2. 自然资源部地球化学探测重点实验室, 中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所, 廊坊 065000
2. Key Laboratory of Geochemical Exploration, Ministry of Natural Resources, Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China
关键金属(Critical Metals)和关键矿产资源(Critical Minerals)是国际上近年新提出的资源概念,是指对新能源、新材料、信息技术等新兴产业和国防军工等行业,具有不可替代重大用途的一类元素及其矿床的总称(Gulley et al., 2018)。这些元素绝大部分都属于稀有元素(如Li、Be、Rb、Cs、Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf、W、Sn等)、稀土元素(La、Ce、Pr、Nd、Sm、Eu、Gd、Tb、Dy、Ho、Er、Tm、Yb、Lu、Sc、Y)、稀散元素(Ga、Ge、Se、Cd、In、Te、Re、Tl)和部分稀少稀贵元素(PGE、Cr、Co等)(蒋少涌等,2019;翟明国等,2019)。由于我国锑、铋和砷资源在世界上占有绝对优势,As、Sb和Bi三种元素未被归入上述“四稀”元素,但国际上许多学者认为它们均属于关键金属(Gunn,2014;Mudd et al., 2017),因此本文将其列为其它关键元素一并讨论(图 1)。

|
图 1 根据相对供应风险指数(BGS, 2015)用元素周期表所示的关键元素(据Mudd et al., 2017) 图中颜色代表相对供应风险指数:红色=8.5~10.0;橙色=7.5~8.5;黄色=6.0~7.5;浅黄色=5.0~6.0 Fig. 1 The extent of critical elements represented by the periodic table of elements (after Mudd et al., 2017) by using the recent BGS Risk List (BGS, 2015) Colours adapted from the BGS (2015) relative supply risk index: red=8.5~10; orange=7.5~8.5; yellow=6~7.5; light yellow 5~6 |
造山型金矿床是全球已探明金资源储量最多的金矿床类型(Weatherley and Henley, 2013),它们大多具有类似的微量元素异常组合,其中有许多为关键金属(Goldfarb et al., 2016, 2017),然而目前对该类型金矿床的工业开采一般只考虑其含金量。而随着对关键金属需求的急剧增大,亟需综合利用其中的关键金属;尤其是当某些关键金属的供应受控于一个国家时,可能导致其它国家将不得不开发某些特定中-小型金矿床中的高品位关键金属(Gunn,2014)。因此,深入了解造山型金矿床中关键金属资源的历史和现状,揭示其富集特征和利用趋势已成为迫在眉睫的重大战略任务。
胶东是当今世界仅有的探明金资源储量超过5000吨的三个金矿省之一,该区已发现金矿床150余处,以不足全国0.2%的陆地面积孕育中国约1/3的探明金矿资源储量(截至2018年底,中国累计查明金矿资源储量为13638.40吨)(Ministry of Natural Resources, PRC, 2019)。胶东也是全球唯一已知发育于前寒武纪变质地体内的晚中生代巨型金矿省,其内金矿床赋存于新太古代-古元古代角闪岩相等高级变质地体中,金成矿作用发生于约120Ma、晚于围岩约2000Ma(Deng et al., 2003, 2015a, 2020a;Yang et al., 2014, 2017;杨立强等,2014a)。它独特的地质背景与金成矿系统蕴含全球意义的科学问题,使其成为检验造山型金矿床成矿新理论和新模型的关键地区(Goldfarb et al., 2019;Groves et al., 2020)。同时,胶东也是我国最重要的黄金基地,其采金最早始于春秋时期,两千多年以来几乎始终完全是为了开采其中的黄金(公元1078年胶东黄金年产量即占全国总产量的89.5%,且自1976年以来其黄金年产量连续位居全国第一)。长期以来,科学家们对胶东金矿床开展了大量研究(参见翟明国等, 2001, 2004;Mao et al., 2003, 2011;Chen et al., 2005;Deng et al., 2006, 2017a, 2018, 2019;Yang et al., 2007, 2016a;杨立强等, 2014b, 2019;Zhu et al., 2015;Deng and Wang, 2016等综述性论文及其参考文献),但对其中的关键金属尚缺乏专门报道。为提升对胶东金矿床中关键金属资源的认识,本文在简要评述全球造山型金矿床中关键金属基本特征的基础上,剖析了胶东金矿床中关键元素的赋存状态、含量分布与富集特征,初步探讨了关键金属超常富集的特征与机理,提出了亟待深化的研究领域和未来方向。
1 造山型金矿床中关键金属基本特征 1.1 矿物学特征大多数造山型金矿床形成于3~20km深度,通常含2%~5%的金属矿物,以黄铁矿和毒砂为主(Groves et al., 1998;Goldfarb et al., 2005)。然而,在较高的温度下(约>350℃),磁黄铁矿在碎屑变质-沉积岩容矿的造山型金矿床中普遍占主导地位,在相对还原的变质-沉积岩容矿的造山型金矿床中毒砂的含量大于黄铁矿;而在更浅层脆性环境中,锑金矿、辉锑矿、辰砂、锑-铋矿物和砷矿物可作为共/伴生矿物出现,其中作为主要含砷矿物的雄黄和雌黄含量可能比毒砂更高(Li et al., 2014, 2015, 2020;Yang et al., 2016b, c)。此外,白钨矿在许多造山型金矿床中常见,且往往被视为成矿早阶段形成的热液矿物(杨立强等, 2010, 2011a, b)。
值得指出的是,多种碲(主要包括含金、银、铋、铅和钯的碲化物)矿物在造山型金矿床中普遍存在,尤其是中-酸性侵入岩容矿的造山型金矿床往往发育大量碲矿物(Mériaud and Jébrak,2017)。然而,尽管大部分被开采的金矿石中有含金的碲矿物,但这些高浓度的碲迄今仍未被回收利用(Goldfarb et al., 2017)。
1.2 金属迁移与沉淀近年来,对巨型矿床/区岩石圈尺度的研究表明,某些类型的岩浆在穿过大陆岩石圈地幔时,会萃取成矿组分(如金刚石、金和铂族元素等),沿岩石圈块体边缘的世界级矿床可能是有利于岩浆-流体汇聚的上地壳和与地幔交代作用有关的下地壳耦合的产物(Fiorentini et al., 2018),即巨型矿床的形成受控于岩石圈结构与组成。对不同规模和成矿背景的造山型金矿床的对比研究结果显示,不同于较小的矿床,巨型矿床的形成可能需要更广泛的物源区和特定的成矿过程(Selvaraja et al., 2017)。尤其是关键元素以地壳丰度低(稀)、共/伴生产出(伴)和赋存矿物颗粒细小(细)为主要特征,增加了认识其超常富集成矿的难度(翟明国等,2019);因此,亟需按成矿系统的思路,将成矿作用的始、终态和成矿过程紧密结合,对金属的源、运、聚及其岩石圈结构与组成的控制等开展系统研究。
1.2.1 金属萃取与迁移硅酸盐熔体中贵金属浓度长期被认为由硫化物的矿物稳定性控制,只有硫化物不饱和的岩浆才能从地幔中萃取大量金属(Mungall,2002);然而对玄武岩和安山岩玻璃的系列实验发现,在相对氧化的、硫化物饱和的地幔环境中,金属可以硫化物的形式溶解在硅酸盐熔体中,形成富金属岩浆(Botcharnikov et al., 2011)。而Au-Bi-Na-Cl-S-H-O系统300~450℃的计算模拟表明,熔体中金的浓度比与其共存流体中的金高几个数量级,即含金熔体可能比非饱和流体的成矿贡献更大,也说明成矿流体系统可能包含了大量更复杂的多金属熔体(Tooth et al., 2008)。同时,对印度尼西亚火山喷发后释放的火山熔体和气体中金属浓度的分析表明,金属可以在流体出溶之后、熔体与流体混合过程中加入到成矿流体(Nadeau et al., 2010);而在造山型金矿床中,在最大溶解度以下,金会在硫化物晶格内形成Au-Bi-Te固溶体,在同成矿作用构造变形中进一步富集,从而发育金与碲化物密切共生的现象(李瑞红等,2019)。这些不同于已有成矿模式的成果,为从源区萃取金属的条件及其进入成矿流体时机的研究提供了新的视角。
长期以来,成矿流体中金的迁移形式往往被限定为金的硫-氢和氯络合物,As、Hg、Sb以硫络合物的形式迁移(Deng et al., 2015b;Goldfarb and Groves, 2015; Wang et al., 2015;Yang et al., 2016d, 2017;Guo et al., 2020),成矿流体中的多钨酸盐离子被认为可能对钨的输运起重要作用(Wood and Samson, 2000),而对Te和Bi的输运机制仍存在很大争议。基于成矿与成岩硫化物的微区原位分析数据的对比(Large et al., 2012)、或使用热力学模拟计算不同P-T条件下成矿流体内不同元素的状态(Zhong et al., 2015a),表明除Au之外,流体系统中的Ag、As、Sb、Hg、Mo、W等金属元素也会发生浓度的变化(Pitcairn et al., 2010)。原位X射线吸收光谱和溶解度测量、结合分子动力学和热力学模拟,证明成矿流体中硫的自由基(S31)对金属的来源、聚集和分布有着重要的控制作用(Pokrovski et al., 2015)。此外,在科拉超深钻孔深9052~10744m深度处的石英流体包裹体中,金以纳米颗粒的形式发生了超常富集(Prokofiev et al., 2020);同时,南太平洋纽瓦南热液喷口区黑烟囱流体中发现的胶体金(Gartman et al., 2018)以及澳大利亚Callie金矿床的纳米级金胶体组构和蚀变地质证据(Petrella et al., 2020),证实了长期以来关于金属在热液中经历胶体迁移的假设(Hannington and Garbe-Schönberg,2019)。这些研究成果对金属迁移形式的认识提供了有益补充。
1.2.2 金属沉淀机制关键元素的最大特点是“稀”,它们的地壳丰度很低(一般为10-6级以下),因此需要数百至上万倍的超常富集,才能形成有价值的工业矿床,成矿往往需要十分苛刻的条件和特殊的作用过程(涂光炽等,2004)。尽管近年来对关键元素超常富集过程和成矿机理的研究取得较多重要进展,但是相关问题依然存在,尤其对金矿床中的共/伴生关键元素尚缺乏相关研究,其迁移-超常富集的苛刻条件目前远未得到清晰揭示(Goldfarb et al., 2017)。例如,长期以来的主流观点均将流体沸腾作用视为中-低温热液碲-金矿床中金和银碲化物沉淀的主导机制(Simmons et al., 2005)。然而,基于对三道湾子金矿床精细矿物学研究的热力学模拟和计算发现,流体沸腾作用不能导致金和银碲化物的沉淀,反而可促使其发生进一步溶解。而导致其发生沉淀的主要机制为:(1)从碱性岩浆中形成的含H2Te的气体组分通过凝结作用与大气降水为主导的成矿流体混合(αHTe(aq)-升高),可直接导致热液体系中大量的金和银呈碲化物的形式沉淀;(2)围岩发生的大量硫化作用(黄铁矿的形成)(αHS(aq)-降低)可以破坏金和银的硫络合物迁移,进而促使其发生大量沉淀(Zhai et al., 2018)。这些不同于已有成矿模式的成果,为流体中关键金属沉淀机制的研究提供了新的视角。
综上可见,关键元素的源区性质与萃取作用、在流体中的运移过程和沉淀机制等对其富集起控制作用。而随着对关键金属需求的持续增长,作为沟通成矿系统源-运-储的核心与纽带,成矿流体性质与演化被视为造山型金矿床中共/伴生关键金属可能被回收需要考虑的终极控制因素(Goldfarb et al., 2016)。
1.3 关键金属资源受控于类似的成矿流体系统的地球化学性质和金属输运及沉淀的物理化学条件,大多数造山型金矿床特征的元素组合是Ag-Au-As-Bi-Sb-Te-W-B±Hg(图 2),其中Te和W分别属于稀散和稀有元素,As、Sb和Bi属于其它关键元素(Goldfarb et al., 2016)。
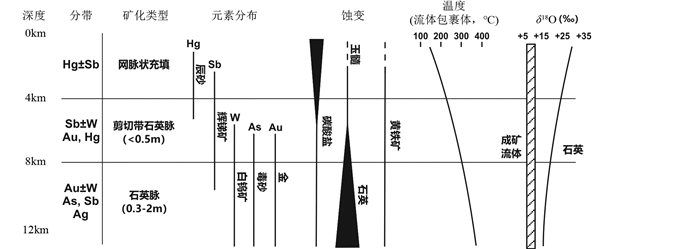
|
图 2 加拿大科迪勒拉造山型金矿床和相关矿床的垂直分带(据Nesbitt et al., 1989) Fig. 2 Summary of vertical zoning in orogenic gold and related deposits in the Canadian Cordillera, showing changes in mineralization style, mineralogy/geochemistry, and oxygen isotope composition of metalliferous quartz with changing depth and fluid temperature (after Nesbitt et al., 1989) Significant concentrations of As and W characterize many mesozonal and hypozonal orogenic gold deposits, whereas along many deep crustal faults in Cordilleran orogens, the vein systems are Sb rich at shallower levels and Hg rich at shallowest levels |
砷是许多造山型金矿床中含量最丰富的关键元素,特别是在含毒砂的中、深成环境中。20世纪90年代早期,加纳的Ashanti和Bogosu金矿床开采的副产品中发现了少量的砷(Edelstein,1995)。该时期,世界上最大的砷生产商是位于法国中部山区的Salisgne金矿床,共产出近40万吨砷(Demange et al., 2006)。然而,由于与砷有关的环境问题和对砷的需求有限,目前大多数国家很少将造山型金矿床中伴生的砷作为潜在的砷资源。但是,2012年全球超过50%的砷是在中国的含金硫化矿石焙烧过程中被回收的(http://mcgroup.co.uk/researches/arsenic),它们大部分来自川西浅成造山型或类卡林型金矿床中的雄黄和雌黄(Goldfarb et al., 2014)。
锑是在浅成造山型金矿床中被发现的(Goldfarb et al., 2005)。在许多情况下,古代的小型锑矿床现在是开采更大的造山型金矿床的场所(Bortnikov et al., 2010)。中国约占全球15000吨锑年产量的90%(Gunn,2014),其中大部分来自世界上最大的锑产地——已有500多年采矿历史的江南造山带中的锡矿山锑矿床(胡瑞忠等,2016)。尽管目前尚不清楚该矿床是属于类卡林型矿床,还是形成于比区域造山型金矿床略浅的浅成锑矿床(Goldfarb et al., 2014);但全球许多浅成造山型金矿区蕴藏着大量的锑矿资源,当这两种金属出现在同一脉系中则形成金锑矿床。而这些矿床的赋矿围岩都是碳酸盐建造,似乎暗示碳酸盐建造容矿的浅成造山型金锑矿区可能是未来最重要的锑资源接替区。
在造山型金矿床的开采历史上也发现了钨,特别是白钨矿。显生宙造山型金矿床多具有金-锑-钨富集特征,如世界上最大的造山型金矿床——Muruntau即显示金-钨之间的强相关性(Uspenskiy and Aleshin, 1993)。但是,由于大型-超大型矽卡岩型和岩浆热液脉型钨矿床的产能完全可以满足世界需求,因此造山型金矿床很少被认为是钨的潜在来源。
众多大型-超大型造山型金矿床有异常高的碲含量,特别是在含金的碲化物矿物中。在Golden Mile这一世界上最大的太古宙造山型金矿床虽然大部分金赋存于富砷的黄铁矿中,但约20%的金赋存于晚期的碲化物矿物中(Bateman and Hagemann, 2004),发育碲汞矿、碲金矿、碲金银矿和碲银矿等19种碲化物矿物;它们以细粒集合体、块状分离体(massive segregations)、与自然金的复合颗粒、黄铁矿和黝铜矿族矿物中的包裹体和共生矿物,以及碳酸盐、石英和电气石中的包裹体的形式出现;具有从内带的碲金矿→碲银矿,再到外带很晚的碲汞矿的明显矿物分带(Mueller and Muhling, 2013)。
世界上最大的古元古代造山型金矿床——加纳的Ashanti,在碲化物-石英-赤铁矿组合中共发现11种碲化物矿物与晚期少量的金在大规模金成矿事件之后聚集成矿。碲化物具有从内带的脉内富碲汞矿集合体、到沿脉壁和围岩中以碲铅矿为主的集合体的分带特征,且晚期碲-金与深成赤铁矿和针铁矿同时形成,反映了成矿流体的冷却过程和相关氧化环境演化(Bowell et al., 1990)。
显生宙造山型金矿床的普遍特征是富含金、银的碲化物矿物大量发育,可能与其围岩中的侵入体为脉型矿床就位提供了有利的容矿构造有关,表明中-酸性侵入岩提供的相对氧化的环境对碲化物的析出起着重要的控制作用(Ivanov et al., 2000)。尤其是俄罗斯和中亚地区许多显生宙造山型金矿床的铂和钯的品位都很高,虽然其中部分可能反映了黑色页岩寄主岩中PGE的高背景,但大部分显然与含碲矿物有关(Distler and Yudovskaya, 2005)。
综上可见,大部分造山型金矿床的开采一般只考虑其含金量,而砷、锑、钨、碲被视为其共/伴生关键金属元素。少部分造山型金矿床已开采砷、钨和锑,但将来它们难以继续提供大量钨;而砷由于环境问题和需求有限,将很少会被视为潜在资源。相反,造山型金矿床中丰富的含碲矿物可能是未来潜在的重要关键金属资源,而碳酸盐建造容矿的浅成造山型金矿区可能是未来最重要的锑资源接替区。
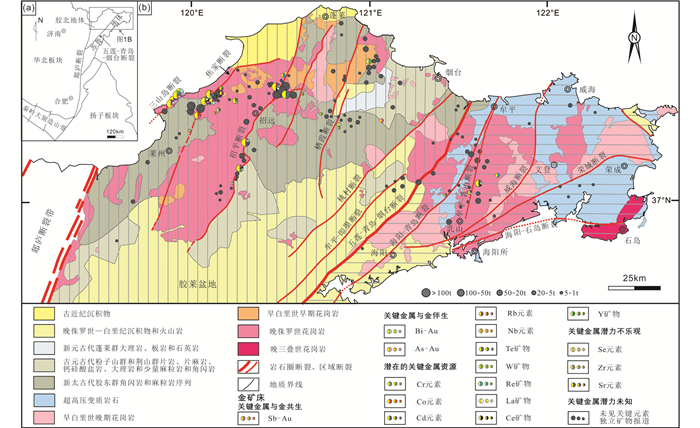
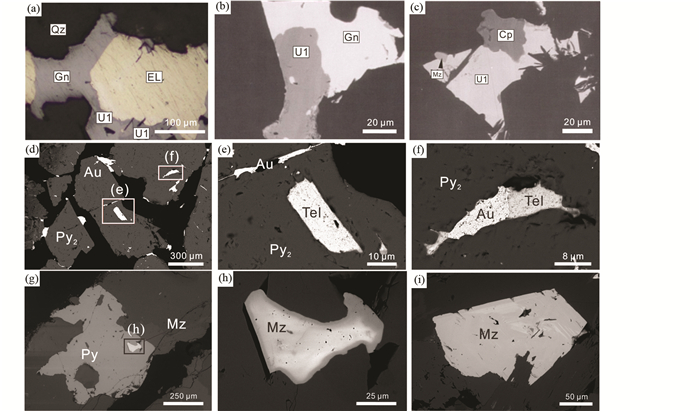
2 胶东金矿床中关键元素赋存状态 2.1 矿物学特征胶东众多金矿床中共/伴生产出的含关键元素的矿物虽然含量较低、颗粒微细、不易被发现,但研究者们仍鉴别出富含稀散元素Te的系列碲化物、富含稀土元素La和Ce的独居石和金红石、富含稀有金属W的白钨矿和黑钨矿等数十种含关键元素矿物(图 3、图 4),报道了它们的产出特征(表 1)。例如,在招莱金矿集区的埠南金矿床中发现了陈国达矿(Ag9FeTe2S4)和一些未定名的硫碲化物,包括Ag16FeBiTe3S8和Ag6TeS2等(谷湘平等,2008)。陈国达矿产于含金-银的黄铜矿-石英脉中,呈半自形-他形粒状与方铅矿、黄铜矿、碲银矿、银金矿、自然银、未定名的Ag16FeBiTe3S8和Ag6TeS2共生,并被自然银和螺状硫银矿包围交代(图 4)。与胶北隆起中的金矿床相比,苏鲁地体中牟乳带金矿床的碲银矿、碲金矿和碲金银矿等含碲矿物更为常见(陈光远等,1989);尤其是在乳山(又名金青顶)金矿床中出现丰富的碲及硫碲化物矿物,如碲金矿、碲银矿、碲金银矿、碲铅矿、碲铜矿、碲铋矿、碲镍矿、碲汞矿、自然碲等呈密切共生的集合体或联生体产出在黄铁矿等硫化物及石英等脉石矿物粒间或裂缝中,还可在含金石英脉和蚀变围岩中见到与石英和黄铁矿等共生的独居石,钾化花岗岩中多发育磷钇矿(孙国曦等,2002;胡文瑄等,2005;刘建朝等,2010)。
|
图 3 胶东金矿床中关键金属资源类型与空间分布简图(据Yang et al., 2017修改) 详细描述见表 1和表 3及正文说明 Fig. 3 Simplified geological map of the Jiaodong gold province showing the distribution of reported minerals and contents of critical elements in gold deposits (modified after Yang et al., 2017) |
|
图 4 胶东典型金矿床中稀散元素Te的载体矿物陈国达矿(Ag9FeTe2S4;据谷湘平等,2008)和碲铋矿(据Yang et al., 2016b)及含LREE的独居石(据Deng et al., 2020a)矿物学特征 (a)金岭金矿埠南银金矿与陈国达矿、方铅矿密切共生;(b)陈国达矿与方铅矿密切共生;(c)陈国达矿与黄铜矿、独居石密切共生;(d-f)金与碲铋矿密切共生;(g、h)焦家金矿中热液独居石与黄铁矿密切共生;(i)玲珑金矿含LREE的独居石. Au-自然金;Cp-黄铜矿;EL-银金矿;Gn-方铅矿;Mz-独居石;Py-黄铁矿;Qz-石英;Tel-碲铋矿;U1-陈国达矿 Fig. 4 Mineralogical characteristics of Te-bearing tellurosulphides Ul (after Gu et al., 2008) and tellurobismuthite (after Yang et al., 2016b), and LREE-bearing monazite (after Deng et al., 2020a) of typical gold deposit in Jiaodong |
此外,对含关键元素矿物特征、化学组成、形成条件及其与金成矿的关系也有少量报道,但主要是针对牟乳带金矿床的碲化物,对其它矿床和其它矿物的相关研究相对薄弱(表 1)。
|
|
表 1 胶东部分金矿床已知的含关键元素的独立矿物(据Yang et al., 2017修改) Table 1 Reported minerals of critical elements from the Jiaodong gold deposits (modified after Yang et al., 2017) |
对胶东金矿床中关键元素赋存状态的认识尚处于探索阶段,初步研究表明,明显不同于金以可见金为主的赋存状态,它们以“细”为特征,主要以如下形态出现:(1)以极细小矿物(粒径≥0.1μm)与其它矿物形成复杂共生组合,如稀散元素Te主要赋存于陈国达矿、碲银矿、硫锑铜银矿、碲铋银矿和辉碲铋矿内,稀有元素W主要赋存于白钨矿和黑钨矿内,稀土元素La和Ce主要赋存于独居石、磷钇矿和金红石内(图 3、表 1);(2)以纳米级颗粒(粒径 < 0.1μm)分散在其它矿物的晶面上或超显微裂隙中,如通过对玲珑金矿床自然金和自然银颗粒的电子探针测试、面扫描、SEM图像和能谱分析,表明Te、B、Cr和Nb可能以纳米颗粒分散在金或银矿物的晶面上或超显微裂隙中(Yang et al., 2013);(3)以微量元素的形式作为其它矿物的类质同象固溶体混入物,如Rb与钾的地球化学性质相近,而参与钾矿物的晶格中(在锂云母中可高达4.5%);Re在辉钼矿晶格中主要呈类质同象占据Mo的位置、Te在黄铁矿晶格中也往往呈类质同象占据S的位置(刘英俊等,1984)。
3 胶东金矿床中关键元素含量分布与富集特征胶东金矿床成矿元素为Au-Ag±(S-Cu-Pb-Zn),呈现出中-低温矿化组合特征(徐述平等,2010),但迄今尚缺乏对于共/伴生关键元素的专门研究。为此,我们选择胶东最重要的招莱金矿集区的三山岛、焦家和招平三条金矿带中的12个典型金矿床,初步对比研究了其中关键元素的含量分布和相对于华北克拉通地壳元素丰度的富集特征,结果如表 2、表 3和图 5-图 8所示。
|
|
表 2 胶东典型金矿床中关键元素的含量统计 Table 2 Content statistics of critical elements in the selected Jiaodong gold deposits |
|
|
表 3 胶东典型金矿床关键元素的富集系数 Table 3 Enrichment factors of critical and near-critical elements in the selected Jiaodong gold deposits |
|
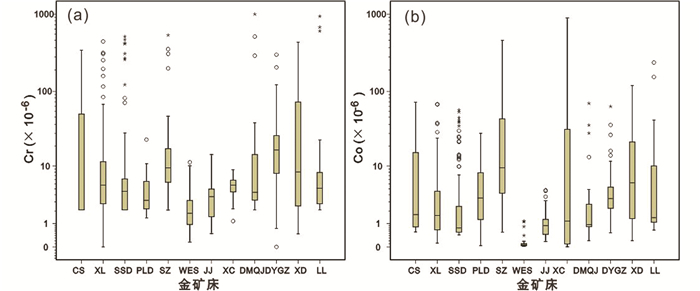
图 5 胶东典型金矿床中稀贵元素Cr (a)和Co (b)含量箱线图 Fig. 5 Boxplots of chromium (a) and cobalt (b) contents in the selected Jiaodong gold deposits |
|
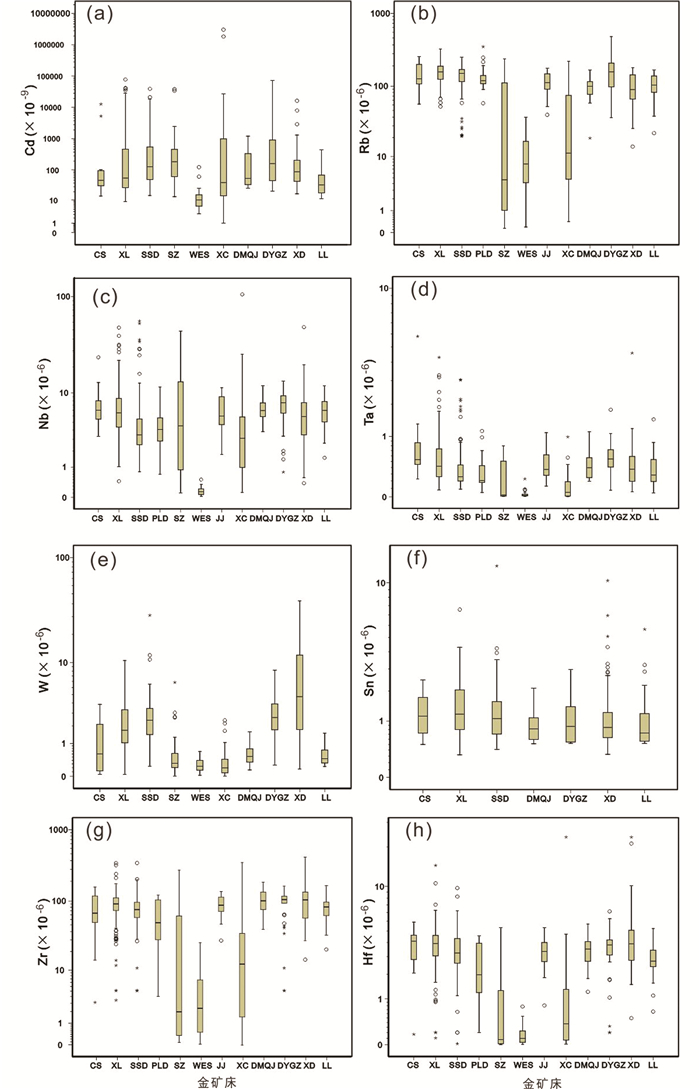
图 6 胶东典型金矿床中稀散元素Cd(a),稀有元素Rb(b)、Nb(c)、Ta(d)、W(e)、Sn(f)、Zr(g)和Hf(h)含量箱线图 Fig. 6 Boxplots of cadmium (a), rubidium (b), niobium (c), tantalum (d), tungsten (e), tin (f), zirconium (g) and hafnium (h) contents in the selected Jiaodong gold deposits |
|
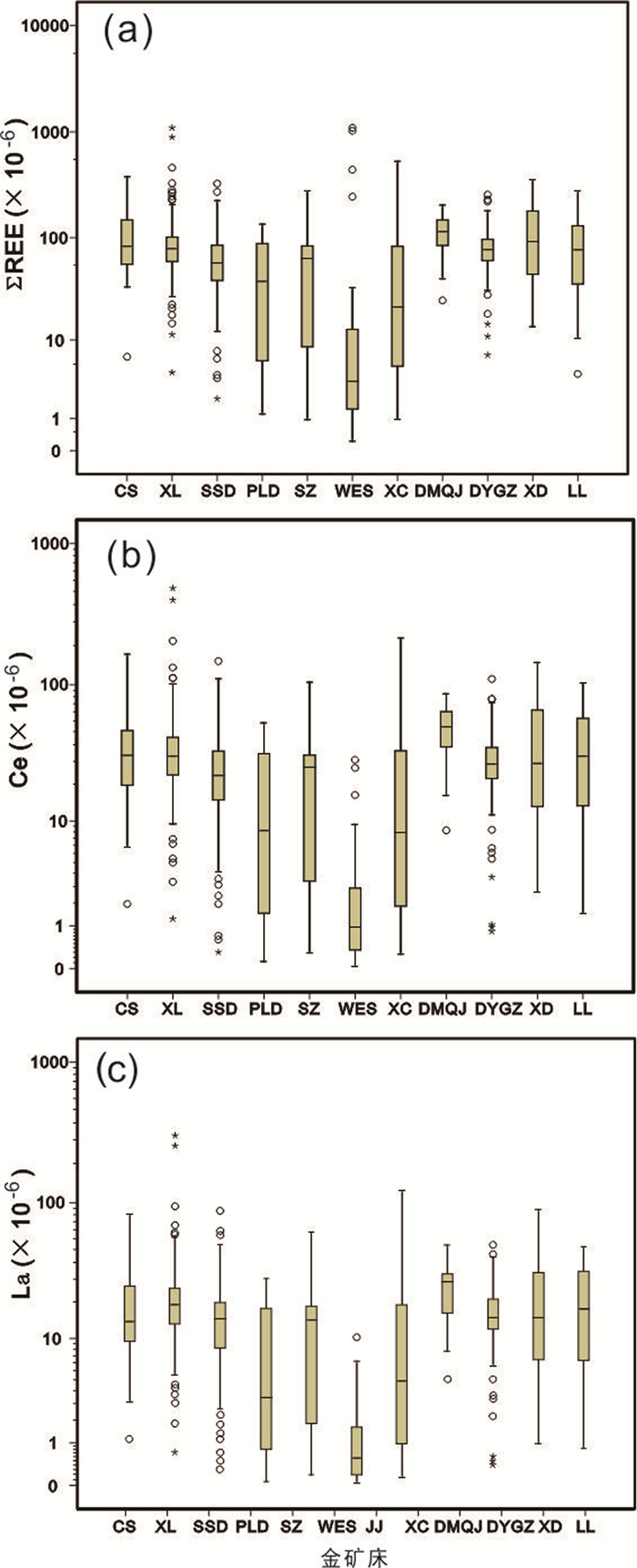
图 7 胶东典型金矿床中∑REE(a)、Ce(b)和La(c)含量箱线图 Fig. 7 Boxplots of ∑REE (a), cerium (b) and lanthanum (c) contents in the selected Jiaodong gold deposits |
|
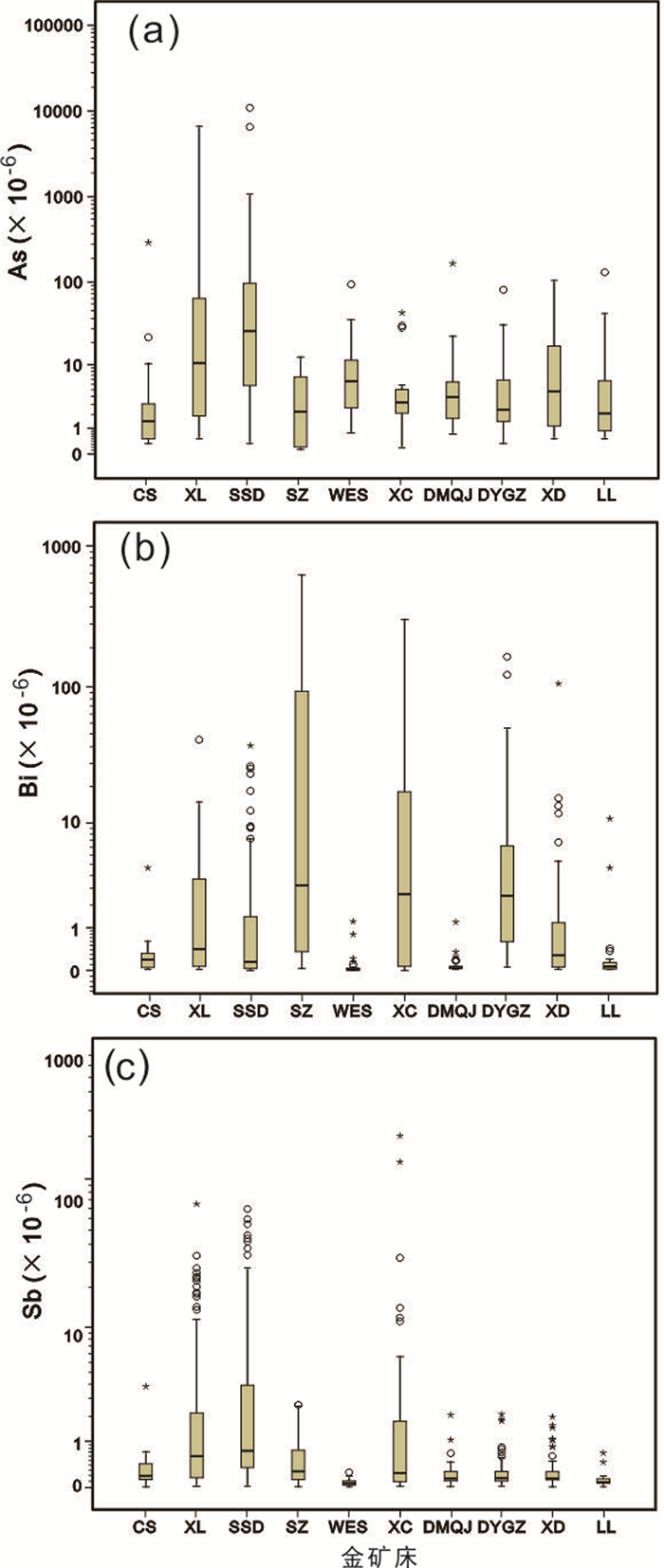
图 8 胶东典型金矿床中其它关键元素As(a)、Bi(b)和Sb(c)含量箱线图 Fig. 8 Boxplots of arsenic (a), bismuth (b) and antimony (c) contents in the selected Jiaodong gold deposits |
本次分析的稀贵元素包括Cr和Co,其地壳丰度分别为90×10-6和20×10-6(黎彤和倪守斌,1990),在华北克拉通的地壳丰度分别为84×10-6和22×10-6(迟清华和鄢明才,2007)。相对于华北克拉通地壳元素丰度,各金矿床Cr和Co含量整体偏低,但大部分出现高值异常。其中,Cr高值异常在招平金矿带相对发育,最高值为994.3×10-6、最大富集系数达11.8。在三山岛金矿带的新立和三山岛金矿床Cr高值异常也较发育,最大富集系数为6.1;而焦家金矿带仅在寺庄金矿床出现个别高值异常、最大富集系数为6.4(图 5a)。Co的高值异常在寺庄、新城和玲珑三个金矿床相对发育,含量最高值(894×10-6)和最大富集系数(40.6)出现在新城金矿床(图 5b)。
3.2 稀散元素本次分析了稀散元素Cd,它在地球各地质端元中的含量极低,其原始地幔和地壳(洋壳与陆壳)丰度分别为0.04×10-6和0.2×10-6(0.19×10-6与0.14×10-6)(Taylor and McLennan, 1985),在华北克拉通的地壳丰度为80×10-9(迟清华和鄢明才,2007)。相对于华北克拉通的地壳元素丰度,胶东金矿床中Cd的含量整体明显偏高,除焦家和望儿山金矿床之外的其它金矿床均出现大量高值异常,其上四分位数富集系数均>4,表现为强烈富集。其中,Cd的最高值出现在新城金矿床,对应的富集系数高达37775、上四分位数富集系数为12.8。大尹格庄矿床的上四分位数富集系数也达到11.8、最高值对应的富集系数为902(图 6a)。
3.3 稀有元素本次分析的稀有元素包括Rb、Sn、Zr、Hf、Nb、Ta和W,其中Rb的地壳丰度为30×10-6(黎彤和倪守斌,1990),在华北克拉通的地壳丰度为63×10-6(迟清华和鄢明才,2007)。相对于华北克拉通的地壳元素丰度,三山岛金矿带中所有金矿床和招平金矿带的大尹格庄金矿床Rb的含量中位数整体明显偏高,均表现为强烈富集;尤其在仓上和大尹格庄金矿床其上四分位数分别为201.6×10-6和208.9×10-6,对应的富集系数分别为3.2和3.3(图 6b)。
Nb和Ta的地壳丰度分别为20×10-6和2×10-6(黎彤和倪守斌,1990),在华北克拉通的地壳丰度分别为10×10-6和0.6×10-6(迟清华和鄢明才,2007)。本次分析的各金矿床Nb的算术平均值均低于华北克拉通的地壳丰度,但在寺庄金矿床上四分位数值显示为较富集,在三山岛和新城金矿床Nb含量最大值分别为56.3×10-6和105×10-6,对应的富集系数分别为5.6和10.5(图 6c)。本次分析的各金矿床Ta的含量整体较低,最高值5.32×10-6出现在仓上金矿床、对应的最大富集系数为8.8(图 6d)。
W和Sn的地壳丰度分别为1.1×10-6和1.7×10-6(黎彤和倪守斌,1990),在华北克拉通的地壳丰度分别为0.6×10-6和1.2×10-6(迟清华和鄢明才,2007)。相对于华北克拉通的地壳丰度,三山岛、新立、大尹格庄和夏甸金矿床W含量的算术平均值和上四分位数均表现为相对高值,其中夏甸金矿床的算术平均值富集系数为14、最大富集系数为66,三山岛金矿床的最大富集系数为48(图 6e)。各金矿床中Sn含量普遍较低,仅三山岛和夏甸金矿床出现个别高值异常,其最大富集系数分别为10和8(图 6f)。
Zr和Hf的地壳丰度分别为190×10-6和5.3×10-6(黎彤和倪守斌,1990),在华北克拉通的地壳丰度分别为146×10-6和4×10-6(迟清华和鄢明才,2007)。相对于华北克拉通的地壳丰度,各金矿床中Zr和Hf的含量和富集系数整体均较低。Zr仅在三山岛、新立和夏甸金矿床出现个别较富集的高值异常,最大富集系数为3(图 6g)。Hf在三山岛金矿带和招平金矿带的夏甸金矿床为较富集至强烈富集;尤其在夏甸金矿床中其算术平均值和上四分位数均为稍富集,最大富集系数可达5.5倍,且变异系数较小。虽然新城金矿床中Hf的最大富集系数也达5.5,但变异系数较大(图 6h)。
3.4 稀土元素本次分析了全部16种稀土元素,∑REE地壳丰度为112×10-6(其中,La=35×10-6、Ce=66×10-6、Pr=9.1×10-6、Nd=40×10-6、Sm=7.06×10-6、Eu=2.1×10-6、Gd=6.1×10-6、Tb=1.2×10-6、Dy=4.5×10-6、Ho=1.3×10-6、Er=1.3×10-6、Tm=0.5×10-6、Yb=3.1×10-6、Lu=0.8×10-6、Sc=25×10-6、Y=31×10-6)(黎彤和倪守斌,1990),在华北克拉通的地壳丰度为166.5×10-6(其中,La=29×10-6、Ce=55×10-6、Pr=6.2×10-6、Nd=25×10-6、Sm=4.4×10-6、Eu=1.21×10-6、Gd=3.8×10-6、Tb=0.6×10-6、Dy=3.3×10-6、Ho=0.67×10-6、Er=1.9×10-6、Tm=0.29×10-6、Yb=1.85×10-6、Lu=0.29×10-6、Sc=18×10-6、Y=15×10-6)(迟清华和鄢明才,2007)。
相对于华北克拉通的地壳丰度,各金矿床的∑REE含量普遍不高,仅在新立和望儿山金矿床出现个别高值异常,最大富集系数分别为6.5和6.6,表现为强烈富集(图 7a)。然而,新立和夏甸金矿床La、Ce、Pr、Nd和Sm等轻稀土元素强烈富集,其中新立金矿床中Ce最高值为481.9×10-6、最大富集系数为8.7(图 7b),La、Nd和Sm的最大富集系数分别为10.0、6.7和4.4(图 7c)。而望儿山金矿床中-重稀土元素Sm、Eu、Gd、Tb、Dy、Er、Tm、Yb、Lu、Sc和Y强烈富集,其中Y最高值为586×10-6、最大富集系数为39.1,其它元素的最大富集系数在4.5(Sc)~42.8(Tm)之间变化。
3.5 其它关键元素其它关键元素As、Bi和Sb的地壳丰度分别为1.5×10-6、0.025×10-6和0.2×10-6(黎彤和倪守斌,1990),在华北克拉通的地壳丰度分别为1.5×10-6、0.14×10-6和0.15×10-6(迟清华和鄢明才,2007),与此相比,它们在各金矿床中均表现为强烈富集。其中,As在仓上、新立和三山岛金矿床中最大富集系数分别为194、4437和7264(图 8a);Bi在寺庄和新城金矿床的最大富集系数分别为4435.7和2142.9,尤其是其上四分位数富集系数在寺庄金矿床也高达674倍(图 8b);Sb在新立、三山岛和新城金矿床的最大富集系数分别为455.9、423和1273(图 8c)。
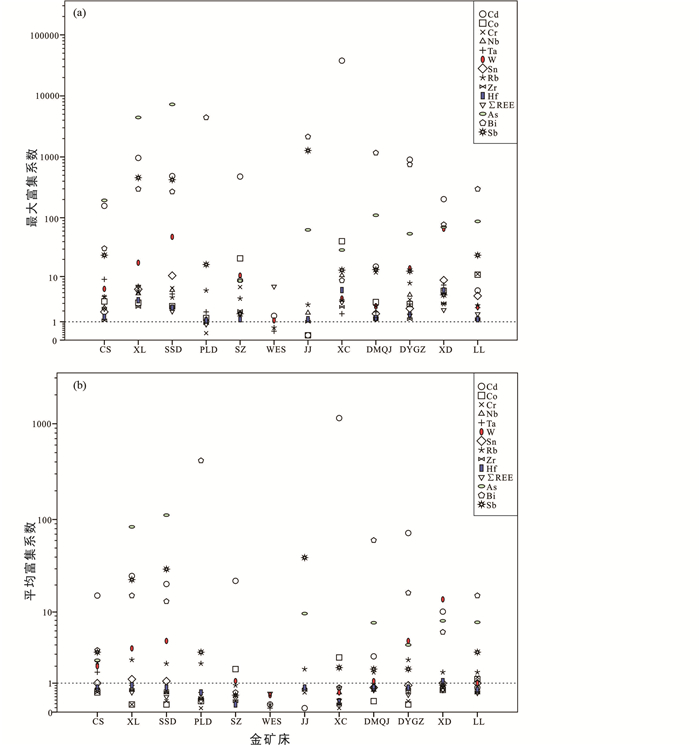
综上可见,相对于华北克拉通的地壳元素丰度,胶东上述各典型金矿床中均有关键元素发生了不同程度的强烈富集(图 9)。其中,其它关键元素As、Bi和Sb在各金矿床中均强烈富集。此外,三山岛金矿带中各金矿床均强烈富集稀贵元素Cr、稀散元素Cd、稀有元素Ta和W四种关键元素;仓上、新立和三山岛金矿床还分别强烈富集稀有元素Rb,稀有元素Nb、Rb、W、Sn和轻稀土元素La、Ce、Pr、Nd、Sm、Eu。而焦家金矿带中各金矿床的差别较大:产于焦家断裂带上盘胶东群变质岩中的平里店金矿床强烈富集稀散元素Cd和稀有元素Rb两种关键元素;产于焦家断裂带下盘晚中生代花岗岩内的望儿山金矿床强烈富集Sm、Eu、Gd、Tb、Dy、Er、Tm、Yb、Lu、Sc和Y十二种中-重稀土元素;产于焦家断裂带内的寺庄、焦家和新城金矿床分别强烈富集Co、Cd、W和Sn五种,Cd一种,Co、Cd、Hf、La、Pr、Nd、Sm、Eu八种关键元素。招平金矿带由北向南,各金矿床强烈富集的关键元素逐渐增多;即由大磨曲家金矿床的Cr、Cd两种,经玲珑金矿床的Co、Cr、Cd、Sn四种和大尹格庄金矿床的Cd、Nb、Rb、W、Sn五种,到夏甸金矿床的Cr、Cd、Nb、Ta、W、Sn、Hf七种。
|
图 9 胶东典型金矿床中关键元素的富集系数 (a)最大富集系数为各金矿床中关键元素含量最高值/华北克拉通地壳元素丰度;(b)平均富集系数为各金矿床中关键元素含量算术平均值/华北克拉通的地壳元素丰度.同一矿床按不同元素富集系数值大小排序;从高到低,就是其优势元素系列;富集系数≥4为强烈富集,2~4为明显富集,1.25~2为较富集,1~1.25为稍富集,1为接近背景值.数据来源同表 3 Fig. 9 Enrichment factors of critical and near-critical elements in the selected Jiaodong gold deposits |
如前所述,相对于华北克拉通的地壳元素丰度,本次分析的胶东典型金矿床中稀贵元素Cr和Co,稀散元素Cd,稀有元素Rb、Nb、Ta、Hf、W和Sn,除Ho之外的其它15种稀土元素,其它关键元素Sb、Bi和As均发生了不同程度富集(图 9、表 3);同时,还在众多金矿床中发现了大量含关键元素的矿物(图 3、表 1)。因此,根据伴生有用组分综合评价的系列规范(表 4)和上述分析的关键元素富集程度,结合其载体矿物发现情况和金矿床勘查开发实际,初步将胶东金矿床内关键元素归为五类,具体阐述如下。
|
|
表 4 胶东金矿床内伴生关键元素综合利用参考性工业指标 Table 4 Reference industrial indicators of comprehensive utilization of critical and near-critical elements in the Jiaodong gold deposits |
关键元素超常富集与金形成共/伴生矿床(体),目前已知的仅有关键元素Sb。新近发现的岔夼金锑矿床位于胶北隆起南部臧家庄凹陷与胶莱凹陷之间的隆起区上,是山东省目前唯一被报道的金锑共/伴生矿床(体)。其赋矿围岩为古元古代荆山群一套中-低级变质的碎屑岩和碳酸盐沉积,矿化带严格受NNE向断裂带控制,总体走向0°~20°,长280m、宽4~10m。矿体厚0.79~3.48m,平均1.50m;金品位1.21~5.77g/t,平均1.97g/t;锑品位1.21%~21.27%,平均5.55%(孙绪德等,2018)。而对全球金锑矿床的研究表明,碳酸盐建造容矿的浅成造山型金锑矿区可能是未来最重要的锑资源接替区(Goldfarb et al., 2016)。虽然目前岔夼金锑矿床规模较小,其成矿地质条件与全球最重要的金锑矿集区——华南也有所不同(Zhang et al., 2019a),但其碳酸盐建造容矿的浅成造山型金锑矿区的本质属性完全一致,表明该区域可能成为未来重要锑资源接替区。
4.1.2 达到伴生组分综合评价品位关键元素超常富集达到伴生组分综合评价品位,包括稀散元素Cd、稀贵元素Co、稀有元素Nb、Rb,其它关键元素As和Bi(图 10、表 4)。其中,稀散元素Cd富集程度最高、且高值异常分布范围最广,三条金矿带中均有达到伴生组分综合评价品位的极高异常值;尤其是在新城金矿床的最大富集系数达37775、平均富集系数为1145.6,均远高于625的浓度系数,具备近期被综合利用的资源条件。
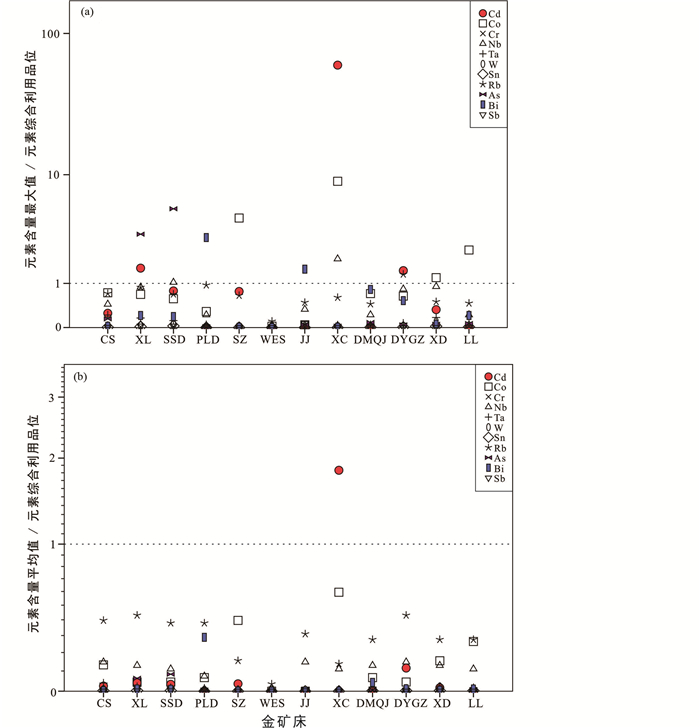
|
图 10 胶东典型金矿床中超常富集的关键元素的浓度系数 (a)最大浓度系数为各金矿床中超常富集的关键元素含量最高值/伴生有用组分综合评价品位;(b)平均浓度系数为各金矿床中超常富集的关键元素含量算术平均值/伴生有用组分综合评价品位。同一矿床按不同元素浓度系数值大小排序;从高到低,就是其优势元素系列;≥1表示达到伴生组分综合评价品位 Fig. 10 Concentration factors of critical and near-critical elements in the selected Jiaodong gold deposits |
其次,稀贵元素Co在新城和寺庄金矿床中的最大富集系数分别为40.6和20.8,均远高于4.5的浓度系数。稀有金属Nb在三山岛和新城金矿床的最大富集系数分别为5.6和10.5,均高于5.4的浓度系数;Rb在大尹格庄金矿床的最大富集系数为7.6,高于5.8的浓度系数,显示出良好的资源潜力。
此外,关键元素As在新立和三山岛金矿床中的极高异常均达到综合评价品位;Bi在寺庄和新城金矿床中的极高异常达到综合评价品位,尤其是在寺庄金矿床其上四分位数富集系数也高达674(浓度系数为1428.6),可视为重要的潜在接替资源。
4.1.3 接近伴生组分综合评价品位或已发现超常富集的载体矿物关键元素超常富集接近伴生组分综合评价品位或已发现超常富集的载体矿物,包括稀贵元素Cr,稀散元素Se、Te、Re,稀有元素W和LREE(图 10、表 1)。
值得指出的是,稀贵元素Cr是我国极为紧缺的关键金属资源。据2011~2015年USGS的数据统计,我国Cr的对外依存度高达99%。而胶东金矿床共/伴生的铬铝云母亚族矿物普遍富Cr,其中含铬绢云母和含铬多硅绢云母中Cr2O3均占0.1%~1.0%、铬多硅绢云母中Cr2O3高达1.0%~10.0%(鲁安怀和陈光远,1994),且Cr含量高低与绢英岩化蚀变强度正相关(Zuo et al., 2016)。总体上看,Cr在蚀变岩型金矿床中的富集程度明显强于石英脉型和过渡类型金矿床,这与该类型金矿床中普遍发育铬云母化蚀变的特征一致。尤其是,部分金矿床中铬云母化蚀变带可宽达数十米,显示出良好的资源潜力。
稀散元素Se和Te的地壳丰度分别为0.05×10-6和3×10-9,在华北克拉通的地壳丰度为0.11×10-6和8×10-9(迟清华和鄢明才,2007)。二者在胶东半岛均较为富集,尤其在金矿床共/伴生的碲矿物中超常富集Te,如埠南金矿床中陈国达矿的Te含量为17.23%~18.75%(谷湘平等,2008)、新城金矿床中碲铋矿的Te和Bi(地壳丰度为0.048×10-6)含量分别为31.58%~38.39%和55.18%~56.33%(Yang et al., 2016b;李瑞红等,2019)。而碲矿物是胶东目前发现产出矿床最多的含关键元素的独立矿物,随着全球对关键金属需求的急剧增长,胶东金矿床中丰富的含碲矿物可能是未来潜在的重要关键金属资源。
稀散元素Re是地球中含量最低的元素之一,它在原始地幔、亏损地幔和陆壳中的丰度分别为0.28×10-9(McDonough and Sun, 1995)、0.12×10-9和2×10-9(Sun et al., 2003),在华北克拉通的地壳丰度为0.1×10-9(迟清华和鄢明才,2007)。而胶东金矿床中伴生的辉钼矿普遍富Re,如三山岛金矿床深部伟晶岩中辉钼矿的Re含量为4.66×10-6~29.20×10-6(文博杰等,2015)、赵家和大磨曲家金矿床中辉钼矿的Re含量分别高达1.42×10-4和1.11×10-4(万多,2014),且近年来不断有类似的报道,暗示区域Re具有一定的综合利用前景。
此外,紧邻牟乳金矿集区的福山王家庄铜矿床伴生Cd平均含量为0.01%、Se为0.0009%、Te为0.001%、In为0.00015%,均可回收利用(孔庆友等,2006);栖霞香夼铅锌矿床还伴生有Sn(平均含量为20×10-6)、Sb(156×10-6)、Co(12×10-6)、Ni(15×10-6)、Cd(120×10-6)、Ga(17×10-6)、In(8×10-6)、Ge(20×10-6)、Ti(4×10-6)、Bi(62×10-6)、Se和Te(涂光炽等,1989)。位于招莱金矿集区中的莱西塔埠头伟晶岩型稀土矿床是山东已探明的二处稀土矿床之一,其矿化大多发育于玲珑花岗岩中的钾长石伟晶岩中。含稀土的矿物主要有褐帘石、氟碳铈镧矿、磷灰石、锆石、钍石、榍石。稀土氧化物总量平均品位为1.603%,以Ce、La、Y和Nd的氧化物为主,其含量分别为0.494%~1.598%、0.213%~0.635%、0.088%~0.318%和0.162%~0.497%;伴生U(平均品位为0.0180%)、Th(0.5674%)、Nb2O5(0.0886%)、Ta2O5(0.008%)和Zr2O5(2.384%)均可综合利用(孔庆友等,2006)。此外,鲁西是我国东部最重要的稀土矿区,其中郗山与碱性岩有关的稀土-金(银)矿是我国第三大轻稀土矿床,REE和Au密切共生(Wei et al., 2019b),其稀土矿物碳酸铈钠矿和菱钙锶铈矿均属国内首次发现(于学峰等,2010),其云母Rb-Sr定年结果为119±1.4Ma(蓝廷广等,2011),与胶东金矿床成矿时代完全一致(Deng et al., 2020a;Zhang et al., 2020c)。这些从侧面佐证了该区具备上述关键元素超常富集成矿的地质背景,也为进一步开展区域成矿对比研究提供了天然实验室。
4.1.4 其它关键金属元素除上述3类关键元素之外,还有如下两类:(1)本次分析远低于伴生组分综合评价品位,而载体矿物稀少且细小或尚未被发现(表 3,表 4),发生超常富集的可能性相对较低,被综合利用的前景不乐观,包括稀有元素Ta、Hf和Sn,HREE;(2)本次未分析,也尚未发现载体矿物,超常富集与否不清,被作为伴生资源综合利用的前景不明,包括上述四类之外的其它元素。
4.2 胶东金矿床中关键金属超常富集机理相对于其它元素,关键元素以在自然界十分稀少且难以富集为特征(翟明国等,2019)。而本次分析的胶东12处典型金矿床内共27种关键元素发生了不同程度富集,且已发现含12种关键元素的系列独立矿物出现在各主要金矿带中的31处金矿床内;尤其是部分金矿床内发育多种含关键元素的独立矿物、且有多种关键元素发生了超常富集,它们共同依附于金矿体、构成密切相关的共/伴生体系,导致矿石中矿物组合和元素组成复杂多样。然而,由于它们的地球化学性质差异明显,所以各有其富集机制。但是,迄今几乎所有的胶东金矿床的研究均是针对金,对共/伴生关键元素尚缺乏应有的关注;尤其是对关键元素超常富集机理未能引起重视,尚缺乏针对性的专门深入研究。
尽管如此,已有工作仍发现了一些很有意义的成矿地质现象。例如,对岔夼金锑矿床的初步研究发现,相对于Au来说,Sb的空间分布极不均匀、呈跳跃式变化,且金与锑的总体相关性较低(相关系数为0.36;孙绪德等,2018);即宏观上,Sb与Au密切共生形成金锑矿床;而在矿体和矿石尺度上,它们的富集空间明显分离。其实,在世界其它地方也发现了这种金锑“共生-分离”的现象。近年来,通过微区原位分析(Large et al., 2012)和成矿热力学模拟(Zhong et al., 2015a)等研究表明,Sb比Au的溶解度对温度变化更加敏感(Zotov et al., 2003);Fe-Sb-S-O-H体系内,温度的降低是导致锑沉淀的最有利因素(Chen et al., 2018)。由于金和锑矿沉淀时不同的物理化学条件,导致它们富集于不同的空间部位(Wang et al., 2013)。这些工作无疑促进了对金锑共生-分离现象的认识,然而造成这一现象的主导机制和关键控制因素及其对胶东地区的适用性仍需进一步深入探讨。
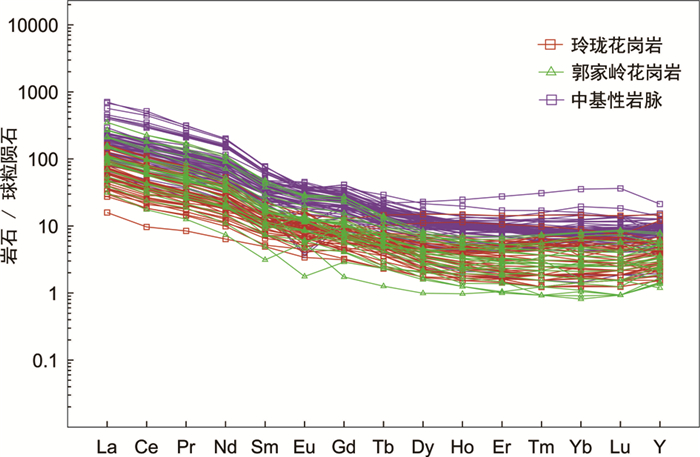
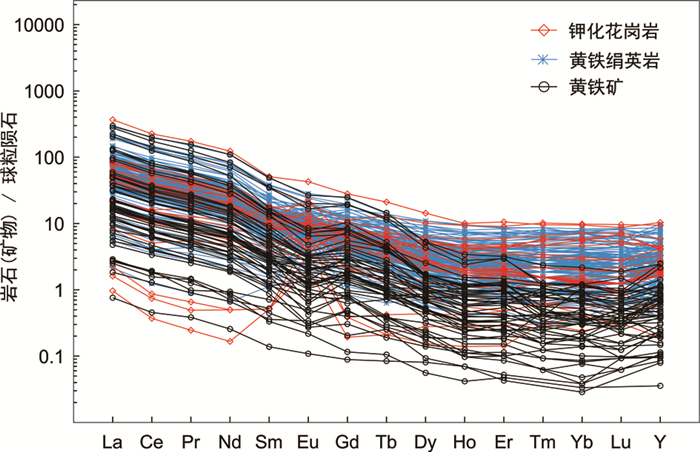
长期以来,对胶东金矿床中相关地质体的稀土元素含量积累了大量数据。本次汇编了胶东金矿床主要赋矿围岩、主要蚀变岩和载金黄铁矿的稀土元素组成,发现尽管它们的REE组成变化较大,但仍呈现规律性趋势。其中,主要赋矿围岩包括:165~150Ma侵位的玲珑花岗岩、135~126Ma侵位的郭家岭花岗岩和130~110Ma侵位的中-基性岩脉,它们的ΣREE分别为21.46×10-6~191.91×10-6、32.39×10-6~404.23×10-6和73.79×10-6~827.75×10-6;可见越晚侵位的赋矿围岩,其ΣREE值越高(图 11);即随着晚中生代地质构造演化,胶东金矿床赋矿围岩中的REE越富集。而钾化花岗岩、黄铁绢英岩和金矿石中载金黄铁矿的ΣREE分别为1.2×10-6~422.84×10-6、7.78×10-6~359.2×10-6和0.92×10-6~358.37×10-6;总体来看,三者的分布均比较分散;其中,钾化花岗岩的ΣREE呈现向高、低两端发散的趋势,黄铁绢英岩的ΣREE相对略显集中,而黄铁矿的ΣREE从高到低都有出现(图 12)。造成这一现象的原因是什么?受控于什么因素?是REE的源区不同、还是受控于晚中生代成矿地质作用?这些都是值得深入研究的重要科学问题。而近年来,对稀土元素在热液中的迁移与沉淀的大量试验和模拟研究表明,流体的pH和配体含量变化、降温,以及磷酸盐、碳酸盐、氟化物的加入均可促使稀土络合物失稳,诱发稀土元素的沉淀(Verplanck,2017);然而,目前对稀土元素在同一体系中不同络合形式的综合研究仍十分薄弱,尚不能准确判断控制稀土络合物稳定性诸多因素的可能贡献和成矿机理(佘海东等,2018)。显然,要解决上述难题,亟需从关键元素的源、运、聚全过程开展系统深入研究。
|
图 11 胶东金矿床主要赋矿围岩的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线 数据来源:玲珑花岗岩数据来自杨敏之和吕古贤,1996;Yang et al., 2012, 2017, 2018;Li et al., 2013;刘向东等,2019.郭家岭花岗岩数据来自杨敏之和吕古贤,1996;Goss et al., 2010;Yang et al., 2012;宋明春等,2013;Wang et al., 2014a;张潮等,2016.中-基性岩脉数据来自Yang et al., 2004;Tang et al., 2008;王建国等,2009;Goss et al., 2010;Ma et al., 2014;Huang et al., 2016;Deng et al., 2017b;Liang et al., 2018 Fig. 11 Rare-earth elements chondrite standardization curve of main host rocks in the Jiaodong gold deposit |
|
图 12 胶东金矿床主要蚀变岩和载金矿物的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) 数据来源:钾化花岗岩数据来自Li et al., 2013, 2019;宋明春等,2013;赵睿等,2015;张潮等,2016;刘向东等,2019.黄铁绢英岩数据来自王建国等,2009;Li et al., 2013, 2019;宋明春等,2013;赵睿等,2015;张潮等,2016;刘向东等,2019;李瑞红等,2019.黄铁矿数据来自郭林楠等,2019;李杰等,2020 Fig. 12 Rare-earth elements chondrite standardization curve of main altered host rocks and gold-bearing minerals in the Jiaodong gold deposit (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
关键金属作为全球高科技产业不可或缺的战略性资源,其成矿作用和找矿勘查均是目前国际矿床学领域关注的热点(毛景文等,2019)。而作为全球已探明金资源储量最多的金矿床类型,造山型金矿床共/伴生关键元素的成矿作用和找矿勘查尚未被研究者所重视,对关键元素迁移与超常富集成矿的苛刻条件目前远未得到清晰揭示,这严重制约了对该类型金矿床中关键元素分布规律的深入认识和对其资源潜力的合理评估。
胶东被视为检验造山型金矿床成矿新理论和新模型的关键地区,其内多种关键元素超常富集,然而迄今除勘查发现了小型的岔夼金锑矿床和开展了少量的基本矿物学工作之外,尚未见对关键元素成矿作用的研究报道。虽然本文初步探讨了胶东典型金矿床中关键元素的赋存状态、含量分布与超常富集特征,但是相关问题依然存在:关键元素赋存状态和分布规律的研究极其薄弱,关键元素源-运-聚超常富集过程与成矿机理、以及促使其迁移成矿的主控因素和苛刻条件的研究尚属空白。亟待开展对胶东金矿床中关键元素源-运-聚超常富集机理的研究,回答关键元素的源区性质与鉴别标志是什么、是什么因素促使关键元素迁移和超常富集成矿的、控制其迁移和超常富集的苛刻条件有哪些等系列问题,为“非常规类型关键元素成矿系统”和胶东及类似金矿床中关键元素的综合利用提供理论基础。
4.3.1 关键元素赋存状态与分布规律如前所述,胶东金矿床中关键元素往往以微米矿物集合体、纳米颗粒或更细小的类质同象固溶体形式出现,且空间分布极不均匀。为什么同类型的金矿石中有些关键元素超常富集成矿、而有些则不出现关键元素?如何甄别其不同呈现形态及其经历的复杂过程、有效区分其成矿与否的标准是什么?目前均不得而知。
近年来,分析测试技术特别是原位微区分析技术的进步,为深入开展关键元素在复杂体系和在复杂地质过程中的地球化学性状研究提供了可能。其中,场发射扫描电镜、场发射大晶体电子探针、激光剥蚀等离子体质谱、纳米离子探针、X射线衍射仪等先进设备,能够准确获取地质样品原位微米尺度的元素、同位素组成和晶体结构特征;而扫描隧道显微镜、聚焦离子束、球差校正透射电镜、原子探针、同步辐射光源等尖端设备,能够提供样品纳米尺度元素、同位素组成和晶体结构信息。这些原位微区分析技术的引入和合理应用,将能够在微米和纳米尺度对元素含量、晶体结构和同位素组成进行分析,大大促进关键元素赋存状态与分布规律研究的进步。
在此基础上,通过对不同矿物、矿石、矿床(体)、矿带(区)等分别开展系统对比研究,将可能获取多重尺度上含关键元素矿物的晶体结构、元素含量和同位素组成的空间变化图案,为进一步开展关键元素源-运-聚超常富集机理研究奠定坚实基础。
4.3.2 关键元素源区性质与萃取机制成矿物质的来源是热液成矿系统研究的首要问题,然而传统的金矿床成因模式均是基于同位素间接示踪成矿物质来源,结论往往不明确。而关键元素常依附金共/伴生成矿,对其源区的判断更为困难,胶东金矿床中关键元素究竟来自何处目前尚无相关报道。它们与金是来自于同一源区、还是各自不同?如何从源区萃取进入流体系统?以何种机制萃取?受控于何种因素?目前均无从认识。
近年来,新兴金属同位素直接示踪技术飞速发展,在示踪成矿金属来源和演化方面的独特优势逐渐显现,为这一问题的解决创造了条件,为关键元素成矿作用的深入研究提供了新的平台。利用这些方法技术,通过对多种重要金矿床类型持续探索,获得了大量新的成果认识。例如,对西澳伊尔冈克拉通和加拿大亚比提比克拉通太古宙造山型金矿床多元硫同位素(32S、33S、34S和36S)的分析结果,揭示金来源于地壳变质围岩(Selvaraja et al., 2017)和长英质岩浆或地幔(Xue et al., 2013);而对克拉通边缘富金斑岩矿床赋矿围岩中角闪岩和石榴石角闪岩包体全岩地球化学(包括Cu-Au含量)和锆石Hf同位素研究表明,富集金属下地壳的再循环作用是形成非弧斑岩型多金属矿床的关键原因(Hou et al., 2017)。同时,地幔中自然金的发现(Tassara et al., 2017),提供了交代岩石圈地幔的再富集作用是控制巨型金矿床(区)形成与定位关键因素的首个直接证据(Deng et al., 2020b)。这些成果对合理解释巨型矿床(区)中金属的来源提供了可供选择的新观点,也为胶东进一步开展关键金属相关工作提供了有益的研究思路借鉴。
4.3.3 关键元素输运过程与深部驱动以往矿床学关注的焦点是成矿物质的来源和沉淀机制,即成矿作用的始态和终态,而对成矿过程的研究相对滞后,关键元素这方面的表现更为明显,胶东金矿床中关键元素成矿过程的研究尚属空白。近年来,随着分析测试和热力学实验及数值模拟等技术的进步,为突破这一制约成矿学理论进步的瓶颈提供了可能。
(1) 将热力学实验与数值模拟有机结合,在厘定成矿流体的物理化学性质(Zhai et al., 2018)、明确成矿流体中金属络合物的主要类型(Zhai and Liu, 2014)、推断成矿流体的演化路径(Bigot and Jébrak,2015)、估算成矿流体的初始同位素组成(Wagner et al., 2009)等方面取得了系列进展。对造山型金锑矿床的研究表明,在温度较低(< 250℃)的条件下,锑往往以Sb3+与氢氧化物或硫氢络合物的形式运移,而Sb4+为在较高温(≥250℃)或近地表偏氧化条件的主要价态形式(Mosselmans et al., 2000);只有在强酸性的流体中,才会出现SbCl3等氯化物(Obolensky et al., 2009)。
(2) 将非线性科学与化学动力学及构造动力学理论引入成矿过程的研究(如王偲瑞等,2016),力求定量表达流体与岩石相互反应的机制和速率,如厘定不同水/岩比或P-T条件下的矿物组合(Hedenquist and Taran, 2013)、预测不同P-T条件下流体通过不同岩石序列的反应平衡相组成(Zhong et al., 2015b)、揭示热液蚀变带的形成及其时空结构演化(Evans et al., 2006)。
(3) 由于微区微量测试技术的进步,使得对不同成矿阶段产物的元素和同位素组成的原位测定成为可能,这为较精细地了解成矿介质的组成和刻画成矿过程提供了先决条件。例如,利用SIMS对代表不同成矿阶段的石英、磷灰石和独居石等进行原位U-Th-Pb年代学及氧同位素测试(Deng et al., 2020a),并对同一矿物或其共生矿物开展LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb年代学和微量元素成分测试(Yang et al., 2016a;Zhang et al., 2020c),可获取成矿过程中不同阶段的精细年代学及流体的元素组成和变化,将有助于揭示关键元素在不同成矿阶段的超常富集过程,更加合理地构建成矿模式。
4.3.4 关键元素沉淀条件与聚集机理由于直接与矿床的现今位置与状态密切相关,目前对该领域的研究相对较多,但仍有众多方面认识不清。例如,传统上认为PGE在地质过程中具有高度惰性,其活动性多与幔源岩浆作用息息相关(Wang et al., 2014b);但越来越多的地质证据表明PGE也具有热液活动性,具体表现在不同构造环境下热液活动导致的卤水、矿石矿物或地质体中PGE的富集(Ding et al., 2018);然而,之前对于天然样品的研究主要集中在PGE的岩浆和成矿作用方面,而实验研究则主要集中在PGE溶解度和赋存方式方面;对PGE的沉淀机制,尚缺乏接近自然的复杂流体成分和物理化学条件的深入研究(严海波等,2020)。
此外,综合研究表明造山型金锑矿床中不同性质的流体混合促使流体温度迅速降低(Wang et al., 2013),由于锑对温度变化最为敏感,因此其溶解度受到的影响最大,易发生辉锑矿的沉淀(Chen et al., 2018);而断裂带剧烈活动诱发流体压力的周期性降低,也会促使流体温度的骤降,引起大量辉锑矿沉淀(Hagemann and Lüders,2003)。在此过程中,流体中原先存在的CH4、CO2与H2S气体逃逸,流体温度降低,进一步促使含金的硫氢络合物分解,导致金沉淀(Zhang et al., 2019a)。这些工作似乎解释了金锑共生-分离现象,但无法说明是何种因素导致同一流体系统中同时发生流体混合和流体不混溶作用,亟待开展进一步深入研究。
4.3.5 非常规类型关键元素成矿系统如上所述,胶东金矿床中多种关键元素超常富集达到或接近伴生组分综合评价品位。由于具有独特的地质背景、复杂的元素组合和巨大的矿石储量,胶东金矿床中的关键元素是与传统的成矿专属性认识不同的矿床新类型,其成矿作用尚难以完全用传统的关键元素成矿理论解释;而且涉及的矿床数量众多、共/伴生关键元素种类复杂、覆盖的区域面积宽广、资源潜力巨大,因此本文称之为“胶东非常规类型关键元素成矿系统”。
实际上,随着近年来研究工作的不断深入,一些与传统的关键元素成矿专属性认识不同的新类型矿床时有发现。以稀散元素矿床为例,主要包括:“黄铁矿型”富Tl矿床(范裕等,2007)、“辉锑矿型”富Se矿床(张德和王顺金,1994)、“富有机质型”富Ga矿床(秦勇等,2009)、“铁矿型”富Ge(Ga、In)矿床(杨光明,1980)和“海底多金属结壳型”富Te(Tl)矿床(温汉捷等,2019)等。
同时,非常规类型关键元素矿床往往具有巨大的资源潜力,资源量可超过传统的关键元素矿床。如金顶铅锌矿床中富含的“黄铁矿型”Tl矿化,其一个矿床的资源量可占全球的一半左右(17000吨,USGS Report,2018);富有机质岩系(煤、黑色页岩)中的镓资源远高于传统的铝土矿和铅锌矿床中的镓资源(Dai et al., 2006);海底铁锰结壳中碲资源将完全颠覆以往的传统认识(温汉捷等,2019)。
综上可见,胶东金矿床中的关键元素成矿作用不能被现有成矿模式所涵盖,且目前国内外对此类矿床中关键元素的研究程度极低,尚未引起应有关注,对其认识极其薄弱。而胶东金矿床的勘查和研究积累厚实、资料丰富,是开展“非常规类型关键元素成矿系统”深入研究的理想选区。同时,胶东金矿省内蕴藏的矿石量巨大、已有矿业基础设施和选矿设备完善、选矿工艺先进,一旦查明某种或某些关键元素具有工业或战略开采/研究价值,可以相比其他矿山以更快、更低成本开展相关工作和/或被回收利用。因此,建议针对胶东金矿床中关键元素源-运-聚超常富集机理这一关键科学问题,将其成矿背景的独特性与成矿系统的特殊性及关键元素超常富集的必然性作为一个整体进行研究,通过利用新兴金属同位素、微区原位分析测试和热力学实验及数值模拟等技术方法,剖析关键元素选择性超常富集的过程与成矿机制,揭示制约关键元素选择性富集成矿关键要素的配置关系,提出其成矿模式,明确其成因类型,为丰富“非常规类型关键元素成矿系统”理论体系和胶东及类似金矿床中关键元素的综合利用提供理论基础。
5 结论胶东金矿床中共/伴生关键元素种类繁多、潜力巨大。相对于华北克拉通的地壳元素丰度,稀贵元素Cr和Co,稀散元素Cd,稀有元素Rb、Nb、Ta、Hf、W和Sn,除Ho之外的其它15种稀土元素,其它关键元素Sb、Bi和As在胶东金矿床中均发生了不同程度的富集;其中,Sb超常富集与Au共生形成浅成造山型金锑矿床,Cd、Co、Nb、Rb、As和Bi超常富集达到伴生组分综合评价品位(Cd已具备被综合利用的资源条件),Cr、Se、Te、Re、W和LREE超常富集接近伴生组分综合评价品位或已发现超常富集的载体矿物,可作为未来重要的潜在接替资源。
胶东金成矿系统的勘查和研究积累厚实、资料丰富,是深入开展“非常规类型关键元素成矿系统”的理想选区;亟待利用新兴金属同位素、微区原位分析测试和热力学实验及数值模拟等技术方法,深入研究其中关键元素源-运-聚超常富集机理,为丰富“非常规类型关键元素成矿系统”理论体系和胶东及类似金矿床中关键元素的综合利用提供理论基础。
胶东金矿省内蕴藏的矿石量巨大、已有矿业基础设施和选矿设备完善、选矿工艺先进,因此一旦查明某种或某些关键元素具有工业或战略开采/研究价值,可以相比其他矿山以更快、更低成本开展相关工作和/或被回收利用。
致谢 论文的完成得益于与Richard Goldfarb教授、David Groves教授、邓军教授、张静教授、王庆飞教授、龚庆杰教授、和文言副教授、李楠副研究员、翟德高副教授等的探讨。野外工作得到山东省地质矿产勘查开发局、山东省地质科学研究院、山东黄金集团有限公司和山东招金股份有限公司及各金矿山工作人员的大力支持与帮助。研究生张宏睿、王偲瑞、张少颖、魏瑜吉、刘向东、叶广利、汪浩、孙晓龙和杨伟等参与了部分研究工作。谨此致谢。
Bateman R and Hagemann S. 2004. Gold mineralisation throughout about 45Ma of Archaean orogenesis:Protracted flux of gold in the Golden Mile, Yilgarn craton, Western Australia. Mineralium Deposita, 39(5-6): 536-559 |
BGS. 2015. Risk List 2015:An Update to the Supply Risk Index for Elements or Element Groups that are of Economic Value. British Geological Survey (BGS) |
Bigot L and Jébrak M. 2015. Gold mineralization at the syenite-hosted Beattie gold deposit, Duparquet, Neoarchean Abitibi Belt, Canada. Economic Geology, 110(2): 315-335 |
Bortnikov NS, Gamynin GN, Vikent'eva OV, Prokof'ev VY and Prokop'ev AV. 2010. The Sarylakh and Sentachan gold-antimony deposits, Sakha-Yakutia:A case of combined mesothermal gold-quartz and epithermal stibnite ores. Geology of Ore Deposits, 52(5): 339-372 |
Botcharnikov RE, Linnen RL, Wilke M, Holtz F, Jugo PJ and Berndt J. 2011. High gold concentrations in sulphide-bearing magma under oxidizing conditions. Nature Geoscience, 4(2): 112-115 |
Bowell RJ, Foster RP and Stanley CJ. 1990. Telluride mineralization at Ashanti gold mine, Ghana. Mineralogical Magazine, 54(377): 617-627 |
Chai P, Zhang ZY and Hou ZQ. 2019. Geological and fluid inclusion constraints on gold deposition processes of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(4): 955-971 |
Chen GY, Shao W and Sun DS. 1989. Mineralogy and Prospecting of Jiaodong Gold Deposit. Chongqing: Chongqing Press, 1-250 (in Chinese)
|
Chen J, Yang RD, Du LJ, Zheng LL, Gao JB, Lai CK, Wei HR and Yuan MG. 2018. Mineralogy, geochemistry and fluid inclusions of the Qinglong Sb-(Au) deposit, Youjiang basin (Guizhou, SW China). Ore Geology Reviews, 92: 1-18 |
Chen YJ, Pirajno F and Qi JP. 2005. Origin of gold metallogeny and sources of ore-forming fluids, Jiaodong Province, eastern China. International Geology Review, 47(5): 530-549 |
Chi QH and Yan MC. 2007. Handbook of Elemental Abundance for Applied Geochemistry. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-148 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Dai SF, Ren DY and Li SS. 2006. Discovery of the superlarge gallium ore deposit in Jungar, Inner Mongolia, North China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(18): 2243-2252 |
Dai XL, Deng XW, Peng SL and Yang B. 2011. Significance of the Linglong granite in the metallogenic system of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit in eastern Shandong Province. Geology and Prospecting, 47(3): 370-379 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Demange M, Pascal ML, Raimbault L, Armand J, Forette MC, Serment R and Touil A. 2006. The Salsigne Au-As-Bi-Ag-Cu deposit, France. Economic Geology, 101(1): 199-234 |
Deng J, Yang LQ, Sun ZS, Wang JP, Wang QF, Xin HB and Li XJ. 2003. A metallogenic model of gold deposits of the Jiaodong granite-greenstone belt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(4): 537-546 |
Deng J, Yang LQ, Ge LS, Wang QF, Zhang J, Gao BF, Zhou YH and Jiang SQ. 2006. Research advances in the Mesozoic tectonic regimes during the formation of Jiaodong ore cluster area. Progress in Nature Science, 16(8): 777-784 |
Deng J, Chen YM and Liu Q, et al. 2010. The Gold Metallogenic System and Mineral Resources Exploration of Sanshandao Fault Zone, Shandong Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-371 (in Chinese)
|
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Carranza EJM and Lu YJ. 2015a. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry. Mineralium Deposita, 50(8): 987-1006 |
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF and Pan RG. 2015b. Origin of the Jiaodong-type Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Constraints from fluid inclusion and C-D-O-S-Sr isotope compositions. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 674-686 |
Deng J and Wang QF. 2016. Gold mineralization in China:Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Research, 36: 219-274 |
Deng J, Wang QF and Li GJ. 2017a. Tectonic evolution, superimposed orogeny, and composite metallogenic system in China. Gondwana Research, 50: 216-266 |
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF, Dilek Y and Liang YY. 2017b. Isotopic characterization and petrogenetic modeling of Early Cretaceous mafic diking:Lithospheric extension in the North China craton, eastern Asia. GSA Bulletin, 129(11-12): 1379-1407 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Santosh M and Yao EY. 2018. Crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the south-eastern North China Craton. Earth-Science Reviews, 182: 251-272 |
Deng J, Yang LQ, Li RH, Groves DI, Santosh M, Wang ZL, Sai SX and Wang SR. 2019. Regional structural control on the distribution of world-class gold deposits:An overview from the Giant Jiaodong Gold Province, China. Geological Journal, 54(1): 378-391 |
Deng J, Qiu KF, Wang QF, Goldfarb RJ, Yang LQ, Zi JW, Geng JZ and Ma Y. 2020a. In-situ dating of hydrothermal monazite and implications on the geodynamic controls of ore formation in the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Economic Geology DOI:10.5382/econgeo.4711 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Santosh M, Liu XF, Liang YY, Yang LQ, Zhao R and Yang L. 2020b. Remobilization of metasomatized mantle lithosphere:A new model for the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Mineralium Deposita, 55(2): 257-274 |
Ding X, Harlov DE, Chen B and Sun WD. 2018. Fluids, metals, and mineral/ore deposits. Geofluids, 2018: Article ID 145240
|
Ding ZJ, Sun FY, Liu FL, Liu JH, Peng QM, Ji P, Li BL and Zhang PJ. 2015. Mesozoic geodynamic evolution and metallogenic series of major metal deposits in Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(10): 3045-3080 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Distler VV and Yudovskaya MA. 2005. Polymetallic PGE-Au mineralization of the Sukhoi Log deposit, Russia. In: Mungall J (ed.). Exploration for Deposits of Platinum-Group Elements. Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Series, 35: 457-485
|
Edelstein D. 1995. Arsenic: U. S. Geological Survey Minerals Yearbook 1995, 71-74
|
Evans KA, Phillips GN and Powell R. 2006. Rock-buffering of auriferous fluids in altered rocks associated with the Golden Mile-style mineralization, Kalgoorlie gold field, Western Australia. Economic Geology, 101(4): 805-817 |
Fan Y, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Zhang QM, Wu MA, Hou JM and Hu QH. 2007. Geological-geochemical features and genesis of Xiangquan independent thallium deposit in Hexian County, Anhui Province. Mineral Deposits, 26(6): 597-608 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Fiorentini ML, LaFlamme C, Denyszyn S, Mole D, Maas R, Locmelis M, Caruso S and Bui TH. 2018. Post-collisional alkaline magmatism as gateway for metal and sulfur enrichment of the continental lower crust. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 223: 175-197 |
Gartman A, Hannington M, Jamieson JW, Peterkin B, Garbe-Schönberg D, Findlay AJ, Fuchs S and Kwasnitschka T. 2018. Boiling-induced formation of colloidal gold in black smoker hydrothermal fluids. Geology, 46(1): 39-42 |
Goldfarb RJ, Baker T, Dubé B, Groves DI, Hart CJR and Gosselin P. 2005. Distribution, character, and genesis of gold deposits in metamorphic terran. In: Hedenquist JW, Thompson JFH, Goldfarb RJ and Richards JP (eds.). Economic Geology, 100th Anniversary Volume. Colorado, USA: Society of Economic Geologists, 407-450
|
Goldfarb RJ, Taylor RD, Collins GS, Goryachev NA and Orlandini OF. 2014. Phanerozoic continental growth and gold metallogeny of Asia. Gondwana Research, 25(1): 48-102 |
Goldfarb RJ and Groves DI. 2015. Orogenic gold:Common or evolving fluid and metal sources through time. Lithos, 233: 2-26 |
Goldfarb RJ, Hofstra AH and Simmons SF. 2016. Critical elements in Carlin, epithermal, and orogenic gold deposits. In: Rare Earth and Critical Elements in Ore Deposits. Littleton, CO: Society of Economic Geologists, 18: 217-244
|
Goldfarb RJ, Berger BR, George MW and Seal RR II. 2017. Tellurium. In: Schulz KJ, DeYoung JH Jr, Seal RR II and Bradley DC (eds.). Critical Mineral Resources of the United States: Economic and Environmental Geology and Prospects for Future Supply. U. S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1802: R1-R27
|
Goldfarb RJ, Qiu KF, Deng J, Chen YJ and Yang LQ. 2019. Orogenic gold deposits of China. Society of Economic Geologists Special Publication, 113: 263-324 |
Goss SC, Wilde SA, Wu FY and Yang JH. 2010. The age, isotopic signature and significance of the youngest Mesozoic granitoids in the Jiaodong Terrane, Shandong Province, North China Craton. Lithos, 120(3-4): 309-326 |
Groves DI, Goldfarb RJ, Gebre-Mariam M, Hagemann SG and Robert F. 1998. Orogenic gold deposits:A proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types. Ore Geology Reviews, 13(1-5): 7-27 |
Groves DI, Santosh M, Deng J, Wang QF, Yang LQ and Zhang L. 2020. A holistic model for the origin of orogenic gold deposits and its implications for exploration. Mineralium Deposita, 55(2): 275-292 |
Gu XP, Watanabe M, Hoshino K and Shibata Y. 2003. New find of silver tellurosulphides from the Funan gold deposit, East Shandong, China. European Journal of Mineralogy, 15(1): 147-155 |
Gu XP, Watanabe M, Xie XD, Peng XL, Nakamuta Y, Ohkawa M, Hoshino K, Ohsumi K and Shibata Y. 2008. Chenguoda mine (Ag9FeTe2S4):A new sulfur telluride mineral found in gold deposits in Jiaodong region. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(17): 2064-2070 (in Chinese) |
Gulley AL, Nassar NT and Xun S. 2018. China, the United States, and competition for resources that enable emerging technologies. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(16): 4111-4115 |
Gunn G. 2014. Critical Metals Handbook. New York: Wiley, 1-439
|
Guo LN, Huang CM, Zhang L, Chen BH, Li RH and Liu Y. 2019. Source of ore-forming fluids in the Luoshan gold deposit, Jiaodong:Constrains from REE and trace element features of auriferous pyrite in the altered-rock type and auriferous quartz vein type ores. Geoscience, 33(1): 121-136 |
Guo LN, Deng J, Yang LQ, Wang ZL, Wang SR, Wei YJ and Chen BH. 2020. Gold deposition and resource potential of the Linglong gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula:Geochemical comparison of ore fluids. Ore Geology Reviews, 120: 103434 |
Hagemann SG and Lüders V. 2003. P-T-X conditions of hydrothermal fluids and precipitation mechanism of stibnite-gold mineralization at the Wiluna lode-gold deposits, Western Australia:Conventional and infrared microthermometric constraints. Mineralium Deposita, 38(8): 936-952 |
Hai DJ. 2013. Genetic mineralogy and deep ore prospecting of the Songjiazhuang gold deposit in Rushan County, Shandong Province. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1-65 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Hannington M and Garbe-Schönberg D. 2019. Detection of gold nanoparticles in hydrothermal fluids. Economic Geology, 114(2): 397-400 |
Hedenquist JW and Taran YA. 2013. Modeling the formation of advanced argillic lithocaps:Volcanic vapor condensation above porphyry intrusions. Economic Geology, 108(7): 1523-1540 |
Hou ZQ, Zhou Y, Wang R, Zheng YC, He WY, Zhao M, Rvans NJ and Wenberg RF. 2017. Recycling of metal-fertilized lower continental crust:Origin of non-arc Au-rich porphyry deposits at cratonic edges. Geology, 45(6): 563-566 |
Hu FF, Fan HR, Yang JH, Wan YS, Liu DY, Zhai MG and Jin CW. 2004. Metallogenic age of quartz vein type gold deposit in Rushan, Jiaodong:Hydrothermal zircon U-Pb measurement by SHRIMP method. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(12): 1191-1198 (in Chinese) |
Hu RZ, Fu SL and Xiao JF. 2016. Major scientific problems on low-temperature metallogenesis in South China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(11): 3239-3251 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu WX, Sun GX, Zhang WL and Wang ZK. 2005. Au-Ag telluride minerals and their precipitation mechanism in the Rushan gold deposit, Shandong. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 25(2): 177-182 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Huang XL, He PL, Wang X, Zhong JW and Xu YG. 2016. Lateral variation in oxygen fugacity and halogen contents in early cretaceous magmas in Jiaodong area, east China:Implication for triggers of the destruction of the North China Craton. Lithos, 248-251: 478-492 |
Ivanov SM, Ansdell KM and Melsore DL. 2000. Ore texture and stable isotope constraints on ore deposition mechanisms at the Kumtor lode gold deposit. Society of Economic Geologists, Short Course Poster Session, Extended Abstract Volume: 47-52
|
Jiang SY, Wen HJ, Xu C, Wang Y, Su HM and Sun WD. 2019. Earth sphere cycling and enrichment mechanism of critical metals:Major scientific issues for future research. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 33(2): 112-118 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Kong QY, Zhang TZ, Yu XF, Xu JX, Pan YL and Li XS. 2006. Deposits in Shandong Province. Jinan: Shandong Science and Technology Press, 1-902 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Lan TG, Fan HR, Hu FF, Yang GF and Wang Y. 2011. Genesis of the Weishan REE deposit, Shandong Province:Evidences from Rb-Sr isochron age, LA-MC-ICPMS Nd isotopic compositions and fluid inclusions. Geochemistry, 40(5): 428-442 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Large R, Thomas H, Craw D, Henne A and Henderson S. 2012. Diagenetic pyrite as a source for metals in orogenic gold deposits, Otago Schist, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 55(2): 137-149 |
Li J, Song MC, Liang JL, Jiang MY, Li SY, Ding ZJ and Su F. 2020. Source of ore-forming fluids of the Jiaojia deeply-seated gold deposit:Evidences from trace elements and sulfur-helium-argon isotopes of pyrite. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(1): 297-313 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li L, Santosh M and Li SR. 2015. The 'Jiaodong type' gold deposits:Characteristics, origin and prospecting. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 589-611 |
Li N, Deng J, Yang LQ, Goldfarb RJ, Zhang C, Marsh E, Lei SB, Koenig A and Lowers H. 2014. Paragenesis and geochemistry of ore minerals in the epizonal gold deposits of the Yangshan gold belt, West Qinling, China. Mineralium Deposita, 49(4): 427-449 |
Li N, Yang LQ, Groves DI, Li HX, Liu XW, Liu J, Ye Y, Li HR, Liu CX and Yin C. 2020. Tectonic and district to deposit-scale structural controls on the Ge'erke orogenic gold deposit within the Dashui-Zhongqu District, West Qinling. Ore Geology Reviews, 120: 103436 |
Li RH, Albert NN, Yun MH, Meng YS and Du H. 2019. Geological and geochemical characteristics of the Archean basement-hosted gold deposit in Pinglidian, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China:Constraints on auriferous quartz-vein exploration. Minerals, 9(1): 62 |
Li RH, Yang LQ, Hun MH, An P, Qiu KF and Meng YS. 2019. Genetic relationship between micro-deformation and gold enrichment of gold-bearing pyrite in Jiaodong:Constraint from EBSD fabrics and geochemistry. Mineral Deposits, 38(2): 303-318 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li RX, Xu SH, Yang ZL, Liu TP, Wang YQ and Xie TC. 2017. Geochemical study on fluid inclusion and H-O isotope of Daobeizhuangzi gold deposit in Xiadian gold field in Jiaodong Province. Shandong Land and Resources, 33(8): 15-20 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li T and Ni SB. 1990. The Chemical Abundance of the Earth and its Crust. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-136 (in Chinese)
|
Li XC, Fan HR, Santosh M, Hu FF, Yang KF and Lan TG. 2013. Hydrothermal alteration associated with Mesozoic granite-hosted gold mineralization at the Sanshandao deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 53: 403-421 |
Liang YY, Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF, Qin C, Yang Y, Zhou M and Jiang JY. 2018. Major and trace element, and Sr isotope compositions of clinopyroxene phenocrysts in mafic dykes on Jiaodong Peninsula, southeastern North China Craton:Insights into magma mixing and source metasomatism. Lithos, 302-303: 480-495 |
Liu JC, Li XF, Liu YF, Wang BY, Mi NZ and Zhang X. 2010. Mineralogical characteristics of telluride and their precipitation mechanism in the Jinqingding gold deposit, eastern Shandong, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(9): 1319-1328 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu XD, Deng J, Zhang L, Lin SY, Zhou ML, Song YZ, Xu XL and Lian CQ. 2019. Hydrothermal alteration of the Sizhuang gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(5): 1551-1565 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu Y, Yang LQ, Guo LN, Li RH, Gao BF, Meng YS and Zhang RZ. 2014. Composition of ore-forming fluids in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit of the Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2507-2517 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu YJ, Cao LM, Li ZL, Wang HN, Chu TQ and Zhang JR. 1984. Geochemistry of Elements. Beijing: Science Press, 1-548 (in Chinese)
|
Liu YZ, Yang LQ, Wang SR, Liu XD, Wang H, Li DP, Wei PF, Cheng W and Chen BY. 2019. Origin and evolution of ore-forming fluid and gold-deposition processes at the Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Minerals, 9(3): 189 |
Lu AH and Chen GY. 1994. Typomorphic characteristics of chemical composition of chromo-alumino-mica from gold deposits of Jiaojia type. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 13(4): 353-361 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Lv JY, Wang FJ, Hu BQ, Wang XR, Zhang P and Teng F. 2017. Geological characteristics and ore prospecting direction of a new type gold deposit hosted in fine-grained granite in Kunyushan area in Shandong Province:Setting Xiawolong gold depostit as an example. Shandong Land and Resources, 33(9): 1-6 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ma GG. 2011. Genetic mineralogy and deep prospects of Linglong gold deposit in Zhaoyuan, east Shandong Province. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1-113 (in Chinese)
|
Ma L, Jiang SY, Hou ML, Dai BZ, Jiang YH, Yang T, Zhao KD, Pu W, Zhu ZY and Xu B. 2014. Geochemistry of Early Cretaceous calc-alkaline lamprophyres in the Jiaodong Peninsula:Implication for lithospheric evolution of the eastern North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 25(2): 859-872 |
Ma WD, Fan HR, Liu X, Pirajno F, Hu FF, Yang KF, Yang YH, Xu WG and Jiang P. 2017. Geochronological framework of the Xiadian gold deposit in the Jiaodong province, China:Implications for the timing of gold mineralization. Ore Geology Reviews, 86: 196-211 |
Ma WD, Fan HR, Liu X and Yang KF. 2017. The in-situ trace elements, quartz fluid inclusions and H-O-S-HE-AR isotopes of pyrite:An indicator of gold mineralization in Xiadian gold deposit, northwest Jiaodong. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, (Suppl.): 487 (in Chinese) |
Mao JW, Wang YT, Zhang ZH, Yu JJ and Niu BG. 2003. Geodynamic settings of Mesozoic large-scale mineralization in North China and adjacent areas. Science in China (Series D), 46(8): 838-851 |
Mao JW, Pirajno F and Cook N. 2011. Mesozoic metallogeny in East China and corresponding geodynamic settings:An introduction to the special issue. Ore Geology Reviews, 43(1): 1-7 |
Mao JW, Yuan SD, Xie GQ, Song SW, Zhou Q, Gao YB, Liu X, Fu XF, Cao J, Zeng ZL, Li TG and Pan XY. 2019. New advances on metallogenic studies and exploration on critical minerals of China in 21st century. Mineral Deposits, 38(5): 935-969 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
McDonough WF and Sun SS. 1995. The composition of the Earth. Chemical Geology, 120(3-4): 223-253 |
Mériaud N and Jébrak M. 2017. From intrusion-related to orogenic mineralization:The Wasamac deposit, Abitibi Greenstone Belt, Canada. Ore Geology Reviews, 84: 289-308 |
Ministry of Natural Resources, PRC. 2019. China Mineral Resources 2019. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-68
|
Mosselmans JFW, Helz GR, Pattrick RAD, Charnock JM and Vaughan DJ. 2000. A study of speciation of Sb in bisulfide solutions by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Applied Geochemistry, 15(6): 879-889 |
Mudd GM, Jowitt SM and Werner TT. 2017. The world's by-product and critical metal resources:Part Ⅰ:Uncertainties, current reporting practices, implications and grounds for optimism. Ore Geology Reviews, 86: 924-938 |
Mueller AG and Muhling JR. 2013. Silver-rich telluride mineralization at Mount Charlotte and Au-Ag zonation in the giant Golden Mile deposit, Kalgoorlie, Western Australia. Mineralium Deposita, 48(3): 295-311 |
Mungall JE. 2002. Roasting the mantle:Slab melting and the genesis of major Au and Au-rich Cu deposits. Geology, 30(10): 915-918 |
Nadeau O, Williams J, Anthony E and Stix J. 2010. Sulphide magma as a source of metals in arc-related magmatic hydrothermal ore fluids. Nature Geoscience, 3(7): 501-505 |
Nesbitt BE, Muehlenbachs K and Murowchick JB. 1989. Genetic implications of stable isotope characteristics of mesothermal Au deposits and related Sb and Hg deposits in the Canadian Cordillera. Economic Geology, 84(6): 1489-1506 |
Obolensky AA, Gushchina LV, Borisenko AS, Borovikov AA and Nevol'ko PA. 2009. Computer thermodynamic modeling of the transport and deposition of Sb and Au during the formation of Au-Sb deposits. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 50(11): 950-965 |
Pan YC. 1994. Discovery of bismuth opaque mineral in Jiaodong gold deposit and its geological significance. Gold Geological Technology, (1): 80-83 (in Chinese) |
Petrella L, Thébaud N, Fougerouse D, Evans K, Quadir Z and Laflamme C. 2020. Colloidal gold transport:A key to high-grade gold mineralization?. Mineralium Deposita DOI:10.1007/s00126-020-00965-x |
Pitcairn IK, Olivo GR, Teagle DAH and Craw D. 2010. Sulfide evolution during prograde metamorphism of the Otago and Alpine schists, New Zealand. Canadian Mineralogist, 48(5): 1267-1295 |
Pokrovski GS, Kokh MA, Guillaume D, Borisova AY, Gisquet P, Hazemann JL, Lahera E, Del Net W, Proux O, Testemale D, Haigis V, Jonchière R, Seitsonen AP, Ferlat G, Vuilleumier R, Saitta AM, Boiron MC and Dubessy J. 2015. Sulfur radical species form gold deposits on Earth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(44): 13484-13489 |
Prokofiev VY, Banks DA, Lobanov KV, Selektor SL, Milichko VA, Akinfiev NN, Borovikov AA, Lüders V and Chicherov MV. 2020. Exceptional concentrations of gold nanoparticles in 1.7Ga fluid inclusions from the Kola superdeep borehole, Northwest Russia. Scientific Reports, 10(1): 1108 |
Qin Y, Wang WF, Cheng AG, Liu XH and Zhao JL. 2009. Study of ore-forming potential of gallium in coal for the first group of state programmed mining districts. Coal Geology of China, 21(1): 17-21 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Selvaraja V, Caruso S, Fiorentin ML, LaFlamme CK and Bui TH. 2017. Atmospheric sulfur in the orogenic gold deposits of the Archean Yilgarn Craton, Australia. Geology, 45(8): 691-694 |
She HD, Fan HR, Hu FF, Yang KF, Yang ZF and Wang QW. 2018. Migration and precipitation of rare earth elements in the hydrothermal fluids. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(12): 3567-3581 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Shen K, Hu SX, Sun JG, Ling HF, Zhao YY and Sun MZ. 2000. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit in eastern Shandong, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 16(4): 542-550 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Simmons SF, White NC and John DA. 2005. Geological characteristics of epithermal precious and base metal deposits. In: Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume. Colorado, USA: Society of Economic Geologists, 485-522
|
Song MC, Song YX, Shen K, Jiang HL and Li SY. 2013. Geochemical features of deeply-seated gold deposit and discussions on some associated problems in Jiaojia gold ore field, Shandong Peninsula, China. Geochimica, 42(3): 274-289 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Song MC, Zhang JJ, Zhang PJ, Yang LQ, Liu DH, Ding ZJ and Song YX. 2015. Discovery and tectonic-magmatic background of superlarge gold deposit in offshore of northern Sanshandao, Shandong Peninsula, China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(2): 365-383 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun GX, Hu WX, Hu SX, Zhang WL, Zhang GH and Geng XH. 2002. Rare-earth minerals in the gold-bearing quartz vein in the Rushan gold deposit in East China and their significances. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 38(3): 446-456 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Sanders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345
|
Sun WD, Bennett VC, Eggins SM, Arculus RJ and Perfit MR. 2003. Rhenium systematics in submarine MORB and back-arc basin glasses:Laser ablation ICP-MS results. Chemical Geology, 196(1-4): 259-281 |
Sun XD, Tang CH, Yu S and Yang K. 2018. Geological characteristics and genesis of Chakuang gold-antimony deposit in Yantai, Shandong Province. Gold, 39(11): 14-18 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Tang J, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Gong B, Zha XP and Liu XM. 2008. Zircon U/Pb age and geochemical constraints on the tectonic affinity of the Jiaodong Terrane in the Sulu Orogen, China. Precambrian Research, 161(3-4): 389-418 |
Tassara S, González-Jiménez JM, Rech M, Schilling ME, Morata D, Begg G, Saunders E, Griffin WL, O'Reilly SY, Grégoire M, Barra F and Corgne A. 2017. Plume-subduction interaction forms large auriferous provinces. Nature Communications, 8(1): 843 |
Taylor SR and McLennan SM. 1985. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution: An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary Rocks. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific
|
Tooth B, Brugger J, Ciobanu C and Liu WH. 2008. Modeling of gold scavenging by bismuth melts coexisting with hydrothermal fluids. Geology, 36(10): 815-818 |
Tu GC, Yin HH and Yu CM. 1989. Pb-Zn deposits in China. In: Deposits in China (Ⅰ). Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Tu GC, Gao ZM, Hu RZ, Zhang Q, Li ZY, Zhao ZH and Zhang BG. 2004. The Geochemistry and Ore-Forming Mechanism of the Dispersed Elements. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-424 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
U. S. Geological Survey (USGS). 2018. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2018. U. S. Geological Survey, 1-200
|
Uspenskiy YI and Aleshin AP. 1993. Patterns of scheelite mineralization in the Muruntau gold deposit, Uzbekistan. International Geology Review, 35(11): 1037-1051 |
Verplanck PL. 2017. The role of fluids in the formation of rare earth element deposits. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 17: 758-761 |
Wagner T, Mlynarczyk MSJ, Williams-Jones AE and Boyce AJ. 2009. Stable isotope constraints on ore formation at the San Rafael tin-copper deposit, Southeast Peru. Economic Geology, 104(2): 223-248 |
Wan D. 2014. Study on Metallogenic regularities and metallogenic prognosis of gold deposits in northern Zhaoping fracture, Jiaodong area, Shangdong, China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-188 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Wang CY, Zhou MF, Yang SH, Qi L and Sun YL. 2014b. Geochemistry of the Abulangdang intrusion:Cumulates of high-Ti picritic magmas in the Emeishan large igneous province, SW China. Chemical Geology, 378-379: 24-39 |
Wang JG, Liu HC, Deng J, Zhang J, Liu BG and Qian J. 2009. REE characteristics of the Xiejiagou gold deposit, eastern Shandong Province and its significance to mineralizations. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(10): 1497-1504 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang SR, Yang LQ and Kong PF. 2016. Permeability structure and gold deposits cluster mechanism along the Jiaojia fault, China:Structure stress transfer modeling. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2494-2508 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang SR, Yang LQ, Wang JG, Wang EJ and Xu YL. 2019. Geostatistical determination of ore shoot plunge and structural control of the Sizhuang world-class epizonal orogenic gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Minerals, 9(4): 214 |
Wang ZL, Yang LQ, Deng J, Santosh M, Zhang HF, Liu Y, Li RH, Huang T, Zheng XL and Zhao H. 2014a. Gold-hosting high Ba-Sr granitoids in the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, East China:Petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 95: 274-299 |
Wang ZL, Yang LQ, Guo LN, Marsh E, Wang JP, Liu Y, Zhang C, Li RH, Zhang L, Zheng XL and Zhao RX. 2015. Fluid immiscibility and gold deposition in the Xincheng deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China:A fluid inclusion study. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 701-717 |
Wang ZP, Xia Y, Song XY, Liu JZ, Yang CF and Yan BW. 2013. Study on the evolution of ore-formation fluids for Au-Sb ore deposits and the mechanism of Au-Sb paragenesis and differentiation in the southwestern part of Guizhou Province, China. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 32(1): 56-68 |
Weatherley DK and Henley RW. 2013. Flash vaporization during earthquakes evidenced by gold deposits. Nature Geoscience, 6(4): 294-298 |
Wei PF, Yu XF, Li DP, Liu Q, Yu LD, Li ZS, Geng K, Zhang Y, Sun YQ and Chi NJ. 2019b. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology, and Lu-Hf isotopes of the Chishan alkaline complex, western Shandong, China. Minerals, 9(5): 293 |
Wei YJ, Yang LQ, Feng JQ, Wang H, Lv GY, Li WC and Liu SG. 2019a. Ore-fluid evolution of the Sizhuang orogenic gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Minerals, 9(3): 190 |
Wen BJ, Fan HR, Hu FF, Yang KF, Liu X, Cai YC, Sun ZF and Sun ZF. 2015. The genesis of pegmatite-type molybdenum mineralization in Sanshandao, and their implications for molybdenum deposit in Jiaodong, East China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(4): 1002-1014 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wen HJ, Zhou ZB, Zhu CW, Luo CG, Wang DZ, Du SJ, Li XF, Chen MH and Li HY. 2019. Critical scientific issues of super-enrichment of dispersed metals. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(11): 3271-3291 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wood SA and Samson IM. 2000. The hydrothermal geochemistry of tungsten in granitoid environments:Ⅰ. Relative solubilities of ferberite and scheelite as a function of T, P, pH, and mNaCl. Economic Geology, 95(1): 143-182 |
Xu JH, Xie YL, Han Y and Li QM. 2004. Characteristics of gold-bearing sulfides and their geological significance in Sanshandao gold deposit, eastern Shandong Province. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, (1): 1-6 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu SP, Yang LQ, Zhang SJ and Guo CY. 2010. Metallogenic indication element characteristics and application of gold deposit in Zhaoyuan-Pingdu fault zone. Gold Science and Technology, 18(5): 7-11 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xue YX, Campbell I, Ireland TR, Holden P and Armstrong R. 2013. No mass-independent sulfur isotope fractionation in auriferous fluids supports a magmatic origin for Archean gold deposits. Geology, 41(7): 791-794 |
Yan HB, Ding X, Wang Y, Mi M and Sun WD. 2020. The mobility of platinum-group elements in the hydrothermal fluids. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(1): 85-98 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang GM. 1980. Study on the occurrence status of iron in the hematite-type rare earth ore. Geology and Exploration, (7): 35-40 (in Chinese) |
Yang JH, Chung SL, Zhai MG and Zhou XH. 2004. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of mafic dikes from the Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Evidence for vein-plus-peridotite melting in the lithospheric mantle. Lithos, 73(3-4): 145-160 |
Yang KF, Fan HR, Santosh M, Hu FF, Wilde SA, Lan TG, Lu LN and Liu YS. 2012. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust:Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of Late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton. Lithos, 146-147: 112-127 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Ge LS, Wang QF, Zhang J, Gao BF, Jiang SQ and Xu H. 2007. Metallogenic epoch and genesis of the gold deposits in Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China:A regional review. Progress in Nature Science, 17(2): 138-143 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Zhang J, Guo CY, Gao BF, Gong QJ, Wang QF, Jiang SQ and Yu HJ. 2008. Decrepitation thermometry and compositions of fluid inclusions of the Damoqujia gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China:Implications for metallogeny and exploration. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 19(4): 378-390 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Guo CY, Zhang J, Jiang SQ, Gao BF, Gong QJ and Wang QF. 2009. Ore-forming fluid characteristics of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China. Resource Geology, 59(2): 181-193 |
Yang LQ, Liu JT, Zhang C, Wang QF, Ge LS, Wang ZL, Zhang J and Gong QJ. 2010. Superimposed orogenesis and metallogenesis: An example from the orogenic gold deposits in Ailaoshan gold belt, Southwest China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(6): 1723-1739 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Zhao K and Liu JT. 2011a. Tectono-thermochronology and gold mineralization events of orogenic gold deposits in Ailaoshan orogenic belt, Southwest China: Geochronological constraints. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2519-2532 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Zhao K, Liu JT, Ge LS, Zhou DQ, Li SH and Cao BB. 2011b. Geological characteristics and genetic type of Daping gold deposit in the Ailaoshan orogenic belt, SW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(12): 3800-3810 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Goldfarb RJ, Zhang J, Gao BF and Wang ZL. 2014. 40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the formation of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit: New implications for timing and duration of hydrothermal activity in the Jiaodong gold province, China. Gondwana Research, 25(4): 1469-1483 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Zhang L, Guo LN, Song MC and Zheng XL. 2014a. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2447-2467 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang LQ, Deng J and Wang ZL, 2014b. Ore-controlling structural pattern of Jiaodong gold deposits: Geological-geophysical integration constraints. In: Chen Y, Jin Z, Shi Y, Yang W and Zhu R (eds). The Deep-seated Structures of Earth in China. Beijing: Sciences Press, 1006-1030 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang LQ, Deng J, Guo RP, Guo LN, Wang ZL, Cheng BH, Wang BH and Wang XD. 2016a. World-class Xincheng gold deposit: An example from the giant Jiaodong Gold Province. Geoscience Frontiers, 7(3): 419-430 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Guo LN, Li RH, Groves DI, Danyushevsky LV, Zhang C, Zheng XL and Zhao H. 2016b. Relationships between gold and pyrite at the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Implications for gold source and deposition in a brittle epizonal environment. Economic Geology, 111(1): 105-126 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Li N, Zhang C, Ji XZ and Yu JY. 2016c. Isotopic characteristics of gold deposits in the Yangshan Gold Belt, West Qinling, central China: Implications for fluid and metal sources and ore genesis. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 168: 103-118 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Guo LN, Wang ZL, Li XZ and Li JL. 2016d. Origin and evolution of ore fluid, and gold-deposition processes at the giant Taishang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 72: 585-602 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Zhang L, Goldfarb RJ, Yuan WM, Weinberg RF and Zhang RZ. 2016e. Thermochronologic constraints on evolution of the Linglong Metamorphic Core Complex and implications for gold mineralization: A case study from the Xiadian gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 72: 165-178 |
Yang LQ, Guo LN, Wang ZL, Zhao RX, Song MC and Zheng XL. 2017. Timing and mechanism of gold mineralization at the Wang'ershan gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 88: 491-510 |
Yang LQ, Dilek Y, Wan ZL, Weinberg RF and Liu Y. 2018. Late Jurassic, high Ba-Sr Linglong granites in the Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Lower crustal melting products in the eastern North China craton. Geological Magazine, 155(5): 1040-1062 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Song MC, Yu XF, Wang ZL, Li RH and Wang SR. 2019. Structure control on formation and localization of giant deposits: An example of Jiaodong gold deposits in China. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 43(3): 431-446 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang MZ and Lv GX. 1996. The Geology-Geochemistry of Gold Deposits of the Greenstone Belt in Jiaodong District, China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-221 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang QY, Shen JF, Li SR, Santosh M, Luo ZH and Liu Y. 2013. Oxygen, boron, chromium and niobium enrichment in native Au and Ag grains: A case study from the Linglong gold deposit, Jiaodong, eastern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 62: 537-546 |
Yu XF, Tang HS, Han ZZ and Li CY. 2010. Geological characteristics and origin of rare earth elements deposits related with alkaline rock in the Chishan-Longbaoshan area, Shandong Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(3): 407-417 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai DG and Liu JJ. 2014. Gold-telluride-sulfide association in the Sandaowanzi epithermal Au-Ag-Te deposit, NE China: Implications for phase equilibrium and physicochemical conditions. Mineralogy and Petrology, 108(6): 853-871 |
Zhai DG, Williams-Jones AE, Liu JJ, Tombros SF and Cook NJ. 2018. Mineralogical, fluid inclusion, and multiple isotope (H-O-S-Pb) constraints on the genesis of the Sandaowanzi epithermal Au-Ag-Te deposit, NE China. Economic Geology, 113(6): 1359-1382 |
Zhai JP, Xu GP and Hu K. 1998. Mineral, ore forming fluid and isotope characteristics of the Qixia gold deposit and their implications. Mineral Deposits, 17(4): 307-313 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai MG, Yang JH and Liu WJ. 2001. Jiaodong large-scale gold deposit cluster and large-scale metallogenesis. Science in China (D), 31(7): 545-552 (in Chinese) |
Zhai MG, Fan HR, Yang JH and Miao LC. 2004. Large-scale cluster of gold deposits in East Shandong: Anorogenic metallogenesis. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(1): 85-98 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai MG, Wu FY, Hu RZ, Jiang SY, Li WC, Wang RC, Wang DH, Qi T, Qin KZ and Wen HJ. 2019. Critical metal mineral resources: Current research status and scientific issues. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 33(2): 106-111 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang BL, Yang LQ, Huang SY, Liu Y, Liu WL, Zhao RX, Xu YB and Liu SG. 2014. Hydrothermal alteration in the Jiaojia gold deposit, Jiaodong, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2533-2545 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang C, Huang T, Liu XD, Liu Y, Zhao H and Wang XD. 2016. Hydrothermal alteration of the Xincheng gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2433-2450 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang D and Wang SJ. 1994. Mineralogical characteristics and geological significance of Se, Te-rich stibnite in Sb ore belt, southern Anhui Province. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 19(2): 169-173 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang K. 2019. Scanning electron microscope study on the silver metallogenic period in the Dayingezhuang gold and silver polymetallic deposit, Jiaodong, Shandong Province. Western Resources, (1): 57-58 (in Chinese) |
Zhang L, Yang LQ, Wang Y, Weinberg RF, An P and Chen BY. 2017. Thermochronologic constrains on the processes of formation and exhumation of the Xinli orogenic gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 81: 140-153 |
Zhang L, Yang LQ, Groves DI, Sun SC, Liu Y, Wang JY, Li RH, Wu SG, Gao L, Guo JL, Chen XG and Chen JH. 2019a. An overview of timing and structural geometry of gold, gold-antimony and antimony mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogen, southern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 115: 103173 |
Zhang L, Yang LQ, Weinberg RF, Groves DI, Wang ZL, Li GW, Liu Y, Zhang C and Wang ZK. 2019b. Anatomy of a world-class epizonal orogenic-gold system: A holistic thermochronological analysis of the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Gondwana Research, 70: 50-70 |
Zhang L, Groves DI, Yang LQ, Wang GW, Liu XD, Li DP, Song YX, Shan W, Sun SC and Wang ZK. 2020a. Relative roles of formation and preservation on gold endowment along the Sanshandao gold belt in the Jiaodong gold province, China: Importance for province- to district-scale gold exploration. Mineralium Deposita, 55(2): 325-344 |
Zhang L, Groves DI, Yang LQ, Sun SC, Weinberg RF, Wang JY, Wu SG, Gao L, Yuan LL and Li RH. 2020b. Utilization of pre-existing competent and barren quartz veins as hosts to later orogenic gold ores at Huangjindong gold deposit, Jiangnan Orogen, southern China. Mineralium Deposita, 55(2): 363-380 |
Zhang L, Weinberg RF, Yang LQ, Groves DI, Sai SX, Matchan E, Phillips D, Kohn BP, Miggins DP, Liu Y and Deng J. 2020c. Mesozoic orogenic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A focused event at 120±2Ma during cooling of pregold granite intrusions. Economic Geology, 115(2): 415-441 |
Zhang Y, Liu LD, Sun JG, Chen GH, Zhang HX, Yan FC and Yang KC. 2008. Two phase overprinting mineralization in Huangbuling gold deposit in northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 38(1): 21-26 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao R, Liu XF, Pan RG and Zhou M. 2015. Element behaviors during alteration and mineralization: A case study of the Xinli (altered rock type) gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(11): 3420-3440 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhong RC, Brugger J, Chen YJ and Li WB. 2015a. Contrasting regimes of Cu, Zn and Pb transport in ore-forming hydrothermal fluids. Chemical Geology, 395: 154-164 |
Zhong RC, Brugger J, Tomkins AG, Chen YJ and Li WB. 2015b. Fate of gold and base metals during metamorphic devolatilization of a pelite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 171: 338-352 |
Zhou QF, Li SR, Chen HY, Song YB, Zhang YQ, Zhang XB and Cui JC. 2011. Discovery and geological significance of telluride minerals in the Yinggezhuang gold deposit, Rushan, Jiaodong. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(6): 1847-1856 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhu RX, Fan HR, Li JW, Meng QR, Li SR and Zeng QD. 2015. Decratonic gold deposits. Science China (Earth Sciences), 58(9): 1523-1537 |
Zotov AV, Shikina ND and Akinfiev NN. 2003. Thermodynamic properties of the Sb(Ⅲ) hydroxide complex Sb(OH)3(aq) at hydrothermal conditions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(10): 1821-1836 |
Zuo HY, Lu AH, Gu XP, Ma WD, Cui Y, Yi LW, Lei H, Wang ZL, Zhang DX and Liu JP. 2016. Typomorphic feature of chromium sericite in granite hosted gold deposits in Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Applied Clay Science, 119: 49-58 |
陈光远, 邵伟, 孙岱生. 1989. 胶东金矿成因矿物学与找矿. 重庆: 重庆出版社, 1-250.
|
迟清华, 鄢明才. 2007. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-148.
|
戴雪灵, 邓湘伟, 彭省临, 杨斌. 2011. 玲珑花岗岩在大尹格庄金矿成矿系统中的作用. 地质与勘探, 47(3): 370-379. |
邓军, 陈玉民, 刘钦, 等. 2010. 胶东三山岛断裂带金成矿系统与资源勘查. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-371.
|
丁正江, 孙丰月, 刘福来, 刘建辉, 彭齐鸣, 纪攀, 李碧乐, 张丕建. 2015. 胶东中生代动力学演化及主要金属矿床成矿系列. 岩石学报, 31(10): 3045-3080. |
范裕, 周涛发, 袁峰, 张千明, 吴明安, 候明金, 胡清华. 2007. 安徽和县香泉独立铊矿床的地质地球化学特征及成因探讨. 矿床地质, 26(6): 597-608. |
谷湘平, Watanabe M, 谢先德, 彭省临, Nakamuta Y, Ohkawa M, Hoshino K, Ohsumi K, Shibata Y. 2008. 陈国达矿(Ag9FeTe2S4):胶东地区金矿床中发现的硫碲化物新矿物. 科学通报, 53(17): 2064-2070. |
郭林楠, 黄春梅, 张良, 陈炳翰, 李瑞红, 刘跃. 2019. 胶东罗山金矿床成矿流体来源:蚀变岩型和石英脉型矿石载金黄铁矿稀土与微量元素特征约束. 现代地质, 33(1): 121-136. |
海东婧. 2013.山东乳山宋家庄金矿成因矿物学与深部远景研究.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1-65
|
胡芳芳, 范宏瑞, 杨进辉, 万渝生, 刘敦一, 翟明国, 金成伟. 2004. 胶东乳山含金石英脉型金矿的成矿年龄:热液锆石SHRIMP法U-Pb测定. 科学通报, 49(12): 1191-1198. |
胡瑞忠, 付山岭, 肖加飞. 2016. 华南大规模低温成矿的主要科学问题. 岩石学报, 32(11): 3239-3251. |
胡文瑄, 孙国曦, 张文兰, 王昭坤. 2005. 山东乳山金矿中金-银碲化物的矿物学特征与沉淀机理. 矿物学报, 25(2): 177-182. |
蒋少涌, 温汉捷, 许成, 王焰, 苏慧敏, 孙卫东. 2019. 关键金属元素的多圈层循环与富集机理:主要科学问题及未来研究方向. 中国科学基金, 33(2): 112-118. |
孔庆友, 张天祯, 于学峰, 徐军祥, 潘元林, 李献水. 2006. 山东矿床. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社, 1-902.
|
蓝廷广, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨奎锋, 王永. 2011. 山东微山稀土矿矿床成因:来自云母Rb-Sr年龄、激光Nd同位素及流体包裹体的证据. 地球化学, 40(5): 428-442. |
李杰, 宋明春, 梁金龙, 姜梦瑶, 李世勇, 丁正江, 苏菲. 2020. 焦家深部金矿床成矿流体来源:来自黄铁矿微量元素及S-He-Ar同位素的约束. 岩石学报, 36(1): 297-313. |
李瑞红, 杨立强, 恽孟河, 安平, 邱昆峰, 孟银生. 2019. 胶东黄铁矿显微构造变形与金富集关系:黄铁矿EBSD组构和地球化学约束. 矿床地质, 38(2): 303-318. |
李瑞翔, 徐韶辉, 杨真亮, 刘天鹏, 王永庆, 解天赐. 2017. 胶东夏甸金矿区道北庄子金矿床流体包裹体和氢氧同位素地球化学研究. 山东国土资源, 33(8): 15-20. |
黎彤, 倪守斌. 1990. 地球和地壳的化学元素丰度. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-136.
|
刘建朝, 李旭芬, 刘亚非, 汪帮耀, 米乃哲, 张雪. 2010. 胶东牟平-乳山金矿带金青顶金矿碲化物矿物的特征及沉淀机制. 地质通报, 29(9): 1319-1328. |
刘向东, 邓军, 张良, 林少一, 周明岭, 宋宇宙, 徐晓磊, 连琛芹. 2019. 胶西北寺庄金矿床热液蚀变作用. 岩石学报, 35(5): 1551-1565. |
刘育, 杨立强, 郭林楠, 李瑞红, 高帮飞, 孟银生, 张瑞忠. 2014. 胶东大尹格庄金矿床成矿流体组成. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2507-2517. |
刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 王鹤年, 储同庆, 张景荣. 1984. 元素地球化学. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-548.
|
鲁安怀, 陈光远. 1994. 焦家式金矿中铬铝云母化学成分的标型性. 岩石矿物学杂志, 13(4): 353-361. |
吕军阳, 王福江, 胡秉谦, 王欣然, 张朋, 滕飞. 2017. 山东昆嵛山岩体中与细粒花岗岩有关的新类型金矿床地质特征及找矿方向——以下卧龙矿床为例. 山东国土资源, 33(9): 1-6. |
马广刚. 2011.胶东玲珑金矿成因矿物学与深部远景研究.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1-113
|
马伟东, 范宏瑞, 刘玄, 杨奎锋. 2017. 胶西北夏甸金矿黄铁矿原位微量元素、石英流体包裹体以及H-O-S-He-Ar同位素研究对金矿成矿过程的指示. 矿物学报, (增): 487. |
毛景文, 袁顺达, 谢桂青, 宋世伟, 周琦, 高永宝, 刘翔, 付小方, 曹晶, 曾载淋, 李通国, 樊锡银. 2019. 21世纪以来中国关键金属矿产找矿勘查与研究新进展. 矿床地质, 38(5): 935-969. |
潘玉成. 1994. 胶东金矿中含铋不透明矿物的发现及其地质意义. 黄金地质科技, (1): 80-83. |
秦勇, 王文峰, 程爱国, 刘新花, 赵建岭. 2009. 首批煤炭国家规划矿区煤中镓的成矿前景. 中国煤炭地质, 21(1): 17-21. |
佘海东, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨奎锋, 杨占峰, 王其伟. 2018. 稀土元素在热液中的迁移与沉淀. 岩石学报, 34(12): 3567-3581. |
沈昆, 胡受奚, 孙景贵, 凌洪飞, 赵懿英, 孙明志. 2000. 山东招远大尹格庄金矿成矿流体特征. 岩石学报, 16(4): 542-550. |
宋明春, 宋英昕, 沈昆, 姜洪利, 李世勇. 2013. 胶东焦家深部金矿矿床地球化学特征及有关问题讨论. 地球化学, 42(3): 274-289. |
宋明春, 张军进, 张丕建, 杨立强, 刘殿浩, 丁正江, 宋英昕. 2015. 胶东三山岛北部海域超大型金矿床的发现及其构造-岩浆背景. 地质学报, 89(2): 365-383. |
孙国曦, 胡文瑄, 胡受奚, 张文兰, 张光辉, 耿仙湖. 2002. 胶北乳山金矿含金石英脉中稀土矿物的发现及其意义. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 38(3): 446-456. |
孙绪德, 唐存华, 于森, 杨坤. 2018. 山东烟台岔夼金锑矿床地质特征及成因探讨. 黄金, 39(11): 14-18. |
涂光炽, 尹汗辉, 喻茨玫. 1989.中国铅锌矿床.见: 中国矿床-上册.北京: 地质出版社
|
涂光炽, 高振敏, 胡瑞忠, 张乾, 李朝阳, 赵振华, 张宝贵. 2004. 分散元素地球化学及成矿机制. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-424.
|
万多. 2014.山东胶东地区招平断裂带北段金矿成矿规律与成矿预测.博士学位论文.长春: 吉林大学, 1-188
|
王建国, 刘洪臣, 邓军, 张静, 刘秉光, 钱进. 2009. 胶东谢家沟金矿稀土元素特征及其成矿意义. 地质学报, 83(10): 1497-1504. |
王偲瑞, 杨立强, 孔鹏飞. 2016. 焦家断裂渗透性结构与金矿床群聚机理:构造应力转移模拟. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2494-2508. |
文博杰, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨奎锋, 刘玄, 蔡亚春, 孙之夫, 孙宗锋. 2015. 胶西北三山岛伟晶岩型脉状钼矿化成因及对胶东钼成矿的指示意义. 岩石学报, 31(4): 1002-1014. |
温汉捷, 周正兵, 朱传威, 罗重光, 王大钊, 杜胜江, 李晓峰, 陈懋弘, 李红谊. 2019. 稀散金属超常富集的主要科学问题. 岩石学报, 35(11): 3271-3291. |
徐九华, 谢玉玲, 韩屹, 李前懋. 2004. 三山岛金矿床载金硫化物特征及其地质意义. 华南地质与矿产, (1): 1-6. |
徐述平, 杨立强, 张蜀冀, 郭春影. 2010. 胶东招平断裂带金矿成矿指示元素特征及找矿应用. 黄金科学技术, 18(5): 7-11. |
严海波, 丁兴, 王焰, 糜梅, 孙卫东. 2020. 铂族元素流体活动性. 岩石学报, 36(1): 85-98. |
杨光明. 1980. 赤铁矿型锗矿石中锗的赋存状态研究. 地质与勘探, (7): 35-40. |
杨立强, 刘江涛, 张闯, 王庆飞, 葛良胜, 王中亮, 张静, 龚庆杰. 2010. 哀牢山造山型金成矿系统:复合造山构造演化与成矿作用初探. 岩石学报, 26(6): 1723-1739. |
杨立强, 邓军, 赵凯, 刘江涛. 2011a. 哀牢山造山带金矿成矿时序及其动力学背景探讨. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2519-2532. |
杨立强, 邓军, 赵凯, 刘江涛, 葛良胜, 周道卿, 李士辉, 曹宝宝. 2011b. 滇西大坪金矿床地质特征及成因初探. 岩石学报, 27(12): 3800-3810. |
杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 张良, 郭林楠, 宋明春, 郑小礼. 2014a. 胶东中生代金成矿系统. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2447-2467. |
杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮. 2014b.胶东金矿控矿构造样式: 地质-地球物理综合约束.见: 陈运泰, 金振民, 石耀霖, 杨文采, 朱日祥主编.中国大陆地球深部结构与动力学研究——庆贺滕吉文院士从事地球物理研究60周年.北京: 科学出版社, 1006-1030
|
杨立强, 邓军, 宋明春, 于学峰, 王中亮, 李瑞红, 王偲瑞. 2019. 巨型矿床形成与定位的构造控制:胶东金矿集区剖析. 大地构造与成矿学, 43(3): 431-446. |
杨敏之, 吕古贤. 1996. 胶东绿岩带金矿地质地球化学. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-221.
|
于学峰, 唐好生, 韩作振, 李长有. 2010. 山东郗山-龙宝山地区与碱性岩有关的稀土矿床地质特征及成因. 地质学报, 84(3): 407-417. |
翟建平, 徐光平, 胡凯. 1998. 栖霞金矿矿物、流体和同位素特征及意义. 矿床地质, 17(4): 307-313. |
翟明国, 杨进辉, 刘文军. 2001. 胶东大型黄金矿集区及大规模成矿作用. 中国科学(D辑), 31(7): 545-552. |
翟明国, 范宏瑞, 杨进辉, 苗来成. 2004. 非造山带型金矿——胶东型金矿的陆内成矿作用. 地学前缘, 11(1): 85-98. |
翟明国, 吴福元, 胡瑞忠, 蒋少涌, 李文昌, 王汝成, 王登红, 齐涛, 秦克章, 温汉捷. 2019. 战略性关键金属矿产资源:地质出版社现状与问题. 中国科学基金, 33(2): 106-111. |
张炳林, 杨立强, 黄锁英, 刘跃, 刘文龙, 赵荣新, 徐咏彬, 刘胜光. 2014. 胶东焦家金矿床热液蚀变作用. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2533-2545. |
张潮, 黄涛, 刘向东, 刘育, 赵海, 王旭东. 2016. 胶西北新城金矿床热液蚀变作用. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2433-2450. |
张德, 王顺金. 1994. 皖南锑矿带富硒、碲辉锑矿的矿物学特征及其地质意义. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 19(2): 169-173. |
张克. 2019. 胶东大尹格庄金银多金属矿床银成矿期扫描电镜研究. 西部资源, (1): 57-58. |
张渊, 刘连登, 孙景贵, 陈国华, 张洪喜, 闫复传, 杨开春. 2008. 胶东西北部黄埠岭金矿床两期次叠加成矿. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 38(1): 21-26. |
赵睿, 刘学飞, 潘瑞广, 周勉. 2015. 胶东新立构造蚀变岩型金矿床元素地球化学行为. 岩石学报, 31(11): 3420-3440. |
周起凤, 李胜荣, 陈海燕, 宋玉波, 张运强, 张秀宝, 崔举超. 2011. 胶东乳山英格庄金矿碲化物的发现及其意义. 岩石学报, 27(6): 1847-1856. |
 2020, Vol. 36
2020, Vol. 36

