胶东地区位于我国华北板块东南缘,在晚中生代经历了大规模的岩石圈减薄事件,并伴随有大量的岩浆活动和成矿作用(Zhai and Santosh, 2013; Deng and Wang, 2016; Deng et al., 2018)。该地区侵入岩主要包括晚侏罗世花岗岩、早白垩世中期花岗闪长岩、早白垩世晚期花岗岩和二长花岗岩,以及早白垩世脉岩;此外,发育大量早白垩世金矿床(Goss et al., 2010; Goldfarb et al., 2014; Goldfarb and Santosh, 2014; Deng et al., 2015; Santosh and Pirajno, 2015; Yang et al., 2015, 2016a, b; Wang et al., 2016a; Liu et al., 2018)。
脉岩群形成于伸展构造环境中,可以为研究岩浆源区组成和区域地球动力学背景提供的证据(Ernst et al., 1995; Hou et al., 2008; Deng et al., 2014)。胶东地区广泛分布的早白垩世脉岩为研究该地区深部岩浆演化提供了理想的条件(Deng et al., 2017b)。加强脉岩成因研究,有助于揭示地幔组成、壳-幔相互作用,对认识该地区构造演化及动力学背景具有重要意义。前人对胶东白垩世脉岩的研究多集中于基性脉岩(Liu et al., 2009; Guo et al., 2014; Ma et al., 2014, 2016; Cai et al., 2015; Deng et al., 2017a; Liang et al., 2018),只有少数涉及中-酸性脉岩,且此类研究中通常将中-酸性脉岩归为一类(陈斌等, 2006; Tan et al., 2007, 2008; Cai et al., 2013, 2015; Liu et al., 2018)。本次研究中的石英闪长脉岩与闪长脉岩不但在岩石结构构造与矿物组成上有明显差异,两种岩性中的同类矿物也具有显著的矿物学与微区地球化学特征区别,指示两者很可能具有不同的岩浆源区及演化过程。并且,在对脉岩全岩的研究中,样品往往容易受到后期蚀变的影响,不能准确分析原岩的地球化学特征,进而影响对母岩浆演化与动力学过程反演的认识。同时,全岩分析更倾向于母岩浆整体的形成与转移过程,对于岩浆演化不同时期中的元素迁移、温压变化等不能提供细致的证据。针对上述问题,矿物学研究中黑云母、斜长石等造岩矿物贯穿整个岩浆演化过程,可作为寄主岩石岩浆演化不同阶段的指示剂,用于追踪岩浆演化过程。例如对斜长石环带核部与边部同步分析,能够显示岩浆在不同阶段元素的富集、分散趋势;对原生黑云母的微区地球化学分析能准确地反映岩浆演化不同阶段矿物结晶的物理化学条件(陈斌等, 2006; 王刚等, 2014; 杨立强等, 2014; 赵沔等, 2015; Guo et al., 2018)。
本次研究在胶东半岛采集了一系列石英闪长脉岩与闪长脉岩样品,主要开展矿物学和矿物微区地球化学特征研究,并结合已有全岩地球化学数据,对石英闪长脉岩与闪长脉岩的岩石学成因进行了详细研究,进而准确探讨该地区深部岩浆演化及其驱动力。
1 地质背景华北克拉通是地球上最古老的克拉通之一,形成于新太古代到古元古代期间(Zhao and Zhai, 2013),包括中央造山带、西部和东部板块(Wang et al., 2015, 2016b)。该克拉通南接秦岭-大别-苏鲁造山带,东邻太平洋汇聚体系(Ye et al., 2000)。华北克拉通自形成至晚古生代期间处于相对稳定的地台状态,而后在中生代时期其东部块体经历了大规模的岩石圈减薄事件(Yang et al., 2007; Deng et al., 2017a)。晚中生代时期,华北克拉通东部岩石圈减薄达到高峰并导致大规模的岩浆作用以及金成矿作用(Li and Li, 2007; Sun et al., 2007; Deng et al., 2017b)。
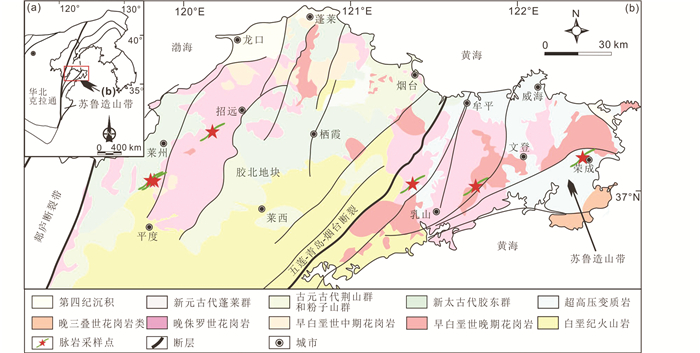
胶东半岛位于华北克拉通东南部,区内主要发育EW、NE、NNE和NW向构造(图 1a);该区出露地层以前寒武纪变质基底为主,主要包括新太古代麻粒岩、角闪岩、片麻岩和绿片岩,古元古代片麻岩、片岩、大理岩和硅质岩,以及新元古代变粒岩、大理岩和片岩等(Zheng et al., 2003)。研究区主要出露的岩体可以分为三期:1)晚三叠世花岗岩(227~205Ma),如小石岛岩体、甲子山岩体、刑家岩体和搓山岩体等;2)侏罗世黑云母二长花岗岩(160~145Ma),如玲珑岩体、昆嵛山岩体和栾家河岩体等;3)早白垩世花岗闪长脉岩和二长花岗岩(137~100Ma),如郭家岭岩体、崂山岩体和三佛山岩体等(Chen et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2010; Yang et al., 2012, 2014; Ma et al., 2013)。胶东半岛被五莲-烟台断裂带分为两部分,胶北地体和苏鲁造山带(Zheng et al., 2003; Deng et al., 2017b)。苏鲁造山带主要发育三叠世超高压变质岩,以及少量柯石英榴辉岩、石英岩和片岩(Zhang, 2012)。
|
图 1 华北克拉通地质简图(a, 据Zhao and Zhai, 2013修改)和胶东半岛地质图及脉岩采样位置(b, 据Deng et al., 2015修改) Fig. 1 Index map of the North China Craton showing the location of the Jiaodong Peninsula (a, modified after Zhao and Zhai, 2013) and simplified geological map of the Jiaodong Peninsula (b, modified after Deng et al., 2015), showing the samples locations in this study |
大量的早白垩世脉岩群分布于整个胶东半岛。年代学研究(包括全岩K-Ar,黑云母、角闪石Ar-Ar,和锆石U-Pb定年)显示,胶东脉岩群的形成时期为135~110Ma,在大约125Ma时期达到高峰(Guo et al., 2004; Yang et al., 2004; Tan et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2009; Zhang, 2012; Cai et al., 2013, 2015; Ma et al., 2014, 2016; Li et al., 2016; Liang et al., 2018)。而通过对赋矿围岩和成矿后期脉岩的SHRIMP U-Pb锆石测年,以及对热液流体矿物或矿石的Ar-Ar和Rb-Sr测年,统计出胶东金矿主要形成年龄约为120Ma(Yang and Zhou, 2001; Deng et al., 2003a, b; Zhang et al., 2003; Li et al., 2006; Guo et al., 2013)。胶东脉岩群与该地区金成矿基本为同一时期的地质产物。
2 脉岩岩相学特征本次研究的6条脉岩样品包含2条石英闪长脉岩和4条闪长脉岩。样品取样均远离金矿化的地区,以避免相关热液活动的影响。2条石英闪长脉岩均取自胶北地块(LZYD-1、PDDZ-1),4条闪长脉岩取自胶北地块和苏鲁造山带(PDDZ-3、RSYZ-1、RSZT-3、RCYT-1)。该地区中酸性脉岩产状与区域断裂构造产状基本一致,受区域地质构造控制。采样脉岩均为NE 40°~50°走向,倾角20°~80°不等。脉岩侵入形态多样,包括透镜状岩墙与枝杈状岩株,宽度1~10m不等,其围岩包括花岗岩、麻粒岩、角闪岩等(图 1b)。
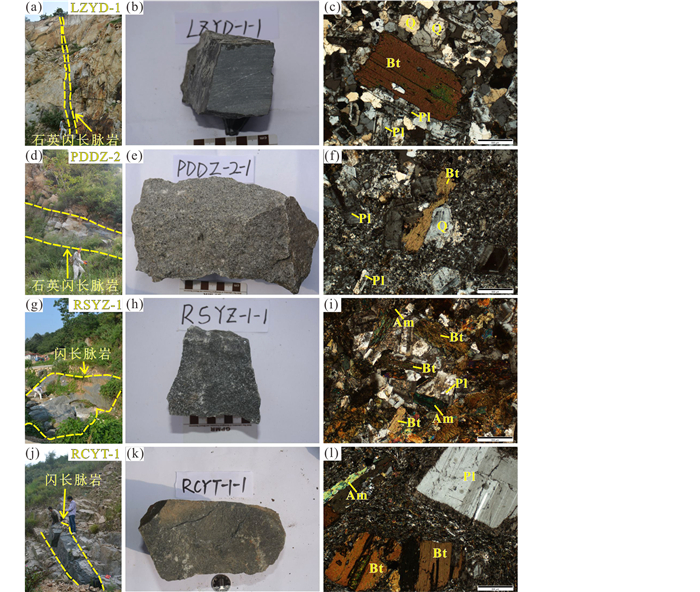
石英闪长脉岩(LZYD-1、PDDZ-1)呈灰-深灰色,细粒结构,块状构造。主要矿物组合为自形柱状斜长石(~40%),其中少量有明显环带结构;半自形粒状角闪石(15%~25%),石英(10%~15%),钾长石(~10%),黑云母(<5%)等(图 2a-f)。
|
图 2 胶东早白垩世石英闪长脉岩(a-f)和闪长脉岩(g-l)野外产状与岩相学特征图 Bt-黑云母;Pl-斜长石;Am-角闪石;Q-石英 Fig. 2 Representative field and major mineral assemblages photographs of quartz diorite dikes (a-f) and diorite dikes (g-l) in the Jiaodong Peninsula Bt-biotite; Pl-plagioclase; Am-amphibole; Q-quartz |
3条闪长脉岩(PDDZ-3、RSYZ-1、RSZT-3)呈灰色,细粒结构,块状构造。主要矿物组合为自形柱状无环带斜长石(35%~50%),半自形粒状角闪石(10%~30%),钾长石(~10%),黑云母(~5%),以及少量石英与黄铁矿等(图 2g-i)。闪长脉岩RCYT-1呈灰黑色,细粒结构,斑状构造,斑晶由较大颗粒的自形黑云母(~15%)与斜长石(~15%)组成,基质矿物主要包括斜长石(35%~40%)、角闪石(10%~20%)、黑云母(10%~15%),以及少量石英与黄铁矿(图 2j-l)。
3 分析方法矿物电子探针分析在中国地质大学(北京)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室电子探针实验室完成。电子探针分析仪器为EMPA- 1600,激发电压为15kV,激发电流为10A,束斑直径为1μm,标准样品采用美国SPI公司52种标准矿物测试。电子探针使用60倍放大倍数采集BSE图像。分析过程中Si和Mg元素的标样为橄榄石,Ti元素的标样为金红石,Al和K元素标样为钠长石,Fe元素的标样为石榴石,Mg元素的标样为红宝石,Ca元素的标样为透辉石,Cr元素的标样为铬铁矿,测试误差小于1%。
矿物的微量元素分析在合肥工业大学矿床勘探中心(ODEC)原位矿物地球化学实验室中完成。分析采用激光烧蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(LA-ICP-MS)对抛光后的薄片进行测定。激光烧蚀系统中的信号平滑装置以氦气作为运载气体,补充气体氩气通过T形接头与载气混合(宁思远等, 2017; 汪方跃等, 2017)。每次分析先进行20s空白测试,之后在8Hz、能量2J/cm2的条件下,以直径为35mm的均匀光斑分析40s。以磁铁矿和赤铁矿为标样测试同位素包括:25Mg, 27Al, 28Si, 43(44)Ca, 45Sc, 49Ti, 51V, 53Cr, 55Mn, 57Fe, 59Co, 60Ni, 65Cu, 66Zn, 71Ga, 74Ge, 88Sr, 89Y, 90Zr, 93Nb, 95Mo, 97Mo, 111Cd, 115In, 118Sn, 137Ba, 178Hf, 181Ta, 182W, 209Bi,同时测量钙和钼的多种同位素,以检验数据的一致性。以钛铁矿为标样测试同位素包括:7Li, 11B, 23Na, 25Mg, 27Al, 29Si, 42Ca, 45Sc, 49Ti, 51V, 53Cr, 55Mn, 57Fe, 59Co, 60Ni, 65Cu, 66Zn, 71Ga, 74Ge, 85Rb, 88Sr, 89Y, 90Zr, 93Nb, 97Mo, 109Ag, 111Cd, 118Sn, 121Sb, 133Cs, 137Ba, 139La, 140Ce, 141Pr, 146Nd, 147Sm, 153Eu, 157Gd, 159Tb, 163Dy, 165Ho, 166Er, 169Tm, 172Yb, 175Lu, 178Hf, 181Ta, 182W, 208Pb, 209Bi, 232Th, 238U。之后以GSE-1G、GSC-1G、BCR-2G以及NIST612为外标绘制校准曲线。矿物微量元素含量利用多个参考玻璃(GSE-1G、GSC-1G和NIST612为外标)作为多外标无内标的方法进行定量计算(Liu et al., 2008),BCR-2G作为质量品控标准玻璃中元素含量的推荐值参考GeoReM数据库(http://georem.mpch-mainz.gwdg.de/)。硅酸盐矿物和氧化物矿物的微量元素成分根据多个参考材料进行校准,整体分析误差为5%~10%。
4 矿物地球化学特征 4.1 黑云母本次研究脉岩中黑云母矿物主量元素分析数据如表 1所示,原位微量元素分析数据如表 2所示。
|
|
表 1 胶东石英闪长脉岩与闪长脉岩中斜长石和黑云母矿物主量元素表(wt%) Table 1 Major element compositions (wt%) of biotite and plagioclase from quartz diorite and diorite dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula |
|
|
表 2 胶东石英闪长脉岩与闪长脉岩中斜长石黑云母矿物微量元素表(单位:×10-6) Table 2 Trace element compositions (×10-6) of biotite and plagioclase from quartz diorite and diorite dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula |
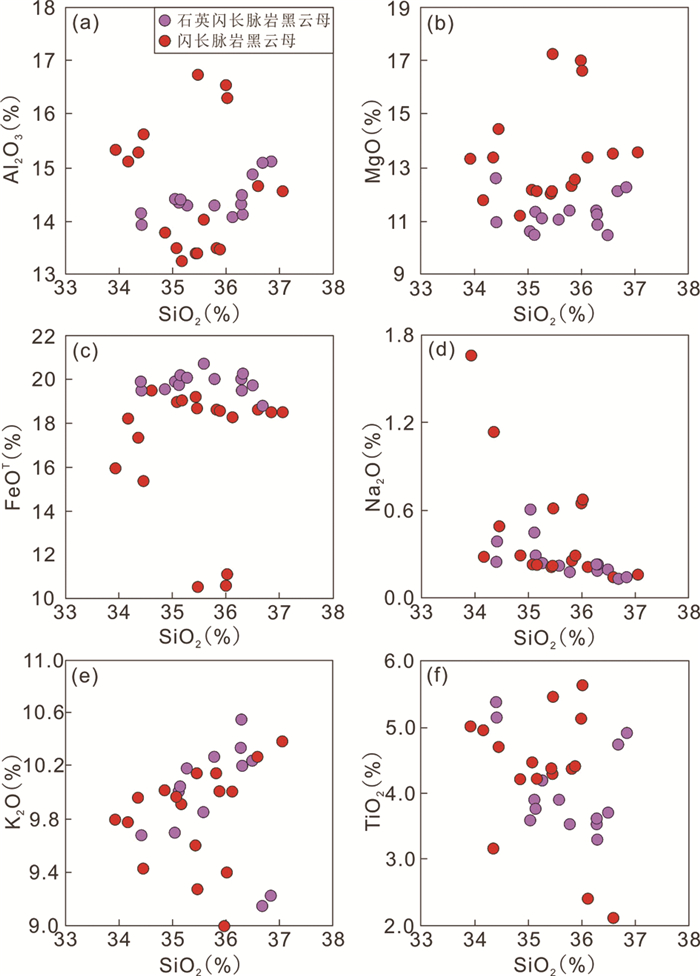
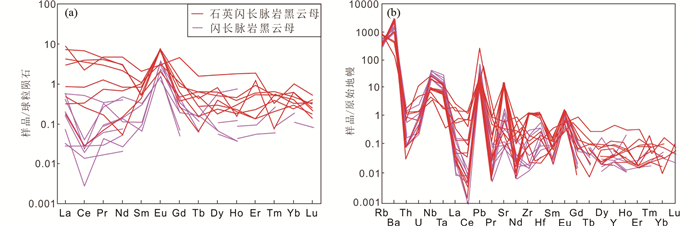
闪长脉岩中的黑云母以高MgO含量(11.2%~17.3%)和低FeOT含量(10.5%~19.6%)为特征,CaO含量在检测线以下,其余主量元素含量变化范围相对较大:Al2O3(13.2%~16.7%)、K2O(8.95%~10.4%)、TiO2(1.82%~5.64%)及SiO2(33.9%~37.1%)(图 3)。根据谢应雯和张玉泉(1987)提出的黑云母MF值分类方法,以22个氧离子为标准计算黑云母阳离子数,MF=2Mg/(Mg+Fe2++Mn),为镁黑云母与富镁黑云母(MF:1.00~1.49)。闪长脉岩中的黑云母矿物有一定程度的LREE含量浮动与Eu正异常,并存在明显的LILE富集与HFSE亏损(图 4)。
|
图 3 胶东石英闪长脉岩和闪长脉岩中黑云母矿物SiO2与主量元素含量对比图 Fig. 3 The plots of SiO2 against selected major element contents of biotite from quartz diorite and diorite dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula |
|
图 4 黑云母球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 4 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized immobile trace element patterns (b) of biotite from quartz diorite and diorite dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
石英闪长脉岩中的黑云母则具有较低的MgO含量(10.4%~12.6%)与较高的FeOT含量(18.5%~20.7%),且Al2O3(13.9%~15.1%)、K2O(9.14%~10.6%)、TiO2(3.30%~5.39%)及SiO2(34.4%~36.8%)含量变化范围相对狭小,但CaO含量同样在检测线以下(图 3)。石英闪长脉岩中的黑云母为富铁黑云母与镁黑云母(MF:0.96~1.08)。微量元素分析结果与闪长脉岩类似,有一定程度的LREE含量浮动与明显的Eu正异常,并存在LILE富集与HFSE亏损现象(图 4)。
4.2 斜长石脉岩中斜长石矿物主量元素数据如表 1所示,原位微量元素数据如表 2所示。
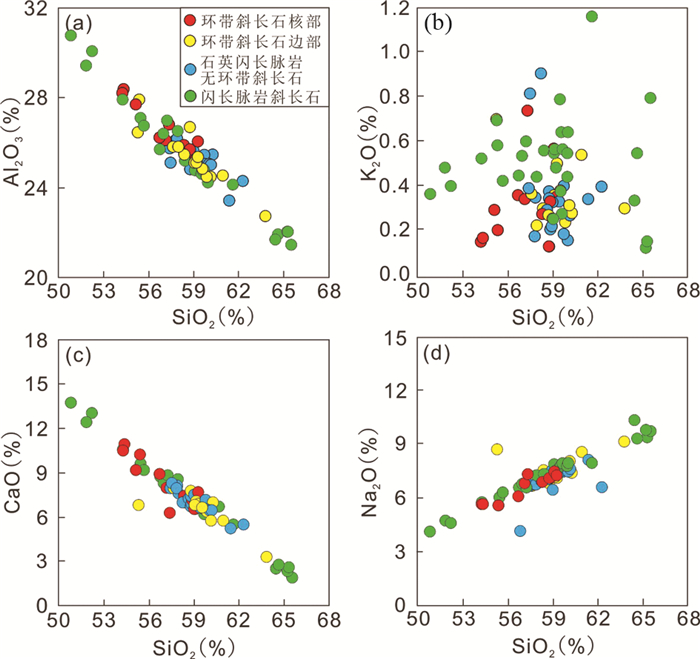
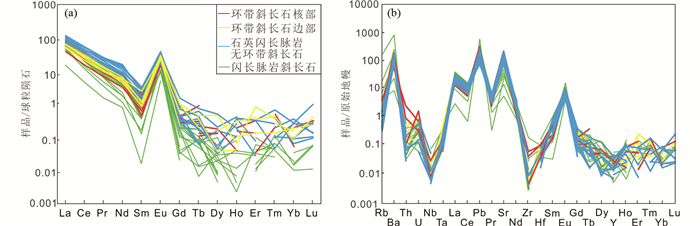
闪长脉岩中的斜长石多为半自形细粒结构,单矿物成分相对均一,无环带现象。整体主量元素含量变化范围相对较大:Al2O3(21.4%~30.8%)、Na2O(3.46%~10.1%)、CaO(1.94%~13.8%)及SiO2(50.8%~65.5%)(图 5)。斜长石牌号为10~69,主要为中长石(60%),还有少量钠长石(23%)和拉长石(16%)。微量元素方面,闪长脉岩的斜长石呈现出明显的LREE富集与HREE亏损,以及Eu正异常,并存在LILE富集与HFSE亏损现象(图 6)。
|
图 5 胶东石英闪长脉岩和闪长脉岩中斜长石矿物SiO2与主量元素含量对比图 Fig. 5 The plots of SiO2 against selected major element contents of plagioclase from quartz diorite and diorite dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula |
|
图 6 斜长石球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and (b) primitive mantle-normalized immobile trace element patterns of plagioclase from quartz diorite and diorite dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
石英闪长脉岩中斜长石粒度相对较大,且部分斜长石矿物出现明显的环带结构。整体上,石英闪长脉岩中的斜长石Al2O3(22.7%~28.4%)、Na2O(5.58%~9.16%)、CaO(3.33%~11.0%)及SiO2(54.3%~63.8%)的含量变化范围相比较于闪长脉岩中更为狭小(图 5)。石英闪长脉岩中的斜长石牌号为17~52,绝大多数都是中长石(90%)。微量元素方面,与闪长脉岩的斜长石表现出相同的稀土元素特征,并存在LILE富集与HFSE亏损现象(图 6)。
5 讨论 5.1 岩石成因 5.1.1 石英闪长脉岩早期研究表明,胶东石英闪长脉岩具有埃达克质特征,即较高的全岩SiO2和Al2O3含量,高Sr/Y(76~149)与La/Yb(41~91)比值,指示其源于华北克拉通东部古老的加厚下地壳部分熔融(Liu et al., 2018)。然而,该地区石英闪长脉岩较高的Mg#值(50~60,高于纯地壳熔融物)和Cr(30.4×10-6~76.6×10-6)和Ni(6.03×10-6~45.5×10-6)含量具有一定的地幔特征,且与源自华北克拉通加厚下地壳的玲珑花岗岩(160~144Ma)相比,石英闪长脉岩具有较低的(87Sr/86Sr)i值和较高的εNd(t)、εHf(t)值,上述证据表明其母岩浆并非单一来源,很可能涉及一定的幔源物质(Liang et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2018)。本次研究通过矿物学特征和矿物微区地球化学特征,对石英闪长脉岩母岩浆演化过程进行详细解释,并对流体混入、构造扰动,扩散作用等多种可能影响石英闪长脉岩成因的因素进行讨论,进而更加准确地解释胶东石英闪长脉岩的成因。
本次研究石英闪长脉岩中黑云母的CaO含量均低于检测线,说明其结晶后基本没有受到大气流体循环或岩石后期蚀变(如绿泥石化或绢云母化)的改造(Kumar and Pathak, 2010; 王刚等, 2014)。与此同时,石英闪长脉岩中斜长石矿物以良好线性变化特征从高钙基性斜长石向高钠酸性斜长石转变(图 5),说明斜长石均来自母岩浆的分离结晶,结晶后并未遭受后期改造(陈斌等, 2006)。因此,石英闪长脉岩中黑云母和斜长石矿物形态特征及微区地球化学变化均可以指示母岩浆的整体演化过程。
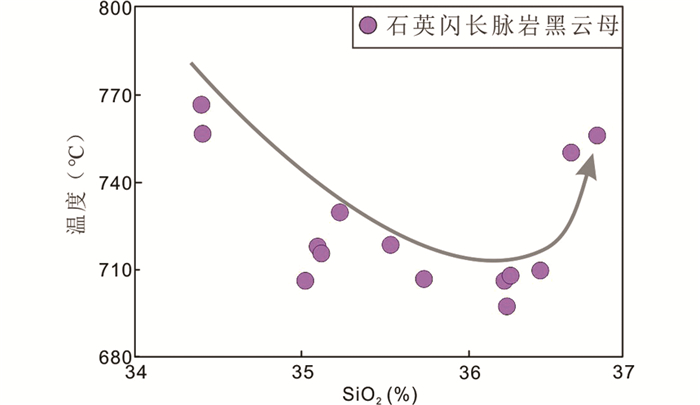
岩浆演化过程中流体混入与构造扰动是两个影响结晶矿物物质组分的重要因素(Guo et al., 2018)。Stone (2000)研究表明,黑云母中的Fe2+/(Fe2++Mg)比值范围反映该矿物形成后是否有大气流体,俯冲流体或变质流体改造,黑云母矿物未受到后期流体影响时为原生黑云母,其Fe2+/(Fe2++Mg)比值仅由母岩浆组分决定因而相对稳定,表现为例如0.575~0.599、0.320~0.368、0.349~0.430等小范围波动。本次研究胶东石英闪长脉岩中黑云母矿物具有变化范围较小的Fe2+/(Fe2++Mg)比值范围(0.4568~0.5127),符合原生黑云母特征,且黑云母矿物的生成贯穿母岩浆演化过程,因此母岩浆在岩浆演化过程中并没有明显的大气流体,俯冲流体或变质流体混入。构造作用往往会导致岩浆房温压条件大幅度改变,进而影响结晶矿物的组分(Guo et al., 2018)。黑云母结晶温压计算方法参照Henry et al. (2005)和Uchida et al. (2007),即以22个氧离子数为标准,当满足条件Ti阳离子在0.04~0.60范围内,(XMg=Mg/(Mg+Fe))在0.275~1.00范围内时,T(℃)={[ln(Ti)-a-c(XMg)3]/b}0.333,XMg=Mg/(Mg+Fe),a=-2.3594,b=4.6482×10-9,c=-1.7283;P(×100MPa)=3.03×TAl-6.53(±0.33)。通过计算,本次研究石英闪长脉岩中黑云母矿物Ti阳离子数为0.36~0.59,XMg值为0.49~0.54,均符合上述条件。计算结果表明石英闪长脉岩中的黑云母矿物结晶温度和压力分别为T=698~766℃,P=0.80~1.27kbar,该温度变化范围相对较小,且与前人对其他在封闭条件下黑云母矿物从岩浆中结晶的温度范围研究成果近似(T=629~684℃, 郭耀宇等, 2015),说明石英闪长脉岩的形成未受明显的构造影响。此外,胶东石英闪长脉岩中斜长石成分相对单一,90%属于中长石,且只有部分大颗粒斜长石具有环带结构,这表明岩浆房整体经历了一个相对稳定的结晶过程。同时,当岩浆受到构造作用影响时,会造成矿物晶体的快速结晶进而导致斜长石矿物无法与宿主熔体达到充分平衡,且容易受到岩浆房边界层成分的强烈影响而富含Fe和Mg元素(Singer et al., 1995)。本次研究石英闪长脉岩中的斜长石矿物铁镁含量均相对较低(Fe:1127×10-6~3179×10-6;Mg:10.4×10-6~117.4×10-6),且与未受构造作用影响的中酸性火成岩斜长石矿物相比较铁镁元素含量范围相近甚至更低(Fe:1460×10-6~4422×10-6;Mg:0.3×10-6~367.2×10-6;Guo et al., 2018)。综上所述,胶东石英闪长脉岩岩浆在演化过程中基本未受到大气流体,俯冲流体或变质流体混入或构造作用的影响。
胶东石英闪长脉岩中黑云母显示出较小的MF范围(0.96~1.08,平均1.00),同时具有镁黑云母和铁黑云母的特征,这两类黑云母通常指示下地壳或壳幔混合源区(谢应雯和张玉泉, 1987)。此外,通过结晶压力可计算结晶深度,采用P=ρ×g×H换算,其中ρ=2700kg/m3,g=9.8m/s2,石英闪长脉岩中黑云母矿物结晶深度为3.05~4.85km,平均深度为3.95km,指示下地壳区域。这与前人对胶东石英闪长脉岩全岩地球化学特征研究所得到的岩浆源区一致,由此推测石英闪长脉岩源区很可能为华北克拉通东部古老的加厚下地壳(Liu et al., 2018)。
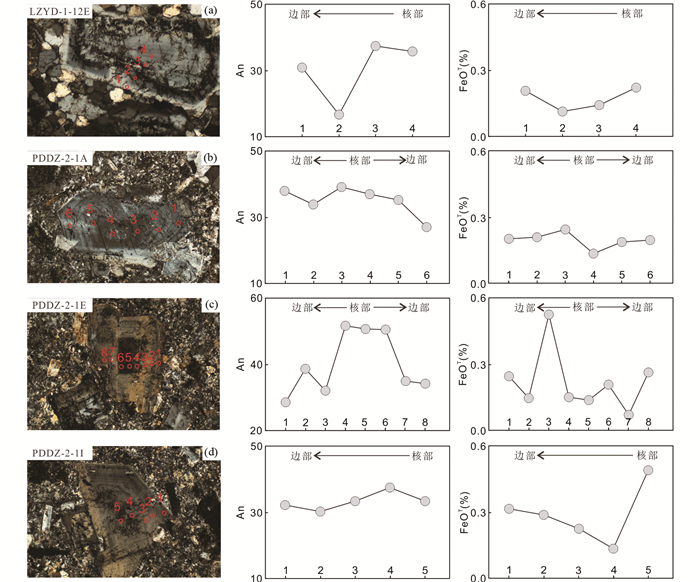
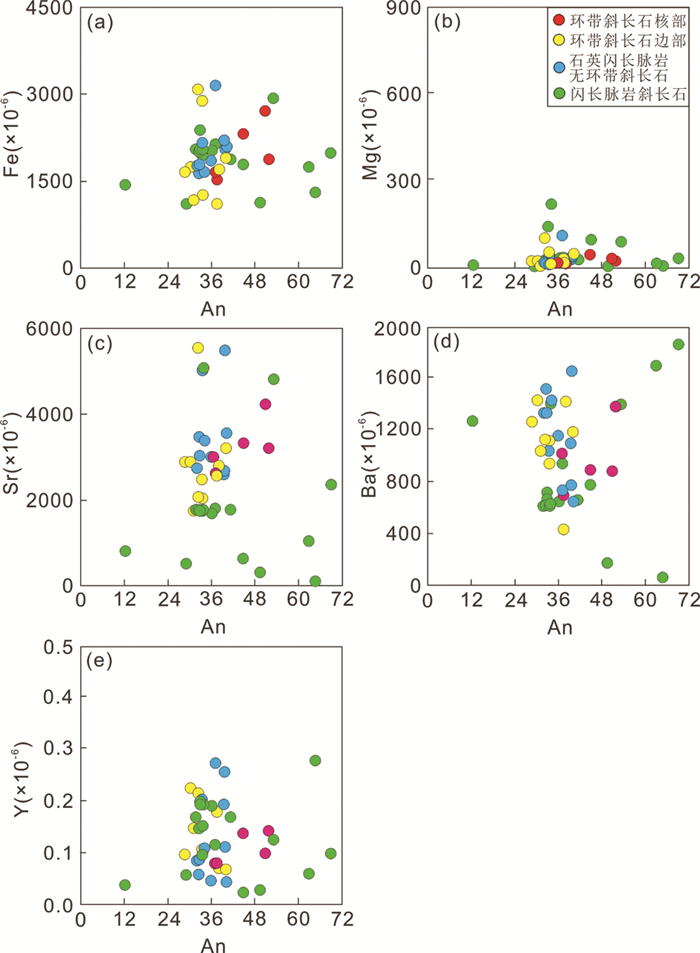
胶东石英闪长脉岩中的斜长石矿物90%属于中长石,且只有部分大颗粒斜长石具有环带结构,这表明岩浆房整体经历了一个相对稳定的结晶过程,混入的幔源岩浆含量较低(陈斌等, 2006)。斜长石环带均为正环带,核部小且富钙,边部宽且富钠,少量环带边部出现一定的富钙现象(图 7)。此外,从核部到边部Mg和Al元素含量明显降低(核部Mg=25.31×10-6~60.73×10-6,平均38.13×10-6,Al2O3=25.23%~28.41%,平均26.52%;边部Mg=10.41×10-6~47.65×10-6,平均25.04×10-6,Al2O3=22.72%~26.80%,平均25.28%),Si含量则逐渐上升(核部SiO2=54.26%~59.27%,平均57.22%;边部SiO2=55.29%~63.80%,平均59.16%),说明环带斜长石中富钙的小核很可能代表早期从基性岩浆中结晶出的斜长石残留,而边部相对富钠的斜长石则来源于晚期下地壳浆(图 5)。同时,石英闪长脉岩中其余无环带结构的斜长石Si和Al元素含量特征与环带斜长石边部近似(Al2O3=23.40%~27.76%,平均25.48%;SiO2=57.45%~62.30%,平均59.15%),说明其同样形成于岩浆演化晚期的下地壳源区(图 5),指示下地壳区域为石英闪长脉岩岩浆的主要演化区域,且岩浆房中的壳幔混合作用有限,主要发生在演化早期阶段,少量环带斜长石边部的钙含量升高现象说明后期还可能也有少量的镁铁质岩浆混入。此外,石英闪长脉岩中黑云母矿物中SiO2含量与结晶温度良好的负相关说明随着岩浆演化程度加深,早期混入的基性岩浆逐渐减少,残余岩浆中SiO2含量增高,岩浆房温度缓缓降低,最后出现一定升温,对应上述后期的少量镁铁质岩浆的二次混入(图 8)。
|
图 7 石英闪长脉岩中环带斜长石矿物镜下照片与其核部到边部An和FeOT含量变化图 Fig. 7 The photomicrograph of the zoned plagioclase phenocrysts from quartz diorite dikes in Jiaodong Peninsula with the variations of An and FeOT from core-to-rim Each row represents the composition of a single crystal as determined by EMPA |
|
图 8 石英闪长脉岩黑云母矿物SiO2与结晶温度相关图 Fig. 8 Diagram of SiO2 against crystallization temperature of biotite from quartz diorite dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula |
综上所述,胶东石英闪长脉岩源自下地壳部分熔融,并在岩浆演化早期和晚期有一定程度幔源镁铁质岩浆混入,整个过程并未受到的大气流体,俯冲流体或变质流体混入与构造作用的影响。
5.1.2 闪长脉岩前人对胶东闪长脉岩的研究发现其具有高Mg#值,高MgO、Cr、Ni含量等地幔源区特征。同时,闪长脉岩中LILE与LREE富集以及HFSE亏损的特征与阿留申岛弧玄武岩一致,而后者源自俯冲板释放流体引起的地幔楔橄榄岩部分熔融作用(Liu et al., 2017)。此外,胶东闪长脉岩具有较高的Rb/Y比与全岩(87Sr/86Sr)i值,以及较低的Nb/Zr、Th/Yb、Hf/Sm比和负εNd(t)、εHf(t)特征,这与胶东同期岛弧基性脉岩相似,也指示有俯冲板块衍生流体参与的富集岩石圈地幔源区(Ma et al., 2014; Deng et al., 2017a)。因此该区闪长脉岩很可能源自由俯冲板块流体或熔体交代所形成富集岩石圈地幔部分(Tan et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2017)。
本次研究中的胶东闪长脉岩黑云母矿物具有较高的MgO含量,较低的FeOT含量,以及检测线以下的CaO含量,说明其结晶后基本没有受到大气流体或后期变质作用(如绿泥石化和绢云母化)的影响(Kumar and Pathak, 2010; 王刚等, 2014)。闪长脉岩中斜长石矿物主量元素变化同样具有良好线性特征(图 5),说明斜长石从母岩浆分离结晶后并未遭受后期改造(陈斌等, 2006)。此外,闪长脉岩中斜长石矿物没有明显的环带结构,说明岩浆分离结晶过程中处于较为均一的状态。前人对于胶东闪长脉岩的Sr-Nd同位素分析发现其全岩(87Sr/86Sr)i值并未随着SiO2含量升高而增加,且εNd(t)与SiO2含量也无线性变化关系。且脉岩的Sr(498×10-6~967×10-6)和Ba(1093×10-6~1837×10-6)含量远高于大陆地壳平均值(Sr=325×10-6, Ba=390×10-6; Rudnick and Fountain, 1995),说明闪长脉岩岩浆在熔融演化过程中没有受到地壳污染(Liu et al., 2018)。
胶东闪长脉岩中黑云母MF值(MF:1.00~1.49,平均1.17)说明其主要为镁黑云母,指示深部地幔岩浆源区(谢应雯和张玉泉, 1987)。黑云母中的Fe2+/(Fe2++Mg)比值范围较大(0.25~0.49),说明母岩浆中结晶的黑云母矿物很可能受到了大气流体、俯冲流体或变质流体的影响(Stone, 2000)。由于源区为深部地幔且后期没有壳源岩浆混染,大气流体与变质流体影响的可能性很小,因此很可能有俯冲相关流体的参与。Pearce and Stern (2006)指出,矿物中Y与HREE元素基本不受俯冲物质改造的影响,闪长脉岩中的斜长石矿物具有大范围An值以及Fe, Mg, Sr, Ba等元素含量变化,但其Y(0.03×10-6~0.28×10-6)与HREE含量(例如:Gd:0.003×10-6~0.140×10-6;Tb:0.003×10-6~0.031×10-6)相对均一(图 6、图 9),这些特征指示闪长脉岩母岩浆的演化过程很可能有俯冲相关流体参与。由此推测,胶东地区闪长脉岩源自有俯冲相关流体参与的深部幔源区域,与前人通过全岩地球化学特征研究证实的该区闪长脉岩源自由俯冲板块流体或熔体交代所形成富集岩石圈地幔部分熔融作用的观点一致(Tan et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2017)。
|
图 9 胶东石英闪长脉岩与闪长脉岩斜长石矿物An与代表性微量元素对比图 Fig. 9 The plots of An against selected trace element contents of plagioclase from quartz diorite and diorite dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula |
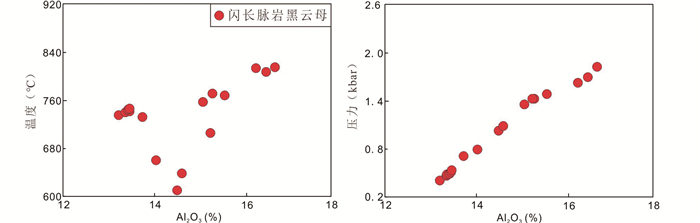
闪长脉岩斜长石中的Y与HREE含量与石英闪长脉岩环带斜长石核部元素含量(Y:0.08×10-6~0.18×10-6;Gd:0.060×10-6~0.200×10-6;Tb:0.006×10-6~0.039×10-6)近似,说明后者的富钙残留小核很可能与闪长脉岩为同一源区。同时,本次研究中闪长脉岩的斜长石矿物在微量元素含量上有明显差异(如:Fe, Mg, Sr, Ba等元素)(图 9)。斜长石中Sr(124×10-6~5089×10-6)和Ba(64×10-6~1861×10-6)元素存在明显的大范围含量变化,已有研究表明这一现象主要是由母岩浆中该矿物的分配系数或熔体成分改变引起(Blundy and Wood, 1991; Bédard, 2006)。斜长石矿物中元素分配系数与其An值具有直接联系,然而本次研究中胶东闪长脉岩中斜长石的Sr和Ba元素含量与An值之间基本不存在线性关系(图 9),说明分配系数的变化不是造成斜长石微量元素的差异的主要因素(Blundy and Wood, 1994)。由此推测,闪长脉岩中斜长石Sr和Ba元素含量差异很可能与演化过程中母岩浆成分变化相关。贯穿整个岩浆演化过程的黑云母矿物中Si与Al含量呈现良好的线性变化关系,可以代表母岩浆演化过程中的成分改变。通过计算,闪长脉岩中黑云母矿物结晶温压条件为T=611~816℃,P=0.47~1.82kbar,结晶温度与黑云母Al含量有一定正相关关系,同时结晶压力与Al含量呈高度正相关(图 10)。由此推测胶东地区闪长脉岩岩浆在深部地幔源区形成后,母岩浆因不断上涌减压结晶成岩导致不同阶段结晶的黑云母与斜长石矿物存在较大组分差异,同时少量幔源闪长脉岩岩浆上涌至下地壳区域参与了石英闪长脉岩的形成,环带斜长石中的小核为闪长脉岩岩浆中的斜长石残留物。
|
图 10 闪长脉岩黑云母矿物Al2O3与结晶温度相关性图及与结晶压力相关性图 Fig. 10 Diagrams of Al2O3 against crystallization temperature and against crystallization pressure of biotite from diorite dikes in Jiaodong Peninsula |
综上所述,胶东闪长脉岩源自俯冲的板片来源的流体或沉积物混入所形成富集岩石圈地幔源区,闪长脉岩岩浆形成后且未受到壳源物质的混染,在上涌过程中经历减压结晶成岩,同时少量幔源闪长脉岩岩浆上涌至下地壳区域参与形成石英闪长脉岩,环带斜长石中的小核为闪长脉岩岩浆斜长石残留物。
5.2 地质构造背景大量研究已经证明,华北克拉通东部在晚中生代处于伸展环境中,其岩石圈经历了大规模减薄事件,并伴有大量的岩浆活动(Menzies et al., 1993; Deng et al., 2003a; Yang et al., 2007)。胶东早白垩世石英闪长脉岩与闪长脉岩岩浆也在此背景下形成。但是,该区岩石圈减薄的机制有多种观点。本次研究胶东脉岩中造岩矿物微区地球化学特征发现,其地幔源区有明显的洋壳俯冲相关流体的加入,这与Deng et al. (2017b)提出的古太平洋板回撤导致的热-机械侵蚀模型相一致。约178Ma以来,华北克拉通最东部经历古太平洋板块低角度向西俯冲交代(Maruyama et al., 1997; Li and Li, 2007; Dilek and Sandvol, 2009; Mao et al., 2011)。自160Ma起,古太平洋板块改变了俯冲方向,并随后开始板块回撤(Wu et al., 2007; Jiang et al., 2010; Mao et al., 2011; Ma et al., 2014),这一过程导致了华北克拉通东部强烈的构造活动和区域性变形(Wu et al., 2007; Jiang et al., 2010; Mao et al., 2011),最终导致软流圈地幔上升,使得岩石圈地幔熔融-减薄(Ma et al., 2014; Deng et al., 2017a)。胶东半岛深部软流圈地幔侵蚀加热导致了胶东半岛富集岩石圈地幔的部分熔融,形成早白垩世闪长脉岩。随后,部分幔源镁铁质岩浆持续上涌加热导致加厚的古下地壳部分熔融形成石英闪长脉岩。
6 结论本文利用电子探针(EMPA)与激光剥蚀电感藕合等离子质谱(LA-ICP-MS)技术分析了胶东早白垩世中-酸性脉岩中主要造岩矿物(斜长石和黑云母)的主、微量元素组成;并结合岩石地球化学特征,对胶东中生代中-酸性脉岩的岩浆源区和岩浆演化进行了研究探讨。主要结论包括:
(1) 本次研究脉岩的黑云母与斜长石矿物均没有受到大气流体循环或岩石后期蚀变(如绿泥石化或绢云母化)的改造,为原生矿物。
(2) 本次研究中胶东石英闪长脉岩源自加厚下地壳部分熔融,并在岩浆演化早期和晚期有一定程度幔源镁铁质岩浆混入,整个过程并未受到的大气流体,俯冲流体或变质流体混入与构造作用的影响。
(3) 本次研究中胶东闪长脉岩源自俯冲板片来源的流体或沉积物混入所形成富集岩石圈地幔源区,闪长脉岩岩浆形成后且未受到壳源物质的混染,在上涌过程中经历减压结晶成岩,同时少量幔源闪长脉岩岩浆上涌至下地壳区域参与形成石英闪长脉岩,环带斜长石中的小核为闪长脉岩岩浆斜长石残留物。
(4) 胶东早白垩世中-酸性脉岩形成于古太平洋板俯冲-回撤导致的热-机械侵蚀诱发岩石圈地幔减薄背景下,软流圈地幔上涌加热导致了胶东富集岩石圈地幔的部分熔融,形成了地幔熔体。这些幔源熔体经历分离结晶形成早白垩世闪长脉岩。随后,部分幔源镁铁质岩浆持续上涌加热导致加厚的古下地壳部分熔融形成石英闪长脉岩。
致谢 感谢邓军教授在工作中的指导,感谢团队老师与同学们给予的帮助,感谢两位审稿人的宝贵建议!谨以此文恭祝翟裕生院士九十大寿,祝您日月昌明,松鹤长春。
Bédard JH. 2006. Trace element partitioning in plagioclase feldspar. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(14): 3717-3742 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2006.05.003 |
Blundy J and Wood B. 1994. Prediction of crystal-melt partition coefficients from elastic moduli. Nature, 372(6505): 452-454 DOI:10.1038/372452a0 |
Blundy JD and Wood BJ. 1991. Crystal-chemical controls on the partitioning of Sr and Ba between plagioclase feldspar, silicate melts, and hydrothermal solutions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 55(1): 193-209 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(91)90411-W |
Cai YC, Fan HR, Santosh M, Liu X, Hu FF, Yang KF, Lan TG, Yang YH and Liu YS. 2013. Evolution of the lithospheric mantle beneath the southeastern North China Craton:Constraints from mafic dikes in the Jiaobei terrain. Gondwana Research, 24(2): 601-621 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.11.013 |
Cai YC, Fan HR, Santosh M, Hu FF, Yang KF and Hu ZC. 2015. Subduction-related metasomatism of the lithospheric mantle beneath the southeastern North China Craton:Evidence from mafic to intermediate dykes in the northern Sulu orogen. Tectonophysics, 659: 137-151 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2015.07.037 |
Chen B, Liu CQ and Tian W. 2006. Magma-mixing between mantle-and crustal-derived melts in the process of Mesozoic magmatism, Taihangshan:Constraints from petrology and geochemistry. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(2): 140-147 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Chen JF, Xie Z, Li HM, Zhang XD, Zhou TX, Park YS, Ahn KS, Chen DG and Zhang X. 2003. U-Pb zircon ages for a collision-related K-rich complex at Shidao in the Sulu ultrahigh pressure terrane, China. Geochemical Journal, 37: 35-46 DOI:10.2343/geochemj.37.35 |
Deng J, Yang LQ, Sun ZS, Wang JP, Wang QF, Xin HB and Li XJ. 2003a. A metallogenic model of gold deposits of the Jiaodong granite-greenstone belt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(4): 537-546 |
Deng J, Liu W, Sun ZS, Wang JP, Wang QF, Zhang QX and Wei YG. 2003b. Evidence of mantle-rooted fluids and multi-level circulation ore-forming dynamics:A case study from the Xiadian gold deposit, Shandong province, China. Science in China (Series D), 46(Suppl): 123-134 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ and Santosh M. 2014. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China. Earth-Science Review, 138: 268-299 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.05.015 |
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF and Pan RG. 2015. Origin of the Jiaodong-type Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Constraints from fluid inclusion and C-D-O-S-Sr isotope compositions. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 674-686 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.04.018 |
Deng J and Wang QF. 2016. Gold mineralization in China:Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Research, 36: 219-274 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.003 |
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF, Dilek Y and Liang YY. 2017a. Isotopic characterization and petrogenetic modeling of Early Cretaceous mafic diking-Lithospheric extension in the North China Craton, eastern Asia. GSA Bulletin, 129(11-12): 1379-1407 DOI:10.1130/B31609.1 |
Deng J, Wang QF and Li GJ. 2017b. Tectonic evolution, superimposed orogeny, and composite metallogenic system in China. Gondwana Research, 50: 216-266 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.02.005 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Santosh M and Yao EY. 2018. Crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the south-eastern North China Craton. Earth-Science Reviews, 182: 251-272 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.001 |
Dilek Y and Sandvol E. 2009. Seismic structure, crustal architecture and tectonic evolution of the Anatolian-African plate boundary and the Cenozoic orogenic belts in the eastern Mediterranean region. In:Murphy JB, Keppie JD and Hynes AJ (eds.). Ancient Orogens and Modern Analogues. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 327(1): 127-160 |
Ernst RE, Head JW, Parfitt E, Grosfils E and Wilson L. 1995. Giant radiating dyke swarms on Earth and Venus. Earth-Science Reviews, 39(1-2): 1-58 DOI:10.1016/0012-8252(95)00017-5 |
Goldfarb RJ and Santosh M. 2014. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits:Are they unique. Geoscience Frontiers, 5(2): 139-153 |
Goldfarb RJ, Taylor RD, Collins GS, Goryachev NA and Orlandini OF. 2014. Phanerozoic continental growth and gold metallogeny of Asia. Gondwana Research, 25(1): 48-102 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.03.002 |
Goss SC, Wilde SA, Wu FY and Yang JH. 2010. The age, isotopic signature and significance of the youngest Mesozoic granitoids in the Jiaodong Terrane, Shandong Province, North China Craton. Lithos, 120(3-4): 309-326 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.019 |
Guo F, Fan WM, Wang YJ and Zhang M. 2004. Origin of early Cretaceous calc-alkaline lamprophyres from the Sulu orogen in eastern China:Implications for enrichment processes beneath continental collisional belt. Lithos, 78(3): 291-305 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.05.001 |
Guo F, Fan WM, Li CW, Wang CY, Li HX, Zhao L and Li JY. 2014. Hf-Nd-O isotopic evidence for melting of recycled sediments beneath the Sulu Orogen, North China. Chemical Geology, 381: 243-258 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.04.028 |
Guo K, Zhai SK, Wang XY, Yu ZH, Lai ZQ, Chen S, Song ZJ, Ma Y, Ch en, Z X, Li XH and Zeng ZG. 2018. The dynamics of the southern Okinawa Trough magmatic system:New insights from the microanalysis of the An contents, trace element concentrations and Sr isotopic compositions of plagioclase hosted in basalts and silicic rocks. Chemical Geology, 497: 146-161 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.09.002 |
Guo P, Santosh M and Li SR. 2013. Geodynamics of gold metallogeny in the Shandong Province, NE China:An integrated geological, geophysical and geochemical perspective. Gondwana Research, 24(3-4): 1172-1202 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.02.004 |
Guo YY, He WY, Li ZC, Ji XZ, Han Y, Fang WK and Yin C. 2015. Petrogenesis of Ge'erkuohe porphyry granitoid, western Qinling:Constraints from mineral chemical characteristics of biotites. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(11): 3380-3390 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Henry DJ, Guidotti CV and Thomson JA. 2005. The Ti-saturation surface for low-to-medium pressure metapelitic biotites:Implications for geothermometry and Ti-substitution mechanisms. American Mineralogist, 90(2-3): 316-328 DOI:10.2138/am.2005.1498 |
Hou GT, Santosh M, Qian XL, Lister GS and Li JH. 2008. Configuration of the Late Paleoproterozoic supercontinent Columbia:Insights from radiating mafic dyke swarms. Gondwana Research, 14(3): 395-409 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2008.01.010 |
Jiang YH, Jiang SY, Ling HF and Ni P. 2010. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Late Jurassic shoshonitic lamprophyre dikes from the Liaodong Peninsula, NE China. Mineralogy and Petrology, 100(3-4): 127-151 DOI:10.1007/s00710-010-0124-8 |
Kumar S and Pathak M. 2010. Mineralogy and geochemistry of biotites from Proterozoic granitoids of western Arunachal Himalaya:Evidence of bimodal granitogeny and tectonic affinity. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 75(5): 715-730 DOI:10.1007/s12594-010-0058-0 |
Li JW, Vasconcelos P, Zhou MF, Zhou XF and Ma CQ. 2006. Geochronology of the Pengjiakuang and Rushan gold deposits, eastern Jiaodong Gold Province, northeastern China:Implications for regional mineralization and geodynamic setting. Economic Geology, 101(5): 1023-1038 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.101.5.1023 |
Li L, Li SR, Santosh M, Li Q, Gu Y, Lü WJ, Zhang HF, Shen JF and Zhao GC. 2016. Dyke swarms and their role in the genesis of world-class gold deposits:Insights from the Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 130: 2-22 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.06.015 |
Li ZX and Li XH. 2007. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China:A flat-slab subduction model. Geology, 35(2): 179-182 DOI:10.1130/G23193A.1 |
Liang YY, Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF, Qin C, Li Y, Yang Y, Zhou M and Jiang JY. 2018. Major and trace element, and Sr isotope compositions of clinopyroxene phenocrysts in mafic dykes on Jiaodong Peninsula, southeastern North China Craton:Insights into magma mixing and source metasomatism. Lithos, 302-303: 480-495 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2018.01.031 |
Liu S, Hu RZ, Gao S, Feng CX, Yu BB, Feng GY, Qi YQ, Wang T and Coulson IM. 2009. Petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic mafic dykes in the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern North China Craton and implications for the foundering of lower crust. Lithos, 113(3-4): 621-639 |
Liu XF, Wang QF, Zhang QZ, Yang SJ, Zhang Y, Liang YY and Qing C. 2017. Transformation from Permian to Quaternary bauxite in southwestern South China Block driven by superimposed orogeny:A case study from Sanhe ore deposit. Ore Geology Reviews, 90: 998-1017 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.12.027 |
Liu XF, Deng J, Liang YY, Wang QF, Pan RG, Qing C and Yang Y. 2018. Petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous intermediate-felsic dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula, south-eastern North China Craton:Constraints from geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes. Gondwana Research, 60: 69-93 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2018.04.005 |
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Gao S, Günther D, Xu J, Gao CG and Chen HH. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34-43 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 |
Ma L, Jiang SY, Dai BZ, Jiang YH, Hou ML, Pu W and Xu B. 2013. Multiple sources for the origin of Late Jurassic Linglong adakitic granite in the Shandong Peninsula, eastern China:Zircon U-Pb geochronological, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence. Lithos, 162-163: 251-263 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.01.009 |
Ma L, Jiang SY, Hofmann AW, Dai BZ, Hou ML, Zhao KD, Chen LH, Li WJ and Jiang HY. 2014. Lithospheric and asthenospheric sources of lamprophyres in the Jiaodong Peninsula:A consequence of rapid lithospheric thinning beneath the North China Craton. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 124: 250-271 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2013.09.035 |
Ma L, Jiang SY, Hofman AW, Xu YG, Dai BZ and Hou ML. 2016. Rapid lithospheric thinning of the North China Craton:New evidence from cretaceous mafic dikes in the Jiaodong Peninsula. Chemical Geology, 432: 1-15 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.03.027 |
Mao JW, Pirajno F and Cook N. 2011. Mesozoic metallogeny in East China and corresponding geodynamic settings:An introduction to the special issue. Ore Geology Reviews, 43(1): 1-7 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.09.003 |
Maruyama S, Isozaki Y, Kimura G and Terabayashi M. 1997. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands:Plate tectonic synthesis from 750Ma to the present. The Island Arc, 6(1): 121-142 DOI:10.1111/iar.1997.6.issue-1 |
Menzies MA, Fan WM and Zhang M. 1993. Palaeozoic and Cenozoic lithoprobes and the loss of >120km of Archaean lithosphere, Sino-Korean craton, China. In:Prichard HM, Harris NBW and Neary CR (eds.). Magmatic Processes and Plate Tectonics. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 76(1): 71-81 |
Ning SY, Wang FY, Xue WD and Zhou TF. 2017. Geochemistry of the Baoshan pluton in the Tongling region of the Lower Yangtze River Belt. Geochimica, 46(5): 397-412 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Pearce JA and Stern RJ. 2006. Origin of back-arc basin magmas:Trace element and isotope perspectives. In:Christie DM, Fisher CR, Lee SM and Givens S (eds.). Back-Arc Spreading Systems:Geological, Biological, Chemical, and Physical Interactions. Washington, DC:American Geophysical Union, 166: 63-86 DOI:10.1029/GM166 |
Rudnick RL and Fountain DM. 1995. Nature and Composition of the continental crust:A lower crustal perspective. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(3): 267-309 DOI:10.1029/95RG01302 |
Santosh M and Pirajno F. 2015. The Jiaodong-type gold deposits:Introduction. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 565-567 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.09.018 |
Singer BS, Dungan MA and Layne GD. 1995. Textures and Sr, Ba, Mg, Fe, K and Ti compositional profiles in volcanic plagioclase:Clues to the dynamics of calc-alkaline magma chambers. American Mineralogist, 80(7-8): 776-798 DOI:10.2138/am-1995-7-815 |
Stone D. 2000. Temperature and pressure variations in suites of Archean felsic plutonic rocks, Berens river area, northwest superior province, Ontario, Canada. The Canadian Mineralogist, 38(2): 455-470 DOI:10.2113/gscanmin.38.2.455 |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes. In:Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345 DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 |
Sun WD, Ding X. Hu YH and Li XH. 2007. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the west Pacific. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 262(3-4): 533-542 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.08.021 |
Tan J, Wei JH, Li YH, Tan WJ, Guo DZ and Yang CF. 2007. Geochemical characteristics of Late Mesozoic dikes, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China Craton:Petrogenesis and geodynamic setting. International Geology Review, 49(10): 931-946 DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.49.10.931 |
Tan J, Wei JH, Guo LL, Zhang KQ, Yao CL, Lu JP and Li HM. 2008. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and phenocryst EPMA of dikes, Guocheng, Jiaodong Peninsula:Implications for North China Craton lithosphere evolution. Science in China (Series D), 51: 1483-1500 |
Uchida E, Endo S and Makino M. 2007. Relationship between solidification depth of granitic rocks and formation of hydrothermal ore deposits. Resource Geology, 57(1): 47-56 DOI:10.1111/rge.2007.57.issue-1 |
Wang CM, Deng J, Santosh M, Carranza EJM, Gong QJ, Guo CY, Xia R and Lai XR. 2015. Timing, tectonic implications and genesis of gold mineralization in the Xincheng gold deposit, China:C-H-O isotopes, pyrite Rb-Sr and zircon fission track thermochronometry. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 659-673 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.04.022 |
Wang CM, Lu YJ, He XY, Wang QH and Zhang J. 2016a. The Paleoproterozoic diorite dykes in the southern margin of the North China Craton:Insight into rift-related magmatism. Precambrian Research, 277: 26-46 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2016.02.009 |
Wang FY, Ge C, Ning SY, Nie LQ, Zhong GX and White NC. 2017. A new approach to LA-ICP-MS mapping and application in geology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(11): 3422-3436 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang G, Wang ZQ, Zhang YL and Wang KM. 2014. Mineral chemistry characteristics of biotite in trachyte from Ziyang area in North Daba Mountains and its genetic significance. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 34(3): 343-350 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang QF, Deng J, Liu XF, Zhao R and Cai SH. 2016b. Provenance of late carboniferous bauxite deposits in the North China Craton:New constraints on marginal arc construction and accretion processes. Gondwana Research, 38: 86-98 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.015 |
Wu FY, Yang JH, Lo CH, Wilde SA, Sun DY and Jahn BM. 2007. The Heilongjiang group:A Jurassic accretionary complex in the Jiamusi Massif at the western Pacific margin of northeastern China. The Island Arc, 16(1): 156-172 DOI:10.1111/iar.2007.16.issue-1 |
Xie YW and Zhang YQ. 1987. Typomorphic peculiarities of biotites from different genetic types of granite in the Hengduanshan region. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 7(3): 245-254 (in Chinese) |
Yang JH and Zhou XH. 2001. Rb-Sr, Sm-Nd, and Pb isotope systematics of pyrite:Implications for the age and genesis of lode gold deposits. Geology, 29(8): 711-714 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0711:RSSNAP>2.0.CO;2 |
Yang JH, Chung SL, Zhai MG and Zhou XH. 2004. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of mafic dikes from the Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Evidence for vein-plus-peridotite melting in the lithospheric mantle. Lithos, 73(3-4): 145-160 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2003.12.003 |
Yang JH, Wu FY, Chung SL, Lo CH, Wilde SA and Davis GA. 2007. Rapid exhumation and cooling of the Liaonan metamorphic core complex:Inferences from 40Ar/39Ar thermochronology and implications for Late Mesozoic extension in the eastern North China Craton. GSA Bulletin, 119(11-12): 1405-1414 DOI:10.1130/B26085.1 |
Yang KF, Fan HR, Santosh M, Hu FF, Wilde SA, Lan TG, Lu LN and Liu YS. 2012. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust:Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton. Lithos, 146-147: 112-127 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.035 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Zhang L, Guo LN, Song MC and Zheng XL. 2014. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2447-2467 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Guo LN, Wang ZL, Li XZ and Li JL. 2016a. Origin and evolution of ore fluid, and gold-deposition processes at the giant Taishang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 72: 585-602 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.08.021 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Guo LN, Li RH, Groves DI, Danyushevsky LV, Zhang C, Zheng XL and Zhao H. 2016b. Relationships between gold and pyrite at the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Implications for gold source and deposition in a brittle epizonal environment. Economic Geology, 111(1): 105-126 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.111.1.105 |
Yang QY, Santosh M, Shen JF and Li SR. 2014. Juvenile vs. recycled crust in NE China:Zircon U-Pb geochronology, Hf isotope and an integrated model for Mesozoic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula. Gondwana Research, 25(4): 1445-1468 |
Yang ZM, Lu YJ, Hou ZQ and Chang ZS. 2015. High-Mg diorite from Qulong in southern Tibet:Implications for the genesis of adakite-intrusions and associated porphyry Cu deposits in collisional orogens. Journal of Petrology, 56(2): 227-254 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egu076 |
Ye K, Cong BL and Ye DN. 2000. The possible subduction of continental material to depths greater than 200km. Nature, 407(6805): 734-736 DOI:10.1038/35037566 |
Zhai MG and Santosh M. 2013. Metallogeny of the North China Craton:Link with secular changes in the evolving Earth. Gondwana Research, 24(1): 275-297 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.02.007 |
Zhang HF. 2012. Destruction of ancient lower crust through magma underplating beneath Jiaodong Peninsula, North China Craton:U-Pb and Hf isotopic evidence from granulite xenoliths. Gondwana Research, 21(1): 281-292 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.05.013 |
Zhang J, Zhao ZF, Zheng YF and Dai MN. 2010. Postcollisional magmatism:Geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids in the Sulu orogen, China. Lithos, 119(3-4): 512-536 |
Zhang XO, Cawood PA, Wilde SA, Liu RQ, Song HL, Li W and Snee LW. 2003. Geology and timing of mineralization at the Cangshang gold deposit, north-western Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Mineralium Deposita, 38(2): 141-153 DOI:10.1007/s00126-002-0290-7 |
Zhao GC and Zhai MG. 2013. Lithotectonic elements of Precambrian basement in the North China Craton:Review and tectonic implications. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1207-1240 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.08.016 |
Zhao M, Yang SY, Zuo RG, Zhao KD, Jiang YH, Ling HF and Chen PR. 2015. Magmatic evolution characteristics of Xiangshan volcanic-intrusive complex from the Gan-Hang Belt:Studies on the mineral chemistry of plagioclase and biotite. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(3): 759-768 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zheng YF, Fu B, Gong B and Li H. 2003. Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie-Sulu orogen in China:Implications for geodynamics and fluid regime. Earth-Science Reviews, 62(1-2): 105-161 DOI:10.1016/S0012-8252(02)00133-2 |
陈斌, 刘超群, 田伟. 2006. 太行山中生代岩浆作用过程中的壳幔岩浆混合作用:岩石学和地球化学证据. 地学前缘, 13(2): 140-147. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.02.012 |
郭耀宇, 和文言, 李在春, 戢兴忠, 韩愉, 房维科, 殷超. 2015. 西秦岭格尔括合花岗闪长斑岩岩石成因:黑云母矿物学特征约束. 岩石学报, 31(11): 3380-3390. |
宁思远, 汪方跃, 薛维栋, 周涛发. 2017. 长江中下游铜陵地区宝山岩体地球化学研究. 地球化学, 46(5): 397-412. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.05.001 |
汪方跃, 葛粲, 宁思远, 聂利青, 钟国雄, White NC. 2017. 一个新的矿物面扫描分析方法开发和地质学应用. 岩石学报, 33(11): 3422-3436. |
王刚, 王宗起, 张英利, 王坤明. 2014. 北大巴山紫阳地区粗面岩黑云母化学特征及成因意义. 矿物学报, 34(3): 343-350. |
谢应雯, 张玉泉. 1987. 横断山不同成因类型花岗岩类岩石中黑云母的标型特征. 矿物学报, 7(3): 245-254. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1987.03.007 |
杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 张良, 郭林楠, 宋明春, 郑小礼. 2014. 胶东中生代金成矿系统. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2447-2467. |
赵沔, 杨水源, 左仁广, 赵葵东, 姜耀辉, 凌洪飞, 陈培荣. 2015. 赣杭构造带相山火山侵入杂岩的岩浆演化特征——来自斜长石和黑云母的化学成分研究. 岩石学报, 31(3): 759-768. |
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35


