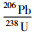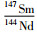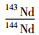2. 中国科学院地球科学研究院, 北京 100029;
3. 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所, 中国科学院矿物学与成矿学重点实验室, 广州 510640;
4. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
2. Institutions of Earth Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029, China;
3. Key Laboratory of Mineral and Metallogeny, Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510640, China;
4. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
吕梁(滹沱)运动后,华北克拉通在太古宙-古元古代变质结晶基底之上,沿南、北两大裂陷槽发育了巨厚的裂谷系沉积(Zhai et al., 2015)。在华北北部燕山地区,主要由长城系、蓟县系、青白口系组成;南部则主要由熊耳群火山岩系及其上的中-新元古代火山-沉积岩系组成,如,分布于渑池-确山地层小区的汝阳群、洛峪群,嵩箕地层小区的五佛山群以及熊耳山-小秦岭地层小区的官道口群、栾川群等(蒋干清, 1994; 王跃峰, 2000; 高林志等, 2002; 河南省地质矿产厅, 2008; 苏文博等, 2012; 赵太平等, 2015)。基于早先工作,人们认为它们在层位上与长城系-蓟县系-青白口系大体相当(王曰伦, 1980; 关保德等, 1988; 河南省地质矿产局, 1989; 白谨等, 1996; 陈晋镳等, 1999; 高林志等, 2002; 苏文博, 2016)。
在豫陕交界的洛南-卢氏地区,官道口群不整合覆盖于熊耳群为代表的火山岩之上,是一套较稳定的滨海-浅海相沉积序列,以陆缘碎屑岩-碳酸盐岩为主。其中,该群下部原高山河组厚度可达3707m(河南省地质矿产局, 1989),是熊耳群之上最古老的沉积盖层和中元古代早期沉积作用记录最丰富的层位之一。李钦仲等(1985)根据其岩性组合及所含的叠层石特征,认为它可能与长城系相当。考虑到原高山河组石英砂岩和上覆官道口群碳酸盐岩地层代表两套不同的岩石组合、两种不同的沉积环境,并且二者之间有沉积间断,不少学者和区调资料已建议将其单独命名为高山河群(李文厚, 1991; 河南省地质矿产局, 1989; 尹崇玉和高林志, 1997; 赵太平等, 2015)。
由于早期缺少高分辨率的同位素年代地层学资料,华北南部晚前寒武纪地层的划分以及如何与蓟县剖面进行精确对比一直存在很大争议。苏文博等(2012)通过对河南汝州阳坡剖面洛峪口组顶部层凝灰岩进行锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年代学研究,首次获得1611±8Ma的高精度年龄,限定了该层位的沉积上限,表明洛峪群和下伏汝阳群以及相当层位均应归属中元古界长城系。值得注意的是,李承东等(2017)最近在相同地区的洛峪口组也开展了凝灰岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年研究,虽然其~1630Ma的年龄结果与前者有所差异但也证实上述归属是完全合理的。另一方面,近些年在汝阳群、五佛山群底部陆续有年轻碎屑锆石的报道,其年龄值广布于1655~1820Ma之间(胡国辉等, 2012a, b; Hu et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2016; Meng et al., 2018)。笔者早先曾对河南官道口地区的高山河群做过研究,但由于当时采样有限、层位过高等原因,且最年轻碎屑锆石的年龄值为~1850Ma,未能有效约束其起始年龄界限(Zhu et al., 2011),也未很好识别其物源区的物质组成。因此,本次研究在区域上按层位由下至上依次选择高山河群沉积岩进行碎屑锆石年代学和地球化学分析,探讨其沉积时限和物源特征,为华北南部“长城系”的划分和厘定提供进一步的科学依据。
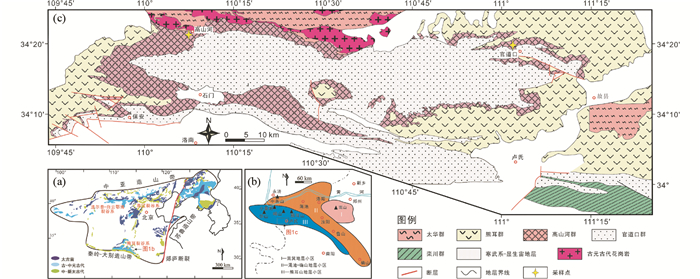
1 区域地质背景华北克拉通南部广泛分布太古宙-古元古代早期结晶基底和较为完整的中、新元古代盖层,岩石序列发育完整,是记录前寒武纪地质的典型地区之一(图 1)。太华杂岩是豫西地区最古老的变质基底,区域变质程度主要为绿帘角闪岩相-角闪岩相(Diwu et al., 2014),主要由太古宙TTG片麻岩、花岗片麻岩、钾质花岗岩、斜长角闪岩以及古元古代具典型表壳岩特征的富铝泥质变质岩、长英质片麻岩、含磁铁矿大理岩、石英岩等(Wan et al., 2006; Diwu et al., 2014; Jia et al., 2016; 张瑞英和孙勇, 2017)。其中,2.8~2.7Ga以及2.6~2.5Ga两期岩浆作用以大规模的TTG岩石组合为特征,代表华北南部中太古代晚期和新太古代晚期两次重要的陆壳生长事件(Liu et al., 2009; 第五春荣等, 2010; Jia et al., 2016)。同时,太华杂岩中还识别出~2.3Ga的英云闪长质片麻岩、斜长角闪岩和钾质花岗片麻岩(Huang et al., 2012; Yu et al., 2013; Diwu et al., 2014; Jia et al., 2019),Hf同位素显示它们主要源自太古宙古老地壳物质的再造,可能与伸展构造体制下陆壳减薄引发的部分熔融有关(Jia et al., 2019)。
|
图 1 华北克拉通前寒武纪地质简图(a, 据Peng et al., 2007)、华北克拉通南缘中-新元古代地层分区图(b, 据赵太平等, 2015)和高山河群分布简图(c, 据陕西省地质矿产局, 1989; 河南省地质矿产局, 1989) Fig. 1 Major Precambrian geological distribution of the NCC (a, after Peng et al., 2007), Meso-Neoproterozoic stratigraphic distribution of the southern NCC (b, after Zhao et al., 2015) and distribution of the Gaoshanhe Group (c, after BGMRS, 1989; BGMRH, 1989) |
熊耳群火山岩系不整合覆盖于太华变质杂岩之上,主要由厚的熔岩流组成,夹少量薄层碎屑沉积岩和火山碎屑岩(赵太平等, 2002)。熊耳群火山岩的喷发时限大致为1.78~1.75Ga(赵太平等, 2001, 2004; Peng et al., 2008; He et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2010; Cui et al., 2011, 2013),与区域内同时代基性岩墙群同属华北克拉通中元古代大岩浆岩省的重要组成部分,形成于非造山环境(Peng et al., 2007, 2008; Peng, 2015; Zhai et al., 2015)。
高山河群主要分布于陕西洛南及河南洛宁、灵宝、卢氏一带,总的趋势是西侧厚、层位较全,东南薄且层位有所缺失(图 1c)。它与下伏熊耳群呈不整合接触,部分地区可见一层复成分底砾岩。主要岩性为中细粒石英砂岩,泥质粉砂岩和泥岩,夹页板岩、白云岩、火山岩和铁矿层,由下自上分为鳖盖子组、二道河组、陈家涧组,(陕西省地质矿产局, 1989)。这三个岩段的岩性组合明显不同,识别标志清楚(图 2)。下部鳖盖子组以出现一层厚约1m左右的紫红色复成分细砾岩为顶界标志,以紫红色-灰白色厚层石英砂岩为主(河南省地质矿产局, 1989),底部可见数十米至几十米厚度不等、层位基本稳定的安山质火山岩夹层(赵太平等, 2015),上、下分别以杂色凝灰岩-泥页岩过渡;中部二道河组以中厚层状紫红或灰色细砂岩、紫红色中-薄层状粉砂岩为主,以出现灰绿色页岩为结束标志;上部陈家涧组以紫红色-肉红色薄-中层细粒石英砂岩为主,中部有较多的灰绿色泥页岩,部分地区顶部发育含铁矿层。

|
图 2 洛南-卢氏地区高山河群地层柱状图(据河南省地质矿产厅, 2008; Wang et al., 2018a) G1L-石英砂岩底部层位;G1M-石英砂岩中部层位;G1U-石英砂岩顶部层位;G2-沉凝灰岩层位 Fig. 2 Schematic stratigraphic section of the Gaoshanhe Group in Luonan-Lushi area (after BGMRH, 2008; Wang et al., 2018a) G1L-Lower sandstone; G1M-Middle sandstone; G1U-Upper sandstone; G2-sedimentary tuff |
高山河群上覆的官道口群和栾川群厚达3000~5500m(河南省地质矿产厅, 2008),是华北南部发育最好的中-新元古界。官道口群为一套碳酸盐岩沉积建造,与高山河群为平行不整合或角度不整合接触。根据岩石地层特征和叠覆关系等,长期以来人们将官道口群底界龙家园组下部(有的称之为下段)与洛峪口组进行对比(武铁山, 1982, 1997; 关保德等, 1988; 河南省地质矿产局, 1989; 王志宏等, 2008),官道口群主体对比于蓟县系(苏文博, 2016)。栾川群主要是一套原岩为含碳碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩和碱性火山岩组成的绿片岩相滨海-浅海相沉积,与官道口群为整合或平行不整合接触关系。基于年代学对比并考虑到岩性特征、叠覆关系、区域分布等,苏文博(2016)将其归属为“青白口系”。
2 锆石年代学和地球化学特征 2.1 分析方法将新鲜岩石样品(约5kg)清除表面浮尘后粉碎至80目,经过淘洗和分选在实体显微镜下手工挑出待测锆石。锆石分选工作在河北省廊坊宇能岩石矿物分选技术服务有限公司完成。锆石定年分析测试之前,在双目显微镜下选择晶形较完好、没有可见矿物包裹体的不同形态和类型的锆石,用环氧树脂制成锆石靶样,磨至露出锆石晶体核部。锆石阴极发光图像的拍摄在武汉上谱分析科技有限责任公司完成,仪器为高真空扫描电子显微镜(JMS-IT100)并配备GATANmINICL系统。锆石U-Pb定年采用LA-ICP-MS方法,测试工作在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成。详细的仪器参数与分析流程见Liu et al. (2007)。测定的U-Pb同位素比值及元素含量采用Gilliter Ver 4.0程序计算得到,U-Pb年龄采用Isoplot程序计算(Ludwig, 2003)。
主量元素分析分别在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所岩矿分析实验室和武汉上谱分析科技有限责任公司完成,运用X射线荧光光谱仪AXIOSmineral完成。分析方法采用标准曲线法,XRF分析精度为2%。微量元素测试分别在中国科学技术大学壳幔物质与环境重点实验室和武汉上谱分析科技有限责任公司完成,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)进行测试,分析精度优于10%。
Nd化学分离和同位素比值测试在中国科学技术大学中科院壳幔物质与环境重点实验室完成。测试仪器为MAT-262热电离质谱计。Nd同位素比值测定采用146Nd/144Nd=0.7219进行标准化,Sm-Nd的全流程实验本底小于50pg,147Sm/144Nd误差(2σ)小于0.5%。详细化学流程和同位素比值测试参见Chen et al.(2000, 2007)。
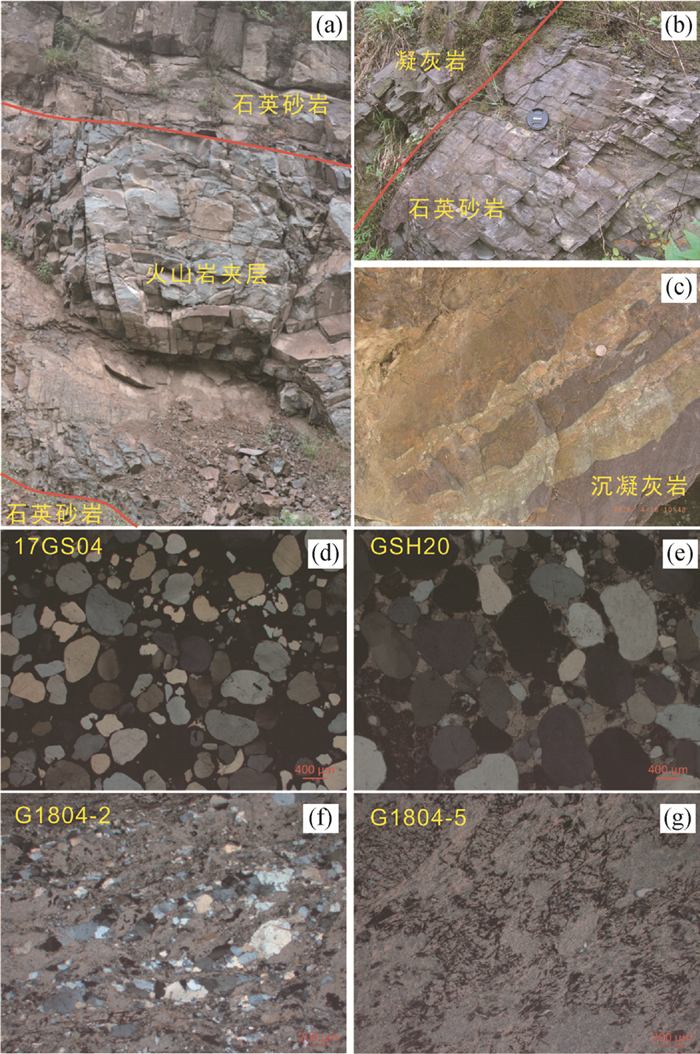
2.2 样品描述和岩相学特征样品主要来自陕西洛南巡检镇、河南卢氏官道口镇等地区(采样点坐标见电子版附表 1),岩石类型包括两类,紫红色或灰白色石英砂岩(G1)以及灰绿-灰紫色沉凝灰岩(G2)(图 3a-c)。选择不同层位上的样品进行锆石年代学研究、岩石地球化学及同位素地球化学分析。进行LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年测试的石英砂岩样品分别采自高山河群底部层位(17GS02、17GS04)和顶部层位(GSH21),沉凝灰岩样品(17GS06、G1804-3、G1804-6)靠近火山岩夹层,其相对层位见图 2。石英砂岩镜下呈变余细粒结构或砂状结构等,石英含量最高可达95%以上,胶结类型以硅质胶结为主,或泥质胶结,磨圆度较高(图 3d, e)。沉凝灰岩呈凝灰质胶结,晶屑主要为石英和长石,含量约占20%~30%,局部含有大量枝状或网脉状暗色矿物集合体,未发现玻璃质(图 3f, g)。
|
|
附表 1 华北克拉通南缘高山河群碎屑沉积岩的锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb同位素数据 Appendix Table 1 LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb isotopic data of clastic sedimentary rocks from the Gaoshanhe Group, southern margin of the NCC |
|
图 3 高山河群碎屑沉积岩野外产状(a-c)及镜下显微照片(d、e,石英砂岩;f、g,沉凝灰岩) Fig. 3 The occurrence (a-c) and micrographic photos (d, e, quartz sandstone; f, g, sedimentary tuff) of the rocks from the Gaoshanhe Group |
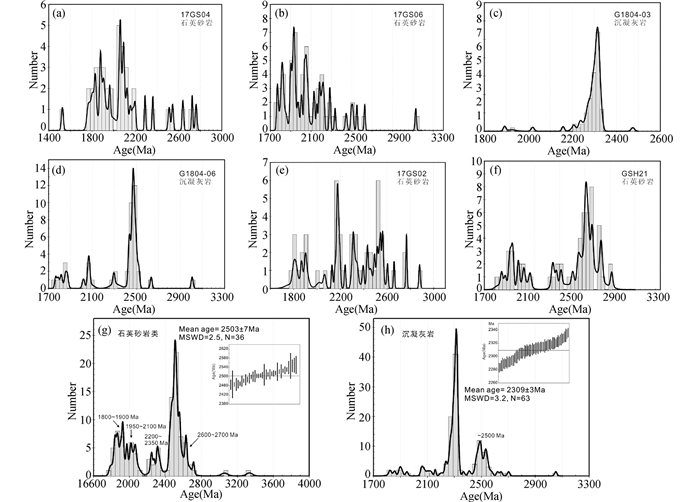
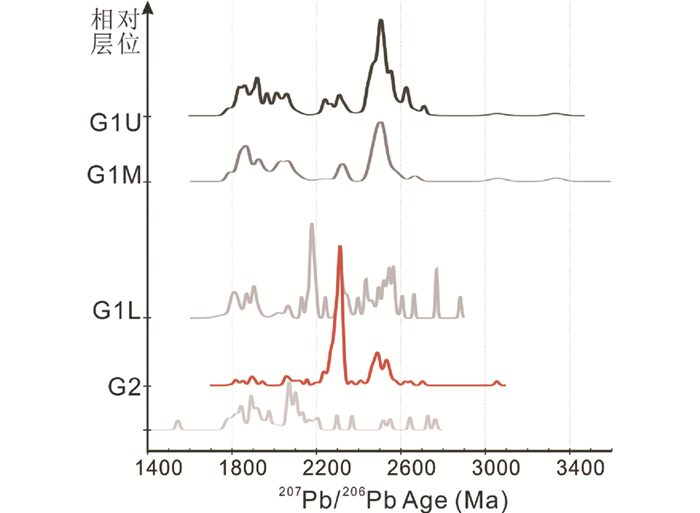
高山河群样品中的锆石数量较多,粒度在50~100μm。半透明,无色到浅棕黄色,粒状或短圆柱状,磨圆度较高。CL图像(图 4)显示锆石内部结构多样,具岩浆环带或环带结构较弱,或CL强度成面状、杂斑状分布。附表 1为6个碎屑沉积岩样品的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄数据。207Pb/206Pb表面年龄值变化范围大致为1800~2800Ma(谐和度(100×206Pb/238U年龄/207Pb/206Pb年龄)=90~115),表明物质来源主要为早元古代-新太古代物质沉积。另有数颗锆石具有3.05~3.13Ga的谐和年龄,暗示源区中存在古太古代物质。值得注意的是,两类样品中锆石年龄峰值明显不同,高山河群底部石英砂岩的锆石年龄图谱峰值不明显,但随层位的上移,太古宙物质对源区的贡献增大(图 5a, e),直至中上-顶部层位的石英砂岩出现峰值为2500~2700Ma(图 5f)。石英砂岩类中碎屑锆石具有显著的~2500Ma的年龄峰值(2503±7Ma,MSWD=2.5,N=36),几个次级峰值分布于1800~1900Ma、1950~2100Ma、2200~2350Ma和2600~2700Ma(图 5g)。另外,石英砂岩中还出现少量1800~1950Ma的锆石(附表 1),它们具有谐和性较差(谐和度>120)、CL图像无清晰岩浆环带的特点,应该与古元古代变质作用有关。位于火山岩夹层顶、底的沉凝灰岩类G2显示源区中古元古代物质由逐渐添加到逐渐减少的趋势(图 5c, d),碎屑锆石年龄图谱形成明显的古元古代~ 2300Ma峰值,63个测试点的加权平均年龄为2309±3Ma(MSWD=3.2),同时存在~2.5Ga的次级峰值(图 5h)。

|
图 4 高山河群碎屑沉积岩中典型碎屑锆石的阴极发光(CL)图像 图中黄色空心圆为锆石年龄测试点,红色比例尺100μm,束斑直径32μm Fig. 4 Cathode-luminescence (CL) images of typical detrital zircons from the Gaoshanhe Group Yellow circles are analytical point. Red measuring scale is 100μm and analyse diameter is 32μm |
|
图 5 高山河群碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄直方图(锆石谐和度90~115) Fig. 5 U-Pb age histograms of concordant zircon 207Pb/206Pb ages (concordant percent ranges from 90~115) |
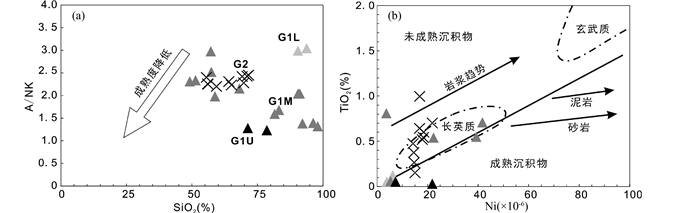
本次研究中G1组石英砂岩层位均在火山岩夹层之上,按层位由下至上标记为G1L,G1M,G1U。结合前人数据(祝禧艳, 2010; 胡国辉等, 2013),它们的SiO2含量为71.34%~93.81%,Fe2O3T+MgO的含量为2.00%~6.84%,大部分样品的MgO、CaO、K2O的含量均较低(表 1)。顶部层位的2个样品SiO2含量明显偏低,GSH20含有较高的Al2O3含量(9.91%)和K2O含量(7.92%),与其中长石大多为钾长石有关;GSH21中具有相对高的MgO(5.37%)、CaO(8.12%)含量,烧失量LOI也偏大(12.16%),则与其含有较多的碳酸盐矿物有关,如方解石或白云石。G1M组的主量元素含量取平均值后,SiO2含量为75.01%,Al2O3含量为10.02%,全碱含量(Na2O+K2O)为4.68%。随着层位升高,高山河群石英砂岩的SiO2含量逐渐降低,成熟度指数Al2O3/(Na2O+K2O)的比值由~3到2.14到1.24~1.28,显示成熟度降低的趋势(图 6a)。
|
|
表 1 华北克拉通南缘高山河群碎屑沉积岩的主量元素(wt%)和微量元素(×10-6)地球化学数据 Table 1 Major (wt%) and trace element (×10-6) data of clastic sedimentary rocks from the Gaoshanhe Group, southern margin of the NCC |
|
图 6 A/NK- SiO2图解(a)和TiO2-Ni图解(b)(据Floyd et al., 1990) G1M数据祝禧艳, 2010; 胡国辉等, 2013.浅灰色三角形-G1L;深灰色三角形-G1M;黑色三角形-G1U;黑色叉形-G2.后图图例及数据来源同此图 Fig. 6 A/NK vs. SiO2 diagram (a) and TiO2 vs. Ni diagram (b) (after Floyd et al., 1990) Data of G1M after Zhu, 2010; Hu et al., 2013. Light gray triangle-G1L; dark gray triangle-G1M; dark triangle-G1U; dark cross-G2. Symbols and data are the same in the below figures |
G2组沉凝灰岩样品的元素含量相对均一,SiO2含量为52.02%~71.64%,具有较高的Al2O3含量(12.65%~22.07%)、K2O(4.97%~9.07%),中等含量的Fe2O3T+MgO(5.20%~11.38%)。除个别样品外,大部分沉凝灰岩中的CaO含量相对较低,在1%以下。较高的LOI(2.58%~8.13%)表明沉凝灰岩中可挥发性组分相对多,可能受到了后期蚀变作用的影响。
在TiO2-Ni图解上(图 6b),G1U和G1L组石英砂岩落入成熟沉积物的区域,表明其源区成熟度较高或离源区的距离较远;大部分G1M石英砂岩和G2组凝灰岩落入长英质范围内,暗示长英质物质对源区的贡献。G1组稀土元素含量中等,∑REE的变化范围为24.7×10-6~292×10-6,显示右倾的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(图 7a),(La/Yb)N比值变化于7.30~37.1。除个别样品外,Ce显示轻微正异常,Eu显示负异常,δCe和δEu值分别为0.90~1.23,0.68~1.09。G2组稀土元素总量明显大于G1,∑REE的变化范围为72.2×10-6~443×10-6,同样显示右倾的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(图 7b),(La/Yb)N比值变化于5.08~61.3,δCe和δEu值分别为1.04~1.14,0.53~0.96,显示正的Ce异常和负的Eu异常。

|
图 7 高山河群石英砂岩(a)和沉凝灰岩(b)球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 7 Chondrite-normalized REE pattern of quartz sandstone (a) and sedimentary tuff (b) from the Gaoshanhe Group (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
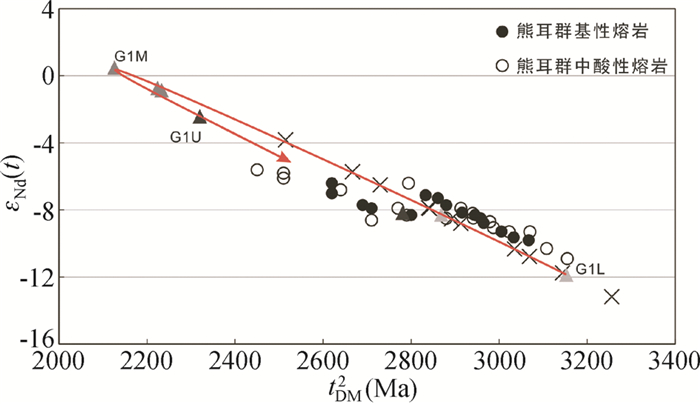
层位由下至上的石英砂岩143Nd/144Nd值分布在0.5114~0.5115(G1L)、0.5117~0.5119(G1M)和0.5112~0.5114(G1U)之间(表 2)。按沉积时限的估算,分别回溯至1700Ma、1650Ma和1600Ma,对应εNd(t)值分别为-11.9~-8.3、-0.8~+0.5和-8.2~-2.4,显示由富集至弱亏损又至富集的演化特征(图 8);二阶段Nd模式年龄tDM2的分布范围分别为2.87~3.17Ga、2.13~2.23Ga和2.32~2.78Ga。
|
|
表 2 华北克拉通南缘高山河群碎屑沉积岩的全岩Nd同位素组成 Table 2 Nd isotopic data of clastic sedimentary rocks from the Gaoshanhe Group, southern margin of the NCC |
|
图 8 高山河群碎屑沉积岩的εNd(t)-tDM2图解 熊耳群火山岩数据赵太平等, 2002; He et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2010, 2019 Fig. 8 εNd(t) vs. tDM2 diagram of sedimentary rocks from the Gaoshanhe Group Data of Xiong'er volcanic rocks from Zhao et al., 2002; He et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2010, 2019 |
沉凝灰岩143Nd/144Nd值分布在0.5109~0.5116之间,回算至1700Ma,εNd(t)值为-13.2~-3.8,对应tDM2为2.51~3.26Ga,表明源区应该主要为太古宙古老地壳物质。
3 讨论 3.1 高山河群碎屑沉积岩的沉积时限1600Ma是目前仍然通用的全球元古宙固结纪(Statherian)和盖层纪(Calymmian)的分界年龄(国际地层委员会),也是国内年代地层划分方案中采用的长城纪与蓟县纪的分界(王鸿祯和李光岑, 1990; 全国地层委员会, 2001, 2002)。由于陕西洛南侵入官道口群龙家园组中下段地层之中的麻坪碱性正长岩其锆石年龄值为1598±9Ma(柳晓艳, 2011; 邓小芹等, 2015),加之笔者最近在豫西龙家园组底部砂岩中获得碎屑锆石的最小年龄峰值为1616±5Ma(MSWD=1.1,N=28)(待发表数据),二者共同限定龙家园组的起始沉积时限为1600~1610Ma,代表华北南缘蓟县系的最底部层位。已有数据表明,渑池-确山地层小区的汝阳群云梦山组和嵩箕地层小区的五佛山群马鞍山组底部砂岩的最年轻碎屑锆石年龄为~1.7Ga(胡国辉等, 2012a; Hu et al., 2014; Meng et al., 2018)。本次研究中,高山河底部最年轻的一组锆石年龄为1760~1770Ma,指示高山河群沉积时代的下限。
区域上,目前报道的熊耳群火山岩时代集中于1.78~1.75Ga(赵太平等, 2004; Peng et al., 2008; Cui et al., 2011, 2013)。考虑到其与熊耳群之间的沉积缺失,以及区域上与云梦山组和五佛山组的地层对比关系,暂将高山河群的沉积时限定位1.70~1.60Ga之间。因此,熊耳群之上、龙家园组之下的高山河群在年代地层划分上应属国内中元古界长城系(1800~1600Ma)上部,或国际古元古界固结系(Statherian System, 1800~1600Ma)上部。
需要指出的是,华北南缘高山河群鳖盖子组及汝阳群云梦山组底部稳定发育的玄武安山质火山岩夹层,具有熊耳群中基性熔岩相似的岩性和地球化学特征,以安山质-玄武质为主,富铁和富钾(河南省地质矿产厅, 1989; 吕国芳等, 1993; 赵太平等, 2015),是厘定该岩组起始沉积时限的关键线索之一。在卢氏苏村镇福地村东、潭头镇井峪沟、秋扒镇三关庙等剖面的野外观察发现,沉凝灰岩出露在紧邻这套火山岩的上、下层位,在野外呈现过渡性产状,二者下伏数米至数十米不等的石英砂岩与熊耳群呈不整合接触。笔者已对该夹层火山岩进行了高精度年代学研究(待发表),同样支持高山河群沉积时代为长城纪。虽然目前尚无法证实火山岩夹层及凝灰岩同属熊耳期火山活动的产物,本次研究中发现这套沉凝灰岩与熊耳群火山岩的岩石地球化学特征和Nd同位素组成类似,至少表明它们之间可能存在成因或岩浆源区上的某种关联。
3.2 沉积物质来源碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、主量-微量元素地球化学特征和Nd同位素组成可以为沉积岩的源区提供重要信息(李献华, 1996; Liu et al., 2014)。高山河群碎屑岩的锆石年龄主要分布于1800~2800Ma之间,表明古元古代-新太古代物质对源区的贡献显著。然而,来自高山河群不同层位碎屑岩的源区组成具有差别,由下至上显示复杂-简单-复杂-简单的演化特征(图 9)。在玄武安山质火山岩夹层层位之下的样品中,大部分锆石207Pb/206Pb年龄分布于1800~2200Ma,同时有~2300Ma、~2500Ma、~2600Ma、~2800Ma的锆石出现,显示源区以古元古代中-晚期物质为主(图 5a),古元古代晚期-新太古代早期物质对源区也有贡献,1800~2300Ma峰值开始加强后(图 5b),至沉凝灰岩层位出现2309±3Ma的单峰值(图 5c),表明靠近火山岩夹层的层位,其源区补给明显受到~2.3Ga岩浆事件的影响;层位上移,古元古代~2300Ma物质减少(图 5d, e),2500~2600Ma碎屑锆石增多并最终形成2503±7Ma的显著峰值(图 5f),表明新太古代物质对源区的贡献逐渐增多并稳定供给;1950~2100Ma和2250~2300Ga次级峰值的存在,表明古元古代中-晚期物质对源区的持续补给但所占比例已逐渐减小。
|
图 9 高山河群相对层位的碎屑锆石年龄图谱变化图(G1M数据来自Zhu et al., 2011) Fig. 9 Variation of 207Pb/206Pb age peaks of detrital zircons from relative layers (data of the G1M from Zhu et al., 2011) |
碎屑沉积岩的物质来源主要有三种:剥蚀的克拉通变质基底,活动陆缘增生盆地中的火山岩-深成岩,古老地壳物质的再循环(Chen et al., 2009)。1.8~1.85Ga和~2.5Ga是华北克拉通前寒武纪两期最重要的构造-岩浆-热事件(翟明国, 2006; 翟明国和彭澎, 2007; Zhai et al., 2010; Zhai and Santosh, 2011, 2013; Wan et al., 2015; Zhai and Zhou, 2015),在遍布华北的变质-岩浆-沉积-成矿作用中均有记录。本次研究中,高山河群的碎屑沉积岩同样记录了这两期地质事件。与此同时,相当比例的斑杂状或无岩浆环带的不谐和锆石(谐和度>120)(附表 1)年龄分布在1.8~1.95Ga,与鄂尔多斯、内蒙古凉城等地的麻粒岩相变质作用的时代一致(Zhao et al., 2006; Santosh et al., 2009; 翟明国, 2009; Wan et al., 2013),也与太华杂岩的高压麻粒岩相变质峰期吻合(Lu et al., 2017),表明它们应该来自华北克拉通变质基底。
沉凝灰岩G2中的锆石显示晶型好、生长环带清晰的岩浆锆石特点,但数量众多并且粒度不均一(图 4),薄片中原始凝灰结构不完整,几乎没有玻屑组分保存(图 3e-f),因此应属于以碎屑物质为主,源于近距离搬运的沉凝灰岩。这些沉凝灰岩具有中等程度的SiO2含量、高铁、高钾(表 1),其中碎屑锆石年龄以2200~2300Ma为主,这与熊耳群玄武安山质熔岩中的捕获锆石年龄分布一致(赵太平等, 2004; Wang et al., 2019),并且二者具有相似的Nd同位素组成,均显示富集地幔特征(图 8; 赵太平等, 2002; He et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2010, 2019)。岩石地球化学特征和同位素地球化学特征均表明沉凝灰岩与熊耳群火山岩具有强烈的亲缘性。
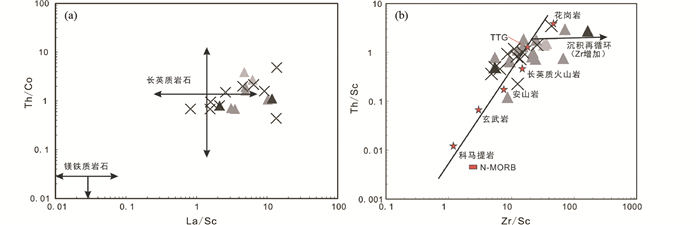
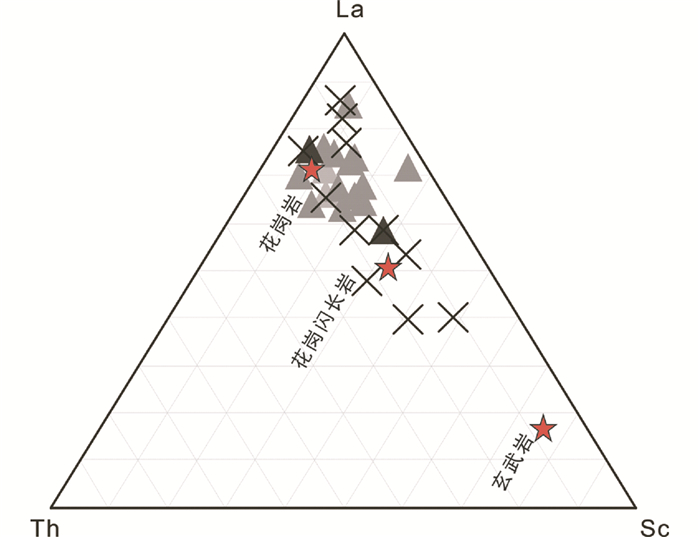
虽然部分样品显示出较高的LOI含量,可能与蚀变作用相关。但是,Co、Ni、La、Th、Zr、Sc等微量-稀土元素在后期地质过程中保持稳定,是判断源区组成的良好指示剂。Th/Co-La/Sc图解显示(图 10a, Lopez et al., 2005),高山河群碎屑沉积岩的源区主要为长英质物质,这与右倾的稀土配分模式和负的Eu异常特征保持一致,因为长英质物质通常在风化作用中由于长石的分异或分解而造成Eu亏损(Cullers and Graf, 1984; Condie et al., 1992)。同时,相比于石英砂岩,La-Th-Sc图解中凝灰岩G2显示向“安山岩”或“玄武岩”区域过渡,表明基性物质对其源区也有一定贡献(图 10b、图 11, Lopez et al., 2005)。底部和顶部石英砂岩(G1L+G1U)均来自稳定的成熟物源区(图 6b),但前者具有更高的成熟度(图 6a)。
|
图 10 高山河群碎屑沉积岩的Th/Co-La/Sc图解(a, 据Lopez et al., 2005)和Th/Sc-Zr/Sc图解(b, 据Nesbitt and Young, 1989) Fig. 10 Th/Co vs. La/Sc diagram (a, after Lopez et al., 2005) and Th/Sc vs. Zr/Sc diagram (b, after Nesbitt and Young, 1989) of sedimentary rocks from the Gaoshanhe Group |
|
图 11 高山河群碎屑沉积岩的La-Th-Sc判别图解(据Lopez et al., 2005) Fig. 11 La-Th-Sc diagram of sedimentary rocks from the Gaoshanhe Group (after Lopez et al., 2005) |
石英砂岩G1中锆石及镜下石英颗粒磨圆程度高,分选性差(图 3c, d、图 4),由于其成熟度较高,那么这些特征很可能与沉积再循环过程有关,而非搬运距离或快速沉积过程造成。岩石中的Th/Sc值与Zr/Sc通常形成正相关关系,但沉积再循环过程中,由于Zr元素的逐渐富集使得Zr/Sc值不断增加,Th/Sc值却保持不变或很小改变(McLennan et al., 1993)。高山河群凝灰岩Zr/Sc-Th/Sc基本都沿正相关线分布,但是石英砂岩源区略复杂,主要来自长英质和TTG物质,同时显示出Zr增加的趋势,也支持高山河群碎屑沉积物源经历了再循环过程(图 10b, McLennan et al., 1993)。
3.3 区域地层对比以及对构造演化的指示长城系是华北克拉通由结晶基底的固结(造山运动的结束)到稳定盖层广泛发育的最早见证者,在燕辽地区蓟县剖面记录的最为典型。通过碎屑沉积岩、基性岩墙群和花岗质侵入岩等地质体的年代学研究,限定燕辽等华北北缘地区“长城系”(常州沟组-串岭沟组-团山子组-大红峪组)的沉积时限在1.73~1.62Ga(陆松年和李惠民, 1991; 郁建华等, 1996; 万渝生等, 2003; 杨进辉等, 2005; 高维等, 2008; Lu et al., 2008; 彭澎等, 2011; 和政军等, 2011a, b; 张拴宏等, 2013; Zhang et al., 2015),甚至起始沉积时代在1.65Ga之后(李怀坤等, 2011; Li et al., 2013),明显晚于华北南缘1.78~1.75Ga熊耳期火山活动。通过详细的野外探勘,熊耳群之上高山河群鳖盖子组及汝阳群云梦山组底部的玄武-安山质火山岩夹层以及顶部的含铁石英砂岩层位在区域上性状一致、延伸稳定,可分别控制二者之间底、顶对比。而基于豫西南洛峪群顶部中发育的层凝灰岩夹层中保存了较好的原始凝灰结构和晶屑组分,被认为可与大红峪组火山岩对比(苏文博等, 2012),其锆石U-Pb年龄~1600Ma用于精确标定华北南缘“长城系”顶界(苏文博等, 2012; 李承东等, 2017)。已有学者提出燕辽地区的“长城系”应该位于熊耳群之上,可能只相当于汝阳群-洛峪群的中上部(苏文博等, 2012; 苏文博, 2016)。
近年来元古宙沉积岩中的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄数据表明,华北北缘、燕辽、山东-徐淮、华北南缘甚至朝鲜半岛的各个裂谷盆地沉积作用都记录了华北克拉通重要的前寒武纪构造-岩浆-热事件,以2.7~2.9Ga和~2.5Ga、~1.85Ma为高峰值,分别对应华北克拉通的克拉通化和活化再造(Zhai et al., 2015),造成大规模该时期的变质岩和岩浆岩出露,继而风化剥蚀后出现大量既有岩浆成因也有变质成因的碎屑锆石。高山河群石英砂岩中出现古元古代晚期1800~1900Ma、1950~2100Ma、2200~2350Ma及新太古代~2500Ma、2600~2700Ma的碎屑锆石,正是对上述华北重要地质事件的记录,物源区即是华北克拉通内部的前寒武纪基底物质。因此,高山河群与其它区域长城系记录的华北克拉通前寒武纪构造热事件几乎完全一致。
古元古代~2.45Ga开始,全球性的岩浆活动骤减并持续至2.25~2.20Ga(Condie, 1998; Condie et al., 2009; Belousova et al., 2010; Condie and Aster, 2010),被认为与克拉通化后的板块作用进入调整期有关(Pehrsson et al., 2014; Zhai and Santosh, 2013)。然而越来越多的研究证实,2.45~2.20Ga并非华北克拉通的地壳演化“沉寂期”或构造-岩浆活动“静寂期”,华北中部、北部和东部在该时期广泛发育正片麻岩、火山岩和未变形花岗岩(Zhou et al., 2016和其中的文献)。近年来,阴山地块和鄂尔多斯地块交界的孔兹岩带以及华北中部的元古宙地层都陆续发现相当数量的2.0~2.4Ga碎屑锆石(Wan et al., 2009; Dong et al., 2014; Du et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2018b),对应华北克拉通古元古代麻粒岩相变质作用之前的岩浆活动,与太古宙/元古宙之后的地球演化“静寂期”以及引起全球裂谷事件和休伦冰期的构造之间的联系密切。但从已有报道来看,无论岩浆岩中的继承/捕获锆石还是沉积岩中碎屑锆石,均未发现古元古代早-中期物质对燕辽地区中晚元古界的源区有显著贡献,仅在十三陵地区串岭沟组粉砂岩中出现少量2200~2400Ma的碎屑锆石和~2300Ma的弱峰值(Wan et al., 2011; Ding et al., 2018)。
在华北南部,洛南-豫西地区高山河群碎屑岩自下而上的沉积物源发生了明显变化,尤其是在底部火山岩夹层附近,以古元古代~2310Ma地壳物质的加入为显著特征。近年随着研究的深入,小秦岭地区古元古代早期岩石被陆续报道,包括TTG片麻岩、斜长角闪岩、变辉长岩等,2.4~2.2Ga的花岗岩更为普遍。这些岩浆岩的锆石年龄集中在2360~2240Ma,峰值为2310Ma(第五春荣等, 2007; Diwu et al., 2014; Huang et al., 2012; Zhou et al., 2014),与高山河群沉凝灰岩中碎屑锆石年龄峰值完全一致。鲁山下汤地区出露~2.30Ga片麻岩状花岗岩,全岩Nd同位素和锆石Hf同位素均显示富集特征,tDM(Nd)为2.75Ga,tDM(Hf)为2823~3255Ma(黄道袤等, 2012)。石英砂岩底部G1L和沉凝灰岩G2的Nd同位素组成特征、二阶段模式年龄与上述~2300Ma花岗岩类岩石十分类似,表明高山河群古元古代碎屑物质源区与“静寂期”岩浆活动关系密切。因此,华北克拉通南部这些2.30~2.31Ga的岩石-物质记录正是修正全球地壳演化“沉寂期”或全球岩浆-构造“静寂期”观点的最佳研究窗口。
4 结论(1) 华北克拉通南缘中元古界高山河群底部凝灰岩中碎屑锆石显示特殊的~2300Ma年龄峰值,Nd同位素组成与熊耳群火山岩类似,显示它们具有成因或源区上的关联性。
(2) 高山河群的碎屑物质源区主要来源于古元古代-中晚太古代长英质物质。由下至上,石英砂岩的成熟度降低,表明来自沉积再循环的物质减少。Nd同位素组成显示富集至弱亏损又至富集的趋势,表明沉积物源具有多元性并与物质组分差异密切相关。
(3) 高山河群碎屑沉积岩中最年轻的一组碎屑锆石年龄为1760~1770Ma,可大致指示其沉积时代的下限。结合上覆官道口群的底界1600~1610Ma,确定高山河群是华北南缘“长城系”的重要组成部分。其源区主要为来自古元古代晚期1800~1900Ma、1950~2100Ma、2200~2350Ma及新太古代~2500Ma、2600~2700Ma的碎屑物质,与区域上长城系记录的华北克拉通前寒武纪构造热事件一致,二者具有可对比性。
致谢 本次研究中Nd同位素测试分析工作得到中国科学技术大学陈福坤教授和肖平老师的支持和帮助;碎屑锆石年代学工作得到西北大学第五春荣教授和弓化栋老师以及中国地质科学院地质力学研究所胡国辉助理研究员的帮助;河南省地质调查院王世炎总工和中国地质大学(北京)苏文博教授在野外地质考察中给予了指导,二位前辈连同张健教授、万渝生研究员的宝贵意见对本文的提高至关重要。赵太平研究员对本次研究给予了大量的支持和帮助。在此一并表示衷心感谢!
Bai J, Huang GX and Wang HC. 1996. Precambrian Crustal Evolution of China. 2nd Edition. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Belousova EA, Kostitsyn YA, Griffin WL, Begg GC, O'Reilly SY and Pearson NJ. 2010. The growth of the continental crust:Constraints from zircon Hf-isotope data. Lithos, 119(3-4): 457-466 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.07.024 |
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Henan Province (BGMRH). 1989. Regional Geology of Henan Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Henan Province (BGMRH). 2008. Lithostratigraphy of Henan Province. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press (in Chinese)
|
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Shaanxi Province (BGMRS). 1989. Regional Geology of Shaanxi Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Chen FK, Hegner E and Todt W. 2000. Zircon ages and Nd isotopic and chemical compositions of orthogneisses from the Black Forest, Germany:Evidence for a Cambrian magmatic arc. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 88(4): 791-802 DOI:10.1007/s005310050306 |
Chen FK, Li XH, Wang XL, Li QL and Siebel W. 2007. Zircon age and Nd-Hf isotopic composition of the Yunnan Tethyan belt, southwestern China. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 96(6): 1179-1194 DOI:10.1007/s00531-006-0146-y |
Chen FK, Zhu XY, Wang W, Wang F, Trung HP and Wolfgang S. 2009. Single-grain detrital muscovite Rb-Sr isotopic composition as an indicator of provenance for the Carboniferous sedimentary rocks in northern Dabie, China. Geochemical Journal, 43(4): 257-273 DOI:10.2343/geochemj.1.0023 |
Chen JB, Zhang PY, Gao ZJ and Sun SF. 1999. Lexicon of China Stratigraphy:Mesoproterozoic Era. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
China Stratigraphic Commission. 2001. Guide for Chinese Stratigraphic and Its Instruction. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
China Stratigraphic Commission. 2002. Instruction of Chinese Geological Time Scale. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Condie KC, Boryta MD, Liu JZ and Qian XL. 1992. The origin of Khondalites:Geochemical evidence from the Archean to Early Proterozoic granulite belt in the North China craton. Precambrian Research, 59(3-4): 207-223 DOI:10.1016/0301-9268(92)90057-U |
Condie KC. 1998. Episodic continental growth and supercontinents:A mantle avalanche connection?. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 163(1-4): 97-108 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00178-2 |
Condie KC, O'Neill C and Aster RC. 2009. Evidence and implications for a widespread magmatic shutdown for 250My on Earth. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 282(1-4): 294-298 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2009.03.033 |
Condie KC and Aster RC. 2010. Episodic zircon age spectra of orogenic granitoids:The supercontinent connection and continental growth. Precambrian Research, 180(3-4): 227-236 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2010.03.008 |
Cui ML, Zhang BL and Zhang LC. 2011. U-Pb dating of baddeleyite and zircon from the Shizhaigou diorite in the southern margin of North China Craton:Constrains on the timing and tectonic setting of the Paleoproterozoic Xiong'er Group. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 184-193 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.01.010 |
Cui ML, Zhang LC, Zhang BL and Zhu MT. 2013. Geochemistry of 1.78Ga A-type granites along the southern margin of the North China Craton:Implications for Xiong'er magmatism during the break-up of the supercontinent Columbia. International Geology Review, 55(4): 496-5094 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2012.736709 |
Cullers RL and Graf J. 1984. Rare earth elements in igneous rocks of the continental crust:Intermediate and silicic rocks-ore petrogenesis. Developments in Geochemistry, 2: 275-316 DOI:10.1016/B978-0-444-42148-7.50013-7 |
Deng XQ, Zhao TP, Peng TP, Gao XY and Bao ZW. 2015. Petrogenesis of 1600Ma Maping A-type granite in the southern margin of the North China Craton and its tectonic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(6): 1621-1635 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ding J, Shi YR, Kröner A and Anderson JL. 2018. Constraints on sedimentary ages of the Chuanlinggou Formation in the Ming Tombs, Beijing, North China Craton:LA-ICP-MS and SHRIMP U-Pb dating of detrital zircons. Acta Geochimica, 37(2): 257-280 DOI:10.1007/s11631-017-0211-1 |
Diwu CR, Sun Y, Lin CL, Liu XM and Wang HL. 2007. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes and their geological significance of Yiyang TTG gneisses from Henan Province, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 253-262 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Diwu CR, Sun Y, Dong ZC, Wang HL, Chen DL, Chen L and Zhang H. 2010. In situ U-Pb geochronology of Hadean zircon xenocryst (4.1~3.9Ga) from the western of the Northern Qinling Orogenic Belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(4): 1171-1174 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Diwu CR, Sun Y, Zhao Y and Lai SC. 2014. Early Paleoproterozoic (2.45~2.20Ga) magmatic activity during the period of global magmatic shutdown:Implications for the crustal evolution of the southern North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 255: 627-640 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2014.08.001 |
Dong CY, Wan YS, Wilde SA, Xu ZY, Ma MZ, Xie HQ and Liu DY. 2014. Earliest Paleoproterozoic supracrustal rocks in the North China Craton recognized from the Daqingshan area of the Khondalite Belt:Constraints on craton evolution. Gondwana Research, 25: 1535-1553 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.021 |
Du LL, Yang CH, Wyman DA, Nutman AP, Zhao L, Lu ZL, Song HX, Geng YS and Ren LD. 2017. Zircon U-Pb ages and Lu-Hf isotope compositions from clastic rocks in the Hutuo Group:Further constraints on Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the Trans-North China Orogen. Precambrian Research, 303: 291-314 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.04.007 |
Floyd PA, Leveridge BE, Franke W, Shail R and Dörr W. 1990. Provenance and depositional environment of Rhenohercynian synorogenic greywackes from the Giessen Nappe, Germany. Geologische Rundschau, 79(3): 611-626 DOI:10.1007/BF01879205 |
Gao LZ, Yin CY and Wang ZQ. 2002. New view of the Neoproterozoic strata on the southern margin of the North China platform. Geological Bulletin of China, 21(3): 130-135 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Gao W, Zhang CH, Gao LZ, Shi XY, Liu YM and Song B. 2008. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age of rapakivi granite in Miyun, Beijing, China, and its tectono-stratigraphic implications. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(6): 793-798 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Guan BD, Geng WC, Rong ZQ and Du HY. 1988. The Middle and Late Proterozoic Strata of the Northern Slope of East Qinling, Henan Province. Zhengzhou: Henan Science and Technology Press: 41-49 (in Chinese)
|
He YH, Zhao GC, Sun M and Han YG. 2010. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of volcanic rocks in the Xiaoshan and Waifangshan areas along the southern margin of the North China Craton:Constraints from bulk-rock geochemistry and Sr-Nd isotopic composition. Lithos, 114(1-2): 186-199 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.08.008 |
He ZJ, Niu BG, Zhang XY, Zhao L and Liu RY. 2011a. Discovery of the paleo-weathered mantle of the rapakivi granite covered by the Proterozoic Changzhougou Formation in the Miyun area, Beijing and their detrital zircon dating. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(5): 798-802 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
He ZJ, Zhang XY, Niu BG, Liu RY and Zhao L. 2011b. The paleo-weathering mantle of the Proterozoic rapakivi granite in Miyun County, Beijing and the relationship with the Changzhougou Formation of Changchengian System. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(4): 123-130 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu GH, Zhao TP, Zhou YY and Yang Y. 2012a. Depositional age and provenance of the Wufoshan Group in the southern margin of the North China Craton:Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopic compositions. Geochimica, 41(4): 326-342 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu GH, Zhou YY and Zhao TP. 2012b. Geochemistry of Proterozoic Wufoshan Group sedimentary rocks in the Songshan area, Henan Province:Implications for provenance and tectonic setting. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(11): 3692-3704 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu GH, Zhao TP, Zhou YY and Wang SY. 2013. Meso-Neoproterozoic sedimentary formation in the southern margin of the North China Craton and its geological implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(7): 2491-2507 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu GH, Zhao TP and Zhou YY. 2014. Depositional age, provenance and tectonic setting of the Proterozoic Ruyang Group, southern margin of the North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 246: 296-318 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2014.03.013 |
Huang DM, Zhang DH, Wang SY, Zhang YX, Dong CY, Liu DY and Wan YS. 2012. 2.3Ga magmatism and 1.94Ga metamorphism in the Xiatang area, southern margin of the North China Craton:Evidence from whole-rock geochemistry and zircon geochronology and Hf isotope. Geological Review, 58(3): 565-576 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Huang XL, Wilde SA, Yan QJ and Zhong JW. 2012. Geochronology and petrogenesis of gray gneisses from the Taihua Complex at Xiong'er in the southern segment of the Trans-North China Orogen:Implications for tectonic transformation in the Early Paleoproterozoic. Lithos, 134-135: 236-252 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.01.004 |
Jia XL, Zhu XY, Zhai MG, Zhao Y, Zhang H, Wu JL and Liu T. 2016. Late Mesoarchean crust growth event:Evidence from the ca. 2.8Ga granodioritic gneisses of the Xiaoqinling area, southern North China Craton. Science Bulletin, 61(12): 974-990 DOI:10.1007/s11434-016-1094-y |
Jia XL, Zhai MG, Xiao WJ, Sun Y, Ratheesh-Kumar RT, Yang H, Zhou KF and Wu JL. 2019. Late Neoarchean to Early Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the southern North China Craton:Evidence from geochemistry, zircon geochronology and Hf isotopes of felsic gneisses from the Taihua complex. Precambrian Research, 326: 222-239 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.11.013 |
Jiang GQ, Zhou HR and Wang ZQ. 1994. Stratigraphic sequence, sedimentary environment and its tectono-paleogeographic significance of the Luanchuan Group, Luanchuan area, Henan Province. Geoscience, 8(4): 430-440 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li CD, Zhao LG, Chang QS, Xu YW, Wang SY and Xu T. 2017. Zircon U-Pb dating of tuff bed from Luoyukou Formation in western Henan Province on the southern margin of the North China Craton and its stratigraphic attribution discussion. Geology in China, 44(3): 511-525 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li HK, Su WB, Zhou HY, Geng JZ, Xiang ZQ, Cui YR, Liu WC and Lu SN. 2011. The base age of the Changchengian System at the northern North China Craton should be younger than 1670Ma:Constraints from zircon U-Pb LA-MC-ICPMS dating of a granite-porphyry dike in Miyun County, Beijing. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(3): 108-120 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li HK, Lu SN, Su WB, Xiang ZQ, Zhou HY and Zhang YQ. 2013. Recent advances in the study of the Mesoproterozoic geochronology in the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 72: 216-227 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.02.020 |
Li QZ, Yang YZ and Jia JC. 1985. Research on the Late Precambrian Stratum in Southern North China Craton (Shaanxi Province). Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press (in Chinese)
|
Li WH. 1991. Clasolite tidal flat deposits of gaoshanhe group in the southern margin of the North China Platform. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 9(3): 98-105 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li XH. 1996. Nd isotopic evolution of sediments from the southern margin of the Yangtze block and its tectonic significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 12(3): 359-369 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu CH, Zhao GC, Liu FL and Han YG. 2014. Nd isotopic and geochemical constraints on the provenance and tectonic setting of the low-grade meta-sedimentary rocks from the Trans-North China Orogen, North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 94: 137-189 |
Liu DY, Wilde SA, Wan YS, Wang SY, Valley JW, Kita N, Dong CY, Xie HQ, Yang CX, Zhang YX and Gao LZ. 2009. Late Mesoarchean-Early Neoarchean tectonothermal events at the southern margin of the North China Craton:Evidence of multiple events from SHRIMP U-Pb dating and hafnium isotope analysis of zircons from metamorphosed supracrustal rocks and tonalites. Chemical Geology, 261(1-2): 140-154 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.10.041 |
Liu XM, Gao S, Diwu CR, Yuan HL and Hu Z. 2007. Simultaneous in-situ determination of U-Pb age and trace elements in zircon by LA-ICP-MS in 20μm spot size. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52: 1257-1264 DOI:10.1007/s11434-007-0160-x |
Liu XY. 2011. Chronological, petrological and geochemical characteristics of the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic alkali-rich intrusive rocks along the southern part of the North China Craton. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Lopez JMG, Bauluz B, Fernández-Nieto C and Oliete CY. 2005. Factors controlling the trace-element distribution in fine-grained rocks:The Albian kaolinite-rich deposits of the Oliete Basin (NE Spain). Chemical Geology, 214(1-2): 1-19 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.08.024 |
Lu JS, Zhai MG, Lu LS, Wang HYC, Chen HX, Peng T, Wu CM and Zhao TP. 2017. Metamorphic P-T-t path retrieved from metapelites in the southeastern Taihua metamorphic complex, and the Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the southern North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 134: 352-364 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.12.001 |
Lu SN and Li HM. 1991. A precise U-Pb single zircon age determina-tion for the volcanics of Dahongyu Formation, Changcheng System in Jixian. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Science, (1): 137-146 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Lu SN, Zhao GC, Wang HC and Hao GJ. 2008. Precambrian metamorphic basement and sedimentary cover of the North China Craton:A review. Precambrian Research, 160(1-2): 77-93 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.017 |
Ludwig KR. 2003. ISOPLOT 3: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Geochronology Centre Special Publication
|
Lü GF, Guan BD and Wang YX. 1993. Characteristic and tectonic background of the volcanic interlayers from the Gaoshanhe and Yunmengshan groups, western Henan. Henan Geology, 11(1): 37-43 (in Chinese) |
McLennan SM, Hemming S, McDaniel DK and Hanson GN. 1993. Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics. In: Johnsson MJ and Basu A (eds.). Processes Controlling the Composition of Clastic Sediments. Boulder, Colorado, USA: Geological Society of America, Special Paper, 284: 21-40
|
Meng Y, Zuo PF, Zheng DS, Sun FB, Wang PX, Wang ZJ and Li Y. 2018. The earliest clastic sediments overlying the Xiong'er volcanic rocks:Implications for the Mesoproterozoic tectonics of the southern North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 305: 268-282 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.12.001 |
Nesbitt HW and Young GM. 1989. Formation and diagenesis of weathering profiles. The Journal of Geology, 97(2): 129-147 |
Pehrsson SJ, Buchan KL, Eglington BM, Berman RG and Rainbird RH. 2014. Did plate tectonics shutdown in the Palaeoproterozoic? A view from the Siderian geologic record. Gondwana Research, 26(3-4): 803-815 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2014.06.001 |
Peng P, Zhai MG, Guo JH, Kusky T and Zhao TP. 2007. Nature of mantle source contributions and crystal differentiation in the petrogenesis of the 1.78Ga mafic dykes in the central North China craton. Gondwana Research, 12(1-2): 29-46 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2006.10.022 |
Peng P, Zhai MG, Ernst RE, Guo JH, Liu F and Hu B. 2008. A 1.78Ga large igneous province in the North China craton:The Xiong'er volcanic province and the North China dyke swarm. Lithos, 101(3-4): 260-280 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.07.006 |
Peng P, Liu F, Zhai MG and Guo JH. 2012. Age of the Miyun dyke swarm:Constraints on the maximum depositional age of the Changcheng System. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(1): 105-110 DOI:10.1007/s11434-011-4771-x |
Peng P. 2015. Late Paleoproterozoic-Neoproterozoic (1800~514Ma) mafic dyke swarms and rifts in North China. In: Zhai MG (ed.). Precambrian Geology of China. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 171-204
|
Santosh M, Wan YS, Liu DY, Dong CY and Li JH. 2009. Anatomy of zircons from an Ultrahot Orogen:The amalgamation of the North China Craton within the supercontinent Columbia. The Journal of Geology, 117(4): 429-443 DOI:10.1086/598949 |
Su WB, Li HK, Xu L, Jia SH, Geng JZ, Zhou HY, Wang ZH and Pu HY. 2012. Luoyu and Ruyang Group at the south margin of the North China Craton (NCC) should belong in the Mesoproterozoic Changchengian System:Direct constraints from the LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb age of the Tuffite in the Luoyukou Formation, Ruzhou, Henan, China. Geological Survey and Research, 35(2): 96-108 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Su WB. 2016. Revision of the Mesoproterozoic chronostratigraphic subdivision both of North China and Yangtze Cratons and the relevant issues. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(6): 156-185 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345
|
Wan YS, Zhang QD and Song TR. 2003. SHRIMP ages of detrital zircons from the Changcheng System in the Ming Tombs area, Beijing:Constraints on the protolith nature and maximum depositional age of the Mesoproterozoic cover of the North China Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(22): 2500-2506 |
Wan YS, Wilde SA, Liu DY, Yang CX, Song B and Yin XY. 2006. Further evidence for~1.85Ga metamorphism in the Central Zone of the North China Craton:SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircon from metamorphic rocks in the Lushan area, Henan Province. Gondwana Research, 9(1-2): 189-197 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2005.06.010 |
Wan YS, Liu DY, Dong CY, Xu ZY, Wang ZJ, Wilde SA, Yang YH, Liu ZH and Zhou HY. 2009. The Precambrian Khondalite Belt in the Daqingshan area, North China Craton: Evidence for multiple metamorphic events in the Palaeoproterozoic era. In: Reddy SM, Mazumder R, Evans DAD and Collins AS (eds.). Palaeoproterozoic Supercontinents and Global Evolution. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 323: 73-97
|
Wan YS, Liu DY, Wang W, Song TR, Kroner A, Dong CY, Zhou HY and Yin XY. 2011. Provenance of Meso-to Neoproterozoic cover sediments at the Ming Tombs, Beijing, North China Craton:An integrated study of U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic measurement of detrital zircons and whole-rock geochemistry. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 219-242 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.02.009 |
Wan YS, Xie HQ, Yang H, Wang ZJ, Liu DY, Kroner A, Wilde SA, Geng YS, Sun LY, Ma MZ, Liu SJ, Dong CY and Du LL. 2013. Is the Ordos Block Archean or Paleoproterozoic in age? Implications for the precambrian evolution of the North China Craton. American Journal of Science, 313(7): 683-711 DOI:10.2475/07.2013.03 |
Wan YS, Liu DY, Dong CY, Xie HQ, Kröner A, Ma MZ, Liu SJ, Xie SW and Ren P. 2015. Formation and evolution of Archean continental crust of the North China Craton. In: Zhai MG (ed.). Precambrian geology of China. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 59-136
|
Wang CM, He XY, Carranza EJM and Cui CM. 2019. Paleoproterozoic volcanic rocks in the southern margin of the North China Craton, central China:Implications for the Columbia supercontinent. Geoscience Frontiers, 10: 1543-1560 DOI:10.1016/j.gsf.2018.10.007 |
Wang HZ and Li GC. 1990. Correlation of the International Time Scale. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Wang K, Wang TS, Wang ZC, Luo P, Li QF, Fang J and Ma K. 2018a. Characteristics of Changchengian rifts in southern margin of North China Craton and its hydrocarbon geological conditions. Petroleum Research, 3(3): 269-282 DOI:10.1016/j.ptlrs.2018.05.002 |
Wang X, Li XP and Han ZZ. 2018b. Zircon ages and geochemistry of amphibolitic rocks from the Paleoproterozoic Erdaowa Group in the Khondalite Belt, North China Craton and their tectonic implications. Precambrian Research, 317: 253-267 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2018.09.005 |
Wang XL, Jiang SY and Dai BZ. 2010. Melting of enriched Archean subcontinental lithospheric mantle:Evidence from the ca. 1760Ma volcanic rocks of the Xiong'er Group, southern margin of the North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 182(3): 204-216 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2010.08.007 |
Wang YF. 2000. Preliminary researching on the volcanic rock of Dahongkou Formation, Luanchuan Group. Henan Geology, 18(3): 181-189 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang YL. 1980. The Sinian of China. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press (in Chinese)
|
Wang ZH, Zhang XL, Tu S and Li JH. 2008. Stratigraphy and Paleontology in Henan Province:Precambrian of the First Book. Zhengzhou: Yellow River Conservancy Press (in Chinese)
|
Wu TS. 1982. Comparison and epoch of the western Henan-type Sinian strata. Regional Geology of China, (1): 73-81 (in Chinese) |
Wu TS. 1997. Studies on Multiple Stratigraphic Division and Comparison in China (14) Lithostratigraphy of Shanxi Province. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press (in Chinese)
|
Yang JH, Wu FY, Liu XM and Xie LW. 2005. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes and their geological significance of the Miyun rapakivi granites from Beijing, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(6): 1633-1644 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yin CY and Gao LZ. 1997. New Finding of the macroscopic metaphyta in the Neoproterozoic Luoyukou Formation, Luoyu Group in Lushan, western Henan. Geological Review, 43(4): 355 (in Chinese) |
Yu JH, Fu HQ, Haapala I, Ramo TO, Vaasjoki M and Mortensen JK. 1996. A 1.70Ga anorogenic rapakivi granite suite in the northern part of North China Craton. Journal of Geology & Mineral Research in North China, 11(3): 341-350 |
Yu XQ, Liu JL, Li CL, Chen SQ and Dai YP. 2013. Zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotope analysis on the Taihua Complex:Constraints on the formation and evolution of the Trans-North China Orogen. Precambrian Research, 230: 31-44 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.12.008 |
Zhai MG. 2006. Geological significance of the Neoarchean global cratonization event and the boundary between Archean and Proterozoic. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 30(4): 419-421 (in Chinese) |
Zhai MG and Peng P. 2007. Paleoproterozoic events in the North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(11): 2665-2682 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai MG. 2009. Two kinds of granulites (HT-HP and HT-UHT) in North China Craton:Their genetic relation and geotectonic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(8): 1753-1771 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai MG, Li TS, Peng P, Hu B, Liu F, Zhang YB and Guo JH. 2010. Precambrian key tectonic events and evolution of the North China Craton. In: Kusky T, Zhai MG and Xiao WJ (eds.). The Evolving Continents. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 338: 235-262
|
Zhai MG and Santosh M. 2011. The Early Precambrian odyssey of the North China Craton:A synoptic overview. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 6-25 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.02.005 |
Zhai MG and Santosh M. 2013. Metallogeny of the North China Craton:Link with secular changes in the evolving Earth. Gondwana Research, 24(1): 275-297 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.02.007 |
Zhai MG, Hu B, Zhao TP, Peng P and Meng QR. 2015. Late Paleoproterozoic-Neoproterozoic multi-rifting events in the North China Craton and their geological significance:A study advance and review. Tectonophysics, 662: 153-166 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2015.01.019 |
Zhang HF, Zhang J, Zhang GW, Santosh M, Yu H, Yang YH and Wang JL. 2016. Detrital zircon U-Pb, Lu-Hf, and O isotopes of the Wufoshan Group:Implications for episodic crustal growth and reworking of the southern North China craton. Precambrian Research, 273: 112-128 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2015.12.004 |
Zhang RY and Sun Y. 2017. Formation and evolution of Early Precambrian basement in the southern North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(10): 3027-3041 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Ye H, Hu JM and Wu F. 2013. New constraints on ages of the Chuanlinggou and Tuanshanzi formations of the Changcheng System in the Yan-Liao area in the northern North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(7): 2481-2490 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang YB, Li QL, Lan ZW, Wu FY, Li XH, Yang JH and Zhai MG. 2015. Diagenetic xenotime dating to constrain the initial depositional time of the Yan-Liao Rift. Precambrian Research, 271: 20-32 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2015.09.024 |
Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA, Li SZ, Liu SW and Zhang J. 2006. Composite nature of the North China granulite-facies belt:Tectonothermal and geochronological constraints. Gondwana Research, 9(3): 337-348 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2005.10.004 |
Zhao TP, Zhou MF, Jin CW, Guan H and Li HM. 2001. Discussion on age of the Xiong'er Group in southern margin of North China Craton. Chinese Journal of Geology, 36(3): 326-334 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao TP, Jin CW, Zhai MG, Xia B and Zhou MF. 2002. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Xiong'er Group in the southern regions of the North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 18(1): 59-69 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao TP, Zhai MG, Xia B, Li HM, Zhang YX and Wan SY. 2004. Zircon U-Pb SHRIMP dating for the volcanic rocks of the Xiong'er Group:Constraints on the initial formation age of the cover of the North China Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(23): 2495-2502 DOI:10.1007/BF03183721 |
Zhao TP, Deng XQ, Hu GH, Zhou YY, Peng P and Zhai MG. 2015. The Paleoproterozoic-Mesoproterozoic boundary of the North China Craton and the related geological issues:A review. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(6): 1495-1508 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhou YY, Zhai MG, Zhao TP, Lan ZW and Sun QY. 2014. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of the Early Paleoproterozoic potassic granite in the Lushan area, southern margin of the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 94: 190-204 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.03.003 |
Zhou YY, Sun QY, Zhao TP and Diwu CR. 2016. The Paleoproterozoic continental evolution in the southern North China Craton: Constrains from Magmatism and sedimentation. In: Zhai MG, Zhao Y and Zhao TP (eds.). Main Tectonic Events and Metallogeny of the North China Craton. Singapore: Springer, 251-277
|
Zhu XY. 2010. Evolution and provenance of the basement in the eastern Qinlin Orogen, China: Evidence from geochemistry and zircon U-Pb geochronology. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zhu XY, Chen FK, Li SQ, Yang YZ, Nie H, Siebel W and Zhai MG. 2011. Crustal evolution of the North Qinling terrain of the Qinling Orogen, China:Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopic composition. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 194-204 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.12.009 |
白谨, 黄光学, 王惠初. 1996. 中国前寒武纪地壳演化. 第二版. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
陈晋镳, 张鹏远, 高振家, 孙淑芬. 1999. 中国地层典:中元古界. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
邓小芹, 赵太平, 彭头平, 高昕宇, 包志伟. 2015. 华北克拉通南缘1600Ma麻坪A型花岗岩的成因及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 31(6): 1621-1635. |
第五春荣, 孙勇, 林慈銮, 柳小明, 王洪亮. 2007. 豫西宜阳地区TTG质片麻岩锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素地质学. 岩石学报, 23(2): 253-262. |
第五春荣, 孙勇, 董增产, 王洪亮, 陈丹玲, 陈亮, 张红. 2010. 北秦岭西段冥古宙锆石(4.1~3.9Ga)年代学新进展. 岩石学报, 26(4): 1171-1174. |
高林志, 尹崇玉, 王自强. 2002. 华北地台南缘新元古代地层的新认识. 地质通报, 21(3): 130-135. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.03.004 |
高维, 张传恒, 高林志, 史晓颖, 刘耀明, 宋彪. 2008. 北京密云环斑花岗岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其构造意义. 地质通报, 27(6): 793-798. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.06.007 |
关保德, 耿午辰, 戎治权, 杜慧英. 1988. 河南省东秦岭北坡中-上元古界. 郑州: 河南科学技术出版社: 41-49.
|
河南省地质矿产局. 1989. 河南省区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
河南省地质矿产厅. 2008. 河南省岩石地层. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社.
|
和政军, 牛宝贵, 张新元, 赵磊, 刘仁燕. 2011a. 北京密云元古宙常州沟组之下环斑花岗岩古风化壳岩石的发现及其碎屑锆石年龄. 地质通报, 30(5): 798-802. |
和政军, 张新元, 牛宝贵, 刘仁燕, 赵磊. 2011b. 北京密云元古宙环斑花岗岩古风化壳及其与长城系常州沟组的关系. 地学前缘, 18(4): 123-130. |
胡国辉, 赵太平, 周艳艳, 杨阳. 2012a. 华北克拉通南缘五佛山群沉积时代和物源区分析:碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素证据. 地球化学, 41(4): 326-342. |
胡国辉, 周艳艳, 赵太平. 2012b. 河南嵩山地区元古宙五佛山群沉积岩的地球化学特征及其对物源区和构造环境的制约. 岩石学报, 28(11): 3692-3704. |
胡国辉, 赵太平, 周艳艳, 王世炎. 2013. 华北克拉通南缘中-新元古代沉积地层对比研究及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 29(7): 2491-2507. |
黄道袤, 张德会, 王世炎, 张毅星, 董春艳, 刘敦一, 万渝生. 2012. 华北克拉通南缘豫西下汤地区2.3Ga岩浆作用和1.94Ga变质作用-锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素组成及全岩地球化学研究. 地质论评, 58(3): 565-576. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.03.017 |
蒋干清, 周洪瑞, 王自强. 1994. 豫西栾川地区栾川群的层序、沉积环境及其构造古地理意义. 现代地质, 8(4): 430-440. |
李承东, 赵利刚, 常青松, 许雅雯, 王世炎, 许腾. 2017. 豫西洛峪口组凝灰岩锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb年龄及地层归属讨论. 中国地质, 44(3): 511-525. |
李怀坤, 苏文博, 周红英, 耿建珍, 相振群, 崔玉荣, 刘文灿, 陆松年. 2011. 华北克拉通北部长城系底界年龄小于1670Ma:来自北京密云花岗斑岩岩脉锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb年龄的约束. 地学前缘, 18(3): 108-120. |
李钦仲, 杨应章, 贾金昌. 1985. 华北地台南缘(陕西部分)晚前寒武纪地层研究. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社.
|
李文厚. 1991. 华北地台南缘高山河群碎屑岩潮坪沉积. 沉积学报, 9(3): 98-105. |
李献华. 1996. 扬子南缘沉积岩的Nd同位素演化及其大地构造意义. 岩石学报, 12(3): 359-369. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1996.03.001 |
柳晓艳. 2011.华北克拉通南缘古-中元古代碱性岩岩石地球化学与年代学研究及其地质意义.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质科学院
|
陆松年, 李惠民. 1991. 蓟县长城系大红峪组火山岩的单颗粒锆石U-Pb法准确定年. 中国地质科学院院报, (1): 137-146. |
吕国芳, 关保德, 王耀霞. 1993. 豫西高山河组云梦山组火山岩特点及其构造背景. 河南地质, 11(1): 37-43. |
彭澎, 刘富, 翟明国, 郭敬辉. 2011. 密云岩墙群的时代及其对长城系底界年龄的制约. 科学通报, 56(35): 2975-2980. |
全国地层委员会. 2001. 中国地层指南及中国地层指南说明书(修订版). 北京: 地质出版社.
|
全国地层委员会. 2002. 中国区域年代地层(地质年代)表说明书. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
陕西省地质矿产局. 1989. 陕西省区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
苏文博, 李怀坤, 徐莉, 贾松海, 耿建珍, 周红英, 王志宏, 蒲含勇. 2012. 华北克拉通南缘洛峪群-汝阳群属于中元古界长城系——河南汝州洛峪口组层凝灰岩锆石LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb年龄的直接约束. 地质调查与研究, 35(2): 96-108. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2012.02.003 |
苏文博. 2016. 华北及扬子克拉通中元古代年代地层格架厘定及相关问题探讨. 地学前缘, 23(6): 156-185. |
万渝生, 张巧大, 宋天锐. 2003. 北京十三陵长城系常州沟组碎屑锆石SHRIMP年龄:华北克拉通盖层物源区及最大沉积年龄的限定. 科学通报, 48(18): 1970-1975. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.18.014 |
王鸿祯, 李光岑. 1990. 国际地层时代对比表. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
王跃峰. 2000. 栾川群大红口组火山岩研究初探. 河南地质, 18(3): 181-189. |
王曰伦. 1980. 中国震旦亚界. 天津: 天津科学技术出版社.
|
王志宏, 张兴辽, 屠森, 李进化. 2008. 河南省地层古生物研究:第一分册前寒武纪. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社.
|
武铁山. 1982. 豫西(型)震旦系地层的对比统一划分和时代问题. 中国区域地质, (1): 73-81. |
武铁山. 1997. 全国地层多重划分对比研究(14)山西省岩石地层. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社.
|
杨进辉, 吴福元, 柳小明, 谢烈文. 2005. 北京密云环斑花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 21(6): 1633-1644. |
尹崇玉, 高林志. 1997. 豫西鲁山新元古界洛峪群洛峪口组宏观后生植物新发现. 地质论评, 43(4): 355. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1997.04.016 |
郁建华, 付会芹, 哈巴拉I, 拉莫OT, 发斯乔基M, 莫坦森JK. 1996. 华北克拉通北部1.70Ga非造山环斑花岗岩岩套. 华北地质矿产杂志, 11(3): 341-350. |
翟明国. 2006. 新太古代全球克拉通事件与太古宙-元古宙分界的地质涵义. 大地构造与成矿, 30(4): 419-421. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2006.04.002 |
翟明国, 彭澎. 2007. 华北克拉通古元古代构造事件. 岩石学报, 23(11): 2665-2682. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.001 |
翟明国. 2009. 华北克拉通两类早前寒武纪麻粒岩(HT-HP和HT-UHT)及其相关问题. 岩石学报, 25(8): 1753-1771. |
张瑞英, 孙勇. 2017. 华北克拉通南部早前寒武纪基底形成与演化. 岩石学报, 33(10): 3027-3041. |
张拴宏, 赵越, 叶浩, 胡健民, 吴飞. 2013. 燕辽地区长城系串岭沟组及团山子组沉积时代的新制约. 岩石学报, 29(7): 2481-2490. |
赵太平, 周美夫, 金成伟, 关鸿, 李惠民. 2001. 华北陆块南缘熊耳群形成时代讨论. 地质科学, 36(3): 326-334. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2001.03.007 |
赵太平, 金成伟, 翟明国, 夏斌, 周美夫. 2002. 华北陆块南部熊耳群火山岩的地球化学特征与成因. 岩石学报, 18(1): 56-69. |
赵太平, 翟明国, 夏斌, 李惠民, 张毅星, 万渝生. 2004. 熊耳群火山岩锆石SHRIMP年代学研究:对华北克拉通盖层发育初始时间的制约. 科学通报, 49(22): 2342-2349. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.22.015 |
赵太平, 邓小芹, 胡国辉, 周艳艳, 彭澎, 翟明国. 2015. 华北克拉通古/中元古代界线和相关地质问题讨论. 岩石学报, 31(6): 1495-1508. |
祝禧艳. 2010.东秦岭造山带基底演化与属性: 地球化学和年代学证据.博士学位论文.北京: 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所 http://www.irgrid.ac.cn/handle/1471x/221016?mode=full&submit_simple=Show+full+item+record
|
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35