2. 防灾科技学院地球科学学院, 三河 065201;
3. 自然资源部东北亚矿产资源评价重点实验室, 长春 130061
2. School of Earth Science, Institute of Disaster Prevention, Sanhe 065201, China;
3. Key Laboratory of Mineral Resources Evaluation of Northeast Asia, Ministry of Natural and Resources of China, Changchun 130061, China
延边地区位于华北板块北缘东段与中亚造山带(CAOB)交汇处。受古太平洋板块俯冲的影响,该区中生代时期构造、岩浆活动强烈,形成许多钼、金、铜及铅锌矿床。自20世纪70年代末,该区已发现的大中型斑岩型钼矿、中温热液型金矿及铜镍硫化物矿床数十个,学者们对这些矿床进行了大量的研究,在矿床地质特征、成岩成矿时代、矿床成因及构造背景等方面积累了丰富资料(王辉等,2011;Zhang et al., 2013;Deng et al., 2014;Zhang et al., 2015;Wang et al., 2017)。延边地区近些年新发现的铅锌矿床数量有限(李勇,2017;杨群等,2018;Yang et al., 2020),年代学、岩石地球化学和成矿作用的研究相对较少,该类矿床的成因类型、成矿时代及构造背景尚不明确。
红太平铜多金属矿床位于吉林省汪清县境内,发现于20世纪70年代。由于矿床规模小、覆盖严重、矿化类型复杂,理论研究薄弱,至今缺乏主要控矿因素、成矿年龄、构造背景等方面的系统研究资料,致使对其矿床成因类型划分上一直存在争议。例如,宋群(1991)根据该矿床主矿体(层状矿体)赋存于庙岭组海相火山岩系中,产状与地层一致,矿石具有典型的沉积构造特征,以及矿石硫同位素组成和流体包裹体H-O同位素特征,认为该矿床属于与火山热液或热泉活动有关的块状硫化物矿床;张扬等(2012)根据矿床层状主矿体地质特征、成矿元素含量及硫同位素特征,认为该矿床属海底火山沉积-变质改造矿床。
近年来的勘查和研究资料表明,除层状主矿体外,红太平矿区还发育有脉状矿体。脉状矿体产于英安岩附近的NW向构造破碎带中,受断裂控制,与英安岩脉近平行。此外,英安岩脉及其附近的脉状铅锌矿体明显切穿层状矿体,表明脉型矿化晚于层状矿化,因此其成岩时代的厘定对确定层状主矿体的形成时代及矿床成因具有重要意义。
为此,本文在红太平矿床脉状矿体的矿化特征、成因类型以及与英安岩关系研究基础上,开展了英安岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年和岩石地球化学分析、脉状矿体中金属硫化物Rb-Sr法测年,综合判断脉型铅锌矿化的成因类型、物质源区、成矿时代和构造背景,进而为红太平铜多金属矿床的成矿期次和成因研究奠定基础。
1 成矿地质背景大地构造位置上,红太平多金属矿床所处的延边地区位于中亚造山带东段的兴蒙造山带东端,敦化-密山断裂以南,西拉木伦-长春断裂以北,被夹持于松嫩-张广才岭地块、佳木斯-兴凯地块和华北板块之间(图 1a)。
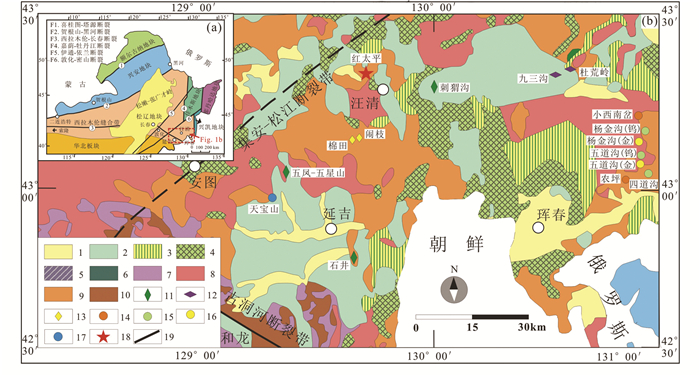
|
图 1 东北地区构造单元划分(a,据Jia et al., 2004;Wu et al., 2007, 2011)和延边东部区域地质矿产图(b,据金炳成等,2012;陈聪,2017) 1-新生界;2-中生界;3-中-上二叠统;4-下-中二叠统;5-石炭系;6-寒武-志留系;7-前寒武系;8-中生代岩浆岩;9-石炭-二叠纪岩浆岩;10-寒武-志留纪岩浆岩;11-低硫化型浅成低温热液型Au矿;12-高硫化型浅成低温热液型Au矿;13-与侵入岩有关的Au矿床;14-斑岩型Au-Cu矿床;15-热液脉型Wu矿床;16-热液脉型Au矿床;17-多成因Pb-Zn-Cu-Mo多金属矿床;18-红太平Cu多金属矿床;19-断层 Fig. 1 Tectonic divisions of Northeast China (a, after Jia et al., 2004; Wu et al., 2007, 2011) and regional geological and deposit distribution map of the eastern Yanbian area (b, after Jin et al., 2012; Chen, 2017) 1-Cenozoic; 2-Mesozoic; 3-Middle-Upper Permian; 4-Lower-Middle Permian; 5-Carboniferous; 6-Cambrian-Silurian; 7-Precambrian; 8-Mesozoic magmatite; 9-Carboniferous-Permian magmatite; 10-Cambrian-Silurian magmatite; 11-low sulphidation epithermal Au deposits; 12-high sulphidation epithermal Au deposits; 13-Au deposits associated with intrusive rocks; 14-porphyry Au-Cu deposits; 15-hydrothermal Wu deposits; 16-hydrothermal Au deposits; 17-multi-genetic Pb-Zn-Cu-Mo polymetallic deposits; 18-Cu polymetallic deposit in Hongtaiping; 19-fault |
研究区主要发育晚古生代和中生代地层(图 1b)。前者包括石炭系山秀岭组(C3s)及二叠系青龙村群(P1Q)、五道沟群(P1W)、寺洞沟群(P1SD)、解放村群(P1J)、大蒜沟组(P1d)、庙岭组(P1m)、柯岛组(P1k)及开山屯组(P2k)等。其中,山秀岭组为一套陆源碎屑岩、海相中性火山岩和火山碎屑岩组合;青龙村群主要以一套片麻岩类为主,局部含大理岩夹层的变质岩组合;五道沟群为一套以绿片岩等为主的低级变质岩组合;寺洞沟组主要由变质细砂岩、粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩等组成;解放村群为一套变质沉积建造;大蒜沟组由火山碎屑岩、碎屑岩及灰岩组成;庙岭组为浅海相陆源碎屑-火山岩-火山碎屑岩建造;柯岛组为火山碎屑岩及浊积岩建造;开山屯组为磨拉石建造(Jia et al., 2004;Ren et al., 2016;陈聪,2017),反映海相沉积向陆相沉积转变的沉积环境。中生代地层主要为陆相火山-沉积岩系,由中酸性火山熔岩、火山碎屑岩和碎屑沉积岩组成,岩性以中、高钾钙碱性安山岩和玄武岩以及低钾碱性玄武岩、安山岩为主。
受多期构造运动影响,延边东部断裂及褶皱发育。早古生代期间,受古亚洲洋俯冲作用影响,主要发育EW向及SN向区域性断裂构造,其中,EW向断裂控制早古生代地层和侵入岩的空间分布,而SN向断裂对晚古生代地层、岩浆岩及矿床分布具有重要控制作用。中、新生代,本区处于古太平洋构造域,主要发育NE向、NW向和NNE向断裂(Chen et al., 2014, 2017;Ren et al., 2016)。
据现有资料,区内主要发育加里东期橄榄岩-辉石岩-辉长岩和碱性花岗岩、海西期辉石闪长岩-花岗闪长岩-二长花岗岩和钾长花岗岩、印支期橄榄岩-辉石岩-辉长岩、石英闪长岩-花岗闪长岩-二长花岗岩-碱长花岗岩以及燕山期中酸性侵入岩和火山岩。燕山期岩浆侵入作用可分为以下四期:早侏罗世(200~180Ma)、中-晚侏罗世(170~150Ma)、早白垩世(130Ma)和早白垩世晚期(110~105Ma)(赵宏光,2007;付长亮,2009)。
多期次的构造岩浆活动,为区内不同期次的内生金属成矿作用提供了有利的地质条件。区内已发现近百个矿床(点),成因类型多(斑岩型、矽卡岩型、中温热液脉型、浅成低温热液型等),矿种丰富(Cu、Fe、Au、Pb-Zn-Ag、W、Mo等),使延边东部成为中国东北部陆缘重要的贵金属和有色金属矿集区(图 1b)。
2 矿区地质与矿床地质特征 2.1 矿区地质矿区主要出露二叠系庙岭组及柯岛组(图 2a)。其中,庙岭组作为红太平矿床层状矿体的主要含矿地层,为一套由凝灰岩、安山质凝灰岩、流纹岩、砂岩、板岩和泥灰岩类复理石建造,夹有海底火山喷发的安山质熔岩、次火山岩或中酸性凝灰岩,顶部则完全由安山质火山碎屑沉积岩组成,沉积韵律清楚,层理发育,含海相珊瑚及腕足类化石,属于浅海相陆源碎屑-火山岩-火山碎屑岩建造(张扬等,2012;Ren et al., 2016)。柯岛组由海相火山碎屑沉积岩类、火山碎屑岩及浊积岩组成(宋群,1991)。
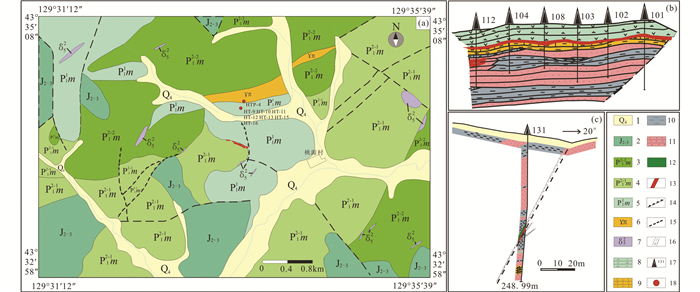
|
图 2 延边红太平矿区地质图(a, 据吉林省有色金属地质勘查局六〇五队, 2009①)、Ⅰ号矿体群纵剖面示意图(b,据张扬等,2012)和6号勘探线剖面图(c) 1-第四系;2-中-上侏罗统;3-下二叠统庙岭组上岩段上部层;4-下二叠统庙岭组上岩段下部层;5-下二叠统庙岭组下岩段;6-燕山期中酸性侵入岩;7-海西晚期-燕山期中性侵入岩;8-安山质凝灰岩;9-泥灰岩;10-板岩;11-砂岩;12-英安岩;13-矿体;14-正断层;15-推测断层;16-破碎带;17-钻孔及编号;18-取样位置 Fig. 2 Geological sketch map of Hongtaipong deposit (a), partly vertical section of No.Ⅰore bodies (b, after Zhang et al., 2012) and geological profile map of the 6# exploration line (c) 1-Quaternary; 2-Upper-Middle Jurassic; 3-Lower Permian Miaoling Fomation upper layer of upper strata; 4-Lower Permian Miaoling Fomation lower layer of upper strata; 5-Lower Permian Miaoling Fomation lower strata; 6-Yanshanian intermediate-acid intrusive rocks; 7-Late-Hercynian-Yanshanian intermediate intrusive rocks; 8-andesitic tuff; 9-marlite; 10-slate; 11-sandstone; 12-dacite; 13-ore body; 14-normal fault; 15-undetermined fault; 16- fracture zone; 17-drill and number; 18-sample location |
① 吉林省有色金属地质勘查局六〇五队. 2009.吉林省汪清县红太平地区银多金属矿地质工作总结
矿区构造主要有NE向断裂,次为NW向断裂。矿区东部NE向正断层对Ⅰ号层状矿体有明显的切割作用;西部NE向正断层被中酸性岩脉侵入;北部NW向断裂中见英安岩侵入,并伴有脉状铅锌矿体,判断其为脉状矿体的控矿断裂。
矿区内未见大的岩体出露,主要发育海西晚期-燕山期闪长岩、英安岩、花岗斑岩、石英斑岩等中-酸性脉岩。其中,英安岩脉分布于脉状矿体附近,与成矿关系密切。
2.2 层状矿体特征层状(似层状)铜多金属矿体是红太平矿区的主矿体和最主要开采对象,共16条。其中,Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ号层状(似层状)矿体规模较大,产状平缓,多赋存于庙岭组火山岩系中,与地层产状一致(图 2b)。
Ⅰ号矿体规模最大,呈似层状赋存于庙岭组上交互层顶部泥灰岩中,其顶板为上岩段安山质凝灰岩。矿体走向30°~50°,NE倾,倾角3°~15°。矿体长570m,宽50~150m,厚0.69~4.11m(平均2.39m)。Ⅱ号矿体产于庙岭组上岩段火山碎屑岩底部的安山质凝灰岩中,位于Ⅰ号矿体之上,规模小,呈扁豆状。Ⅲ号矿体位于Ⅰ号矿体之下,两者垂距约15m左右。规模亦较小,扁豆状。
层状矿体的矿石主要呈条带状、纹层状(图 3a)及块状构造,金属矿物主要为黄铁矿、黄铜矿及闪锌矿,多数呈他形粒状结构或弱交代结构。通过镜下观察,闪锌矿与黄铁矿表现为较弱的交代作用,显示同期特征,且黄铜矿交代黄铁矿,闪锌矿明显交代黄铜矿(图 3b、c)。层状矿体与围岩边界不清楚,以渐变过渡为特征。

|
图 3 红太平矿床层状及脉状矿体的矿石组构特征和英安岩特征 (a)层状矿石;(b、c)纹层状矿石中的金属矿物及其结构特征(反射光);(d)脉状矿石;(e)他形粒状黄铁矿、闪锌矿交代黄铁矿、黄铜矿呈乳滴状分布于闪锌矿内部(反射光);(f)方铅矿交代黄铜矿(反射光);(g)方铅矿交代黄铜矿、闪锌矿交代黄铜矿(反射光);(h)闪锌矿交代黄铜矿(反射光);(i)黄铜矿交代磁铁矿(反射光);(j、k)闪长岩显微特征及其蚀变特征(反射光);(l、m)英安岩野外特征及岩相学特征(m-反射光);(n)闪锌矿交代黄铁矿(反射光);(o)闪锌矿交代黄铜矿,黄铜矿呈乳滴状分布于闪锌矿内部(透射光). Py-黄铁矿;Sp-闪锌矿;Ccp-黄铜矿;Gn-方铅矿;Mag-磁铁矿;Otz-石英;Pl-斜长石;Cal-方解石;Chl-绿泥石;Ep-绿帘石 Fig. 3 The ore textures and ore structural characteristics of stratiform ore body and vein-type ore body and the characteristics of dacite in the Hongtaiping deposit (a) layered ore specimen; (b, c) mineral assemble and microscopic texture of layered ore (under reflected light); (d) vein ore specimen; (e) xenomorphic granular pyrite, pyrite replaced by sphalerite, chalcopyrite distributed in sphalerite in the form of emulsion (under reflected light); (f) chalcopyrite replaced by galenite (under reflected light); (g) chalcopyrite replaced by galenite, chalcopyrite replaced by sphalerite (under reflected light); (h) chalcopyrite replaced by sphalerite (under reflected light); (i) magnetite replaced by chalcopyrite; (j, k) microscopic features of diorite and its alteration (under reflected light); (l, m) feature of field and petrography of dacite (m-under reflected light); (n) pyrite replaced by sphalerite (under reflected light); (o) chalcopyrite replaced by sphalerite, chalcopyrite distributed in sphalerite in the form of emulsion (under transmitted light). Py-pyrite; Sp-sphalerite; Ccp-chalcopyrite; Gn-galenite; Mag-magnetite; Otz-quartz; Pl-plagioclase; Cal-calcite; Chl-chlorite; Ep-epidote |
红太平矿床的脉状矿体受NW向断裂及英安岩脉的控制,呈含硫化物石英脉产于英安岩脉附近的构造破碎带中(图 2c)。
脉状矿体的矿石主要呈脉状、网脉状(图 3d)及浸染状构造,金属矿物主要为黄铁矿、黄铜矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿等,脉石矿物为石英、方解石等。金属矿物主要呈他形粒状结构(图 3e)、骸晶结构(图 3e)、固溶体分离结构(图 3e)、交代残余结构(图 3f-i)等。脉状矿体及附近的围岩中广泛发育较强烈的硅化、绿泥石化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化以及绿帘石化等(图 3j, k)。
根据矿体和矿脉之间的穿切关系以及矿物之间的共生组合、交代与穿插关系,可将红太平铜多金属矿床的成矿过程划分为热水喷流、热液、表生3个成矿期。热液期又分为3个成矿阶段:(1)石英+磁铁矿阶段;(2)石英+黄铁矿+黄铜矿+闪锌矿+方铅矿阶段;(3)石英+碳酸盐阶段。其中第(2)阶段出现大量金属硫化物,为脉状矿化的主要成矿阶段。
3 样品描述与分析方法用于LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年(编号HTP-4)和稀土微量元素分析(编号HTP-4-1~5)的英安岩样品取自露天采坑(43°34′17.6″N、129°33′17.2″E)。所选样品新鲜,无明显矿化或蚀变现象。岩石呈灰白色,具斑状结构,块状构造(图 3l),以斑晶和基质为主。其中斑晶含量为15%,主要由石英(5%)和斜长石(10%)组成;基质为85%,主要由斜长石、石英组成(图 3m)。
锆石颗粒挑选是由河北省廊坊市区域地质调查研究所实验室利用标准重矿物分离技术完成。锆石制靶、反射光、透射光、阴极发光(CL)以及LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素分析均在自然资源部东北亚矿产资源评价重点实验室完成。使用德国相干公司(Coherent)COMPEx Geolas Pro型193nm ArF准分子激光器,采用美国安捷伦公司7900型四极杆等离子质谱仪,测试激光剥蚀束斑直径为24μm,能量密度10J/cm2。以高纯度的氦气作为载气流,氩气为辅助气(Jackson et al., 2004;Yuan et al., 2004)。元素浓度计算采用NIST610作为外标,Si为内标,采用国际标准锆石91500作为同位素比值的外部校正,同位素比值及年龄误差均为1σ。Yuan et al.(2004)描述了实验测定过程及仪器参数。同位素比值及元素含量计算采用ICPMSDataCal (Version 6.7)(Liu et al., 2008)测定,锆石加权平均值计算及图件绘制采用Isoplot (Version 3.0)(Ludwing, 2003, 2004)程序进行。其中普通铅校正使用Anderson(2002)给出的程序计算。
岩石样品的微量元素分析测试在中国科学院地球化学研究所矿床地球化学重点实验室完成。对5个英安岩样品进行了微量元素和稀土元素的测定。微量和稀土元素的测定采用美国PerkinElmer公司生产的ELAN9000型电感耦合等离子质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定,分析精度和准确度优于10%。取样和分析步骤的细节见Qi and Zhou(2008)。
从含硫化物石英-方解石脉的脉状矿石中提取新鲜样品,制备光片和薄片,岩相学和矿相学研究发现,矿石中闪锌矿交代黄铁矿呈残余结构(图 3n),闪锌矿交代黄铜矿,黄铜矿呈乳滴状分布于闪锌矿内部(图 3o)。矿物组合类型为:石英+黄铁矿+闪锌矿组合和黄铁矿+黄铜矿+闪锌矿组合。用于金属硫化物Rb-Sr同位素测年的硫化物取自原生矿石堆富含金属硫化物的石英-方解石脉。从中挑选3个闪锌矿样品(HT-10、HT-12、HT-15)、2个黄铁矿样品(HT-11、HT-16)和2件黄铜矿样品(HT-9、HT-13)。金属硫化物Rb-Sr测年,先将样品粉碎至40~80目,在双目镜下挑选出不含可识别杂质的闪锌矿、黄铁矿及黄铜矿样品,经去离子水在超声波中清洗,在烘箱中低温蒸干,再研磨至200目以上,每件单矿物样品称取0.1~0.2g。金属矿物中Rb、Sr的含量较低,有些甚至低于0.01×10-6,为确保Rb-Sr同位素定年的可行性,先挑选多个闪锌矿、黄铁矿及黄铜矿样品在南京大学现代分析中心同位素分析室进行Rb、Sr含量草测分析,在此基础之上,挑选适合定年的7件金属硫化物样品在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成了Rb、Sr含量和同位素组成的测试。具体的分析步骤如下:将称取好的粉末样品用混合酸溶解,取清液加入阳离子交换柱分离,再采用高压密闭溶解样品及阳离子交换技术进行分离和提纯,并进行质朴分析。质谱测定采用ISOPROBE-T热电离质谱计,单带,M+,可调多法拉第接收器接收,测定方法见文献(王银喜等,2007)。质量分馏校正用86Sr/88Sr=0.1194,标准测量结果NBS987为0.710250±7,Rb为2×10-10g,Sr为2×10-10g。Rb-Sr同位素年龄计算使用Isoplot/Ex Version 3.75(Ludwing,2012),λ=1.42×10-11a-1,87Rb/86Sr分析误差为±1%,87Sr/86Sr分析误差为±0.005%,置信度为95%(Qiu et al., 2013)。
4 测试结果 4.1 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年锆石阴极发光(CL)图像(图 4)显示,红太平矿区英安岩中锆石为无色透明自形-半自形柱状,长80~150μm,长宽比2.0~3.0。锆石颗粒表面光滑干净,内部具明暗相间的环带结构,发育有岩浆韵律环带,且多数锆石晶体的内外核环带都有明显的界限。

|
图 4 红太平矿区英安岩中锆石CL图像、测点及其206Pb/238U模式年龄 Fig. 4 CL images, dating spots and 206Pb/238U age of zircons from the dacite in the Hongtaiping deposit |
锆石U-Pb法测年结果见表 1。28个锆石颗粒的Th含量在52.2×10-6~180×10-6之间(平均值为109.2×10-6),U含量在173.1×10-6~494.2×10-6之间(平均值为304.1×10-6),锆石Th/U比值介于0.30~0.53,平均值为0.36(大于0.1)。结合锆石CL图像及Th/U比值说明锆石均具有典型的岩浆成因(宋彪等,2002;Bowring and Schmitz, 2003)。
|
|
表 1 红太平矿床英安岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年数据 Table 1 LA-MC-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results of dacite in the Hongtaiping deposit |
28个测点的206Pb/238U年龄为201±6Ma~210±6Ma,样品数据点位于或非常接近谐和线,显示数据的可靠性。28个测点206Pb/238U年龄的加权平均值为204.1±2.0Ma(MSWD=0.24,n=28,图 5a),代表了英安岩的结晶年龄。
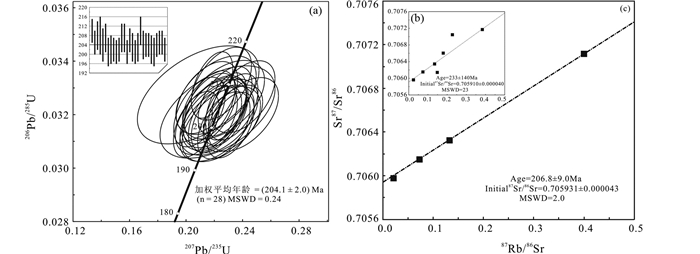
|
图 5 红太平矿床英安岩谐和及加权平均年龄图(a)和脉状铅锌矿石硫化物样品Rb-Sr等时线年龄图(b、c) Fig. 5 Concordia diagram of U-Pb age and weighted average age of zircon grains in dacite (a) and Rb-Sr isochron diagram of sulfide samples (b, c) from vein-type Pb-Zn ore in the Hongtaiping deposit |
闪锌矿、黄铁矿及黄铜矿Rb、Sr含量及同位素组成的测定结果见表 2。7件金属硫化物样品中的Rb含量在0.035× 10-6~1.460×10-6之间(平均值为0.420×10-6),Sr含量在3.40×10-6~10.60×10-6之间(平均值为5.89×10-6);87Rb/86Sr比值范围较大,介于0.0206~0.3980(平均值=0.1689),87Sr/86Sr比值范围较小,介于0.705954~0.707101(平均值=0.706469)。
|
|
表 2 红太平矿床脉状矿体中闪锌矿、黄铁矿和黄铜矿的Rb-Sr同位素组成 Table 2 Rb-Sr isotope compositions of the sphalerite, pyrite and chalcopyrite in the vein-type ore body in the Hongtaiping deposit |
在87Rb/86Sr-87Sr/86Sr图解中,7件样品点的等时线年龄为233±140Ma(MSWD=23),(87Sr/86Sr)i值为0.705910±0.000040,其中3件样品点(HT-9、HT-13、HT-16)明显偏离总体趋势(图 5b),年龄误差与等时线的MSWD值均较大,这可能基于以下两点原因:首先,黄铁矿与黄铜矿中的Rb-Sr同位素体系可能受到后期流体改造作用的影响,早期金属硫化物也容易被后期的金属硫化物沿裂隙充填,Rb和Sr值也受控于其内矿物的流体包裹体(Han et al., 2007);其次,黄铁矿与黄铜矿中较低含量的Rb和Sr,也可能成为导致测试误差偏大的原因。因此,在处理年龄时这3件样品不予考虑,剩余4件样品点(HT-10、HT-11、HT-12和HT-15)显示了一致的线性相关关系,金属硫化物等时线年龄为206.8±9.0Ma(MSWD=2.0),(87Sr/86Sr)i值为0.705931±0.000043(图 5c),其MSWD值较前者显示相对高的可靠性,该年龄可以代表金属硫化物(闪锌矿和黄铁矿)的结晶年龄,即红太平矿床脉状铅锌矿化的成矿年龄。
4.3 稀土元素及微量元素特征英安岩微量元素组成如表 3所示。稀土元素总量(∑REE)为122.9×10-6~149.0×10-6,平均值为130.7×10-6;在稀土元素配分模式图上,配分曲线相对右倾(图 6a),显示轻稀土元素富集,重稀土元素亏损,分馏较明显;(La/Yb)N=7.59~8.48,轻稀土元素(LREEs)相对于重稀土元素(HREEs)富集(LREE/HREE=7.99~8.48),显示明显负Eu异常(δEu=0.65~0.68),Ce无明显异常(δCe=1.08~1.10)。
|
|
表 3 红太平矿床英安岩微量元素组成(×10-6) Table 3 Trace element compositions in the dacite from the Hongtaiping deposit (×10-6) |
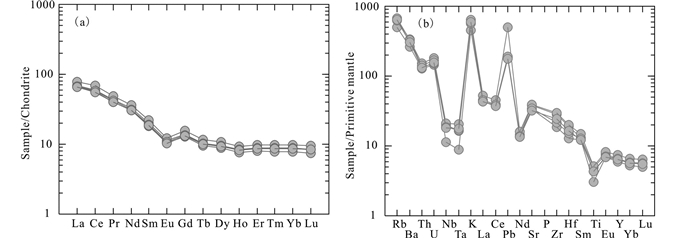
|
图 6 红太平矿床英安岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Taylor and McLennan, 1985) Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized diagram (b) of dacite in the Hongtaiping Cu polymetal deposit (normalization values after Taylor and McLennan, 1985) |
英安岩原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图显示(图 6b),相对富集大离子亲石元素(LILEs)Rb、Ba、K和活泼的不相容元素Th、U,而亏损高场强元素(HFSEs)Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf和Ti。Rb/Sr比值在0.45~0.62之间,均值0.54,接近地壳与地幔之间。Nb/Ta值在14.4~17.6之间,均值为15.8,介于地壳(11)与地幔(17.5)之间(Taylor and McLennan, 1985,1995)。
5 讨论 5.1 脉状矿体成因类型空间上,脉状矿体产于英安岩脉与围岩接触带附近,二者沿NW向断裂平行产出,受同组构造控制;时间上,脉状矿体金属硫化物Rb-Sr等时线年龄206.8±9.0Ma与英安岩锆石206Pb/238U同位素年龄204.1±2.0Ma基本一致,表明英安岩与脉状铅锌矿体具有密切的时间关系。
成因上,脉状铅锌矿体、英安岩受构造裂隙控制明显,矿石具有中温热液矿床的矿物组合、矿石结构和矿石构造;矿体与英安岩以及二者接触带附近发育强烈的硅化、绿泥石化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化、绿帘石化等中温蚀变现象,表明在脉状矿体形成的过程中,伴随着强烈的中温热液活动。因此认为,红太平矿床脉状铅锌矿体成因上应属于中温热液脉型,英安岩脉岩为脉状矿体的形成提供了足够的成矿物质,为含矿热液的运移提供了热能。
5.2 成岩成矿时代由于出现了大量高精度、低检出限的质谱仪使得对黄铁矿(杨进辉和周新华,2000)、闪锌矿等热液矿物进行年代测定成为可能(Nakai et al., 1993;胡乔青等,2012;Cao et al., 2015;Hu et al., 2015)。刘建明等(1998)认为热液矿床的成矿时代可达几百万年,而热液矿物(如闪锌矿)形成时间只有几十万年。因此,热液矿物组合的Rb-Sr等时线法定年比用单一矿物定年更理想也更精确(Hu et al., 2015)。近年来,金属硫化物Rb-Sr同位素定年被广泛应用于矿床年代学研究,并有越来越多的成功实例(Nakai et al., 1990, 1993;胡乔青等,2012;郑伟等,2013)。
金属硫化物Rb-Sr同位素定年的基本前提是矿物具有同源性、同时性、封闭性和(87Sr/86Sr)i初始值的一致性,同时具有(87Sr/86Sr)i值的差异性(李文博等,2002)。本次用于金属硫化物Rb-Sr同位素测年的4件硫化物样品(HT-10、HT-11、HT-12和HT-15)均来自同一硫化物石英-金属硫化物矿脉,具有明显的共生关系。矿物组合(闪锌矿、黄铁矿)属于同一成矿时期,同时具有较好的结晶形态,满足Rb-Sr同位素定年的基本条件。
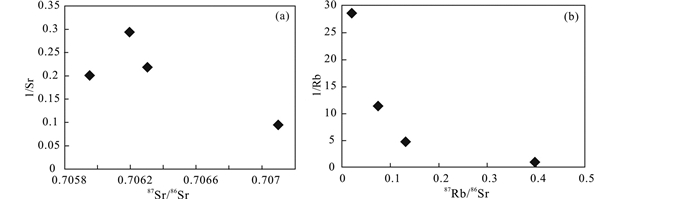
1/Sr- 87Sr/86Sr图(图 7a)和1/Rb-87Rb/86Sr图(图 7b)通常用于判断闪锌矿及金属硫化物生长过程中(87Sr/86Sr)i值是否保持不变(李文博等,2002)。在1/Sr-87Sr/86Sr图和1/Rb-87Rb/86Sr图上投点显示,4件金属硫化物样品(HT-10、HT-11、HT-12和HT-15)之间并不存在线性关系,说明矿物中的同位素属于相对封闭且属同源(Pettke and Diamond, 1996),也体现了数据的合理性,说明闪锌矿及其共生矿物(黄铁矿)在生长过程中(87Sr/86Sr)i值基本保持不变,因此该等时线具有实际地质意义。4件金属硫化物样品获得Rb-Sr等时线年龄为206.8±9.0Ma(MSWD=2.0),与成矿英安岩锆石中28个测点的206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值204.1±2.0Ma(MSWD=0.24)基本一致,证明英安岩与脉状铅锌矿体具有密切的时间关系,表明红太平脉型铅锌矿化的成矿时代为晚三叠世末期。
|
图 7 红太平矿床脉状矿体共生金属硫化物1/Sr-87Sr/86Sr(a)和1/Rb-87Rb/86Sr(b)关系图 Fig. 7 Diagrams of 1/Sr vs. 87Sr/86Sr (a) and 1/Rb vs. 87Rb/86Sr (b) of paragenetic sulfide minerals from the vein-type ore body in the Hongtaiping deposit |
红太平矿区英安岩富集LREEs、LILEs(Rb、Ba、K)和不相容元素(Th、U),亏损HFSEs(Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf和Ti),表明其与岛弧型火山岩有成因关系;同时结合明显的负Eu异常、Rb/Sr值(均值0.54)和Nb/Ta值(均值15.8)特征,可指示原始岩浆可能来自壳幔混合作用(Taylor and McLennan, 1985,1995)。
(87Sr/86Sr)i值是判断成岩成矿物质来源的重要指标,常用来示踪成矿物质来源、岩浆流体及深源流体壳幔混染作用。当(87Sr/86Sr)i值>0.710时,成矿物质来源为地壳,而当(87Sr/86Sr)i值< 0.705时为地幔(侯明兰等,2006)。已有研究表明,现代海水中(87Sr/86Sr)i值为0.7093±0.0005,海洋碳酸盐岩中(87Sr/86Sr)i值为0.7081±0.0010。本文研究结果表明,红太平脉状矿体中金属硫化物Rb-Sr等时线年龄为206.8±9.0 Ma,(87Sr/86Sr)i值为0.705931±0.000043,MSWD值为2.0(图 5c)。应用Geokit软件(路远发,2004)计算可得各金属硫化物的(87Sr/86Sr)i值(表 2)。由表 2可以看出,红太平矿床闪锌矿及黄铁矿87Sr/86Sr比值为0.705954~0.707101,平均值为0.706390,这与图 6c中Rb-Sr等时线所给出的(87Sr/86Sr)i值(0.705931)基本一致。
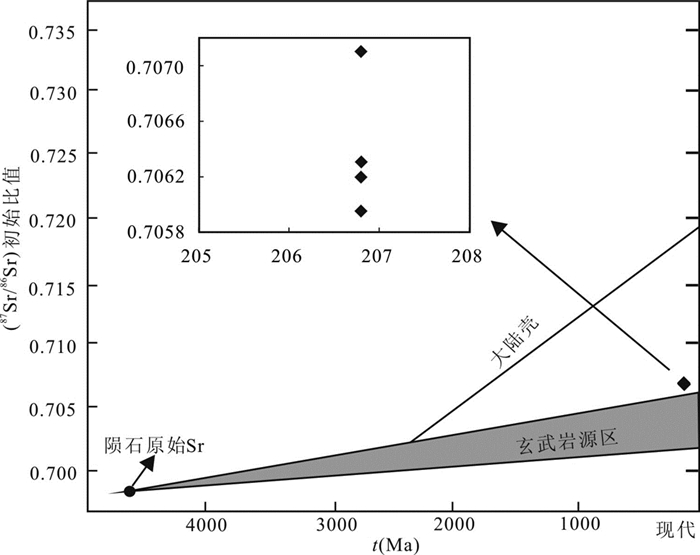
红太平矿床金属硫化物的(87Sr/86Sr)i值(0.705954~0.707101,均值0.706390)略高于地幔Sr的初始值(0.704),而明显低于大陆壳Sr的初始比值(0.719),表明红太平矿床脉型铅锌矿化的成矿物质主要来源于地幔,有少量的下地壳物质加入。另外,在地幔和地壳的Sr同位素演化图解中(图 8),红太平矿床金属硫化物的Sr同位素初始值落在大陆地壳增长线和玄武岩源区之间,并靠近玄武岩源区,同样也反映了成矿物质主要为地幔来源,有少量壳源物质加入的特征。综上认为,红太平矿床中生代的脉型铅锌矿化成矿物质主要来源于地幔,有少量的下地壳物质加入。
|
图 8 红太平矿床脉状矿体中闪锌矿和黄铁矿锶同位素在地幔和地壳中的演化图解(底图据Faure, 1986) Fig. 8 Evolution diagram in the mantle and the crust of Sr isotope in sphalerite and pyrite of vein type ore body of the Hongtaiping Cu polymetal deposit (base map after Faure, 1986) |
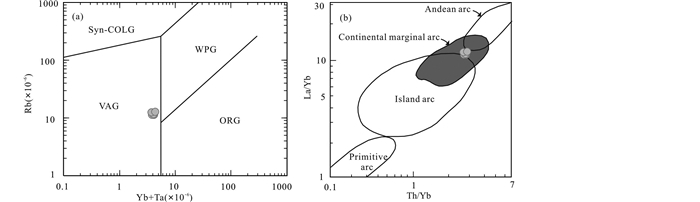
红太平矿区与脉状矿化密切相关的英安岩明显富集Rb、Ba、U和Th,亏损Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf、Y、Yb和Lu等,符合火山弧花岗岩的微量元素组合特征(Pearce et al., 1984;Pearce,1996);且其稀土元素球粒陨石标准化模式也与现代活动大陆边缘钙碱性花岗岩类类似(Borg and Clynne, 1998)。在Rb-(Yb+Ta)构造环境判别图解上(图 9a),英安岩样品落入火山弧花岗岩区内;在La/Yb-Th/Yb图解上(图 9b),样品落入大陆边缘弧区域内。
|
图 9 红太平矿床英安岩构造判别图解(底图据Pearce et al., 1984; Condie, 1989; Eby, 1992) Fig. 9 Tectonic discrimination diagrams for dacite in the Hongtaiping deposit (a) Rb vs. (Yb+Ta) polt; (b) La/Yb vs. Th/Yb plot (after Pearce et al., 1984; Condie, 1989; Eby, 1992). VAG-volcanic arc granites; Syn-COLG-syn-collisional granites; WPG-within-plate granites; ORG- ocean ridge granites |
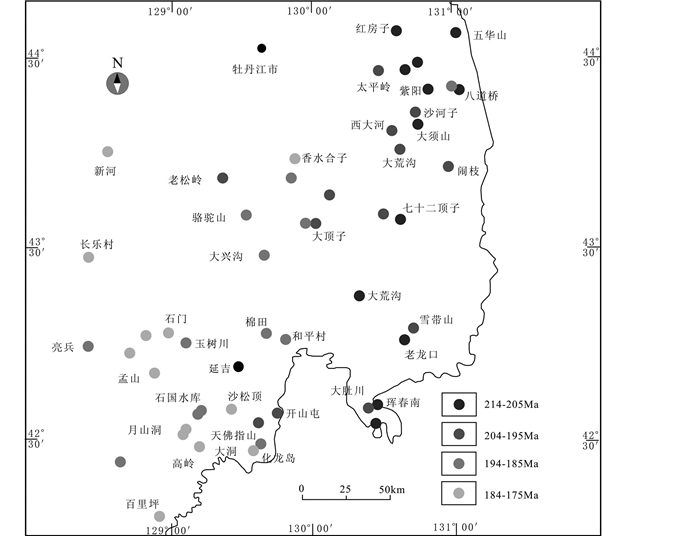
近些年来,延边地区厘定出多个晚三叠世至早侏罗世侵入岩(图 10、表 4)。三叠世晚期岩浆岩为一套钙碱性系列岩石,岩性组合为:辉长岩-闪长岩-英云闪长岩-石英闪长岩-花岗闪长岩-二长花岗岩-花岗岩,说明构造环境已经发生变化,大量岛弧火山岩的出现,标志着后碰撞环境的结束,新的火成岩具有俯冲带岩石地球化学特征和活动大陆边缘岩石组合的特点(张艳斌等,2002;Zhang et al., 2004;孙德有等,2004; Wu et al., 2011;张超等, 2014a, 2014b;王超,2018)。此外,随时代由老变新,该区侵入岩的分布范围存在自东向西演化的现象,指示了该区处于洋壳向陆壳之下俯冲的大地构造环境。越来越多学者根据吉黑东部构造、岩浆岩提出古太平洋向西俯冲开始于晚三叠世(彭玉鲸等, 2002, 2009, 2012;周建波等,2016);之后,包括延边地区在内的中国东北地区进入环太平洋构造域,构造岩浆活动强烈,或改造或继承先期断裂,形成一系列规模不等、性质不同的盆地和断陷,不同方向断裂的交汇部位,是火山喷发、次火山岩侵位和成矿的有利空间(秦克章等,2017)。
|
图 10 延边地区早中生代侵入岩分布示意图 Fig. 10 The sketch distribution map of the Early Mesozoic intrusions in Yanbian area |
|
|
表 4 延边地区早中生代侵入岩同位素年龄统计表 Table 4 Isotope ages of the Early Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Yanbian area |
综上认为,晚三叠世末期,古太平洋板块开始向欧亚板块俯冲,深部岩浆在构造的驱动下,沿断裂通道迅速运移到地壳浅部,形成大量的钙碱性岩浆岩;岩浆期后热液沿断裂在上升过程中,随着温度、压力、盐度以及酸碱度pH值等物理化学条件的改变,沿着构造裂隙充填交代,铅锌等矿质在有利的部位富集成矿,形成红太平矿床的脉状铅锌矿体,同时在断裂破碎带中发生硅化、绿泥石化、碳酸盐化、绢云母化等蚀变作用。
6 结论(1) 红太平铜多金属矿床发育层状铜多金属矿体和脉状铅锌矿体。其中,脉状铅锌矿体受控于近NW向断裂构造,明显穿切层状矿体,与英安岩脉具有密切的时空及成因关系,成因类型为中温热液脉型。
(2) 与脉型铅锌矿化具有密切时空及成因联系的英安岩脉LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为204.1±2.0Ma,脉状铅锌矿体中金属硫化物的Rb-Sr等时线年龄为206.8±9Ma。表明本矿区脉型矿化应形成于晚三叠世末期。
(3) 与脉型铅锌矿化密切相关的英安岩的初始岩浆可能来自壳幔混合作用;根据金属硫化物的较高Sr同位素初始比值可判断脉型铅锌矿化成矿物质主要为壳幔混源,形成于活动大陆边缘的构造环境,与晚三叠世-早侏罗世(T3-J1)古太平洋板块向欧亚板块的俯冲作用密切相关。
致谢 核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心和中国科学院地球化学研究所矿床地球化学重点实验室在Rb-Sr同位素测试分析和微量元素测试分析中给予了悉心的指导和热心的帮助;审稿专家对文中不足之处提出了宝贵的修改建议。在此一并表示衷心感谢!
Anderson T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59-79 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X |
Borg LE and Clynne MA. 1998. The petrogenesis of felsic calcalkaline magmas from the southernmost Cascades, California:Origin by partial melting of basaltic lower crust. Journal of Petrology, 39(6): 1197-1222 DOI:10.1093/petroj/39.6.1197 |
Bowring SA and Schmitz MD. 2003. High-precision U-Pb zircon geochronology and the stratigraphic record. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 305-326 DOI:10.2113/0530305 |
Cao HW, Zhang ST, Santosh M, Zheng L, Tang L, Li D, Zhang XH and Zhang YH. 2015. The Luanchuan Mo-W-Pb-Zn-Ag magmatic-hydrothermal system in the East Qinling metallogenic belt, China:Constrains on metallogenesis from C-H-O-S-Pb isotope compositions and Rb-Sr isochron ages. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 111: 751-780 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.06.005 |
Chen C, Ren YS, Zhao HL, Zou XT, Yang Q and Hu ZC. 2014. Permian age of the Wudaogou Group in eastern Yanbian:Detrital zircon U-Pb constraints on the closure of the Palaeo-Asian Ocean in Northeast China. International Geology Review, 56(14): 1754-1768 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2014.956348 |
Chen C. 2017. Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic tectonic evolution and regional metallogenic regularity of the eastern Yanbian area, NE China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-201 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Chen C, Ren YS, Zhao HL, Yang Q and Shang QQ. 2017. Age, tectonic setting, and metallogenic implication of Phanerozoic granitic magmatism at the eastern margin of the Xing'an-Mongolian Orogenic Belt, NE China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 144: 368-383 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.02.012 |
Condie KC. 1989. Geochemical changes in basalts and andesites across the Archean-Proterozoic boundary:Identification and significance. Lithos, 23(1-2): 1-18 DOI:10.1016/0024-4937(89)90020-0 |
Deng J, Yuan W, Carranza EJM, Yang L, Wang C, Yang L and Hao N. 2014. Geochronology and thermochronometry of the Jiapigou gold belt, northeastern China:New evidence for multiple episodes of mineralization. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 89: 10-27 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.03.013 |
Eby GN. 1992. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Geology, 20(7): 641-644 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2 |
Faure G. 1977. Principles of Isotope Geology. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc., 1-120
|
Faure G. 1986. Principles of Isotope Geology. 2nd Edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 183-199
|
Fu CL. 2009. The geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of granitoid from Xiaoxi'nancha in Hunchun area, Jilin Province. Master Degree Thesis. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-76 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Han YG, Li XH, Zhang SH, Zhang YH and Chen FK. 2007. Single grain Rb-Sr dating of euhedral and cataclastic pyrite from the Qiyugou gold deposit in western Henan, central China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(13): 1820-1826 DOI:10.1007/s11434-007-0248-3 |
Hou ML, Jiang SY, Jiang YH and Ling HF. 2006. S-Pb isotope geochemistry and Rb-Sr geochronology of the Penglai gold field in the eastern Shandong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(10): 2525-2533 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu QQ, Wang YT, Wang RT, Li JH, Dai JZ and Wang SY. 2012. Ore-forming time of the Erlihe Pb-Zn deposit in the Fengxian-Taibai ore concentration area, Shaanxi Province:Evidence from the Rb-Sr isotopic dating of sphalerites. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(1): 258-266 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu QQ, Wang YT, Man JW, Wei R, Liu SY, Ye DJ, Yuan QH and Dou P. 2015. Timing of the formation of the Changba-Lijiagou Pb-Zn ore deposit, Gansu Province, China:Evidence from Rb-Sr isotopic dating of sulfides. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 103: 350-359 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.021 |
Jackson SE, Pearson NJ, Griffin WL and Belorsova EA. 2004. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon gochronology. Chemical Geology, 211(1-2): 47-69 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.06.017 |
Jia DC, Hu RZ, Lu Y and Qiu XL. 2004. Collision belt between the Khanka block and the North China block in the Yanbian Region, Northeast China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 23(2): 211-219 DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00123-8 |
Jin BC. 2012. Characteristics of Paleozoic sedimentary from East Chin-Korean Peninsula and its tectonic evolution. Ph. D. Dissertation. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-124 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Li WB, Huang ZL, Xu DR, Chen J, Xu C and Guan T. 2002. Rb-Sr isotopic method on zinc-lead ore deposits:A review. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 26(4): 436-441 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li Y. 2017. Ore genesis and tectonic setting of Xiaohongshilazilead-zinc deposit in Panshi area, Jilin Province. Master Degree Thesis. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-58 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Liu JM, Zhao SR, Shen J, Jiang N and Huo WG. 1998. Review on direct isotopic dating of hydrothermal ore-forming processes. Progress in Geophysics, 13(3): 46-55 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Gao S, Günther D, Xu J, Gao CG and Chen HH. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34-43 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 |
Lu YF. 2004. GeoKit:A geochemical toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Geochimica, 33(5): 459-464 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ludwing KR. 2003. ISOPLOT 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication
|
Ludwing KR. 2004. ISOPLOT/Ex, Version 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley, California: Berkeley Geochronology Center
|
Ludwing KR. 2012. User's Manual for ISOPLOT 3.75: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center
|
Nakai SI, Halliday AN, Kesler SE and Jones HD. 1990. Rb-Sr dating of sphalerites from Tennessee and the genesis of Mississippi Valley type ore deposits. Nature, 346(6282): 354-357 DOI:10.1038/346354a0 |
Nakai SI, Halliday AN, Kesler SE, Jones HD, Kyle JR and Lane TE. 1993. Rb-Sr dating of sphalerites from Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) ore deposits. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 57(2): 417-427 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(93)90440-8 |
Pearce JA, Harris NBW and Tindle AG. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983 DOI:10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 |
Pearce JA. 1996. Sources and settings of granitic rocks. Episodes, 19(4): 120-125 DOI:10.18814/epiiugs/1996/v19i4/005 |
Peng YJ, Ji CH and Xin YL. 2002. Petrology and geochronology of the Paleo-Jilin-Heilongjiang orogenic belt in the adjacent areas of China, Russia and Korea. Geology and Resources, 11(2): 65-75 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Peng YJ, Zhai YC and Zhang HH. 2009. Age determination and characteristics of the Late Indosinian-Yanshanian metallogenetic events of Jilin Province. Jilin Geology, 28(3): 1-5, 14 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Peng YJ, Qi CD, Zhou XD, Lu XB, Dong HC and Li Z. 2012. Transition from Paleo-Asian Ocean domain to Circum-Pacific Ocean domain for the Ji-Hei composite orogenic belt:Time mark and relationship to global tectonics. Geology and Resources, 21(3): 261-265 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Pettke T and Diamond LW. 1996. Rb-Sr dating of sphalerite based on fluid inclusion-host mineral isochrons:A clarification of why it works. Economic Geology, 91(5): 951-956 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.91.5.951 |
Qi L and Zhou MF. 2008. Platinum-group elemental and Sr-Nd-Os isotopic geochemistry of Permian Emeishan flood basalts in Guizhou Province, SW China. Chemical Geology, 248(1-2): 83-103 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.11.004 |
Qin KZ, Zhai MG, Li GM, Zhao JX, Zeng QD, Gao J, Xiao WJ, Li JL and Sun S. 2017. Links of collage orogenesis of multiblocks and crust evolution to characteristic metallogeneses in China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(2): 305-325 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Qiu JT, Song WJ, Jiang CX, Wu H and Dong RM. 2013. CGDK:An extensible CorelDRAW VBA program for geological drafting. Computers & Geosciences, 51: 34-48 |
Ren YS, Chen C, Zou XT, Zhao HL, Hao YJ, Hou HN, Hu ZC and Jiang GH. 2016. The age, geological setting, and types of gold deposits in the Yanbian and adjacent areas, NE China. Ore Geology Reviews, 73: 284-297 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.03.013 |
Song B, Zhang YH and Liu DY. 2002. Introduction to the Naissance of SHRIMP and its contribution to isotope geology. Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 23(1): 58-62 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Song Q. 1991. Geological features of the Hongtaiping polymetallic deposit and the significance in regional prospecting for ore deposits. Jilin Geology, (4): 22-28 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunder A D and Norry M J(eds.). Magmatism in Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society London Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345
|
Sun DY, Wu FY, Zhang YB and Gao S. 2004. The final closing time of the west Lamulun River-Changchun-Yanji plate suture zone:Evidence from the Dayushan granitic pluton, Jilin Province. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 34(2): 174-181 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Taylor SR and McLennan SM. 1985. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution: An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary Rocks. Oxford: Blackwell Science
|
Taylor SR and McLennan SM. 1995. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(2): 241-265 DOI:10.1029/95RG00262 |
Wang C. 2018. The research of Early-Middle Mesozoic igneous rocks in eastern Jilin and Heilongjiang provinces and its tectonic implications. Ph. D. Dissertation. Changchun: Jilin University (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Wang H, Ren YY, Zhao HL, Ju N and Qu WJ. 2011. Re-Os dating of molybdenite from the Liushengdian molybdenum deposit in Antu area of Jilin Province and its geological significance. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 32(6): 707-715 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang YX, Gu LX, Zhang ZZ, Wu CZ, Li HM and Yang JD. 2007. Sr-Nd-Pb isotope geochemistry of rhyolite of the Late Carboniferous Dashitou Group in eastern Tianshan. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(7): 1749-1755 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang ZG, Wang KY, Wan D, Yassa K, Yang TN and Liang YH. 2017. Metallogenic age and hydrothermal evolution of the Jidetun Mo deposit in central Jilin Province, Northeast China:Evidence form fluid inclusions, isotope systematics, and geochronology. Ore Geology Reviews, 89: 731-751 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.07.014 |
Wu FY, Zhao GC, Sun DY, Wilde SA and Yang JH. 2007. The Hulan Group:Its role in the evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt of NE China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 30(3-4): 542-556 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.01.003 |
Wu FY, Sun DY, Ge WC, Zhang YB, Grant ML, Wilde SA and Jahn BM. 2011. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(1): 1-30 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014 |
Wu PF, Sun DY, Wang TH, Gou J, Li R, Liu W and Liu XM. 2013. Geochronology, geochemical characteristic and petrogenesis analysis of diorite in Helong of Yangbian area, NE China. Geological Journal of China Universities, 19(4): 600-610 |
Yang DG, Sun D and Gou J. 2017. U-Pb ages of zircons from Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Yanbian area, Jilin Province, NE China:Transition of the Paleo-Asian oceanic regime to the circum-Pacific tectonic regime. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 143: 171-190 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.04.019 |
Yang JH and Zhou XH. 2000. Rb-Sr isochron ages of the ore and gold bearing minerals in Linglong gold deposit and it's ore-forming ages, eastern of Jiaozhou Peninsula. Chinese Science Bulletin, 45(14): 1547-1553 (in Chinese) DOI:10.1360/csb2000-45-14-1547 |
Yang Q, Ren YS, Sun ZM, Hao YJ, Zhang B, Sun XH and Lu SY. 2018. Geochronologic evidence of Late Paleozoic magmatic-hydrothermal mineralization in Tianbaoshan metallogenic region, Yanbian area:A case study of the Xinxing lead-zinc (silver) deposit. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(10): 3153-3166 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang Q, Ren YS, Li Y, Hao YJ and Li JM. 2020. Age and tectonic setting of mesothermal magmatic hydrothermal vein-type Pb-Zn-(Ag) mineralization in the Xiaohongshilazi deposit, Central Jilin Province, Northeast China. Resource Geology, 70(1): 70-88 |
Yuan HL, Gao S, Liu XM, Li HM, Günther D and Wu FY. 2004. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28(3): 353-370 DOI:10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb00755.x |
Zhang C. 2017. The Mesozoic tectonic evolution of Yangbian area in the eastern segment of northern margin of the North China Block. Ph. D. Dissertation. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-137 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zhang C, Guo W, Xu ZY, Liu ZH, Liu YJ and Lei CC. 2014a. Study on geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of monzogranite from the Yanbian area, eastern Jilin Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(2): 512-526 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang C, Xu ZY, Liu ZH, Li SC, Shi Y and Fan ZW. 2014b. Petrogenesis of the Late Mesozoic Liudong pluton in Yanbian area NE China:Evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 44(1): 145-157 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang Y, Chen Q, Yang HB, Wu WQ and Wang DC. 2012. Geological features and genesis of Hongtaiping Cu-polymetallic ore deposit of Jilin Province. Jilin Geology, 31(3): 48-52 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang Y, Sun JG, Chen YJ and Zhao KQ. 2013. Re-Os and U-Pb geochronology of porphyry Mo deposits in central Jilin Province:Mo ore-forming stages in Northeast China. International Geology Review, 55(14): 1763-1785 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2013.794915 |
Zhang Y, Xing SW, Song QH, Wang Y, Yu ZT, Du XH, Ma YB and Zhang ZJ. 2015. Re-Os and U-Pb geochronology of porphyry and skarn types copper deposits in Jilin Province, NE China. Resource Geology, 65(4): 394-404 DOI:10.1111/rge.12074 |
Zhang YB, Wu FY, Li HM, Lu XP, Sun DY and Zhou HY. 2002. Single grain zircon U-Pb ages of the Huangniling granite in Jilin Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 18(4): 475-481 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang YB, Wu FY, Wilde SA, Zhai MG, Lu XP and Sun DY. 2004. Zircon U-Pb ages and tectonic implications of 'Early Paleozoic' granitoids at Yanbian, Jilin Province, Northeast China. The Island Arc, 13(4): 484-505 DOI:10.1111/j.1440-1738.2004.00442.x |
Zhao HD. 2009. Paleozoic igneous rock assemblages and tectonic evolution in southern Xiaoxing'anling-northern Zhangguangcailing, northeastern China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-109 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zhao HG. 2007. Studies on the ore forming models of Mesozoic epithermal gold-copper deposits in Yanbian, Jilin province. Ph. D. Dissertation. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-194 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zheng W, Chen MH, Xu LG, Zhao HJ, Ling SB, Wu Y, Hu YG, Tian Y and Wu XD. 2013. Rb-Sr isochron age of Tiantang Cu-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit in Guangdong Province and its geological significance. Mineral Deposits, 32(2): 259-272 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhou JB, Shi AG and Jing Y. 2016. Combined NE China blocks:Tectonic evolution and supercontinent reconstructions. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 46(4): 1042-1055 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
陈聪. 2017.延边东部晚古生代-中生代构造演化与区域成矿规律.博士学位论文.长春: 吉林大学, 1-201
|
付长亮. 2009.珲春小西南岔地区花岗岩类的时代、地球化学特征与成因.硕士学位论文.长春: 吉林大学, 1-76
|
侯明兰, 蒋少涌, 姜耀辉, 凌洪飞. 2006. 胶东蓬莱金成矿区的S-Pb同位素地球化学和Rb-Sr同位素年代学研究. 岩石学报, 22(10): 2525-2533. |
胡乔青, 王义天, 王瑞廷, 李建华, 代军治, 王双彦. 2012. 陕西省凤太矿集区二里河铅锌矿床的成矿时代:来自闪锌矿Rb-Sr同位素年龄的证据. 岩石学报, 28(1): 258-266. |
金炳成. 2012.中国东部-朝鲜半岛古生代沉积特征及构造演化.博士学位论文.长春: 吉林大学, 1-124
|
李文博, 黄智龙, 许德如, 陈进, 许成, 管涛. 2002. 铅锌矿床Rb-Sr定年研究综述. 大地构造与成矿学, 26(4): 436-441. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2002.04.015 |
李勇. 2017.吉林省磐石市小红石砬子铅锌矿床成因与构造背景.硕士学位论文.长春: 吉林大学, 1-58
|
刘建明, 赵善仁, 沈洁, 姜能, 霍卫国. 1998. 成矿流体活动的同位素定年方法评述. 地球物理学进展, 13(3): 46-55. |
路远发. 2004. GeoKit:一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包. 地球化学, 33(5): 459-464. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2004.05.004 |
彭玉鲸, 纪春华, 辛玉莲. 2002. 中俄朝毗邻地区古吉黑造山带岩石及年代记录. 地质与资源, 11(2): 65-75. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2002.02.001 |
彭玉鲸, 翟玉春, 张鹤鹤. 2009. 吉林省晚印支期-燕山期成矿事件年谱的拟建及特征. 吉林地质, 28(3): 1-5, 14. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-2427.2009.03.001 |
彭玉鲸, 齐成栋, 周晓东, 卢兴波, 董红辰, 李壮. 2012. 吉黑复合造山带古亚洲洋向滨太平洋构造域转换:时间标志与全球构造的联系. 地质与资源, 21(3): 261-265. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2012.03.001 |
秦克章, 翟明国, 李光明, 赵俊兴, 曾庆栋, 高俊, 肖文交, 李继亮, 孙枢. 2017. 中国陆壳演化、多块体拼合造山与特色成矿的关系. 岩石学报, 33(2): 305-325. |
宋彪, 张玉海, 刘敦一. 2002. 微量原位分析仪器SHRIMP的产生与锆石同位素地质年代学. 质谱学报, 23(1): 58-62. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-2997.2002.01.011 |
宋群. 1991. 红太平多金属矿床地质特征及区域找矿意义. 吉林地质, (4): 22-28. |
孙德有, 吴福元, 张艳斌, 高山. 2004. 西拉木伦河-长春-延吉板块缝合带的最后闭合时间:来自吉林大玉山花岗岩体的证据. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 34(2): 174-181. |
王超. 2018.吉黑东部中生代早中期火成岩研究及其构造意义.博士学位论文.长春: 吉林大学, 1-92
|
王辉, 任云生, 赵华雷, 鞠楠, 屈文俊. 2011. 吉林安图刘生店钼矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素定年及其地质意义. 地球学报, 32(6): 707-715. DOI:10.3975/cagsb.2011.06.08 |
王银喜, 顾连兴, 张遵忠, 吴昌志, 李惠民, 杨杰东. 2007. 东天山晚石炭世大石头群流纹岩Sr-Nd-Pb同位素地球化学研究. 岩石学报, 23(7): 1749-1755. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.07.020 |
武鹏飞, 孙德有, 王天豪, 苟军, 李蓉, 刘玮, 柳小明. 2013. 延边和龙地区闪长岩的年代学、地球化学特征及岩石成因研究. 高校地质学报, 19(4): 600-610. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2013.04.006 |
杨进辉, 周新华. 2000. 胶东地区玲珑金矿矿石和载金矿物Rb-Sr等时线年龄与成矿时代. 科学通报, 45(14): 1547-1553. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.14.018 |
杨群, 任云生, 孙振明, 郝宇杰, 张博, 孙新浩, 陆思宇. 2018. 延边天宝山矿集区晚古生代岩浆-热液成矿的年代学证据——以新兴铅锌(银)矿床为例. 岩石学报, 34(10): 3153-3166. |
张超. 2014.华北板块北缘东段延边地区中生代构造演化.博士学位论文.长春: 吉林大学, 1-137
|
张超, 郭巍, 徐仲元, 刘正宏, 刘永江, 雷聪聪. 2014a. 吉林东部延边地区二才长花岗岩年代学、岩石成因学籍其构造意义研究. 岩石学报, 30(2): 512-526. |
张超, 徐仲元, 刘正宏, 李世超, 时溢, 范志伟. 2014b. 东北延边地区晚中生代柳洞岩体的成因:锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学证据. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44(1): 145-157. |
张扬, 陈奇, 杨洪波, 吴伟群, 王堆仓. 2012. 吉林红太平铜多金属矿床地质特征及成因探讨. 吉林地质, 31(3): 48-52. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-2427.2012.03.013 |
张艳斌, 吴福元, 李惠民, 路孝平, 孙德有, 周红英. 2002. 吉林黄泥岭花岗岩体的单颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄. 岩石学报, 18(4): 475-481. |
赵寒冬. 2009.东北地区小兴安岭南段-张广才岭北段古生代火成岩组合与构造演化.博士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1-109
|
赵宏光. 2007.延边中生代浅成热液铜金矿床的成矿模式研究.博士学位论文.长春: 吉林大学, 1-194
|
郑伟, 陈懋弘, 徐林刚, 赵海杰, 凌世彬, 吴越, 胡耀国, 田云, 吴晓东. 2013. 广东天堂铜铅锌多金属矿床Rb-Sr等时线年龄及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 32(2): 259-272. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.02.003 |
周建波, 石爱国, 景妍. 2016. 东北地块群:构造演化与古大陆重建. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 46(4): 1042-1055. |
 2020, Vol. 36
2020, Vol. 36


