2. 山东省第六地质矿产勘查院, 威海 264209;
3. 山东黄金矿业股份有限公司焦家金矿, 莱州 261441
2. No.6 Exploration Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources of Shandong Province, Weihai 264209, China;
3. Jiaojia Gold Company, Shandong Gold Mining Stock Co., Ltd., Laizhou 261441, China
胶东是我国最重要的金矿集区(Deng et al., 2003b),已探明金资源储量>4500吨(宋明春, 2015; Deng et al., 2019)。其中,“焦家式”破碎带蚀变岩型金矿床是区内最重要的金矿床类型(李士先等, 2007; 宋明春等, 2014; Li et al., 2015; Song et al., 2015),占胶东已探明金资源量的90%以上(杨立强等, 2014; 张炳林等, 2014; 张良等, 2014, 2016; 张瑞忠等, 2016)。该类型金矿典型特征是发育大规模热液蚀变作用,矿体均赋存在蚀变带内,热液蚀变作用与金矿化有着密切的时空及成因联系(Deng et al., 2015b; 赵睿等, 2015; 张潮等, 2016; Yang et al., 2014, 2016b, c; Zhang et al., 2017; 张炳林等, 2017)。热液蚀变作用的实质就是流体与围岩发生水岩反应,流体-岩石反应过程的研究对揭示热液蚀变过程中元素迁移规律,分析热液蚀变机理,探讨热液演化、成矿元素活化迁移及沉淀机制等具有重要的意义(Browne, 1978; Pirajno, 2009; Chinnasamy and Mishra, 2013; Qiu et al., 2016; Smith et al., 2017)。
寺庄金矿床位于胶东金矿集区焦家金矿田南部,是典型的“焦家式”破碎带蚀变岩型金矿,自20世纪60年代发现以来,已有50余年勘查开采历史,累计探明金资源量100余吨,已达到超大型金矿床规模。前人对该矿床蚀变特征和成矿机制已开展了初步研究工作(杨之利等, 2007; 崔书学等, 2008; 崔书学和袁文花, 2008; Qian et al., 2011; 王恩敬等, 2012; 王思红等, 2014; 卫清等, 2015; 王力和孙丽伟, 2016),其中,卫清等(2018)探讨了钾长石化和绢英岩化蚀变过程元素迁移规律,但在热液蚀变温度、氧逸度、pH值等物理化学条件及热液蚀变过程金的迁移、沉淀方面尚缺乏系统研究。本文在详细的野外地质调查和岩相学观察基础上,查清了寺庄金矿床蚀变矿化类型及蚀变矿化时空结构,系统采集了不同蚀变矿化类型的岩/矿石样品,进行了主量、微量和稀土元素地球化学分析和长石电子探针分析,运用质量平衡方法总结了热液蚀变过程元素迁移规律,运用二长石温度计估算了钾长石化蚀变的形成温度,利用稀土元素组成分析了钾长石化、绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化蚀变的氧化还原条件,结合前人成矿期流体包裹体显微测温数据,探讨了寺庄金矿床热液蚀变过程元素迁移规律、蚀变矿化物理化学条件和金迁移沉淀机制。
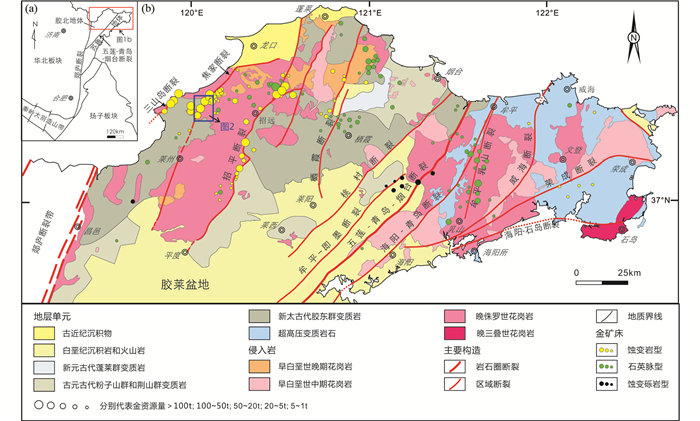
1 地质背景 1.1 区域地质胶东是一个主要由前寒武纪变质基底岩石和超高压变质岩块组成、中生代构造-岩浆作用发育的内生热液金矿集区(图 1; 杨立强等, 2014; Yang et al., 2016d, 2017; Deng et al., 2018, 2019; Zhang et al., 2019)。前寒武变质基底自下而上可分为上太古界胶东岩群(Tang et al., 2007; Tam et al., 2011)、下元古界荆山群(董春燕等, 2010; 刘平华等, 2011)、下-中元古界粉子山群(谢士稳等, 2014)和上元古界蓬莱群(初航等, 2011)。超高压变质岩块主要由新太古代-古元古代及新元古代的花岗质片麻岩,表壳岩夹榴辉岩和超基性岩透镜体组成(Ames et al., 1996; 刘利双等, 2018)。中生代岩浆岩按形成时代从早到晚可分为晚三叠世花岗岩类(225~205Ma)(陈竟志和姜能, 2011);晚侏罗世(165~150Ma)玲珑和栾家河花岗岩类(Zhang et al., 2010; Jiang et al., 2012; Ma et al., 2013; Yang et al., 2018);早白垩世早期(132~123Ma)郭家岭花岗闪长岩类(刘跃等, 2014; 耿科等, 2016);早白垩世晚期(118~110Ma)艾山花岗岩类(Goss et al., 2010)。此外,区内还分布有大量中基性脉岩(Deng et al., 2003a),年龄集中在110~130Ma(Deng et al., 2017)。区内北东和北北东向断裂构造发育,自西向东依次为三山岛断裂、焦家断裂、招远-平度断裂、栖霞断裂、桃村断裂、牟平-即墨断裂、五莲-青岛-烟台断裂、海阳-青岛断裂、牟平-乳山断裂、威海断裂、荣成断裂,这些断裂控制了胶东90%以上已探明的金资源量(Deng and Wang, 2016)。
|
图 1 胶东构造地质与金矿分布简图(据Yang et al., 2017, 2018修改) Fig. 1 Simplified geological map of the Jiaodong gold province showing the distribution of major fault zones, Precambrian metamorphic rocks, Mesozoic granitoid intrusions, sedimentary rocks and gold deposits (modified after Yang et al., 2017, 2018) |
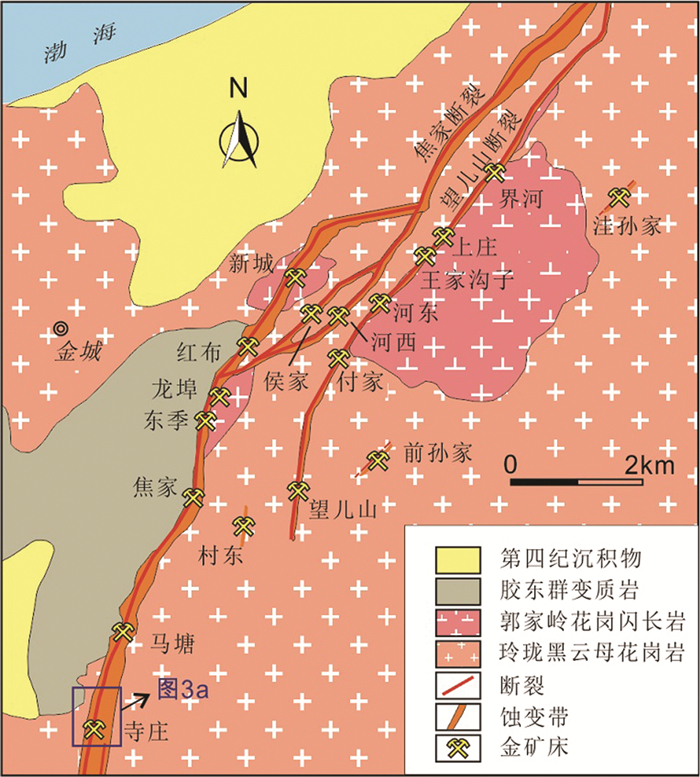
研究区位于胶东金矿集区西北部焦家金矿田内。区内主要控矿断裂为焦家断裂,该断裂纵贯全区,南段基本沿胶东群变质岩和玲珑黑云母花岗岩接触带展布,北段切割玲珑黑云母花岗岩和郭家岭花岗闪长岩(图 2),走向10°~70°,倾向北西,倾角20°~50°,该断裂控制的金矿床资源总量已超过1200t(Deng et al., 2015a)。此外,平行于焦家断裂在其下盘发育河西、侯家、望儿山等次级断裂,这些断裂向北与焦家断裂交会(Yang et al., 2016d, 2017)。区内出露地层主要有胶东群和第四系,胶东群主要分布在区内西南侧焦家断裂带上盘(图 2),岩性为黑云斜长片麻岩、斜长角闪岩、黑云变粒岩与黑云片岩。第四系主要分布在区内北部滨海地区,在西南部也有少量出露。岩浆岩主要为晚侏罗世玲珑黑云母花岗岩和早白垩世早期郭家岭花岗闪长岩。
|
图 2 焦家金矿田地质简图(据Yang et al., 2016d, 2017修改) Fig. 2 Simplified geological map of the Jiaojia goldfield (modified after Yang et al., 2016d, 2017) |
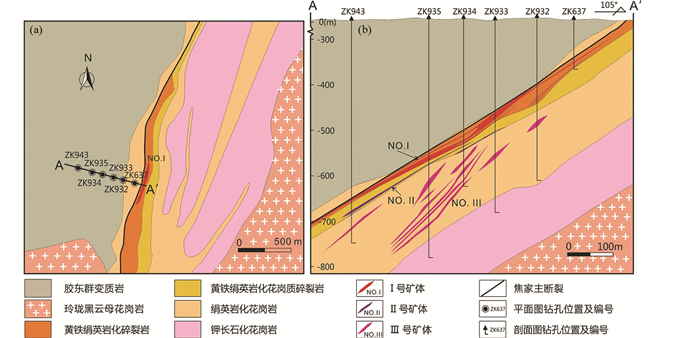
寺庄金矿床(37°22′23″~37°22′49″N、120°06′32″~120°07′00″E)位于焦家金矿田最南端(图 2)。矿区内出露的地层主要为胶东群,岩浆岩主要为玲珑黑云母花岗岩,二者被焦家断裂分割(图 3a)。玲珑黑云母花岗岩呈浅灰白色-浅褐色-浅肉红色(图 4a),花岗结构,块状构造(图 4f),主要组成矿物为石英、钾长石、斜长石、黑云母。矿区内主要构造为焦家断裂及其下盘的次级断裂,矿区内焦家断裂走向近SN-NE向,倾向NW,倾角30°~45°,宽80~500m。焦家主断裂下盘自西向东发育3条规模较大的近SN-NE向次级断裂,倾向NW,倾角42°~78°(图 3a)。
|
图 3 寺庄金矿床地质简图(a)和AA′线地质剖面图(b) Fig. 3 Sketch map of the Sizhuang gold deposit (a) plan view of the Sizhuang gold deposit; (b) geological cross-section along line AA′ |
|
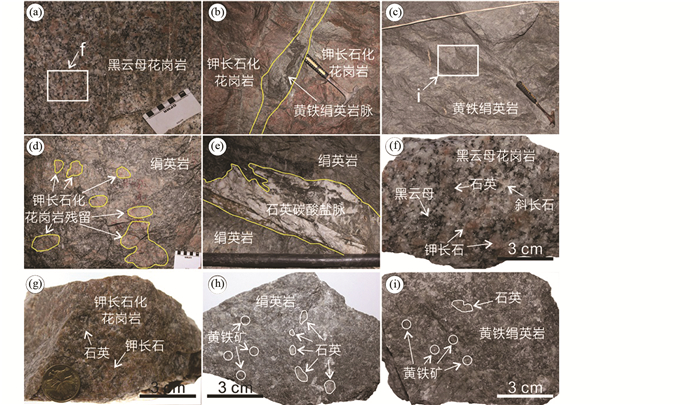
图 4 寺庄金矿床典型蚀变矿化野外及手标本照片 (a)新鲜玲珑黑云母花岗岩;(b)脉状黄铁绢英岩穿切面状钾长石化花岗岩;(c)面状黄铁绢英岩;(d)面状绢英岩内包裹钾长石化花岗岩团块;(e)石英-碳酸盐脉穿切面状绢英岩;(f)块状玲珑黑云母花岗岩;(g)块状钾长石化花岗岩;(h)致密块状绢英岩;(i)致密块状黄铁绢英岩 Fig. 4 Typical features of alteration and mineralization in the Sizhuang gold deposit (a) fresh Linglong biotite granite; (b) pyrite-sericite-quartz vein cuts across the K-feldspar alteration; (c) pyrite-sericite-quartz alteration; (d) K-feldspar alteration breccia is encapsulated by sericite-quartz alteration; (e) calcite-quartz vein cuts across the sericite-quartz alteration; (f) massive Linglong biotite granite; (g) massive K-feldspar altered granite; (h) massive sericite-quartz altered rock; (i) massive pyrite-sericite-quartz altered rock |
矿体主要分布在焦家断裂主裂面之下,矿体的规模、产状、形态及品位受控于焦家主断裂及其派生次级裂隙构造(图 3a),矿体产状与主裂面一致或大致平行(图 3b),走向北东,倾向北西,倾角26°~45°。按矿体赋存部位及地质特征可划分3个矿体,编号Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ。Ⅰ号矿体产于主裂面之下0~36m的黄铁绢英岩化碎裂岩内,以浸染状矿化为主(图 5g),脉状矿化次之。Ⅱ号矿体赋存于主裂面之下50~89m的黄铁绢英岩化花岗质碎裂岩内,以浸染状、细脉状矿化为主,团块状矿化次之;Ⅲ号矿体赋存于主裂面之下105~315m绢英岩化花岗岩带内的黄铁绢英化花岗质碎裂岩中,以脉状(图 5h, i)、网脉状矿化为主,浸染状、团块状矿化次之。Ⅰ号和Ⅲ号矿体为主矿体,Ⅱ号矿体规模较小。Ⅰ号矿体金资源量约占探明金资源总量的31%,呈似层状展布,沿走向及倾向具明显的舒缓波状特征,具分枝复合、膨胀夹缩现象(图 3b),走向17°~24°,平均走向20°,倾向北西,倾角27°~35°,平均倾角31°,走向长200~480m,斜深202~1192m,矿体厚度1.5~23.8m,平均厚度10.4m,金品位1.21~5.46g/t,平均品位3.03g/t。Ⅲ号矿体金资源量约占探明金资源总量的68%,矿体形态呈脉状、透镜状(图 3b),走向345°~36°,倾向南西或北西,倾角26°~45°,平均倾角36°,走向长180~904m,矿体厚度1.2~14.6m,平均厚度3.7m,金品位1.27~17.2g/t,平均品位3.33g/t。
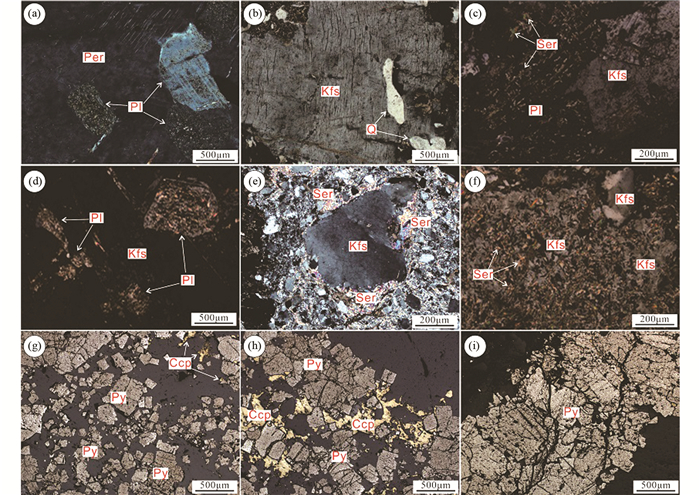
|
图 5 寺庄金矿床典型蚀变矿化显微照片 (a)钾长石化花岗岩中热液条纹长石包裹斜长石,斜长石部分蚀变成绢云母(+);(b)钾长石化花岗岩中热液钾长石包裹变形的石英(+);(c)绢英岩化花岗岩中热液钾长石穿切斜长石,斜长石大部分蚀变成鳞片状绢云母(+);(d)绢英岩化花岗岩中钾长石包裹斜长石,斜长石大部分蚀变成鳞片状绢云母(+);(e)绢英岩中热液钾长石边部被鳞片状绢云母交代(+);(f)黄铁绢英岩中热液钾长石被鳞片状绢云母交代成骸晶结构(+);(g)浸染状矿化(-);(h)多金属硫化物脉型矿化(-);(i)黄铁矿脉型矿化(-).矿物代号:Ccp-黄铜矿;Kfs-钾长石;Per-条纹长石;Pl-斜长石;Py-黄铁矿;Q-石英;Ser-绢云母 Fig. 5 Photomicrographs of representative hydrothermally altered rocks and ore in the Sizhuang gold deposit (a) plagioclases were encapsulated by hydrothermal perthite and they were weakly altered by sericite (+); (b) deformed quartzs were encapsulated by hydrothermal K-feldspar (+); (c) plagioclase was cut by hydrothermal K-feldspar and it was mostly altered by sericite (+); (d) plagioclase was encapsulated by hydrothermal K-feldspar and it was mostly altered by sericite (+); (e) hydrothermal K-feldspar was altered by sericite (+); (f) hydrothermal K-feldspar was mostly altered by sericite (+); (g) disseminated mineralization (-); (h) base metal vein mineralization (-); (i) pyrite vein mineralization (-). Abbreviations: Ccp-chalcopyrite; Kfs-K-feldspar; Per-perthite; Pl-plagioclase; Py-pyrite; Q-quartz; Ser-sericite |
矿床热液蚀变类型主要有钾长石化、绢英岩化、黄铁绢英岩化、碳酸盐化等。钾长石化主要呈面状、脉状、团块状产出,以面型蚀变为主(图 4b),形成独立分带,规模很大,该带往往与绢英岩化蚀变带及玲珑黑云母花岗岩呈过渡关系。钾长石化蚀变带宽度一般大于60m,其出露位置距焦家主断裂较远,一般大于100m。钾长石化花岗岩呈肉红色,主要组成矿物有钾长石、斜长石、石英,花岗变晶结构,块状构造(图 4g)。黑云母基本消失,钾长石呈云朵状、土状、斑点状、星点状交代斜长石,颗粒粗大且外形不规则的热液钾长石常包裹原生的斜长石(图 5a)与石英(图 5b)等矿物。绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化主要呈面状、脉状产出,以面型蚀变为主(图 4c),脉状黄铁绢英岩常穿切钾长石化花岗岩(图 4b),部分绢英岩内含有钾长石化花岗岩团块(图 4d),表明钾长石化蚀变早于绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化形成。绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化蚀变形成独立分带,规模很大,宽度一般大于40m,黄铁绢英岩化蚀变紧邻焦家断裂发育,绢英岩化蚀变带分布在黄铁绢英岩化蚀变带外侧,二者与金矿化关系十分密切。绢英岩呈灰绿色,鳞片变晶结构,块状构造,主要组成矿物为绢云母和石英,可见少量黄铁矿(图 4h)。镜下可见斜长石先于钾长石蚀变为细小鳞片状绢云母(图 5c, d)。黄铁绢英岩呈灰色,鳞片变晶结构,致密块状构造,主要组成矿物为绢云母、石英、黄铁矿(图 4i),黄铁矿呈浸染状产出(图 5g)。镜下可见钾长石蚀变成细小鳞片状绢云母(图 5e, f)。碳酸盐化主要以乳白色石英-碳酸盐脉的形式产出,石英-碳酸盐脉常穿切绢英岩(图 4e),脉宽一般3~20cm,规模较小,为成矿后热液蚀变。
2 样品采集与分析测试方法本次共采集新鲜玲珑黑云母花岗岩、不同蚀变类型与蚀变矿化强度的蚀变岩与矿石样品50件,经详细的镜下观察,11件样品用于测试分析,其中,玲珑黑云母花岗岩3件,钾长石化花岗岩3件、绢英岩2件,黄铁绢英岩3件。为探讨热液蚀变过程元素迁移规律及蚀变矿化温度与氧逸度条件,对各样品进行主量、微量与稀土元素测试,结果列于表 1。对玲珑黑云母花岗岩及钾长石化花岗岩内长石矿物进行电子探针分析,测试样品共6件15点,其中原生钾长石测点3个、原生斜长石测点3个、热液钾长石测定5个、蚀变斜长石测定4个,结果列于表 2。
|
|
表 1 寺庄金矿床黑云母花岗岩及蚀变岩主量、微量和稀土元素组成 Table 1 Major, trace and rare earth elements of hydrothermally altered rocks and the Linglong biotite granite in the Sizhuang gold deposit |
|
|
表 2 寺庄金矿床黑云母花岗岩和钾长石化花岗岩中钾长石和斜长石化学组成电子探针分析结果(wt%) Table 2 Chemical content of K-feldspar and plagioclase in the K-feldspar altered granite and the Linglong biotite granite from the Sizhuang gold deposit (wt%) |
全岩主量、微量元素含量分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心进行,主量元素测试采用X射线荧光光谱法,测试仪器为飞利浦PW2404,测试方法和依据为GB/T 14506.28—2010《硅酸盐岩石化学分析方法X射线荧光光谱法测定主、次元素量》,测试精度优于1%;微量元素和稀土元素测试仪器为Finnigan MAT制造的HR-ICP-MS(ElementⅠ),测试方法和依据为DZ/T 0223—2001(电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)方法通则),测试精度优于5%;Au、Ag、As和Hg的测试仪器为原子吸收光谱仪(Z- 2000)、原子荧光光谱仪,测试方法和依据为DZG 93-09《金银矿石分析规程》、GB/T22105—2008土壤中总砷的测定、EJ/T1149—2001含铀矿石中微量铋、汞的测定。长石电子探针分析在中国地质科学研究院国家地质实验测试中心电子探针实验室完成,采用仪器为EPMA1600型电子探针,测试条件:加速电压25kV,电流4.5nA,电子束束斑直径小于1μm。
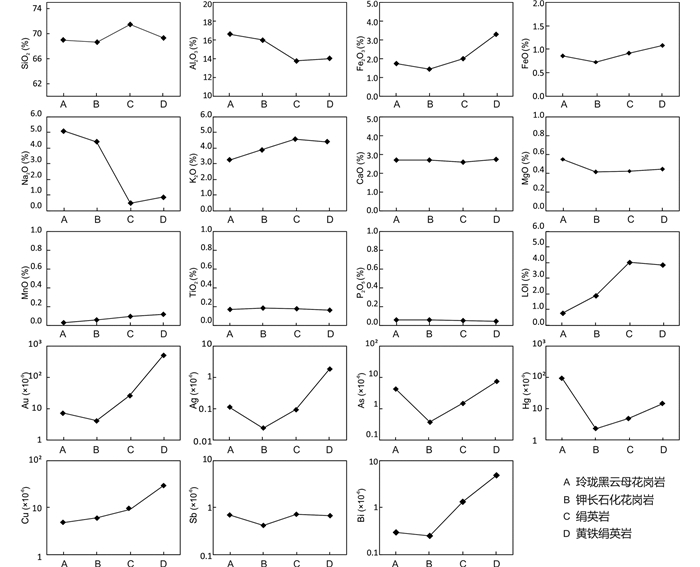
3 分析结果 3.1 主量元素组成主量元素分析结果(表 1)显示:钾长石化花岗岩相对于蚀变原岩玲珑黑云母花岗岩,SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、FeO、Na2O、MgO平均含量降低,K2O、MnO、LOI平均含量升高,CaO、TiO2、P2O5平均含量基本不变。绢英岩和黄铁绢英岩相对于蚀变原岩钾长石化花岗岩,SiO2、Fe2O3、FeO、K2O、MgO、MnO、LOI平均含量升高,Al2O3、Na2O平均含量降低,CaO、TiO2、P2O5平均含量基本不变(图 6)。
|
图 6 寺庄金矿床玲珑黑云母花岗岩及蚀变岩主量和微量元素变化图 Fig. 6 Variation of major elements and trace elements between Linglong biotite granite and hydrothermally altered rocks in the Sizhuang gold deposit |
微量元素分析结果(表 1)显示:钾长石化花岗岩相对于蚀变原岩玲珑黑云母花岗岩,成矿元素Au、Ag和亲铜元素As、Hg、Sb、Bi平均含量降低,Cu平均含量略微升高。绢英岩和黄铁绢英岩相对于蚀变原岩钾长石化花岗岩,成矿元素Au、Ag和亲铜元素As、Hg、Cu、Sb、Bi平均含量均升高,且上述各元素在黄铁绢英岩中的平均含量高于绢英岩中对应组分平均含量(图 6)。
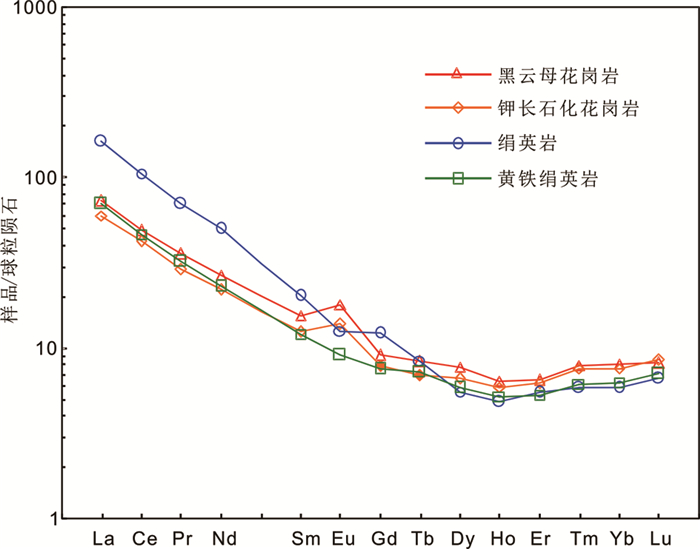
3.3 稀土元素组成稀土元素分析结果(表 1)显示:玲珑黑云母花岗岩、钾长石化花岗岩、绢英岩及黄铁绢英岩稀土元素配分曲线(图 7)均表现为轻稀土相对富集的右倾型。钾长石化花岗岩相对于蚀变原岩玲珑黑云母花岗岩,∑REE、LREE、HREE、LREE/HREE、(La/Yb)N、δEu值均降低,δCe值略微升高。绢英岩和黄铁绢英岩相对于蚀变原岩钾长石化花岗岩,∑REE、LREE、HREE、LREE/HREE、(La/Yb)N值均升高,δEu值明显降低,δCe值略微降低。
|
图 7 寺庄金矿床内玲珑黑云母花岗岩及蚀变岩稀土元素配分曲线图(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of hydrothermally altered rocks and Linglong biotite granite in the Sizhuang gold deposit (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
电子探针分析结果(表 2)显示:玲珑黑云母花岗岩和钾长石化花岗岩中斜长石均为奥长石(An组分14.81~20.42)。钾长石化花岗岩中热液钾长石与玲珑黑云母花岗岩中原生钾长石几乎都不含MgO,但K2O、Na2O组分含量有显著差异,SiO2含量有轻微差异,而TiO2、Al2O3、FeO、MnO、CaO、NiO等组分含量变化不大。热液钾长石中K2O组分含量明显高于原生钾长石中对应组分,SiO2组分含量轻微高于原生钾长石中对应组分,而Na2O组分含量明显低于原生钾长石中对应组分,表明钾长石化过程K置换了原生钾长石中的部分Na,使热液钾长石更富集K。
4 讨论 4.1 蚀变过程元素迁移规律质量平衡方法是研究热液蚀变过程中元素迁移的有效方法之一,Gresens (1967)提出的Gresens方程是研究开放系统中元素质量迁移的经典方法,Grant(1986, 2005)对该方程进行了简化。但如何选择不活动元素是进行质量平衡计算的关键问题。在热液流体-岩石反应过程中,Al2O3和TiO2通常被认为是不活动的(Condie and Sinha, 1996),但Al在变形变质作用过程中仍有一定的活动性(Ague, 1994),尤其是长石绢云母化过程中有部分析出(O’Hara, 1988; O’Hara and Blackburn, 1989)。寺庄金矿床广泛发育绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化蚀变,导致Al并不适合作为不活动组分。Ti在岩石中的含量低,而且其活动性小,在热液流体-岩石反应过程中相对稳定,在岩石变形变质过程中的活动性相当有限,是一个理想的参照元素(Condie and Sinha, 1996; Ague, 1997; Klammer, 1997)。因此,本文选定Ti作为不活动组分,利用改进后的质量平衡方程ΔCi=(CTiO/CTiA)CiA-CiO(CTiO,CTiA分别为Ti在蚀变原岩和蚀变岩中的含量;CiO,CiA分别为元素i在蚀变原岩和蚀变岩中的含量;ΔCi为热液蚀变过程中元素i的迁移变化率,正值代表元素迁入,负值代表元素迁出)对寺庄金矿床热液蚀变过程中主要氧化物、微量元素和稀土元素迁移进行定量计算,得到各蚀变过程元素迁移情况如表 3和图 8所示。
|
|
表 3 寺庄金矿床热液蚀变过程主量、微量和稀土元素平均得失量 Table 3 Average gains and losses of major elements, trace elements and rare earth elements during different types of alteration in the Sizhuang gold deposit |
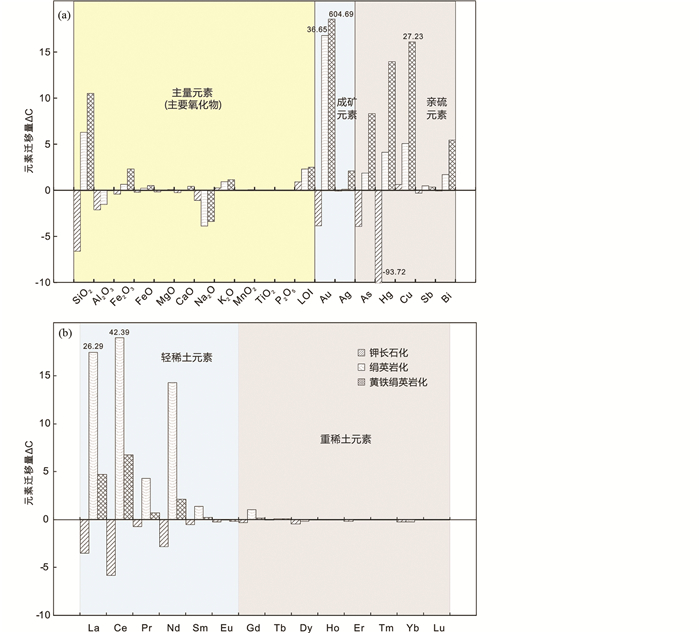
|
图 8 寺庄金矿床热液蚀变过程主要氧化物和微量元素(a)及稀土元素(b)迁移柱状图 Fig. 8 Gains and losses diagram of different elements during different types of hydrothermal alteration in the Sizhuang gold deposit (a) diagram of major and trace elements; (b) diagram of the rare earth elements |
质量平衡计算结果表明:钾长石化过程,主量元素SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、FeO、MgO、CaO、Na2O、P2O5,成矿元素Au、Ag,亲铜元素As、Hg、Sb、Bi(图 8a)和稀土元素(图 8b)均从玲珑黑云母花岗岩中迁出;而K2O、MnO和Cu从流体中迁入玲珑黑云母花岗岩。Na2O、CaO的迁出可能与斜长石蚀变成钾长石有关;SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、FeO、MgO的迁出则可能是由于黑云母的分解引起,因为在金矿床中,当含黑云母的花岗岩遭受钾长石化时,黑云母常先被交代和消失,只有在钾长石化早期可见到其残留矿物,可保存其假象和骸晶结构(胡受奚等, 2004);K的迁入则可能是由于热液钾长石的形成导致。
绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化过程元素迁移行为高度相似,主量元素SiO2、Fe2O3、FeO、MgO、CaO、K2O、MnO,成矿元素Au、Ag,亲铜元素As、Hg、Cu、Sb、Bi和轻稀土元素均从流体中迁入钾长石化花岗岩,尤其是黄铁绢英岩化过程,Au大量迁入,与绝大多数矿体均赋存在黄铁绢英岩化蚀变带内的地质事实相吻合;而主量元素Al2O3、Na2O和重稀土元素从钾长石化花岗岩中迁出。绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化过程SiO2的迁入可能与石英形成相关,K2O、MgO的迁入可能与绢云母形成相关,Fe2O3、FeO的迁入可能与黄铁矿等硫化物形成有关;Al2O3、Na2O的迁出则可能与斜长石和钾长石分解有关。随蚀变强度增强,石英、绢云母和黄铁矿等蚀变矿物含量不断增加,因此,黄铁绢英岩化过程迁入元素的迁移量要高于绢英岩化过程;而随着蚀变强度增强,后期残留的斜长石和钾长石越来越少,因此,黄体绢英岩化过程迁出元素的迁移量要低于绢英岩化过程。
4.2 蚀变矿化温度和氧逸度条件二长石温度计法(ln(XAb·AF/XAb·PF)=0.8-1400/T;XAb=Na/(Na+K+Ca))(Barth, 1951;式中XAb·AF代表碱性长石中钠长石的组分,XAb·PF代表斜长石中钠长石的组分)可大致估算钠长石组分在斜长石系列及碱性长石系列之间的分配达到平衡时的温度条件。寺庄金矿床玲珑黑云母花岗岩和钾长石化花岗岩二长石温度计估算结果(表 4)显示,玲珑黑云母花岗岩中原生钾长石和斜长石平衡温度约479~540℃,而钾长石化花岗岩中热液钾长石和斜长石平衡温度约为392~449℃,指示钾长石化蚀变大约在392~449℃温度范围内发生。而寺庄金矿床成矿期流体包裹体显微测温集中在133~340℃之间(卫清等, 2015; 王力和孙丽伟, 2016),表明绢英岩和黄铁绢英岩化蚀变大约在133~340℃温度范围内发生,明显低于钾长石化蚀变温度。
|
|
表 4 寺庄金矿床玲珑黑云母花岗岩和钾长石化花岗岩二长石温度计估算结果 Table 4 Two feldspar geo-thermometer analysis of the Linglong biotite granite and K-feldspar altered granite from the Sizhuang gold deposit |
已有研究表明,Eu异常可指示流体的温度、fO2和pH等物理化学条件,在高温、相对还原的条件下,Eu易成Eu2+与其他三价REE分离,引起Eu异常(Michard, 1989; Ward et al., 1992)。寺庄金矿床钾长石化花岗岩与玲珑黑云母花岗岩相比,Eu正异常明显减弱,指示形成钾长石化蚀变的流体氧逸度较高,处于相对氧化环境,将玲珑黑云母花岗岩内部分Eu2+氧化成Eu3+带出,引起正Eu异常减弱;而绢英岩和黄铁绢英岩与钾长石化花岗岩相比,Eu正异常变为负异常,指示形成绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化蚀变的流体氧逸度较低,处于相对还原环境,将钾长石化花岗岩内Eu3+还原成Eu2+带出,引起Eu负异常。
4.3 蚀变与金沉淀机制一般情况下,自然金在氧化条件下溶解,还原条件下沉淀,而且金主要以金氯络合物或金硫络合物的形式在热液中迁移(Henley, 1973),在<400℃、弱酸性及中性条件下,金主要以金硫络合物的形式搬运,只有在高温、高盐度、贫H2S、富Cl-的环境中,金的氯络合物才占主导地位(Hayashi and Ohmoto, 1991; Stefánsson and Seward, 2004)。寺庄金矿床黄铁矿为主要载金矿物,未见含氯矿物,且矿石的金含量与硫含量(表 5)呈明显的正相关(图 9a),而与氯相关性不明显(图 9b)。而且,黄铁矿是胶东各类型金矿最主要的载金矿物,金的富集程度与黄铁矿含量正相关(严育通等, 2013; Yang et al., 2016a),寺庄金矿床成矿期流体具有中低温(133~340℃)、中低盐度(0.53%~12% NaCleqv)的特点(卫清等, 2015; 王力和孙丽伟, 2016)。因此,推断寺庄金矿床的金很有可能以金硫络合物的形式迁移。
|
|
表 5 寺庄金矿床矿石中Au、S、Cl含量 Table 5 Au、S and Cl content of the ore in the Sizhuang gold deposit |
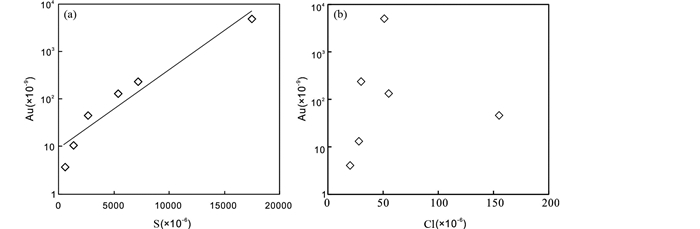
|
图 9 寺庄金矿床Au与S (a)和Cl (b)关系图 Fig. 9 Diagrams of Au vs. S (a) and Au vs. Cl (b) in the Sizhuang gold deposit |
王玉荣和胡受奚(2000)研究表明,碱性流体对斜长石蚀变形成钾长石有利,而酸性流体对斜长石和钾长石蚀变形成绢云母有利,但是绢云母只有在弱酸环境下相对稳定,在强酸环境下会蚀变成高岭石(Sverjensky et al., 1991)。寺庄金矿床成矿前发育大规模的钾长石化,大量斜长石蚀变成钾长石,成矿期在钾长石化基础上形成绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化,斜长石和钾长石不同程度地蚀变成绢云母,推断寺庄金矿床形成钾长石化蚀变的流体呈碱性,而形成绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化的流体呈弱酸性。
综合上述研究,推测成矿前流体温度和氧逸度较高,碱性较大,因而向围岩中进行广泛的渗透交代,形成大范围的钾长石化。成矿期,温度、氧逸度和碱度降低,流体对围岩渗透交代,在钾长石化基础上形成一定范围的绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化,黄铁矿等硫化物的沉淀导致热液中硫的活度降低,破坏了金硫络合物的稳定保存条件,引起金硫络合物分解,导致金沉淀富集成矿。
5 结论(1) 寺庄金矿床在热液作用下,在焦家主断裂下盘发育了大规模的钾长石化、绢英岩化及黄铁绢英岩化蚀变带,钾长石化为成矿前热液蚀变,不同程度地改造了玲珑黑云母花岗岩的结构和矿物组成。绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化为成矿期热液蚀变,伴随金矿化,不同程度地叠加改造了钾长石化花岗岩。
(2) 元素地球化学方面,钾长石化过程,主量元素SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、FeO、MgO、CaO、Na2O、P2O5,成矿元素Au、Ag,亲铜元素As、Hg、Sb、Bi和稀土元素均从玲珑黑云母花岗岩中迁出;而K2O、MnO和Cu从流体中迁入玲珑黑云母花岗岩。绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化过程,主量元素SiO2、Fe2O3、FeO、MgO、CaO、K2O、MnO,成矿元素Au、Ag,亲铜元素As、Hg、Cu、Sb、Bi和轻稀土元素均从流体中迁入钾长石化花岗岩,而主量元素Al2O3、Na2O和重稀土元素均从钾长石化花岗岩中迁出。
(3) 形成钾长石化蚀变的流体为高温(392~449℃)、氧化、碱性的流体,而形成绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化蚀变的流体为中低温(133~340℃)、还原、弱酸性的流体。寺庄金矿床的金可能以金硫络合物的形式迁移,绢英岩化和黄铁绢英岩化过程黄铁矿等硫化物的沉淀导致热液中硫的活度降低,破坏了金硫络合物的稳定保存条件,引起金硫络合物分解,导致金沉淀富集成矿。
致谢 研究工作得到了中国地质大学(北京)杨立强教授的指导;野外工作得到了山东黄金矿业股份有限公司寺庄金矿相关工作人员和中国地质大学(北京)黄涛硕士、冯建秋硕士的支持和帮助;样品测试得到了核工业北京地质研究院地质分析测试研究中心和中国地质科学研究院国家地质实验测试中心电子探针实验室相关工作人员的帮助;成文过程得到了中国地质大学(北京)王中亮和邱昆峰两位老师的帮助;中国地质大学(北京)张炳林博士、王偲瑞博士、魏瑜吉硕士参与了部分研究工作;两位审稿人为本文提供了宝贵的修改意见;在此一并致以诚挚的感谢!
恰逢著名矿床学与区域成矿学家翟裕生院士九十华诞,先生一直对胶东金矿给予高度关注,对胶东金矿科学研究的发展发挥了重要作用,谨以此文祝贺翟裕生院士九十华诞。
Ague JJ. 1994. Mass transfer during Barrovian metamorphism of pelites, south-central Connecticut; Ⅰ:Evidence for changes in composition and volume. American Journal of Science, 294(8): 989-1057 DOI:10.2475/ajs.294.8.989 |
Ague JJ. 1997. Compositional variations in metamorphosed sediments of the Littleton Formation, New Hampshire; discussion. American Journal of Science, 297(4): 440-449 DOI:10.2475/ajs.297.4.440 |
Ames L, Zhou GZ and Xiong BC. 1996. Geochronology and isotopic character of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism with implications for collision of the Sino-Korean and Yangtze cratons, central China. Tectonics, 15(2): 472-489 DOI:10.1029/95TC02552 |
Barth TFW. 1951. The feldspar geologic thermometers. Neues Jahrbuch fur Mineralogie Abhandlungen, 82: 143-154 |
Browne PRL. 1978. Hydrothermal alteration in active geothermal fields. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 6: 229-248 DOI:10.1146/annurev.ea.06.050178.001305 |
Chen JZ and Jiang N. 2011. Petrogenesis of the Late-Triassic alkaline magmatism in the Jiaodong area:Evidence from U-Pb age, Hf-O isotopes of zircons. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(12): 3557-3574 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Chinnasamy SS and Mishra B. 2013. Greenstone metamorphism, hydrothermal alteration, and gold mineralization in the genetic context of the granodiorite-hosted gold deposit at Jonnagiri, Eastern Dharwar Craton, India. Economic Geology, 108(5): 1015-1036 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.108.5.1015 |
Chu H, Lu SN, Wang HC, Xiang ZQ and Liu H. 2011. U-Pb age spectrum of detrital zircons from the Fuzikuang Formation, Penglai Group in Changdao, Shandong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(4): 1017-1028 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Condie KC and Sinha AK. 1996. Rare earth and other trace element mobility during mylonitization:A comparison of the Brevard and Hope Valley shear zones in the Appalachian Mountains, USA. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 14(2): 213-226 DOI:10.1046/j.1525-1314.1996.05899.x |
Cui SX and Yuan WH. 2008. Ore-forming regularity of the second enrichment zone of the Sizhuang gold deposit in Laizhou, Shandong Province. Geological Survey and Research, 31(3): 186-191 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Cui SX, Yuan WH and Yang ZL. 2008. Geological characteristics in the deep of Sizhuang gold deposit in Laizhou City. Northwestern Geology, 41(4): 82-92 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Deng J, Liu W, Sun ZS, Wang JP, Wang QF, Zhang QX and Wei YG. 2003a. Evidence of mantle-rooted fluids and multi-level circulation ore-forming dynamics:A case study from the Xiadian gold deposit, Shandong Province, China. Science in China (Series D), 46(Suppl.1): 123-134 |
Deng J, Yang LQ, Sun ZS, Wang JP, Wang QF, Xin HB and Li XJ. 2003b. A metallogenic model of gold deposits of the Jiaodong granite-greenstone belt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(4): 537-546 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Carranza EJM and Lu YJ. 2015a. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry. Mineralium Deposita, 50(8): 987-1006 DOI:10.1007/s00126-015-0584-1 |
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF and Pan RG. 2015b. Origin of the Jiaodong-type Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Constraints from fluid inclusion and C-D-O-S-Sr isotope compositions. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 674-686 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.04.018 |
Deng J and Wang QF. 2016. Gold mineralization in China:Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Research, 36: 219-274 |
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF, Dilek Y and Liang YY. 2017. Isotopic characterization and petrogenetic modeling of Early Cretaceous mafic diking:Lithospheric extension in the North China craton, eastern Asia. GSA Bulletin, 129(11-12): 1379-1407 DOI:10.1130/B31609.1 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Santosh M and Yao EY. 2018. Crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the south-eastern North China Craton. Earth-Science Reviews, 182: 251-272 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.001 |
Deng J, Yang LQ, Li RH, Groves DI, Santosh M, Wang ZL, Sai SX and Wang SR. 2019. Regional structural control on the distribution of world-class gold deposits:An overview from the giant Jiaodong Gold Province, China. Geological Journal, 54(1): 378-391 DOI:10.1002/gj.v54.1 |
Dong CY, Wang SJ, Liu DY, Wang JG, Xie HQ, Wang W, Song ZY and Wan YS. 2010. Late Palaeoproterozoic crustal evolution of the North China Craton and formation time of the Jingshan Group:Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of meta-intermediate-basic intrusive rocks in eastern Shandong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(6): 1699-1706 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Geng K, Wang RJ, Li HK, Liang TT and Zhang YB. 2016. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of Congjia granodiorite from Northwest Jiaodong area. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 37(1): 90-100 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Goss SC, Wilde SA, Wu FY and Yang JH. 2010. The age, isotopic signature and significance of the youngest Mesozoic granitoids in the Jiaodong Terrane, Shandong Province, North China Craton. Lithos, 120(3-4): 309-326 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.019 |
Grant JA. 1986. The isocon diagram:A simple solution to Gresens' equation for metasomatic alteration. Economic Geology, 81(8): 1976-1982 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.81.8.1976 |
Grant JA. 2005. Isocon analysis:A brief review of the method and applications. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 30(17-18): 997-1004 DOI:10.1016/j.pce.2004.11.003 |
Gresens RL. 1967. Composition-volume relationships of metasomatism. Chemical Geology, 2: 47-65 |
Hayashi KI and Ohmoto H. 1991. Solubility of gold in NaCl-and H2S-bearing aqueous solutions at 250~350℃. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 55(8): 2111-2126 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(91)90091-I |
Henley RW. 1973. Solubility of gold in hydrothermal chloride solutions. Chemical Geology, 11(2): 73-87 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(73)90044-2 |
Hu SX, Ye Y and Fang CQ. 2004. Petrology of the Metasomatically Altered Rocks and its Significance in Prospecting. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 34-36 (in Chinese)
|
Jiang N, Chen JZ, Guo JH and Chang GH. 2012. In situ zircon U-Pb, oxygen and hafnium isotopic compositions of Jurassic granites from the North China Craton:Evidence for Triassic subduction of continental crust and subsequent metamorphism-related 18O depletion. Lithos, 142-143: 84-94 |
Klammer D. 1997. Mass change during extreme acid-sulphate hydrothermal alteration of a Tertiary latite, Styria, Austria. Chemical Geology, 141(1-2): 33-48 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00056-9 |
Li L, Santosh M and Li SR. 2015. The 'Jiaodong-type' gold deposits:Characteristics, origin and prospecting. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 589-611 |
Li SX, Liu CC, An YH, Wang WC, Huang TL and Yang CH. 2007. Geology of Gold Deposits in Jiaodong. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 109-148 (in Chinese)
|
Liu LS, Liu FL, Ji L, Wang W, Wang F, Cai J and Liu PH. 2018. The polygenetic meta-granitic rocks and their geological significance, within the North Sulu ultrahigh-pressure belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(6): 1557-1580 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu PH, Liu FL, Wang F and Liu JH. 2011. U-Pb dating of zircons from Al-rich paragneisses of Jingshan Group in Shandong Peninsula and its geological significance. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 30(5): 829-843 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu Y, Deng J, Wang ZL, Zhang L, Zhang C, Liu XD, Zheng XL and Wang XD. 2014. Zircon U-Pb age, Lu-Hf isotopes and petrogeochemistry of the monzogranites from Xincheng gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2559-2573 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ma L, Jiang SY, Dai BZ, Jiang YH, Hou ML, Pu W and Xu B. 2013. Multiple sources for the origin of Late Jurassic Linglong adakitic granite in the Shandong Peninsula, eastern China:Zircon U-Pb geochronological, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence. Lithos, 162-163: 251-263 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.01.009 |
Michard A. 1989. Rare earth element systematics in hydrothermal fluids. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53(3): 745-750 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(89)90017-3 |
O'Hara K. 1988. Fluid flow and volume loss during mylonitization:An origin for phyllonite in an overthrust setting, North Carolina U. S.A. Tectonophysics, 156(1-2): 21-36 DOI:10.1016/0040-1951(88)90280-6 |
O'Hara K and Blackburn WH. 1989. Volume-loss model for trace-element enrichments in mylonites. Geology, 17(6): 524-527 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1989)017<0524:VLMFTE>2.3.CO;2 |
Pirajno F. 2009. Hydrothermal Processes and Mineral Systems. Dordrecht: Springer, 73-104
|
Qian JP, Chen HY and Meng Y. 2011. Geological characteristics of the Sizhuang gold deposit in the region of Jiaodong, Shandong Province:A study on tectono-geochemical ore prospecting of ore deposits. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 30(4): 593-553 |
Qiu KF, Taylor RD, Song YH, Yu HC, Song KR and Li N. 2016. Geologic and geochemical insights into the formation of the Taiyangshan porphyry copper-molybdenum deposit, western Qinling Orogenic Belt, China. Gondwana Research, 35: 40-58 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.014 |
Smith DJ, Naden J, Jenkin GRT and Keith M. 2017. Hydrothermal alteration and fluid pH in alkaline-hosted epithermal systems. Ore Geology Reviews, 89: 772-779 |
Song MC, Li SZ, Yi PH, Cui SX, Xu JX, Lü GX, Song YX, Jiang HL, Zhou ML, Zhang PJ, Huang TL, Liu CH and Liu DH. 2014. Classification and metallogenic theory of the Jiaojia-style gold deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 44(1): 87-104 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Song MC. 2015. The main achievements and key theory and methods of deep-seated prospecting in the Jiaodong gold concentration area, Shandong Province. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(9): 1758-1771 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Song MC, Li SZ, Santosh M, Zhao SJ, Yu S, Yi PH, Cui SX, Lü GX, Xu JX, Song YX and Zhou ML. 2015. Types, characteristics and metallogenesis of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern North China Craton. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 612-625 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.06.019 |
Stefánsson A and Seward TM. 2004. Gold (Ⅰ) complexing in aqueous sulphide solutions to 500℃ at 500bar. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(20): 4121-4143 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2004.04.006 |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes. In:Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345 DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 |
Sverjensky DA, Hemley JJ and D'Angelo WM. 1991. Thermodynamic assessment of hydrothermal alkali feldspar-mica-aluminosilicate equilibria. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 55(4): 989-1004 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(91)90157-Z |
Tam PY, Zhao GC, Liu FL, Zhou XW, Sun M and Li SZ. 2011. Timing of metamorphism in the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt:New SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of granulites, gneisses and marbles of the Jiaobei massif in the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 19(1): 150-162 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.05.007 |
Tang J, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Gong B and Liu XM. 2007. Geochronology and geochemistry of metamorphic rocks in the Jiaobei terrane:Constraints on its tectonic affinity in the Sulu orogen. Precambrian Research, 152(1-2): 48-82 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.09.001 |
Wang EJ, Guo GJ, Zhao RX, Wang YW, Yu XJ, Lv GY and Wang WT. 2012. Research and application of the mineralization network structure in Sizhuang gold deposit, Shandong Province. Gold Science and Technology, 20(4): 76-80 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang L and Sun LW. 2016. Characteristics of ore forming fluid of the Sizhuang gold deposit in Shandong Province. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 46(6): 1697-1710 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang SH, Yu XJ, Ding MF, Wang WT and Zhang L. 2014. The geological characteristics and deep prospecting direction of the Sizhuang gold deposit. Modern Mining, 30(3): 36-38 (in Chinese) |
Wang YR and Hu SX. 2000. Experimental study of gold activation-transportation in the process of potash metasomatism-alteration:North China platform gold deposit taken as an example. Science in China (Series D), 30(5): 499-508 (in Chinese) |
Ward CD, Mcarthur JM and Walsh JN. 1992. Rare earth element behaviour during evolution and alteration of the Dartmoor granite, SW England. Journal of Petrology, 33(4): 785-815 DOI:10.1093/petrology/33.4.785 |
Wei Q, Fan HR, Lan TG, Liu X, Jiang XH and Wen BJ. 2015. Genesis of Sizhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula:Evidences from fluid inclusion and quartz solubility modeling. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(4): 1049-1062 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wei Q, Fan HR, Lan TG and Liu X. 2018. Hydrothermal alteration and element migration in the Sizhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Province, China. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 37(2): 283-293 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xie SW, Wang SJ, Xie HQ, Liu SJ, Dong CY, Ma MZ, Liu DY and Wan YS. 2014. SHRIMP U-Pb dating of detrital zircons from the Fenzishan Group in eastern Shandong, North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(10): 2989-2998 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yan YT, Zhang N, Li SR and Li YS. 2013. Compositional typomorphic characteristics of pyrite in each type of gold deposit of Jiaodong. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(3): 88-93 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Goldfarb RJ, Zhang J, Gao BF and Wang ZL. 2014. 40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the formation of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit:New implications for timing and duration of hydrothermal activity in the Jiaodong gold province, China. Gondwana Research, 25(4): 1469-1483 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.001 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Zhang L, Guo LN, Song MC and Zheng XL. 2014. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2447-2467 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Guo LN, Li RH, Groves DI, Danyushevskiy LV, Zhang C, Zheng XL and Zhao H. 2016a. Relationships between gold and pyrite at the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Implications for gold source and deposition in a brittle epizonal environment. Economic Geology, 111(1): 105-126 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.111.1.105 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Zhang L, Goldfarb RJ, Yuan WM, Weinberg RF and Zhang RZ. 2016b. Thermochronologic constraints on evolution of the Linglong Metamorphic Core Complex and implications for gold mineralization:A case study from the Xiadian gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 72: 165-178 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.006 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Guo LN, Wang ZL, Li XZ and Li JL. 2016c. Origin and evolution of ore fluid, and gold-deposition processes at the giant Taishang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 72: 585-602 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.08.021 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Guo RP, Guo LN, Wang ZL, Chen BH and Wang XD. 2016d. World-class Xincheng gold deposit:An example from the giant Jiaodong gold province. Geoscience Frontiers, 7(3): 419-430 DOI:10.1016/j.gsf.2015.08.006 |
Yang LQ, Guo LN, Wang ZL, Zhao RX, Song MC and Zheng XL. 2017. Timing and mechanism of gold mineralization at the Wang'ershan gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 88: 491-510 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.06.027 |
Yang LQ, Dilek Y, Wang ZL, Weinberg RF and Liu Y. 2018. Late Jurassic, high Ba-Sr Linglong granites in the Jiaodong Peninsula, East China:Lower crustal melting products in the eastern North China Craton. Geological Magazine, 155(5): 1040-1062 DOI:10.1017/S0016756816001230 |
Yang ZL, Zhang X and Jiang HL. 2007. Geological characteristics of Sizhuang gold deposit in Laizhou City of Shandong Province. Land and Resources in Shandong Province, 23(5): 6-10 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang BL, Yang LQ, Huang SY, Liu Y, Liu WL, Zhao RX, Xu YB and Liu SG. 2014. Hydrothermal alteration in the Jiaojia gold deposit, Jiaodong, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2533-2545 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang BL, Shan W, Li DP, Xiao BJ, Wang ZL and Zhang RZ. 2017. Hydrothermal alteration in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(7): 2256-2272 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang C, Huang T, Liu XD, Liu Y, Zhao H and Wang XD. 2016. Hydrothermal alteration of the Xincheng gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2433-2450 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang J, Zhao ZF, Zheng YF and Dai MN. 2010. Postcollisional magmatism:Geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids in the Sulu orogen, China. Lithos, 119(3-4): 512-536 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.005 |
Zhang L, Liu Y, Li RH, Huang T, Zhang RZ, Chen BH and Li JK. 2014. Lead isotope geochemistry of Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2468-2480 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang L, Li GW, Zheng XL, An P and Chen BY. 2016. 40Ar/39Ar and fission-track dating constraints on the tectonothermal history of the world-class Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2465-2476 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang L, Yang LQ, Wang Y, Weinberg RF, An P and Chen BY. 2017. Thermochronologic constrains on the processes of formation and exhumation of the Xinli orogenic gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 81: 140-153 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.026 |
Zhang L, Yang LQ, Weinberg RF, Groves DI, Wang ZL, Li GW, Liu Y, Zhang C and Wang ZK. 2019. Anatomy of a world-class epizonal orogenic-gold system:A holistic thermochronological analysis of the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Gondwana Research, 70: 50-70 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2018.12.013 |
Zhang RZ, Wang ZL, Wang SR, Liu Y and Qin WK. 2016. Metallogenic mechanism of Dayingezhuang gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula:Geochemistry constrains from the gold bearing pyrite typomorph and sulfur isotope. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2451-2464 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhao R, Liu XF, Pan RG and Zhou M. 2015. Element behaviors during alteration and mineralization:A case study of the Xinli (altered rock type) gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(11): 3420-3440 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
陈竟志, 姜能. 2011. 胶东晚三叠世碱性岩浆作用的岩石成因——来自锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf-O同位素的证据. 岩石学报, 27(12): 3557-3574. |
初航, 陆松年, 王惠初, 相振群, 刘欢. 2011. 山东长岛地区蓬莱群辅子夼组碎屑锆石年龄谱研究. 岩石学报, 27(4): 1017-1028. |
崔书学, 袁文花. 2008. 莱州市寺庄金矿区第二金矿富集带成矿规律. 地质调查与研究, 31(3): 186-191. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2008.03.006 |
崔书学, 袁文花, 杨之利. 2008. 莱州寺庄金矿床深部地质特征. 西北地质, 41(4): 82-92. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2008.04.004 |
董春艳, 王世进, 刘敦一, 王金光, 颉颃强, 王伟, 宋志勇, 万渝生. 2010. 华北克拉通古元古代晚期地壳演化和荆山群形成时代制约——胶东地区变质中-基性侵入岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年. 岩石学报, 27(6): 1699-1706. |
耿科, 王瑞江, 李洪奎, 梁太涛, 张玉波. 2016. 胶西北丛家花岗闪长岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学研究. 地球学报, 37(1): 90-100. |
胡受奚, 叶瑛, 方长泉. 2004. 交代蚀变岩岩石学及其找矿意义. 北京: 地质出版社, 34-36.
|
李士先, 刘长春, 安郁宏, 王为聪, 黄太岭, 杨承海. 2007. 胶东金矿地质. 北京: 地质出版社, 109-148.
|
刘利双, 刘福来, 冀磊, 王伟, 王舫, 蔡佳, 刘平华. 2018. 北苏鲁超高压变质带内多成因类型的变花岗质岩石及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 34(6): 1557-1580. |
刘平华, 刘福来, 王舫, 刘建辉. 2011. 山东半岛荆山群富铝片麻岩锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 30(5): 829-843. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.05.007 |
刘跃, 邓军, 王中亮, 张良, 张潮, 刘向东, 郑小礼, 王旭东. 2014. 胶西北新城金矿床二长花岗岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及Lu-Hf同位素组成. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2559-2573. |
宋明春, 李三忠, 伊丕厚, 崔书学, 徐军祥, 吕古贤, 宋英昕, 姜洪利, 周明岭, 张丕建, 黄太岭, 刘长春, 刘殿浩. 2014. 中国胶东焦家式金矿类型及其成矿理论. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44(1): 87-104. |
宋明春. 2015. 胶东金矿深部找矿主要成果和关键理论技术进展. 地质通报, 34(9): 1758-1771. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.09.017 |
王恩敬, 郭广军, 赵荣欣, 王彦伟, 于晓杰, 吕广耀, 王伟涛. 2012. 山东寺庄金矿床构造-矿化网络结构研究及应用. 黄金科学技术, 20(4): 76-80. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-2518.2012.04.015 |
王力, 孙丽伟. 2016. 山东省寺庄金矿床成矿流体特征. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 46(6): 1697-1710. |
王思红, 于晓杰, 丁明飞, 王伟涛, 张龙. 2014. 寺庄金矿矿床地质特征及深部找矿方向预测. 现代矿业, 30(3): 36-38. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2014.03.010 |
王玉荣, 胡受奚. 2000. 钾交代蚀变过程中金活化转移实验研究——以华北地台金矿为例. 中国科学(D辑), 30(5): 499-508. |
卫清, 范宏瑞, 蓝廷广, 刘玄, 姜晓辉, 文博杰. 2015. 胶东寺庄金矿床成因:流体包裹体与石英溶解度证据. 岩石学报, 31(4): 1049-1062. |
卫清, 范宏瑞, 蓝廷广, 刘玄. 2018. 胶东寺庄金矿热液蚀变作用与元素迁移规律. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 37(2): 283-293. |
谢士稳, 王世进, 颉颃强, 刘守偈, 董春艳, 马铭株, 刘敦一, 万渝生. 2014. 华北克拉通胶东地区粉子山群碎屑锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年. 岩石学报, 30(10): 2989-2998. |
严育通, 张娜, 李胜荣, 李永生. 2013. 胶东各类型金矿床黄铁矿化学成分标型特征. 地学前缘, 20(3): 88-93. |
杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 张良, 郭林楠, 宋明春, 郑小礼. 2014. 胶东中生代金成矿系统. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2447-2467. |
杨之利, 张旭, 姜洪利. 2007. 山东省莱州市寺庄金矿床地质特征. 山东国土资源, 23(5): 6-10. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2007.05.002 |
张炳林, 杨立强, 黄锁英, 刘跃, 刘文龙, 赵荣新, 徐咏彬, 刘胜光. 2014. 胶东焦家金矿床热液蚀变作用. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2533-2545. |
张炳林, 单伟, 李大鹏, 肖丙建, 王中亮, 张瑞忠. 2017. 胶东大尹格庄金矿床热液蚀变作用. 岩石学报, 33(7): 2256-2272. |
张潮, 黄涛, 刘向东, 刘育, 赵海, 王旭东. 2016. 胶西北新城金矿床热液蚀变作用. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2433-2450. |
张良, 刘跃, 李瑞红, 黄涛, 张瑞忠, 陈炳翰, 李金奎. 2014. 胶东大尹格庄金矿床铅同位素地球化学. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2468-2480. |
张良, 李广伟, 郑小礼, 安平, 陈兵宇. 2016. 胶东三山岛金矿床构造-热历史:40Ar/39Ar和裂变径迹年代学制约. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2465-2476. |
张瑞忠, 王中亮, 王偲瑞, 刘育, 秦文凯. 2016. 胶西北大尹格庄金矿床成矿机理:载金黄铁矿标型及硫同位素地球化学约束. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2451-2464. |
赵睿, 刘学飞, 潘瑞广, 周勉. 2015. 胶东新立构造蚀变岩型金矿床元素地球化学行为. 岩石学报, 31(11): 3420-3440. |
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35


