2. 中国地质调查局沈阳地质调查中心, 沈阳 110034;
3. 中国海洋大学海底科学与探测技术教育部重点实验室, 海洋高等研究院, 海洋地球科学学院, 青岛 266100;
4. 青岛海洋科学与技术国家实验室, 海洋矿产资源评价与探测技术功能实验室, 青岛 266237;
5. 自然资源部东北亚矿产资源评价重点实验室, 长春 130061
2. Shenyang Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, China Geological Survey, Shenyang 110034, China;
3. MOE Key Lab of Submarine Geoscience and Prospecting Techniques, Institute for Advanced Ocean Study, College of Marine Geosciences, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China;
4. Laboratory for Marine Mineral Resources, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266237, China;
5. Key Laboratory of Mineral Resources Evaluation in Northeast Asia, Ministry of Natural Resources, Changchun 130061, China
大兴安岭地区位于中亚造山带东段,是区域构造演化历史中一个重要地质单元,对研究中亚造山带的构造演化历史具有重要的意义(徐备等, 2014; Xiao et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2017)。该区是由额尔古纳、兴安和松辽地块伴随着古亚洲洋的不断消减拼贴所形成的统一陆块群(图 1a)(徐备等, 2014; Liu et al., 2017),因与古亚洲洋最终闭合的时间和位置关系密切,一直是东北地区乃至中亚造山带研究的热点地区(Jahn et al., 2009; 崔芳华等, 2013; 徐备等, 2014; Cui et al., 2015; Xiao et al., 2015; 刘永江等, 2016; 李成禄等, 2017; Feng et al., 2018a, b, 2019;李睿华等, 2018; 梁琛岳等, 2018; 董金龙等, 2018; Ji et al., 2018; Qu et al., 2019)。由于缺少贺根山-黑河一线大兴安岭中段岩浆、构造和古地理环境的制约,目前关于兴安地块与松辽地块之间缝合带的形成时间存在较大的争议(苏养正, 1996; 孙德有等, 2000; 周长勇等, 2005; 唐克东等, 2011; 赵院冬等, 2013; 徐备等, 2014; Liu et al., 2017; Feng et al., 2018b; Ma et al., 2019a, b)。一种观点认为兴安地块与松辽地块于泥盆纪发生碰撞缝合(苏养正, 1996; 唐克东等, 2011; 徐备等, 2014; Zhao et al., 2017),其缝合带位置沿艾力格庙-锡林浩特-黑河一线(徐备等, 2014; Zhao et al., 2017),该观点证据主要为沿艾力格庙、苏尼特左旗、锡林浩特和大石寨到黑河一线分布的早古生代岩浆岩、混杂岩和磨拉石盆地;另一种观点认为兴安地块与松辽地块缝合带位置为贺根山-黑河一线,其碰撞缝合时间为晚石炭世(崔芳华等, 2013; Liu et al., 2017; Feng et al., 2018a; 马永非等, 2018; Ma et al., 2019a, b),该观点主要证据包括:贺根山-黑河一线早古生代及晚古生代两期岩浆弧,早石炭世呈现“北海南陆”、晚石炭世呈现“南海北陆”的古地理格局以及沿该线分布的多宝山岛弧、贺根山蛇绿岩和晚石炭世S型及A型花岗岩。这些争议产生的一个重要原因在于对贺根山-黑河缝合带中段的研究程度较弱,缺少与缝合带相关的岩石学时空约束证据,从而造成了对兴安地块和松辽地块拼贴时间和位置的不同认识。鉴于此,有必要对贺根山-黑河缝合带中段地区展开深入系统的地质研究。

|
图 1 研究区大地构造位置图(a, 据Liu et al., 2017修改)及区域地质图(b) Fig. 1 Tectonic location (a, modified after Liu et al., 2017) and simplified geological maps (b) of study area |
扎兰屯地区位于贺根山-黑河缝合带中段,其晚古生代岩浆岩的岩石成因及构造背景不仅可以用来约束扎兰屯地区晚古生代构造演化特征,也能为限定贺根山-黑河缝合带晚古生代期间的构造格局及演化历史提供重要参考资料。因此,本文以大兴安岭扎兰屯南部早二叠世花岗岩为研究对象,厘定花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年代学格架,分析花岗岩的岩石地球化学特征,探讨花岗岩岩石成因及构造背景,揭示兴安地块和松辽地块的拼合过程及贺根山-黑河缝合带中段构造演化历史。
1 区域地质背景研究区位于内蒙古自治区东部扎兰屯市南侧,大地构造位置位于兴蒙造山带贺根山-黑河缝合带中段,是松辽地块与兴安地块的重要拼贴部位(图 1a)。兴安地块主体由中生代火山岩、沉积岩和零星分布的古生代花岗质岩石、火山岩及沉积地层组成,其“前寒武纪变质岩基底”问题仍存在较大争议(Cui et al., 2015)。松辽地块主要由松辽盆地、小兴安岭-张广才岭及部分南大兴安岭组成,其大部分被松辽盆地中新生代沉积物覆盖。近年来在松辽地块东缘、南部及西缘均有早前寒武纪年龄的相关报道(Wang et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2017)。研究区位于松辽地块和兴安地块交接部位,其出露的地层主要为中生代和晚古生代火山-沉积地层(图 1b)。晚古生代地层较为复杂,由下而上包括大民山组、红水泉组、宝力高庙组、格根敖包组、寿山沟组、大石寨组、哲斯组和林西组;中生代地层主要以火山岩为主。而岩浆岩主要以古生代侵入岩和中生代火山岩为主。古生代侵入岩主要分布在研究区的东部,呈北北东向展布,在大民山组、格根敖包组和大石寨组地层中含有少量浅变质的古生代火山岩及火山碎屑岩夹层。中生代岩浆岩以火山岩为主,包括哈达陶勒盖期、老龙头期、满克头鄂博期、玛尼吐期、白音高老期、龙江期、光华期和甘河期火山岩。
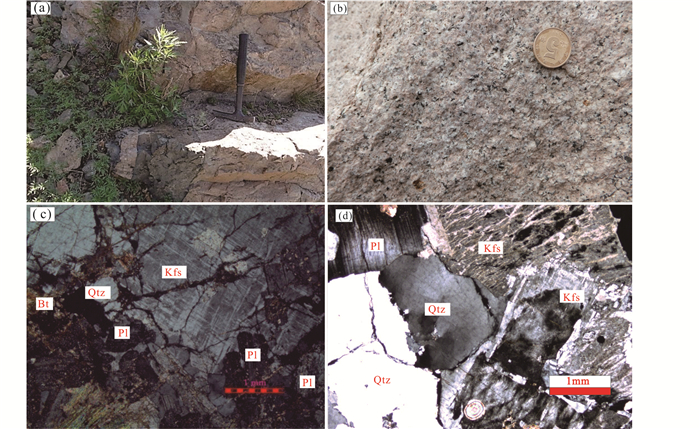
2 样品描述及岩相学特征早二叠世花岗岩在研究区内呈北北东向展布,该花岗岩侵入到早期古生代沉积地层中,岩体中见有古生代地层捕虏体和细粒闪长岩包体(秦涛等, 2017),此外早二叠世花岗岩被后期中生代岩浆活动破坏或被中生代火山岩地层覆盖(图 2)。本次工作对出露于研究区的二长花岗岩和碱长花岗岩进行了岩相学、岩石地球化学和年代学样品分析。样品TWKSD05(二长花岗岩)采自徐地营子东侧30km外的新鲜露头处;样品TW11(碱长花岗岩)采自扎兰屯市西南侧30km外的新鲜露头处;样品2015TW02(二长花岗岩)采自罕达罕东北30km外的新鲜露头处(图 1b)。样品特征描述如下:二长花岗岩为中细粒花岗结构,块状构造,主要组成矿物为石英(20%)、斜长石(35%)、碱性长石(主要为条纹长石和正长石,含量40%)和黑云母(5%),岩石发生碎裂,沿裂隙填充绿泥石和云母类矿物(图 2c);碱长花岗岩具有中细粒花岗结构,块状构造,主要组成矿物为条纹长石(60%)、石英(35%)及黑云母(5%)(图 2d)。

|
图 2 扎兰屯地区早二叠世花岗岩野外及岩相学特征 Bt-黑云母;Qtz-石英;Pl-斜长石;Kfs-钾长石 Fig. 2 Field and petrography features of Early Permian granites in Zhalantun area |
锆石的分选工作在河北省廊坊市科大矿物分选技术股份有限公司完成,样品制靶和CL图像采集和锆石U-Pb测年工作在中国地质科学院国家地质实验室完成。锆石测年所采用的仪器为Thermo Element Ⅱ型MC-ICP-MS及与之配套的New wave UP213激光剥蚀系统,激光束斑直径为30μm。普通铅校正采用Andersen (2002)的方法,并采用哈佛大学国际标准锆石91500作为外部校正(Yuan et al., 2004),详细实验测试过程可参见文献(Yuan et al., 2004)。所测年龄结果计算采用国际标准程序Isoplot(ver3.0),其所获得的测试数据、加权平均年龄的误差均为1σ,谐和度在95%以上的数据为有效数据。
主量元素和痕量元素的分析在国土资源部沈阳矿产资源监督检测中心完成。采用X射线荧光光谱法(XRF-1500)对主量元素进行分析,采用电感耦合等离子质谱法(X series 2型ICP-MS质谱仪)对稀土、微量元素进行分析。主量元素和稀土、微量元素精度和准确度分别优于5%和10%。
4 分析结果 4.1 锆石U-Pb测年结果本文对扎兰屯南部地区早二叠世二长花岗岩和碱长花岗岩共3件样品进行了锆石U-Pb年代学分析(表 1),测试结果如下。
|
|
表 1 扎兰屯地区早二叠世花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄结果 Table 1 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb data of Early Permian granites in Zhalantun area |
样品TWKSD05(二长花岗岩):锆石呈半自形-自形,具有岩浆震荡环带(图 3a),大小约80~120μm。所有锆石的Th/U值为0.20~1.00,具有岩浆成因锆石的特征。对样品TWKSD05的30粒锆石进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学分析,除2粒锆石(-3和-29)外,其余锆石颗粒年龄均位于谐和线上及其附近(图 3b)。所测年龄结果可以分为四组:(1)212±5Ma~223±5Ma(2粒,212±5Ma未在谐和线上);(2)267±6Ma~273±7Ma(2粒);(3)287±7Ma~314±8Ma(13粒),加权平均年龄为298±6Ma(MSWD=2,n=13)(图 3c);(4)327±8Ma~351±10Ma(13粒,351±10Ma锆石颗粒未在谐和线上),加权平均年龄为335±5Ma(MSWD=0.97,n=12)(图 3d)。
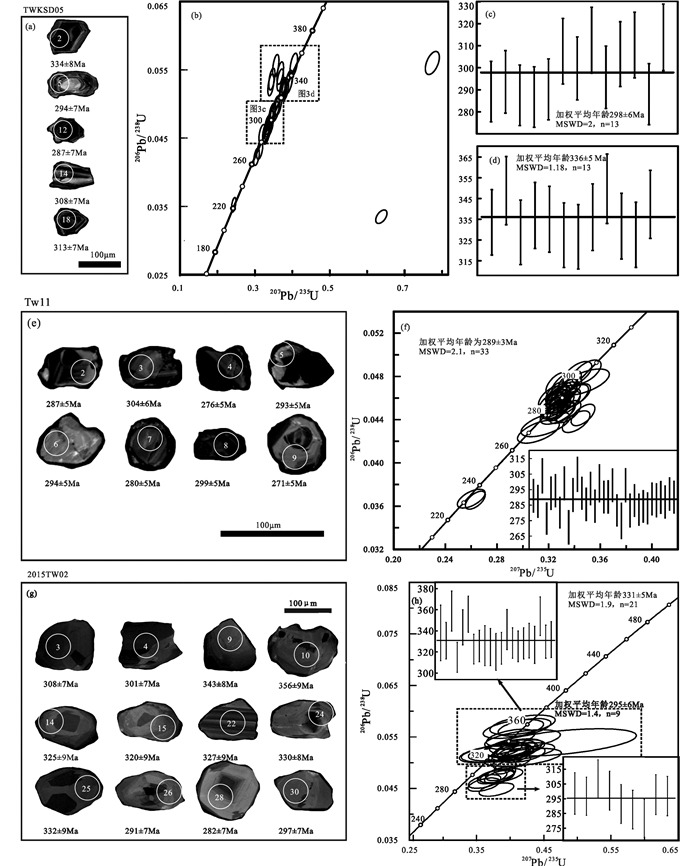
|
图 3 扎兰屯地区早二叠世花岗岩锆石阴极发光图像及年龄 Fig. 3 Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of zircon grains and the dating results of the Early Permian granites in Zhalantun area |
样品TW11(碱长花岗岩):锆石呈半自形-自形形态,大小约50~120μm,Th/U值为0.28~1.05,岩浆震荡环带明显(图 3e),具有岩浆成因锆石的特征。对样品TW11的35颗锆石进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学分析,206Pb/238U表面年龄为231±4Ma~305±6Ma,2粒锆石206Pb/238U年龄为231±4Ma和232±4Ma,其余33颗锆石加权平均年龄为289±3Ma(MSWD=2.1,n=33),所有锆石颗粒年龄均位于谐和线上及其附近(图 3f)。
样品2015TW02(二长花岗岩):锆石呈半自形到自形形态,大小约100~120μm,所测锆石具有岩浆震荡环带(图 3g),Th/U值为0.37~0.85,具有岩浆成因锆石的特征。对样品2015TW02的30颗锆石进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄测定,其206Pb/238U表面年龄可分为两组:一组锆石年龄为282±7Ma~308±7Ma加权平均年龄为295±6Ma(MSWD=1.4,n=9);一组锆石年龄为315±7Ma~359±9Ma,加权平均年龄为331±5Ma(MSWD=1.9,n=21);所有锆石颗粒年龄均位于谐和线上及其附近(图 3h)。
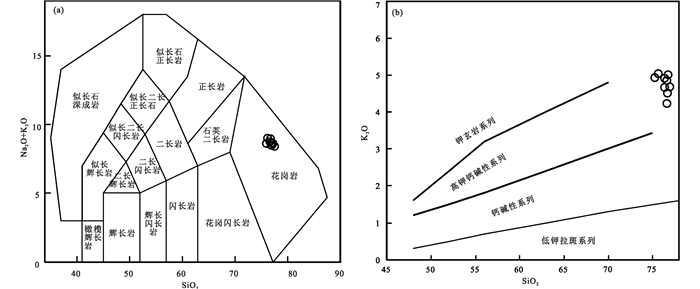
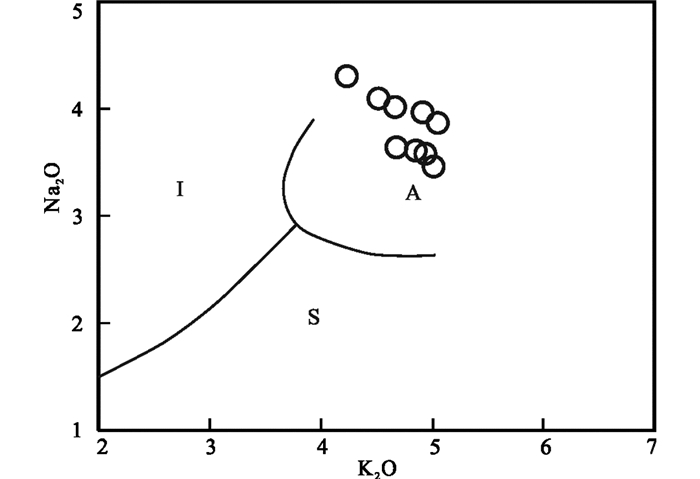
4.2 地球化学特征 4.2.1 主量元素研究区花岗岩SiO2含量为75.70%~76.99%,Al2O3含量为12.42%~12.97%,K2O含量为4.23%~5.04%,Na2O含量为3.46%~4.31%,FeO含量为0.18%~0.54%,Fe2O3含量为0.5%~0.85%,MgO含量为0.05%~0.23%,CaO含量为0.36%~0.56%,TiO2含量为0.06%~0.09%,FeO/MgO的比值为0.9~5.4,A/CNK为1~1.07 (表 2),属弱过铝质岩石。在TAS图解(图 4a)和硅碱图解(图 4b)中,花岗岩样品分别落入亚碱性和高钾钙碱性范围内,在K2O-Na2O图解中(图 5),所有样品落入了A型花岗岩的范围内。
|
|
表 2 扎兰屯地区早二叠世花岗岩主量元素(wt%)和微量元素(×10-6)组成 Table 2 Major (wt%) and trace (×10-6) element compositions for the Early Permian granites in Zhalantun area |
|
图 4 扎兰屯地区早二叠世花岗岩TAS图解(a, 底图据Irvine and Baragar, 1971)和SiO2-K2O图解(b, 底图据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) Fig. 4 TAS (a, base map after Irvine and Baragar, 1971) and SiO2 vs. K2O (b, base amp after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) diagrams of Early Permian granites in Zhalantun area |
|
图 5 扎兰屯地区早二叠世花岗岩K2O-Na2O判别图解(底图图据Collins et al., 1982) Fig. 5 The discrimination diagrams of K2O vs. Na2O for Early Permian granites in Zhalantun area (base map after Collins et al., 1982) |
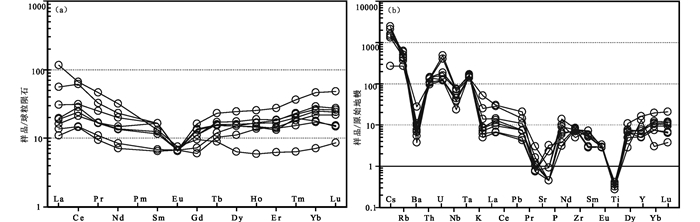
早二叠世花岗岩的稀土总量为38.27×10-6~127.1×10-6 (表 2),在球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(图 6a)中,样品具有轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损的右倾“海鸥”型特征,其(La/Yb)N除1个样品数值较高(16.1),其余样品比值为0.35~3.15,多数样品具有明显的负Eu异常(δEu=0.41~1.08)。原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(图 6b)显示花岗岩相对富集大离子亲石元素(LILEs,如Cs、Rb、K)和高场强元素Th,亏损高场强元素(HFSEs,如Nb、Ta),其Sr、P、Ti元素也表现出明显的负异常。样品中10000Ga/Al比值为为2.8~4,接近于经典A型花岗岩的10000Ga/Al比值(~3.75, Whalen et al., 1987)。样品的Sc、V、Ni、Co含量较低,分别为1.26×10-6~3.8×10-6、2.3×10-6~11.48×10-6、2×10-6~3.24×10-6和0.67×10-6~5.39×10-6。
|
图 6 扎兰屯地区早二叠世花岗岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a,标准化值据Boynton, 1984)及原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b,标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, normalization values after Boynton, 1984) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams (b, normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) for the Early Permian granites in Zhalantun area |
本文对研究区3个花岗岩样品(TWKSD05,TW11,2015TW02)进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学分析。3个样品所有锆石均呈半自形到自形,具有岩浆震荡环带且Th/U比值>0.10,因此锆石年龄可以代表岩体的侵位年龄。在样品TWKSD05和TW11中含有少量年轻锆石(共6颗,年龄分别为~220Ma和~270Ma)(图 7),考虑研究区及邻区存在三叠纪和晚二叠世构造岩浆事件,因此~220Ma和~270Ma锆石年龄被解释为花岗岩侵位以后的构造热事件。而样品TWKSD05和2015TW02中含有大量早石炭世(~330Ma)锆石年龄(图 7),所有锆石年龄均位于谐和线上及其附近(图 3)。研究区存在~330Ma的花岗岩(另文发表),且该时期花岗岩与本文研究花岗岩空间距离较近,两者呈侵入接触关系,因此TWKSD05和2015TW02中早石炭世锆石应为捕获锆石。剔除年轻锆石和捕获锆石,3个花岗岩样品的加权平均年龄分别为298±6Ma,289±3Ma和295±6Ma(图 3),为早二叠世。
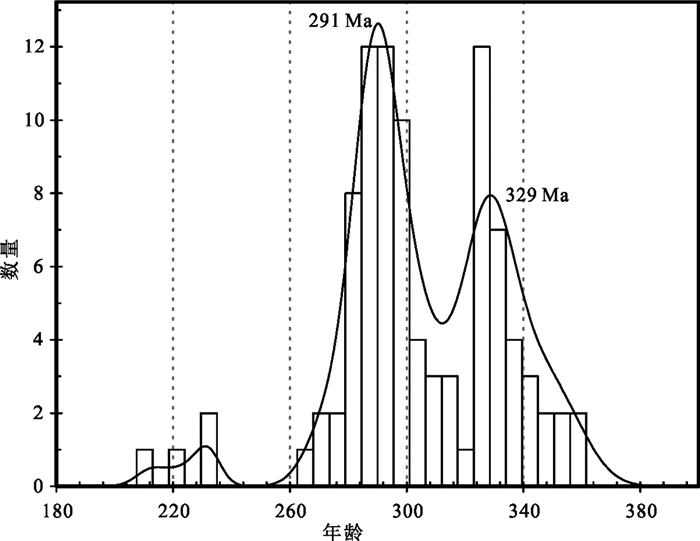
|
图 7 扎兰屯地区早二叠世花岗岩单颗粒锆石年龄分布特征 Fig. 7 The histogram of ages of zircon grains of Early Permian granites in Zhalantun area |
原始定义的A型花岗岩具有碱性、无水、非造山的地球化学属性(Eby, 1992)。研究区早二叠世花岗岩主要组成矿物为碱性长石、斜长石和石英,岩石地球化学特征表现为高硅、富碱、贫P2O5、CaO、和MgO,此外,样品具有较高的FeO/MgO比值和低的Ba、Sr和Eu元素含量以及海鸥型的稀土配分模式特征(图 6b)。研究区早二叠世花岗岩与A型花岗岩的岩石地球化学特征相似,在花岗岩成因类别判别图(图 5、图 8)中,早二叠世花岗岩样品多数落入A型花岗岩范围内,进一步说明研究区早二叠世花岗岩为A型花岗岩。
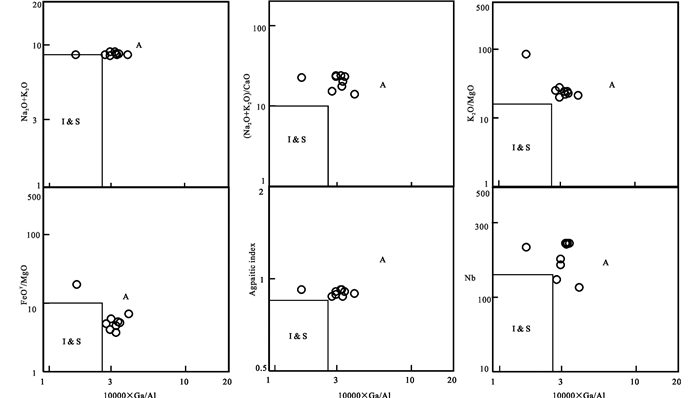
|
图 8 扎兰屯地区早二叠世A型花岗岩判别图解(据Whalen et al., 1987) Fig. 8 The discrimination diagrams of Early Permian A-type granites in Zhalantun area (after Whalen et al., 1987) |
A型花岗岩的成因和岩浆源区性质目前存在较大的争议,其成因主要存在以下三种方式:壳幔物质的混合熔融(Goodenough et al., 2000; Kemp et al., 2005; Bonin, 2007),幔源岩浆的分异或部分熔融(Kemp et al., 2005; Bonin, 2007),壳源物质的部分熔融(Collins et al., 1982; Eby, 1990)。研究区A型花岗岩具有高硅、高铝、富碱和富LREE的特征,暗示起源于下地壳的高钾、正常水含量的长英质岩石,所有样品具有较低Sc、Ni、Co、V含量,明显不同于幔源岩浆或镁铁质原岩分离形成的A型花岗岩特征(吴福元等, 2007);此外,幔源岩浆分异或部分熔融获得的A型花岗岩需要有大面积同时期的中基性岩浆岩(Wu et al., 2002),详细的野外地质调查发现,研究区及邻区主要出露不同时代的花岗质岩石,而晚石炭世-早二叠世中基性岩浆岩出露面积较小,因此研究区内早二叠世花岗岩不是幔源岩浆分异或部分熔融的产物,其较高的SiO2含量和较低的MgO含量也进一步说明研究区内早二叠世花岗岩成因与幔源岩浆无关(Bonin, 2007)。在哈克图解(图 9)中,早二叠世花岗岩的TiO2、MgO、K2O和Na2O等与SiO2无明显的相关性,表明岩浆未经历明显的分离结晶作用;其Nb/Ta(4.88~21.9)(地壳为11.0,地幔为17.5)(Green, 1995)和Zr/Hf(8.32~29.1)(地壳为11.00,地幔为36.27)介于地幔与地壳比值之间;野外地质调查及岩相学研究发现研究区早二叠世花岗岩岩体内部发育少量基性岩和较多的细粒闪长质包体(秦涛等, 2017),该岩相学特征表明早二叠世花岗岩岩浆源区应具有岩浆混合作用的特征,考虑样品TWKSD05和2015TW02中含有大量~330Ma的捕获锆石,研究区早二叠世花岗岩不是壳源物质部分熔融的产物,其岩浆源区应具有岩浆混合作用特征。综合岩相学、岩石地球化学和捕获锆石特征,研究区内早二叠世A型花岗岩应是壳幔物质混合熔融的产物。
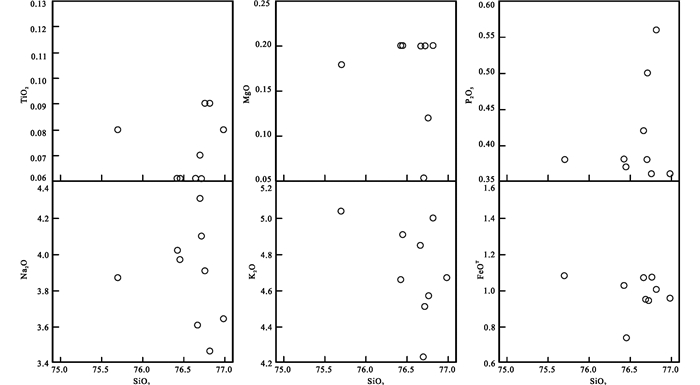
|
图 9 扎兰屯地区早二叠世花岗岩哈克图解 Fig. 9 The plots of Haker of Early Permian granites in Zhalantun area |
A型花岗岩代表伸展环境,Eby (1992)进一步将A型花岗岩分为A1型和A2型,且A1型花岗岩代表了大陆裂谷或板内伸展环境,A2型花岗岩则代表了弧后、后碰撞、走滑等构造环境下的伸展。在A型花岗岩构造环境判别图解(图 10a)中,研究区早二叠世花岗岩所有样品落入了A2型花岗岩的范围内,暗示其应形成于与弧后、后碰撞或走滑等有关的伸展环境中。岩相学研究表明,研究区A型花岗岩未发生明显的变形与变质行为,且岩石地球化学特征显示没有经历显著的结晶分异作用(5.2.1中已论述),故可以用岩石地球化学特征反应其形成时的构造背景。在R1与R2构造环境判别图解(图 10b)上,早二叠世花岗岩样品落入造山后区域,在SiO2-Al2O3和SiO2-(FeOT/(FeOT+MgO))图解(图 10c, d)中,A型花岗岩样品后碰撞的范围内。研究区A型花岗岩位于扎兰屯南部,其形成与贺根山-黑河缝合带的构造演化密切相关,结合研究区A2型花岗岩年代学、岩石地球化学特征及区域岩浆演化事件(5.3中详细阐述),本研究认为研究区早二叠世A型花岗岩形成于兴安地块与松辽地块碰撞造山后的伸展阶段。
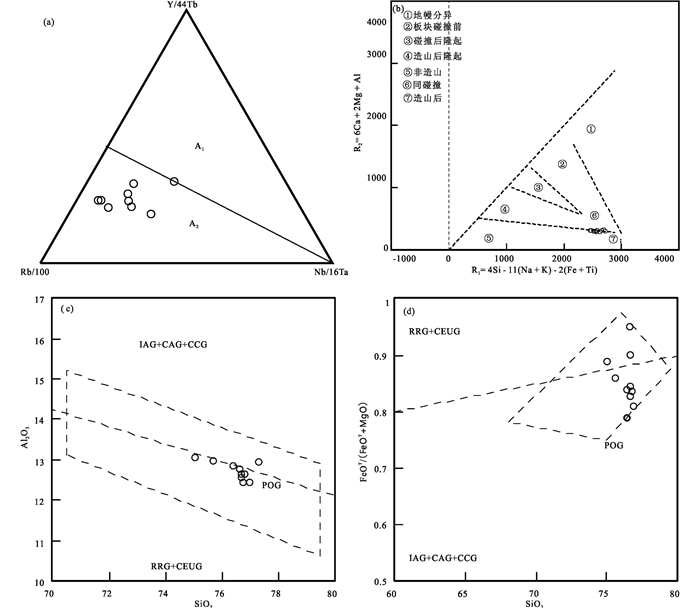
|
图 10 扎兰屯地区早二叠世花岗岩构造环境判别图解(a, 据Eby, 1992;b, 据Batchelor and Bowden, 1985;c,d, 据Maniar and Piccoli, 1989) IAG-岛弧花岗岩类;CAG-大陆弧花岗岩类;CCG-大陆碰撞花岗岩;POG-后造山花岗岩类;RRG-与裂谷有关的花岗岩类;CEUG-与大陆造陆抬升有关的花岗岩类 Fig. 10 The tectonic discrimination diagrams of Early Permian granites in the Zhalantun area (a, after Eby, 1992; b, after Batchelor and Bowden, 1985, c, d, after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989) |
刘永江等(2010)和Liu et al. (2017)通过分析东北地区沉积相和古地理环境发现以晚石炭世为时间界线,东北地区沿贺根山-嫩江-黑河一线发生了“北海南陆”变为“北陆南海”的巨大的海陆变迁,因此贺根山-嫩江-黑河是一条非常重要的构造带。近年来,不同学者从蛇绿岩套、沉积相和古地理环境及岩浆事件等方面对贺根山-黑河缝合带进行了研究(洪大卫等, 1994; 周长勇等, 2005; Miao et al., 2007, 2008; Liu et al., 2017; 冯志强等, 2019; Ma et al., 2019a, b),以其限定松辽地块和兴安地块的闭合时间及演化机制。Liu et al. (2017)对贺根山-黑河缝合带岩浆弧特征进行了研究,并系统总结出沿贺根山-黑河分布的与俯冲作用相关的两条早古生代(480~420Ma)和晚古生代(360~330Ma)岩浆弧,两条岩浆弧的存在说明贺根山-黑河洋在早、晚古生代时期发生过两次俯冲作用。扎兰屯位于贺根山-黑河缝合带中段,其晚古生代的岩浆活动对于约束晚古生代贺根山-黑河缝合带中段的构造演化具有重要意义。张渝金等(2015)在扎兰屯地区泥盆纪大民山组地层中识别出了含有海相生物化石的生物成因硅质岩和硅质泥岩,且通过地球化学特征判定硅质岩和硅质泥岩形成于离大陆较近的大陆坡或边缘海的高盐度海水环境。此外,扎兰屯南部大民山组(安山岩年龄为360Ma)基性玄武岩岩石地球化学特征与板内洋岛玄武岩(OIB)特征一致,中酸性火山岩具有弧火山岩的特点,因此晚泥盆世期间大兴安岭中段应处于俯冲汇聚阶段(张渝金等, 2016a),该特征与Liu et al. (2017)提出的晚石炭世以前“北海南陆”的古地理环境一致。近年来在大兴安岭中段陆续识别出一系列与俯冲碰撞有关的早石炭世早期钙碱性岩浆事件(包括辉长岩、玄武岩、安山岩、花岗岩闪长岩、二长花岗岩、流纹岩)(Feng et al., 2018a; Zhang et al., 2018; Ma et al., 2019b),这些具有岛弧或活动大陆边缘性质的岩浆活动应与贺根山-黑河洋的俯冲闭合有关。此后,大兴安岭中段晚石炭世早期又发育了一系列与挤压碰撞、后碰撞、后造山有关的埃达克质岩石、Ⅰ型和S型花岗岩(崔芳华等, 2013; 张渝金等, 2016b; Ma et al., 2019b),预示了晚石炭早期贺根山-黑河缝合带处于碰撞造山隆升的过程。晚石炭世晚期-早二叠世,贺根山-黑河缝合带进入了俯冲汇聚之后的“后碰撞”调节阶段,此时,在孙吴、嫩江-黑河、扎兰屯-蘑菇气、贺根山一带形成了与造山后伸展有关的A2型花岗岩和流纹岩(洪大卫等, 1994; Wu et al., 2002; Li et al., 2014; Ma et al., 2019a)(图 11)。研究区A2型花岗岩侵位时代为早二叠世(~290Ma),其与邻区同期A型花岗岩和流纹岩(洪大卫等, 1994; Wu et al., 2002; Jahn et al., 2009; Li et al., 2014; Ma et al., 2019a)共同侵位于兴安地块与松辽地块碰撞造山后的伸展环境中(图 12)。大兴安岭中段岩浆演化过程与古地理环境变迁时空耦合特征表明兴安地块与松辽地块碰撞应该发生在早石炭世-晚石炭世早期,晚石炭世早期由于兴安地块于松辽地块的拼贴,贺根山-黑河缝合带最终形成,晚石炭世晚期到早二叠世期间贺根山-黑河缝合带中段处于造山后伸展环境(图 12),此时,大兴安岭地区古地理环境以贺根山-黑河一线为界由早期的“北海南陆”变为晚期的“北陆南海”(Liu et al., 2017)。
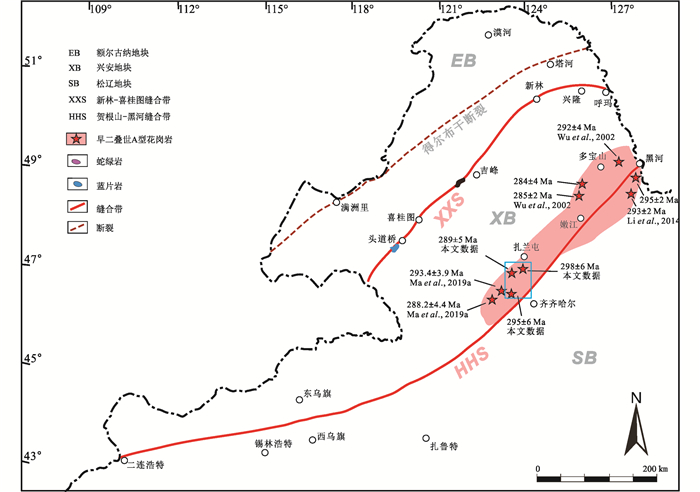
|
图 11 大兴安岭嫩江-黑河一线早二叠世A型花岗岩分布图 Fig. 11 The distribution map of Early Permian A-type granites in Nenjiang-Heihe area, the Great Xing'an Range |
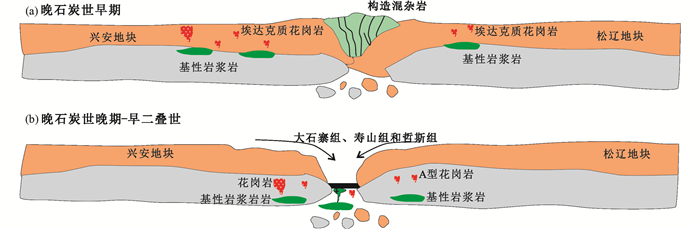
|
图 12 大兴安岭中段扎兰屯地区晚石炭世-早二叠世构造演化模式图 Fig. 12 The Late Carboniferous-Early Permian model for the tectonic evolution of Zhalantun area in middle Great Xing'an Range |
(1) 扎兰屯地区早二叠世花岗岩的形成年龄为289~298Ma。早二叠世花岗岩具有高硅、高铝、富碱和LREE特征及低FeO/MgO比值和低的Ba、Sr、Eu含量,属于A2型花岗岩,其岩浆具有岩浆混合作用的特征,是壳幔混合作用的产物。
(2) 早二叠世A型岩浆岩沿贺根山-嫩江-蘑菇气一线呈北北东向展布,早二叠世期间贺根山-黑河缝合带中段处于后碰撞伸展环境。扎兰屯地区早二叠世A2型花岗岩形成于伸展构造背景下,其形成于兴安地块与松辽地块拼贴碰撞后的“后碰撞”调节作用阶段。
(3) 晚泥盆世到早二叠世期间,扎兰屯地区晚古生代构造演化经历了俯冲-碰撞拼贴-地壳加厚隆升-碰撞后伸展的构造演化过程,贺根山-黑河缝合带在扎兰屯地区形成时间应为晚石炭世早期。
致谢 本文数据整理得到了山东理工大学本科生杨凯和马超的大力支持。感谢匿名审稿专家对本文提出的宝贵修改意见。
Andersen T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59-79 |
Batchelor RA and Bowden P. 1985. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters. Chemical Geology, 48(1-4): 43-55 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(85)90034-8 |
Bonin B. 2007. A-type granites and related rocks: Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects. Lithos, 97(1-2): 1-29 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.12.007 |
Boynton WV. 1984. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. In: Henderson P (ed.). Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 63-114
|
Collins WJ, Beams SD, White AJR and Chappell BW. 1982. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 80(2): 189-200 DOI:10.1007/BF00374895 |
Cui FH, Zheng CQ, Xu XC, Yao WG, Shi L, Li J and Xu JL. 2013. Late Carboniferous magmatic activities in the Quanshenglinchang area, Great Xing'an Range: Constrains on the timing of amalgamation between Xing'an and Songnen massifs. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(9): 1247-1263 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Cui FH, Zheng CQ, Xu XC, Yao WG, Ding X, Shi L and Li J. 2015. Detrital zircon ages of the Jiageda and Woduhe formations: Constrains on the tectonic attribute of the Xing'an terrane in the central Great Xing' an Range, NE China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113: 427-442 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.017 |
Dong JL, Bai ZD, Xu DB and Luo ZB. 2018. Tectonic nature and geological significance for two types of Neoproterozoic and Late Paleozoic rock assemblages in Yakeshi region, Great Hinggan Range. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(6): 1758-1774 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Eby GN. 1990. The A-type granitoids: A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis. Lithos, 26(1-2): 115-134 DOI:10.1016/0024-4937(90)90043-Z |
Eby GN. 1992. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Geology, 20(7): 641-644 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2 |
Feng ZQ, Li WM, Liu YJ, Jin W, Wen QB, Liu BQ, Zhou JP, Zhang TA and Li XY. 2018a. Early Carboniferous tectonic evolution of the northern Heihe-Nenjiang-Hegenshan suture zone, NE China: Constraints from the mylonitized Nenjiang rhyolites and the Moguqi gabbros. Geological Journal, 53(3): 1005-1021 DOI:10.1002/gj.2940 |
Feng ZQ, Liu YJ, Li L, She HQ, Jiang LW, Du BY, Liu YW, Li WM, Wen QB and Liang CY. 2018b. Subduction, accretion, and collision during the Neoproterozoic-Cambrian orogeny in the Great Xing'an Range, NE China: Insights from geochemistry and geochronology of the Ali River ophiolitic mélange and arc-type granodiorites. Precambrian Research, 311: 117-135 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2018.04.013 |
Feng ZQ, Liu YJ, Li L, Jin W, Jiang LW, Li WM, Wen QB and Zhao YL. 2019. Geochemical and geochronological constraints on the tectonic setting of the Xinlin ophiolite, northern Great Xing'an Range, NE China. Lithos, 326-327: 213-229 |
Feng ZQ, Liu YJ, Jin W, Jiang LW, Li WM, Wen QB, Li XY, Zhang TA, Du BY and Zhang L. 2019. Spatiotemporal distribution of ophiolites in the northern Great Xing'an Range and its relationship with the geotectonic evolution of NE China. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(2): 120-136 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Goodenough KM, Upton BGJ and Ellam RM. 2000. Geochemical evolution of the Ivigtut granite, South Greenland: A fluorine-rich "A-type" intrusion. Lithos, 51(3): 205-221 |
Green TH. 1995. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system. Chemical Geology, 120(3-4): 347-359 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(94)00145-X |
Hong DW, Huang HZ, Xiao YJ, Xu HM and Jin MY. 1994. The Permian alkaline granites in central Inner Mongolia and their geodynamic significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 68(3): 219-230 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Irvine TN and Baragar WRA. 1971. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 8(5): 523-548 DOI:10.1139/e71-055 |
Jahn BM, Litvinovskyb BA, Zanvilevichb AN and Reichowc M. 2009. Alkaline granitoid magmatism in the Mongolian-Transbaikalian Belt: Evolution, petrogenesis and tectonic significance. Lithos, 113(3-4): 521-539 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.06.015 |
Ji Z, Ge WC, Yang H, Tian DX, Chen HJ and Zhang YL. 2018. Late Carboniferous-Early Permian high- and low-Sr/Y granitoids of the Xing'an Block, northeastern China: Implications for the Late Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Lithos, 322: 179-196 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2018.10.014 |
Kemp AIS, Wormald RJ, Whitehouse MJ and Price RC. 2005. Hf isotopes in zircon reveal contrasting sources and crystallization histories for alkaline to peralkaline granites of Temora, southeastern Australia. Geology, 33(10): 797-800 DOI:10.1130/G21706.1 |
Li CL, Xu WX, Li SR, Song ZC, Wang Z, Qu H, Zhao ZH and Xu GZ. 2017. Zircon U-Pb ages, geochemical characteristics and tectonic implications of the Early Permian granites in Huolongmen area, Northeast Da Hinggan Mountains. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 37(3): 46-54 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li RH, Zhang H, Sun FY, Wu G, Zhang YT and Wang S. 2018. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Ershiyizhan intrusive rocks in the northern Great Hinggan Range, and its prospecting implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(6): 1725-1740 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li Y, Xu WL, Wang F, Tang J, Pei FP and Wang ZJ. 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of Late Paleozoic volcanic rocks on the western margin of the Songnen-Zhangguangcai Range Massif, NE China: Implications for the amalgamation history of the Xing'an and Songnen-Zhangguangcai Range massifs. Lithos, 205: 394-410 |
Liang CY, Liu YJ, Li W, Liu BR, Li WM, Zhang D and Liu TJ. 2018. The extensional uplift style of north part of the Da Hinggan Mountains: Evidences from ductile deformation zone of Keluo-Galashan. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(10): 2873-2900 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu YJ, Zhang XZ, Jin W, Chi XG, Wang CW, Ma ZH, Han GQ, Wen QB, Zhao YL, Wang WD and Zhao XF. 2010. Late Paleozoic tectonic evolution in northeast China. Geology in China, 37(4): 943-951 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu YJ, Liu BQ, Feng ZQ, Wen QB, Li WM, Zhang TA, Li XY and Du BY. 2016. SIMS zircon U-Pb age, petrogeochemistry and its tectonic implication of Laodaokou diorite in the mid-north part of Great Xing'an Range. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 46(2): 482-498 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu YJ, Li WM, Feng ZQ, Wen QB, Neubauer F and Liang CY. 2017. A review of the Paleozoic tectonics in the eastern part of Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Gondwana Research, 43: 123-148 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.013 |
Ma YF, Liu YJ, Qin T, Sun W and Zang YQ. 2018. Carboniferous granites in the Jalaid Banner area, middle Great Xing'an Range, NE China: Petrogenesis, tectonic background and orogeny accretionary implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(10): 2931-2955 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ma YF, Liu YJ, Wang Y, Qian C, Si QL, Tang Z and Qin T. 2019a. Geochronology, petrogenesis, and tectonic implications of Permian felsic rocks of the Central Great Xing'an Range, NE China. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 108(2): 427-453 DOI:10.1007/s00531-018-1661-3 |
Ma YF, Liu YJ, Wang Y, Tang Z, Qian C, Qin T, Feng ZQ, Sun W and Zang YQ. 2019b. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Carboniferous felsic rocks in the central Great Xing'an Range, NE China: Implications for the amalgamation history of Xing'an and Songliao-Xilinhot blocks. Geological Journal, 54(1): 482-513 DOI:10.1002/gj.3198 |
Maniar PD and Piccoli PM. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101(5): 635-643 DOI:10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2 |
Miao LC, Liu DY, Zhang FQ, Fan WM, Shi YR and Xie HQ. 2007. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb ages of the "Xinghuadukou Group" in Hanjiayuanzi and Xinlin areas and the "Zhalantun Group" in Inner Mongolia, Da Hinggan Mountains. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(8): 1112-1124 DOI:10.1007/s11434-007-0131-2 |
Miao LC, Fan WM, Liu DY, Zhang FQ, Shi YR and Guo F. 2008. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Hegenshan ophiolitic complex: Implications for late-stage tectonic evolution of the Inner Mongolia-Daxinganling Orogenic Belt, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32(5-6): 348-370 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.11.005 |
Peccerillo A and Taylor AR. 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63-81 |
Qin T, Li LC, Tang Z, Jiang B, Qian C, Sun W, Na FC and Shi L. 2017. A study on the petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Siban granite mass in Zhalantun area, Great Khingan. Journal of Geomechanics, 23(3): 369-381 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Qu P, Li NB, Niu HC, Yang WB, Shan Q and Zhang ZY. 2019. Zircon and apatite as tools to monitor the evolution of fractionated Ⅰ-type granites from the central Great Xing'an Range, NE China. Lithos, 348-349: 105207 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105207 |
Su YZ. 1996. Some problems of Paleozoic biostratigraphy in northeastern China. Jilin Geology, 15(3-4): 66-69 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun DY, Wu FY, Li HM and Lin Q. 2001. Emplacement age of the postorogenic A-type granites in northwestern Lesser Xing'an Ranges, and its relationship to the eastward extension of Suolushan-Hegenshan-Zhalaite collisional suture zone. Chinese Science Bulletin, 46(5): 427-432 |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345
|
Tang KD, Shao JA and Li YF. 2011. Songnen Massif and its research significance. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(3): 57-65 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang F, Xu WL, Gao FH, Zhang HH, Pei FP, Zhao L and Yang Y. 2014. Precambrian terrane within the Songnen-Zhangguangcai Range Massif, NE China: Evidence from U-Pb ages of detrital zircons from the Dongfengshan and Tadong groups. Gondwana Research, 26(1): 402-413 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.06.017 |
Whalen JB, Currie KL and Chappell BW. 1987. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419 DOI:10.1007/BF00402202 |
Wu FY, Sun DY, Li HM, Jahn BM and Wilde S. 2002. A-type granites in northeastern China: Age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis. Chemical Geology, 187(1-2): 143-173 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00018-9 |
Wu FY, Li XH, Yang JH and Zheng YF. 2007. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(6): 1217-1238 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wu XW, Zhang C, Zhang YJ, Guo W, Zhang C, Cui TR, Yang YJ, Hu JF and Song WB. 2018. 2.7Ga monzogranite on the Songnen Massif and its geological implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(3): 1265-1266 DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.13609 |
Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Sun S, Li JL, Huang BC, Han GM, Yuan C, Sun M and Chen HL. 2015. A tale of amalgamation of three Permo-Triassic collage systems in Central Asia: Oroclines, sutures, and terminal accretion. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 43: 477-507 DOI:10.1146/annurev-earth-060614-105254 |
Xu B, Zhao P, Bao QZ, Zhou YH, Wang YY and Luo ZW. 2014. Preliminary study on the pre-Mesozoic tectonic unit division of the Xing-Meng Orogenic Belt (XMOB). Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(7): 1841-1857 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yuan HL, Gao S, Liu XM, Li HM, Günther D and Wu FY. 2004. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28(3): 353-370 DOI:10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb00755.x |
Zhang C, Wu XW, Guo W, Zhang YJ and Quan JY. 2017. Discovery of the 1.8Ga granite on the western margin of the Songnen Massif, China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(4): 1497-1498 DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.13379 |
Zhang Y, Pei FP, Wang ZW, Xu WL, Li Y, Wang F and Zhou ZB. 2018. Late Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the central Great Xing'an Range, Northeast China: Geochronological and geochemical evidence from igneous rocks. Geological Journal, 53(1): 282-303 |
Zhang YJ, Wu XW, Yang YJ, Jiang B, Guo W and Zhang C. 2015. Geochemistry and sedimentary environment of the siliceous rocks from Devonian Daminshan Formation in northern Daxinganling. Geology and Resources, 24(3): 173-178 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang YJ, Zhang C, Wu XW, Cui TR, Yang YJ, Chen HJ, Jiang B, Guo W and Ma YF. 2016a. Geochronology and geochemistry of Late Paleozoic marine volcanic from the Zhalantun area in northern Dahinggan Mountains and its geological significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(10): 2706-2720 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang YJ, Wu XW, Yang YJ, Cui TR, Jiang B, Guo W, Zhang C, Qian C, Chen HJ, Li W, Li LC and Si QL. 2016b. Discovery and geological significance of adakitic rocks in the Late Paleozoic Gegenaobao Formation in Zhalantun area, middle Daxinganling Mountains. Geology and Resources, 25(3): 227-236 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao P, Xu B and Zhang CH. 2017. A rift system in southeastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Constraint from sedimentological, geochronological and geochemical investigations of the Late Carboniferous-Early Permian strata in northern Inner Mongolia (China). Gondwana Research, 47: 342-357 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.06.013 |
Zhao YD, Zhao J, Wang KL, Che JY, Wu DT, Xu FM and Li SC. 2013. Characteristics of the Late Carboniferious post-orogenic Dayinhe intrusion in the northwest of the Xiao Hinggan Mountains and their geological implications. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 32(1): 63-72 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhou CY, Wu FY, Ge WC, Sun DY, Rahman AAA, Zhang JH and Cheng RY. 2005. Age, geochemistry and petrogenesis of the cumulate gabbro in Tahe, northern Da Hinggan Mountain. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3): 763-775 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
崔芳华, 郑常青, 徐学纯, 姚文贵, 施璐, 李娟, 徐久磊. 2013. 大兴安岭全胜林场地区晚石炭世岩浆活动研究:对兴安地块与松嫩地块拼合时间的限定. 地质学报, 87(9): 1247-1263. |
董金龙, 白志达, 徐德兵, 罗志波. 2018. 大兴安岭牙克石地区新元古代与晚古生代两类岩石组合的构造属性及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 34(6): 1758-1774. |
冯志强, 刘永江, 金巍, 蒋立伟, 李伟民, 温泉波, 李小玉, 张铁安, 杜兵盈, 马永非, 张丽. 2019. 东北大兴安岭北段蛇绿岩的时空分布及与区域构造演化关系的研究. 地学前缘, 26(2): 120-136. |
洪大卫, 黄怀曾, 肖宜君, 徐海明, 靳满元. 1994. 内蒙古中部二叠纪碱性花岗岩及其地球动力学意义. 地质学报, 68(3): 219-230. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1994.03.001 |
李成禄, 徐文喜, 李胜荣, 宋志超, 王卓, 曲晖, 赵忠海, 徐国战. 2017. 大兴安岭东北部霍龙门地区早二叠世花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及构造意义. 矿物岩石, 37(3): 46-54. |
李睿华, 张晗, 孙丰月, 武广, 张宇婷, 王硕. 2018. 大兴安岭北段二十一站岩体年代学、地球化学及其找矿意义. 岩石学报, 34(6): 1725-1740. |
梁琛岳, 刘永江, 李伟, 刘勃然, 李伟民, 张夺, 刘同君. 2018. 大兴安岭北段伸展隆升样式:来自科洛-嘎拉山韧性变形带的证据. 岩石学报, 34(10): 2873-2900. |
刘永江, 张兴洲, 金巍, 迟效国, 王成文, 马志红, 韩国卿, 温泉波, 赵英利, 王文弟, 赵喜峰. 2010. 东北地区晚古生代区域构造演化. 中国地质, 37(4): 943-951. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.04.010 |
刘永江, 刘宾强, 冯志强, 温泉波, 李伟民, 张铁安, 李小玉, 杜兵盈. 2016. 大兴安岭中北段老道口闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及构造意义. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 46(2): 482-498. |
马永非, 刘永江, 秦涛, 孙巍, 臧延庆. 2018. 大兴安岭中段扎赉特旗地区石炭纪花岗岩的岩石成因、构造背景及对增生造山作用的指示. 岩石学报, 34(10): 2931-2955. |
秦涛, 李林川, 唐振, 江斌, 钱程, 孙巍, 那福超, 施璐. 2017. 大兴安岭扎兰屯地区四班岩体岩石成因及构造环境研究. 地质力学学报, 23(3): 369-381. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.03.005 |
苏养正. 1996. 中国东北区古生代生物地层学几个问题. 吉林地质, 15(3-4): 66-69. |
孙德有, 吴福元, 李惠民, 林强. 2000. 小兴安岭西北部造山后A型花岗岩的时代及与索伦山-贺根山-扎赉特碰撞拼合带东延的关系. 科学通报, 45(20): 2217-2222. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.20.019 |
唐克东, 邵济安, 李永飞. 2011. 松嫩地块及其研究意义. 地学前缘, 18(3): 57-65. |
吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 郑永飞. 2007. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题. 岩石学报, 23(6): 1217-1238. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.001 |
徐备, 赵盼, 鲍庆中, 周永恒, 王炎阳, 罗志文. 2014. 兴蒙造山带前中生代构造单元划分初探. 岩石学报, 30(7): 1841-1857. |
张渝金, 吴新伟, 杨雅军, 江斌, 郭威, 张超. 2015. 大兴安岭北段泥盆纪大民山组硅质岩地球化学特征及沉积环境. 地质与资源, 24(3): 173-178. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2015.03.002 |
张渝金, 张超, 吴新伟, 崔天日, 杨雅军, 陈会军, 江斌, 郭威, 马永非. 2016a. 大兴安岭北段扎兰屯地区晚古生代海相火山岩年代学和地球化学特征及其构造意义. 地质学报, 90(10): 2706-2720. |
张渝金, 吴新伟, 杨雅军, 崔天日, 江斌, 郭威, 张超, 钱程, 陈会军, 李伟, 李林川, 司秋亮. 2016b. 大兴安岭扎兰屯地区晚古生代格根敖包组埃达克岩的发现及地质意义. 地质与资源, 25(3): 227-236. |
赵院冬, 赵君, 王奎良, 车继英, 吴大天, 许逢明, 李世超. 2013. 小兴安岭西北部晚石炭世造山后达音河岩体的特征及其地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 32(1): 63-72. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.01.005 |
周长勇, 吴福元, 葛文春, 孙德有, Rahman AAA, 张吉衡, 程瑞玉. 2005. 大兴安岭北部塔河堆晶辉长岩体的形成时代、地球化学特征及其成因. 岩石学报, 21(3): 763-775. |
 2020, Vol. 36
2020, Vol. 36


