(20%)无色,油脂光泽,他形粒状,粒径为0.1~1mm,多充填在矿物颗粒间。副矿物为黄铁矿等,常为粒状集合体。
3.2 锆石U-Pb定年锆石挑选工作在廊坊市地科勘探技术服务有限公司完成,在南京宏创地质勘查技术服务有限公司进行锆石靶的制备和阴极发光(CL)图像的采集工作。锆石U-Pb定年在中国冶金地质总局山东局测试中心利用LA-ICP-MS测定,仪器采用X Serise2电感耦合等离子体质谱仪,实验过程中仪器工作参数为:激光剥蚀束斑直径为32μm,频率为10Hz,有效采集时间为45s,采用国际标准锆石91500进行分馏校正,使用TEMORA和Qinghu作为监控标样。采用Glitter4.4程序进行样品的同位素比值和元素含量数据处理。获得数据通过Isoplot(ver3.0)(Ludwig, 2003)宏程序完成计算与谐和图的生成。本文采集的4件样品锆石ICP-MS U-Pb分析结果列于表 1。
|
|
表 1 二道河矿床锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb分析结果 Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data of the Erdaohe deposit |
锆石Hf同位素原位分析在内蒙古自治区地质调查院实验室采用Neptune多接收电感耦合等离子质谱仪LA-MC-ICP-MS测试完成。仪器的运行条件和详细的实验流程参数见吴福元等(2007)。测定时采用国际标准锆石91500(176Hf/177Hf=0.282294±0.000015, 176Lu/177Hf=0.00031)作为外标,激光剥蚀束斑直径为32μm,频率为10Hz,能量为100mJ。本文样品的锆石Hf同位素数据列于表 2。
|
|
表 2 二道河矿床锆石Lu-Hf同位素组成分析结果 Table 2 Lu-Hf isotopic compositions of zircons from the Erdaohe deposit |
石榴子石电子探针主量元素分析在中国冶金地质总局山东局测试中心完成,仪器型号为日本电子JXA-8230,加速电压15kV,束流1×10-8A,束斑1μm。采用PRZ方法校正,分析标样为美国SPI公司的53种矿物,测试精度优于1%。本文采集的2件样品石榴子石电子探针分析结果列于表 3。
|
|
表 3 二道河矿床石榴子石电子探针分析结果(wt%) Table 3 EPMA results (wt%) of garnets from the Erdaohe deposit |
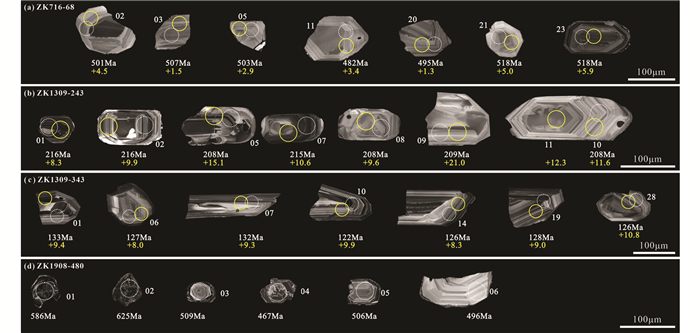
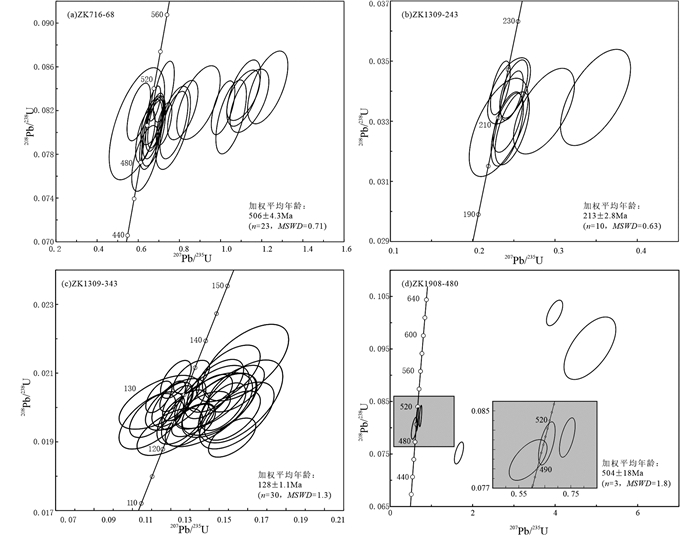
绿帘石化细粒花岗闪长岩样品(ZK716-68)锆石为无色透明或略带浅黄色,呈自形-半自形柱状,粒径在50~200μm之间,长宽比介于1:1~2.5:1,少量颗粒中见少许包裹体和裂隙,部分锆石发育一层很薄的增生边,可能是后期变质或蚀变的结果。阴极发光(CL)图像(图 6a)显示锆石具有较为清晰的岩浆振荡环带。对其中23粒锆石进行U-Pb同位素分析,Th/U比值大多介于0.7~1.2之间,23个测试点所得出的206Pb/238U年龄值大多介于521~482Ma之间,23个分析点在206Pb/238U-207Pb/235U谐和图上均落在谐和线上或附近,个别样品可能由于铅丢失位于谐和线下方(图 7a)。206Pb/238U加权年龄平均值为506±4.3Ma(MSWD=0.71)。
|
图 6 二道河矿床各类岩体及矽卡岩锆石代表性CL图像 图中白色虚线圈和黄色实线圈分别为U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素测试点 Fig. 6 Representative cathodoluminescence (CL) images of zircons from different intrusions and skarns in the Erdaohe deposit The white dashed and yellow solid circles denote the locations of the U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic analysis, respectively |
|
图 7 二道河矿床各类岩体及矽卡岩锆石U-Pb谐和图解 Fig. 7 Zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams of different intrusions and skarns in the Erdaohe deposit |
绿帘石化细粒闪长岩样品(ZK1309-243)锆石为无色透明或略带浅黄色,呈自形-半自形柱状,粒径在50~150μm之间,长宽比介于1:1~3:1,少量颗粒中见少许包裹体和裂隙,部分锆石发育一层很薄的增生边。阴极发光(CL)图像(图 6b)显示锆石具有较为清晰的岩浆振荡环带。对其中10粒锆石进行U-Pb同位素分析,其Th/U比值大多介于0.6~1.0之间,10个测试点所得出的206Pb/238U年龄值介于216~208Ma之间,10个分析点在206Pb/238U-207Pb/235U谐和图上均落在谐和线上或附近(图 7b),206Pb/238U加权年龄平均值为213±2.8Ma(MSWD=0.77)。
花岗斑岩样品(ZK1309-343)锆石为无色透明或略带浅黄色,呈自形-半自形柱状,粒径在80~200μm之间,长宽比介于1.5:1~3:1,少量颗粒中见少许包裹体和裂隙。阴极发光(CL)图像(图 6c)显示锆石具有较为清晰的岩浆振荡环带。对其中30粒锆石进行U-Pb同位素分析,Th/U比值大多介于0.5~1.0之间,206Pb/238U年龄值介于136~122Ma之间,在206Pb/238U-207Pb/235U谐和图上均落在谐和线上或附近(图 7c),206Pb/238U加权年龄平均值为128±1.1Ma(MSWD=1.3)。
石榴石矽卡岩样品(ZK1908-480)锆石为无色透明或略带浅黄色,多呈自形-半自形柱状,粒径在50~150μm之间,长宽比介于1:1~2:1,少量颗粒中见少许包裹体和裂隙。阴极发光(CL)图像(图 6d)显示锆石分为两类,一类为具有较为清晰的岩浆振荡环带,Th/U比值介于0.8~1.1之间,暗示其为岩浆成因;另一类不发育振荡环带,Th、U含量相对较高,由于该样品为石榴石矽卡岩,且具有明显振荡环带的锆石边部也多具有此类锆石的增生边,因此认为此类锆石为热液成因(Wu and Zheng, 2004),但已发育蜕晶化,不具有定年意义。3个岩浆锆石的测试点在206Pb/238U-207Pb/235U谐和图上均落在谐和线上或附近(图 7d),206Pb/238U加权年龄平均值为504±18Ma(MSWD=1.8),与相邻岩体(ZK716-68)锆石U-Pb年龄一致,其余不和谐年龄可能是受成矿热液作用导致铅丢失导致的。
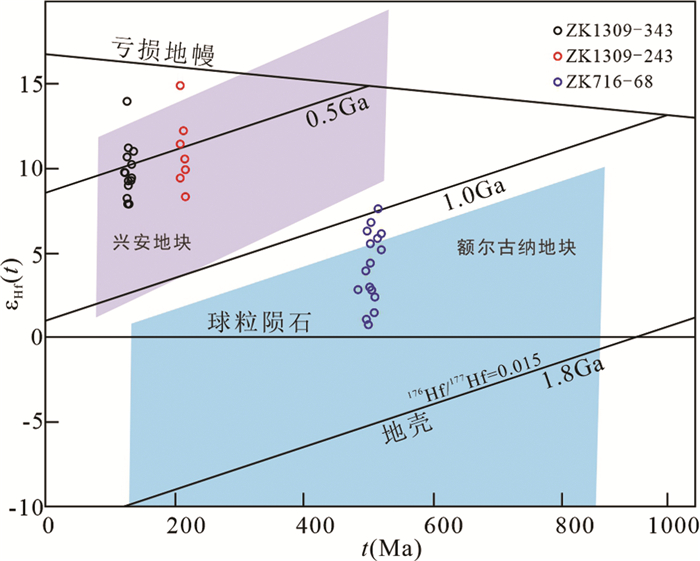
4.2 锆石原位Hf同位素所有样品锆石除个别Hf同位素组成差别较大外,其余均具有较为均一的Hf同位素组成。绿帘石化细粒花岗闪长岩样品(ZK716-68)的176Hf/177Hf值变化于0.282489~0.282666,通过其结晶年龄计算,εHf(t)值为0.9~6.9,相应的Hf同位素二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)介于1552~1110Ma之间。绿帘石化细粒闪长岩样品(ZK1309-243)的176Hf/177Hf值变化于0.282882~0.283077,通过其结晶年龄计算,εHf(t)值为8.3~15.1,相应的Hf同位素二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)介于792~293Ma之间。花岗斑岩样品(ZK1309-343)的176Hf/177Hf值变化于0.282918~0.283097,通过其结晶年龄计算,εHf(t)值为7.9~14.1,相应的Hf同位素二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)介于762~303Ma之间。
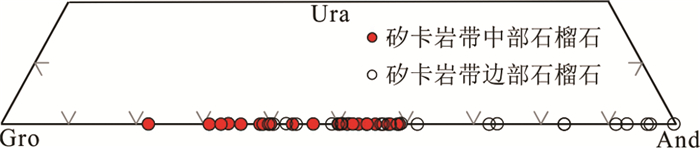
4.3 石榴子石电子探针矽卡岩带中部石榴子石(ZK1309-261)的SiO2含量变化范围为35.89%~37.72%、MgO为0.00%~0.08%、MnO为0.42%~0.96%。FeO与Al2O3含量变化较大,FeO为12.51%~19.73%、Al2O3为7.10%~12.55%(表 3)。端元组分以钙铝榴石(41.02%~78.18%)为主,其次为钙铁榴石(21.79%~58.98%),含有极少的钙铬榴石(0.00%~0.09%),属于钙铝榴石-钙铁榴石固溶体系列(Gro41-78And22-59Ura0-0.1)(图 8),样品还含有少量的TiO2(0.08%~0.50%)。
|
图 8 二道河矿床石榴子石端元组分三角图解 And-钙铁榴石;Gro-钙铝榴石;Ura-钙铬榴石 Fig. 8 Ternary diagrams of garnets from the Erdaohe deposit And-andradite; Gro-grossularite; Ura-uvarovite |
矽卡岩带边部石榴子石(ZK1908-456)的SiO2含量变化范围为34.03%~37.44%、MgO为0.00%~0.04%、MnO为0.20%~0.94%,FeO与Al2O3含量变化较大,FeO为14.47%~29.51%、Al2O3为0.06%~11.16%(表 3)。端元组分以钙铁榴石(39.63%~99.65%)为主,其次为钙铝榴石(0.31%~60.37%),含有极少的钙铬榴石(0.00%~0.11%),属于钙铁榴石-钙铝榴石固溶体系列(And40-100 Gro0-60Ura0-0.1)(图 8),与矽卡岩带中部石榴子石不同的是,样品不含TiO2。
选取的4颗环带构造发育的新鲜石榴子石沿切面进行主量元素电子探针分析测试,分别标记为G1、G2、G3、G4号石榴子石(图 9),其中G1、G2号石榴子石来自矽卡岩带中部,G3、G4号石榴子石来自矽卡岩带边部。G1、G2号石榴子石成分变化较小,在其核部和幔部较为稳定,各组分变化不大,钙铝榴石和钙铁榴石组分含量各占50%左右,且钙铁榴石组分稍多,至边部时,钙铝榴石组分呈现震荡增高趋势,达70%~80%,在石榴子石核部可见透辉石、方解石包裹(图 9a, b)。G3、G4号石榴子石成分变化较大,总体表现为核部和边部以钙铁榴石为主,幔部钙铝榴石有增高的趋势,基本以边部的纯钙铁榴石结束晶体的生长,通过环带特征对比,G4号石榴子石先于G3号石榴子石生长,记录更为完整的信息,透辉石在幔部和边部被包裹(图 9c, d)。

|
图 9 二道河矿床石榴子石环带成分变化示意图 (a)到(d)分别为G1到G4环带钙铝榴石、钙铁榴石端元组分变化. Cal-方解石;Di-透辉石 Fig. 9 Composition variation diagrams of garnet zonation of the Erdaohe deposit From (a) to (d) are the changes of endmember of grossularite and andradite in G1 to G4 zoning, respectively. Cal-calcite; Di-diopside |
二道河银铅锌矿的形成与矿区广泛发育的古生代-中生代长英质岩体关系密切,形成时代跨度大,岩性主要包括花岗岩、花岗闪长岩、闪长岩、花岗斑岩等,其中花岗岩和花岗闪长岩规模最大,出露面积约38km2,侵位于奥陶系地层中,其他类型岩体主要以岩枝、岩脉形式出现(图 1b)。根据前人研究成果,区域上广泛发育的花岗岩和花岗闪长岩年龄在336~300Ma之间(张健等, 2011; 崔芳华等, 2013; 杨发亭, 2016),而本文测得绿帘石化细粒花岗闪长岩锆石年龄为506±4.3Ma,石榴石矽卡岩内锆石年龄为504±18Ma,与相邻绿帘石化细粒花岗闪长岩一致,并且二道河矿区二长闪长岩(226±2Ma)中也有502±7Ma的锆石存在(Yang et al., 2021),表明在二道河矿区还发育了一期早古生代早期的岩浆作用。区域上,500Ma左右的岩浆作用在兴安地块也并不孤立(Miao et al., 2007; 陈会军等, 2021)。
矽卡岩带中穿插的脉状侵入体主要为闪长岩和花岗斑岩,本文测得绿帘石化细粒闪长岩年龄为213±2.8Ma,与Yang et al.(2021)测得二长闪长岩年龄(226±2Ma)相似,而矿区还发现有145Ma左右的闪长岩发育(杨发亭, 2016, 2018; Guo et al., 2021),表明矿区内闪长岩至少存在两期岩浆活动。本文测得花岗斑岩年龄为128±1.1Ma,与杨发亭(2016)其中一个花岗斑岩样品年龄(126.7±0.7Ma)相似,略年轻于其他文献花岗斑岩年龄131.4±0.3Ma (He et al., 2021)、133.6±0.5Ma(Chen et al., 2021)和133.4±3.4Ma、133.7±1.2Ma(杨发亭, 2016),表明该区花岗斑岩也至少有两期岩浆活动。
通过野外地质调查发现,花岗斑岩样品新鲜,未发育绿帘石化(图 5e, f),锆石无增生边现象(图 6d),而绿帘石化细粒花岗闪长岩和绿帘石化闪长岩样品均发育明显的绿帘石化和绿泥石化(图 5a-d),部分锆石可见增生边现象(图 6a, b),而该区域其他同时代岩体锆石未发现增生边现象(崔芳华等, 2013; 张超等, 2013; Sun et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2016; 于倩, 2017),说明本文所采样品发育的增生边不是区域性的,应该是受矿区热液活动影响造成的(Wu and Zheng, 2004; Deng et al., 2015)。结合钻探编录情况,花岗斑岩未发育蚀变和矿化现象,呈脉状切穿矿体及矽卡岩,判断其是成矿后岩浆活动的产物(图 2c),其年龄晚于闪锌矿的Rb-Sr同位素年龄130.5±1.9Ma也可印证这一推论(Chen et al., 2021)。因此,二道河矿区存在早古生代-中生代的多期岩浆活动(表 4),成矿过程复杂。
|
|
表 4 二道河矿区岩体年代学统计 Table 4 Statistic age data of intrusions in the Erdaohe deposit |
此外,绿帘石化细粒花岗闪长岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为506±4.3Ma,这与其围岩(中-上奥陶统裸河组)地层时代不一致,表明裸河组形成时代有可能为早-中寒武世。值得一提的是,最新年龄数据显示多宝山铜矿围岩多宝山组已将其形成时代由中奥陶世更新为中寒武世(Zhao et al., 2019)。
5.2 成矿过程探讨野外调查发现,二道河矿区矽卡岩分带特征不明显,石榴石矽卡岩与绿帘石矽卡岩往往相互穿插(图 4a),显示了多期次矽卡岩化过程。石榴子石的组成可以指示其形成时的物理化学条件(赵斌等, 1983; 赵一鸣等, 1990; Meinert, 1992; Jamtveit et al., 1993),钙铁榴石比钙铝榴石在更高的氧逸度下形成(Jamtveit et al., 1993),因为在相对氧化的条件下, Fe主要以三价形式(Fe3+)存在, 形成钙铁榴石和透辉石(刘晓菲等, 2014; 彭惠娟等, 2014; 朱乔乔等, 2014; Xie et al., 2015)。钙铁榴石的形成更加有利于成矿物质的沉淀(Gao et al., 2014)。二道河矿床矽卡岩带中部(ZK1309-261-G1、G2)和边部(ZK1908-456-G3、G4)均发育类似的石榴石矽卡岩,但其形成过程完全不同:矽卡岩带边部石榴子石中颗粒较大者(G4号石榴子石,图 9d)记录了两期不同的结晶特征,即该石榴子石核部以钙铁榴石为主,环带特征不明显,未包裹透辉石等其他矽卡岩矿物,表明核部石榴子石在形成过程中热液成分相对稳定,以富铁流体为主;核部与幔部界线与正常形成的环带成分变化特征显著不同,具有出现溶蚀以及交代现象,在核部与幔部接触带附近可见少量黄铁矿等金属硫化物(图 9d),并且该石榴子石幔部-边部与其相邻颗粒较小的石榴子石环带特征一致(图 9c, d),与矽卡岩带中部石榴子石(G1、G2)呈现一定的相关性,可能为另一期流体作用的结果:表现为矽卡岩带中部与边部石榴子石结晶起始阶段均表现为钙铁榴石与钙铝榴石组分近似相等,但矽卡岩带中部石榴子石甚至在核部包裹了方解石等晚期矽卡岩矿物(G2, 图 9b)。通过CL图像还可以看出,矽卡岩带中部石榴子石由内向外表现为周期性出现钙铁榴石组分缓慢增高,而后突然降低(G1、G2),矽卡岩带边部石榴子石正好相反,周期性出现钙铁榴石组分突然增高,而后逐渐降低(G3、G4)的特征(图 9),这种现象的出现暗示石榴石矽卡岩的形成经历了至少两期不同性质流体活动的影响。
前人在二道河矿床开展的稳定同位素研究认为成矿热液来源与岩浆岩关系更为密切(张璟等, 2017; He et al., 2021),勘探揭露的关系显示矽卡岩带边部石榴子石紧邻细粒花岗闪长岩岩体,矽卡岩带中部的石榴子石则更加靠近闪长岩等脉状侵入体(图 2),石榴石矽卡岩内发育与相邻绿帘石化细粒花岗闪长岩一致的锆石年龄,本文认为矿区内发育的细粒花岗闪长岩与矽卡岩矿床的形成关系密切,即早期的细粒花岗闪长岩体由于规模较大,热液成分较为稳定,岩体携带了部分铅锌银等成矿物质,在二道河矿区及附近富集(图 4b);晚期的细粒闪长岩及花岗斑岩等在侵入过程中再次形成矽卡岩,从而导致矽卡岩分带不明显,出现各类矽卡岩相互穿插的情况(图 4a),并使早期富集的闪锌矿、方铅矿等硫化物重熔,在有利的部位形成了规模较大的铅锌银矿(Zhong et al., 2018; 图 2),从出露的细粒闪长岩脉边部出现闪锌矿与方铅矿矿体而无矽卡岩产生(图 3),矿石矿物具有重结晶特征(图 4c, d),可以认为该期岩浆活动将早期矿石颗粒萃取并携带至地表浅部;本文所采花岗斑岩无矿化蚀变发育(图 5),锆石无增生边发育(图 6),分布特征与矽卡岩化和矿化关系不大(图 2),因此,花岗斑岩为成矿后形成的岩体,对矿体产生了破坏作用。
由于闪锌矿在高于200℃的热液中不稳定(Hayashi et al., 1990),而二道河矿床在矽卡岩化阶段温度可以达到400℃以上(He et al., 2021; 焦天龙等, 2021),结合二道河地区发育多期次岩浆作用,各类矽卡岩相互穿插(图 4a),闪锌矿、方铅矿等具有重结晶特征(图 4c, d),以及石榴子石至少两期不同性质流体活动的影响等特征,都暗示了二道河银铅锌矿至少经历了两期以上的矿化事件,而这些矿化事件都有可能造成Rb-Sr同位素年代学系统因形成开放系统而被最后一期矿化事件重置(陈文等, 2011),从而导致闪锌矿Rb-Sr同位素年龄记录了最后一期成矿事件的年龄(Chen et al., 2021)。
5.3 矿区岩体形成背景探讨矿床类型、成因和时空分布特征通常是受构造演化和地球动力学环境所控制(Sillitoe, 2000; Qin et al., 2002; Richards, 2003, 2013; Wan et al., 2011; 秦克章等, 2017; Zhao et al., 2018),二道河矿区岩体的形成背景研究对二道河银铅锌矿成因有着重要的相关性。二道河矿床位于中亚造山带东段的兴安地块中部,该区在早古生代早期经历了额尔古纳地块和兴安地块的拼合,并广泛发育岩浆作用和变质作用(Ge et al., 2005; Zhou et al., 2011; Miao et al., 2015; Zhou et al., 2015; 许文良等, 2019),而500Ma左右被大多数地质学家认为是额尔古纳地块与兴安地块拼合的时间(Ge et al., 2005; Han et al., 2011, 2012, 2015; Zhou et al., 2011, 2015; Feng et al., 2016, 2017; Liu et al., 2017; 许文良等, 2019),二道河矿区发育的506±4.3Ma的细粒花岗闪长岩锆石Hf同位素εHf(t)值为0.9~6.9,两阶段模式年龄tDM2=1.5~1.1Ga,在Hf同位素组成演化图解上分布在亏损地幔线与球粒陨石参考线之间,表明花岗闪长岩的原生岩浆可能来源于下地壳部分熔融,并且这些锆石主要位于额尔古纳地块范围内,部分向兴安地块范围靠近(图 10),其成因可能与额尔古纳地块和兴安地块的拼合有关;闪长岩锆石年龄为213±2.8Ma、花岗斑岩锆石年龄为128±1.1Ma,它们的εHf(t)值分别为8.3~15.1和7.9~14.1,两阶段模式年龄均为tDM2=0.8~0.3Ga,在Hf同位素组成演化图解上也分布于亏损地幔线与球粒陨石参考线之间,表明闪长岩和花岗斑岩的原生岩浆可能来源于新生的地壳部分熔融(图 10),它们的形成可能分别与蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合(陈志广等, 2010; Tang et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2021)及古太平洋板块俯冲有关(Chen et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2021; 焦天龙等, 2021)。因此,二道河地区经历了多次构造体系叠加与演化,对矿床的形成和富集产生了重要的影响。
|
图 10 二道河矿床各类岩体及矽卡岩锆石εHf(t)与U-Pb年龄图解 “兴安地块”和“额尔古纳地块”范围据Feng et al., 2017 Fig. 10 εHf(t) vs. U-Pb age plot of zircons from different intrusions and skarns in the Erdaohe deposit The scopes of the Xing'an and Erguna blocks from Feng et al., 2017 |
通过对大兴安岭中段新近发现二道河银铅锌矿发育的岩体锆石年代学、Hf同位素以及石榴子石电子探针研究,得出以下结论:
(1) 二道河银铅锌矿主要围岩是细粒花岗闪长岩,其锆石年龄为506±4.3Ma,细粒闪长岩锆石年龄为213±2.8Ma,花岗斑岩锆石年龄为128±1.1Ma,表明矿区存在多期岩浆活动。
(2) 二道河银铅锌矿矽卡岩类型为钙质矽卡岩,石榴石矽卡岩与绿帘石矽卡岩常呈相互穿插关系,闪锌矿、方铅矿等具有重结晶特征,石榴子石至少两期不同性质流体活动的影响等,表明二道河银铅锌矿至少经历了两期以上的矿化事件。
(3) 细粒花岗闪长岩、细粒闪长岩以及花岗斑岩锆石的εHf(t)值分别为0.9~6.9、8.3~15.1和7.9~14.1,对应的二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)分别为1.6~1.1Ga、0.8~0.3Ga和0.8~0.3Ga,表明本区原生岩浆可能来源于新生地壳部分熔融,其形成可能与额尔古纳地块和兴安地块的拼合有关,细粒闪长岩和花岗斑岩的形成可能分别与蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合及古太平洋板块俯冲有关。
致谢 野外工作过程中得到了国森矿业有限责任公司大力支持;实验过程得到了中国冶金地质总局山东局测试中心李凤春老师、林培军老师,内蒙古自治区地质调查院实验室肖剑伟老师的帮助;本文撰写过程中得到了中国地质大学(北京)李小伟副教授、河海大学叶现韬副教授的帮助与指导;审稿人提出了宝贵的意见和建议;在此一并表示感谢。
Chen C, Lv XB, Gun MS and Yang JS. 2021. Metallogenic chronology and tectonic setting of the Erdaohe Pb-Zn-Ag deposit in Inner Mongolia, NE China: Constraints from sphalerite Rb-Sr dating, zircon U-Pb dating, and Hf isotope analysis. Ore Geology Reviews, 134: 104067 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104067
|
Chen HJ, Fu JY, Qian C, Pang XJ and Zhong H. 2021. Chronology and spatiotemporal distribution of Pre-Mesozoic granites in northeast China. Geological Bulletin of China, 40(6): 827-844 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen W, Wan YS, Li HQ, Zhang ZQ, Dai TM, Shi ZE and Sun JB. 2011. Isotope geochronology: Technique and application. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(11): 1917-1947 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen ZG, Zhang LC, Lu BZ, Li ZL, Wu HY, Xiang P and Huang SW. 2010. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Taipingchuan copper-molybdenum deposit in Inner Mongolia, and its geological significances. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(5): 1437-1449 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Cui FH, Zheng CQ, Xu XC, Yao WG, Shi L, Li J and Xu JL. 2013. Late Carboniferous magmatic activities in the Quanshenglinchang area, Great Xing'an Range: Constrains on the timing of amalgamation between Xing'an and Songnen massifs. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(9): 1247-1263 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Cui XW, Jiang SH, Li HB and Chang YH. 2015. Integrated prospecting model of Erdaohe silver-lead-zinc deposit in the Zhalantun area, Inner Mongolia. Mineral Exploration, 6(6): 667-678 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Deng XD, Li JW and Wen G. 2015. U-Pb geochronology of hydrothermal zircons from the Early Cretaceous iron skarn deposits in the Handan-Xingtai district, North China craton. Economic Geology, 110(8): 2159-2180 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.110.8.2159
|
Feng ZQ, Liu YJ, Liu BQ, Wen QB, Li WM and Liu Q. 2016. Timing and nature of the Xinlin-Xiguitu Ocean: Constraints from ophiolitic gabbros in the northern Great Xing'an Range, eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 105(2): 491-505 DOI:10.1007/s00531-015-1185-z
|
Feng ZQ, Liu YJ, Li YR, Li WM, Wen QB, Liu BQ, Zhou JP and Zhao YL. 2017. Ages, geochemistry and tectonic implications of the Cambrian igneous rocks in the northern Great Xing'an Range, NE China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 144: 5-21 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.12.006
|
Gao X, Yang LQ, Deng J, Meng JY, Yang CH and Li JX. 2014. The characteristics of garnet in the Hongniu skarn copper deposit, western Yunnan, China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(Suppl.2): 515-516
|
Ge WC, Wu FY, Zhou CY and Abdel Rahman AA. 2005. Emplacement age of the Tahe granite and its constraints on the tectonic nature of the Ergun block in the northern part of the Da Hinggan Range. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(18): 2097-2105 DOI:10.1360/982005-207
|
Gun MS, Lü XB, Zeng DG, Li J, Chen C, Li JY and Wang HJ. 2021. Geological characteristics and ore-forming material sources of the Erdaohe Pb-Zn-Ag polymetallic deposits in the northern-central part of the Greater Khingan Mountains. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 41(2): 150-162 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1016/j.chnaes.2020.10.003
|
Guo XG. 2020. Metallogenesis of Erdaohe skarn-type lead-zinc deposit in the middle segment of the Great Hinggan Range. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Guo XG, Li JW, Li CJ and Jiao TL. 2021. Geochronology, geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes of ore-related diorites in the Erdaohe Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, Great Hinggan Range, NE China: Constraints on timing, petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Lithos, 386-387: 106005 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2021.106005
|
Han GQ, Liu YJ, Neubauer F, Genser J, Li W, Zhao YL and Liang CY. 2011. Origin of terranes in the eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt, NE China: U-Pb ages of detrital zircons from Ordovician-Devonian sandstones, North Da Xing'an Mts.. Tectonophysics, 511(3-4): 109-124 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2011.09.002
|
Han GQ, Liu YJ, Neubauer F, Jin W, Genser J, Ren SM, Li W, Wen QB, Zhao YL and Liang CY. 2012. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic compositions of detrital zircons from the Permian sandstones in Da Xing'an Mountains, NE China: New evidence for the eastern extension of the Erenhot-Hegenshan suture zone. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 49: 249-271 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.11.011
|
Han GQ, Liu YJ, Neubauer F, Bartel E, Genser J, Feng ZQ, Zhang L and Yang MC. 2015. U-Pb age and Hf isotopic data of detrital zircons from the Devonian and Carboniferous sandstones in Yimin area, NE China: New evidences to the collision timing between the Xing'an and Erguna blocks in eastern segment of Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97: 211-228 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.08.006
|
Hayashi K, Sugaki A and Kitakaze A. 1990. Solubility of sphalerite in aqueous sulfide solutions at temperatures between 25 and 240℃. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 54(3): 715-725 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(90)90367-T
|
He J, Huang M and Cong YN. 2019. Geological features and prospecting signs of Erdaohe silver-lead-zinc deposit, Inner Mongolia. Inner Mongolia Science Technology & Economy, (12): 58 (in Chinese)
|
He XL, Yu QY, Liu SY, Yang MJ and Zhang D. 2021. Origin of the Erdaohe Ag-Pb-Zn deposit, central Great Xing'an Range, Northeast China: Constraints from fluid inclusions, zircon U-Pb geochronology, and stable isotopes. Ore Geology Reviews, 137: 104309 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104309
|
Jamtveit B, Wogelius RA and Fraser DG. 1993. Zonation patterns of skarn garnets: Records of hydrothermal system evolution. Geology, 21(2): 113-116 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0113:ZPOSGR>2.3.CO;2
|
Jiao TL, Li JW, Guo XG, She HQ, Ren CH and Li CJ. 2021. Discussion on the ore-forming fluids and materials sources of Erdaohe Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, Inner Mongolia. Geology in China: 1-24 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li SD, Wang KY, Wang YC, Zhang XB and Quan HY. 2017. Genesis of the Bairendaba Ag-Zn-Pb deposit, southern Great Xing'an Range, NE China: A fluid inclusion and stable isotope study. Geofluids, 2017: 1206587
|
Li Y, Ding LL, Xu WL, Wang F, Tang J, Zhao S and Wang ZJ. 2015. Geochronology and geochemistry of muscovite granite in Sunwu area, NE China: Implications for the timing of closure of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(1): 56-66 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li YL, Zhou HW, Xiao WJ, Zhong ZQ, Yin SP and Li FL. 2012. Superposition of Paleo-Asian and West-Pacific tectonic domains in the eastern section of the Solonker suture zone: Insights from petrology, geochemistry and geochronology of deformed diorite in Xar Moron Fault Zone, Inner Mongolia. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 37(3): 433-450 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu XF, Yuan SD, Shuang Y, Yuan YB, Mi JR and Xuan YS. 2014. In situ LA-ICP-MS REE analyses of the skarn garnets from the Jinchuantang tin-bismuth deposit in Hunan Province, and their significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(1): 163-177 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu YJ, Li WM, Feng ZQ, Wen QB, Neubauer F and Liang CY. 2017. A review of the Paleozoic tectonics in the eastern part of Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Gondwana Research, 43: 123-148 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.013
|
Ludwig KR. 2003. Isoplot/Ex, Version 3: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Berkeley, Special Publication, No. 4
|
Meinert LD. 1992. Skarns and skarn deposits. Geoscience Canada, 19(4): 145-162
|
Meinert LD, Dipple GM and Nicolescu S. 2005. World skarn deposits. In: Economic Geology, 100th Anniversary Volume. Littleton, Colorado: Society of Economic Geologists, 299-336
|
Miao LC, Liu DY, Zhang FQ, Fan WM, Shi YR and Xie HQ. 2007. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb ages of the "Xinghuadukou Group" in Hanjiayuanzi and Xinlin areas and the "Zhalantun Group" in Inner Mongolia, Da Hinggan Mountains. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(8): 1112-1124 DOI:10.1007/s11434-007-0131-2
|
Miao LC, Zhang FC and Jiao SJ. 2015. Age, protoliths and tectonic implications of the Toudaoqiao blueschist, Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 105: 360-373 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.028
|
Peng HJ, Li HY, Pei RF, Zhang CQ, Zhou YM, Tian G, Li JX and Long F. 2014. Mineralogical characteristics and metallogeny of the Hongniu-Hongshan copper deposit in Zhongdian area, Yunnan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(1): 237-256 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Qin KZ, Sun S, Li JL, Fang TH, Wang SL and Liu W. 2002. Paleozoic epithermal Au and porphyry Cu deposits in North Xinjiang, China: Epochs, features, tectonic linkage and exploration significance. Resource Geology, 52(4): 291-300 DOI:10.1111/j.1751-3928.2002.tb00140.x
|
Qin KZ, Zhai MG, Li GM, Zhao JX, Zeng QD, Gao J, Xiao WJ, Li JL and Sun S. 2017. Links of collage orogenesis of multiblocks and crust evolution to characteristic metallogeneses in China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(2): 305-325 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Richards JP. 2003. Tectono-magmatic precursors for porphyry Cu-(Mo-Au) deposit formation. Economic Geology, 98(8): 1515-1533 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.98.8.1515
|
Richards JP. 2013. Giant ore deposits formed by optimal alignments and combinations of geological processes. Nature Geoscience, 6(11): 911-916 DOI:10.1038/ngeo1920
|
Şengör AMC, Natal'In BA and Burtman VS. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia. Nature, 364(6435): 299-307 DOI:10.1038/364299a0
|
Shao JD, Wang H, Zhang M and Zhao WT. 2011. Division of tectonic units and their geological features in Inner Mongolia. Resources, (2): 51-56 (in Chinese)
|
Sillitoe RH. 2000. Gold-rich porphyry deposits: Descriptive and genetic models and their role in exploration and discovery. Reviews in Economic Geology, 13: 315-345
|
Sun W, Chi XG, Zhao Z, Pan SY, Liu JF, Zhang R and Quan JY. 2014. Zircon geochronology constraints on the age and nature of 'Precambrian metamorphic rocks' in the Xing'an block of Northeast China. International Geology Review, 56(6): 672-694 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2014.883183
|
Tang J, Xu WL, Wang F, Wang W, Xu MJ and Zhang YH. 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of Early-Middle Triassic magmatism in the Erguna Massif, NE China: Constraints on the tectonic evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean. Lithos, 184-187: 1-16 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.10.024
|
Tang J, Xu WL, Wang F, Zhao S and Li Y. 2015. Geochronology, geochemistry, and deformation history of Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous intrusive rocks in the Erguna Massif, NE China: Constraints on the Late Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk orogenic belt. Tectonophysics, 658: 91-110 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2015.07.012
|
Tang J, Xu WL, Wang F, Zhao S and Wang W. 2016. Early Mesozoic southward subduction history of the Mongol-Okhotsk oceanic plate: Evidence from geochronology and geochemistry of Early Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Erguna Massif, NE China. Gondwana Research, 31: 218-240 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2014.12.010
|
Wan B, Xiao WJ, Zhang LC, Windley BF, Han CM and Quinn CD. 2011. Contrasting styles of mineralization in the Chinese Altai and East Junggar, NW China: Implications for the accretionary history of the southern Altaids. Journal of the Geological Society, 168(6): 1311-1321 DOI:10.1144/0016-76492011-021
|
Wang T, Guo L, Zhang L, Yang QD, Zhang JJ, Tong Y and Ye K. 2015. Timing and evolution of Jurassic-Cretaceous granitoid magmatisms in the Mongol-Okhotsk belt and adjacent areas, NE Asia: Implications for transition from contractional crustal thickening to extensional thinning and geodynamic settings. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97: 365-392 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.005
|
Wang Z, Niu Y and Yao D. 2012. Discovery and significance of Ag-polymetallic deposit in Inner Mongolia Erdaohe. Journal of Shandong University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 26(1): 46-49 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wu FY, Li XH, Zheng YF and Gao S. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185-220 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wu FY, Sun DY, Ge WC, Zhang YB, Grant ML, Wilde SA and Jahn BM. 2011. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(1): 1-30 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
|
Wu YB and Zheng YF. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15): 1554-1569 DOI:10.1007/BF03184122
|
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Zhu QQ, Yao L, Li YH, Li W and Zhao HJ. 2015. Geochemical constraints on Cu-Fe and Fe skarn deposits in the Edong district, Middle-Lower Yangtze River metallogenic belt, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 64: 425-444 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.08.005
|
Xu WL, Pei FP, Wang F, Meng E, Ji WQ, Yang DB and Wang W. 2013. Spatial-temporal relationships of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in NE China: Constraints on tectonic overprinting and transformations between multiple tectonic regimes. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 74: 167-193 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.003
|
Xu WL, Sun CY, Tang J, Luan JP and Wang F. 2019. Basement nature and tectonic evolution of the Xing'an-Mongolian Orogenic belt. Earth Science, 44(5): 1620-1646 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang FT. 2016. Geologic features of Erdaohe silver polymetallic deposit and its ore finding prediction in Middle Daxing'anling Mountains. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Yang FT. 2018. Geologic features of Erdaohe silver polymetallic deposit and its ore finding prediction in Middle Daxing'anling Mountains. Western Resources, (6): 69-70 (in Chinese)
|
Yang H, Ge WC, Yu Q, Ji Z, Liu XW, Zhang YL and Tian DX. 2016. Zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopes, bulk-rock geochemistry and petrogenesis of Middle to Late Triassic Ⅰ-type granitoids in the Xing'an Block, Northeast China: Implications for Early Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the central Great Xing'an Range. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 119: 30-48 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.01.012
|
Yang JS, Lü XB, Gun MS and Chen C. 2021. Early Mesozoic subduction of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean and its effect on the central Great Xing'an Range: Insights from the monzodiorite in the Erdaohe deposit. Geological Journal, 56(3): 1604-1624 DOI:10.1002/gj.4002
|
Yu Q. 2017. Petrogenesis of the Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Xing'an terrane, and its geological implication. Ph. D. Dissertation. Changchun: Jilin University (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zeng QD, Liu JM, Yu CM, Ye J and Liu HT. 2011. Metal deposits in the Da Hinggan Mountains, NE China: Styles, characteristics, and exploration potential. International Geology Review, 53(7): 846-878 DOI:10.1080/00206810903211492
|
Zhang C, Liu ZH, Xu ZY, Li SC, Fan ZW and Li G. 2013. Characteristics and genesis of the Wuyi Forestry Center granite in the Da Hinggan Mountains. Geological Bulletin of China, 32(2): 365-373 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang J, Chen JS, Li BY, Gao Y and Zhang YL. 2011. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of Late Paleozoic granites in Taerqi area, Inner Mongolia. Global Geology, 30(4): 521-531 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang J, Shao J, Jiang S and Yang HZ. 2017. A study of the stable isotope geochemistry of Erdaohe Pb-Zn ore deposit in Inner Mongolia. Geological Review, 63(S1): 225-227 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhao B, Li TJ and Li ZP. 1983. Experimental study of physico-chemical conditions of the formation of skarns. Geochimica, (3): 256-267 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhao C, Song GX, Qin KZ, Li GM, Li ZZ, Jin LY, Meng ZJ and Zhang XN. 2017. Indosinian ore-bearing magma source, alteration mineralogy and prospecting signification of the Fulin skarn copper deposit in the northern Great Xing'an Range, NE China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(2): 455-475 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhao C, Qin KZ, Song GX, Li GM, Li ZZ, Pang XY and Wang L. 2018. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of ore-related porphyry in the Duobaoshan Cu deposit within the eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Heilongjiang Province, NE China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 165: 352-370 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.07.002
|
Zhao C, Qin KZ, Song GX, Li GM and Li ZZ. 2019. Early Palaeozoic high-Mg basalt-andesite suite in the Duobaoshan Porphyry Cu deposit, NE China: Constraints on petrogenesis, mineralization, and tectonic setting. Gondwana Research, 71: 91-116 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2019.01.015
|
Zhao YM, Lin WW, Bi CS, Li DX and Jiang CJ. 1990. Skarn Deposits of China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-354 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zheng P, Wang Z, Song YK, Shao J and Niu Y. 2013. Discovery and significance of the Erdaohe silver polymetal deposit in Inner Mongolia. Geology and Resources, 22(6): 488-492 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhong SH, Feng CY, Seltmann R, Dolgopolova A, Andersen JCØ, Li DX and Yu M. 2018. Sources of fluids and metals and evolution models of skarn deposits in the Qimantagh metallogenic belt: A case study from the Weibao deposit, East Kunlun Mountains, northern Tibetan Plateau. Ore Geology Reviews, 93: 19-37 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.12.013
|
Zhou JB, Wilde SA, Zhang XZ, Zhao GC, Liu FL, Qiao DW, Ren SM and Liu JH. 2011. A >1300km Late Pan-African metamorphic belt in NE China: New evidence from the Xing'an block and its tectonic implications. Tectonophysics, 509(3-4): 280-292 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2011.06.018
|
Zhou JB, Wang B, Wilde SA, Zhao GC, Cao JL, Zheng CQ and Zeng WS. 2015. Geochemistry and U-Pb zircon dating of the Toudaoqiao blueschists in the Great Xing'an Range, Northeast China, and tectonic implications. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97: 197-210 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.011
|
Zhu QQ, Xie GQ, Li W, Zhang F, Wang J, Zhang P and Yu BF. 2014. In situ analysis of garnets from the Jingshandian iron skarn deposit, Hubei Province, and its geological implications. Geology in China, 41(6): 1944-1963 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
陈会军, 付俊彧, 钱程, 庞雪娇, 钟辉. 2021. 东北地区前中生代花岗岩类年龄与时空分布. 地质通报, 40(6): 827-844. |
陈文, 万渝生, 李华芹, 张宗清, 戴橦谟, 施泽恩, 孙敬博. 2011. 同位素地质年龄测定技术及应用. 地质学报, 85(11): 1917-1947. |
陈志广, 张连昌, 卢百志, 李占龙, 吴华英, 相鹏, 黄世武. 2010. 内蒙古太平川铜钼矿成矿斑岩时代、地球化学及地质意义. 岩石学报, 26(5): 1437-1449. |
崔芳华, 郑常青, 徐学纯, 姚文贵, 施璐, 李娟, 徐久磊. 2013. 大兴安岭全胜林场地区晚石炭世岩浆活动研究: 对兴安地块与松嫩地块拼合时间的限定. 地质学报, 87(9): 1247-1263. |
崔学武, 姜胜华, 李洪宝, 常耀辉. 2015. 内蒙古二道河银铅锌矿床综合找矿模式. 矿产勘查, 6(6): 667-678. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2015.06.003 |
衮民汕, 吕新彪, 曾道国, 李杰, 陈超, 李建阳, 王华建. 2021. 大兴安岭中北段二道河铅锌银多金属矿床地质特征与成矿物质来源. 矿物学报, 41(2): 150-162. |
郭向国. 2020. 大兴安岭中段二道河矽卡岩型铅锌矿成矿作用研究. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京)
|
和静, 黄明, 丛亚楠. 2019. 内蒙古二道河银铅锌矿床地质特征与找矿标志. 内蒙古科技与经济, (12): 58. |
焦天龙, 李进文, 郭向国, 佘宏全, 任程昊, 李长俭. 2021. 内蒙古二道河铅锌银矿床成矿流体、物质来源及成因探讨. 中国地质: 1-24. |
李益龙, 周汉文, 肖文交, 钟增球, 尹淑苹, 李福林. 2012. 古亚洲构造域和西太平洋构造域在索伦缝合带东段的叠加: 来自内蒙吉林西县西拉木伦断裂带内变形闪长岩的岩石学、地球化学和年代学证据. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 37(3): 433-450. |
李宇, 丁磊磊, 许文良, 王枫, 唐杰, 赵硕, 王子进. 2015. 孙吴地区中侏罗世白云母花岗岩的年代学与地球化学: 对蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合时间的限定. 岩石学报, 31(1): 56-66. |
刘晓菲, 袁顺达, 双燕, 原垭斌, 弥佳茹, 轩一撒. 2014. 湖南金船塘锡铋矿床石榴子石原位LA-ICP-MS稀土元素分析及其意义. 岩石学报, 30(1): 163-177. |
彭惠娟, 李洪英, 裴荣富, 张长青, 周云满, 田广, 李建新, 龙飞. 2014. 云南中甸红牛-红山矽卡岩型铜矿床矿物学特征与成矿作用. 岩石学报, 30(1): 237-256. |
秦克章, 翟明国, 李光明, 赵俊兴, 曾庆栋, 高俊, 肖文交, 李继亮, 孙枢. 2017. 中国陆壳演化、多块体拼合造山与特色成矿的关系. 岩石学报, 33(2): 305-325. |
邵积东, 王惠, 张梅, 赵文涛. 2011. 内蒙古大地构造单元划分及其地质特征. 西部资源, (2): 51-56. |
王忠, 牛勇, 姚德. 2012. 内蒙古二道河银多金属矿床的发现及其意义. 山东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 26(1): 46-49. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6197.2012.01.011 |
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185-220. |
许文良, 孙晨阳, 唐杰, 栾金鹏, 王枫. 2019. 兴蒙造山带的基底属性与构造演化过程. 地球科学, 44(5): 1620-1646. |
杨发亭. 2016. 大兴安岭中段二道河银多金属矿床地质特征及找矿预测. 硕士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京)
|
杨发亭. 2018. 大兴安岭中段二道河银多金属矿床成矿规律及找矿预测. 西部资源, (6): 69-70. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-562X.2018.06.028 |
于倩. 2017. 兴安地块晚古生代-早中生代侵入岩的成因及其地质意义. 博士学位论文. 吉林: 吉林大学
|
张超, 刘正宏, 徐仲元, 李世超, 范志伟, 李刚. 2013. 大兴安岭五一林场花岗岩体地球化学特征及成因. 地质通报, 32(2): 365-373. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.02.015 |
张健, 陈井胜, 李泊洋, 高妍, 张彦龙. 2011. 内蒙古塔尔气地区晚古生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素特征. 世界地质, 30(4): 521-531. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2011.04.003 |
张璟, 邵军, 江山, 杨宏智. 2017. 内蒙古二道河铅锌矿床稳定同位素地球化学研究. 地质论评, 63(S1): 225-227. |
赵斌, 李统锦, 李昭平. 1983. 夕卡岩形成的物理化学条件实验研究. 地球化学, (3): 256-267. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1983.03.005 |
赵超, 宋国学, 秦克章, 李光明, 李真真, 金露英, 孟昭君, 张夏楠. 2017. 大兴安岭北段富林矽卡岩铜矿床成因: 印支期含矿岩浆源区特征、蚀变矿物学及勘查意义. 岩石学报, 33(2): 455-475. |
赵一鸣, 林文蔚, 毕承思, 李大新, 蒋崇俊. 1990. 中国矽卡岩矿床. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-354.
|
郑萍, 王忠, 宋玉坤, 邵军, 牛勇. 2013. 内蒙古二道河银多金属矿床的发现及其意义. 地质与资源, 22(6): 488-492. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2013.06.009 |
朱乔乔, 谢桂青, 李伟, 张帆, 王建, 张平, 于炳飞. 2014. 湖北金山店大型矽卡岩型铁矿石榴子石原位微区分析及其地质意义. 中国地质, 41(6): 1944-1963. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.06.012 |
 2021, Vol. 37
2021, Vol. 37