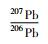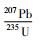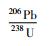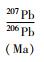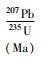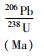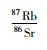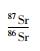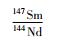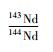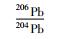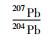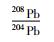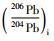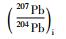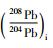2. 山东离子探针中心, 济南 250013;
3. 中国地质大学地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室, 北京 100083;
4. 山东省地质博物馆, 济南 250014
2. Shandong SHRIMP Center, Jinan 250013, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China;
4. Shandong Geological Museum, Jinan 250014, China
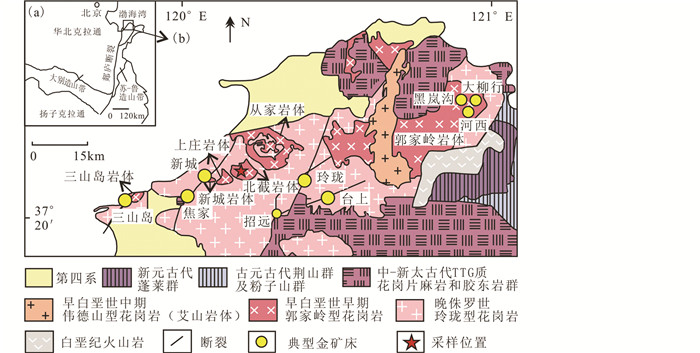
胶东半岛西北部是我国重要的金矿床密集区,三山岛、焦家、新城、玲珑、台上等超大型金矿床分布于该区(图 1)。区内的晚侏罗世玲珑型花岗岩和早白垩世郭家岭型花岗岩赋存了胶东95%以上的金资源储量,是胶东金矿最主要的赋矿围岩(Yang et al., 2006, 2016a; Zhai and Santosh, 2013; Goldfarb and Santosh, 2014; Yan et al., 2014; Deng et al., 2015a, b, 2018)。赋矿的郭家岭型花岗岩一直是国内外学者研究的热点(Deng et al., 2003a, 2011; Chen et al., 2005; Li et al., 2006; Fan et al., 2007; Yang et al., 2008, 2009, 2014; Tan et al., 2012; Yang and Badal, 2013; 杨立强等, 2014, 2020)。然而,目前对于郭家岭型花岗岩的成因或其形成的大地构造背景及其与金成矿的关系,尚存在较多的不同意见。在花岗岩类成因方面,一些学者将其归为埃达克岩石,认为俯冲增厚的大陆地壳部分熔融形成郭家岭花岗岩(Hou et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2010; Deng and Wang, 2016; Deng et al., 2017a, b);许多研究者认为其属于高Ba-Sr花岗岩(刘跃等,2014;王中亮等,2014),是壳幔相互作用的结果(Yang et al., 2012; Yang and Badal, 2013; 刘跃等,2014;王中亮等,2014);此外,杨进辉等(2003)则认为郭家岭型花岗岩地球化学特征类似于年轻的TTG(< 3.0Ga)和Na质花岗岩,是由下地壳镁铁质岩石脱水部分熔融作用形成的。在花岗岩类与金成矿的关系方面,许多研究者认为金矿床为郭家岭型花岗岩岩浆期后热液矿床(Wang et al., 1998;李士先等,2007;罗贤冬等,2014);也有研究者提出,胶东金矿成矿主要与早白垩世中期的伟德山型花岗岩及其同期的脉岩、火山岩有关(刘辅臣等,1984;孙景贵等,2000;罗振宽等,2001;宋明春,2014),早白垩世中期大规模岩浆作用引发了强烈的流体活动和成矿物质活化(Song et al., 2014, 2015; 宋明春等, 2014)。可见,进一步研究郭家岭型花岗岩岩的成因,对深化理解胶东早白垩世大规模金成矿的大地构造背景及岩浆活动与金矿化的关系具有十分重要的意义。
|
图 1 胶西北区域地质略图(据Wang et al., 2014修改) Fig. 1 The simplified geological map of the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula (modified after Wang et al., 2014) |
前人对归属于郭家岭型花岗岩的郭家岭岩体、丛家岩体、上庄岩体、新城岩体等的岩石地球化学、同位素地球化学和同位素年代学做过详细系统的研究(杨进辉等,2003;Hou et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2010;Yang et al., 2012, 2006; Yang and Badal, 2013;Wang et al., 2014; 罗贤冬等,2014;刘跃等,2014;王中亮等,2014),而对同属于郭家岭型花岗岩的北截岩体仅进行过同位素年龄测试工作(Wang et al., 1998;耿科等,2015)。本文通过对北截岩体进行详细的野外地质调查和显微镜下观察,区分出细粒花岗闪长岩、含斑细粒花岗闪长岩、斑状中粒花岗闪长岩、斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩及花岗伟晶岩脉5种侵入岩,并对其进行了系统的矿物化学、主微量元素地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素研究,确定了北截岩体的地球化学类型,进一步约束了郭家岭型花岗岩的形成时代及岩石成因,揭示了其成岩构造环境,探讨了岩浆活动与金成矿的关系。
1 区域地质概况胶西北位于华北克拉通东南缘胶东半岛西北部(图 1;Deng et al., 2003a, b; Tan et al., 2008),苏鲁超高压变质带北部,郯庐断裂带东侧,区内广泛发育NNE向展布的郯庐断裂系的各级构造。其结晶基底岩系主要由中-新太古代TTG质花岗片麻岩、新太古代胶东岩群、古元古代粉子山群和荆山群,及新元古代蓬莱群变质岩组成(Tam et al., 2011;Li et al., 2012)。区域中生代岩浆活动十分发育,主要为晚侏罗世玲珑型花岗岩、早白垩世早期郭家岭型花岗岩和早白垩世中期伟德山型花岗岩(艾山花岗岩体)(图 1;Sun et al., 2007; Ma et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2014)。玲珑型花岗岩岩性主要为黑云母花岗岩,其锆石U-Pb年龄为166~149Ma(Jiang et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012),被认为是加厚的下地壳(主要是TTG质花岗片麻岩和胶东岩群)部分熔融的产物(Zhang et al., 2010; Jiang et al., 2012)。郭家岭型花岗岩侵入于玲珑型花岗岩体中,由郭家岭、丛家、北截、上庄、新城和三山岛等岩体组成(图 1),总面积约514km2,各岩体呈北东东向不连续带状分布,自东向西岩体面积由大变小。岩性主要为二长闪长岩、石英二长岩、花岗闪长岩和二长花岗岩,其锆石U-Pb年龄为132~126Ma(Hou et al., 2007; Yang et al., 2012)。

|
图 2 北截岩体地质图据(耿科等,2015修改) Fig. 2 Geological map of Beijie pluton (modified after Geng et al., 2015) |
北截岩体位于丛家岩体西南侧,形态为近东西向的椭圆状,出露面积约15km2,主要由花岗闪长岩组成,呈岩株状侵入玲珑岩体中(图 2,宋明春和王沛成,2003)。伟德山型花岗岩的艾山岩体侵入郭家岭型花岗岩和玲珑型花岗岩中,呈近南北走向将郭家岭岩体切割为东西两部分,主要由斑状中粗粒二长花岗岩组成,含少量花岗闪长岩,形成时间为116±1Ma(Goss et al., 2010),被认为是来源于幔源基性岩浆与壳源酸性岩浆相互作用产生的基性岩浆底侵引起的地壳底部岩石部分熔融形成的(Goss et al., 2010;杨宽等,2012)。在研究区东部的藏格庄盆地及研究区以南的胶莱盆地中,发育有与早白垩世花岗岩同时代(130~110Ma)的青山群火山岩(Fan et al., 2001; Liu et al., 2009),由玄武岩、玄武粗安岩、粗面岩、安山岩、流纹岩等组成(宋明春和王沛成,2003),其成因是交代的富集岩石圈地幔部分熔融形成(Fan et al., 2001)。
2 样品采集与岩相学特征以往区域地质调查将北截岩体划归为郭家岭序列大草屋单元,认为这一岩体是由斑状粗中粒含黑云花岗闪长岩组成(宋明春和王沛成,2003)的单一岩性侵入体。我们通过详细的野外观察发现,北截岩体岩性组成并非单一,是由多种岩性侵入体组成的复式岩体。野外宏观上,岩石呈灰白色至浅肉红色,根据粒度大小和有无斑晶,分为细粒花岗闪长岩、含斑细粒花岗闪长岩、斑状中粒花岗闪长岩、斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩和花岗伟晶岩脉。本文在认真观察识别各种岩性侵入体的基础上,于招远市大刘家村北400m处自然露头和招远市北朱家村西北700m处人工采石坑,采集了新鲜的花岗闪长岩和花岗伟晶岩脉样品(图 2)。
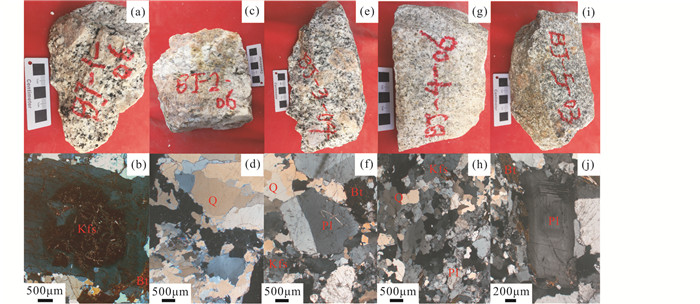
花岗闪长岩主要造岩矿物为斜长石(45%~50%)、钾长石(20%~22%)、石英(20%~25%)和少量黑云母(5%~7%)、角闪石(1%~5%),副矿物有锆石、磷灰石、磁铁矿等。具似斑状结构的花岗闪长岩,斑晶主要为钾长石,粒径多1~3cm,偶见石英斑晶;基质由长英质矿物和暗色矿物组成。斜长石呈自形-半自形板状,聚片双晶较为发育,部分大颗粒可见环带构造。钾长石呈半自形-他形粒状,少数大颗粒可见卡式双晶。石英呈他形粒状充填在长石颗粒间,粒度大小不一,常呈集合体状分布,与长石一起形成粗-细粒花岗结构(图 3)。黑云母呈细小碎片、长条状,角闪石呈柱状分布于石英与长石的边缘。其中,斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩(BJ1,图 3a,b),呈似斑状结构,斑晶含量约20%,粒径10~30mm,基质呈粗粒半自形粒状结构,粒径0.5~1mm;斑状中粒花岗闪长岩(BJ3,图 3e,f),呈似斑状结构,斑晶含量约20%,粒径10~30mm,基质呈中粒半自形粒状结构,粒径0.25~0.5mm;细粒花岗闪长岩(BJ4,图 3g,h),呈细粒半自形粒状结构,主要矿物粒径0.05~0.25mm;含斑细粒花岗闪长岩(BJ5,图 3i,j),呈似斑状结构,斑晶含量约5%,粒径10mm左右,基质呈细粒半自形粒状结构,粒径0.05~0.25mm。
|
图 3 北截岩体手标本及显微镜照片 (a)浅肉红色斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩;(b)钾长石斑晶;(c)浅肉红色花岗伟晶岩;(d)石英呈集合体状分布;(e)浅肉红色斑状中粒花岗闪长岩;(f)中粒半自形粒状结构;(g)浅灰白色细粒斑状花岗闪长岩;(h)细粒半自形粒状结构;(i)浅肉红色-灰白色含斑细粒花岗闪长岩;(j)环带状斜长石斑晶.Q-石英;Kfs-钾长石;Pl-斜长石;Bt-黑云母 Fig. 3 Petrological characteristics of Beijie pluton (a) light flesh-pink porphyritic megagrained granodiorite; (b) K-feldspar phenocysts; (c) light flesh-pink granite pegmatite; (d) quartz concentrated in distribution; (e) light flesh-pink porphyritic medium-grained granodiorite; (f) medium-grained hypidiomorphic texture; (g) light off-white porphyritic fine-grained granodiorite; (h) fine-grained hypidiomorphic texture; (i) light flesh-pink to off-white porphyritic fine-grained granodiorite; (j) plagioclase phenocryst with zone.Q-quartz; Kfs- K-feldspar; Pl-plagioclase; Bt-biotite |
花岗伟晶岩呈脉状侵入花岗闪长岩中,具花岗伟晶结构(BJ2,图 3c,d),主要由斜长石(45%~50%)、钾长石(20%~22%)和石英(20%~25%)组成,含有少量角闪石(1%~5%)和副矿物磁铁矿等。钾长石呈半自形-他形粒状,晶体粒度10~30mm,斜长石呈自形-半自形板状,聚片双晶较为发育。石英呈他形粒状充填在长石颗粒间,粒度大小不一,常呈集合体状分布。
3 分析方法 3.1 电子探针分析电子探针测试工作在山东省地质科学研究院自然资源部金矿成矿过程与资源利用重点实验室完成,仪器型号为日本电子(JEOL)JXA-8230,波谱分析所用加速15kV,电流1×10-8A,束斑直径1~10μm。所用标准样品均为加拿大Astimex标样。
3.2 主量和微量元素分析主量元素、微量元素的分析测试工作分别是在自然资源部济南矿产资源监督检测中心和核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成的。主量元素分析使用Philips PW2404型X荧光光谱仪(XRF)完成,分析精度优于1%,其中FeO采用化学容量法测定,Fe2O3T为荧光光谱仪(XRF)测试所得的全铁的量,FeO的含量是通过湿化学分析方法得到的;微量元素分析使用Finnigan MAT Element I型电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)完成,分析精度多小于3%,温度20℃,湿度30%。测试过程中分别使用国际标准进行监控。
3.3 锆石LA-ICP-MS年龄测定锆石的分选在廊坊市峰泽源岩矿检测技术实验室完成的,先将岩样粉碎至300μm,再用浮选和电磁选方法分离,最后在双目镜下进行单颗粒锆石挑选。靶样、锆石透射光、反射光显微照相以及锆石阴极发光(CL)显微照相均由中国地质大学(北京)科学研究院制作和完成的。锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测试工作在北京锆年领航科技有限公司的激光等离子体质谱实验室完成,分析仪器为美国New Wave Research Inc公司生产的193nm激光剥蚀进样系统(UP193SS)和美国Agilent科技有限公司生产的Agilent7500a型四级杆等离子体质谱仪联合构成的激光等离子体质谱仪(LA-ICP-MS)。工作条件为:测试点束斑直径30μm,激光频率10Hz,预剥蚀时间5s,剥蚀采样时间45s,ICP-MS辅助气为Ar,流速1.13L/min,数据处理软件为Glitter4.4.1。年龄计算以标准锆石91500为外标进行同位素比值校正,标准锆石TEMORA和Qinghu为监控盲样;元素含量以国际标样NIST610为外标,Si为内标计算NIST612和NIST614为监控盲样。204Pb标准值和校正参考Anderson(1984)。实验详细方法参考Song et al.(2010)和Wang et al.(2012)。
3.4 Sr-Nd-Pb同位素分析Sr-Nd-Pb同位素测试在北京科荟测试技术有限公司完成。使用仪器为Finnigan MAT262多通道质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)。Sr和Nd同位素比值测定分别采用87Sr/88Sr=0.1194、146Nd/144Nd=0.7219进行标准化,详细的实验流程见Zhang et al.(2002)。铅同位素分析采用HF酸(2% HNO3)在高温高压条件下将粉末样品完全溶解,在装有交换柱上分离纯化Pb样品,质量分馏校正系数为每质量单位1‰,该校正系数源于对铅标准物质NBS981的大量测试所获得的数据。实验中国际标样分析结果分别为NBS 987 87Sr/86Sr=0.710248±13(2SD,n=35);GSB Nd 143Nd/144Nd=0.512185±8(2SD,n=68);CAGS Pb 206Pb/204Pb=17.9708±0.0009(2SD,n=22),207Pb/204Pb=15.5626±0.0010(2SD,n=22),208Pb/204Pb=38.4059±0.0024(2SD,n=22)。
4 分析结果 4.1 矿物化学对北截岩体斑状粗粒花岗岩(BJ1-1)和细粒花岗闪长岩(BJ4-1)中的黑云母进行了电子探针分析(表 1),结果表明这两组岩石中黑云母成分没有显著差别,均具有富MgO、FeOT、高Al2O3,低TiO2的特点。斑状粗粒花岗岩中黑云母MF值为0.44~0.47,Fe/(Fe+Mg)值为0.48~0.52;细粒花岗闪长岩中黑云母MF值为0.37~0.39,Fe/(Fe+Mg)值为0.56~0.60。
|
|
表 1 北截岩体花岗闪长岩中黑云母电子探针分析数据(Wt%) Table 1 Major oxide compositions of biotites in the Beijie granodiorite(wt%) |
选择北截岩体中五组共20件样品进行岩石地球化学分析,五组样品分别为斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩、斑状中粒花岗闪长岩、细粒花岗闪长岩、含斑细粒花岗闪长岩和花岗伟晶岩,其主量、微量和稀土元素组成见表 2。
|
|
表 2 北截岩体主量(wt%)和微量(×10-6)元素组成 Table 2 Major (wt%) and trace (×10-6) element compositions of Beijie pluton |
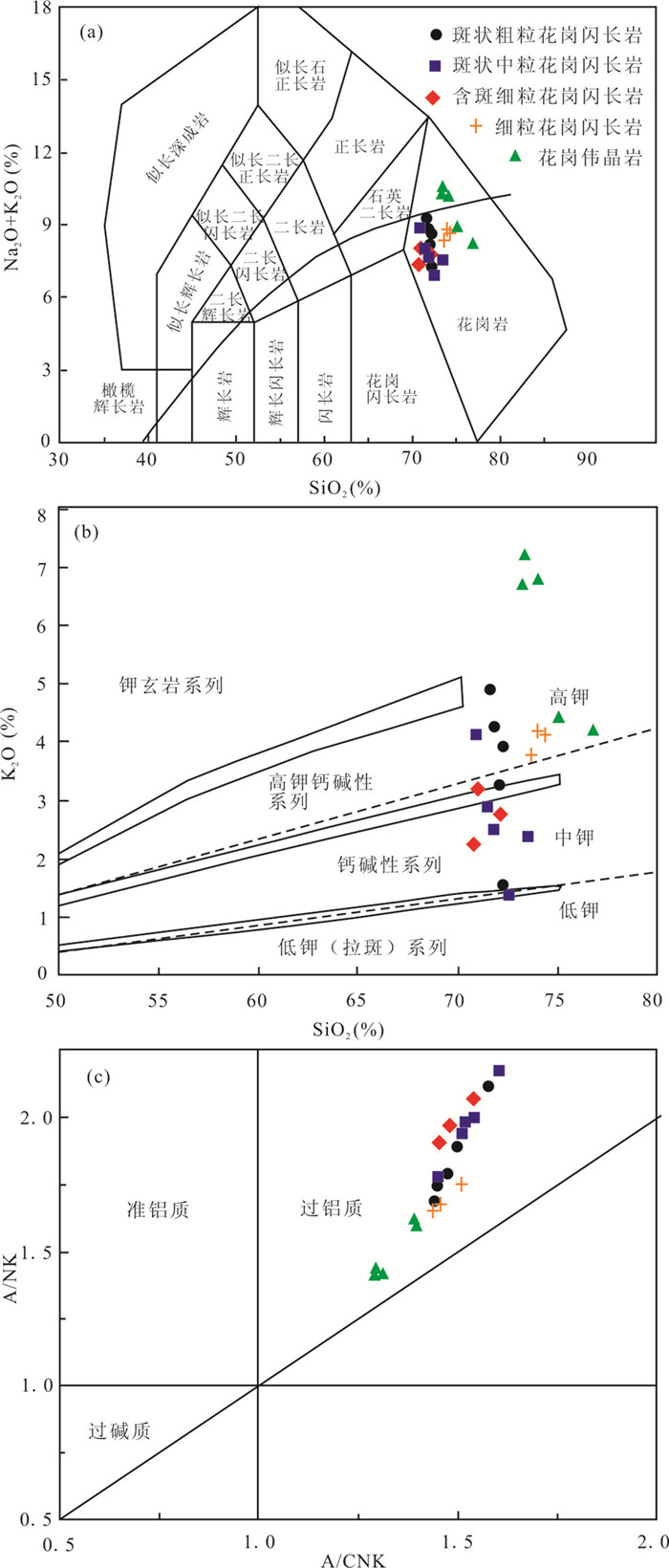
所有花岗闪长岩样品SiO2含量为70.82%~74.40%,K2O含量为1.39%~4.91%,Na2O含量为4.40%~5.74%,总碱值(Na2O+K2O)为6.92%~9.31%。在TAS图解中,样品投点于接近花岗闪长岩的花岗岩范围(图 4a);在SiO2-K2O图解(图 4b)上,主要投点于高钾钙碱性-钙碱性系列;岩石的镁指数(Mg#)为21.93~30.11,铝指数(A/CNK)为1.43~1.60,属于过铝质花岗岩(图 4c)。
|
图 4 北截岩体TAS图解(a,据Middlemost, 1994)、SiO2-K2O图解(b,据Morrison, 1980)和A/CNK-A/NK图解(c,据Middlemost, 1994) 图 5、图 8、图 10、图 11、图 13图例同此图 Fig. 4 TAS diagram (a, after Middlemost, 1994), SiO2 vs.K2O diagram (b, after Morrison, 1980) and A/CNK vs.A/NK diagram (c, after Middlemost, 1994) for the Beijie pluton The legends in Fig.5, Fig.8, Fig.10, Fig.11, Fig.13 are the same as in this figure |
花岗伟晶岩SiO2含量相对较高,为73.27%~76.80%,K2O含量为4.19%~7.20%,钾含量较高,Na2O含量为3.27%~4.42%,Na2O+K2O值为8.14%~10.47%。在TAS图解中,样品落入花岗岩范围(图 4a);在SiO2-K2O图解上属于高钾钙碱性-钾玄岩系列(图 4b);镁指数(Mg#)为6.69~14.09,铝指数(A/CNK)为1.29~1.39,属于过铝质花岗岩(图 4c)。
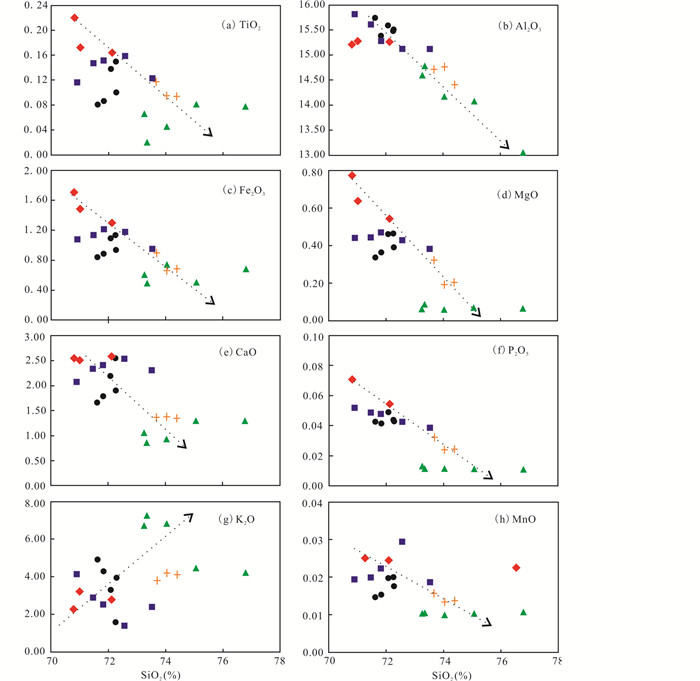
在Harker图解上(图 5),花岗闪长岩和伟晶岩的SiO2与其余的氧化物之间具有良好的相关性,SiO2含量与TiO2、Fe2O3T、MgO、CaO、P2O5和MnO含量呈负相关,与K2O含量呈正相关,而且由含斑细粒花岗闪长岩-斑状中粒花岗闪长岩-斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩-细粒花岗闪长岩-花岗伟晶岩呈连续演化关系。
|
图 5 北截岩体花岗闪长岩和伟晶岩主量元素与SiO2协变图 Fig. 5 Diagrams of SiO2 vs.predominant oxides of the granodiorite and pegmatite from Beijie pluton |
所有花岗闪长岩的样品的微量元素和稀土元素特征都高度一致。其∑REE为25.57×10-6~85.41×10-6,(La/Yb)N=18.39~45.76,LREE/HREE比值为13.13~21.40,指示轻、重稀土元素发生了强烈分异;δEu为1.16~2.61,具有较为明显的正铕异常;δCe为0.79~1.33,具有较弱的铈负异常到较弱的铈正异常;稀土配分曲线为右倾型式(图 6a),LREE高度富集,HREE相对亏损且曲线较平坦。在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图上(图 6b),花岗闪长岩的微量元素显示富集Rb、Sr、Ba、Pb等大离子亲石元素(LILE),亏损Nd、Ta、Zr、Hf等高场强元素(HFSE),与郭家岭岩体花岗闪长岩和新城岩体二长花岗岩的特征相似(杨进辉等,2003;王中亮等,2014)。
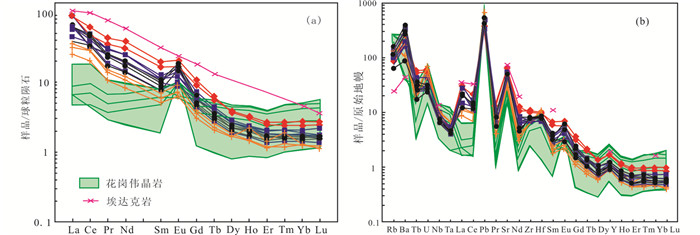
|
图 6 北截岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) 埃达克岩石数据引自Martin(1999) Fig. 6 REE chondrite-normalized patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagrams (b) of the granodiorite and pegmatite from Beijie pluton (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) The data for adakitic granitoids from Martin(1999) |
花岗伟晶岩与花岗闪长岩的稀土特征略有不同,∑REE为7.60×10-6~26.98×10-6,(La/Yb)N=1.58~6.09,指示轻、重稀土元素分馏较弱;LREE/HREE比值为2.61~7.21,呈LREE一般富集的右倾分布型式(图 6a);δEu为0.94~7.54,具有弱的负铕异常到强的正铕异常,其中一个样品的正铕异常可达7.54;δCe为1.01~1.31,具有弱的铈正异常。花岗伟晶岩的其他微量元素特征与花岗闪长岩相似,在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图上(图 6b),花岗伟晶岩的微量元素显示富集Rb、Sr、Ba、Pb等大离子亲石元素(LILE),其中高度富集Pb,亏损Nd、Ta、Zr、Hf等高场强元素(HFSE)。
4.3 锆石U-Pb年龄对北截岩体斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩(BJ1-1)和花岗伟晶岩(BJ2-1)2件样品进行锆石U-Pb年龄测定。锆石多为浅灰色,自形柱状、短柱状,晶形完整,表面光滑。阴极发光照片显示(图 7a,b),绝大多数锆石具有振荡环带,属于岩浆结晶期锆石。大多数锆石都具有核幔结构,反映其继承性生长的特点。样品中锆石颗粒较大,内部结构清晰,环带规整,长宽比1:1.5~1:5,符合岩浆锆石的特征。内核多为浑圆状,浅白色,表明较老。部分锆石结晶后又经受过流体作用,具有一层暗色边缘。U含量较低,为42×10-6~1388×10-6,Th含量为26×10-6~903×10-6,Th/U比值为0.04~1.17,变化不大且接近于1 (表 3),也反映这些锆石均属岩浆成因。
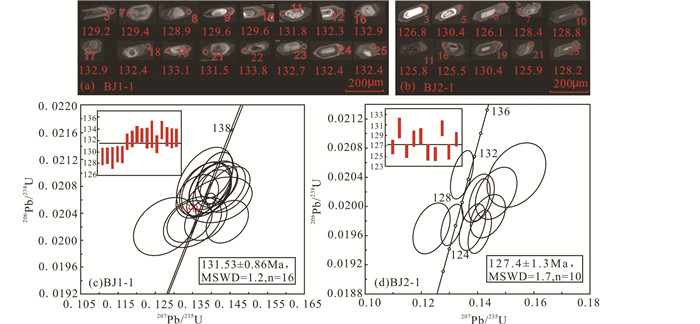
|
图 7 北截岩体花岗闪长岩和伟晶岩锆石阴极发光图像(a、b)和锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图(c、d) Fig. 7 CL images (a, b) and U-Pb concordia diagrams (c, d) of zircons for the granodiorite and pegmatite from Beijie pluton |
|
|
表 3 北截岩体花岗闪长岩和花岗伟晶岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年结果 Table 3 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages of the granodiorite and pegmatite from Beijie pluton |
BJ1-1样品的16个测点取得了较为一致的206Pb/238U年龄,波动范围为128.9~133.8Ma,加权平均值为131.53±0.86Ma(MSWD=1.2)(表 3、图 7c)。
BJ2-1样品的10个测点取得了较为一致的206Pb/238U年龄,波动范围为125.5~130.4Ma,加权平均值为127.4±1.3Ma(MSWD=1.7)(表 3、图 7d)。
4.4 Sr-Nd-Pb同位素对北截岩体中的斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩(BJ1)、花岗伟晶岩脉(BJ2)、斑状中粒花岗闪长岩(BJ3)、细粒花岗闪长岩(BJ4)、含斑细粒花岗闪长岩(BJ5)进行Sr、Nd、Pb同位素测试分析,实验结果列于表 4。
|
|
表 4 北截岩体花岗闪长岩和花岗伟晶岩Sr-Nd同位素组成 Table 4 Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of the granodiorite and pegmatite from Beijie pluton |
① 李大鹏等.2019.国家自然科学基金项目“探索胶东金矿成矿物质来源的新证据——岩石学、矿物学约束”(41503038)课题报告.55-60
结果显示,北截岩体5种样品的Sr-Nd同位素特征比较相似,显示了同源岩浆的特性。花岗闪长岩的87Sr/86Sr值(0.710883~0.712100)略低于花岗伟晶岩(0.713065~0.713373),εNd(t)值(-16.57~-11.17)略高于花岗伟晶岩(-18.53~-18.06);二者的143Nd/144Nd值极为相似,为0.511711~0.512002,初始87Sr/86Sr(ISr)在同一范围内,为0.710658~0.711568。计算的亏损地幔模式年龄(tDM2)分别为2107~2153Ma(似斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩)、2387~2425Ma(花岗伟晶岩脉)、2145~2202Ma(似斑状中粒花岗闪长岩)、2220~2267Ma(细粒花岗闪长岩)和1831~1976Ma(含斑细粒花岗闪长岩)。
北截岩体样品的Pb同位素组成列于表 5。初始Pb同位素组成中,斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩、斑状中粒花岗闪长岩和含斑细粒花岗闪长岩的(206Pb/204Pb)i极为相近(17.455~17.945),略高于伟晶岩脉和细粒花岗闪长岩(17.047~17.262);前三者的(207Pb/204Pb)i也极为相近(15.526~15.577),略高于伟晶岩脉和细粒花岗闪长岩(15.490~15.510);三者的(208Pb/204Pb)i(38.061~38.389)也略高于伟晶岩脉和细粒花岗闪长岩(37.744~37.965)。
|
|
表 5 北截岩体花岗闪长岩和花岗伟晶岩Pb同位素组成 Table 5 Pb isotopic compositions of the granodiorite and pegmatite from Beijie pluton |
北截岩体斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩的锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb加权平均年龄为131.53±0.86Ma,16个测点的年龄数据集中于5Ma的较小变化范围内,说明这些锆石是同一次岩浆事件的产物,其加权平均年龄指示了花岗闪长岩的侵位时间。这一年龄值与前人获得的该岩体的形成年龄(128±6Ma)比较接近(Wang et al., 1998)。
花岗伟晶岩脉的锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb加权平均年龄为127.4±1.3Ma,其年龄值低于花岗闪长岩年龄,与野外观察的伟晶岩脉侵入花岗闪长岩的事实吻合,说明花岗闪长岩的测年结果是可靠的。花岗伟晶岩10个锆石测点的最大年龄值为130.4Ma,位于花岗闪长岩16个测点年龄范围之间,说明二者形成时间具有连续性。花岗伟晶岩与花岗闪长岩在时间和空间上的紧密伴生,以及其SiO2与其余的氧化物之间呈现的良好线性关系(图 5),指示二者具有成因联系,伟晶岩是由形成花岗闪长岩的岩浆进一步演化形成的。
以往对北截岩体周边的其它郭家岭序列花岗闪长岩进行了较多同位素年龄测试,其中郭家岭岩体花岗闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄为125.4±2.2Ma(罗贤冬等,2014),丛家岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄为126.0±0.6和123.0±0.5Ma(Yang and Badal, 2013),上庄岩体花岗闪长岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为128.8±2.0Ma(罗贤冬等,2014)和129±1Ma(Yang and Badal, 2013),新城岩体石英二长岩锆石U-Pb年龄为128±1Ma~132±1Ma(Wang et al., 2014)、二长花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为123±1Ma(刘跃等,2014),三山岛岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄为128±2Ma(Wang et al., 1998)。北截岩体的年龄值与新城石英二长岩、上庄花岗闪长岩等一致,而略高于其它岩体,说明北截岩体是郭家岭型花岗岩早阶段的侵入体。
5.2 地球化学性质与岩石成因上述主量和微量元素测试结果表明,北截岩体的岩石样品总体显示花岗岩地球化学特征,为高钾钙碱性-钙碱性系列、过铝质花岗岩。除花岗伟晶岩外,绝大部分样品的Na2O/K2O>1,属钠质花岗岩。稀土配分型式为轻稀土富集型,具正铕异常,微量元素的Ba、Sr含量高。岩石的这种地球化学特征与太古宙TTG岩系、埃达克岩和科迪勒拉安第斯等地的Na质花岗岩及高Ba-Sr花岗岩相似,而与典型岛弧环境的花岗岩类明显不同(杨进辉等,2003)。在矿物组成上,岩石中斜长石含量为钾长石含量的2倍以上,暗色矿物由少量角闪石和黑云母组成,按实际矿物含量分类为典型的花岗闪长岩类。具有岩浆演化早期阶段的岩相学特征,与根据同位素年龄测试结果推断的岩石形成顺序吻合。岩相学观察表明,斜长石和钾长石均具有反环带结构,而且斜长石有被熔蚀现象,可能与中-基性岩浆的注入有关(Anderson,1984),指示北截花岗闪长岩具有岩浆混合成因(Wyllie et al., 1962;Xu et al., 2004)。
北截岩体花岗闪长岩和伟晶岩的主量元素具有良好的线性关系,在Harker图解中(图 5),由含斑细粒花岗闪长岩、斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩、细粒花岗闪长岩至花岗伟晶岩,随SiO2含量增加TiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、MgO、CaO、P2O5和MnO呈线性降低,K2O则与SiO2呈正相关关系,呈现典型的同源岩浆演化特征,早期岩浆富Fe、Mg、Ca,晚期岩浆富Si、K。在La/Sm-La和Rb/Nb-Rb/Zr相关图解中(图 8),样品数值投点大致呈斜线排列,显示了部分熔融演化趋势。
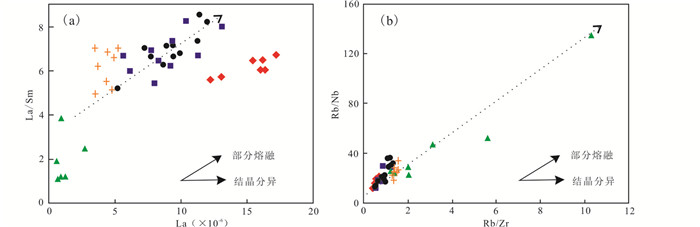
|
图 8 北截岩体La/Sm-La(a)和Rb/Nb-Rb/Zr(b)相关图解(底图据谭俊等,2006) Fig. 8 La/Sm vs.La (a) and Rb/Nb vs.Rb/Zr (b) diagrams for the granodiorite and pegmatite of the Beijie pluton (base map after Tan et al., 2006) |
花岗闪长岩富SiO2,贫MgO、MnO和CaO,A/CNK接近或大于1,富集大离子亲石元素和轻稀土元素,亏损高场强元素,显示了壳源地球化学特征。在黑云母源区投点图上(图 9),样品投点全部落入壳源区,总体显示壳源特征;但黑云母MgO的含量(9.59%~10.49%)高于壳源的玲珑型花岗岩(平均9.5%)(赛盛勋等,2016),指示有幔源物质混入的特点。岩石具有高Sr/Y比值(41~479),在Sr/Y-Y图解(图 10a)上,所有样品均落入埃达克岩区域(Defant and Drummond, 1990; Martin et al., 2005),由斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩、斑状中粒花岗闪长岩、含斑细粒花岗闪长岩、细粒花岗闪长岩至花岗伟晶岩Sr/Y逐渐降低,呈现由埃达克岩向岛弧岩石区演化的趋势。岩石在偏高的全碱含量(K2O+Na2O=7.30%~10.47%)、低的Al2O3含量(13.04%~15.82%)和MgO含量(0.06%~0.77%)以及相对平坦的重稀土配分模式(图 6a)方面,则与典型埃达克岩有明显差异。岩石具有高Ba(258×10-6~3330×10-6)、Sr(283×10-6~1371×10-6)和低Rb(39.3×10-6~172×10-6)、Y(1.2×10-6~7.28×10-6)、Yb(0.08×10-6~0.77×10-6)含量特征,与高Ba-Sr花岗岩的地球化学特征相似(Fowler et al., 2001; Ye et al., 2008; Peng et al., 2013)。
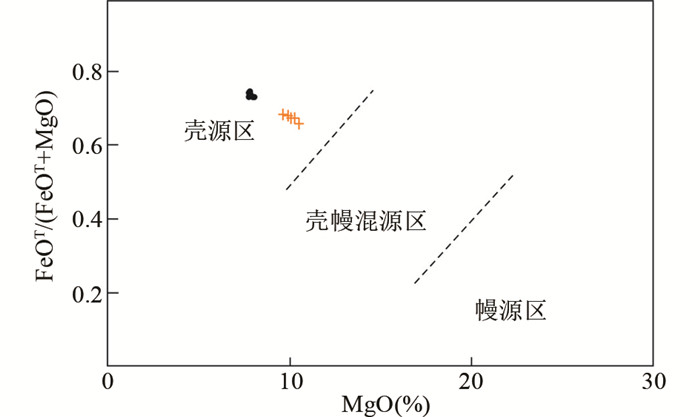
|
图 9 北截岩体花岗闪长岩黑云母源区投点图(底图据楼亚儿和杜杨松, 2006) Fig. 9 Diagram of the source of biotites for the granodiorite of the Beijie pluton (base map after Lou and Du, 2006) |
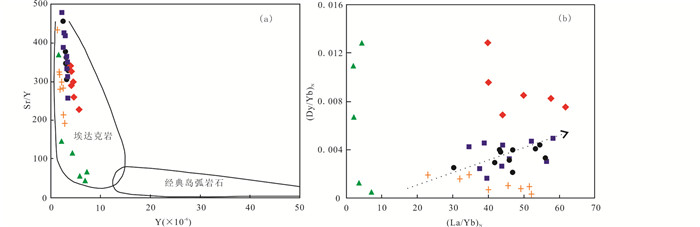
|
图 10 北截岩体Sr/Y-Y图解(a,底图据Martin et al., 2005)和(Dy/Yb)N-(La/Yb)N图解(b) Fig. 10 Diagrams of Sr/Y vs.Y (a, base map after Martin et al., 2005) and (Dy/Yb)N vs.(La/Yb)N (b) for the granodiorite and pegmatite from the Beijie pluton |
岩石富集放射性成因铅((206Pb/204Pb)i=17.047~17.945),在Pb同位素物源判别图解(图 11)上,所有数据均落入下地壳区域附近;样品的Sr/Y比值(41~479)特征,与由加厚下地壳部分熔融形成的花岗岩(He et al., 2011)相似;Nd同位素模式年龄(tDM2)为2107~2425Ma,与古元古代荆山群和粉子山群的同位素年龄一致(宋明春和王沛成,2003;Li et al., 2012);另外,岩石具有的高Bb、Sr和低Y特征,与来源于加厚下地壳部分熔融的玲珑花岗岩(Zhang et al., 2010; Jiang et al., 2012)类似。因此认为,由胶北早前寒武纪变质基底岩石组成的加厚下地壳部分熔融是北截岩体的重要物质来源。岩石ISr值(0.710658~0.711568)位于华北下地壳范围;εNd(t)值(-18.53~-11.17)高于壳源的玲珑型花岗岩(-25.1,Yang et al., 2012),与胶东地区的基性脉岩接近(Yang et al., 2004),在Sr-Nd相关图上落入以往测试的郭家岭型花岗岩范围(图 12),接近于EM2型富集地幔源区,不同于玲珑花岗岩和胶东岩群样品的投点范围,这表明岩体中有幔源物质混入。在同属郭家岭型花岗岩的丛家和郭家岭岩体中见有岩浆成因的微粒闪长质包体,一般认为微粒闪长质包体是岩浆混合的结果(Goss et al., 2010)。综合分析认为,北截岩体既具有地壳物质来源特征,又有地幔物质来源的信息,是下地壳酸性岩浆与幔源基性岩浆混合作用的结果。
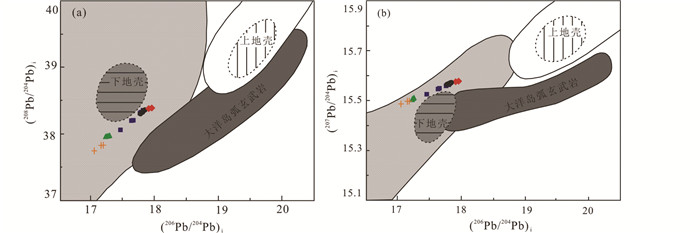
|
图 11 北截岩体Pb同位素物质源区判别图解(底图据Doe and Zartman, 1979) Fig. 11 Source divisional diagram of Pb isotope for the granodiorite and pegmatite from the Beijie pluton (base map after Doe and Zartman, 1979) |
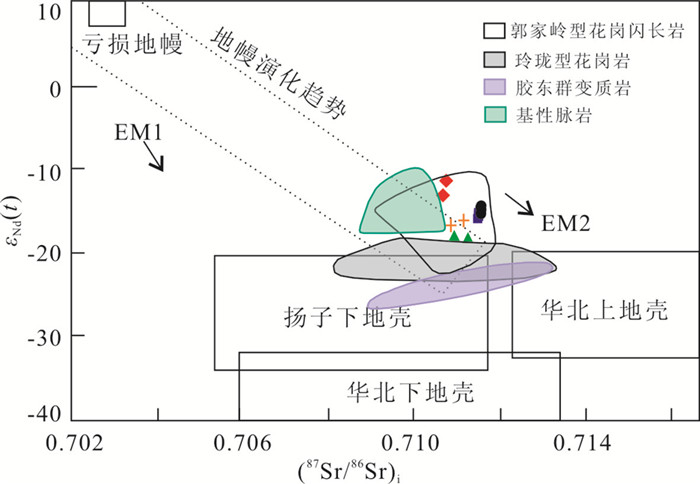
|
图 12 北截岩体的εNd(t)-ISr图解(底图据Defant and Drummond, 1990) 数据范围来源:胶东岩群据杨进辉等(2003);基性脉岩据Yang et al.(2012);玲珑型花岗岩据杨进辉等(2003),Zhang et al.(2010),Yang et al.(2012),Jiang et al.(2012)和Ma et al.(2013);郭家岭型花岗岩据杨进辉等(2003),Yang et al.(2012),王中亮等(2014);扬子下地壳、华北上地壳和下地壳据Jahn et al.(1999) Fig. 12 εNd(t) vs.ISr diagram for Late-Mesozoic magmaic rocks from the Beijie pluton, Jiaodong Peninsula (base map after Defant and Drummond, 1990) Data range sources: Jiaodong Group (Yang et al., 2003); Linglong granitoids (Yang et al., 2003, 2012; Zhang et al., 2010; Jiang et al., 2012; Ma et al., 2013); Guojialing granitoids (Yang et al., 2003, 2012; Wang et al., 2014); Yangze Craton, upper and lower crusts of the North China Craton (Jahn et al., 1999) |
北截岩体较高的Sr、Ba丰度、低的Rb/Sr、中等K/Rb比值,暗示岩浆作用过程中不会有大量长石和云母的分离结晶作用。而高的La/Yb、Sr/Y比值和低Y、Yb含量,以及(Dy/Yb)N与(La/Yb)N呈现正相关关系(图 10b),反映出酸性端元的岩浆源区有大量石榴子石残留(Liu et al., 2010;He et al., 2011)。岩石具正铕异常,重稀土较强烈亏损,暗示源区由石榴石+辉石组成,没有斜长石残留,残留相为榴辉岩。
北截岩体中伟晶岩的元素地球化学特征表明,其与花岗闪长岩有亲缘关系,二者具有同源岩浆演化特点,伟晶岩由富含挥发份的花岗质母岩浆的残余岩浆结晶分异产生(Fuertes-Fuente et al., 2000)。伟晶岩的稀土元素总量明显偏低,很可能是岩浆演化过程中副矿物(如磷灰石)结晶分离作用所造成的,个别样品稀土元素含量变化较大则可能与磷灰石等矿物的分异有关(禹丽等,2015)。
5.3 成岩构造环境元素Rb、Y和Nb能有效区分不同构造环境下形成的花岗岩类,包括火山弧花岗岩、同碰撞花岗岩、板内花岗岩和洋脊花岗岩等。在花岗岩Nb-Y和Ta-Yb构造环境判别图解上(图 13),北截岩体样品全部落入火山弧花岗岩范围内;在Hf-Rb-Ta三角图解上(图 14),所有样品也均为火山弧花岗岩。而研究表明,高Ba-Sr花岗岩形成于张性的或者非挤压的构造背景中,包括岩石圈拉张环境或碰撞造山后与重力垮塌作用有关的构造环境等(Fowler et al., 2001; Ye et al., 2008; Peng et al., 2013)。可见,以北截岩体为代表的郭家岭型花岗岩的构造环境与形成于侏罗纪后碰撞挤压环境的玲珑花岗岩(Yang et al., 2012)完全不同,而与早白垩世中期的伟德山型花岗岩构造环境(Song et al., 2019)相似。玲珑型花岗岩形成于三叠纪华北板块与扬子板块强烈碰撞之后,具后碰撞花岗岩类特征,显示有受华北和扬子克拉通共同影响的印记,物质来源包括造山带俯冲杂岩和加厚的华北克拉通下地壳(Yang et al., 2012);伟德山型花岗岩具有岛弧花岗岩特征,显示了受太平洋板块俯冲和华北克拉通破坏影响的特征,物质来源于华北太古宙地壳和富集岩石圈地幔熔融(Song et al., 2019)。郭家岭型花岗岩则具有二者之间的过渡性特征,其Sr、Y含量具有与玲珑型花岗岩相似的埃达克岩特征(Yang et al., 2012),Sr、Nd同位素特征则与伟德山型花岗岩、基性脉岩接近(Yang et al., 2004;Song et al., 2019),而其构造环境也显示了与伟德山型花岗岩及白垩纪基性脉岩的共同性,可能是太平洋板块俯冲过程中在欧亚板块边缘产生的火山弧的组成部分。
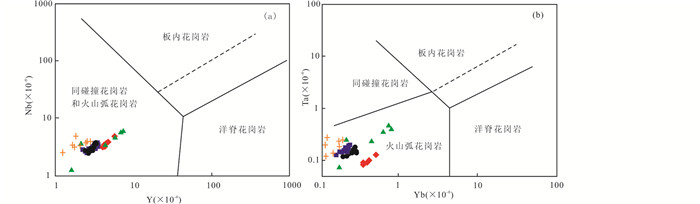
|
图 13 北截岩体Nb-Y(a)和Ta-Yb(b)大地构造环境判别图解(据Pearce et al., 1984) 虚线区域为洋脊花岗岩异常区 Fig. 13 Nb vs.Y (a) and Ta vs.Yb (b) discrimination diagrams for the granodiorite and pegmatite from Beijie pluton (after Pearce et al., 1984) Dashed line arises from the boundary line abnormal ridges ORG |
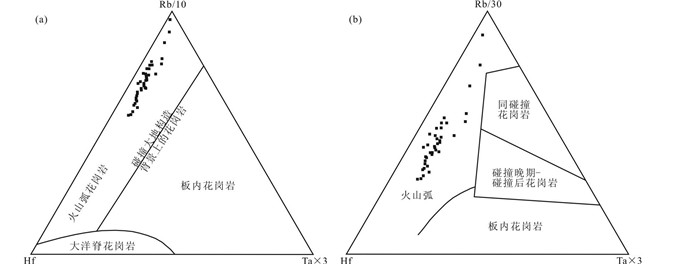
|
图 14 北截岩体Hf-Rb/10-3Ta (a)和Hf-Rb/30-3Ta (b)大地构造环境判别图解(据Harris et al., 1986) Fig. 14 Hf-Rb/10-3Ta (a) and Hf-Rb/30-3Ta (b) discrimination diagrams for the granodiorite and pegmatite from Beijie pluton (after Harris et al., 1986) |
研究表明,胶东地区在中三叠世受华北克拉通与扬子克拉通强烈碰撞的影响(宋明春等,2020a),陆壳强烈加厚。侏罗纪(约150Ma)时地幔开始上隆,岩石圈由加厚向减薄转化,造山带根部垮塌,由造山带物质或扬子克拉通和华北克拉通基底物质混合组成的下地壳活化,大范围陆壳重熔,岩浆上侵形成了玲珑型花岗岩(图 15a)。白垩纪,华北克拉通东缘经历了克拉通破坏、岩石圈减薄并伴随软流圈物质上涌(Menzie et al., 1993; Gao et al., 2002, 2009; Xu et al., 2009; Yang et al., 2012),发生了强烈的构造活动、岩浆作用及盆地裂陷,在胶东地区产生了诸如沂沭裂谷系、胶莱盆地、花岗岩类、火山岩系、中-基性脉岩等广泛的构造岩浆活动,北截岩体即形成于这一构造岩浆背景中,其同位素年龄显示,岩体形成于早白垩世构造岩浆活动阶段的早期,是这一构造阶段的初幕。华北克拉通岩石圈减薄及其伴生的软流圈物质上涌与古太平洋板块的俯冲有关(Goss et al., 2010; Santosh, 2010),早白垩世早期(约130Ma),处于太平洋板块俯冲的较早阶段,壳幔作用尚较弱,引发的岩浆活动规模不大,在欧亚板块边缘形成少量火山弧环境的郭家岭型花岗岩,并有幔源的基性脉岩产生(图 15b),郯庐断裂开始形成。早白垩世中期(约120Ma),俯冲板块的前端后撤,岩石圈地幔拆沉,软流圈由深部向浅部上涌,引起减压熔融,富集的岩石圈地幔部分熔融产生基性岩浆。热的基性岩浆上升到地壳底部发生底侵,引起了地壳底部岩石的部分熔融,产生花岗质岩浆。基性岩浆上侵分异出煌斑岩、高镁闪长岩(宋明春等,2020b)等,幔源和壳源岩浆混合及结晶分异形成胶东地区大范围分布的伟德山型花岗岩、崂山型花岗岩和青山群火山岩等。同时,郯庐断裂强烈活动,并产生“热隆-伸展”构造和大规模金成矿作用(宋明春等,2018)(图 15c)。
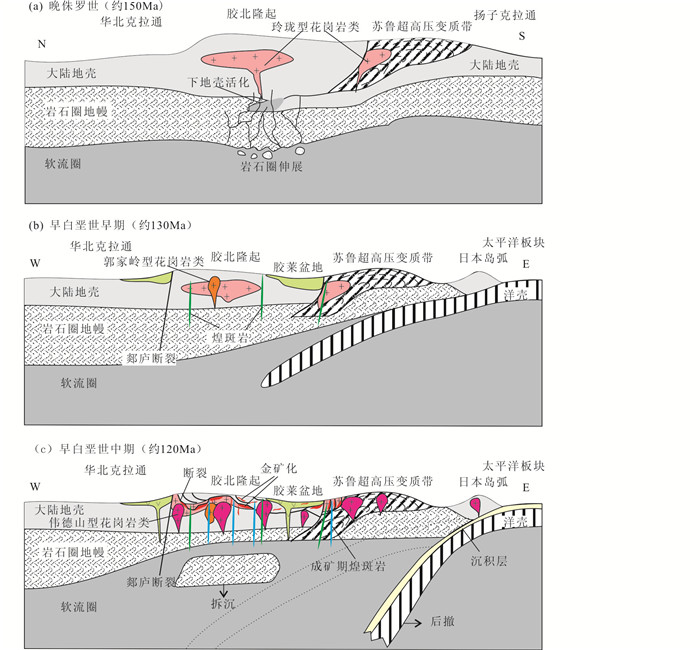
|
图 15 胶东晚中生代岩浆活动的地球动力学机制(据Yang et al., 2012;Ma et al., 2014;宋明春等,2015修改) Fig. 15 Geodynamic mechanism of Late Mesozoic magmatic activity in Jiaodong (modified after Yang et al., 2012; Ma et al., 2014; Song et al., 2015) |
关于胶东金矿与中生代岩浆活动的关系及成矿动力学背景和成矿模式前人已进行了较多研究(Yang et al., 2016b;Song et al., 2017, 2019;宋明春等, 2018, 2019;Deng et al., 2020a, b;Groves et al., 2020;Zhang et al., 2020)。鉴于包括北截岩体在内的郭家岭型花岗岩内部和周边分布有很多金矿床,许多地质工作者认为郭家岭型花岗岩岩浆活动与金成矿密切相关,将金矿床归类为郭家岭型花岗岩岩浆期后热液矿床(Wang et al., 1998;罗贤冬等,2014)。然而,本文测试的北截岩体的形成年龄,明显早于金矿成矿时代,即使岩浆活动末期的花岗伟晶岩的同位素年龄(127.4±1.3Ma)也高于大部分研究者公认的金矿成矿年龄(120Ma左右)(翟明国等,2001;宋明春等,2014)。总体分析,胶东金矿的成矿时间晚于郭家岭型花岗岩5Myr以上(翟明国等,2001)。前人对胶东西北部金矿床成矿深度的估算结果表明,成矿深度上限为2~3km,下限为5~8km(郭春影等,2011);测算的郭家岭岩体侵位深度约为13±1.6km(张华锋等,2006)。可见,金矿的成矿深度浅于郭家岭花岗岩侵位深度5km以上(宋英昕等,2017)。综合考虑成矿时代与岩浆活动的时差及岩浆期后热液可能存在的时间范围(< 0.8Myr),大量流体参与金成矿的事实(沈昆等,2000;Fan et al., 2007;Song et al., 2014;杨立强等,2014;Deng and Wang, 2016;Deng et al., 2020a, b),本文和部分研究者(姜晓辉等,2011;宋明春等,2015;Song et al., 2019)认为金成矿流体可能不是来自于这种花岗岩岩浆期后热液。
灵北断裂是胶西北焦家金断裂成矿带下盘的一条重要控矿断裂,断裂全长约50km,走向40°~60°,断裂西南段穿切玲珑型花岗岩,其北东段至北截一带切割北截岩体(图 2),沿该断裂分布有北截、蚕庄、灵山沟、黄埠岭等中小型金矿床和多个金矿点。在北截地区,灵北断裂明显切割郭家岭型花岗闪长岩,断裂宽4~30m,构造岩主要为花岗质碎裂岩和角砾岩,绢云母化、硅化和团块状黄铁矿化发育,北截金矿赋存于该断裂破碎带中。按照地质体的相互关系,确定北截地区地质事件由早至晚的形成顺序为:玲珑型花岗岩→郭家岭型花岗岩(北截岩体)→灵北断裂→金矿化,北截金矿显然是在郭家岭型花岗岩形成固结并被灵北脆性断裂破坏后再形成的。这种花岗岩显然已不能为金成矿提供流体或热动力条件,但由于岩体中断裂裂隙发育而为金成矿提供了赋矿空间,其在金成矿中的作用同赋矿的玲珑型花岗岩和早前寒武纪基底变质岩系一样。
野外地质调查显示,郭家岭型花岗岩被伟德山型花岗岩侵入,鉴于伟德山型花岗岩的艾山、海阳、牙山、三佛山、伟德山等岩体侵位深度普遍小于3.5km(张华锋等, 2006),说明伟德山型花岗岩侵位时,郭家岭型花岗闪长岩发生了强烈隆升。大量同位素年龄测试表明,伟德山型花岗岩侵位的峰值年龄为114Ma(Song et al., 2019),从郭家岭型花岗岩侵位至伟德山型花岗岩形成,在约10Myr内,郭家岭型花岗岩岩体的隆升量达10km左右(豆敬兆等, 2015)。可见,胶东地区早白垩世早中期,发生了大规模岩浆活动和强烈的地壳隆升事件,早白垩世也是华北克拉通破坏的峰期和伸展构造大量发育期,岩浆活动、地壳隆升和伸展构造共同构成了“热隆-伸展”构造系统(宋明春等, 2018)。包括北截岩体在内的郭家岭型花岗岩于早白垩世早期侵位后,快速隆升降温,在区域伸展构造作用下产生一系列断裂裂隙,为金成矿提供了有利空间。随着早白垩世中期伟德山型花岗岩的强烈活动,出现了较广泛分布的含金流体,由于地壳快速隆升,流体显著降温,在郭家岭型花岗岩、玲珑型花岗岩和前寒武变质岩中的先成断裂构造中聚集的丰富含金流体,在适当的温压条件下流体沸腾、金质沉淀成矿。
6 结论(1) 北截岩体斑状粗粒花岗闪长岩和花岗伟晶岩脉的锆石U-Pb年龄分别为131.53±0.86Ma和127.4±1.3Ma,二者为同一期岩浆活动的产物,为郭家岭型花岗岩早阶段的岩浆侵入体。
(2) 北截岩体岩石具有高的全碱、Ba、Sr含量,低的Al2O3、MgO、Rb、Y、Yb含量特征,及相对平坦的重稀土配分模式,与高Ba-Sr花岗岩的地球化学特征相似。
(3) 北截岩体的ISr值为0.710658~0.711568,εNd(t)为-18.53~-11.17,二阶段模式年龄为2107~2425Ma;Pb同位素数据均落于下地壳区域。结合岩石地球化学认为,北截岩体既具有地壳物质来源特征,又有地幔物质来源的信息,是下地壳酸性岩浆与幔源基性岩浆混合作用的结果,郭家岭型花岗岩是太平洋板块向欧亚板块俯冲产生的欧亚板块边缘火山弧的组成部分。
(4) 郭家岭型花岗岩为胶东大规模金成矿提供了有利的赋存空间,而不是成矿流来源或热动力条件。
致谢 山东省地质调查院刘汉栋研究员在野外工作期间提供了大力支持;论文写作过程中得到了中国地质大学(北京)邓军教授团队的热情帮助;两位审稿人为论文提出宝贵意见;在此一并表示最诚挚的感谢!
Anderson AT. 1984. Probable relations between plagioclase zoning and magma dynamics, Fuego Volcano, Guatemala. American Mineralogist, 69(7-8): 660-676 |
Chen YJ and Pirajno F and Qi JP. 2005. Origin of gold metallogeny and sources of ore-forming fluids, Jiaodong province, eastern China. International Geology Review, 47(5): 530-549 DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.47.5.530 |
Defant MJ and Drummond MS. 1990. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature, 347(6294): 662-665 DOI:10.1038/347662a0 |
Deng J, Yang LQ, Sun ZS, Wang JP, Wang QF and Xin HB and Li XJ. 2003a. A metallogenic model of gold deposits of the Jiaodong granite-greenstone belt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(4): 537-546 DOI:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2003.tb00134.x |
Deng J, Liu W, Sun ZS, Wang JP, Wang QF and Zhang QX and Wei YG. 2003b. Evidence of mantle-rooted fluids and multi-level circulation ore-forming dynamics:A case study from the Xiadian gold deposit, Shandong Province, China. Science in China (Series D), 46(1): 123-134 DOI:10.1360/03dz9033 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Wan L, Liu H and Yang LQ and Zhang J. 2011. A multifractal analysis of mineralization characteristics of the Dayingezhuang disseminated-veinlet gold deposit in the Jiaodong gold province of China. Ore Geology Reviews, 40(1): 54-64 |
Deng J, Liu XF and Wang QF and Pan RG. 2015a. Origin of the Jiaodong-type Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Constraints from fluid inclusion and C-D-O-S-Sr isotope compositions. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 674-686 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.04.018 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L and Carranza EJM and Lu YJ. 2015b. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry. Mineralium Deposita, 50(8): 987-1006 DOI:10.1007/s00126-015-0584-1 |
Deng J and Wang QF. 2016. Gold mineralization in China:Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Research, 36: 219-274 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.003 |
Deng J and Wang QF and Li GJ. 2017a. Tectonic evolution, superimposed orogeny, and composite metallogenic system in China. Gondwana Research, 50: 216-266 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.02.005 |
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF and Dilek Y and Liang YY. 2017b. Isotopic characterization and petrogenetic modeling of Early Cretaceous mafic diking:Lithospheric extension in the North China Craton, eastern Asia. GSA Bulletin, 129(11-12): 1379-1407 DOI:10.1130/B31609.1 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L and Santosh M and Yao EY. 2018. Crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the south-eastern North China Craton. Earth-Science Reviews, 182: 251-272 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.001 |
Deng J, Qiu KF, Wang QF, Goldfarb R, Yang LQ, Zi JW and Geng JZ and Ma Y. 2020a. In situ dating of hydrothermal monazite and implications for the geodynamic controls on ore formation in the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Economic Geology, 115(3): 671-685 DOI:10.5382/econgeo.4711 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Santosh M, Liu XF, Liang YY, Yang LQ and Zhao R and Yang L. 2020b. Remobilization of metasomatized mantle lithosphere:A new model for the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Mineralium Deposita, 55(2): 257-274 DOI:10.1007/s00126-019-00925-0 |
DePaolo DJ. 1981. Neodymium isotopes in the Colorado Front Range and crust-mantle evolution in the Proterozoic. Nature, 291(5812): 193-196 DOI:10.1038/291193a0 |
Doe BR and Zartman RE.1979.Plumbotectonics: I.The phanerozoic.In: Barnes HL (ed.).Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits.New York: John Wiley, 22-70
|
Dou JZ and Fu S and Zhang HF. 2015. Consolidation and cooling paths of the Guojialing granodiorites in Jiaodong Peninsula:Implication for crustal uplift and exhumation. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(8): 2325-2336 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Fan HR, Hu FF and Yang JH and Zhai MG. 2007. Fluid evolution and large-scale gold metallogeny during Mesozoic tectonic transition in the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. In:Zhai MG, Windley BF, Kusky TM and Meng QM (eds.).Mesozoic Sub-Continental Lithospheric Thinning Under Eastern Asia.Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 280(1): 303-316 DOI:10.1144/SP280.16 |
Fan WM, Guo F, Wang YJ and Lin G and Zhang M. 2001. Post-orogenic bimodal volcanism along the Sulu orogenic belt in eastern China. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part A:Solid Earth and Geodesy, 26(9-10): 733-746 DOI:10.1016/S1464-1895(01)00123-5 |
Fowler MB, Henney PJ and Darbyshire DPF and Greenwood PB. 2001. Petrogenesis of high Ba-Sr granites:The Rogart pluton, Sutherland. Journal of the Geological Society, 158(3): 521-534 DOI:10.1144/jgs.158.3.521 |
Fuertes-Fuente M, Martin-Izard A and Boiron MC and Viñuela JM. 2000. P-T path and fluid evolution in the Franqueira granitic pegmatite, Central Galicia, northwestern Spain. The Canadian Mineralogist, 38(5): 1163-1175 DOI:10.2113/gscanmin.38.5.1163 |
Gao S, Rudnick RL, Carlson RW and McDonough WF and Liu YS. 2002. Re-Os evidence for replacement of ancient mantle lithosphere beneath the North China Craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 198(3-4): 307-322 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00489-2 |
Gao S, Zhang JF and Xu WL and Liu YS. 2009. Delamination and destruction of the North China Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(19): 3367-3378 |
Geng K, Wang RJ, Li HK and Shan W and Li DP. 2015. Zircon SHRIMP age of diorite-porphyrite in Beijie gold deposit from the northwest Jiaodong area and its geological implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(6): 1099-1107 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Goldfarb RJ and Santosh M. 2014. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits:Are they unique?. Geoscience Frontiers, 5(2): 139-153 DOI:10.1016/j.gsf.2013.11.001 |
Goss SC, Wilde SA and Wu FY and Yang JH. 2010. The age, isotopic signature and significance of the youngest Mesozoic granitoids in the Jiaodong Terrane, Shandong Province, North China Craton. Lithos, 120(3-4): 309-326 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.019 |
Groves DI, Santosh M, Deng J, Wang QF and Yang LQ and Zhang L. 2020. A holistic model for the origin of orogenic gold deposits and its implications for exploration. Mineralium Deposita, 55(2): 275-292 DOI:10.1007/s00126-019-00877-5 |
Guo CY, Zhang WZ, Ge LS, Qing M and Gao BF and Xia R. 2011. Estimation on mineralization depth and erosion of gold deposits in the northwestern area of Jiaodong Peninsula. Metal Mine, 40(8): 112-115 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Harris NBW and Pearce JA and Tindle AG. 1986. Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism. In:Coward MP and Ries AC (eds.).Collision Tectonics.Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 19(1): 67-81 DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1986.019.01.04 |
He YS, Li SG, Hoefs J, Huang F and Liu SA and Hou ZH. 2011. Post-collisional granitoids from the Dabie orogen:New evidence for partial melting of a thickened continental crust. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(13): 3815-3838 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2011.04.011 |
Hou ML, Jiang YH, Jiang SY and Ling HF and Zhao KD. 2007. Contrasting origins of Late Mesozoic adakitic granitoids from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, East China:Implications for crustal thickening to delamination. Geological Magazine, 144(4): 619-631 DOI:10.1017/S0016756807003494 |
Jahn BM, Wu FY and Lo CH and Tsai CH. 1999. Crust-mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust:Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from post-collisional mafic-ultramafic intrusions of the northern Dabie complex, central China. Chemical Geology, 157(1-2): 119-146 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00197-1 |
Jiang N, Chen JZ and Guo JH and Chang GH. 2012. In situ zircon U-Pb, oxygen and hafnium isotopic compositions of Jurassic granites from the North China craton:Evidence for Triassic subduction of continental crust and subsequent metamorphism-related 18O depletion. Lithos, 42-143: 84-94 |
Jiang XH, Fan HR, Hu FF, Yang KF, Lan TG and Zheng XL and Jin NX. 2011. Comparative studies on fluid inclusion in different depths and ore genesis of the Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(5): 1327-1340 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li JW, Vasconcelos P, Zhou MF and Zhao XF and Ma CQ. 2006. Geochronology of the Pengjiakuang and Rushan gold deposits, eastern Jiaodong gold province, northeastern China:Implications for regional mineralization and geodynamic setting. Economic Geology, 101(5): 1023-1038 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.101.5.1023 |
Li SX, Liu CC, An YH, Wang WC and Huang TL and Yang CH. 2007. Geology of Gold Deposits in Jiaodong. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-423 (in Chinese)
|
Li SZ, Zhao GC, Santosh M, Liu X, Dai LM, Suo YH, Tam PY and Song MC and Wang PC. 2012. Paleoproterozoic structural evolution of the southern segment of the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 200-203: 59-73 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.01.007 |
Liu FC, Lu ZX, Fan YX and Kong QC and Gong RT. 1984. Discussion on the relationship between mafic dyke and mineralization in Linglong gold deposit. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, (4): 37-45 (in Chinese) |
Liu S, Hu RZ, Gao S, Feng CX, Yu BB, Qi YQ, Wang T and Feng GY and Coulson IM. 2009. Zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of adakitic volcanic rocks from Jiaodong, Shandong Province, eastern China:Constraints on petrogenesis and implications. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(5): 445-458 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.02.008 |
Liu SA, Li SG and He YS and Huang F. 2010. Geochemical contrasts between Early Cretaceous ore-bearing and ore-barren high-Mg adakites in central-eastern China:Implications for petrogenesis and Cu-Au mineralization. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(24): 7160-7178 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2010.09.003 |
Liu Y, Deng J, Wang ZL, Zhang L, Zhang C, Liu XD and Zheng XL and Wang XD. 2014. Zircon U-Pb age, Lu-Hf isotopes and petrogeochemistry of the monzogranites from Xincheng gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2559-2573 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Lou YE and Du YS. 2006. Characteristics and genesis of biotites from the Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Fanchang-Tongling area, Anhui Province. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 26(2): 175-180 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Luo XD, Yang XY and Duan LA and Sun WD. 2014. Geochemical and geochronological study of the gold-related Guojialing pluton and Shangzhuang pluton in Jiaobei block. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(10): 1874-1888 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Luo ZK and Guan K and Miao LC. 2001. Discussion on the relationship between lamprophyre veins and mineralization in Linglong gold deposit from Jiaodong. Gold Geology, 7(4): 15-21 (in Chinese) |
Ma L, Jiang SY, Dai BZ, Jiang YH, Hou ML and Pu W and Xu B. 2013. Multiple sources for the origin of Late Jurassic Linglong adakitic granite in the Shandong Peninsula, eastern China:Zircon U-Pb geochronological, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence. Lithos, 162-163: 251-263 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.01.009 |
Ma L, Jiang SY, Hofmann AW, Dai BZ, Hou ML, Zhao KD, Chen LH and Li JW and Jiang YH. 2014. Lithospheric and asthenospheric sources of lamprophyres in the Jiaodong Peninsula:A consequence of rapid lithospheric thinning beneath the North China Craton?. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 124: 250-271 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2013.09.035 |
Martin H. 1999. Adakitic magmas:Modern analogues of Archaean granitoids. Lithos, 46(3): 411-429 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00076-0 |
Martin H, Smithies RH, Rapp R and Moyen JF and Champion D. 2005. An overview of adakite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG), and sanukitoid:Relationships and some implications for crustal evolution. Lithos, 79(1-2): 1-24 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.04.048 |
Menzies MA and Fan WM and Zhang M. 1993. Palaeozoic and Cenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of >120km of Archaean lithosphere, Sino-Korean craton, China. In:Prichard HM, Alabaster T, Harris NBW and Neary CR (eds.).Magmatic Processes and Plate Tectonics.Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 76(1): 71-81 |
Middlemost EAK. 1994. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth-Science Reviews, 37(3-4): 215-224 DOI:10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9 |
Morrison GW. 1980. Characteristics and tectonic setting of the shoshonite rock association. Lithos, 13(1): 97-108 |
Pearce JA and Harris NBW and Tindle AG. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983 DOI:10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 |
Peng TP, Wilde SA and Fan WM and Peng BX. 2013. Late Neoarchean potassic high Ba-Sr granites in the Taishan granite-greenstone terrane:Petrogenesis and implications for continental crustal evolution. Chemical Geology, 344: 23-41 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.02.012 |
Sai SX, Zhao TM, Wang ZL and Huang SY and Zhang L. 2016. Petrogenesis of Linglong biotite granite:Constraints from mineralogical characteristics. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2477-2493 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Santosh M. 2010. Assembling North China Craton within the Columbia supercontinent:The role of double-sided subduction. Precambrian Research, 178(1-4): 149-167 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2010.02.003 |
Shen K, Hu SX, Sun JG, Ling HF and Zhao YY and Sun MZ. 2000. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit in eastern Shandong, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 16(4): 542-550 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Song MC and Wang PC. 2003. Regional Geology of Shandong Province. Jinan: Shandong Map Publishing House, 1-970 (in Chinese)
|
Song MC, Deng J, Yi PH, Yang LQ, Cui SX, Xu JX, Zhou ML, Huang TL and Song GZ and Song YX. 2014. The kiloton class Jiaojia gold deposit in eastern Shandong Province and its genesis. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(3): 801-824 DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.12239 |
Song MC, Li SZ, Yi PH, Cui SX, Xu JX, Lv GX, Song YX, Jiang HL, Zhou ML, Zhang PJ, Huang TL and Liu CC and Liu DH. 2014. Classification and metallogenic theory of the Jiaojia-style gold deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 44(1): 87-104 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Song MC, Li SZ, Santosh M, Zhao SJ, Yu S, Yi PH, Cui SX, Lv GX, Xu JX and Song YX and Zhou ML. 2015. Types, characteristics and metallogenesis of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern North China Craton. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 612-625 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.06.019 |
Song MC, Zhang JJ, Zhang PJ, Yang LQ, Liu DH and Ding ZJ and Song YX. 2015. Discovery and tectonic-magmatic background of superlarge gold deposit in offshore of northern Sanshandao, Shandong Peninsula, China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(2): 365-383 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Song MC, Wang SS, Yang LX, Li J and Li SY and Ding ZJ. 2017. Metallogenic epoch of nonferrous metallic and silver deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China and its geological significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(4): 1305-1325 DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.13363 |
Song MC, Li J, Li SY, Ding ZJ, Tan XF and Zhang ZL and Wang SJ. 2018. Late Mesozoic thermal upwelling-extension structure and its dynamics back-ground in eastern Shandong Province. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 48(4): 941-964 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Song MC, Zhou JB, Song YX, Wang B, Li SY and Li J and Wang SS. 2019. Mesozoic Weideshan granitoid suite and its relationship to large-scale gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Geological Journal DOI:10.1002/gj.3607 |
Song MC, Song YX, Ding ZJ, Wei XF, Sun SL, Song GZ, Zhang JJ and Zhang PJ and Wang YG. 2019. The discovery of the Jiaojia and the Sanshandao giant gold deposits in Jiaodong Peninsula and discussion on the relevant issues. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 43(1): 92-110 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Song MC, Zhou JB, Lin SY, Li J, Li SY, Song YX and Wang B and Liu PR. 2020a. The tectonic affinity of the Meso-Neoproterozoic low-grade metamorphic mafic rocks in the northern margin of the Sulu UHP metamorphic belt and its tectonic significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(2): 315-332 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2020.02.01 |
Song MC, Li J, Zhou JB, Song YX, Li SY, Wang B and Ding ZJ and Zhang ZL. 2020b. The discovery and tectonic setting of the early cretaceous high-Mg diorites in the Jiaodong Peninsula. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(1): 279-296 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2020.01.22 |
Song SG, Niu YL, Wei CJ and Ji JQ and Su L. 2010. Metamorphism, anatexis, zircon ages and tectonic evolution of the Gongshan block in the northern Indochina continent:An eastern extension of the Lhasa Block. Lithos, 120(3-4): 327-346 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.021 |
Song YX, Song MC, Ding ZJ, Wei XF, Xu SH, Li J, Tan XF, Li SY, Zhang ZL, Jiao XM and Hu H and Cao J. 2017. Major advances on deep prospecting in Jiaodong gold ore cluster and its metallogenic characteristics. Gold Science and Technology, 25(3): 4-18 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun JG, Hu SS and Ling HF and Ye Y. 2000. Element geochemistry and origin of high potassic-potassic dike rocks in two types of goldfields in Northwest Jiaodong, Shandong, China. Geochimica, 29(2): 143-152 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun SS and McDonough WF.1989.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes.In: Sanders AD and Norry MJ (eds.).Magmatism in Ocean Basins.Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345
|
Sun WD, Ding X and Hu YH and Li XH. 2007. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the West Pacific. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 262(3-4): 533-542 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.08.021 |
Tam PY, Zhao GC, Liu FL, Zhou XW and Sun M and Li SD. 2011. Timing of metamorphism in the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt:New SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of granulites, gneisses and marbles of the Jiaobei massif in the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 19(1): 150-162 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.05.007 |
Tan J, Wei JH, Yang CF, Feng B and Tan WJ and Guo DZ. 2006. Geochemstry and tectonic setting of dikes in the Guocheng area, Jiaodong Peninsula. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(8): 1177-1188 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Tan J, Wei JH, Guo LL, Zhang KQ, Yao CL and Lu JP and Li HM. 2008. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and phenocryst EPMA of dikes, Guocheng, Jiaodong Peninsula:Implications for North China Craton lithosphere evolution. Science in China (Series D), 51(10): 1483-1500 DOI:10.1007/s11430-008-0079-3 |
Tan J, Wei JH and Audétat A and Pettke T. 2012. Source of metals in the Guocheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China Craton:Link to Early Cretaceous mafic magmatism originating from Paleoproterozoic metasomatized lithospheric mantle. Ore Geology Reviews, 48: 70-87 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.02.008 |
Wang LG, Qiu YM, McNaughton NJ, Groves DI, Luo ZK, Huang JZ and Miao LC and Liu YK. 1998. Constraints on crustal evolution and gold metallogeny in the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China, from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon studies of granitoids. Ore Geology Reviews, 13(1-5): 275-291 DOI:10.1016/S0169-1368(97)00022-X |
Wang ZL, Gong QJ, Sun X and Wu FF and Wang WX. 2012. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology of quartz porphyry from the Niutougou gold deposit in Songxian County, Henan Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(2): 370-382 DOI:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2012.00666.x |
Wang ZL, Yang LQ, Deng J, Santosh M, Zhang HF, Liu Y, Li RH, Huang T and Zheng XL and Zhao H. 2014. Gold-hosting high Ba-Sr granitoids in the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, East China:Petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 95: 274-299 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.03.001 |
Wang ZL, Zhao RX, Zhang Q, Lu HW and Li JL and Cheng W. 2014. Magma mixing for the high Ba-Sr Guojialing-type granitoids in Northwest Jiaodong Peninsula:Constraints from petrogeochemistry and Sr-Nd isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2595-2608 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wyllie PJ and Cox KG and Biggar GM. 1962. The habit of apatite in synthetic systems and igneous rocks. Journal of Petrology, 3(2): 238-243 DOI:10.1093/petrology/3.2.238 |
Xu XS, Fan QC, O'Reilly SY, Jiang SY, Griffin WL and Wang RC and Qiu JS. 2004. U-Pb dating of zircons from quartz diorite and its enclaves at Tongguanshan in Anhui and its petrogenetic implication. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(19): 2073-2082 DOI:10.1360/04wd0137 |
Xu YG, Li HY and Pang CJ and He B. 2009. On the timing and duration of the destruction of the North China Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(19): 3379-3396 |
Yan YT, Zhang N and Li SR and Li YS. 2014. Mineral chemistry and isotope geochemistry of pyrite from the Heilangou gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Geoscience Frontiers, 5(2): 205-213 DOI:10.1016/j.gsf.2013.05.003 |
Yang JH, Zhu MF and Liu W and Zhai MG. 2003. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Guojialing granodiorites from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 19(4): 692-700 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang JH, Chung SL and Zhai MG and Zhou XH. 2004. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of mafic dikes from the Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Evidence for vein-plus-peridotite melting in the lithospheric mantle. Lithos, 73(3-4): 145-160 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2003.12.003 |
Yang K, Wang JP, Lin JZ, Zheng JX and Yang GZ and Ji H. 2012. Petrogeochemical characteristics and genetic significance of the Aishan pluton in Jiaodong Peninsula. Geology and Exploration, 48(4): 693-703 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang KF, Fan HR, Santosh M, Hu FF, Wilde SA, Lan TG and Lu LN and Liu YS. 2012. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust:Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of Late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong terrane, the North China Craton. Lithos, 146-147: 112-127 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.035 |
Yang LQ, Deng J and Wang QF and Zhou YH. 2006. Coupling effects on gold mineralization of deep and shallow structures in the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(3): 400-411 DOI:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2006.tb00257.x |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Zhang J, Guo CY, Gao BF, Gong QJ, Wang GF and Jiang SQ and Yu HJ. 2008. Decrepitation thermometry and compositions of fluid inclusions of the Damoqujia gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China:Implications for metallogeny and exploration. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 19(4): 378-390 DOI:10.1016/S1002-0705(08)60071-0 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Guo CY, Zhang J, Jiang SQ, Gao BF and Gong QJ and Wang QF. 2009. Ore-forming fluid characteristics of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Gold Province, China. Resource Geology, 59(2): 181-193 DOI:10.1111/j.1751-3928.2009.00089.x |
Yang LQ and Badal J. 2013. Mirror symmetry of the crust in the oil/gas region of Shengli, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 78: 327-344 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.05.001 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Goldfarb RJ, Zhang J and Gao BF and Wang ZL. 2014. 40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the formation of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit:New implications for timing and duration of hydrothermal activity in the Jiaodong gold province, China. Gondwana Research, 25(4): 1469-1483 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.001 |
Yang LQ, Deng J and Wang ZL.2014.Ore-controlling structural pattern of Jiaodong gold deposits: Geological-geophysical integration constraints.In: Chen YT, Jin ZM, Shi YL, Yang WC and Zhu RX (eds.).The Deep-Seated Structures of Earth in China.Beijing: Sciences Press, 1006-1030 (in Chinese)
|
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Zhang L, Goldfarb RJ, Yuan WM and Weinberg RF and Zhang RZ. 2016a. Thermochronologic constraints on evolution of the Linglong Metamorphic Core Complex and implications for gold mineralization:A case study from the Xiadian gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 72(1): 165-178 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.006 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Guo LN, Li RH, Groves DI, Danyushevsky LV, Zhang C and Zheng XL and Zhao H. 2016b. Relationships between gold and pyrite at the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Implications for gold source and deposition in a brittle epizonal environment. Economic Geology, 111(1): 105-126 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.111.1.105 |
Yang LQ, Li RH, Gao X, Qiu KF and Zhang L. 2020. A preliminary study of extreme enrichment of critical elements in the Jiaodong gold deposits, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(5): 1285-1314 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.01 |
Ye HM, Li XH and Li ZX and Zhang CL. 2008. Age and origin of high Ba-Sr appinite-granites at the northwestern margin of the Tibet Plateau:Implications for Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Western Kunlun orogenic belt. Gondwana Research, 13(1): 126-138 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2007.08.005 |
Yu L, Wang QF and Li GJ and Gao L. 2015. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology of granitic pegmatites from Caojian area in the northern Baoshan block, and their geological significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(11): 3281-3296 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai MG and Yang JH and Liu WJ. 2001. Large clusters of gold deposits and large-scale metallogenesis in the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Science in China (Series D), 44(8): 758-768 DOI:10.1007/BF02907205 |
Zhai MG and Santosh M. 2013. Metallogeny of the North China Craton:Link with secular changes in the evolving Earth. Gondwana Research, 24(1): 275-297 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.02.007 |
Zhang HF, Gao S, Zhong ZQ, Zhang BR and Zhang L and Hu SH. 2002. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of Cretaceous granitoids:Constraints on tectonic framework and crustal structure of the Dabieshan ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic belt, China. Chemical Geology, 186(3-4): 281-299 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00006-2 |
Zhang HF, Li SR and Zhai MG and Guo JH. 2006. Crust uplift and its implications in the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(2): 285-295 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang J, Zhao ZF and Zheng YF and Dai MN. 2010. Post-collisional magmatism:Geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids in the Sulu orogen, China. Lithos, 119(3-4): 512-536 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.005 |
Zhang L, Weinberg RF, Yang LQ, Groves DI, Sai SX, Matchan E, Phillips D, Kohn BP, Miggins DP and Liu Y and Deng J. 2020. Mesozoic orogenic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China:A focused event at 120±2Ma during cooling of Pregold granite intrusions. Economic Geology, 115(2): 415-441 DOI:10.5382/econgeo.4716 |
豆敬兆, 付顺, 张华锋. 2015. 胶东郭家岭岩体固结冷却轨迹与隆升剥蚀. 岩石学报, 31(8): 2325-2336. |
耿科, 王瑞江, 李洪奎, 单伟, 李大鹏. 2015. 胶西北地区北截金矿闪长玢岩锆石SHRIMP年龄及其地质意义. 地质学报, 89(6): 1099-1107. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.06.008 |
郭春影, 张文钊, 葛良胜, 卿敏, 高帮飞, 夏锐. 2011. 胶东西北部金矿形成深度与剥蚀程度概略评价. 金属矿山, 40(8): 112-115. |
姜晓辉, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨奎锋, 蓝廷广, 郑小礼, 金念宪. 2011. 胶东三山岛金矿中深部成矿流体对比及矿床成因. 岩石学报, 27(5): 1327-1340. |
李士先, 刘长春, 安郁宏, 王为聪, 黄太岭, 杨承海. 2007. 胶东金矿地质. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-423.
|
刘辅臣, 卢作祥, 范永香, 孔庆存, 宫润潭. 1984. 玲珑金矿中基性脉岩与矿化关系探讨. 地球科学(武汉地质学院学报), (4): 37-45. |
刘跃, 邓军, 王中亮, 张良, 张潮, 刘向东, 郑小礼, 王旭东. 2014. 胶西北新城金矿床二长花岗岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及Lu-Hf同位素组成. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2559-2573. |
楼亚儿, 杜杨松. 2006. 安徽繁昌-铜陵中生代侵入岩的黑云母特征和成因探讨. 矿物学报, 26(2): 175-180. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2006.02.010 |
罗贤冬, 杨晓勇, 段留安, 孙卫东. 2014. 胶北地块与金成矿有关的郭家岭岩体和上庄岩体年代学及地球化学研究. 地质学报, 88(10): 1874-1888. |
罗振宽, 关康, 苗来成. 2001. 胶东玲珑金矿田煌斑岩脉与成矿关系的讨论. 黄金地质, 7(4): 15-21. |
赛盛勋, 赵天明, 王中亮, 黄锁英, 张良. 2016. 玲珑黑云母花岗岩成因:矿物学特征约束. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2477-2493. |
沈昆, 胡受奚, 孙景贵, 凌洪飞, 赵懿英, 孙明志. 2000. 山东招远大尹格庄金矿成矿流体特征. 岩石学报, 16(4): 542-550. |
宋明春, 王沛成. 2003. 山东省区域地质. 济南: 山东省地图出版社, 1-970.
|
宋明春, 李三忠, 伊丕厚, 崔书学, 徐军祥, 吕古贤, 宋英昕, 姜洪利, 周明岭, 张丕建, 黄太岭, 刘长春, 刘殿浩. 2014. 中国胶东焦家式金矿类型及其成矿理论. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44(1): 87-104. |
宋明春, 张军进, 张丕建, 杨立强, 刘殿浩, 丁正江, 宋英昕. 2015. 胶东三山岛北部海域超大型金矿床的发现及其构造-岩浆背景. 地质学报, 89(2): 365-383. |
宋明春, 李杰, 李世勇, 丁正江, 谭现锋, 张照录, 王世进. 2018. 鲁东晚中生代热隆-伸展构造及其动力学背景. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 48(4): 941-964. |
宋明春, 宋英昕, 丁正江, 魏绪峰, 孙绍立, 宋国政, 张军进, 张丕建, 王永国. 2019. 胶东焦家和三山岛巨型金矿床的发现及有关问题讨论. 大地构造与成矿学, 43(1): 92-110. |
宋明春, 周建波, 林少一, 李杰, 李世勇, 宋英昕, 王斌, 刘鹏瑞. 2020a. 苏鲁超高压变质带北缘古-新元古代浅变质基性岩的构造属性及其意义. 岩石学报, 36(2): 315-332. |
宋明春, 李杰, 周建波, 宋英昕, 李世勇, 王斌, 丁正江, 张照录. 2020b. 胶东早白垩世高镁闪长岩类的发现及其构造背景. 岩石学报, 36(1): 279-296. |
宋英昕, 宋明春, 丁正江, 魏绪峰, 徐韶辉, 李杰, 谭现峰, 李世勇, 张照录, 焦秀美, 胡弘, 曹佳. 2017. 胶东金矿集区深部找矿重要进展及成矿特征. 黄金科学技术, 25(3): 4-18. |
孙景贵, 胡受奚, 凌洪飞, 叶瑛. 2000. 胶西北两类金矿田的高钾-钾质脉岩元素地球化学与成岩作用研究. 地球化学, 29(2): 143-152. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2000.02.006 |
谭俊, 魏俊浩, 杨春福, 冯波, 谭文娟, 郭大招. 2006. 胶东郭城地区脉岩类岩石地球化学特征及成岩构造背景. 地质学报, 80(8): 1177-1188. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.08.011 |
王中亮, 赵荣新, 张庆, 鲁辉武, 李京濂, 程蔚. 2014. 胶西北高Ba-Sr郭家岭型花岗岩岩浆混合成因:岩石地球化学与Sr-Nd同位素约束. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2595-2608. |
杨进辉, 朱美妃, 刘伟, 翟明国. 2003. 胶东地区郭家岭花岗闪长岩的地球化学特征及成因. 岩石学报, 19(4): 692-700. |
杨宽, 王建平, 林进展, 郑加行, 杨国志, 吉海. 2012. 胶东半岛艾山岩体岩石地球化学特征及成因意义. 地质与勘探, 48(4): 693-703. |
杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮.2014.胶东金矿控矿构造样式: 地质-地球物理综合约束.见: 陈运泰, 金振民, 石耀霖, 杨文采, 朱日祥编.中国大陆地球深部结构与动力学研究——庆贺滕吉文院士从事地球物理研究60周年.北京: 科学出版社, 1006-1030
|
杨立强, 李瑞红, 高雪, 邱昆峰, 张良. 2020. 胶东金矿床中关键金属超常富集特征与机理初探. 岩石学报, 36(5): 1285-1314. |
禹丽, 王庆飞, 李龚健, 高磊. 2015. 保山地块漕涧花岗伟晶岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 31(11): 3281-3296. |
翟明国, 刘文军, 杨进辉. 2001. 胶东大型黄金矿集区及大规模成矿作用. 中国科学(D辑), 31(7): 545-552. |
张华锋, 李胜荣, 翟明国, 郭敬辉. 2006. 胶东半岛早白垩世地壳隆升剥蚀及其动力学意义. 岩石学报, 22(2): 285-295. |
 2020, Vol. 36
2020, Vol. 36