2. 安徽省矿产资源与矿山环境工程技术研究中心, 合肥 230009;
3. 安徽省公益性地质调查管理中心, 合肥 230091;
4. 安徽省勘查技术院, 合肥 230001
2. Anhui Province Engineering Research Center for Mineral Resources and Mine Environments, Hefei 230009, China;
3. Public Geological Survey Management Center of Anhui Province, Hefei 230091, China;
4. Geological Exploration Technologies Institute of Anhui Province, Hefei 230001, China
随着经济的快速发展,矿产资源预测评价的重要性日益加强,浅部矿的找矿勘探已进入瓶颈,深部矿、隐伏矿已成为找矿的工作重心(翟裕生等, 2004; 赵鹏大等, 2004; 赵鹏大, 2007; 曹新志等, 2009; Salama et al., 2016)。定量成矿预测最初在二维平面上进行,结合GIS理论与地物化遥多元信息,以二维图层形式参与定量成矿预测模型计算,在此基础上圈定找矿靶区(赵鹏大等, 2002; 陈建平等, 2008; 肖克炎, 1994; Carranza, 2009)。然而,深部隐伏矿体在地表的异常指示往往较弱,对于传统成矿预测评价方法带来了新的挑战。“三深一土”战略实施后随之而来的深部地信息爆炸(樊俊等, 2018; 杨明桂等, 2018)为成矿预测向三维推进提供了机遇。三维成矿预测强调在深入研究区域及矿床地质特征的基础上,融合地球物理解译信息,并结合三维地质建模方法和三维空间分析方法提取三维预测要素,提取成矿有利区域、实现三维预测靶区的圈定(毛先成等, 2006; 陈建平等, 2007; 肖克炎等, 2012; 袁峰等, 2014; Li et al., 2015, 2019; Nielsen et al., 2015; Payne et al., 2015)。三维预测靶区具有形态、位置、规模等定量化特征,能够为进一步的找矿勘探工作提供更多的参考信息。
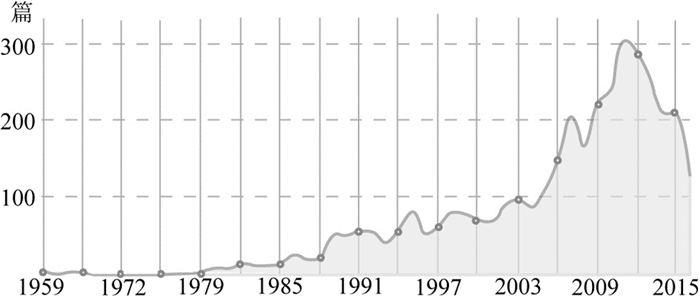
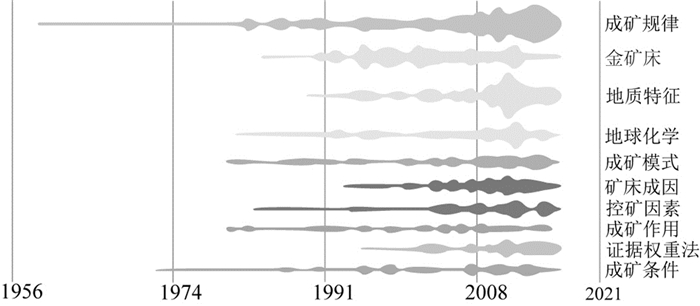
1 二维成矿预测研究现状国内,成矿预测自1959年开始出现相关研究,2011年达到一个高峰(图 1),随着研究的不断深入,出现了越来越多与“成矿预测”相关的关键词,形成了庞大的研究网络,其中成矿作用、成矿规律、成矿模式、矿床成因等关键词的热度居高不下(图 2)。
|
图 1 成矿预测相关文献发表年份统计(源自百度学术) Fig. 1 The quantity of academic papers related to prospectivity modeling (from Baidu Academic) |
|
图 2 成矿预测相关关键词热度统计(源自百度学术) Fig. 2 The keyword popularity related to prospectivity modeling (from Baidu Academic) |
基于国情和评价目的,各国用于矿床预测的方法有所差异。如美国的基于“根据矿床描述性模型圈定可行地段,矿床数估计,通过品位吨位模型估计资源量”的三步式矿产资源潜力评价(肖克炎等, 2006),俄罗斯的基于“对象、标志、方法”三要素的“预测普查组合”法(赵鹏大, 2002)等。多变量预测方程(Agterberg, 1970; Agterberg et al., 1993)、“三联式”成矿预测(赵鹏大, 2002)、“综合信息矿产预测理论与方法”(王世称等, 2000)、非线性成矿预测理论(成秋明, 2006)等研究成果也推动了定量成矿预测的发展。
在上述方法的应用和发展过程中,众多专家学者引入了多学科、跨学科的技术,如地理信息(GIS)技术(赵鹏大等, 1996; 李裕伟等, 2007)、多元统计分析技术(赵鹏大等, 1994)等。2006年开始的全国25种重要矿产资源潜力评价工作全面应用了空间数据库和GIS技术,综合利用了物探、化探和遥感等资料所显示的地质找矿信息,圈定了预测区,并进行了资源量估算。通过上述工作,科学评价了我国矿产资源的潜力, 为我国政府和矿产勘查机构提供技术支撑(肖克炎等, 2014)。
然而,上述成矿预测研究主要基于二维数据开展,相关方法往往应用于对中小比例尺成矿远景区开展预测研究。随着近年来深部矿、隐伏矿成为找矿的主要对象,三维成矿预测及相关方法技术得到了飞速发展,成为深部隐伏矿床预测的重要手段之一。
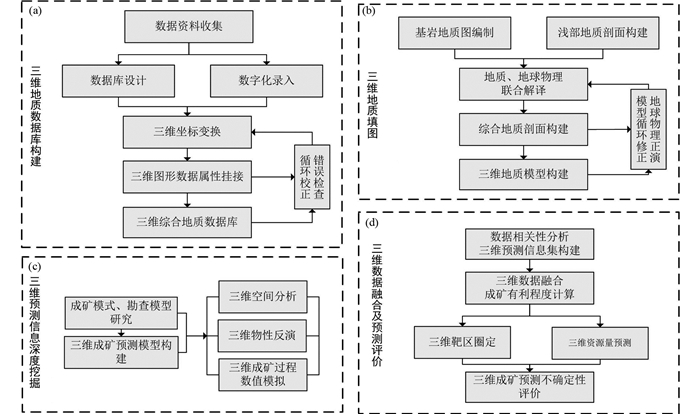
2 三维成矿预测研究现状 2.1 三维成矿预测方法体系随着隐伏矿床三维成矿预测成为成矿预测领域的新生方向及热点,多名学者特别是国内学者相继提出多种三维成矿预测方法与流程,标识着相关研究逐步走向成熟。如“地质信息集成-成矿信息定量提取-立体定量预测”深部矿产资源三维预测方法(毛先成等, 2011, 2016);基于“立方体模型”的区域隐伏矿体三维定量预测评价(陈建平等, 2007, 2014);基于三维可视化信息分析技术的大比例尺矿产预测方法(肖克炎等, 2012; Xiao et al., 2015),基于综合信息的三维成矿预测(袁峰等, 2014)等。袁峰等(2018)综合以往研究,提出了“四步式”三维成矿预测方法,将三维成矿预测工作归纳为三维地质数据库构建、三维地质建模填图、三维预测信息深度挖掘和三维数据融合及预测评价四个关键步骤(图 3)。
|
图 3 “四步式”三维成矿预测方法(据袁峰等, 2018) Fig. 3 "Four-step" prospectivity modeling approach (after Yuan et al., 2018) |
其中,三维地质模型是三维成矿预测的基础,因此三维地质建模也成为三维成矿预测最为重要的环节。三维地质建模相关技术方法需要融合地形、地质填图、钻孔编录、地质剖面以及地球物理反演结果等地学信息,其对多维、多元数据的融合、以及在三维空间内对复杂地质体的表征能力对于以三维地质模型为基础的三维成矿预测研究具有十分重要的意义。
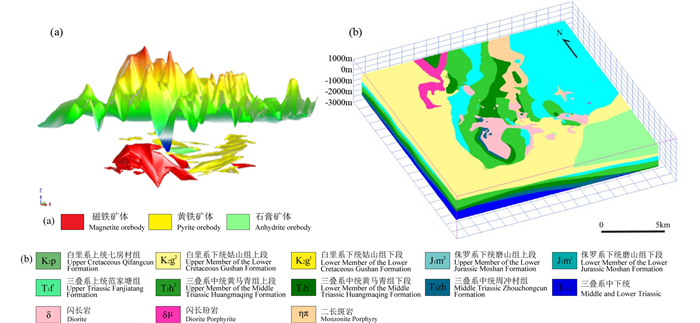
2.2 三维地质建模三维地质建模技术可分为显式三维建模技术以及隐式三维建模技术(李晓晖, 2015)。早期研究中,三维地质模型多采用显式三维建模技术进行构建。相关软件,例如Surpac、GoCAD,Micromine、DiMine、3DMine、MapGIS K9、探矿者等,可以在建模过程中对地质模型的精细结构进行控制,对复杂或精细的地质结构具有优良的三维表达能力(李晓晖, 2015)。基于显式三维建模技术的应用实践已广泛开展并取得了良好的效果(陈建平等, 2007; 孙莉等, 2011; 张明明等, 2011, 2014;图 4a)。然而,基于轮廓线的显式三维建模技术也存在许多缺点和不足,如很难融合不同方向、不同类型、不同范围的多元地学数据;数据精度、数量要求高;进行数据更新或修改模型时,即使小范围的更新和修改,工作量也十分巨大。
|
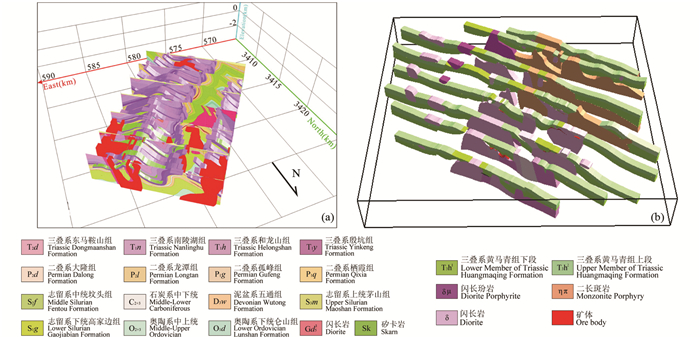
图 4 三维地质建模成果 (a)显式三维地质建模:庐枞盆地泥河铁矿矿体三维地质模型(据张明明等,2011);(b)隐式三维地质建模:宁芜盆地钟姑矿田三维地质模型(据Li et al., 2015) Fig. 4 Three dimensional geological models (a) explicit 3D geological modeling: 3D geological model of orebodies of Nihe deposit within Luzong Basin (after Zhang et al., 2015); (b) implicit 3D geological modeling: 3D geological model of Zhonggu orefield within Ningwu Basin (after Li et al., 2015) |
为克服上述缺点,隐式三维建模技术发展迅速,并开始被广泛应用(Jessell, 2001; Calcagno et al., 2008; Li et al., 2015;图 4b),相关软件如Geomodeller、Leapfrog Geo、Petrel、SKUA、网格天地、CreatarXModeling等,能够基于势场和插值方法自动对模型进行构建,具有计算过程快速,可快速进行数据更新和模型重建的优点;同时,在建模过程中可以充分融合多方向、尺度和方位的各种地质观测数据和地球物理解译数据;对于数据量较少、分布不均的区域也较为适用。然而,隐式三维建模技术会受到网格尺度、数据密度和算法等方面的限制,对于局部复杂地质构造形态尚无法精细控制(李晓晖, 2015)。未来,上述问题的解决定会进一步推动三维地质建模的发展和应用。
三维地质模型的合理性和准确性是三维成矿预测的研究基础和关键所在。三维地质模型通常融合钻孔数据和地球物理解译成果等联合解析深部地质结构。然而,地球物理解译成果具有多解性,三维地质模型存在较强的不确定性。目前,已有学者将多条解译剖面在水平方向进行延展拼合,再基于三维地球物理正演方法与实测地球物理数据进行对比,以验证地球物理解译剖面的合理性和准确性(图 5; Lü et al., 2012; 祁光等, 2012; 付光明, 2017; 丁文祥等, 2018)。上述方法能够快速的开展三维地质模型合理性和准确性的验证,但难以描述多条解译剖面延展拼合构建三维模型对于剖面间地质体的形态变化,同时对于剖面间钻孔等先验数据无法融合应用。为了解决上述问题,目前已逐步开始利用隐式三维建模技术快速融合地球物理解译成果以及地表填图、地质剖面和钻孔等先验地质数据,进而基于三维地质模型成果开展三维地球物理正演工作,实现对地球物理解译成果、三维地质建模方法和参数的合理性和准确性的协同验证(图 6; 丁文祥, 2019)。基于验证对比结果,在隐式三维建模技术的支持下,能够快速反向修正地球物理解译结果并实现三维地质模型的快速更新,进而得到更为合理和可靠的深部地质结构信息。
|
图 5 解译剖面水平方向延展 (a)铜陵地区(据Lü et al., 2012);(b)钟姑矿田(据丁文祥等,2018) Fig. 5 The interpretation section extends horizontally (a) Tongling region (after Lü et al., 2012); (b) Zhonggu ore field (after Ding et al., 2018) |

|
图 6 繁昌盆地三维地质模型及三维地球物理正演结果对比验证(据丁文祥, 2019) Fig. 6 The three-dimensional geological model and the three-dimensional geophysical forward modeling results (after Ding, 2019) |
目前,国内外多个地区相继开展了三维成矿预测工作,成功圈定了多个深部找矿靶区(毛先成等, 2011; Sprague et al., 2006; Fallara et al., 2006; 陈建平等, 2007; Payne et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2015; Xiao et al., 2015; Nielsen et al., 2015; Yuan et al., 2014; Li et al., 2015, 2019)。为进一步推进三维成矿预测理论和方法的研究与具体实践,诸多学者和单位相继开发出多款软件系统。如中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所结合具体大比例尺勘探实际需求的集三维矿山管理、地质勘探、三维可视化和科学分析预测为一体的三维GIS软件“探矿者”,在湘西北、湖北、西藏、新疆等地开展了三维地质体建模、储量估算及立体预测的工作(肖克炎等, 2010; 张婷婷, 2010; 孙莉等, 2011; 刘智宇和肖克炎, 2013; 王琨等, 2015);中国地质大学(吕鹏, 2007)基于立方体预测模型进行了隐伏矿体三维预测系统开发。
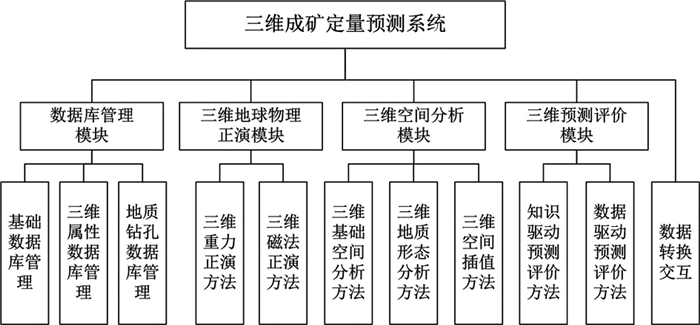
合肥工业大学针对多尺度三维成矿预测需求,开发了“三维成矿定量预测系统”(图 7),该系统能够高效稳定的对多元地学数据进行管理,具备的多种三维空间分析功能能够快速提取三维预测信息,提供的多种三维预测评价方法能够适应不同条件下三维预测要素的融合,开展成矿有利程度的计算并圈定找矿靶区(李晓晖等, 2017)。
|
图 7 三维成矿定量预测系统结构图(据李晓晖等, 2017) Fig. 7 The system structure of three-dimensional quantitative prediction system for mineralization (after Li et al., 2017) |
这一系统已应用于长江中下游成矿带,开展了较为广泛的不同尺度的成矿预测。如,矿床尺度,在宁芜盆地钟姑矿田的白象山和杨庄铁矿床开展了成矿预测,利用证据权重模型、神经网络模型等对矿床深边部隐伏矿体进行了预测(图 8a, b; Hu et al., 2018; Yuan et al., 2014; 李晓晖等, 2014);矿田尺度,已分别在钟姑和月山矿田开展了三维成矿预测,通过综合利用隐式三维地质建模方法、三维空间分析方法、三维物性反演、数据驱动下的Logisitc回归模型等方法技术,定量计算获得成矿有利程度,并依此对深部找矿靶区进行了三维预测(图 8c, d; Li et al., 2015, 2019),相关预测靶区已作为进一步的深部找矿勘探的重点。

|
图 8 三维成矿预测结果 矿床尺度:(a)白象山铁矿床深边部成矿预测(据Yuan et al., 2014);(b)杨庄铁矿床深边部成矿预测(据Hu et al., 2018);矿田尺度:(c)钟姑铁矿田三维成矿预测(据Li et al., 2015修改);(d)月山矿田三维成矿预测(据Li et al., 2019) Fig. 8 The result of three-dimensional prospectivity modeling Deposit scale: (a) prospectivity modeling of the Baixiangshang Fe deposit (after Yuan et al., 2014); (b) prospectivity modeling of the Yangzhuang Fe deposit (after Hu et al., 2018); Orefield scale: (c) three-dimensional prospectivity modeling of the Zhonggu ore field (modified after Li et al., 2015); (d) three-dimensional prospectivity modeling of the Yueshan ore field (after Li et al., 2019) |
已有的研究及实践显示,三维成矿预测在方法理论体系和实际应用等方面均已取得进展。然而,相较于传统的二维成矿预测,三维成矿预测往往受限于三维预测信息的缺乏。如何更好的挖掘二维数据在深度方向的指示能力、将二维数据推演至三维环境,利用数值模拟、机器学习等方法开展数据挖掘、充分发挥已有数据的内蕴信息,将成为三维成矿预测研究向前发展的重要驱动力。
3.1 二维数据的三维推演传统找矿勘查工作中积累有大量的二维数据,如地球物理扫面数据、地球化学勘探数据、地表地质填图数据等。如何将上述大量的二维数据应用于三维成矿预测研究,将成为未来的研究重点之一。
目前,二维数据向三维推演多采用地球物理正反演方法,基于剖面的地质结构地球物理解译方法已应用多年。近年来,基于重磁数据的三维物性反演方法已被广泛使用,其成果已被用于深部地质构造解译及三维成矿预测研究中(Lü et al., 2012;祁光等, 2012; 严加永等, 2014; 郭冬等, 2014)。未来,随着大地电磁三维反演、人工地震三维层析成像以及重磁电震三维联合反演等方法的不断前进,上述方法将为三维成矿预测研究提供更多的三维数据来源。
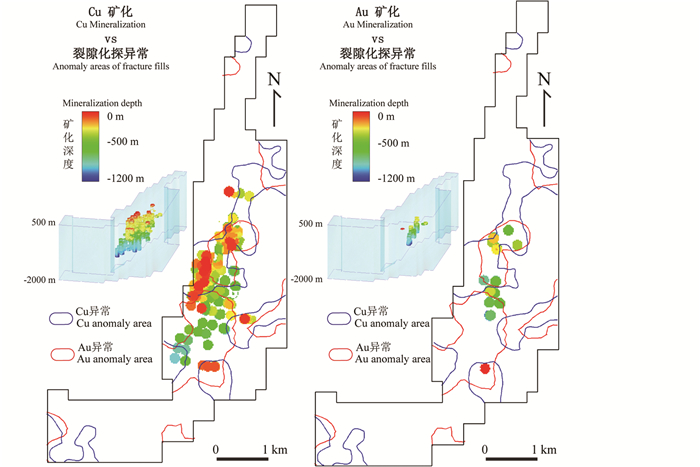
此外,Li et al. (2017)将二维裂隙化探数据与三维矿化信息进行耦合分析,通过建立化探数据与深部矿化之间的空间联系,指示深部找矿靶区位置及深度(图 9)。未来,挖掘二维数据在深度方向的指示能力也应成为获取三维预测要素的重要途径之一。
|
图 9 矿化空间三维结构与裂隙化探数据协同分析(据Li et al., 2017) Fig. 9 Geochemical data of fracture fills and deep concealed mineralization (after Li et al., 2017) |
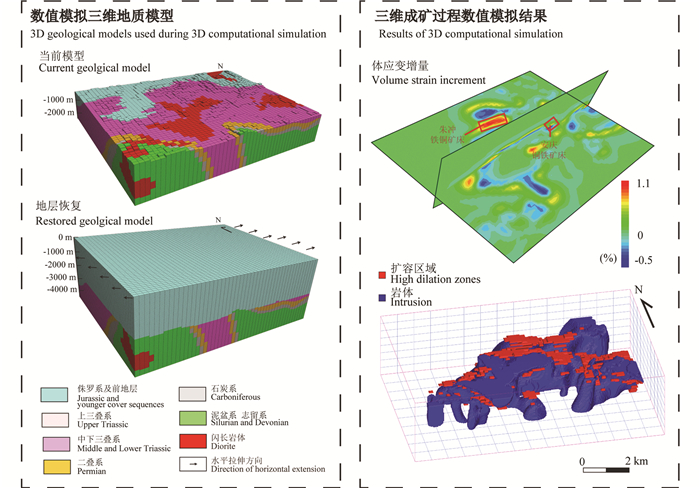
数值模拟方法作为一种新的方法技术手段,已开始逐步应用于成矿过程和机制的研究,从定量化的角度进一步深化对成矿作用相关理论的理解,同时也可为深部矿产资源的找矿预测提供理论指导和找矿方向(Weis et al., 2012; 贾蔡等, 2018; Li et al., 2019)。目前,已有部分国内外学者开展了相关领域的研究探索,例如对矿床形变、流体流动、热传导的耦合模拟,明确矿床空间定位的控制因素(Liu et al., 2011, 2012, 2014, 贾蔡等, 2014, 2018)。随着数值模拟算法和计算能力的提高,三维数值模拟方法已能够在真实的三维地质模型和边界条件的约束下开展计算研究(赵义来和刘亮明, 2011; 孙涛等, 2011; Li et al., 2016, 2019),模拟和预测成矿有利空间或位置,相关成果可为深部找矿预测提供新的三维预测信息(图 10)。如Li et al. (2019)将三维数值模拟方法与三维成矿预测方法进行结合,结果显示数值模拟方法能够有效提高成矿预测结果的预测能力,可为深部矿产资源的找矿预测提供新的有效的预测信息。目前正在实施的国家重点研发计划项目“深地资源勘查”专项中也有大量课题正在开展相关研究。预期在未来的几年,该领域将成为国内外深部矿产资源找矿预测的热点研究方向,也将产出大量研究成果。
|
图 10 月山矿田三维成矿过程数值模拟(据Li et al., 2019) Fig. 10 Three-dimensional numerical simulation of mineralization process of the Yueshan ore field (after Li et al., 2019) |
大数据目前正在引发地球科学领域一场深刻的革命(张旗和周永章, 2018)。随着大数据技术的不断进步,大数据思维在现代成矿预测中的应用越发广泛。目前,机器学习、深度学习的算法已逐步被应用于成矿预测领域,如周永章等(2017)认为以地质-矿床大数据平台为依托,利用大数据挖掘技术与高性能计算能力,能够建立智能地质-矿床模型,为成矿预测提供理论支持和帮助;吴永亮等(2017)利用大数据发现方法实现了地质找矿专题数据的自动采集,利用机器学习方法对地质专题数据进行深层次的挖掘和提取,研究了基于大数据智能的找矿模型预测方法;Zuo (2017)及Zuo and Xiong (2018)基于机器学习方法开展了地球化学异常的识别,研究显示机器学习方法是多元地球化学异常识别的有效工具;Sun et al. (2019)利用机器学习方法开展了成矿预测研究,研究显示机器学习方法可以很好地应用于成矿预测研究,具有良好的研究和应用潜力。
上述研究主要针对理论方法和二维地学数据开展研究和应用。三维地学数据具有海量、多元、多维的特征,理论上更适应于大数据及机器学习方法的应用,其对于三维成矿预测过程中预测指标的确定、预测模型的定量化研究、数据融合及靶区预测等均具有十分重要的意义(周永章等, 2017, 2018)。因此,大数据及机器学习方法显而易见将成为三维成矿预测领域的重要发展趋势。
4 结论综上所述,三维成矿预测理论方法经多年发展,其理论和实践已逐渐趋向成熟,以显式三维建模向隐式三维建模发展、三维成矿预测方法体系建立、三维成矿定量预测软件系统成功研发等为标志,表明成矿预测已经由二维进入三维发展阶段。面对深部矿产资源预测对于数据充分挖掘的需求和挑战,隐式三维地质建模技术、二维数据的有效三维推演、数值模拟方法以及大数据、机器学习等方法技术的进步将合力推动三维成矿预测方法和应用得到进一步的发展,为深部矿产资源的预测勘探提供更为有效、可靠的依据。
谨以此文敬贺恩师岳书仓教授八十八华诞!在此向恩师汇报工作成果,衷心感谢岳老师对我从事成矿预测方向研究的谆谆教诲与大力支持!
Agterberg FP. 1970. Multivariate prediction equations in geology. Journal of the International Association for Mathematical Geology, 2(3): 319-324 DOI:10.1007/BF02312480 |
Agterberg FP, Bonham-Carter GF, Cheng Q and Wright DF. 1993. Weights of evidence modeling and weighted logistic regression for mineral potential mapping. In: Davis JC and Herzfeld UC (eds.). Computers in Geology-25 years of Progress. New York: Oxford University Press, 13-32
|
Calcagno P, Chilès JP, Courrioux G and Guillen A. 2008. Geological modelling from field data and geological knowledge:Part Ⅰ. Modelling method coupling 3D potential-field interpolation and geological rules. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 171(1-4): 147-157 |
Cao XZ, Zhang WS and Sun HS. 2009. Progress in the study of deep exploration in China. Geological Science and Technology Information, 28(2): 104-109 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Carranza EJM. 2009. Geochemical Anomaly and Mineral Prospectivity Mapping in GIS. Handbook of Exploration and Environmental Geochemistry, Vol.11. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1-368
|
Chen JP, Lü P, Wu W, Zhao J and Hu Q. 2007. A 3D method for predicting blind orebodies, based on a 3D visualization model and its application. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(5): 54-62 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1016/S1872-5791(07)60035-9 |
Chen JP, Chen Y and Wang QM. 2008. Study on synthetic informational mineral resource prediction using GIS:A case study in Chifeng region, Inner Mongolia, China. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(4): 18-26 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60035-4 |
Chen JP, Yu M, Yu PP, Shang BC, Zheng X and Wang LM. 2014. Method and practice of 3D geological modeling at key metallogenic belt with large and medium scale. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(6): 1187-1195 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Cheng QM. 2006. Singularity-generalized self-similarity-fractal spectrum (3S) models. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 31(3): 337-348 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ding WX, Yuan F, Li XH, Sun WA, Liu GX and Yang D. 2018. Deep geological structure analysis and metallogenic prediction of Zhonggu ore field in the south section of Ningwu Basin based on gravity and magnetic joint inversion. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(11): 2301-2317 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ding WX. 2019. Combined gravity and magnetic inversion and 3D geological modeling research of Fanchang Basin based on multi-source geoscience constraint information. Master Degree Thesis. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 1-91 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Fallara F, Legault M and Rabeau O. 2006. 3-D integrated geological modeling in the Abitibi Subprovince (Québec, Canada):Techniques and applications. Exploration and Mining Geology, 15(1-2): 27-43 DOI:10.2113/gsemg.15.1-2.27 |
Fan J, Guo YY and Dong SW. 2018. Analysis on DREAM, deep resources exploration and mining:A special project in the framework of national key R & D program of China. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 8(3): 1-6 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Fu GM. 2017. Lithologic identification and streroscopic geological mapping based on three-dimensional inversion of gravity and magnetic field: A case study of Tongling ore concentration area. Master Degree Thesis. Nanchang: East China University of Technology, 1-51 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Guo D, Yan JY, Lü QT, Chen XB and Chen YJ. 2014. 3D density mapping constrained by geological information:Model study and application. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(4): 763-776 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu XY, Yuan F, Li XH, Jowitt SM, Jia C, Zhang MM and Zhou TF. 2018. 3D characteristic analysis-based targeting of concealed Kiruna-type Fe oxide-apatite mineralization within the Yangzhuang deposit of the Zhonggu orefield, southern Ningwu volcanic basin, Middle-Lower Yangtze River metallogenic Belt, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 92: 240-256 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.11.019 |
Jessell M. 2001. Three-dimensional geological modelling of potential-field data. Computers & Geosciences, 27(4): 455-465 |
Jia C, Yuan F, Zhang MM, Li XH, Zhou TF, Shao W, Zheng TK and Gao DM. 2014. Numerical simulation of the process of deposit formation in Baixiangshan iron deposit, Ningwu Basin. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(4): 1031-1040 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Jia C, Yuan F, Li XH, Hu XY, Liao BS, Sun WA, Zhang MM and Sheng L. 2018. Metallogenic dynamics simulation based on multi-source data constraint:A case study of the typical deposit in Zhonggu ore field in Ningwu Basin. Chinese Journal of Geology, 53(4): 1327-1346 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li XH, Yuan F, Zhang MM, Jia C, Zhou TF, Zhang SH, Zheng TK, Gao DM, Hong DL and Liu XM. 2014. 3D localization and quantitative prospectivity mapping using artificial neural networks:A case study of the Baixiangshan mining area, Ningwu Basin. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(4): 644-657 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li XH. 2015.3D prospectivity modeling for concealed orebody and system development. Ph. D. Dissertation. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 1-167 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Li XH, Yuan F, Zhang MM, Jia C, Jowitt SM, Ord A, Zheng TK, Hu XY and Li Y. 2015. Three-dimensional mineral prospectivity modeling for targeting of concealed mineralization within the Zhonggu iron orefield, Ningwu Basin, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 71: 633-654 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.06.001 |
Li XH, Yuan F, Jowitt SM, Zhou KF, Wang JL, Zhou TF, Hu XY, Zhou J and Li Y. 2017. Singularity mapping of fracture fills and its relationship to deep concealed orebodies:A case study of the Shaxi porphyry Cu-Au deposit, China. Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 17(3): 252-260 DOI:10.1144/geochem2016-444 |
Li XH, Yuan F, Ma L, Tang M, Zhang MM, Zhou TF, Jia C and Hu XY. 2017. Development of 3D mineral prospecitivity modelling system and case study. Chinese Journal of Geology, 52(3): 755-770 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li XH, Yuan F, Zhang MM, Jowitt SM, Ord A, Zhou TF and Dai WQ. 2019. 3D computational simulation-based mineral prospectivity modeling for exploration for concealed Fe-Cu skarn-type mineralization within the Yueshan orefield, Anqing district, Anhui Province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 105: 1-17 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.12.003 |
Li YW, Zhao JM and Li CY. 2007. Potential Mineral Resources Evaluation Method Based on GMS, DSS and GIS. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1-1000 (in Chinese)
|
Li ZH, Liu M and Gerya T. 2016. Lithosphere delamination in continental collisional orogens:A systematic numerical study. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 121(7): 5186-5211 DOI:10.1002/2016JB013106 |
Liu LM, Wan CL, Zhao CB and Zhao YL. 2011. Geodynamic constraints on orebody localization in the Anqing orefield, China:Computational modeling and facilitating predictive exploration of deep deposits. Ore Geology Reviews, 43(1): 249-263 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.09.005 |
Liu LM, Zhao YL and Sun T. 2012. 3D computational shape-and cooling process-modeling of magmatic intrusion and its implication for genesis and exploration of intrusion-related ore deposits:An example from the Yueshan intrusion in Anqing, China. Tectonophysics, 526-529: 110-123 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2011.09.006 |
Liu LM, Sun T and Zhou RC. 2014. Epigenetic genesis and magmatic intrusion's control on the Dongguashan stratabound Cu-Au deposit, Tongling, China:Evidence from field geology and numerical modeling. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 144: 97-114 DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.03.008 |
Liu ZY and Xiao KY. 2013. On 3D geological modeling and resources estimation for Zhangcunping phosphate deposit in Hubei. Journal of Geology, 37(4): 616-620 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Lü P. 2007. Cube predicting model based 3D predicting methods of blind orebody and software development. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-161 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Lü QT, Qi G and Yan JY. 2012. 3D geologic model of Shizishan ore field constrained by gravity and magnetic interactive modeling:A case history. Geophysics, 78(1): 25-35 |
Mao XC. 2006. Research on 3D digital deposit and stereo quantitative prediction of concealed ore body. Ph. D. Dissertation. Changsha: Central South University, 1-225 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Mao XC, Zou YH, Chen J, Lai JQ and Peng SL. 2011. Three-Dimensional Visual Prediction of Concealed Orebodies. Changsha: Central South University Press, 1-170 (in Chinese)
|
Mao XC, Zhang MM, Deng H, Zou YH and Chen J. 2016. Three-dimensional visualization prediction method for concealed ore bodies in deep mining areas. Journal of Geology, 40(3): 363-371 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Nielsen SHH, Cunningham F, Hay R, Partington G and Stokes M. 2015. 3D prospectivity modelling of orogenic gold in the Marymia Inlier, Western Australia. Ore Geology Reviews, 71: 578-591 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.02.001 |
Payne CE, Cunningham F, Peters KJ, Nielsen S, Puccioni E, Wildman C and Partington GA. 2015. From 2D to 3D:Prospectivity modelling in the Taupo volcanic zone, New Zealand. Ore Geology Reviews, 71: 558-577 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.11.013 |
Qi G, Lü QT, Yan JY, Wu MA and Liu Y. 2012. Geologic constrained 3D gravity and magnetic modeling of Nihe deposit:A case study. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(12): 4194-4206 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Salama W, Anand RR and Verrall M. 2016. Mineral exploration and basement mapping in areas of deep transported cover using indicator heavy minerals and paleoredox fronts, Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Ore Geology Review, 72: 485-509 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.014 |
Sprague K, de Kemp E, Wong W, McGaughey J, Perron G and Barrie T. 2006. Spatial targeting using queries in a 3-D GIS environment with application to mineral exploration. Computers & Geosciences, 32(3): 396-418 |
Sun L, Xiao KY, Tang JX, Zou W, Li N and Sun Y. 2011. 3-D geologic modeling of the Jiama Cu deposit based on Minexplorer System. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 38(3): 291-297 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun T, Liu LM, Zhao YL and Zou C. 2011. Study on dynamic modeling of complex geo-system based on GOCAD. Mineral Resources and Geology, 25(2): 163-167 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun T, Chen F, Zhong LX, Liu WM and Wang Y. 2019. GIS-based mineral prospectivity mapping using machine learning methods:A case study from Tongling ore district, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 109: 26-49 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.04.003 |
Wang GW, Li R, Carranza EJM, Zhang S, Yan CH, Yan CH, Zhu YY, Qu JN, Hong DM, Song YW, Han JW, Ma ZB, Zhang H and Fan Y. 2015. 3D geological modeling for prediction of subsurface Mo targets in the Luanchuan district, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 71: 592-610 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.03.002 |
Wang K, Xiao KY, Li SM and Gan X. 2015. Three-dimensional geological modeling and reserve estimation based on Minexplorer software in the Limei Pb-Zn Deposit, northwestern Hunan. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(7): 1375-1385 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang SC, Chen YL and Xia LX. 2000. Theory and Method of Comprehensive Information Mineral Prediction. Beijing: Science Press, 1-343 (in Chinese)
|
Weis P, Driesner T and Heinrich CA. 2012. Porphyry-copper ore shells form at stable pressure-temperature fronts within dynamic fluid plumes. Science, 338: 1613-1616 DOI:10.1126/science.1225009 |
Wu YL, Jia ZJ, Chen JP and Zhu YQ. 2017. Construction and prediction of prospecting model based on big data intelligence. China Mining Magazine, 26(9): 79-84 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xiao KY. 1994. The new development of minerogenetic regulation and prediction:The comprehensive information methods. Advance in Earth Sciences, 9(2): 18-23 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xiao KY, Ding JH and Liu R. 2006. The discussion of three-part form of non-fuel mineral resource assessment. Geological Review, 52(6): 793-798 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xiao KY, Chen XG, Li N, Zou W and Sun L. 2010. Geology and mineral resources exploration and evaluation of 3D visualization technology and Minexplorer software development. Mineral Deposits, 29(Suppl.): 758-760 (in Chinese) |
Xiao KY, Li N, Sun L, Zou W and Li Y. 2012. Large scale 3D mineral prediction methods and channels based on 3D information technology. Journal of Geology, 36(3): 229-236 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xiao KY, Sun L, Yin JN, Ding JH, Niu CY, Chen JP and Yang YH. 2014. The prediction and assessment of important mineral resources in China. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 35(5): 543-551 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xiao KY, Li N, Porwal A, Holden EJ, Bagas L and Lu YJ. 2015. Research on GIS-based 3D prospectivity mapping and a case study of Jiama copper-polymetallic deposit in Tibet, China. In: Raju NJ (ed.). Geostatistical and Geospatial Approaches for the Characterization of Natural Resources in the Environment: Challenges, Processes and Strategies. Cham: Springer, 735-740
|
Yan JY, Lü QT, Chen XB, Qi G, Liu Y, Guo D and Chen YJ. 2014. 3D lithologic mapping test based on 3D inversion of gravity and magnetic data:A case study in Lu-Zong ore concentration district, Anhui Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(4): 1041-1053 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang MG, Yu ZZ, Tang WX and Xu MG. 2018. A strategy for deep prospecting. Shanghai Land & Resources, 39(4): 65-74 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yuan F, Li XH, Zhang MM, Jowitt SM, Jia C, Zheng TK and Zhou TF. 2014. Three-dimensional weights of evidence-based prospectivity modeling:A case study of the Baixiangshan mining area, Ningwu Basin, Middle and Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 145: 82-97 DOI:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.05.012 |
Yuan F, Li XH, Zhang MM, Zhou TF, Gao DM, Hong DL, Liu XM, Wang QN and Zhu JB. 2014. Three dimension prospectivity modelling based on integrated geoinformation for prediction of buried orebodies. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(4): 630-643 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yuan F, Li XH, Zhang MM, Jia C and Hu XY. 2018. Research progress of 3D prospectivity modeling. Gansu Geology, 27(1): 32-36 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai YS, Deng J, Wang JP, Peng RM, Liu JJ and Yang LQ. 2004. Researches on deep ore prospecting. Mineral Deposits, 23(2): 142-149 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang MM, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Li XH, Li XY and Jia C. 2011. Reserves estimation of porphyry iron deposit in the Middle-Lower Reaches of Yangtze River area, China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(7): 1215-1222 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang MM, Zhou TF, Yuan F and Li XH. 2014. Three-dimensional morphological analysis method for mineralization related intrusion and prospecting indicators of Nihe iron deposit in Luzong Basin. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(4): 574-583 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang Q and Zhou YZ. 2018. Big data helps geology develop rapidly. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(11): 3167-3172 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang TT. 2010. Three-dimension modeling and prognosis for Caixia Mountain lead-zinc deposit in Xinjiang. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-48 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zhao PD, Hu WL and Li ZJ. 1994. Statistical Prediction of Mineral Deposit. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-272 (in Chinese)
|
Zhao PD, Chi SD and Chen YQ. 1996. A thorough investigation of geo-anomaly:A basis of metallogenic prognosis. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2(4): 361-373 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao PD. 2002. "Three-Component" quantitative resource prediction and assessments:Theory and practice of digital mineral prospecting. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 27(5): 482-489 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao PD, Zhang ST and Chen JP. 2004. Discussion on prediction and appraisement of replaceable resources of crisis mine. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 31(2): 111-117 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao PD. 2007. Quantitative mineral prediction and deep mineral exploration. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(5): 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao YL and Liu LM. 2011. 3D-numerical modeling of coupled geodynamic processes and mineralization at the contact zones of complex plutons:Example from the Anqing Deposit, Anhui Province, China. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 35(1): 128-136 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhou YZ, Li PX, Wang SG, Xiao F, Li JZ and Gao L. 2017. Research progress on big data and intelligent modelling of mineral deposits. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 36(2): 327-331, 344 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhou YZ, Chen S, Zhang Q, Xiao F, Wang SG, Liu YP and Jiao ST. 2018. Advances and prospects of big data and mathematical geoscience. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(2): 255-263 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zuo RG. 2017. Machine learning of mineralization-related geochemical anomalies:A review of potential methods. Natural Resources Research, 26(4): 457-464 DOI:10.1007/s11053-017-9345-4 |
Zuo RG and Xiong YH. 2018. Big data analytics of identifying geochemical anomalies supported by machine learning methods. Natural Resources Research, 27(1): 5-13 DOI:10.1007/s11053-017-9357-0 |
曹新志, 张旺生, 孙华山. 2009. 我国深部找矿研究进展综述. 地质科技情报, 28(2): 104-109. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2009.02.019 |
陈建平, 吕鹏, 吴文, 赵洁, 胡青. 2007. 基于三维可视化技术的隐伏矿体预测. 地学前缘, 14(5): 54-62. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.05.006 |
陈建平, 陈勇, 王全明. 2008. 基于GIS的多元信息成矿预测研究——以赤峰地区为例. 地学前缘, 15(4): 18-26. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.04.003 |
陈建平, 于淼, 于萍萍, 尚北川, 郑啸, 王丽梅. 2014. 重点成矿带大中比例尺三维地质建模方法与实践. 地质学报, 88(6): 1187-1195. |
成秋明. 2006. 非线性成矿预测理论:多重分形奇异性-广义自相似性-分形谱系模型与方法. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 31(3): 337-348. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2006.03.009 |
丁文祥, 袁峰, 李晓晖, 孙维安, 刘光贤, 杨迪. 2018. 基于重磁联合反演的宁芜盆地钟姑矿田深部地质结构解析及成矿预测. 地质学报, 92(11): 2301-2317. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.11.007 |
丁文祥. 2019.基于多源地学信息约束的繁昌盆地重磁联合反演及三维地质建模研究.硕士学位论文.合肥: 合肥工业大学, 1-91
|
樊俊, 郭源阳, 董树文. 2018. DREAM——国家重点研发计划"深地资源勘查开采"重点专项解析. 有色金属工程, 8(3): 1-6. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2018.03.001 |
付光明. 2017.基于重磁三维反演的岩性识别与立体填图.硕士学位论文.南昌: 东华理工大学, 1-51 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10405-1017836659.htm
|
郭冬, 严加永, 吕庆田, 陈向斌, 陈应军. 2014. 地质信息约束下的三维密度填图技术研究及应用. 地质学报, 88(4): 763-776. |
贾蔡, 袁峰, 张明明, 李晓晖, 周涛发, 邵尉, 郑通科, 高道明. 2014. 宁芜盆地白象山铁矿床成矿作用过程数值模拟. 岩石学报, 30(4): 1031-1040. |
贾蔡, 袁峰, 李晓晖, 胡训宇, 廖宝胜, 孙维安. 2018. 基于多源数据约束的成矿动力学模拟——以宁芜盆地钟姑矿田典型矿床为例. 地质科学, 53(4): 1327-1346. |
李晓晖, 袁峰, 张明明, 贾蔡, 周涛发, 张淑虹, 郑通科, 高道明, 洪东良, 刘晓明. 2014. 宁芜盆地白象山矿区人工神经网络三维成矿定位预测研究. 地质学报, 88(4): 644-657. |
李晓晖. 2015.隐伏矿体三维成矿定量预测及系统开发.博士学位论文.合肥: 合肥工业大学, 1-167 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10359-1015723283.htm
|
李晓晖, 袁峰, 马良, 唐敏慧, 张明明, 周涛发, 贾蔡, 胡训宇. 2017. 三维成矿定量预测系统设计与应用实例研究. 地质科学, 52(3): 755-770. |
李裕伟, 赵精满, 李晨阳. 2007. 基于GMS、DSS和GIS的潜在矿产资源评价方法. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
刘智宇, 肖克炎. 2013. 湖北樟村坪磷矿矿床三维地质建模及资源量估算. 地质学刊, 37(4): 616-620. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2013.04.616 |
吕鹏. 2007.基于立方体预测模型的隐伏矿体三维预测和系统开发.博士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学, 1-161 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-2007066897.htm
|
毛先成. 2006.三维数字矿床与隐伏矿体立体定量预测研究.博士学位论文.长沙: 中南大学, 1-225 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10533-2006173423.htm
|
毛先成, 邹艳红, 陈进, 赖健清, 彭省临. 2011. 隐伏矿体三维可视化预测. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 1-170.
|
毛先成, 张苗苗, 邓浩, 邹艳红, 陈进. 2016. 矿区深部隐伏矿体三维可视化预测方法. 地质学刊, 40(3): 363-371. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2016.03.363 |
祁光, 吕庆田, 严加永, 吴明安, 刘彦. 2012. 先验地质信息约束下的三维重磁反演建模研究——以安徽泥河铁矿为例. 地球物理学报, 55(12): 4194-4206. DOI:10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.031 |
孙莉, 肖克炎, 唐菊兴, 邹伟, 李楠, 孙艳. 2011. 基于minexplorer探矿者软件的甲玛铜矿三维地质体建模. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 38(3): 291-297. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2011.03.008 |
孙涛, 刘亮明, 赵义来, 邹亮. 2011. 基于GOCAD平台的复杂地质体系的动力学建模研究. 矿产与地质, 25(2): 163-167. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2011.02.015 |
王琨, 肖克炎, 李胜苗, 甘曦. 2015. 基于探矿者软件(minexplorer)的三维地质建模及储量估算——以湘西北李梅铅锌矿为例. 地质通报, 34(7): 1375-1385. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.07.017 |
王世称, 陈永良, 夏立显. 2000. 综合信息矿产预测理论与方法. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-343.
|
吴永亮, 贾志杰, 陈建平, 朱月琴. 2017. 基于大数据智能的找矿模型构建与预测. 中国矿业, 26(9): 79-84. |
肖克炎. 1994. 应用综合信息法研究成矿规律及成矿预测的新进展. 地球科学进展, 9(2): 18-23. |
肖克炎, 丁建华, 刘锐. 2006. 美国"三步式"固体矿产资源潜力评价方法评述. 地质论评, 52(6): 793-798. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.06.010 |
肖克炎, 陈学工, 李楠, 邹伟, 孙莉. 2010. 地质矿产勘探评价三维可视化技术及探矿者软件开发. 矿床地质, 29(增): 758-760. |
肖克炎, 李楠, 孙莉, 邹伟, 李莹. 2012. 基于三维信息技术大比例尺三维立体矿产预测方法及途径. 地质学刊, 36(3): 229-236. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2012.03.229 |
肖克炎, 孙莉, 阴江宁, 丁建华, 牛翠祎, 陈建平, 杨毅恒. 2014. 全国重要矿产预测评价. 地球学报, 35(5): 543-551. |
严加永, 吕庆田, 陈向斌, 祁光, 刘彦, 郭冬, 陈应军. 2014. 基于重磁反演的三维岩性填图试验——以安徽庐枞矿集区为例. 岩石学报, 30(4): 1041-1053. |
杨明桂, 余忠珍, 唐维新, 徐梅桂. 2018. 论"深地"找矿攻略. 上海国土资源, 39(4): 65-74. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2018.04.015 |
袁峰, 李晓晖, 张明明, 周涛发, 高道明, 洪东良, 刘晓明, 汪启年, 朱将波. 2014. 隐伏矿体三维综合信息成矿预测方法. 地质学报, 88(4): 630-643. |
袁峰, 李晓晖, 张明明, 贾蔡, 胡训宇. 2018. 三维成矿预测研究进展. 甘肃地质, 27(1): 32-36. |
翟裕生, 邓军, 王建平, 彭润民, 刘家军, 杨立强. 2004. 深部找矿研究问题. 矿床地质, 23(2): 142-149. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2004.02.003 |
张明明, 周涛发, 袁峰, 李晓晖, 李修钰, 贾蔡. 2011. 长江中下游地区玢岩型铁矿床资源储量估算研究. 地质学报, 85(7): 1215-1222. |
张明明, 周涛发, 袁峰, 李晓晖. 2014. 庐枞盆地泥河铁矿床成矿岩体三维形态学分析及找矿指标研究. 地质学报, 88(4): 574-583. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2014.04.023 |
张旗, 周永章. 2018. 大数据助地质腾飞:岩石学报2018第11期大数据专题"序. 岩石学报, 34(11): 3167-3172. |
张婷婷. 2010.新疆彩霞山铅锌矿三维建模与立体预测.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学, 1-48 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-2010085246.htm
|
赵鹏大, 胡旺亮, 李紫金. 1994. 矿床统计预测. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-272.
|
赵鹏大, 池顺都, 陈永清. 1996. 查明地质异常:成矿预测的基础. 高校地质学报, 2(4): 361-373. |
赵鹏大. 2002. "三联式"资源定量预测与评价——数字找矿理论与实践探讨. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 27(5): 482-489. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2002.05.002 |
赵鹏大, 张寿庭, 陈建平. 2004. 危机矿山可接替资源预测评价若干问题探讨. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 31(2): 111-117. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2004.02.001 |
赵鹏大. 2007. 成矿定量预测与深部找矿. 地学前缘, 14(5): 1-10. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.05.001 |
赵义来, 刘亮明. 2011. 复杂形态岩体接触带成矿耦合动力学三维数值模拟:以安庆铜矿为例. 大地构造与成矿学, 35(1): 128-136. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2011.01.013 |
周永章, 黎培兴, 王树功, 肖凡, 李景哲, 高乐. 2017. 矿床大数据及智能矿床模型研究背景与进展. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 36(2): 327-331, 344. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2017.02.016 |
周永章, 陈铄, 张旗, 肖凡, 王树功, 刘艳鹏, 焦守涛. 2018. 大数据与数学地球科学研究进展——大数据与数学地球科学专题代序. 岩石学报, 34(2): 255-263. |
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35

