2. 甘肃省地矿局第三地质矿产勘查院, 兰州 730050;
3. 中国地质科学院地质力学研究所动力成岩成矿实验室, 北京 100081
2. No.3 Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, Gansu Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, Lanzhou 730050, China;
3. Laboratory of Dynamic Digenesis and Metallogenesis, Institute of Geomechanics, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100081, China
秦岭造山带是经历长期多次造山作用后形成的复合型大陆造山带,在中国大陆的形成与演化中占有重要地位(张国伟等, 2001)。西秦岭造山带是秦岭造山带的西延部分,被认为是东古特提斯洋的一个分支(Deng et al., 2014; Li et al., 2015a)。自新元古代以来,西秦岭地区经历了长期复杂的造山活动,形成了如今具“三板夹两缝”(华北板块、秦岭微板块、扬子板块以及商丹缝合带和阿尼玛卿-勉略缝合带)特点的复合型造山带(李春昱, 1980;张国伟等, 1996; Meng and Zhang, 2000; Dong et al., 2011; Deng et al., 2017)。西秦岭造山带地质条件复杂,不同时期的岩浆作用发育,成矿地质条件较好,且矿化带密集分布(陈衍景, 2010; Deng et al., 2020)。
西秦岭地区广泛出露印支期花岗岩,目前已探明超过1200吨金与这些印支期花岗质岩石具有密切的空间关系,对于二者是否具有成因关系存在一定的分歧(Mao et al., 2002; Liu et al., 2015; Goldfarb et al., 2019;李建威等, 2019; Qiu et al., 2020)。因此,该区花岗质岩石的成因研究一直是岩石学家和矿床学家研究的焦点,我们期望通过“岩石探针”和“矿床探针”的角度对成岩和成矿作用耦合提出约束。已有研究对于西秦岭造山带东段印支期岩浆作用、成因及其与金钼等多金属成矿作用的关系进行了充分的积累(陈衍景, 2010;邱昆峰, 2015; Qiu et al., 2016, 2017)。相比而言,对于西段,尤其是夏河-合作地区,印支期花岗质岩浆作用的岩石组合、成因及其构造环境的认识十分有限,也存在一定的争议,很大程度上制约了进一步讨论岩浆作用与金成矿的关系。Qiu and Deng (2017)对西秦岭德乌鲁杂岩体进行研究,认为岩浆均可能起源于富钾的基性下地壳的部分熔融,并有幔源岩浆加入,结合区域地质背景认为德乌鲁杂岩体的形成与印支早期活动大陆边缘古特提斯洋的向北俯冲有关;金维浚等(2005)和张旗等(2009)通过对西秦岭具有埃达克质特征的花岗岩进行研究,认为西秦岭印支早期花岗岩属于增厚下地壳部分熔融的产物,且处于活动大陆边缘环境,与古特提斯洋向北俯冲有关;张成立等(2008)对早中生代花岗岩的岩石类型和地球化学特征进行研究,认为源区物质不仅仅是由下地壳物质的部分熔融产生,且存在幔源物质的参与,同时结合岩石地球化学特征,认为岩体的形成与后碰撞早期地壳增厚紧密相关;张宏飞等(2005, 2006)对西秦岭印支早期黑马河花岗岩体的岩石地球化学特征和源区性质进行了研究,认为该期花岗岩来源于中、新元古代下地壳玄武质岩石的部分熔融,形成于俯冲断离的地球动力学背景;骆必继等(2012)对根据岩石地球化学特征认为合作地区美武岩体的源区以壳源岩浆为主,后期有少量幔源物质参与,且美武岩体形成于后碰撞早期的构造背景。很多学者对于西秦岭地区花岗质岩石岩浆源区以及大地构造背景存在着争议,因此继续深入开展西秦岭花岗质岩石研究,提供可靠的同位素年代学和地球化学资料,对于揭示西秦岭构造演化等具有重要意义。
格娄昂金矿床位于甘肃省甘南藏族自治州夏河县扎油乡,属于西秦岭造山带西段夏河-合作矿集区。该矿床最初于1996年勘查工作被发现,甘肃省地矿局第三地质矿产勘查院在2009~2011年项目实施期间取得突破,目前已查明金资源量27.7t,平均品位为2.18g/t(金鼎国等, 2012①金鼎国, 陈耀宇, 柳生祥等. 2012.甘肃省夏河县枣子沟金矿格娄昂矿段292-330线详查报告.甘肃省地矿局第三地质矿产勘查院)。该矿床主要赋矿围岩为花岗质岩石和变沉积岩,金矿体受构造控制,代表夏河-合作地区金矿床的典型特征,是探究赋矿花岗质岩石成因,以期进一步约束金成矿与岩浆作用成因关系的理想研究对象。本文选择格娄昂矿床赋矿英安斑岩与黑云英安斑岩开展岩石学和岩相学、锆石和磷灰石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb地质年代学、全岩主微量和锆石Lu-Hf同位素地球化学研究,查明岩浆作用时代、赋矿岩石成因及其形成的地球动力学背景。
1 区域地质背景秦岭造山带是中央造山带的重要组成部分(张国伟, 2001),以徽成盆地为界,分为西秦岭与东秦岭两个构造单元。秦岭造山带在古生代-三叠纪时期经历了两次大洋板块俯冲和两次板块碰撞,成为了独具特征的典型大陆复合造山带(张国伟等, 1996, 2001;图 1a)。西秦岭造山带全长约600km,呈北西走向,北临祁连造山带,西接昆仑造山带,南临松潘-甘孜造山带,是古特提斯洋俯冲和华南板块与华北板块碰撞的产物(张国伟等, 2004; Dong et al., 2011, 2015)。西秦岭造山带在印支期成矿作用中,富集了金、铅、锌、锑、铜等金属资源,形成了数十个世界级金矿床和50多个规模较小的金矿床,已探明金资源量超过1200吨,是中国第二大金矿区,金矿床类型具有多样性,主要有造山型、岩浆热液型等金矿床(陈衍景, 2010;邱昆峰等, 2014, 2015; Liu et al., 2015; Deng and Wang, 2016; Qiu and Deng, 2017; Deng et al., 2018, 2019; Goldfarb et al., 2019;李建威等, 2019;于皓丞等, 2019; Qiu et al., 2020)。
|
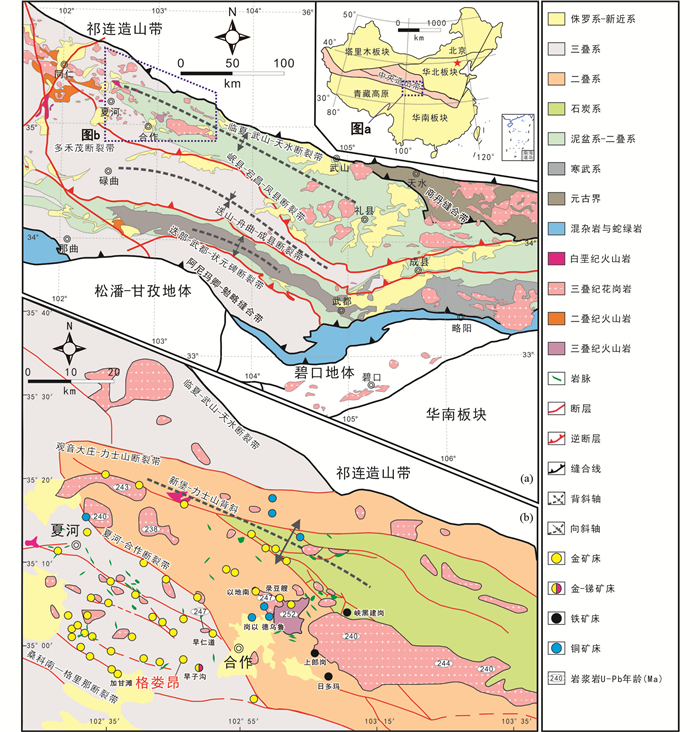
图 1 西秦岭造山带地质简图(a)和西秦岭造山带夏河-合作区域地质简图及矿床分布图(b)(据Qiu and Deng, 2017;于皓丞等, 2019; Qiu et al., 2020修编) Fig. 1 Simplified geological map of the West Qinling orogenic belt in China The inset shows the location of the study area (a); simplified geological map of the Xiahe-Hezuo polymetallic district of the West Qinling gold province, showing the distribution of the Triassic granitoids and ore deposits (b) (modified after Qiu and Deng, 2017; Yu et al., 2019; Qiu et al., 2020) |
夏河-合作地区位于西秦岭造山带西段甘南藏族自治州(图 1a),区内早-中三叠世岩浆岩发育,出露德乌鲁、美武、阿姨山等花岗质岩基、岩株和岩脉(252~235Ma; 金维浚, 2005; Zhang et al., 2006, 2007; Guo et al., 2012;骆必继等, 2012; Luo et al., 2012; Li et al., 2013;徐学义等, 2014; Yang et al., 2015a; Qiu et al., 2018)。出露地层主要包括石炭系含砾板岩、石英砂岩,二叠系火山岩,三叠系砂质板岩、含砾灰岩,侏罗系英安斑岩、安山质角砾凝灰岩和安山凝灰岩和白垩系火山沉积岩(图 1b)。
区域构造线呈北西向,褶皱断裂发育。新堡-力士山背斜为主体褶皱,其轴部位于力士山-德合茂北一带,轴线方向为北西向,倾伏端位于力士山西北侧(梁志录等, 2016)。夏河-合作地区已发现的金矿床均明显受控于区域性断裂带及其次级断裂,控矿断裂主要为三条大致平行的区域性断裂带,从北到南依次为观音大庄-力士山断裂带、夏河-合作断裂带和桑科南-格里那断裂带。夏河-合作断裂是西秦岭地区最为重要的控矿断裂,为含矿流体的运移、富集和沉淀提供了条件(第鹏飞, 2018)。该区域发现了多个储量较大的金矿床,其中包括早子沟(Sui et al., 2018;耿建珍等, 2019;于皓丞等, 2019; Yu et al., 2019; Qiu et al., 2020)、早仁道(Gou et al., 2019)、以地南(Yu et al., 2020b)、录豆艘和老豆(Jin et al., 2017; Yu et al., 2020a)、加甘滩(Qiu et al., 2020)、格娄昂(金鼎国, 2015)等金矿床。
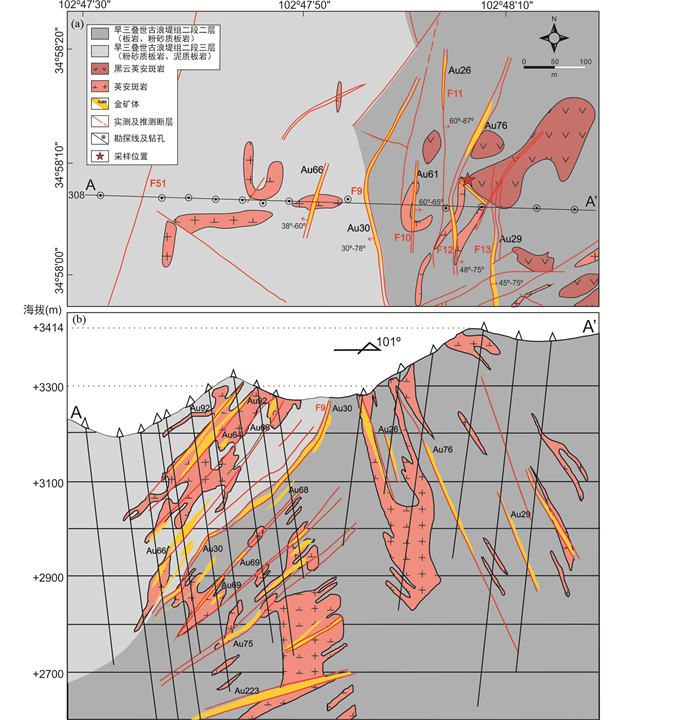
2 矿床地质格娄昂金矿床位于甘肃省甘南藏族自治州合作市城区西南15km处,在西秦岭造山带西段夏河-合作断裂带南侧,累计已查明金资源量27.7t,平均品位2.18g/t(图 1b)。早三叠世古浪堤组二段板岩为该区主要赋矿地层,自下而上发育粉砂质板岩-泥质板岩-钙质板岩的沉积旋回。古浪堤组二段分为3层,一层岩性为灰绿色粉砂板岩;二层位于F9断裂以东,岩性为灰-黄绿色板岩、钙质粉砂质板岩;三层位于F9断裂以西,岩性为灰色粉砂质板岩、灰色泥质板岩。矿区内广泛发育英安斑岩、黑云英安斑岩等中酸性岩脉,侵入到早三叠世板岩地层。
主要蚀变类型有硅化、黄铁矿化、毒砂化、辉锑矿化、碳酸盐化、褐铁矿化、赤铁矿化等。其中金矿化强度与硅化、黄铁矿化、毒砂化、辉锑矿化等矿化蚀变组合强度呈正相关。矿体总体走向近南北,受断裂构造控制明显,主要沿断裂切穿赋矿岩体,断裂交汇部位矿体相对厚大,品位更高(图 2b)。其中主矿体(Au30、Au65、Au66、Au68、Au76、Au206)长度及延伸大于300m,矿化较连续,矿体顶、底板围岩具有与矿体相同的蚀变矿化,但蚀变矿化程度明显较弱。矿石类型主要为砂板岩型、英安斑岩型和角砾岩型3种(金鼎国等, 2012)。
|
图 2 西秦岭格娄昂金矿床地质简图(a)和308号勘探线剖面图(b)(据金鼎国等, 2012和野外地质观测修编) Fig. 2 Sketch geological map (a) and schematic profile of No.308 exploration line (b) of the Gelouang gold deposit (modified after Jin et al., 2012 and our geological observations) |
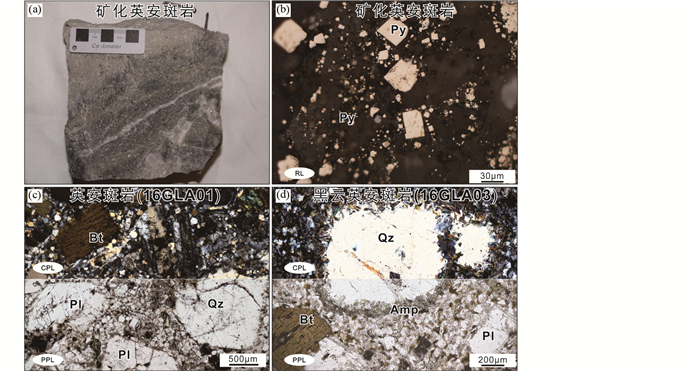
2件新鲜的英安斑岩样品(16GLA01、16GLA02)和2件新鲜的黑云英安斑岩样品(16GLA03、16GLA04)采自于矿区野外露头(图 2a)。英安斑岩样品(16GLA01、16GLA02)呈灰黑色,似斑状结构(图 3c),斑晶(约40%)主要为斜长石(10%~15%)、石英(5%~10%)、黑云母(5%~10%)和角闪石(5%)。石英粒径0.2~1mm,具有溶蚀结构;斜长石粒径0.1~2.5mm,具有卡式双晶结构;黑云母粒径0.2~1mm(图 4c)。基质由斜长石、石英、黑云母和角闪石组成,暗色矿物含量较低,主要为黑云母(5%)与角闪石(5%),副矿物主要为锆石和磷灰石。黑云英安斑岩样品(16GLA03、16GLA04)呈灰黑色,具似斑状结构(图 3d),斑晶(约30%)主要为石英(5%~10%)、斜长石(5%~10%)、黑云母(5%~10%)和角闪石(5%)。石英粒径0.2~1mm,具有溶蚀结构;自形双晶斜长石粒径0.1~2.5mm;黑云母粒径0.2~1mm(图 4d)。基质与斑晶组成相同,但暗色矿物含量较高,主要为黑云母(5%~10%)和角闪石(5%~10%),还可见副矿物锆石和磷灰石。

|
图 3 格娄昂金矿床典型地质体接触关系和手标本照片 (a)英安斑岩侵入早三叠世板岩;(b)英安斑岩与黑云英安斑岩接触;(c、d)英安斑岩与黑云英安斑岩手标本. Bt-黑云母;Pl-斜长石;Qz-石英 Fig. 3 Photographs showing occurrence of dacite porphyry and biotite dacite porphyry in the Gelouang deposit (a) dacite porphyry intruded Early Triassic slate; (b) contact relationship between dacite porphyry and biotite dacite porphyry; (c, d) hand specimen of the dacite porphyry and biotite dacite porphyry. Bt-biotite; Pl-plagioclase; Qz-quartz |
|
图 4 格娄昂矿床英安斑岩与黑云英安斑岩显微岩相学特征 (a、b)矿化英安斑岩及其主要金属矿物; (c、d)新鲜英安斑岩和黑云英安斑岩.Amp-角闪石; Py-黄铁矿.RL-反射光;PPL-透射光;CPL-正交偏光 Fig. 4 Photomicrographs of representative dacite porphyry and biotite dacite porphyry in the Gelouang deposit (a, b) mineralized dacite porphyry and its dominant ore minerals; (c, d) fresh dacite porphyry and biotite dacite porphyry. Amp-amphibole; Py-pyrite. RL-reflected light; PPL-plane-polarized transmitted light; CPL-cross-polarized transmitted light |
锆石与磷灰石单矿物分选在河北省区域地质矿产调查研究所完成,将野外采集的样品破碎至80~120目,通过电磁与重液分选,在双目镜下挑选透明且晶形完好的锆石与磷灰石。挑选代表性的锆石与磷灰石分别放入环氧树脂靶表面,待其固化后打磨抛光。然后对单矿物靶上锆石和磷灰石单矿物拍摄透、反射光及阴极发光照片,该工作在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所完成。
锆石原位LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年工作在中国科学院广州地球化学研究所同位素国家重点实验室完成,选取晶形良好、无色透明的锆石,并在其无裂隙、包裹体的位置进行。采用Resolution公司Resolution M50 Agilent 7500a电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS),激光器为Resolution M50 ArF准激光器(波长193nm)。测试激光束斑直径为30μm。元素含量标样采用美国国家标准技术研究院研制的人工合成硅酸盐标样NIST 610,锆石U-Pb年龄标样为Temora(417Ma, Black et al., 2004)。
磷灰石原位LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄测试和锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析在中国地质调查局天津中心同位素实验室完成。所运用的激光剥蚀多接收器电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICP-MS)是由NEW WAVE 193-FX-ArF准分子激光器与Thermo Fisher公司Neptune型ICP-MS组成,使用He气作为载气来运载激光剥蚀产生的物质。
选取晶形良好、无色透明的磷灰石,并在其无裂隙、包裹体的位置进行U-Pb年龄测试。激光束斑直径为40μm,元素含量标样使用NIST 610。磷灰石U-Pb年龄标样采用Otter Lake(913Ma, Barfod et al., 2005)。数据处理采用ICPMSDataCal 11.8程序(Liu et al., 2010),普通铅校正使用Andersen (2002)方法,年龄计算和数据处理使用Isoplot 3.0程序(Ludwig, 2003),详细实验方法与参数详见Yu et al. (2020a)。
锆石Lu-Hf同位素测点选择在已打U-Pb年龄测点相同或同等位置进行,激光束斑直径为50μm,测试使用GJ-1作为标样,176Hf/177Hf为0.282015±19(2σ)(Elhlou et al., 2006),176Lu的衰变系数为1.865×10-11(Scherer et al., 2001),使用176Hf/177Hf=0.282785±11(2σ)和176Lu/177Hf=0.0336±1(2σ)来计算εHf(t)的值( Blichert-Toft and Albarède, 1997),详细实验方法与参数详见Geng et al. (2017)。
对采集的新鲜岩石样品进行清洗破碎至200目后,在河北省区域地质矿产调查研究所进行主量元素分析。采用AxiosMax X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)测试,FeO采用滴定分析,精度可达1%以内。微量和稀土元素分析在中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所完成,微量与稀土元素分析所应用仪器为美国Thermo公司X Serise Ⅱ电感耦合等离子体质谱仪。首先使用酸溶法对样品进行预处理,再运用ICP-MS法测定,精度优于5%。
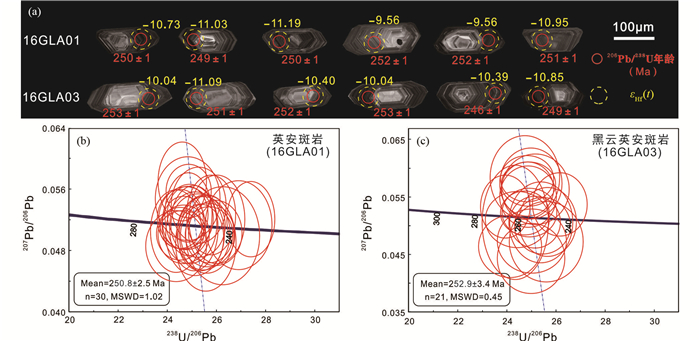
4 分析结果 4.1 锆石U-Pb年代学英安斑岩(16GLA01)与黑云英安斑岩(16GLA03)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果见表 1。阴极发光图像显示样品锆石自形程度较好,长为100~250μm,宽50~150μm,多呈长柱状晶体,发育振荡环带结构(图 5a),与典型岩浆锆石特征一致。英安斑岩样品40个锆石测点中有8个测点谐和度较低,2个测点为继承锆石,其206Pb/238U年龄分别为272±4Ma和792.9±10.7Ma;其余30个测点Th/U比值为0.05~0.26,206Pb/238U年龄范围为231±2Ma~259.4±3Ma,下交点年龄为250.8±2.5Ma(MSWD=1.02,n=30;图 5b)。
|
|
表 1 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果 Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results |
|
图 5 典型锆石阴极发光图像(a)和LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图(b、c) Fig. 5 Representative zircon cathodoluminescence images (a) and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams (b, c) |
黑云英安斑岩样品35个锆石测点中有5个测点的谐和度较低,9个测点为继承锆石,其206Pb/238U分别为1821 ±20Ma、1604±24Ma、285±7Ma、506±9Ma、2029 ±28Ma、2195±27Ma、1648±41Ma、272±3Ma和279±3Ma;其余21个测点Th/U比值为0.03~0.23,206Pb/238U年龄范围为241.9±3Ma~263.8±3Ma,下交点年龄为252.9±3.4Ma(MSWD=0.45,n=21;图 5c)。
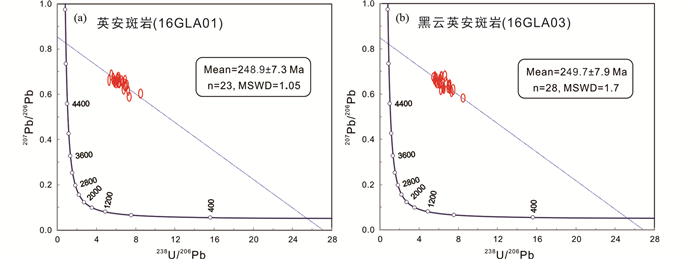
4.2 磷灰石U-Pb年代学英安斑岩(16GLA01)与黑云英安斑岩(16GLA03)LA-ICP-MS磷灰石U-Pb测年结果见表 2。英安斑岩23个磷灰石测点下交点年龄为248.9±7.3Ma(MSWD=1.05,n=23;图 6a)。黑云英安斑岩28个磷灰石测点下交点年龄为249.7±7.9Ma(MSWD=1.7,n=28;图 6b)
|
|
表 2 LA-ICP-MS磷灰石U-Pb定年结果 Table 2 LA-ICP-MS apatite U-Pb dating results |
|
图 6 LA-ICP-MS磷灰石U-Pb年龄谐和图 Fig. 6 LA-ICP-MS apatite U-Pb concordia diagrams |
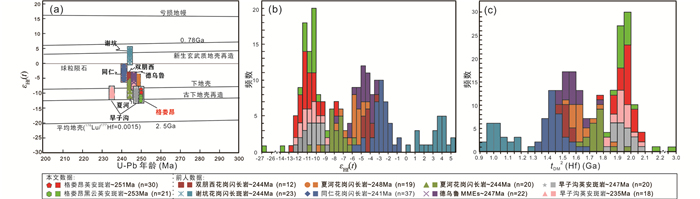
英安斑岩(16GLA01)与黑云英安斑岩(16GLA03)样品锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果见表 3。英安斑岩锆石εHf(t)值范围为-12.69~-7.84,二阶段模式年龄tDM2为2.08~1.78Ga(图 7),176Hf/177Hf值为0.282256~0.282388。除6个点(4、11、20、24、32、34)外,其余测点176Lu/177Hf值均小于0.002(表 3)。黑云英安斑岩锆石εHf(t)值范围为-13.88~-8.61,二阶段模式年龄tDM2为2.15~1.82Ga(图 7),176Hf/177Hf值为0.281857~0.282370。除9个点(3、5、7、12、19、20、22、27、33)外,其余测点176Lu/177Hf值均小于0.002(表 3),说明大多数锆石形成后放射性成因Hf积累有限,176Lu/177Hf能较好反应其形成过程Hf同位素组成(吴福元等, 2007)。
|
|
表 3 LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果 Table 3 LA-MC-ICP-MS zircon Lu-Hf isotope composition |
|
图 7 夏河-合作多金属矿集区三叠纪花岗质岩石锆石Lu-Hf同位素组成 (a)锆石εHf(t)-t图解;(b) εHf(t)频率直方图;(c) tDM2频率直方图.数据来源:Luo et al., 2012;韦萍, 2013; Li et al., 2015a; Qiu and Deng, 2017; Yu et al., 2019;耿建珍等, 2019 Fig. 7 Variations of εHf(t) values versus U-Pb ages (Ma) of zircons of the Triassic granitoids in the Xiahe-Hezuo polymetallic district (a) variations of εHf(t) values versus U-Pb ages (Ma) of zircons; (b) histograms of εHf(t) values; (c) histograms of corresponding two-stage Hf model ages (tDM2). Data sources: Luo et al., 2012; Wei et al., 2013; Li et al., 2015; Qiu and Deng, 2017; Yu et al., 2019; Geng et al., 2019 |
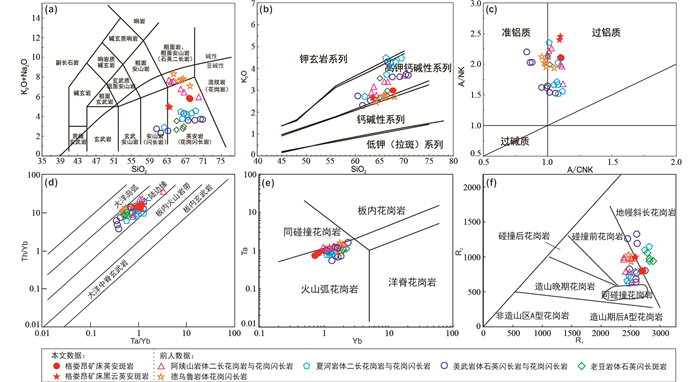
4件样品(英安斑岩16GLA01、16GLA02;黑云英安斑岩16GLA03、16GLA04)主量和微量元素地球化学分析结果见表 4。本文主量元素地球化学讨论中将其含量换算为100%。英安斑岩SiO2含量为67.79%~67.84%,Al2O3含量为16.68%~16.77%,MgO含量为1.53%~1.58%,K2O含量为2.98%~2.99%,Na2O含量为2.83%~2.88%,K2O/Na2O在1.03~1.06之间,Mg#值为45.6~46.4,具有高Al低Mg的特点。黑云英安斑岩SiO2含量为63.62%~63.76%,Al2O3含量为16.67%~16.82%,MgO含量为4.06%~4.13%,K2O含量为2.65%~2.70%,Na2O含量为2.39%~2.41%,K2O/Na2O在1.10~1.13之间,Mg#值为59.9~60.0。在TAS判别图解中,英安斑岩样品均落入英安岩区,黑云英安斑岩样品与英安斑岩样品相比更靠近安山岩,位于安山岩与英安岩区域边界(图 8a)。SiO2-K2O图解显示英安斑岩和黑云英安斑岩属于高钾钙碱性系列(图 8b),A/CNK=1.09~1.112,A/NK=2.103~2.455,属于过铝质系列岩石(图 8c)。
|
图 8 格娄昂矿床英安斑岩和黑云母英安斑岩地球化学与构造环境图解 (a) TAS图解(据 Le Maitre, 1989);(b) K2O-SiO2图解(据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976);(c) A/NK-A/CNK图解(据Maniar and Piccoli, 1989);(d) Th/Yb-Ta/Yb图解(据Gorton and Schandl, 2000);(e) Ta-Yb图解(据Pearce et al., 1984);(f) R2-R1图解(据Batchelor and Bowden, 1985).A/CNK=Al2O3/CaO+Na2O+K2O;A/NK=Al2O3/Na2O+K2O;R1=4Si-11(Na+K)-2(Fe+Ti);R2=6Ca+2Mg+Al;夏河-合作矿集区三叠纪花岗质岩石数据来源:靳晓野等, 2013;骆必继,2013;韦萍等,2013;徐学义等,2014;Qiu and Deng, 2017 Fig. 8 Fig. 8 Lithogeochemistry and tectonic discrimination diagrams of dacite porphyry and biotite dacite porphyry in the Gelouang deposit (a) TAS diagram (after Le Maitre, 1989); (b) K2O vs. SiO2 diagram (after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976); (c) A/NK vs. A/CNK diagram (after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989) (d) Th/Yb vs. Ta/Yb diagram (after Gorton and Schandl, 2000); (e) Ta vs. Yb diagram (after Pearce et al., 1984); (f) R2 vs. R1 diagram (after Batchelor and Bowden, 1985). (A/CNK=Al2O3/CaO+Na2O+K2O, A/NK=Al2O3/Na2O+K2O; R1=4Si-11(Na+K)-2(Fe+Ti); R2=6Ca+2Mg+Al; Data of the Triassic granitoids of the Xiahe-Hezuo polymetallic district sources: Jin et al., 2013; Luo et al., 2013; Wei et al., 2013; Xu et al., 2014; Qiu and Deng, 2017 |
|
|
表 4 英安斑岩和黑云英安斑岩主量元素(wt%)与微量元素(×10-6)分析结果 Table 4 Major (wt%) and trace (×10-6) element compositions of dacite porphyry and biotite dacite porphyry |
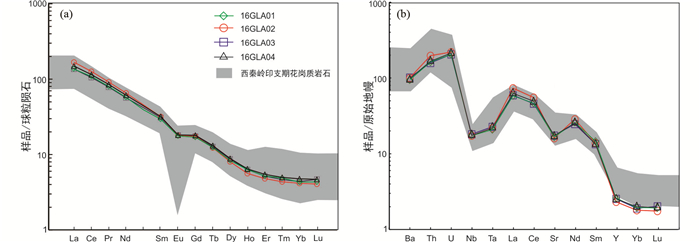
格娄昂金矿床英安斑岩和黑云英安斑岩具有相似的微量元素地球化学特征(表 4、图 9)。稀土元素总量(∑REE)为183.0×10-6~215.9×10-6,LREE/HREE=16.10~20.12,(La/Yb)N比值为31.07~40.59,轻重稀土分异较大,稀土配分曲线为轻稀土富集、重稀土平坦的右倾型(图 9a),具有弱铕负异常(δEu=0.76~0.78)。富集大离子亲石元素,亏损Sr和高场强元素Nb、Ta等(图 9b)。
|
图 9 英安斑岩和黑云英安斑岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(a)与原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) 西秦岭印支期花岗质岩石数据来源:靳晓野等, 2013;骆必继, 2013;韦萍等, 2013;徐学义等, 2014; Qiu and Deng, 2017 Fig. 9 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams (b) of dacite porphyry and biotite dacite porphyry (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) Data of Triassic granitoids in West Qinling sources: Jin et al., 2013; Luo et al., 2013; Wei et al., 2013; Xu et al., 2014; Qiu and Deng, 2017 |
格娄昂金矿床赋矿英安斑岩与黑云英安斑岩接触带不发育烘烤边和冷凝边(图 3b),暗示二者同时侵位。锆石U-Pb年龄分别为250.8±2.5Ma、252.9±3.4Ma,磷灰石U-Pb年龄为248.9±7.3Ma、249.7±7.9Ma,在误差范围内一致,表明英安斑岩与黑云英安斑岩同时于早三叠世侵位,并经历1~4Ma的冷却过程。Yu et al. (2019)报道了早子沟英安斑岩脉侵位年龄为246.1±5.2Ma和248.1±3.8Ma。耿建珍等(2019)在早子沟金锑矿床中得到矿化英安斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄为235.3±3.3Ma。张德贤等(2015)得到德乌鲁岩体石英闪长玢岩锆石U-Pb年龄为245.8±1.7Ma和242.4±1.9Ma。徐学义等(2014)得到阿姨山花岗闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄为241.6±4Ma,德乌鲁花岗闪长岩岩体锆石U-Pb年龄为233.5±1.5Ma。Guo et al. (2012)报道岗察岩体辉长闪长岩和矿化闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄分别为243.8±1.0Ma和234±0.6Ma。上述年代学结果表明,甘南地区花岗质岩石主体形成于252.9~233.5Ma,与格娄昂英安斑岩与黑云英安斑岩都是西秦岭早三叠世岩浆活动的产物。
早子沟金矿床位于格娄昂金矿床东南方向1km,二者具有相似的赋矿岩石、控矿构造和蚀变矿化特征。由于矿区内的中酸性岩脉均被金矿体穿插,且部分岩脉发生强烈的金矿化并形成工业矿体,隋吉祥和李建威(2013)认为早子沟金矿床成矿年代晚于中酸性岩脉侵位年代(233Ma)。他们进而对板岩矿石和脉岩矿石中绢云母分别进行40Ar/39Ar定年,得到坪年龄为219.4±1.1Ma和230±2.3Ma。尽管隋吉祥和李建威(2013)认为230±2.3Ma可能代表早子沟矿床金成矿年代,而219.4±1.1Ma可能是后期热事件导致放射性成因Ar丢失造成的。但考虑到本文得到的脉岩冷却过程持续约1~4Ma,因此脉岩绢云母40Ar/39Ar定年得到的230Ma很可能是脉岩侵位冷却的年龄,而219.4Ma可能为成矿年龄。Qiu et al. (2020)对早子沟矿床中的热液独居石进行U-Pb定年,得到热液独居石的结晶年龄为211.1±3.0Ma,认为该期热液独居石结晶年龄代表了金的成矿年龄。尽管目前尚未有格娄昂金矿床的成矿年代学数据发表,考虑到它与早子沟金矿床相近的地理位置、相似的地质特征,格娄昂金矿床的成矿年代也应为219~211Ma。因此,结合矿体穿切英安斑岩与黑云英安斑岩这一地质现象,我们认为早三叠的岩浆活动并不是格娄昂矿床金成矿的主导因素。
5.2 赋矿岩石成因格娄昂金矿床英安斑岩和黑云英安斑岩样品锆石εHf(t)值为-13.88~-7.84,均落在球粒陨石演化线之下,对应二阶段Hf模式年龄为2.15~1.78Ga,主要集中于2.0~1.9Ga,表明英安斑岩与黑云英安斑岩主要来源于元古宙地壳物质部分熔融。其中一个测点的εHf(t)值达到了-26.65,对应的二阶段Hf模式年龄为2.96Ga,暗示了该地区可能还存在太古宙地壳物质。此外,样品变化范围较大的εHf(t)值,也说明其源区也存在一定的不均一性。耿建珍等(2019)和Yu et al. (2019)获得早子沟英安斑岩εHf(t)值分别为-12.78~-8.76和-12.5~-8.9,其对应的tDM2分别为2.07~1.82Ga和2.08~1.84Ga;双朋西花岗闪长岩εHf(t)=-4.7~-3.6,tDM2为1.57~1.49Ga(Luo et al., 2012);夏河花岗闪长岩εHf(t)=-11.0~-4.0,tDM2为1.97~1.53Ga(韦萍, 2013);同仁花岗闪长岩εHf(t)=-5.9~-0.6,tDM2为1.64~1.32Ga(黄雄飞等, 2014);德乌鲁杂岩体εHf(t)=-8.0~-3.3,tDM2为1.78~1.48Ga(Qiu and Deng, 2017),表明西秦岭甘南夏河-合作矿集区广泛发育的早三叠世岩浆作用是元古宙下地壳部分熔融的产物。英安斑岩与黑云英安斑岩Mg#值范围分别为45.6~46.4和59.9~60.0,高于玄武质下地壳部分熔融产生的熔体(Mg# <45, Rapp and Watson, 1995),表明其在形成过程中可能存在基性物质参与。
格娄昂金矿床英安斑岩和黑云英安斑岩锆石与磷灰石U-Pb同位素年龄在误差范围内一致,微量元素与稀土元素配分模式基本相同(图 9),且在接触边界未观察到冷凝边或烘烤边(图 3b),表明它们可能是相同源区、同一次岩浆作用的产物。此外,它们轻重稀土分异明显,(La/Yb)N=31.07~40.59,明显高于上地壳(11.35; Rudnick and Gao, 2003);较低的Yb(0.89×10-6~1.02×10-6)和Y(10.55×10-6~11.87×10-6)含量,表明它们源区的部分熔融可能受到石榴子石的控制,且源区位置较深(Rapp and Watson, 1995)。同时,英安斑岩和黑云英安斑岩具有较弱的Eu负异常,Sr元素存在一定亏损,表明源区可能存在斜长石残留或者发生了斜长石的分离结晶。在部分熔融过程中,Nb、Ta主要进入角闪石,导致Nb、Ta的亏损(Rollinson, 1993)。由此可见,在熔体形成时,源区主要残留矿物为角闪石、斜长石和石榴子石。
5.3 对地球动力学背景的约束西秦岭地区岩浆岩及其构造演化等方面研究成果丰富(张本仁, 2002;邱庆伦等, 2008;李婷等, 2012;骆必继等, 2012;骆必继, 2013;黄雄飞等, 2013; Yang et al., 2015b; Qiu and Deng, 2017; Qiu et al., 2018)。张克信等(1999)与王永标等(1997)、Wang and Yang (2004)发现阿尼玛卿地区发育早二叠世茅口期生物礁,但缺失晚二叠世地层,认为阿尼玛卿洋在晚二叠末闭合。王国灿等(2004)在研究马尔争-布青山的构造混杂岩带时,发现二叠系格曲组与下伏地层二叠系马尔争组和树维门科组呈角度不整合相接触,提出阿尼玛卿-勉略洋盆的闭合时间为中-晚二叠世之交。骆必继等(2012)认为在后碰撞环境下,俯冲的阿尼玛卿洋壳发生断离导致软流圈上涌,使地幔发生了部分熔融形成幔源岩浆,幔源岩浆在侵位过程中使下地壳发生部分熔融,形成美武岩体花岗质岩石(241.6±4Ma)。以上观点表明阿尼玛卿-勉略洋在早三叠世前已经闭合,且在早三叠世西秦岭地区已经处于后碰撞早期的构造环境。
然而,近些年来部分学者给出了西秦岭在早三叠世正处于与俯冲有关的活动大陆边缘环境的证据。金维浚等(2005)提出冶力关(245±6Ma)、夏河(238±4Ma)花岗岩具有埃达克岩的地球化学特征,与加厚下地壳的部分熔融有关,可能形成于印支早期古特提斯洋北部消减形成的活动陆缘环境。韦萍等(2013)通过岩石地球化学、年代学和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素地球化学研究,认为夏河花岗岩(244~248Ma)形成过程中有幔源岩浆参与,其形成于大陆边缘弧构造环境,表明西秦岭地区阿尼玛卿洋盆的闭合时间不早于244Ma。黄雄飞等(2014)报道了舍哈力吉石英二长岩侵位年龄为234.1±0.5Ma,认为三叠纪早期古特提斯洋壳俯冲极性的改变导致西秦岭区域形成了呈线性分布的印支期岩浆岩带。岳远刚(2014)通过对地层剖面、碎屑锆石年代学及砂岩地球化学研究,认为三叠系洪水川组砂岩具有活动大陆边缘的构造环境特征,将阿尼玛卿洋盆的闭合时间约束到中-晚三叠世。
格娄昂矿床英安斑岩和黑云英安斑岩侵位于约251Ma,具有过铝质高钾钙碱性岩石特征。在Ta-Yb构造环境判别图解中,样品均投点于火山弧花岗岩范围(图 8e),说明它们的形成与俯冲洋壳部分熔融有关。所有样品都表现出负Nb异常,其他高场强元素也存在不同程度的亏损,也表明该期岩浆活动与俯冲有关(Briqueu et al., 1984)。在R2-R1构造环境图解中,样品具有碰撞前构造环境的花岗岩特征(图 8f),且Th/Yb-Ta/Yb图中显示出活动大陆边缘特征(图 8d)。此外,这些岩体的形成年龄与东昆仑地区广泛分布的花岗质岩石年龄一致(Chen et al., 2012; Li et al., 2015a),确定了印支早期西秦岭与东昆仑地区的岩浆活动是由古特提斯洋的俯冲消减引起的(Yan et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2014)。印支早期阿尼玛卿-勉略洋正处于俯冲环境,俯冲板片引起下地壳发生部分熔融,形成中酸性岩浆,侵位、冷凝形成格娄昂英安斑岩和黑云英安斑岩,由此证明在早三叠世西秦岭地区正处于与洋壳俯冲有关的碰撞前活动大陆边缘环境。
6 结论(1) 格娄昂金矿床赋矿斑岩侵位于约251Ma,是西秦岭夏河-合作多金属矿集区广泛发育的早三叠世岩浆活动的产物,限定了格娄昂金成矿作用时间晚于早三叠世。
(2) 格娄昂金矿床英安斑岩和黑云英安斑岩形成于活动大陆边缘构造环境,是洋壳板片北东向俯冲引起古元古代下地壳部分熔融的产物,支持阿尼玛卿-勉略洋早三叠世尚未闭合。
致谢 野外工作得到了甘肃省自然资源厅、甘肃省地矿局、甘南州国土局和早子沟金矿有限公司的帮助和支持;中国地质调查局天津中心耿建珍高级工程师、中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所杨帆高级工程师在样品分析测试方面提供帮助;邓军教授、张静教授和两位匿名审稿专家对文章提出宝贵意见;在此一并感谢。
Andersen T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59-79 |
Barfod GH, Krogstad EJ, Frei R and Albarède F. 2005. Lu-Hf and PbSL geochronology of apatites from Proterozoic terranes:A first look at Lu-Hf isotopic closure in metamorphic apatite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(7): 1847-1859 |
Batchelor RA and Bowden P. 1985. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters. Chemical Geology, 48(1-4): 43-55 |
Black LP, Kamo SL, Allen CM, Davis DW, Aleinikoff JN, Valley JW, Mundil R, Campbell IH, Korsch RJ, Williams IS and Foudoulis C. 2004. Improved 206Pb/238U microprobe geochronology by the monitoring of a trace-element-related matrix effect:SHRIMP, ID-TIMS, ELA-ICP-MS and oxygen isotope documentation for a series of zircon standards. Chemical Geology, 205(1-2): 115-140 |
Blichert-Toft J and Albarède F. 1997. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 148(1-2): 243-258 |
Briqueu L, Bougault H and Joron JL. 1984. Quantification of Nb, Ta, Ti and V anomalies in magmas associated with subduction zones:Petrogenetic implications. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 68(2): 297-308 |
Chen XH, Gehrels G, Yin A, Li L and Jiang RB. 2012. Paleozoic and Mesozoic basement magmatisms of eastern Qaidam Basin, northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau:LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology and its geological significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(2): 350-369 |
Chen YJ. 2010. Indosinian tectonic setting, magmatism and metallogenesis in Qinling Orogen, central China. Geology in China, 37(4): 854-865 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ and Santosh M. 2014. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China. Earth-Science Reviews, 138: 268-299 |
Deng J and Wang QF. 2016. Gold mineralization in China:Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Research, 36: 219-274 |
Deng J, Wang QF and Li GJ. 2017. Tectonic evolution, superimposed orogeny, and composite metallogenic system in China. Gondwana Research, 50: 216-266 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Santosh M and Yao EY. 2018. Crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the south-eastern North China Craton. Earth-Science Reviews, 182: 251-272 |
Deng J, Zhai YS, Mo XX and Wang QF. 2019. Temporal-spatial distribution of metallic ore deposits in China and their geodynamic settings. Society of Economic Geologists Special Publication, 22: 103-132 |
Deng J, Qiu KF, Wang QF, Goldfarb RJ, Yang LQ, Zi JW, Geng JZ and Ma Y. 2020. In-situ dating of hydrothermal monazite and implications on the geodynamic controls of ore formation in the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Economic Geology, 115(3): 671-685 |
Di PF. 2018. Geochemistry and ore-forming mechanism on Zaozigou gold deposit in Xiahe-Hezuo, West Qinling, China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University, 1-96 |
Dong YP, Zhang GW, Neubauer F, Liu XM, Genser J and Hauzenberger C. 2011. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, China:Review and synthesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(3): 213-237 |
Dong YP, Zhang XN, Liu XM, Li W, Chen Q, Zhang GW, Zhang HF, Zhao Y, Sun SS and Zhang FF. 2015. Propagation tectonics and multiple accretionary processes of the Qinling Orogen. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 104: 84-98 |
Elhlou S, Belousova E, Griffin WL, Pearson NJ and O'Reilly SY. 2006. Trace element and isotopic composition of GJ-red zircon standard by laser ablation. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(18S): A158 |
Geng JZ, Qiu KF, Gou ZY and Yu HC. 2017. Tectonic regime switchover of Triassic Western Qinling Orogen:Constraints from LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology and Lu-Hf isotope of Dangchuan intrusive complex in Gansu, China. Geochemistry, 77(4): 637-651 |
Geng JZ, Huang YQ, Jiang YP, Wu L, Zhu R, Yu HC and Qiu KF. 2019. Zircon U-Pb age and Lu-Hf isotopes of the dacite from Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit, West Qinling, China. Geological Survey and Research, 42(3): 166-173 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Goldfarb RJ, Qiu KF, Deng J, Chen YJ and Yang LQ. 2019. Orogenic gold deposits of China. Society of Economic Geologists Special Publication, 22: 263-324 |
Gorton MP and Schandl ES. 2000. From continents to island arcs:A geochemical index of tectonic setting for arc-related and within-plate felsic to intermediate volcanic rocks. The Canadian Mineralogist, 38(5): 1065-1073 |
Gou ZY, Yu HC, Qiu KF, Geng JZ, Wu MQ, Wang YG, Yu HM and Li J. 2019. Petrogenesis of ore-hosting diorite in the Zaorendao gold deposit at the Tongren-Xiahe-Hezuo polymetallic district, West Qinling, China. Minerals, 9(2): 76 |
Guo XQ, Yan Z, Wang ZQ, Wang T, Hou KJ, Fu CL and Li JL. 2012. Middle Triassic arc magmatism along the northeastern margin of the Tibet:U-Pb and Lu-Hf zircon characterization of the Gangcha complex in the West Qinling terrane, central China. Journal of the Geological Society, 169(3): 327-336 |
Huang XF, Mo XX, Yu XH, Li XW, Ding Y, Wei P and He WY. 2013. Zircon U-Pb chronology, geochemistry of the Late Triassic acid volcanic rocks in Tanchang area, West Qinling and their geological significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(11): 3968-3980 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Huang XF, Mo XX, Yu XH, Li XW, Yang MC, Luo MF, He WY and Yu JC. 2014. Origin and geodynamic settings of the Indosinian high Sr/Y granitoids in the West Qinling:An example from the Shehaliji pluton in Tongren area. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(11): 3255-3270 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Jin DG. 2015. Geological characteristics and prospecting prospect of Geluoang gold deposit, Xiahe, Gansu. Gansu Science and Technology, 31(10): 12-14 (in Chinese) |
Jin WJ, Zhang Q, He DF and Jia XQ. 2005. SHRIMP dating of adakites in western Qinling and their implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3): 959-966 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Jin XY, Li JW, Sui JX, Wen G and Zhang JY. 2013. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the genesis and tectonic setting of Dewulu intrusive complex in Xiahe-Hezuo district of western Qinling. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 35(3): 20-38 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Jin XY, Li JW, Hofstra AH and Sui JX. 2017. Magmatic-hydrothermal origin of the Early Triassic Laodou lode gold deposit in the Xiahe-Hezuo district, West Qinling orogen, China:Implications for gold metallogeny. Mineralium Deposita, 52(6): 883-902 |
Le Maitre RW. 1989. A Classification of Igneous Rocks and Glossary of Terms. Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1-193 |
Li CY, Wang Q, Zhang ZM and Liu XY. 1980. A preliminary study of plate tectonics of China. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2: 11-19, 130 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li JW, Sui JX, Jin XY, Wen G, Chang J, Zhu R, Zhan HY and Wu WH. 2019. The intrusion-related gold deposits in the Xiahe-Hezuo district, West Qinling Orogen:Geodynamic setting and exploration potential. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(5): 17-32 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li N, Chen YJ, Pirajno F and Ni ZY. 2013. Timing of the Yuchiling giant porphyry Mo system, and implications for ore genesis. Mineralium Deposita, 48(4): 505-524 |
Li N, Chen YJ, Santosh M and Pirajno F. 2015a. Compositional polarity of Triassic granitoids in the Qinling Orogen, China:Implication for termination of the northernmost paleo-Tethys. Gondwana Research, 27(1): 244-257 |
Li T, Xu XY, Chen JL, Wang HL, Li ZP and Zhang X. 2012. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and tectonic setting of Zhongchuan intrusion, Lixian area, western Qinling orogen. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(6): 875-883 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li XW, Mo XX, Huang XF, Dong GC, Yu XH, Luo MF and Liu YB. 2015b. U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of the Early Indosinian Tongren pluton in West Qinling:Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97: 38-50 |
Liang ZL, Chen GZ, Ma HS and Zhang YN. 2016. Evolution of ore-controlling faults in the Zaozigou gold deposit, western Qinling. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 40(2): 354-366 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu JJ, Liu CH, Carranza EJM, Li YJ, Mao ZH, Wang JP, Wang YH, Zhang J, Zhai DG, Zhang HF, Shan L, Zhu LM and Lu RK. 2015. Geological characteristics and ore-forming process of the gold deposits in the western Qinling region, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 103: 40-69 |
Liu YS, Gao S, Hu ZC, Gao CG, Zong KQ and Wang DB. 2010. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537-571 |
Luo BJ, Zhang HF and Lu XB. 2012. U-Pb zircon dating, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of Early Indosinian intrusive rocks in West Qinling, central China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 164(4): 551-569 |
Luo BJ, Zhang HF and Xiao ZQ. 2012. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the Early Indosinian Meiwu pluton in West Qinling, central China. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(3): 199-213 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Luo BJ. 2013. Petrogenesis, geodynamic processes of the Indosinian magmatism in the West Qinling Orogenic belt, central China.Ph. D. Dissertation.. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 1-191 |
Maniar PD and Piccoli PM. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. GSA Bulletin, 101(5): 635-643 |
Mao JW, Qiu YM, Goldfarb RJ, Zhang ZC, Garwin S and Ren F. 2002. Geology, distribution, and classification of gold deposits in the western Qinling belt, central China. Mineralium Deposita, 37(3): 352-377 |
Meng QR and Zhang GW. 2000. Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, central China. Tectonophysics, 323(3-4): 183-196 |
Pearce JA, Harris NBW and Tindle AG. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983 |
Peccerillo A and Taylor SR. 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63-81 |
Qiu KF, Li N, Taylor RD, Song YH, Song KR, Han WZ and Zhang DX. 2014. Timing and duration of metallogeny of the Wenquan deposit in the West Qinling, and its constrain on a proposed classification for porphyry molybdenum deposits. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2631-2643 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Qiu KF. 2015. Metallogenic system model of the Indosinian porphyry copper-molybdenum deposits in the north margin of the West Qinling.Ph. D. Dissertation. . Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1-194 |
Qiu KF, Song KR and Song YH. 2015. Magmatic-hydrothermal fluid evolution of the Wenquan porphyry molybdenum deposit in the north margin of the Western Qinling, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(11): 3391-3404 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Qiu KF, Taylor RD, Song YH, Yu HC, Song KR and Li N. 2016. Geologic and geochemical insights into the formation of the Taiyangshan porphyry copper-molybdenum deposit, western Qinling Orogenic Belt, China. Gondwana Research, 35: 40-58 |
Qiu KF and Deng J. 2017. Petrogenesis of granitoids in the Dewulu skarn copper deposit:Implications for the evolution of the Paleotethys Ocean and mineralization in Western Qinling, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 90: 1078-1098 |
Qiu KF, Marsh E, Yu HC, Pfaff K, Gulbransen C, Gou ZY and Li N. 2017. Fluid and metal sources of the Wenquan porphyry molybdenum deposit, western Qinling, NW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 86: 459-473 |
Qiu KF, Yu HC, Gou ZY, Liang ZL, Zhang JL and Zhu R. 2018. Nature and origin of Triassic igneous activity in the Western Qinling Orogen:The Wenquan composite pluton example. International Geology Review, 60(2): 242-266 |
Qiu KF, Yu HC, Deng J, McIntire D, Gou ZY, Geng JZ, Chang ZS, Zhu R, Li KN and Goldfarb R. 2020. The giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit in West Qinling, China:Magmatic- or metamorphic-hydrothermal origin?. Mineralium Deposita, 55(2): 345-362 |
Qiu QL, Gong QS, Lu SW and Liu SX. 2008. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of adakitic granitoids in Xiahe County of Gansu Province. Gansu Geology, 17(3): 6-12 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Rapp RP and Watson EB. 1995. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8~32kbar:Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling. Journal of Petrology, 36(4): 891-931 |
Rollinson H. 1993. Using Geochemical Data:Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation, 1-352 |
Rudnick RL and Gao S. 2003. Composition of the continental crust. Treatise on Geochemistry, 3: 1-64 |
Scherer E, Münker C and Mezger K. 2001. Calibration of the lutetium-hafnium clock. Science, 293(5530): 683-687 |
Sui JX and Li JW. 2013. Geochronology and genesis of the Zaozigou gold deposit, Xiahe-Hezuo district, West Qinling. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 33(Suppl.2): 346-347 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sui JX, Li JW, Jin XY, Vasconcelos P and Zhu R. 2018. 40Ar/39Ar and U-Pb constraints on the age of the Zaozigou gold deposit, Xiahe-Hezuo district, West Qinling orogen, China:Relation to Early Triassic reduced intrusions emplaced during slab rollback. Ore Geology Reviews, 101: 885-899 |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes. In:Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345 |
Wang GC, Jia CX, Zhu YH, Xiang SY, Lin QX, Wang QH, An SW and Zhu YS. 2004. New results and major progress in regional geological survey of the Alag Lake sheet. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(5-6): 549-554 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang YB, Huang JC, Luo MS, Tian J and Bai YS. 1997. Paleo-ocean evolution of the southern eastern Kunlun orogenic belt during Hercy-early Indosinian. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 22(4): 369-372 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang YB and Yang H. 2004. Middle Permian palaeobiogeography study in East Kunlun, A'nyêmaqên and Bayan Har. Science in China (Series D), 47(12): 1120-1126 |
Wei P. 2013. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Indosinian granites from Xiahe area, West Qinling. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing:China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1-62 |
Wei P, Mo XX, Yu XH, Huang XF, Ding Y and Li XW. 2013. Geochemistry, chronology and geological significance of the granitoids in Xiahe, West Qinling. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(11): 3981-3992 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wu FY, Li XH, Zheng YF and Gao S. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185-220 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu XY, Chen JL, Gao T, Li P and Li T. 2014. Granitoid magmatism and tectonic evolution in northern edge of the western Qinling terrane, NW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(2): 371-389 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yan Z, Guo XQ, Fu CL, Aitchison J, Wang ZQ and Li JL. 2014. Detrital heavy mineral constraints on the Triassic tectonic evolution of the West Qinling terrane, NW China:Implications for understanding subduction of the Paleotethyan Ocean. The Journal of Geology, 122(5): 591-608 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Dilek Y, Qiu KF, Ji XZ, Li N, Taylor RD and Yu JY. 2015a. Structure, geochronology, and petrogenesis of the Late Triassic Puziba granitoid dikes in the Mianlue suture zone, Qinling Orogen, China. The Geological Society of America Bulletin, 11/12: 1831-1854 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Qiu KF, Ji XZ, Santosh M, Song KR, Song YH, Geng JZ, Zhang C and Hua B. 2015b. Magma mixing and crust-mantle interaction in the Triassic monzogranites of Bikou Terrane, central China:Constraints from petrology, geochemistry, and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic systematic. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 98: 320-341 |
Yu HC, Guo CA, Qiu KF, McIntire D, Jiang GP, Gou ZY, Geng JZ, Pang Y, Zhu R and Li NB. 2019. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the formation of the giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit, West Qinling, China. Minerals, 9(1): 37 |
Yu HC, Li J, Qiu KF, Gou ZY, Geng JZ, Liu WG, Pang Y and Wang BX. 2019. Sm-Nd isotope geochemistry of dolomite in the giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit, West Qinling, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(5): 1519-1531 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yu HC, Qiu KF, Nassif MT, Geng JZ, Sai SX, Duo DW, Huang YQ and Wang J. 2020a. Early orogenic gold mineralization event in the West Qinling related to closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean:Constraints from the Ludousou gold deposit, central China. Ore Geology Reviews, 117: 103217 |
Yu HC, Qiu KF, Sai SX, McIntire DC, Pirajno F, Duo DW, Miggins DP, Wang J, Jia RY and Wu MQ. 2020b. Paleo-tethys late triassic orogenic gold mineralization recorded by the Yidi'nan gold deposit, West Qinling, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 116: 103211 |
Yue YG. 2014. Sedimentary characteristic of Triassic in the southern of the East Kunlun and the constraints on the closing time of A'nimaqing Ocean. Master Degree Thesis. Xi'an:Northwest University, 1-63 |
Zhang BR. 2002. Tectonic geochemical division and orogenic model of Qinling Mountains. In:The 4th World Chinese Conference on Geological Sciences. Nanjing:State Key Laboratory of Metallogeny, Department of Geosciences, Nanjing University (in Chinese)
|
Zhang CL, Wang T and Wang XX. 2008. Origin and tectonic setting of the Early Mesozoic granitoids in Qinling orogenic belt. Geological Journal of China Universities, 14(3): 304-316 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang DX, Shu ZX, Cao H and Lu AH. 2015. Indosinian magmatism and tectonic setting of Xiahe-Hezuo area, western Qinling Mountains:Implications from the Dewulu quartz diorite and Laodou quartz dioritic porphyry. Geology in China, 42(5): 1257-1273 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang GW, Meng QR, Yu ZP, Sun Y, Zhou DW and Guo AL. 1996. Orogenic process and dynamic characteristics of Qinling orogenic belt. Science in China (Series D), 26(3): 193-200 (in Chinese) |
Zhang GW, Zhang BR, Yuan XC and Xiao QH. 2001. Qinling Orogenic Belt and Continental Dynamics. Beijing:Science Press, 1-855 (in Chinese) |
Zhang GW, Guo AL and Yao AP. 2004. Western Qinling-Songpan continental tectonic node in China's continental tectonics. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(3): 23-32 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang HF, Jin LL, Zhang L, Harris N, Zhou L, Hu SH and Zhang BR. 2005. Geochemical and Pb-Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of granitoids from western Qinling belt:Constraints on basement nature and tectonic affinity. Science in China (Series D), 50(2): 84-196 |
Zhang HF, Zhang BR, Harris N, Zhang L, Chen YL, Chen NS and Zhao ZD. 2006. U-Pb zircon SHRIMP ages, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of intrusive rocks from the Longshan-Tianshui area in the southeast corner of the Qilian orogenic belt, China:Constraints on petrogenesis and tectonic affinity. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 27(6): 751-764 |
Zhang HF, Chen YL, Xu WC, Liu R, Yuan HL and Liu XM. 2006. Granitoids around Gonghe basin in Qinghai Province:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(12): 2910-2922 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang HF, Jin LL, Zhang L, Nigel H, Zhou L, Hu S H and Zhang BR. 2007. Geochemical and Pb-Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of granitoids from western Qinling belt:Constraints on basement nature and tectonic affinity. Science in China (Series D), 50(2): 184-196 |
Zhang KX, Huang JC, Yin HF, Wang GC, Wang YB, Feng QL and Tian J. 1999. Application of radiolarians and other fossils in non-Smith strata:Exemplified by the A'nyemaqen melange belt in East Kunlun Mts. Science in China (Series D), 43(4): 364-374 |
Zhang LY, Ding L, Pullen A, Xu Q, Liu DL, Cai FL, Yue YH, Lai QZ, Shi RD, Ducea MN, Kapp P and Chapman A. 2014. Age and geochemistry of western Hoh-Xil-Songpan-Ganzi granitoids, northern Tibet:Implications for the Mesozoic closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Lithos, 190-191: 328-348 |
Zhang Q, Yin XM, Yin Y, Jin WJ, Wang YL and Zhao YQ. 2009. Issues on metallogenesis and prospecting of gold and copper deposits related to adakite and Himalayan type granite in West Qinling. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(12): 3103-3122 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
陈衍景. 2010. 秦岭印支期构造背景、岩浆活动及成矿作用. 中国地质, 37(4): 854-865. |
第鹏飞. 2018. 西秦岭夏河-合作早子沟金矿床地球化学特征及成矿机制研究. 博士学位论文.兰州:兰州大学, 1-96. |
耿建珍, 黄雅琪, 姜桂鹏, 吴磊, 朱锐, 于皓丞, 邱昆峰. 2019. 西秦岭早子沟金锑矿床含矿英安斑岩年代学及其成因. 地质调查与研究, 42(3): 166-173. |
黄雄飞, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 李小伟, 丁一, 韦萍, 和文言. 2013. 西秦岭宕昌地区晚三叠世酸性火山岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 29(11): 3968-3980. |
黄雄飞, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 李小伟, 杨梦楚, 罗明非, 和文言, 于峻川. 2014. 西秦岭印支期高Sr/Y花岗岩类的成因及动力学背景——以同仁地区舍哈力吉岩体为例. 岩石学报, 30(11): 3255-3270. |
金鼎国. 2015. 甘肃省夏河县格娄昂金矿床地质特征及找矿前景分析. 甘肃科技, 31(10): 12-14. |
金维浚, 张旗, 何登发, 贾秀勤. 2005. 西秦岭埃达克岩的SHRIMP定年及其构造意义. 岩石学报, 21(3): 959-966. |
靳晓野, 李建威, 隋吉祥, 文广, 张金阳. 2013. 西秦岭夏河-合作地区德乌鲁杂岩体的侵位时代、岩石成因及构造意义. 地球科学与环境学报, 35(3): 20-38. |
李春昱, 王荃, 张之孟, 刘雪亚. 1980. 中国板块构造的轮廓. 中国地质科学院院报, 2: 11-19, 130. |
李建威, 隋吉祥, 靳晓野, 文广, 昌佳, 朱锐, 詹涵钰, 武文辉. 2019. 西秦岭夏河-合作地区与还原性侵入岩有关的金成矿系统及其动力学背景和勘查意义. 地学前缘, 26(5): 17-32. |
李婷, 徐学义, 陈隽璐, 王洪亮, 李智佩, 张欣. 2012. 西秦岭造山带礼县地区中川岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其构造环境. 地质通报, 31(6): 875-883. |
梁志录, 陈国忠, 麻红顺, 张愿宁. 2016. 西秦岭早子沟金矿控矿断裂形成演化. 大地构造与成矿学, 40(2): 354-366. |
骆必继, 张宏飞, 肖尊奇. 2012. 西秦岭印支早期美武岩体的岩石成因及其构造意义. 地学前缘, 19(3): 199-213. |
骆必继. 2013. 西秦岭造山带印支期岩浆作用及深部过程. 博士学位论文.武汉:中国地质大学(武汉), 1-191. |
邱昆峰, 李楠, Taylor RD, 宋耀辉, 宋开瑞, 韩旺珍, 张东旭. 2014. 西秦岭温泉钼矿床成矿作用时限及其对斑岩型钼矿床系统分类制约. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2631-2643. |
邱昆峰. 2015. 西秦岭北缘印支期斑岩铜钼成矿系统模式. 博士学位论文.北京:中国地质大学(北京), 1-194. |
邱昆峰, 宋开瑞, 宋耀辉. 2015. 西秦岭温泉斑岩钼矿床岩浆-热液演化. 岩石学报, 31(11): 3391-3404. |
邱庆伦, 龚全胜, 卢书伟, 柳生祥. 2008. 甘肃夏河地区印支期埃达克岩的厘定及其意义. 甘肃地质, 17(3): 6-12. |
隋吉祥, 李建威. 2013. 西秦岭夏河-合作地区枣子沟金矿床成矿时代与矿床成因. 矿物学报, 33(增2): 346-347. |
王国灿, 贾春兴, 朱云海, 向树元, 林启祥, 王青海, 安守文, 朱耀生. 2004. 阿拉克湖幅地质调查新成果及主要进展. 地质通报, 23(5-6): 549-554. |
王永标, 黄继春, 骆满生, 田军, 拜永山. 1997. 海西-印支早期东昆仑造山带南侧古海洋盆地的演化. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 22(4): 369-372. |
韦萍. 2013.西秦岭夏河地区印支期花岗岩成因及其构造意义.硕士学位论文.北京:中国地质大学(北京), 1-62
|
韦萍, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 黄雄飞, 丁一, 李小伟. 2013. 西秦岭夏河花岗岩的地球化学、年代学及地质意义. 岩石学报, 29(11): 3981-3992. |
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185-220. |
徐学义, 陈隽璐, 高婷, 李平, 李婷. 2014. 西秦岭北缘花岗质岩浆作用及构造演化. 岩石学报, 30(2): 371-389. |
于皓丞, 李俊, 邱昆峰, 勾宗洋, 耿建珍, 刘文刚, 庞瑶, 王博雄. 2019. 西秦岭甘南早子沟金锑矿床白云石Sm-Nd同位素地球化学及其意义. 岩石学报, 35(5): 1519-1531. |
岳远刚. 2014. 东昆仑南缘三叠系沉积特征及其对阿尼玛卿洋闭合时限的约束. 硕士学位论文.西安:西北大学, 1-63. |
张本仁. 2002.秦岭构造-地球化学分区与造山运动模式.见:第四届世界华人地质科学研讨会论文摘要集.南京:南京大学地球科学系成矿作用研究国家重点实验室
|
张成立, 王涛, 王晓霞. 2008. 秦岭造山带早中生代花岗岩成因及其构造环境. 高校地质学报, 14(3): 304-316. |
张德贤, 束正祥, 曹汇, 鲁安怀. 2015. 西秦岭造山带夏河-合作地区印支期岩浆活动及成矿作用——以德乌鲁石英闪长岩和老豆石英闪长斑岩为例. 中国地质, 42(5): 1257-1273. |
张国伟, 孟庆任, 于在平, 孙勇, 周鼎武, 郭安林. 1996. 秦岭造山带的造山过程及其动力学特征. 中国科学(D辑), 26(3): 193-200. |
张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 肖庆辉. 2001. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学. 北京:科学出版社, 1-855. |
张国伟, 郭安林, 姚安平. 2004. 中国大陆构造中的西秦岭-松潘大陆构造结. 地学前缘, 11(3): 23-32. |
张宏飞, 靳兰兰, 张利, Harris N, 周炼, 胡圣虹, 张本仁. 2005. 西秦岭花岗岩类地球化学和Pb-Sr-Nd同位素组成对基底性质及其构造属性的限制. 中国科学(D辑), 35(10): 914-926. |
张宏飞, 陈岳龙, 徐旺春, 刘荣, 袁洪林, 柳小明. 2006. 青海共和盆地周缘印支期花岗岩类的成因及其构造意义. 岩石学报, 22(12): 2910-2922. |
张克信, 黄继春, 殷鸿福, 王国灿, 王永标, 冯庆来, 田军. 1999. 放射虫等生物群在非史密斯地层研究中的应用——以东昆仑阿尼玛卿混杂岩带为例. 中国科学(D辑), 29(6): 542-550. |
张旗, 殷先明, 殷勇, 金惟俊, 王元龙, 赵彦庆. 2009. 西秦岭与埃达克岩和喜马拉雅型花岗岩有关的金铜成矿及找矿问题. 岩石学报, 25(12): 3103-3122. |
 2020, Vol. 36
2020, Vol. 36


