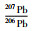高压-超高压变质带位于汇聚板块的边界,是大洋俯冲和大陆碰撞的产物,记录了地壳物质从俯冲到折返的过程(Smith, 1984; Chopin, 1984; Ernst and Liou, 1995; Maruyama et al., 1996; Zheng, 2012; Liu et al., 2016)。俯冲碰撞形成的高压-超高压变质带中的高级变质岩,记录了造山带演化的地质过程,是反演和揭示这些地质过程的重要载体(Carswell and Zhang, 1999; Chopin, 2003; Liu et al., 2007; 郑永飞等, 2013; 张宏福和于红, 2019)。榴辉岩是典型的高压变质基性岩,因常保留多期矿物组合,容易记录变质峰期条件,是研究造山带演化的关键岩石样品。榴辉岩常呈透镜体、块状、似层状产出于围岩片麻岩中,两者一同深俯冲经历高压-超高压变质作用,然后折返回地表。虽然其在造山带中出露有限,却对理解板片俯冲和折返及造山带形成演化有重要意义。
秦岭-桐柏-红安-大别-苏鲁造山带西连祁连-昆仑造山带,构成了横贯我国几千千米的中央造山带。该造山带是全世界规模最大的高压-超高压变质带,并经历了多阶段的演化,一直是研究高压-超高压变质作用和造山带演化的热点地区(Mattauer et al., 1985; Ernst and Liou, 1995; Meng and Zhang, 2000; Liou et al., 2009; Wu and Zheng, 2013; Zheng et al., 2019)。作为该造山带重要组成部分的秦岭-大别造山带,保存了大量不同年代的高压-超高压变质岩石。前人已经对秦岭造山带和大别造山带内的高压-超高压变质岩进行了详细的年代学研究,确定了北秦岭造山带主要分布一系列早古生代的高压-超高压变质岩(Wang et al., 2011; 陈丹玲和刘良, 2011; Cheng et al., 2012; 陈丹玲等, 2015; Liu et al., 2016),大别-苏鲁造山带则以中生代的高压-超高压变质岩为主(Hacker et al., 2000; 陈道公等, 2002; Zheng et al., 2005, 2006; Wu et al., 2006; Gao et al., 2011)。在空间上,桐柏造山带处于秦岭造山带和大别造山带的衔接部位,对理解中央造山带的演化至关重要。同时,相较于研究比较成熟的秦岭造山带和大别造山带内的榴辉岩,桐柏造山带内榴辉岩受到的关注相对较少。因此,本文拟对桐柏地区的榴辉岩及其围岩白云母石英片岩进行详细的岩石学、地球化学以及年代学研究,限定其原岩构造属性及变质时代,探讨桐柏造山带的演化过程。
1 地质背景桐柏造山带是一个复合型造山带,经历了多阶段构造演化,并在三叠纪最终碰撞形成(Wu and Zheng, 2013; 刘晓春等, 2015)。构造上,桐柏造山带处于中央造山带的中间部位(图 1),向西以南阳盆地和秦岭造山带相接,向东以大悟断裂和红安造山带相连(Zhai et al., 1998; 刘晓春等, 2005; Liu et al., 2008; Cheng et al., 2011)。桐柏造山带内部又以松扒断裂为界分为南、北两个构造带:北带主要由宽坪群、二郎坪群、秦岭群、龟山杂岩和南湾复理石等岩石构造单元组成;南带包括八里畈构造糜棱岩带、北部高压榴辉岩带、桐柏杂岩带、南部高压榴辉岩带和蓝片岩-绿片岩带等岩石构造单元。
|
图 1 秦岭-桐柏-红安-大别-苏鲁造山带构造格架图(a,据Wang et al., 2011)和秦岭-桐柏-红安-大别造山带主要地质单元简图(b,据Wu and Zheng, 2013) Fig. 1 Geological sketch map of the Qinling-Tongbai-Hong'an-Dabie-Sulu orogen (a, modified after Wang et al., 2011) and major geological units of the Qinling-Tongbai-Hong'an-Dabie orogen (b, modified after Wu and Zheng, 2013) |
南、北两条高压榴辉岩带分别位于桐柏杂岩的两侧,其内榴辉岩和退变榴辉岩呈透镜体状、块状、似层状产出于白云钠长片麻岩、片岩和大理岩中(刘晓春等, 2005; Liu et al., 2008)。刘晓春等(2005)利用常规温压计计算得到北部高压榴辉岩的形成条件为530~610℃、1.7~2.0GPa,南部高压榴辉岩的形成条件为470~520℃、1.3~1.7GPa;Cheng et al. (2011)通过平均温压计计算得到榴辉岩的形成温压分别为为490~540℃、1.8~2.1GPa;Zhang et al. (2021)将平均温压计、金红石Zr温度计和锆石Ti温度计的结果相结合,认为榴辉岩的峰期变质条件为580~625℃、2.6~2.7Gpa,达到了柯石英榴辉岩相。就年代学研究而言,前人通过榴辉岩锆石U-Pb定年以及石榴石Lu-Hf定年(Liu et al., 2008; Cheng et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2021),限定榴辉岩变质作用发生的时间在256~245Ma,与大别-苏鲁造山带高压-超高压岩石主体变质年龄相近;另外,两条榴辉岩带内变基性岩的原岩侵位年龄主要集中在古元古代(胡娟等, 2012; Zhang et al., 2020b),变沉积岩中的碎屑锆石记录了2.49Ga、1.93Ga和1.85~1.82Ga三期年龄峰值(Liu et al., 2008),这些结果表明桐柏地区在古元古代可能经历了多期构造热事件。
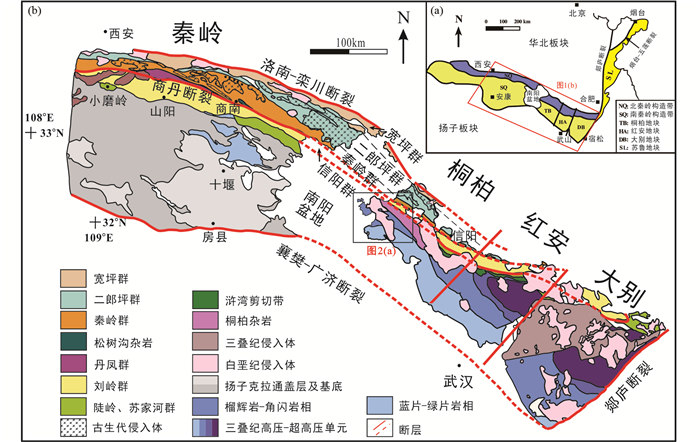
2 岩相学特征本文选取桐柏造山带南部高压榴辉岩带联合口地区的榴辉岩及其围岩白云母石英片岩进行详细研究,采样点位于河南省南阳市唐河县联合口村(32°24′44″N、112°48′25″E)(图 2a)。榴辉岩呈透镜体状出露于白云母石英片岩之中(图 2b)。
|
图 2 桐柏造山带地质图(a)及野外露头照片(b-d) (a)桐柏造山带地质图(据刘晓春等,2005),图中采样位置用五角星表示;(b)桐柏造山带联合口地区榴辉岩及白云母石英片岩野外照片;(c)榴辉岩野外露头照片;(d)白云母石英片岩野外露头照片 Fig. 2 Geological map of the Tongbai orogen (a) and field occurrences of the eclogite (b-d) (a) geological map of the Tongbai orogen (modified after Liu et al., 2005), the star shows the sampling locality; (b) the eclogite and mica quartz schist exposure in Tongbai orogen Lianhekou area; (c) the eclogite; (d) the mica quartz schist |
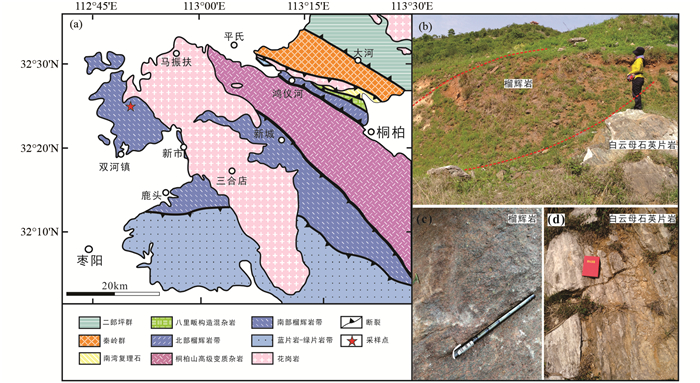
新鲜榴辉岩岩石主体为灰绿色,块状构造,粒状变晶结构(图 2c)。其主要由石榴石(43%)、绿辉石(27%)、角闪石(15%)、多硅白云母(4%)和石英(8%)组成,含少量金红石和榍石等副矿物。石榴石变斑晶为自形-半自形,裂理发育,粒径为0.1~0.8mm。石榴石变斑晶内部发育有包裹体,电子探针分析揭示包裹体主要为绿帘石、角闪石、石英等矿物。绿辉石呈自形-半自形柱状,单偏光镜下呈浅绿色,与角闪石平衡共生。多硅白云母多以半自形片状存在,产于基质或石榴石的边缘位置。石英和金红石等副矿物呈粒状充填于基质中,金红石周围部分被榍石替代(图 3a)。
|
图 3 榴辉岩(a, 单偏光)及白云母石英片岩(b, 正交偏光)显微照片 Grt-石榴石;Omp-绿辉石;Amp-角闪石;Phe-多硅白云母;Qz-石英;Rt-金红石 Fig. 3 Microphotographs of the eclogite (a, plane-polarized light) and mica quartz schist (b, cross-polarized light) Grt-garnet; Omp-omphacite; Amp-amphibole; Phe-phengite; Qz-quartz; Rt-rutile |
白云母石英片岩呈灰白色,片状构造,鳞片粒状变晶结构(图 2d)。主要由石英(75%~80%)、白云母(20%~25%)组成,白云母呈细小鳞片状,定向排列形成片理(图 3b)。
3 分析方法全岩主微量分析在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室进行。全岩主量元素分析使用X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF),采用X射线荧光熔片法对全岩粉末进行分析,分析相对误差一般低于5%。全岩微量元素使用Agilent 7500a电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)分析测试,分析精度和准确度一般优于10%。
矿物的主量元素分析是在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室使用仪器JXA-8230型电子探针仪(EPMA)完成。分析条件为加速电压15kV,束斑电流1×10-8A,束斑直径一般为2μm。
利用重选、磁选手段分选出锆石颗粒,并在双目镜下进一步挑选具有代表性的锆石。将挑选的锆石与标准锆石(Plesovice, Penglai, Qinghu)颗粒粘在环氧树脂靶上,然后打磨抛光至锆石的1/3~1/2处。通过锆石CL图像识别锆石的内部结构,进行选点。在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室使用装载有Gatan CL3+检测器和Oxford能量色散光谱系统的FEI Quanta 400 FEG型扫描电镜拍摄阴极发光(CL)图像。
锆石U-Pb年代学分析在中国科学院广州地球化学研究所同位素地球化学国家重点实验室完成。分析使用Cameca IMS-1280 HR二次离子质谱仪(SIMS)。详细的分析流程见Li et al.(2009)。采用O2-作为一次离子源轰击样品表面,电流强度约为10nA,加速电压为10kV,束斑大小为20μm×30μm,二次离子经过60eV能量窗过滤,质量分辨率为5400。在分析测试过程中,锆石标准样品与未知样品交替进行分析。标准锆石Plesovice进行U-Th-Pb的同位素比值校正,标准锆石Qinghu作为未知样品对数据的精确度进行监控。数据处理采用Isoplot/Ex rev. 2.49软件(Ludwig, 2003)。
锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析是在中国科学技术大学中科院壳幔物质与环境重点实验室完成。分析使用Neptune型仪器并配备了Geolas-193型紫外激光剥蚀系统(LA)的多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱仪。测试时激光的脉冲速率为10Hz,束斑直径为44μm,能量密度为3.5J/cm2。使用176Lu/175Hf=0.02655(Chu et al., 2002)和176Yb/172Yb=0.58849(Wang et al., 2015)分别扣除176Lu和176Yb对176Hf的同质异素体干扰。分析过程中用91500、GJ-1和Plesovice来监控仪器状态和数据质量。
锆石微量元素分析在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室使用飞秒激光剥蚀多接收等离子体质谱仪Agilent 7900完成。分析采用的激光束斑直径为25μm。微量元素含量以标准物质NIST610作为外标,29Si作为内标进行校正。使用ICPMSDataCal进行数据处理(Liu et al., 2010)。
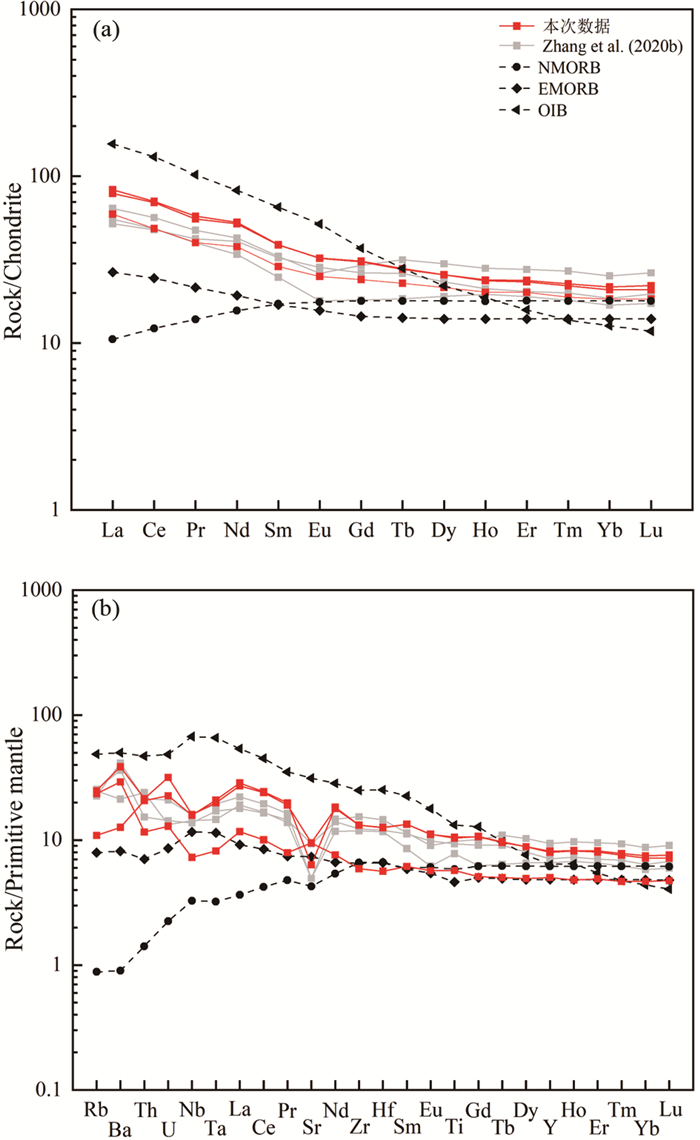
4 分析结果 4.1 全岩地球化学对桐柏榴辉岩全岩主微量元素分析的结果见表 1。结果显示榴辉岩具有较为一致的SiO2含量(49.7%~51.3%)和Al2O3含量(12.4%~13.1%),较低的MgO含量(4.57%~5.32%),较高的Fe2O3T含量(17.0%~17.6%)。此外,P2O5和TiO2的含量分别为0.23% ~0.29%和1.89% ~2.29%,Na2O+K2O的含量为2.80%~2.90%,属于亚碱性玄武岩系列。榴辉岩样品都具有一致的稀土元素配分型式(图 4a),呈现出弱的轻重稀土分异((La/Yb)N=3.23~3.82),无明显的Eu异常(Eu/Eu*=0.93~0.95)。在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图上(图 4b),这些榴辉岩样品富集Ba、U,轻微亏损Nb,未显示出Ta、Zr、Hf的亏损。
|
|
表 1 榴辉岩全岩主量(wt%)和微量(×10-6)元素组成 Table 1 Whole-rock major element (wt%) and trace element (×10-6) compositions of eclogite |
|
图 4 桐柏地区榴辉岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 4 Chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagram of eclogite in Tongbai area (b) (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
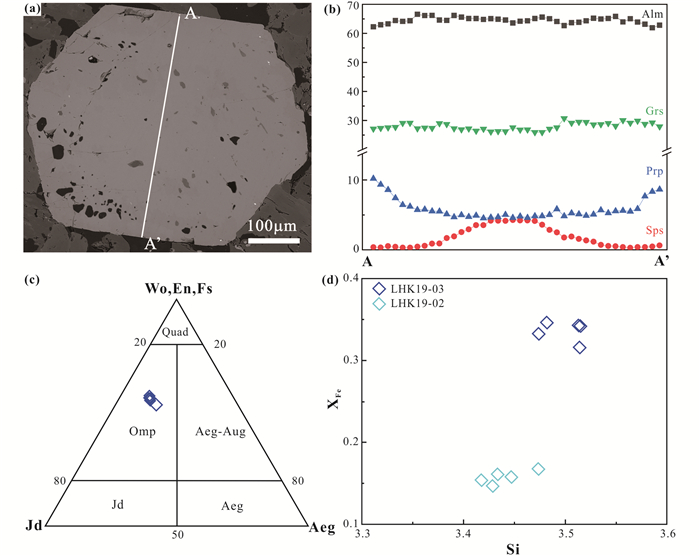
榴辉岩中的石榴石主要为半自形-自形的变斑晶(图 5a)。对石榴石进行电子探针主量元素剖面分析,成分显示铁铝榴石和钙铝榴石的含量相对较高,而镁铝榴石和锰铝榴石的含量相对较低,石榴石端元组分变化范围为Alm62-67Prp5-10Grs26-31Sps0.3-4。石榴石显示出明显的生长环带,从核部到边部,锰铝榴石的含量逐渐下降,镁铝榴石的含量逐渐上升,表现出进变质的生长特征(图 5b)。
|
图 5 矿物化学成分分析及投点图 (a)榴辉岩中石榴石变斑晶背散射照片; (b)图(a)石榴石变斑晶AA’成分剖面图;(c)榴辉岩中绿辉石分类图解(据Morimoto et al., 1988);(d)榴辉岩和白云母石英片岩中多硅白云母化学成分图.Alm-铁铝榴石;Grs-钙铝榴石;Prp-镁铝榴石;Sps-锰铝榴石;Wo-硅灰石;En-顽火辉石;Fs-铁辉石;Jd-硬玉;Omp-绿辉石;Aeg-霓石;Aeg-Aug-霓辉石 Fig. 5 Mineral chemical composition analysis and plots (a) BSE image of garnet from eclogite; (b) compositional zoning profile of garnet AA' according to (a); (c) classification diagram of omphacite from eclogite (Morimoto et al., 1988); (d) compositional diagram of phengite from eclogite and mica quartz schist. Alm-almandine; Grs-grossular; Prp-pyrope; Sps-spessartine; Wo-wollastonite; En-enstatite; Fs-ferrosilite; Jd-jadeite; Omp-omphacite; Aeg-aegirine; Aeg-Aug-aegirine-augite |
榴辉岩中的绿辉石主要由普通辉石和硬玉组成,其Na2O的含量在6.26%~6.53%之间,对应的硬玉分子摩尔含量为31%~33%。在辉石分类投图中均落入绿辉石区域(表 2、图 5c)。
|
|
表 2 榴辉岩和白云母石英片岩代表性矿物主量元素组成(wt%) Table 2 Major element compositions (wt%) of representative minerals from the eclogite and mica quartz schist |
榴辉岩中的多硅白云母Si值在3.48~3.52之间(表 2、图 5d),XFe值在0.32~0.35之间。另外,榴辉岩的围岩白云母石英片岩中白云母Si值也较高,在3.42~3.47之间(图 5d),表明围岩可能与榴辉岩一起经历了深俯冲。
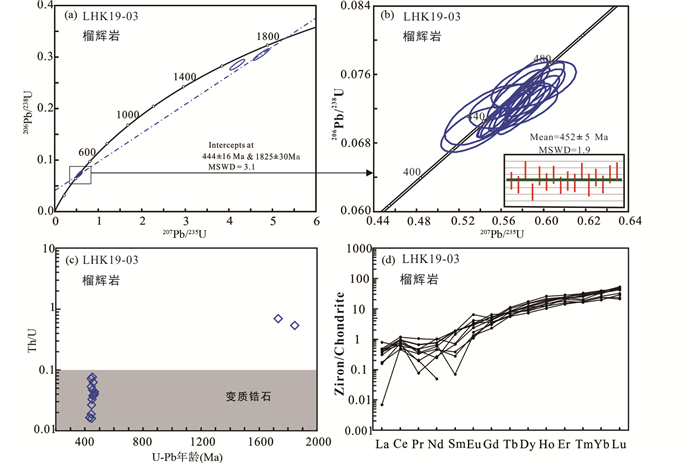
4.3 锆石U-Pb年代学及微量元素 4.3.1 榴辉岩榴辉岩LHK19-03的锆石无色透明,浑圆或短柱状,粒径为20~100μm(图 6)。对其中的18颗锆石进行SIMS U-Pb年龄测定,结果见表 3。分析获得的上下交点年龄分别为1825±30Ma和444±16Ma(图 7a)。其中2颗锆石G4和G18的Th/U比值较高(0.54和0.67),207Pb/206Pb年龄分别为1845±10Ma和1735±13Ma,可能代表岩浆结晶的年龄。其余16颗锆石的CL图像显示锆石多具有弱分带、云雾状分带,无残留锆石核,具有典型的变质锆石的特征(吴元保和郑永飞,2004)。16个年龄值基本都落在谐和线上(图 7b),得到的加权平均年龄为452±5Ma(n=16,MSWD=1.9)。这些锆石具有低的Th(2×10-6~16×10-6)和U(102×10-6~376×10-6)含量以及Th/U比值(图 7c)。对其中较大的10颗变质锆石进行微量元素分析,结果见表 4。球粒陨石标准化的稀土元素配分图中可看出这些锆石显示有平坦的HREE配分型式(图 7d),且不显示显著的Eu负异常(Eu/Eu*=0.81~3.57)。

|
图 6 榴辉岩(LHK19-03)及白云母石英片岩(LHK19-02)中典型锆石的阴极发光图像 虚线圈代表SIMS U-Pb年龄分析位置,实线圈代表LA-MC-ICPMS测试Hf同位素分析位置;U-Pb年龄下面为εHf(t)值 Fig. 6 Cathodoluminescence images of representative zircons for the eclogite (LHK19-03) and mica quartz schist (LHK19-02) The dashed circles show the locations of the SIMS U-Pb age and the solid circles indicate the location of LA-MC-ICPMS Hf isotopic analysis spots. εHf(t) values are marked under U-Pb ages |
|
|
表 3 榴辉岩和白云母石英片岩锆石的SIMS U-Pb年龄 Table 3 SIMS zircon U-Pb age data of eclogite and mica quartz schist |
|
图 7 榴辉岩锆石SIMS U-Pb年龄谐和图(a,b)、年龄-Th/U图(c)及球粒陨石标准化的稀土元素配分图(d, 标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 7 SIMS U-Pb age concordia diagrams of zircons from the eclogite (a, b), U-Pb ages of eclogite versus Th/U ratios (c) and chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns of zircons from eclogite (d, normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
|
|
表 4 榴辉岩和白云母石英片岩锆石微量元素(×10-6) Table 4 Trace element compositions (×10-6) of zircons from eclogite and mica quartz schist |
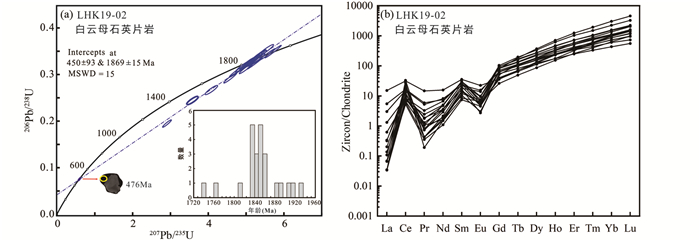
LHK19-02锆石的晶形呈半自形-自形,粒径为50~200μm,长宽比为1~3。CL图像显示锆石具有震荡环带、弱分带,部分锆石具有较窄的变质边(图 6)。对其中的25颗锆石进行SIMS U-Pb年龄测定,结果见表 3。锆石具有较高的Th/U比值(0.10~1.42)。这些分析点获得的上下交点年龄分别为1869±15Ma和450±93Ma(MSWD=15)(图 8a)。其中1颗锆石的暗色变质边部得到了476±7Ma的谐和年龄,其余24颗锆石的U-Pb年龄变化范围为1737~1932Ma。对这些锆石进行微量元素分析,结果见表 4。球粒陨石标准化的稀土元素配分图中呈现出陡峭的MREE-HREE配分型式(图 8b),具有明显的Ce正异常和Eu负异常,为典型的岩浆锆石的特征。
|
图 8 白云母石英片岩锆石SIMS U-Pb年龄谐和图(a)和球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(b,标准化值据Sun and McDonough (1989) Fig. 8 SIMS U-Pb age concordia diagrams (a) and chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns (b, normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) of zircons from mica quartz schist |
锆石中Hf的含量较高,Lu的含量较低,导致锆石具有很低的Lu/Hf比值,在锆石形成后基本没有放射性Hf同位素的积累,所测定的176Hf/177Hf基本代表锆石形成时体系同位素的组成。而一些富集HREE矿物例如石榴石及一些副矿物通常具有高的Lu/Hf比值,这些富集HREE矿物的分解和重结晶会使得锆石的176Hf/177Hf比值发生变化(Amelin et al., 1999; Kinny and Maas, 2003; 陈道公等, 2007)。因此,在高级变质岩如榴辉岩中,变质锆石的高176Hf/177Hf比值指示锆石可能是在石榴石发生结晶或重结晶时形成的(Rubatto, 2002; Zheng et al., 2005; 郑永飞等, 2007; Chen et al., 2010)。
对18颗榴辉岩锆石进行Lu-Hf同位素分析(表 5)。结果显示锆石G4和G18具有较高的176Lu/177Hf比值(0.000499和0.000383),较低的176Hf/177Hf比值(0.281427和0.281530)。将其对应的207Pb/206Pb年龄代入计算,得到εHf(t)值为-7.1和-5.8,两阶段Hf模式年龄为2.74Ga和2.59Ga。其余16颗变质锆石具有很低的176Lu/177Hf比值(0.000011~0.000061),相对一致的176Hf/177Hf比值(0.282403~0.282483),暗示这些变质锆石形成于具有低176Lu/177Hf比值、高176Hf/177Hf比值的变质流体,这种流体的形成可能是与石榴石的重结晶有关。将t=452Ma代入计算,得到εHf(t)值为-3.1~-0.3。
|
|
表 5 榴辉岩和白云母石英片岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素组成 Table 5 Lu-Hf isotope data of zircons from the eclogite and mica quartz schist |
对白云母石英片岩锆石进行Lu-Hf同位素分析(表 5)。结果显示锆石的176Lu/177Hf比值为0.000321~0.001055,176Hf/177Hf比值为0.281213~0.281506。将其对应的207Pb/206Pb年龄代入计算,得到εHf(t)值为-16.5~-3.5,两阶段Hf模式年龄为2.59~3.15Ga。
5 讨论 5.1 榴辉岩的变质年龄本次研究对桐柏造山带南部高压榴辉岩带内岩石进行了详细的SIMS U-Pb定年。获得榴辉岩锆石的206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为452±5Ma(n=16,MSWD=1.9)。根据榴辉岩锆石的CL图像、低Th/U比值(0.02~0.08)以及低176Lu/177Hf比值(0.000011~0.000061),表明锆石为典型的变质锆石(Rubatto, 2002; Zheng et al., 2005; 郑永飞等, 2007)。球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图中显示具有平坦的MREE-HREE配分型式,并且不显示出Eu的负异常,说明这些变质锆石的形成环境存在石榴石而缺少斜长石,指示这些变质锆石形成于榴辉岩相变质条件下(Rubatto, 2002; Rubatto and Hermann, 2007; Chen et al., 2010)。因此,452±5Ma应记录了榴辉岩相变质作用发生的时间。此外,对榴辉岩的围岩白云母石英片岩中的锆石进行U-Pb定年,得到了450±93Ma的下交点年龄,暗示白云母石英片岩与榴辉岩一起经历了深俯冲并记录了此次俯冲事件。
前人已经对桐柏造山带榴辉岩开展了一些年代学研究,并认为榴辉岩相变质的时间主要集中在三叠纪(Liu et al., 2008; Cheng et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2021)。Liu et al. (2008)通过对两条榴辉岩带中的榴辉岩和片麻岩分别进行SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年和白云母Ar-Ar定年,得出榴辉岩相变质作用的时间发生在约255Ma,折返发生在约238Ma。Cheng et al. (2011)通过全岩-石榴石Lu-Hf定年,得到256.4±2.6Ma、252.3±3.4Ma和246.9±3.2Ma三组数据,并认为榴辉岩相变质作用发生的时间不早于256Ma。Zhang et al. (2021)通过对桐柏榴辉岩中的锆石进行详细的年代学和微量元素分析,得出榴辉岩相峰期变质时间为245Ma。本文的发现和前人研究表明,桐柏造山带的榴辉岩记录了两期高压变质作用,一期在发生在452±5Ma,另一期发生在256~245Ma。
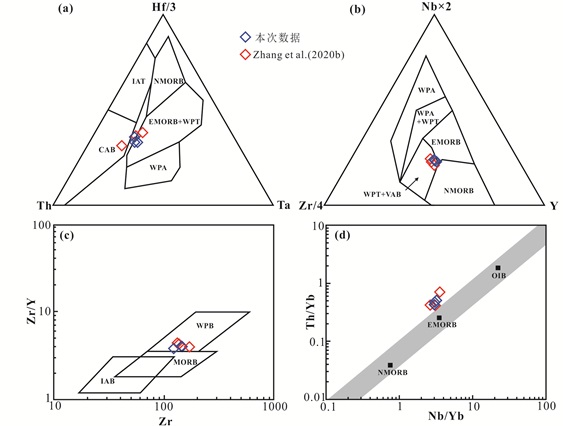
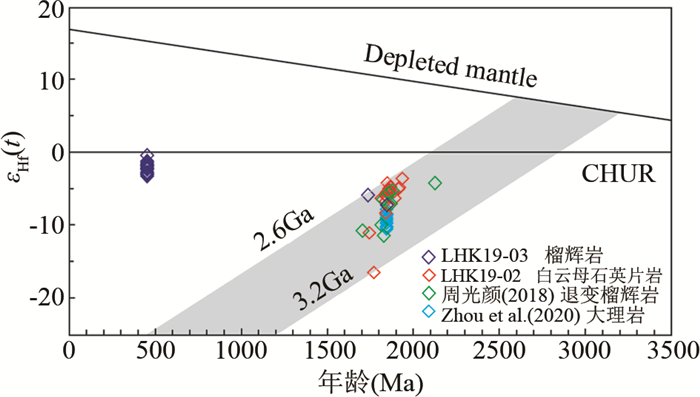
5.2 榴辉岩及白云母石英片岩的原岩性质通常认为,高场强元素、稀土元素和过渡元素在变质作用过程中比较稳定,不易发生变化,可以利用这些不活动性元素来反映变质岩原岩的地球化学性质和构造环境(Becker et al., 2000; 赵子福等, 2005; Zheng and Hermann, 2014)。这些榴辉岩样品表现出轻稀土略富集的特征,无明显的Ta、Zr、Hf的亏损,明显区别于MORB型玄武岩和弧后盆地玄武岩。在Hf-Th-Ta、Nb-Zr-Y和Zr-Zr/Y构造环境判别图解中,桐柏榴辉岩样品点均落于板内玄武岩的范围内(图 9a-c);在Nb/Yb-Th/Yb图解中样品点均落在EMORB-OIB阵列之上,显示原岩经历了不同程度的地壳物质的混染(图 9d)。年代学数据表明,桐柏造山带南部高压榴辉岩带内榴辉岩原岩的形成年龄主要集中在古元古代(Liu et al., 2008; 胡娟等, 2012; 周光颜, 2018; Zhang et al., 2020b)。另外,榴辉岩LHK19-03中两颗岩浆锆石的结晶年龄为1735±13Ma和1845±10Ma,对应的εHf(t)值分别为-5.8和-7.1,两阶段Hf模式年龄为2.59Ga和2.74Ga。这一结果与周光颜(2018)对南部高压榴辉岩带内退变榴辉岩中的岩浆成因锆石Hf同位素测定结果类似,且εHf(t)值均为负值(图 10),进一步说明桐柏榴辉岩原岩受到了古老地壳物质的混染。因此,桐柏榴辉岩的原岩可能为古元古代的板内玄武岩,在侵位过程中有古老地壳物质的加入。
|
图 9 桐柏榴辉岩构造环境判别图解 (a)Hf-Th-Ta图解(据Wood, 1980);(b)Zr-Nb-Y图解(据Meschede, 1986);(c)Zr-Zr/Y图解(据Pearce and Norry, 1979);(d)Nb/Yb-Th/Yb图解(据Pearce, 2008). OIB-洋岛玄武岩;NMORB-正常型洋中脊玄武岩;EMORB-富集型洋脊玄武岩;WPB-板内玄武岩;IAT-岛弧拉斑玄武岩;CAB-钙碱性玄武岩;WPA-板内碱性玄武岩;WPT-板内拉斑玄武岩;VAB-火山弧玄武岩;IAB-岛弧玄武岩 Fig. 9 Tectonic environment discrimination diagrams of Tongbai eclogite (a) Hf-Th-Ta diagram (Wood, 1980); (b) Zr-Nb-Y diagram (Meschede, 1986); (c) Zr-Zr/Y diagram (Pearce and Norry, 1979); (d) Nb/Yb-Th/Yb diagram (Pearce, 2008). OIB-oceanic island basalt; NMORB-N type mid-ocean ridge basalt; EMORB-E type mid-ocean ridge basalt; WPB-within-plate basalt; IAT-island-arc tholeiite; CAB-calc-alkaline basalt; WPA-alkaline within-plate basalt WPT-within-plate tholeiite basalt; VAB-volcanic arc basalt; IAB-island arc basalt |
|
图 10 南部高压榴辉岩带内不同岩石的锆石εHf(t)-年龄图解 Fig. 10 The εHf(t) vs. age diagram of zircons from rocks in the southern HP eclogite zone |
白云母石英片岩中锆石的U-Pb年龄主要分布在1737 ~1932Ma。这些锆石具有高的Th/U比值,明显的Ce正异常以及Eu负异常和富集HREE的配分型式,指示其为典型的岩浆锆石。锆石的εHf(t)值均为负值(-16.5~-3.5),对应的两阶段Hf模式年龄为2.59~3.15Ga,指示其原岩来自于中-新太古代古老地壳在古元古代的再造(图 10)。另外,南部高压榴辉岩带中的副片麻岩、片岩及大理岩中有大量新太古代至古元古代的碎屑锆石,这些年龄与扬子北缘构造热事件的年龄相近,表明桐柏造山带的古老物质可能与扬子北缘有亲缘性(Liu et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2020b; Zhou et al., 2020)。
5.3 构造意义在桐柏造山带内,除榴辉岩外的其它岩石类型也记录了早古生代的变质年龄。Liu et al. (2011)对宽坪群内石榴角闪岩进行锆石U-Pb定年,得到的变质年龄为442±6Ma,与Zhai et al. (1998)通过角闪石Ar-Ar定年得到434±2Ma的变质年龄结果一致;Liu et al. (2011)对二郎坪群中斜长角闪岩的锆石进行U-Pb定年获得440±3Ma的年龄,并解释为角闪岩相变质年龄;秦岭群中麻粒岩的变质年龄主要集中在410~490Ma(向华等, 2009; Liu et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2020a)。这一系列数据表明,早古生代的变质作用在桐柏造山带内是普遍存在的。本次在桐柏造山带榴辉岩中发现一期452±5Ma的高压变质年龄,代表桐柏造山带在早古生代经历了一次深俯冲事件,为桐柏造山带在古生代的构造演化提供了重要制约。两期榴辉岩相变质事件的发现,进一步说明桐柏造山带经历了从古生代到中生代多阶段的构造演化。
另外,在红安-大别造山带内,也零星分布有经历两期高压-超高压变质作用的榴辉岩。Cheng et al. (2016)通过对红安造山带浒湾剪切带内的榴辉岩进行石榴石Lu-Hf定年和锆石U-Pb定年,限定该地区榴辉岩从泥盆纪到三叠纪经历了两期俯冲事件;高山等(2002)对大别英山榴辉岩进行SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年,得到了两组榴辉岩相变质年龄,分别为461±7Ma和262±6Ma;Yang et al. (2010)在黄石盆地的碎屑锆石中发现了石炭纪和三叠纪的变质锆石。因此,秦岭-桐柏-红安-大别造山带加里东期的高压-超高压变质作用,仍需进一步的研究和认识。
6 结论(1) 榴辉岩中变质锆石SIMS定年获得206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为452±5Ma,白云母石英片岩中锆石进行SIMS定年获得450±93Ma的下交点年龄,认为白云母石英片岩与榴辉岩在早古生代一起发生了深俯冲。
(2) 榴辉岩的原岩为玄武岩,形成于板内环境,并且在侵位过程中有古老地壳物质的混染;白云母石英片岩原岩来自于中-新太古代古老地壳在古元古代的再造。
(3) 桐柏造山带内不同岩石中记录的早古生代变质年龄,表明早古生代的变质作用在桐柏造山带内是普遍存在的。同时,桐柏造山带榴辉岩中两期榴辉岩相变质事件的发现,进一步说明桐柏造山带经历了从古生代到中生代多阶段的构造演化。
致谢 野外工作和实验工作得到了张娟、邹东雅、陈安平、唐欢、张慧婷、李诚浩、成倚山等的帮助;两位专家给予了细致的评审;在此一并表示感谢!
Amelin Y, Lee DC, Halliday AN and Pidgeon RT. 1999. Nature of the Earth's earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons. Nature, 399(6733): 252-255 DOI:10.1038/20426
|
Becker H, Jochum KP and Carlson RW. 2000. Trace element fractionation during dehydration of eclogites from high-pressure terranes and the implications for element fluxes in subduction zones. Chemical Geology, 163(1-4): 65-99 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00071-6
|
Carswell DA and Zhang RY. 1999. Petrographic characteristics and metamorphic evolution of ultrahigh-pressure eclogites in plate-collision belts. International Geology Review, 41(9): 781-798 DOI:10.1080/00206819909465169
|
Chen DG, Deloule E, Xia QK, Wu YB and Cheng H. 2002. Metamorphic zircon from Shuanghe ultra-high pressure eclogite, Dabieshan: Ion microprobe and internal micro-structure study. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 18(3): 369-377 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen DG, Ni T and Xie LW. 2007. Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic compositions of ultra-high pressure metamorphic rocks from Dabie Terrain, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 331-342 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen DL and Liu L. 2011. New data on the chronology of eclogite and associated rock from Guanpo area, North Qinling orogeny and its constraint on nature of North Qinling HP-UHP eclogite terrane. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(2): 158-169 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen DL, Ren YF, Gong XK, Liu L and Gao S. 2015. Identification and its geological significance of eclogite in Songshugou, the North Qinling. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(7): 1841-1854 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen RX, Zheng YF and Xie LW. 2010. Metamorphic growth and recrystallization of zircon: Distinction by simultaneous in-situ analyses of trace elements, U-Th-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopes in zircons from eclogite-facies rocks in the Sulu orogen. Lithos, 114(1-2): 132-154 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.08.006
|
Cheng H, Zhang C, Vervoort JD, Wu YB, Zheng YF, Zheng S and Zhou ZY. 2011. New Lu-Hf geochronology constrains the onset of continental subduction in the Dabie orogen. Lithos, 121(1-4): 41-54 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.10.004
|
Cheng H, Zhang C, Vervoort JD, Li XH, Li QL, Wu YB and Zheng S. 2012. Timing of eclogite facies metamorphism in the North Qinling by U-Pb and Lu-Hf geochronology. Lithos, 136-139: 46-59 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.06.003
|
Cheng H, Liu XC, Vervoort JD, Wilford D and Cao DD. 2016. Micro-sampling Lu-Hf geochronology reveals episodic garnet growth and multiple high-P metamorphic events. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 34(4): 363-377 DOI:10.1111/jmg.12185
|
Chopin C. 1984. Coesite and pure pyrope in high-grade blueschists of the Western Alps: A first record and some consequences. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 86(2): 107-118 DOI:10.1007/BF00381838
|
Chopin C. 2003. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism: Tracing continental crust into the mantle. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 212(1-2): 1-14 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00261-9
|
Chu NC, Taylor RN, Chavagnac V, Nesbitt RW, Boella RM, Milton JA, German CR, Bayon G and Burton K. 2002. Hf isotope ratio analysis using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: An evaluation of isobaric interference corrections. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 17(12): 1567-1574 DOI:10.1039/b206707b
|
Ernst WG and Liou JG. 1995. Contrasting plate-tectonic styles of the Qinling-Dabie-Sulu and Franciscan metamorphic belts. Geology, 23(4): 353-356 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0353:CPTSOT>2.3.CO;2
|
Gao S, Qiu YM, Ling WL, McNaughton NJ, Zhang BR, Zhang GW, Zhang ZM, Zhong ZQ and Suo ST. 2002. SHRIMP single zircon U-Pb geochronology of eclogites from Yingshan and Xiongdian. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 27(5): 558-564 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Gao XY, Zheng YF and Chen YX. 2011. U-Pb ages and trace elements in metamorphic zircon and titanite from UHP eclogite in the Dabie orogen: Constraints on P-T-t path. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 29(7): 721-740 DOI:10.1111/j.1525-1314.2011.00938.x
|
Hacker BR, Ratschbacher L, Webb L, McWilliams MO, Ireland T, Calvert A, Dong SW, Wenk HR and Chateigner D. 2000. Exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure continental crust in east central China: Late Triassic-Early Jurassic tectonic unroofing. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105(B6): 13339-13364 DOI:10.1029/2000JB900039
|
Hu J, Liu XC, Qu W and Cui JJ. 2012. Zircon U-Pb ages of Paleoproterozoic metabasites from the Tongbai Orogen and their geological significance. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 33(3): 305-315 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Kinny PD and Maas R. 2003. Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotope systems in zircon. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 327-341 DOI:10.2113/0530327
|
Li XH, Liu Y, Li QL, Guo CH and Chamberlain KR. 2009. Precise determination of Phanerozoic zircon Pb/Pb age by multicollector SIMS without external standardization. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 10(4): Q04010
|
Liou JG, Ernst WG, Zhang RY, Tsujimori T and Jahn BM. 2009. Ultrahigh-pressure minerals and metamorphic terranes: The view from China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3-4): 199-231 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.10.012
|
Liu L, Zhang JF, Green II HW, Jin ZM and Bozhilov KN. 2007. Evidence of former stishovite in metamorphosed sediments, implying subduction to >350km. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 263(3-4): 180-191 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.08.010
|
Liu L, Liao XY, Wang YW, Wang C, Santosh M, Yang M, Zhang CL and Chen DL. 2016. Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the North Qinling Orogenic Belt in Central China: Insights on continental deep subduction and multiphase exhumation. Earth-Science Reviews, 159: 58-81 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.05.005
|
Liu XC, Lou YX and Dong SW. 2005. P-T path of low-temperature eclogites from the Tongbaishan area. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(4): 1081-1093 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu XC, Jahn BM, Dong SW, Lou YX and Cui JJ. 2008. High-pressure metamorphic rocks from Tongbaishan, central China: U-Pb and 40Ar/39Ar age constraints on the provenance of protoliths and timing of metamorphism. Lithos, 105(3-4): 301-318 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2008.04.009
|
Liu XC, Jahn BM, Hu J, Li SZ, Liu X and Song B. 2011. Metamorphic patterns and SHRIMP zircon ages of medium-to-high grade rocks from the Tongbai orogen, central China: Implications for multiple accretion/collision processes prior to terminal continental collision. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 29(9): 979-1002 DOI:10.1111/j.1525-1314.2011.00952.x
|
Liu XC, Li SZ and Jahn BM. 2015. Tectonic evolution of the Tongbai-Hong'an orogen in central China: From oceanic subduction/accretion to continent-continent collision. Science China (Earth Sciences), 58(9): 1477-1496 DOI:10.1007/s11430-015-5145-z
|
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Zong KQ, Gao CG, Gao S, Xu J and Chen HH. 2010. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(15): 1535-1546 DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
|
Ludwig KR. 2003. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 70
|
Maruyama S, Liou JG and Terabayashi M. 1996. Blueschists and Eclogites of the world and their exhumation. International Geology Review, 38(6): 485-594 DOI:10.1080/00206819709465347
|
Mattauer M, Matte P, Malavieille J, Tapponnier P, Maluski H, Qin XZ, Lun LY and Qin TY. 1985. Tectonics of the Qinling belt: Build-up and evolution of eastern Asia. Nature, 317(6037): 496-500 DOI:10.1038/317496a0
|
Meng QR and Zhang GW. 2000. Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, central China. Tectonophysics, 323(3-4): 183-196 DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00106-2
|
Meschede M. 1986. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y diagram. Chemical Geology, 56(3-4): 207-218 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(86)90004-5
|
Morimoto N, Fabries J, Ferguson AK, Ginzburg IV, Ross M, Seifert FA, Zussman J, Aoki K and Gottardi G. 1988. Nomenclature of pyroxenes. Mineralogical Magazine, 52(367): 535-550 DOI:10.1180/minmag.1988.052.367.15
|
Pearce JA and Norry MJ. 1979. Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y, and Nb variations in volcanic rocks. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 69(1): 33-47 DOI:10.1007/BF00375192
|
Pearce JA. 2008. Geochemical fingerprinting of oceanic basalts with applications to ophiolite classification and the search for Archean oceanic crust. Lithos, 100(1-4): 14-48 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.06.016
|
Rubatto D. 2002. Zircon trace element geochemistry: Partitioning with garnet and the link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism. Chemical Geology, 184(1-2): 123-138 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00355-2
|
Rubatto D and Hermann J. 2007. Experimental zircon/melt and zircon/garnet trace element partitioning and implications for the geochronology of crustal rocks. Chemical Geology, 241(1-2): 38-61 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.01.027
|
Smith DC. 1984. Coesite in clinopyroxene in the Caledonides and its implications for geodynamics. Nature, 310(5979): 641-644 DOI:10.1038/310641a0
|
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345 DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
|
Wang H, Wu YB, Gao S, Liu XC, Gong HJ, Li QL, Li XH and Yuan HL. 2011. Eclogite origin and timings in the North Qinling terrane, and their bearing on the amalgamation of the South and North China blocks. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 29(9): 1019-1031 DOI:10.1111/j.1525-1314.2011.00955.x
|
Wang J, Ren TX, Lu H, Zhou T and Zhou YJ. 2015. The absolute isotopic composition and atomic weight of ytterbium using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and development of an Si(?)-traceable ytterbium isotopic certified reference material. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 30(6): 1377-1385 DOI:10.1039/C5JA00054H
|
Wood DA. 1980. The application of a Th-Hf-Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary volcanic province. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 50(1): 11-30 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(80)90116-8
|
Wu YB and Zheng YF. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15): 1554-1569 DOI:10.1007/BF03184122
|
Wu YB, Zheng YF, Zhao ZF, Gong B, Liu XM and Wu FY. 2006. U-Pb, Hf and O isotope evidence for two episodes of fluid-assisted zircon growth in marble-hosted eclogites from the Dabie orogen. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(14): 3743-3761 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2006.05.011
|
Wu YB and Zheng YF. 2013. Tectonic evolution of a composite collision orogen: An overview on the Qinling-Tongbai-Hong'an-Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt in central China. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1402-1428 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.09.007
|
Xiang H, Zhang L, Zhong ZQ, Zhang HF, Zheng JP and Liu L. 2009. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and metamorphism of mafic granulite from north Tongbai, central China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(2): 348-358 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang JH, Cawood PA and Du YS. 2010. Detrital record of mountain building: Provenance of Jurassic foreland basin to the Dabie Mountains. Tectonics, 29(4): TC4011
|
Zhai XM, Day HW, Hacker BR and You ZD. 1998. Paleozoic metamorphism in the Qinling orogen, Tongbai Mountains, central China. Geology, 26(4): 371-374 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026<0371:PMITQO>2.3.CO;2
|
Zhang HF and Yu H. 2019. Petrological and tectonic evolution of orogenic peridotite massif: A case of Songshugou peridotites. Earth Science, 44(4): 1057-1066 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang QQ, Gao XY, Chen RX and Zheng YF. 2020a. Granulites record the tectonic evolution from collisional thickening to extensional thinning of the Tongbai orogen in central China. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 38(3): 265-295 DOI:10.1111/jmg.12522
|
Zhang QQ, Gao XY, Zhang SB and Zheng YF. 2020b. Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the northern Yangtze craton from oceanic subduction through continental collision to continental rifting: Geochronological and geochemical records of metabasites from the Tongbai orogen in central China. Precambrian Research, 350: 105920 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2020.105920
|
Zhang QQ, Gao XY and Zheng YF. 2021. Construction of P-T-t paths for eclogite in the Tongbai orogen by combining phase equilibria modelling with zircon inclusion composition. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 39(8): 947-976 DOI:10.1111/jmg.12598
|
Zhao ZF, Zheng YF, Chen B and Wu YB. 2005. A geochemical study of element and Sr-Nd isotopes for eclogite and gneiss from CCSD core 734 to 933m. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(2): 325-338 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zheng YF, Wu YB, Zhao ZF, Zhang SB, Xu P and Wu FY. 2005. Metamorphic effect on zircon Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systems in ultrahigh-pressure eclogite-facies metagranite and metabasite. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 240(2): 378-400 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.09.025
|
Zheng YF, Zhao ZF, Wu YB, Zhang SB, Liu XM and Wu FY. 2006. Zircon U-Pb age, Hf and O isotope constraints on protolith origin of ultrahigh-pressure eclogite and gneiss in the Dabie orogen. Chemical Geology, 231(1-2): 135-158 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.01.005
|
Zheng YF, Chen RX, Zhang SB, Tang J, Zhao ZF and Wu YB. 2007. Zircon Lu-Hf isotope study of ultrahigh-pressure eclogite and granitic gneiss in the Dabie orogen. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 317-330 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zheng YF. 2012. Metamorphic chemical geodynamics in continental subduction zones. Chemical Geology, 328: 5-48
|
Zheng YF, Zhang LF, Liu L and Chen YX. 2013. Progress in the study of continental deep subduction and ultrahigh pressure metamorphism. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 32(2): 135-158 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zheng YF and Hermann J. 2014. Geochemistry of continental subduction-zone fluids. Earth, Planets and Space, 66(1): 93 DOI:10.1186/1880-5981-66-93
|
Zheng YF, Zhao ZF and Chen RX. 2019. Ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt: Compositional inheritance and metamorphic modification. In: Zhang LF, Zhang ZM, Schertl HP and Wei CJ (eds. ). HP-UHP Metamorphism and Tectonic Evolution of Orogenic Belts. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 474(1): 89-132
|
Zhou GY. 2018. The nature of Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic basement in the northern Yangtze and its geological implication. Ph. D. Dissertation. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 1-186 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zhou GY, Wu YB, Fu B, Li L, Zhang WX and Zhang Y. 2020. Genesis of baddeleyite and high δ18O zircon in impure marble from the Tongbai orogen, Central China: Insights from petrochronology and Hf-O isotope compositions. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 175(8): 75 DOI:10.1007/s00410-020-01714-z
|
陈道公, Deloule E, 夏群科, 吴元保, 程昊. 2002. 大别山双河超高压榴辉岩中变质锆石: 离子探针和微区结构研究. 岩石学报, 18(3): 369-377. |
陈道公, 倪涛, 谢烈文. 2007. 大别地体超高压变质岩石锆石Lu-Hf同位素研究. 岩石学报, 23(2): 331-342. |
陈丹玲, 刘良. 2011. 北秦岭榴辉岩及相关岩石年代学的进一步确定及其对板片俯冲属性的约束. 地学前缘, 18(2): 158-169. |
陈丹玲, 任云飞, 宫相宽, 刘良, 高胜. 2015. 北秦岭松树沟榴辉岩的确定及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 31(7): 1841-1854. |
高山, Qiu YM, 凌文黎, McNaughton NJ, 张本仁, 张国伟, 张泽明, 钟增球, 索书田. 2002. 大别山英山和熊店榴辉岩单颗粒锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 27(5): 558-564. |
胡娟, 刘晓春, 曲玮, 崔建军. 2012. 桐柏造山带古元古代变质基性岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 地球学报, 33(3): 305-315. |
刘晓春, 娄玉行, 董树文. 2005. 桐柏山地区低温榴辉岩变质作用的P-T轨迹. 岩石学报, 21(4): 1081-1093. |
刘晓春, 李三忠, 江博明. 2015. 桐柏-红安造山带的构造演化: 从大洋俯冲/增生到陆陆碰撞. 中国科学(地球科学), 45(8): 1088-1108. |
吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589-1604. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 |
向华, 张利, 钟增球, 张宏飞, 郑建平, 刘理. 2009. 北桐柏地区镁铁质麻粒岩锆石U-Pb年代学及变质作用. 岩石学报, 25(2): 348-358. |
张宏福, 于红. 2019. 造山带橄榄岩岩石学与构造过程: 以松树沟橄榄岩为例. 地球科学, 44(4): 1057-1066. |
赵子福, 郑永飞, 陈斌, 吴元保. 2005. 中国大陆科学钻探工程主孔(734~933m)榴辉岩和片麻岩元素及Sr-Nd同位素地球化学研究. 岩石学报, 21(2): 325-338. |
郑永飞, 陈仁旭, 张少兵, 唐俊, 赵子福, 吴元保. 2007. 大别山超高压榴辉岩和花岗片麻岩中锆石Lu-Hf同位素研究. 岩石学报, 23(2): 317-330. |
郑永飞, 张立飞, 刘良, 陈伊翔. 2013. 大陆深俯冲与超高压变质研究进展. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 32(2): 135-158. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.02.001 |
周光颜. 2018. 扬子北缘晚太古代至古元古代基底性质及其地质意义. 博士学位论文. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 1-186
|
 2021, Vol. 37
2021, Vol. 37