2. 中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心, 天津 300170;
3. 四川省地震局, 成都 610041;
4. 早子沟金矿有限责任公司, 合作 747000
2. Tianjin Center, China Geological Survey, Tianjin 300170, China;
3. Sichuan Earthquake Administration, Chengdu 610041, China;
4. Zaozigou Gold Mine, Hezuo 747000, China
秦岭造山带处于古亚洲洋、特提斯洋和环太平洋三大构造动力学体系的三面围限之中,地质演化复杂,成矿地质条件优越,矿化类型多样且密集,是研究碰撞造山和金锑铜钼多金属矿床找矿勘查工作的理想地区(Zhai et al., 2004;翟裕生等,2008;Deng et al., 2014a;Yang et al., 2015a;Qiu and Deng, 2017)。秦岭锑矿带西接昆仑山锑矿带,并与中亚锑矿带相连,是近十年来查明的重要锑矿带(王永磊等,2013)。
早子沟超大型金锑矿床位于西秦岭造山带西段同仁-夏河-合作地区,是该区最具代表性的金锑矿床,包括蚀变岩型和脉状两种矿化样式。自1996年被发现以来,该矿床已探获金金属量为106吨,平均品位为3.34g/t,锑金属量为13万吨,平均品位为1.34%(梁志录等,2016;韦良喜等,2018;Yu et al., 2019)。前人研究已经基本查明早子沟金锑矿床含矿岩石序列与岩石成因(刘勇等,2012;Sui et al., 2018;Yu et al., 2019)、蚀变与矿化空间分带(代文军等,2011)、控矿构造(梁志录等,2016;韦良喜等,2018)和金的赋存状态(曹晓峰等,2012;包万荣和刘继来,2016)。此外,在其成矿年代学方面也开展了不少工作,隋吉祥和李建威(2013)对蚀变脉岩型矿石进行绢云母Ar-Ar年代学研究,得到很好的绢云母坪年龄为230.1±2.3Ma;Sui et al.(2018)通过高品位矿石绢云母Ar-Ar年代学研究,认为浸染状黄铁矿和毒砂矿化年代为245.6±1.0Ma~242.1±1.0Ma;Qiu et al.(2019)对矿化英安斑岩的热液独居石进行原位LA-ICP-MS定年表明早子沟矿床蚀变岩型矿化形成于209±2Ma。然而,对于脉状金锑矿化的年代则鲜有约束,这也造成对于两种矿化样式的时间和成因关系存在分歧。
此外,已有研究对于该矿床的成矿物质来源也存在争议。曹晓峰等(2012)通过石英氢氧同位素分析认为早子沟成矿流体主要是来自于大气降水的循环作用,未受到印支期及燕山期岩浆活动的影响。包万荣和刘继来(2016)基于硫同位素和岩矿地球化学特征认为早子沟矿床成矿流体为以原生岩浆水和变质成因水为主的多源混合热液。陈瑞莉等(2018)和Sui et al.(2018)通过硫铅同位素组成特征认为早子沟矿床成矿流体主要为岩浆热液来源,并在岩浆侵位过程中萃取沉积地层的还原硫。上述分歧制约了对该矿床成因的深入认识以及在西秦岭造山带西段同仁-夏河-合作地区的矿产勘查。
Sm-Nd同位素体系易保持封闭,抗风化、蚀变的能力强,在已发生Rb、Sr迁移的体系中仍能稳定存在(Farmer and Depaolo, 1987)。因此,147Sm衰变形成的143Nd在含钙矿物中替代Ca2+,易在矿物晶格中保存下来。得益于此,方解石(Su et al., 2009;王加昇和温汉捷,2015)、白云石(张宗清等,2001)、萤石(彭建堂等,2003;衣龙升等,2016)和白钨矿(Liu et al., 2007;彭建堂等,2008;刘善宝等,2017)等含钙热液矿物的Sm-Nd同位素体系得到越来越广泛的应用。一方面,Sm-Nd同位素体系可作为地质体精确定年的有效手段;另一方面,Nd同位素组成也可以示踪成矿流体的来源与演化,进而确定矿床成因(彭建堂等,2003;Barker et al., 2009;陈恒等,2012;刘善宝等,2017)。因此,在野外调研基础上,本文选择早子沟金锑矿床脉状矿化中与辉锑矿和自然金密切共生的白云石为研究对象,系统分析了其Sm、Nd同位素组成,探讨成矿流体来源,为西秦岭同类型金锑矿床的研究提供参考。
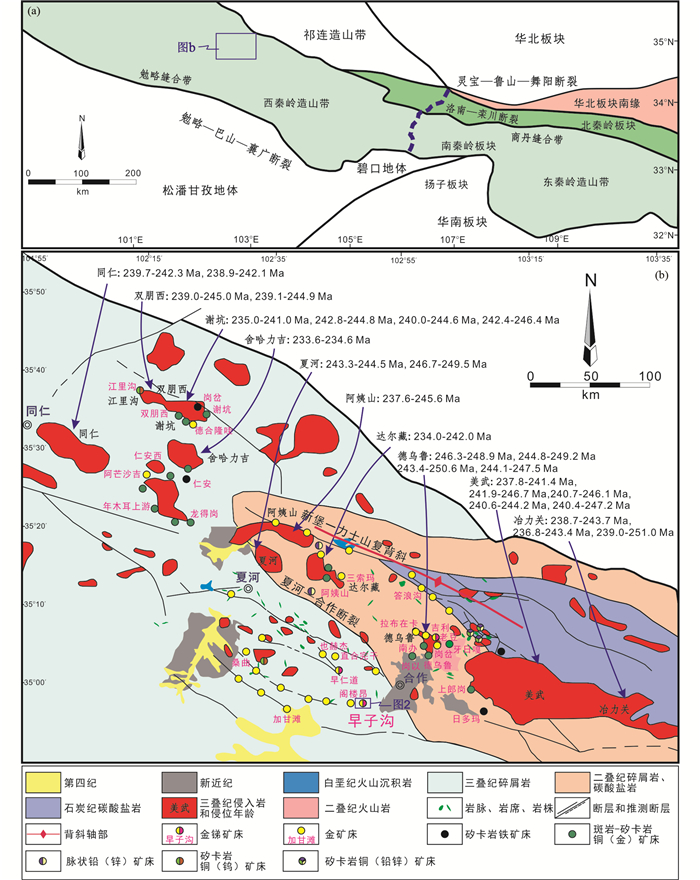
1 区域地质与矿床地质 1.1 区域地质秦岭造山带横亘中国中部,是中央造山带的重要组成部分(张国伟等,2001;Deng and Wang, 2016;Qiu et al., 2016a;Wu et al., 2018;Zhao et al., 2019)。其北以灵宝-鲁山-舞阳断裂为界与华北板块和祁连造山带相邻,南以勉略-巴山-襄广断裂为界与松潘甘孜地体、碧口地体和华南板块相接(图 1a;Deng et al., 2015a, b;Yang et al., 2015b;Dong and Santosh, 2016;Qiu et al., 2018)。自北往南,秦岭造山带被洛南-栾川断裂和商丹缝合带分隔,依次划分为华北板块南缘、北秦岭和南秦岭(Deng et al., 2014b;Duan et al., 2016;Qiu et al., 2016b)。华北板块南缘主要包括新太古代-古元古代角闪岩相-麻粒岩相变质基底、中元古代裂谷成因火山岩、中新元古代海相沉积物、新元古代冰碛岩、寒武-奥陶纪被动大陆边缘沉积物和白垩纪红层(Dong et al., 2016;Deng et al., 2017a)。北秦岭主要由被逆冲断层或韧性剪切带分隔开的宽坪群、二郎坪群和秦岭群组成。其中,宽坪群主要由代表华北板块与北秦岭在新元古代缝合的蛇绿岩和变质碎屑岩组成,二郎坪群主要发育古生代商丹洋向北俯冲形成的弧后盆地蛇绿岩,秦岭群主要岩石组合为古元古代片麻岩、角闪岩和大理岩(张国伟等,2001;Dong et al., 2016)。南秦岭主要出露新元古代变质火山沉积岩和古生代碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩(Dong and Santosh, 2016;Deng et al., 2017b)。
|
图 1 秦岭造山带构造分区图(a)和甘南地区区域地质简图及矿床分布图(b)(据Qiu and Deng, 2017修编) Fig. 1 Major tectonic domains of China and the location of the Qinling Orogenic Belt and the location of the study area (a) and simplified geological map of the Gannan area of the Western Qinling Orogen showing distributions and ages of the Triassic granitoids and ore deposits (b) (modified after Qiu and Deng, 2017) |
西秦岭造山带是秦岭造山带的西延部分,被认为是东古特提斯洋的一个分支。其东以徽成盆地和佛坪穹窿为界与东秦岭相隔,地理位置大致沿宝成铁路一线(Li et al., 2015a;Qiu and Deng, 2017)。西秦岭造山带经历了元古代到中生代晚期华南、华北板块之间的多阶段拼接历程(张国伟等,2001;Deng and Wang, 2016;Geng et al., 2017)。区域内广泛出露的泥盆纪至中三叠世沉积地层记录了与这次俯冲和碰撞相关的变形历史,而前寒武纪基底地层则很少出露(Zhang et al., 2014;Yang et al., 2016)。作为中国大陆中部构造岩浆带的重要组成部分,西秦岭造山带岩浆活动频繁,广泛发生在前寒武纪早期的基底演化至中新生代陆内叠覆造山的各构造演化阶段(Dong and Santosh, 2016;Dong et al., 2016)。中生代岩浆活动亦十分发育,数百个三叠纪花岗岩体侵入整个古生代商丹缝合带和三叠纪阿尼玛卿-勉略缝合带之间,并在随后的抬升剥蚀作用下广泛出露(Li et al., 2015b;Zhang et al., 2016)。西秦岭造山带内的斑岩-矽卡岩矿床的时空分布就与这些印支期侵入岩体密切相关(Qiu et al., 2017)。
同仁-夏河-合作地区位于西秦岭造山带的西段(图 1a),区内主要发育晚古生代-早中生代原岩为海相沉积岩的绿片岩相板岩和三叠纪侵入岩,并有少量二叠纪火山岩和白垩纪火山沉积岩出露(图 1b)。该区主构造线为北西向,发育北西向新堡-力士山复背斜和夏河-合作断裂,并以夏河-合作断裂及其延长线为界可进一步划分为北东部和南西部(梁志录等,2016;韦良喜等,2018;Sui et al., 2018)。北东部主要发育数十个三叠纪花岗质岩基和与之具有密切成因联系的斑岩-矽卡岩铜(金、铁)矿床,如德乌鲁铜矿床、南办铜矿床和岗以铜矿床。花岗质岩基侵位年龄集中于250~235Ma,其形成与古特提斯洋板块的北向俯冲有关(Qiu et al., 2018)。南西部以出露多期中酸性岩株、岩席和岩脉为特征,并发育脉状、浸染状金锑矿床,如早子沟金锑矿床、早仁道金锑矿床和加甘滩金矿床(Qiu and Deng, 2017;Gou et al., 2019)。
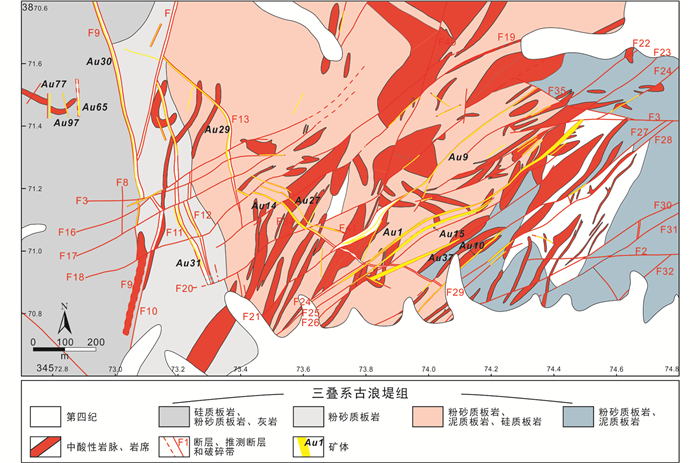
1.2 矿床地质早子沟金锑矿床位于甘肃省甘南藏族自治州合作市那吾乡(34°57′56″ N、102°48′41″ E),目前由甘肃省合作早子沟金矿有限责任公司开采,年处理矿石60万吨(梁志录等,2016)。矿区出露地层主要为三叠系古浪堤组,其主要岩石组合为灰绿色、灰褐色硅质板岩、粉砂质板岩、泥质板岩、石英砂岩和粉砂岩(图 2;梁志录等,2016;Sui et al., 2018;Yu et al., 2019)。矿区发育有大量主体走向为北东向和北北东向的中酸性岩脉和岩席,侵入三叠系古浪堤组板岩中,主要包括石英闪长斑岩、英安斑岩、闪长玢岩、流纹斑岩和花岗闪长岩(Sui et al., 2018;Yu et al., 2019)。早子沟金锑矿床的构造应力场包括5个阶段:(1)主应力方向为NNE向的基底变形阶段,产生NWW向脆韧性断裂;(2)主应力方向为NE向的区域变形及岩浆侵位阶段,产生NW向脆韧性褶皱、断裂;(3)主应力方向为NE向的早期成矿阶段,产生NW向压扭逆冲,SN向扭性、NE向左旋张扭;(4)主应力方向为NNW向的晚期成矿阶段,产生NE向左旋压扭,SN向张扭、NW向右旋张扭;(5)主应力方向为SN向的成矿后阶段,产生NNE向左旋张性断裂(梁志录等,2016;韦良喜等,2018)。
|
图 2 西秦岭甘南地区早子沟金锑矿床地质简图(据梁志录等,2016;Yu et al., 2019修编) Fig. 2 Sketch geologic map of the giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit in the West Qinling, China (modified after Liang et al., 2016; Yu et al., 2019) |
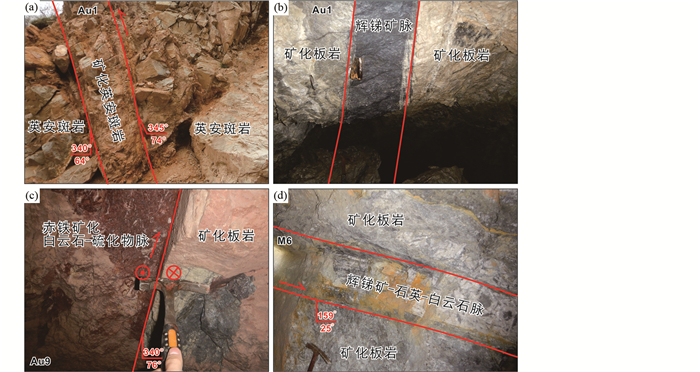
截至2012年底,整个矿区共圈定金锑矿体143个,按产状可分为陡倾斜矿体和缓倾斜矿体两种。共有16个矿体金资源量大于1t,其中Au1、Au9和M6矿体占早子沟金锑矿床总储量超过40%。Au1矿体产于F24逆断层中,是早子沟金锑矿床规模最大的矿体,探获金金属量约20t(图 3a, b)。Au1矿体围岩为英安斑岩和板岩,产状为330°~345°∠64°~83°。矿体金品位为1.00~11.20g/t,平均品位3.47g/t。Au9矿体产于F21左行逆断层中,探获金金属量约15t(图 3c)。Au9矿体围岩为板岩,整体走向55°,倾角较陡,约80°。矿体金品位为1.02~21.90g/t,平均品位3.46g/t。M6矿体产于F3正断层中,探获金金属量约15t(图 3d)。该矿体围岩为英安斑岩和板岩。矿体总体走向80°,倾角较缓,约25°。矿体金品位为1.01~12.97g/t,平均品位4.01g/t(Yu et al., 2019)。
|
图 3 早子沟金锑矿床典型矿化样式 (a)陡倾斜浸染状矿化;(b、c)陡倾斜脉状矿化;(d)缓倾斜脉状矿化 Fig. 3 Field and underground exposure showing mineralization styles of the Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit (a) disseminated ores in nearly vertical orebody; (b, c) load veins in nearly vertical orebody; (d) low-angle lode veins |
早子沟金锑矿床主要发育蚀变岩型(浸染状、细脉状、网脉状)(图 3a)和脉状矿化样式(图 3b, d)。蚀变岩型矿化产于侵入岩和板岩中,金属矿物以黄铁矿和毒砂为主(图 4a, b),是大部分陡倾斜矿体(Au1等)的主要矿化样式。脉状矿化分为两种,分别为金属硫化物-石英-白云石脉型(图 3d)和赤铁矿化白云石-硫化物脉型(图 3c)。金属硫化物-石英-白云石脉型矿化金属硫化物含量高,约占50%,局部可见纯金属硫化物脉(图 3b)。金属硫化物主要为辉锑矿(70%),其次为闪锌矿(10%)、黄铁矿(5%)、毒砂(5%),可见自然金(图 4c, d)。赤铁矿化白云石-硫化物脉型矿化以粗晶白云石为特征,白云石粒径可达8cm。金属硫化物约占20%,以赤铁矿为主(15%),其次有少量黄铁矿(3%)。赤铁矿化白云石-硫化物脉型矿化仅产于Au9等少量矿体,金属硫化物-石英-白云石脉型产于缓倾斜矿体和部分陡倾斜矿体中。

|
图 4 早子沟金锑矿床矿石显微特征 (a)浸染状矿化英安斑岩的毒砂、黄铁矿;(b)硫化物细脉状矿化板岩的毒砂、黄铁矿;(c、d)辉锑矿-石英-白云石脉状矿化的辉锑矿、石英、白云石、自然金. Apy-毒砂;Py-黄铁矿;Stb-辉锑矿;Au-自然金;Qz-石英;Dol-白云石 Fig. 4 Photomicrographs of ore samples at the Zaozigou deposit (a) pyrite and arsenopyrite as disseminated aggregates in porphyritic dacite; (b) pyrite and arsenopyrite veinlet in slate; (c, d) auriferous stibnite-quartz-dolomite vein. Apy-arsenopyrite; Py-pyrite; Stb-stibnite; Au-native gold; Qz-quartz; Dol-dolomite |
早子沟金锑矿床围岩蚀变受构造控制,蚀变程度较弱(梁志录等,2016;韦良喜等,2018),主要发育黄铁矿化、毒砂化、辉锑矿化、绢云母化、硅化和碳酸盐化蚀变。金属矿物主要为辉锑矿,其次为黄铁矿、毒砂、闪锌矿、赤铁矿,并有少量黄铜矿、黝铜矿、自然金。自然金呈他形,主要产于辉锑矿、石英和白云石的裂隙和晶隙中(图 4c, d)。不可见金主要赋存于黄铁矿和毒砂晶格中。非金属矿物主要为石英、白云石、长石、绢云母、黑云母、绿帘石(图 4)。根据矿脉穿插关系与矿物共生组合,可将早子沟矿床成矿作用划分为黄铁矿-黄铜矿-黝铜矿-石英-绢云母(Ⅰ)、黄铁矿-毒砂-石英-绢云母(Ⅱ)、辉锑矿-闪锌矿-石英-白云石-自然金(Ⅲ)和辉锑矿-石英-白云石(Ⅳ)四个阶段(图 5)。

|
图 5 早子沟金锑矿床矿物生成顺序图 实线代表矿物含量相对高,虚线代表矿物含量相对低 Fig. 5 Paragenetic sequence of the Zaozigou deposit interpreted from cross-cutting relationships, ore textures and sulfide assemblages The black full lines indicate high abundance and the black dashed lines represent minor amounts |
本次研究选取早子沟金锑矿床Au1矿体辉锑矿-石英-白云石-自然金脉中的白云石为研究对象,选择2个中段(2760m、2860m)、4个位置共采集9块辉锑矿-石英-白云石-自然金矿脉样品进行白云石的Sm-Nd同位素测试工作(表 1)。样品呈灰黑色,主要矿物为辉锑矿、石英和白云石,有少量自然金、黄铁矿、毒砂。其中,金属矿物辉锑矿呈自形针状、长柱状或他形粒状,具有多色性,呈白-灰白-深灰反射色,发育聚片双晶;自然金呈他形粒状,多分布于辉锑矿、石英内或辉锑矿、石英和白云石间隙中。非金属矿物石英呈他形粒状,白云石呈自形板状。
|
|
表 1 早子沟金锑矿床白云石Sm-Nd同位素组成 Table 1 The Sm-Nd isotopic compositions of the dolomites in the Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit |
将野外采集的样品清洗后粉碎至40~60目,在双目镜下挑选白云石。将初选样品用超净水冲洗并低温蒸干,再使用双目镜将白云石挑纯至99%以上。最后将纯净的白云石样品使用玛瑙研钵研磨至200目以下,进行Sm-Nd同位素测试工作。白云石的Sm-Nd同位素分析工作在中国地质调查局天津中心同位素年代学实验室完成。将溶解后的白云石样品溶液均匀分成两份,其中一份加入适量149Sm-146Nd混合稀释剂,待分离纯化后用于测定Sm、Nd含量。另一份溶液待分离纯化后用于Nd同位素比值测定。Sm-Nd分离流程采用传统AG50W×12阳离子交换树脂和P507树脂相结合的分离流程。Sm、Nd同位素测试均在TRITON热电离质谱仪上进行。由同位素稀释法原理计算得出Sm、Nd含量和147Sm/144Nd同位素比值,利用146Nd/144Nd=0.7219进行质量分馏校正。国际标样LRIG用于监控仪器状态,测定结果为143Nd/144Nd=0.512203;国际标样BCR-2用于监控分析方法的可靠性,测定结果为Sm=6.521×10-6,Nd=28.626×10-6,147Sm/144Nd=0.1377,143Nd/144Nd=0.512655(表 1),位于标准值(0.512635±0.000029)范围内。实验室全流程空白:Nd小于81×10-9,Sm小于74×10-9。具体实验分离流程和仪器测试参数详见刘文刚等(2018)。等时线年龄用ISOPLOT程序计算。
3 分析结果早子沟金锑矿床白云石Sm-Nd元素含量和同位素组成见表 1。白云石Sm含量为0.3221×10-6~4.918×10-6,Nd含量为0.5667×10-6~22.76×10-6。有3个样品147Sm/144Nd和143Nd/144Nd低于检出限。其余6个样品147Sm/144Nd和143Nd/144Nd分别为0.1306~0.2891和0.511847~0.512141,可构筑一条Sm-Nd等时线,t=273±59Ma(n=6;MSWD=50),初始143Nd/144Nd=0.511626。其中4个样品可构筑一条误差更小的等时线,t=282.5±5.1Ma(n=4;MSWD=1.6),初始143Nd/144Nd=0.5116053(图 6)。白云石εNd(0)为-15.42~-9.70,εNd(t)为-13.66~-12.19,tDM2为2033~2097Ma。

|
图 6 早子沟金锑矿床白云石Sm-Nd等时线图(a)和1/Nd-143Nd/144Nd图(b) Fig. 6 Sm-Nd isochron ages (a) and 143Nd/144Nd vs. 1/Nd (b) of dolomites in the Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit |
随着19世纪末衰变定律的发现,同位素地质年代学兴起,国内外学者对矿床的同位素年代学进行了大量探索,成矿年代学也有了较大的发展(Yang et al., 2014;McNaughton and Rasmussen, 2018)。近年来,大量高精度、高灵敏度的实验仪器,特别是同位素质谱仪的研发与投入使用,使同位素定年技术有了长足的进步,矿床同位素定年研究方面也发展出很多方法。常用方法有:对热液含铀副矿物(锆石、独居石、金红石、磷钇矿等)的U-Pb、Pb-Pb法(如邱昆峰和杨立强,2011;Taylor et al., 2015);对绢云母的Ar-Ar分步加热法(如Yang et al., 2014;Deng et al., 2015c);对方解石、闪锌矿的Rb-Sr法(如Yang and Zhou, 2001;Tian et al., 2014;Xiong et al., 2019);对金属矿物(辉钼矿、毒砂、黄铁矿)的Re-Os法(如Chu et al., 2015);对萤石、闪锌矿、方解石等矿物的Sm-Nd或Rb-Sr法(如Peng et al., 2003;Liu et al., 2007)等。早子沟金锑矿床有蚀变岩型矿化和脉状矿化两种矿化样式,脉状矿化矿石中矿物组分比较简单,主要包括辉锑矿、石英和白云石,缺乏或不含辉钼矿、毒砂、黄铁矿、绢云母等定年矿物。所以迄今为止,早子沟乃至西秦岭地区脉状金锑矿化成矿年龄数据尚少有发表。
前人对早子沟金锑矿床围岩进行了较为详细的年代学研究工作。古浪堤组板岩通过孢粉组合对比被认定沉积年代为中晚三叠世(徐亚东等,2007);侵入古浪堤组板岩的中酸性岩脉和岩席侵位年龄为约250~215Ma,主要包括石英闪长斑岩(248.9±1.4Ma~244.8±1.0Ma,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb;Sui et al., 2018)、英安斑岩(246.1±5.0Ma、248.1±3.0Ma,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb;Yu et al., 2019)、花岗闪长斑岩(242.6±0.6Ma、233.4±1.5Ma,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb;第鹏飞,2018)和闪长玢岩(237.5±1.4Ma,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb;Sui et al., 2018;215.5±2.1Ma、216.6±2.4Ma,SHRIMP锆石U-Pb;刘勇等,2012)等。因此,具有明显地质穿切关系的后生脉状金-锑矿化年龄不可能早于250Ma。早子沟金锑矿床脉状矿化辉锑矿、金、石英、白云石密切共生,白云石的形成时间可以直接代表辉锑矿和金的成矿年代。本次白云石Sm-Nd同位素等时线结果为282.5±5.1Ma,明显早于矿床围岩,因此该同位素等时线无效。
Sm-Nd同位素定年需要满足四个条件:(1)相对于Sm、Nd元素而言,目标矿物结晶后要处于封闭状态;(2)热液具有均一的初始Nd同位素;(3)目标矿物从热液体系沉淀生成后要含有足够的Sm、Nd元素;(4)目标矿物要有较大的Sm/Nd分馏,能够构筑等时线(Peng et al., 2003;Barker et al., 2009;Tian et al., 2014;刘善宝等,2017)。显微岩相学研究表明,早子沟金锑矿床脉状金锑矿石中的白云石透明且不含包裹体。同时,在分析测试过程中,对溶解在稀盐酸中的白云石样品进行离心,然后再进行化学分离,这能够有效地分离任何硅酸盐包裹体,保证测试结果代表白云石样品本身,免受富含稀土的硅酸盐矿物包裹体的干扰。Cherniak(1998)指出因Sm、Nd等稀土元素在方解石、白云石等含钙矿物中扩散速率低,认为这些矿物从热液沉淀结晶时,其Sm-Nd同位素体系可以保持封闭状态。方解石、白云石、萤石的Sm-Nd同位素定年在黔西南等地区的锑矿床已经得到成功应用(彭建堂等,2003;王加昇和温汉捷,2015;孙国涛等,2016),这表明在脉状锑矿床中的碳酸盐矿物可以满足Sm-Nd同位素定年的矿物封闭条件。白云石的Sm-Nd等时线图显示六个样品的初始Nd同位素大致相同,为0.511626,这也排除了成矿流体初始Nd同位素组成不均一的可能(图 6a)。本次研究所获得的白云石Sm和Nd含量最高可达4.918×10-6和22.76×10-6也足以满足Sm-Nd同位素定年需求(表 1)。
白云石1/Nd-143Nd/144Nd图显示1/Nd与143Nd/144Nd之间存在良好的线性关系(图 6b),暗示143Nd/144Nd值的变化受1/Nd值变化控制,而受147Sm/144Nd影响微弱,表明白云石Sm/Nd分馏很弱。另外,Nd同位素暗示早子沟矿床碳酸盐矿物中的Nd来源于扬子克拉通北缘或南秦岭的古元古代结晶基底(详见4.2)。这表明成矿流体可能混染了这一古老源区物质,导致本次白云石Sm-Nd同位素定年的结果(282.5±5.1Ma)明显早于围岩(约250Ma)。因此,白云石Sm/Nd分馏很弱且可能混染了古元古代结晶基底物质是导致早子沟金锑矿床白云石无法构筑有效的Sm-Nd同位素等时线的原因。除早子沟超大型金锑矿床外,西秦岭甘南地区还发育有早仁道中型金锑矿床、老豆中型金锑矿床、大沟顶中型锑矿床、美秀南小型锑矿床、张旗小型锑矿床、大寺坡小型锑矿床等一系列脉状(金)锑矿床(图 1b;Jin et al., 2017;Gou et al., 2019)。白云石Sm-Nd同位素体系因其局限性可能同样无法为这些相似脉状(金)锑矿床提供正确的年代学信息。
4.2 成矿流体来源前人对早子沟金锑矿床进行了绢云母、石英H-O和白云石C-O同位素研究工作。根据绢云母-水同位素平衡分馏方程计算,Ⅰ、Ⅱ阶段成矿热液δ18OH2O值为10.1‰~12.4‰,δDH2O值为-56‰~-76‰,靠近岩浆水区域(隋吉祥和李建威,2013)。根据石英-水同位素平衡分馏方程计算,Ⅲ、Ⅳ阶段成矿热液δ18OH2O值为-0.1‰~8.0‰,δDH2O值为-85.1‰~-99.2‰,落于变质水或岩浆水与大气降水混合区域(隋吉祥和李建威,2013;第鹏飞,2018)。这表明早子沟金锑矿床成矿流体可能来源于变质水或岩浆水与大气降水的混合。隋吉祥和李建威(2013)报道了成矿晚期白云石δ13C为-6.45‰~-3.65‰,δ18O为6.76‰~7.86‰,并据此认为成矿流体具有地幔来源属性。然而,Barker et al.(2009)指出碳酸盐矿物的C、O、Sr同位素在流体运移过程中极容易发生均一化,导致其无法准确示踪。Goldfarb and Groves(2015)也认为在流体运移、矿物沉淀的水岩反应过程中查明成矿流体中的碳源是十分困难的。早子沟金锑矿床在成矿晚期成矿流体发生了深部流体与大气降水的混合和均一作用,因此导致白云石的C、O、Sr同位素不能有效示踪成矿流体来源。
相比于C、O、Sr元素,Nd元素地球化学稳定性更好,在区域变质、热液活动、蚀变改造过程中其同位素组成极少发生均一化(Farmer and Depaolo, 1987;Barker et al., 2009;Liu et al., 2018)。因此,Nd同位素可以用来示踪沉淀白云石的成矿流体的源区(彭建堂等,2008;郭耀宇,2016;Liu and Hou, 2017)。如前所述,本次研究中没有构筑出有效的白云石Sm-Nd同位素等时线年龄,早子沟地区岩浆岩侵位年龄限定在215~250Ma,韦良喜等(2018)根据应力场分析认为脉状锑金矿化可能发生在印支晚期,略晚于215Ma。Qiu et al.(2019)通过对与成矿密切相关的热液独居石进行原位LA-ICP-MS年代学研究,表明早子沟矿床浸染状黄铁矿和毒砂矿化形成于约210Ma。因此,本文选择210Ma来计算早子沟金锑矿床白云石的εNd(t)值。
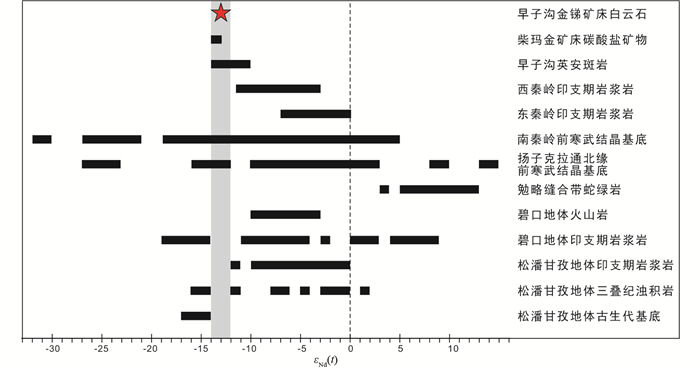
早子沟白云石εNd(0)为-15.42~-9.70,εNd(t)为-13.66~-12.19,变化范围相对较窄,表明样品源区相同。前人对西秦岭造山带及邻区不同地质体的Nd同位素特征进行了统计,西秦岭印支期岩浆岩εNd(t)为-11.55~-3.05,中位数为-6.42;东秦岭印支期岩浆岩εNd(t)为-6.97~-0.43,中位数为-4.25;松潘甘孜地体印支期岩浆岩εNd(t)为-11.43~0.00,中位数为-6.10;碧口地体印支期岩浆岩εNd(t)为-9.45~-3.19,中位数为-6.80;碧口地体火山岩系εNd(t)为-18.12~8.24,中位数为-8.81;松潘甘孜地体浅变质沉积岩εNd(t)为-16.19~1.91,中位数为-4.88;勉略缝合带蛇绿岩εNd(t)为3.15~9.25,中位数为6.07;南秦岭前寒武结晶基底为-31.51~4.25,中位数为-4.33;扬子克拉通北缘前寒武结晶基底为-26.19~2.34,中位数为-3.84(图 7;Li et al., 1996;Xu et al., 2002, 2008;张宗清等, 2002, 2006;闫全人等,2004;Xiao et al., 2007;Zhang et al., 2007a, b; Qin et al., 2008, 2009, 2010, 2013;Jiang et al., 2010;Yang et al., 2015b;郭耀宇,2016)。刘协鲁等(2014)测得西秦岭柴玛金矿床主成矿阶段碳酸盐矿物εNd(t)为-13.46~-13.21,第鹏飞(2018)测得早子沟地区岩浆岩围岩εNd(t)为-14.85~-10.06。这些数据与早子沟金锑矿床白云石εNd(t)值(-13.66~-12.19)接近,落于扬子克拉通北缘和南秦岭的前寒武结晶基底范围内,而不同于秦岭其他地区印支期岩浆岩,碧口地区岩浆岩、火山岩,松潘甘孜地区岩浆岩、浊积岩、古生代基底等,暗示早子沟矿床白云石可能与本区英安斑岩来源相同,均来自扬子克拉通北缘或南秦岭的前寒武结晶基底(图 7)。第鹏飞(2018)通过全岩主微量元素分析表明岩浆岩围岩为偏铝质到过铝质岩石,属于高钾钙碱性系列未分异的花岗岩。这些花岗岩围岩εNd(t)为-12.5~-8.9,Hf的tDM2为1837~2076Ma,暗示它们来自于古元古代地壳的再改造作用(Yu et al., 2019),可能起源于高压、低温条件下古元古代镁铁质地壳的部分熔融(第鹏飞,2018)。同时,早子沟地区英安斑岩Nd的tDM2为1882~2210Ma(第鹏飞,2018),早子沟金锑矿床白云石Nd的tDM2为2033~2132Ma。这表明早子沟金锑矿床脉状金-锑矿化中白云石、英安斑岩围岩和柴玛金矿床中碳酸盐矿物的Nd很可能来自扬子克拉通北缘或南秦岭的古元古代结晶基底。
|
图 7 早子沟金锑矿床白云石εNd(t)值与秦岭及其周边地区对比图数据来源:Li et al., 1996;张宗清等, 2002, 2006;Xu et al., 2002, 2008;闫全人等,2004;Zhang et al., 2007a, b;Xiao et al., 2007;Qin et al., 2008, 2009, 2010, 2013;Jiang et al., 2010;刘协鲁等,2014;Yang et al., 2015b;郭耀宇,2016;第鹏飞,2018 Fig. 7 εNd(t) values of dolomites from the Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit, with comparison to those from Qinling and its adjacent areas |
(1) Nd同位素特征表明早子沟矿床脉状金锑矿化中的白云石与英安斑岩围岩具有相同的Nd源区,且很可能来自扬子克拉通北缘或南秦岭的古元古代结晶基底。
(2) 早子沟金锑矿床成矿期热液白云石Sm-Nd同位素等时线定年为282.5±5.1Ma,早于矿床围岩,与地质事实不符。这种假等时线产生的原因可能是白云石Sm/Nd分馏很弱且成矿流体混染了古元古代结晶基底物质,这一认识将为西秦岭同类型金锑矿床的年代学研究提供参考。白云石Sm-Nd同位素体系可能同样无法为该类型金锑矿床提供正确的年代学信息。
致谢 论文的完成得益于邓军教授、杨立强教授、张静教授的指导和帮助,得益于与曾云川博士、张瑞忠博士、郭耀宇博士、郭林楠博士、高雪博士和鲍新尚博士的探讨。周新华研究员和两位匿名审稿人对论文初稿提出了宝贵的修改意见,加深了我们对Sm-Nd同位素体系的认知和思考。野外工作得到早子沟金矿有限责任公司姜桂鹏、于明海、周飞、郭俊利、朱锐、南福定、杨腾雾和甘肃省地矿局梁志录、金鼎国、麻红顺等老师的帮助与支持。经济地质学家协会基金委员会Hugh McKinstry基金(Hugh McKinstry fund from Society of Economic Geologists Foundation,Inc.)资助了本研究。在此一并表示衷心感谢。
谨以此文祝贺翟裕生院士九十华诞,感谢翟先生为矿床学与区域成矿学做出的杰出贡献!
Bao WR and Liu JL. 2016. Ore-forming sources of Zaozigou deposit. Gansu Science and Technology, 32(14): 41-44 (in Chinese) |
Barker SLL, Bennett VC, Cox SF, Norman MD and Gagan MK. 2009. Sm-Nd, Sr, C and O isotope systematics in hydrothermal calcite-fluorite veins:Implications for fluid-rock reaction and geochronology. Chemical Geology, 268(1-2): 58-66 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.07.009 |
Cao XF, Sanogo MLS, Lü XB, He MC, Chen C, Zhu J, Tang RK, Liu Z and Zhang B. 2012. Ore-forming process of the Zaozigou gold deposit:Constraints from Geological characteristics, gold occurrence and stable isotope compositions. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 42(4): 1039-1054 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Chen H, Hu RZ, Bi XW, Zhu JJ and Shi SH. 2012. Calcite Sm-Nd Isochron age and its geological significance of the 6722 uranium ore deposit, southern Jiangxi Province, China. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 32(1): 52-59 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Chen RL, Chen ZL, Wu JJ, Liang ZL, Han FB, Wang Y, Xiao CH, Wei XL and Shen T. 2018. Fluid inclusions and S-Pb isotopes in Zaozigou gold deposit, Hezuo in Gansu Province. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 48(1): 87-104 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Cherniak DJ. 1998. REE diffusion in calcite. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 160(3-4): 273-287 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00087-9 |
Chu ZY, Yan Y, Chen Z, Guo JH, Yang YH, Li CF and Zhang YB. 2015. A comprehensive method for precise determination of Re, Os, Ir, Ru, Pt, Pd concentrations and Os isotopic compositions in geological samples. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 39(2): 151-169 DOI:10.1111/ggr.2015.39.issue-2 |
Dai WJ, Chen YY, Liu CX, Liu XD and Ma XY. 2011. Wallrock alteration and gold mineralization in Zaozigou gold mine of Gansu Province. Gansu Geology, 20(3): 31-36 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ, Li CS and Wang CM. 2014a. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region, SW China. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 419-437 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.002 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ and Santosh M. 2014b. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China. Earth-Science Reviews, 138: 268-299 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.05.015 |
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF and Pan RG. 2015a. Origin of the Jiaodong-type Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Constraints from fluid inclusion and C-D-O-S-Sr isotope compositions. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 674-686 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.04.018 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ, Hou ZQ, Jiang CZ and Danyushevsky L. 2015b. Geology and genesis of the giant Beiya porphyry-skarn gold deposit, northwestern Yangtze Block, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 70: 457-485 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.02.015 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Carranza EJM and Lu YJ. 2015c. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry. Mineralium Deposita, 50(8): 987-1006 DOI:10.1007/s00126-015-0584-1 |
Deng J and Wang QF. 2016. Gold mineralization in China:Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Research, 36: 219-274 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.003 |
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF, Yildirim D and Liang YY. 2017a. Isotopic characterization and petrogenetic modeling of Early Cretaceous mafic diking-lithospheric extension in the North China craton, eastern Asia. GSA Bulletin, 129(11-12): 1379-1407 DOI:10.1130/B31609.1 |
Deng J, Wang QF and Li GJ. 2017b. Tectonic evolution, superimposed orogeny, and composite metallogenic system in China. Gondwana Research, 50: 216-266 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.02.005 |
Di PF. 2018. Geochemistry and ore-forming mechanism on Zaozigou gold deposit in Xiahe-Hezuo, West Qinling, China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 1-86 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Dong YP and Santosh M. 2016. Tectonic architecture and multiple orogeny of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China. Gondwana Research, 29(1): 1-40 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.009 |
Dong YP, Yang Z, Liu XM, Sun SS, Li W, Cheng B, Zhang FF, Zhang XN, He DF and Zhang GW. 2016. Mesozoic intracontinental orogeny in the Qinling Mountains, central China. Gondwana Research, 30: 144-158 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.05.004 |
Duan M, Niu YL, Kong JJ, Sun P, Hu Y, Zhang Y, Chen S and Li JY. 2016. Zircon U-Pb geochronology, Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic composition and geological significance of the Late-Triassic Baijiazhuang and Lvjing granitic plutons in West Qinling Orogen. Lithos, 260: 443-456 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2016.04.015 |
Farmer GL and DePaolo DJ. 1987. Nd and Sr isotope study of hydrothermally altered granite at San Manuel, Arizona:Implications for element migration paths during the formation of porphyry copper ore deposits. Economic Geology, 82(5): 1142-1151 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.82.5.1142 |
Geng JZ, Qiu KF, Gou ZY and Yu HC. 2017. Tectonic regime switchover of Triassic western Qinling orogen:Constraints from LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology and Lu-Hf isotope of Dangchuan intrusive complex in Gansu, China. Chemie der Erde-Geochem, 77: 637-651 DOI:10.1016/j.chemer.2017.05.001 |
Goldfarb RJ and Groves DI. 2015. Orogenic gold:Common or evolving fluid and metal sources through time. Lithos, 233: 2-26 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.07.011 |
Gou ZY, Yu HC, Qiu KF, Geng JZ, Wu MQ, Wang YG, Yu MH and Li J. 2019. Petrogenesis of ore-hosting diorite in the Zaorendao gold deposit at the Tongren-Xiahe-Hezuo polymetallic district, West Qinling, China. Minerals, 9(2): 76 DOI:10.3390/min9020076 |
Guo YY. 2016. Indosinian orogenic gold metallogenic deposits in the southern belt of the West Qinling, central China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-180 (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Jiang YH, Jin GD, Liao SY, Zhou Q and Zhao P. 2010. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on the origin of Late Triassic granitoids from the Qinling orogen, central China:Implications for a continental arc to continent-continent collision. Lithos, 117(1-4): 183-197 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.02.014 |
Jin XY, Li JW, Hofstra AH and Sui JX. 2017. Magmatic-hydrothermal origin of the Early Triassic Laodou lode gold deposit in the Xiahe-Hezuo district, West Qinling orogen, China:Implications for gold metallogeny. Mineralium Deposita, 52(6): 883-902 DOI:10.1007/s00126-016-0710-8 |
Li N, Chen YJ, Santosh M and Pirajno F. 2015a. Compositional polarity of Triassic granitoids in the Qinling orogen, China:Implication for termination of the northernmost paleo-Tethys. Gondwana Research, 27(1): 244-257 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.09.017 |
Li SG, Sun WD, Zhang GW, Chen JY and Yang YC. 1996. Chronology and geochemistry of metavolcanic rocks from Heigouxia Valley in the Mian-Lue tectonic zone, South Qinling:Evidence for a Paleozoic oceanic basin and its close time. Science in Chine (Series D), 39(3): 300-310 |
Li XW, Mo XX, Huang XF, Dong GC, Yu XH, Luo MF and Liu YB. 2015b. U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of the Early Indosinian Tongren pluton in West Qinling:Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 97: 38-50 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.10.017 |
Liang ZL, Chen GZ, Ma HS and Zhang YN. 2016. Evolution of ore-controlling faults in the Zaozigou gold deposit, western Qinling. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 40(2): 354-366 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu SB, Liu ZQ, Wang CH, Wang DH, Zhao Z and Hu ZH. 2017. Geochemical characteristics of REEs and trace elements and Sm-Nd dating of scheelite from the Zhuxi giant tungsten deposit in Northeast Jiangxi. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(5): 17-30 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu WG, Li GZ, Liu H, Chen Y, Xiao ZB, Zhou HY, Zhang J, Tu JR and Li HM. 2018. Micro-fluorite sample digestion technology and high precision thermionic mass spectrometry determination for Sm-Nd isotopes. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 39(1): 119-124 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu XL, Wang YT, Hu QQ, Wei R, Wang RT, Wen SW, Chen MS and Yang GH. 2014. Sm-Nd isotopic dating of carbonate minerals from the Chaima gold deposit in the Fengxian-Taibai ore concentration area, Shaanxi Province and its implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(1): 271-280 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu Y, Deng J, Li CF, Shi GH and Zheng AL. 2007. REE composition in scheelite and scheelite Sm-Nd dating for the Xuebaoding W-Sn-Be deposit in Sichuan. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(18): 2543-2550 DOI:10.1007/s11434-007-0355-1 |
Liu Y, Liu YH, Dong FC, Li ZH, Yu JK and Ma XP. 2012. Accurate dating of mineralogenetic epoch and its geological significance in Zaozigou gold deposit, Gansu Province. Gold, 33(11): 10-17 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu Y and Hou ZQ. 2017. A synthesis of mineralization styles with an integrated genetic model of carbonatite-syenite-hosted REE deposits in the Cenozoic Mianning-Dechang REE metallogenic belt, the eastern Tibetan Plateau, southwestern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 137: 35-79 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.01.010 |
Liu Y, Chakhmouradian AR, Hou ZQ, Song WL and Kynicky J. 2018. . Development of REE mineralization in the giant Maoniuping deposit (Sichuan, China):Insights from mineralogy, fluid inclusions, and trace-element geochemistry. Mineralium Deposita DOI:10.1007/s00126-018-0836-y |
McNaughton NJ and Rasmussen B. 2018. Geochemical characterization of xenotime formation environments using U-Th. Chemical Geology, 484: 109-119 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.08.016 |
Peng JT, Hu RZ and Burnard PG. 2003. Samarium-neodymium isotope systematics of hydrothermal calcites from the Xikuangshan antimony deposit (Hunan, China):The potential of calcite as a geochronometer. Chemical Geology, 200(1-2): 129-136 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(03)00187-6 |
Peng JT, Hu RZ and Jiang GH. 2003. Samarium-neodymium isotope system of fluorites from the Qinglong antimony deposit, Guizhou Province:Constraints on the mineralizing age and ore-forming materials' sources. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 19(4): 785-791 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Peng JT, Zhang DL, Hu RZ, Wu MJ and Lin YX. 2008. Sm-Nd and Sr isotope geochemistry of hydrothermal scheelite from the Zhazixi W-Sb deposit, western Hunan. Acta Geologica Sinica, 82(11): 1514-1521 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Qin JF, Lai SC and Li YF. 2008. Slab breakoff model for the Triassic post-collisional adakitic granitoids in the Qinling orogen, central China:Zircon U-Pb ages, geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic constraints. International Geology Review, 50(12): 1080-1104 DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.50.12.1080 |
Qin JF, Lai SC, Grapes R, Diwu CR, Ju YJ and Li YF. 2009. Geochemical evidence for origin of magma mixing for the Triassic monzonitic granite and its enclaves at Mishuling in the Qinling orogen (central China). Lithos, 112(3-4): 259-276 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.03.007 |
Qin JF, Lai SC, Grapes R, Diwu CR, Ju YJ and Li YF. 2010. Origin of Late Triassic high-Mg adakitic granitoid rocks from the Dongjiangkou area, Qinling orogen, central China:Implications for subduction of continental crust. Lithos, 120(3-4): 347-367 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.022 |
Qin JF, Lai SC and Li YF. 2013. Multi-stage granitic magmatism during exhumation of subducted continental lithosphere:Evidence from the Wulong pluton, South Qinling. Gondwana Research, 24(3-4): 1108-1126 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.02.005 |
Qiu KF and Yang LQ. 2011. Genetic feature of monazite and its U-Th-Pb dating:Critical considerations on the tectonic evolution of Sanjiang Tethys. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2721-2732 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Qiu KF, Taylor RD, Song YH, Yu HC, Song KR and Li N. 2016a. Geologic and geochemical insights into the formation of the Taiyangshan porphyry copper-molybdenum deposit, Western Qinling Orogenic Belt, China. Gondwana Research, 35: 40-58 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.014 |
Qiu KF, Deng J, Taylor RD, Song KR, Song YH, Li QZ and Goldfarb RJ. 2016b. Paleozoic magmatism and porphyry Cu-mineralization in an evolving tectonic setting in the North Qilian Orogenic Belt, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 122: 20-40 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.02.007 |
Qiu KF and Deng J. 2017. Petrogenesis of granitoids in the Dewulu skarn copper deposit:Implications for the evolution of the Paleotethys Ocean and mineralization in Western Qinling, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 90: 1078-1098 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.09.027 |
Qiu KF, Marsh E, Yu HC, Pfaff K, Gulbransen C, Gou ZY and Li N. 2017. Fluid and metal sources of the Wenquan porphyry molybdenum deposit, Western Qinling, NW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 86: 459-473 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.035 |
Qiu KF, Yu HC, Gou ZY, Liang ZL, Zhang JL and Zhu R. 2018. Nature and origin of Triassic igneous activity in the Western Qinling Orogen:The Wenquan composite pluton example. International Geology Review, 60(2): 242-266 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2017.1334598 |
Qiu KF, Yu HC, Deng J, McIntire D, Gou ZY, Geng JZ, Chang ZS, Zhu R, Liang ZL and Goldfarb RJ. 2019. The giant Zaozigou orogenic Au-Sb deposit in West Qinling, China:Magmatic or metamorphic origin? Mineralium Deposita, under review
|
Su WC, Hu RZ, Xia B, Xia Y and Liu YP. 2009. Calcite Sm-Nd isochron age of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China. Chemical Geology, 258(3-4): 269-274 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.10.030 |
Sui JX and Li JW. 2013. Geochronology and genesis of the Zaozigou gold deposit, Xiahe-Hezuo district, West Qinling. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, (Suppl.2): 346-347 (in Chinese) |
Sui JX, Li JW, Jin XY, Vasconcelos P and Zhu R. 2018. 40Ar/39Ar and U-Pb constraints on the age of the Zaozigou gold deposit, Xiahe-Hezuo district, West Qinling orogen, China:Relation to early Triassic reduced intrusions emplaced during slab rollback. Ore Geology Reviews, 101: 885-899 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.08.014 |
Sun GT, Shen NP, Su WC, Feng YX, Zhao JX, Dong WD and Zhao H. 2016. Characteristics and implication of trace elements and Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of calcites from the Miaolong Au-Sb deposit, Guizhou Province, China. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 36(3): 404-412 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Taylor RD, Goldfarb RJ, Monecke T, Fletcher IR, Cosca MA and Kelly NM. 2015. Application of U-Th-Pb phosphate geochronology to young orogenic gold deposits:New age constraints on the formation of the Grass Valley gold district, Sierra Nevada Foothills Province, California. Economic Geology, 110(5): 1313-1337 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.110.5.1313 |
Tian SH, Gong YL, Yang ZS, Hou ZQ, Liu YC, Song YC, Xue WW, Lu HF, Wang YB, Zhu T and Yu CJ. 2014. Rb-Sr and Sm-Nd isochron ages of the Dongmozhazhua and Mohailaheng Pb-Zn ore deposits in the Yushu area, southern Qinghai and their geological implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(2): 558-569 DOI:10.1111/acgs.2014.88.issue-2 |
Wang JS and Wen HJ. 2015. Sm-Nd dating of hydrothermal calcites from Jiaoli-Lae mercury deposit, Guizhou Province. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 45(5): 1384-1393 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang YL, Chen YC, Wang DH, Xu J, Chen ZH and Liang T. 2013. The principal antimony concentration areas in China and their resource potentials. Geology in China, 40(5): 1366-1378 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wei LX, Chen ZL, Pang ZS, Han FB and Xiao CH. 2018. An analysis of the tectonic stress field in the Zaozigou gold deposit, Hezuo area, Gansu Province. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 39(1): 79-93 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wu YF, Li JW, Evans K, Koenig AE, Li ZK, O'Brien H, Lahaye Y, Rempel K, Hu SY, Zhang ZP and Yu JP. 2018. Ore-forming processes of the Daqiao epizonal orogenic gold deposit, West Qinling orogen, China:Constraints from textures, trace elements, and sulfur isotopes of pyrite and marcasite, and Raman Spectroscopy of carbonaceous material. Economic Geology, 113(5): 1093-1132 DOI:10.5382/econgeo.2018.4583 |
Xiao L, Zhang HF, Clemens JD, Wang QW, Kan ZZ, Wang KM, Ni PZ and Liu XM. 2007. Late Triassic granitoids of the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau:Geochronology, petrogenesis and implications for tectonic evolution. Lithos, 96(3-4): 436-452 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.11.011 |
Xiong YQ, Shao YJ, Mao JW, Wu SC, Zhou HD and Zheng MH. 2019. The polymetallic magmatic-hydrothermal Xiangdong and Dalong systems in the W-Sn-Cu-Pb-Zn-Ag Dengfuxian orefield, SE China:Constraints from geology, fluid inclusions, H-O-S-Pb isotopes, and sphalerite Rb-Sr geochronology. Mineralium Deposita: 1-24 DOI:10.1007/s00126-019-00863-x |
Xu JF, Castillo PR, Li XH, Yu XY, Zhang BR and Han YW. 2002. MORB-type rocks from the Paleo-Tethyan Mian-Lueyang northern ophiolite in the Qinling Mountains, central China:Implications for the source of the low 206Pb/204Pb and high 143Nd/144Nd mantle component in the Indian Ocean. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 198(3-4): 323-337 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00536-8 |
Xu JF, Zhang BR and Han YW. 2008. Geochemistry of the Mian-Lue ophiolites in the Qinling Mountains, central China:Constraints on the evolution of the Qinling orogenic belt and collision of the North and South China cratons. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32(5-6): 336-347 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.11.004 |
Xu YD, Yu JX, Luo GM, Kou XH and Chen FN. 2007. Triassic palynological assemblage of the Gulangdi Formation in Tongren County, Qinghai Province, China. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 32(5): 638-650 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yan QR, Hanson AD, Wang ZQ, Yan Z, Druschke PA, Wang T, Liu DY, Song B and Jiang CF. 2004. Geochemistry and tectonic setting of the Bikou volcanic terrane on the northern margin of the Yangtze plate. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 23(1): 1-11 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang JH and Zhou XH. 2001. Rb-Sr, Sm-Nd, and Pb isotope systematics of pyrite:Implications for the age and genesis of lode gold deposits. Geology, 29(8): 711-714 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0711:RSSNAP>2.0.CO;2 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Goldfarb RJ, Zhang J, Gao BF and Wang ZL. 2014. 40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the formation of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit:New implications for timing and duration of hydrothermal activity in the Jiaodong gold province, China. Gondwana Research, 25(4): 1469-1483 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.001 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Dilek Y, Qiu KF, Ji XZ, Li N, Taylor RD and Yu JY. 2015a. Structure, geochronology, and petrogenesis of the Late Triassic Puziba granitoid dikes in the Mianlue suture zone, Qinling Orogen, China. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 127(11-12): 1831-1854 DOI:10.1130/B31249.1 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Qiu KF, Ji XZ, Santosh M, Song KR, Song YH, Geng JZ, Zhang C and Hua B. 2015b. Magma mixing and crust-mantle interaction in the Triassic monzogranites of Bikou Terrane, central China:Constraints from petrology, geochemistry, and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic systematics. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 98: 320-341 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.023 |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Guo LN, Li RH, Groves DI, Danyushevsky LV, Zhang C, Zheng XL and Zhao H. 2016. Relationships between gold and pyrite at the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Implications for gold source and deposition in a brittle epizonal environment. Economic Geology, 111(1): 105-126 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.111.1.105 |
Yi LS, Fan HR, Zhai MG, Li YX, Ma HF, Tian JJ and Xiu XQ. 2016. Fluorite Sm-Nd isochron and pitchblende U-Pb dating in the Baiyanghe Be-U deposit, Xinjiang and their geological significances. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(7): 2099-2110 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yu HC, Guo CA, Qiu KF, McIntire D, Jiang GP, Gou ZY, Geng JZ, Pang Y, Zhu R and Li NB. 2019. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the formation of the giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit, West Qinling, China. Minerals, 9(1): 37 DOI:10.3390/min9010037 |
Zhai YS, Deng J, Tang ZL, Xiao RG, Song HL, Peng RM, Sun ZS and Wang JP. 2004. Metallogenic systems on the paleocontinental margin of the North China Craton. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(2): 592-603 |
Zhai YS, Wang JP, Deng J, Peng RM and Liu JJ. 2008. Temporal-spatial evolution of metallogenic systems and its significance to mineral exploration. Geoscience, 22(2): 143-150 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang GW, Zhang BR, Yuan XC and Xiao QH. 2001. Qinling Orogenic Belt and Continental Dynamics. Beijing: Science Press, 1-855 (in Chinese)
|
Zhang HF, Jin LL, Zhang L, Harris N, Zhou L, Hu SH and Zhang BR. 2007a. Geochemical and Pb-Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of granitoids from western Qinling belt:Constraints on basement nature and tectonic affinity. Science in China (Series D), 50(2): 184-196 DOI:10.1007/s11430-007-2015-3 |
Zhang HF, Xiao L, Zhang L, Yuan HL and Jin LL. 2007b. Geochemical and Pb-Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of Indosinian granitoids from the Bikou block, northwest of the Yangtze plate:Constraints on petrogenesis, nature of deep crust and geodynamics. Science in China (Series D), 50(7): 972-983 DOI:10.1007/s11430-007-0014-z |
Zhang J, Li L, Gilbert S, Liu JJ and Shi WS. 2014. LA-ICP-MS and EPMA studies on the Fe-S-As minerals from the Jinlongshan gold deposit, Qinling Orogen, China:Implications for ore-forming processes. Geological Journal, 49(4-5): 482-500 DOI:10.1002/gj.v49.4-5 |
Zhang J, Chen YJ, Su QW, Zhang X, Xiang SH and Wang QS. 2016. Geology and genesis of the Xiaguan Ag-Pb-Zn orefield in Qinling orogen, Henan Province, China:Fluid inclusion and isotope constraints. Ore Geology Reviews, 76: 79-93 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.01.003 |
Zhang ZQ, Tang SH, Yuan ZX, Bai G and Wang JH. 2001. The Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr isotopic systems of the dolomites in the Bayan Obo deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(4): 637-642 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang ZQ, Zhang GW and Tang SH. 2002. Geochronology of Metamorphic Strata in the Southern Qinling. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-256 (in Chinese)
|
Zhang ZQ, Zhang GW, Liu DY, Wang ZQ, Tang SH and Wang JH. 2006. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Ophiolite, Granite and Clastic Sedimentary Rocks in the Qinling Orogenic Belt. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-348 (in Chinese)
|
Zhao HS, Wang QF, Groves DI and Deng J. 2019. A rare Phanerozoic amphibolite-hosted gold deposit at Danba, Yangtze Craton, China:Significance to fluid and metal sources for orogenic gold systems. Mineralium Deposita, 54(1): 133-152 DOI:10.1007/s00126-018-0845-x |
包万荣, 刘继来. 2016. 甘肃早子沟金矿床成矿物质来源分析. 甘肃科技, 32(14): 41-44. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0952.2016.14.013 |
曹晓峰, Sanogo MLS, 吕新彪, 何谋春, 陈超, 朱江, 唐然坤, 刘智, 张彬. 2012. 甘肃枣子沟金矿床成矿过程分析——来自矿床地质特征、金的赋存状态及稳定同位素证据. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 42(4): 1039-1054. |
陈恒, 胡瑞忠, 毕献武, 朱经经, 石少华. 2012. 赣南6722铀矿床方解石Sm-Nd等时线年龄及其地质意义. 矿物学报, 32(1): 52-59. |
陈瑞莉, 陈正乐, 伍俊杰, 梁志录, 韩凤彬, 王永, 肖昌浩, 韦良喜, 沈滔. 2018. 甘肃合作早子沟金矿床流体包裹体及硫铅同位素特征. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 48(1): 87-104. |
代文军, 陈耀宇, 刘春先, 刘东晓, 马小云. 2011. 甘肃枣子沟金矿围岩蚀变特征及其与金矿化的关系. 甘肃地质, 20(3): 31-36. |
第鹏飞. 2018.西秦岭夏河-合作早子沟金矿床地球化学特征及成矿机制研究.博士学位论文.兰州: 兰州大学, 1-86
|
郭耀宇. 2016.西秦岭金矿带南亚带印支期造山型金成矿系统.博士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学, 1-180
|
梁志录, 陈国忠, 麻红顺, 张愿宁. 2016. 西秦岭早子沟金矿控矿断裂形成演化. 大地构造与成矿学, 40(2): 354-366. |
刘善宝, 刘战庆, 王成辉, 王登红, 赵正, 胡正华. 2017. 赣东北朱溪超大型钨矿床中白钨矿的稀土、微量元素地球化学特征及其Sm-Nd定年. 地学前缘, 24(5): 17-30. |
刘文刚, 李国占, 刘卉, 陈印, 肖志斌, 周红英, 张健, 涂家润, 李惠民. 2018. 微量萤石样品消解技术及其Sm-Nd同位素高精度热离子质谱法测试. 地球学报, 39(1): 119-124. |
刘协鲁, 王义天, 胡乔青, 魏然, 王瑞廷, 温深文, 陈明寿, 杨光华. 2014. 陕西省凤太矿集区柴蚂金矿床碳酸盐矿物的Sm-Nd同位素测年及意义. 岩石学报, 30(1): 271-280. |
刘勇, 刘云华, 董福辰, 李中会, 于建坤, 马晓平. 2012. 甘肃枣子沟金矿床成矿时代精确测定及其地质意义. 黄金, 33(11): 10-17. |
彭建堂, 胡瑞忠, 蒋国豪. 2003. 萤石Sm-Nd同位素体系对晴隆锑矿床成矿时代和物源的制约. 岩石学报, 19(4): 785-791. |
彭建堂, 张东亮, 胡瑞忠, 吴梦君, 林源贤. 2008. 湘西渣滓溪钨锑矿床白钨矿的Sm-Nd和Sr同位素地球化学. 地质学报, 82(11): 1514-1521. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.11.006 |
邱昆峰, 杨立强. 2011. 独居石成因特征与U-Th-Pb定年及三江特提斯构造演化研究例析. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2721-2732. |
隋吉祥, 李建威. 2013. 西秦岭夏河-合作地区枣子沟金矿床成矿时代与矿床成因. 矿物学报, (增2): 346-347. |
孙国涛, 沈能平, 苏文超, 俸月星, 赵建新, 彭建堂, 董文斗, 赵海. 2016. 贵州苗龙金锑矿床方解石微量元素、Sr-Nd同位素地球化学特征及其意义. 矿物学报, 36(3): 404-412. |
王加昇, 温汉捷. 2015. 贵州交犁拉峨汞矿床方解石Sm-Nd同位素年代学. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 45(5): 1384-1393. |
王永磊, 陈毓川, 王登红, 徐珏, 陈郑辉, 梁婷. 2013. 中国锑矿主要矿集区及其资源潜力探讨. 中国地质, 40(5): 1366-1378. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.05.003 |
韦良喜, 陈正乐, 庞振山, 韩凤彬, 肖昌浩. 2018. 甘肃省合作市早子沟金矿床构造应力场分析. 地球学报, 39(1): 79-93. |
徐亚东, 喻建新, 罗根明, 寇晓虎, 陈奋宁. 2007. 青海省同仁县古浪堤中上三叠统古浪堤组孢粉组合及其地层意义. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 32(5): 638-650. |
闫全人, Hanson AD, 王宗起, 闫臻, Druschke PA, 王涛, 刘敦一, 宋彪, 姜春发. 2004. 扬子板块北缘碧口群火山岩的地球化学特征及其构造环境. 岩石矿物学杂志, 23(1): 1-11. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2004.01.001 |
衣龙升, 范宏瑞, 翟明国, 李月湘, 马汉峰, 田建吉, 修晓茜. 2016. 新疆白杨河铍铀矿床萤石Sm-Nd和沥青铀矿U-Pb年代学及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 32(7): 2099-2110. |
翟裕生, 王建平, 邓军, 彭润民, 刘家军. 2008. 成矿系统时空演化及其找矿意义. 现代地质, 22(2): 143-150. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2008.02.001 |
张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 肖庆辉. 2001. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-855.
|
张宗清, 唐索寒, 袁忠信, 白鸽, 王进辉. 2001. 白云鄂博矿床白云岩的Sm-Nd、Rb-Sr同位素体系. 岩石学报, 17(4): 637-642. |
张宗清, 张国伟, 刘敦一, 王宗起, 唐索寒, 王进辉. 2006. 秦岭造山带蛇绿岩、花岗岩和碎屑沉积岩同位素年代学和地球化学. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-348.
|
张宗清, 张国伟, 唐索寒. 2002. 南秦岭变质地层同位素年代学. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-256.
|
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35


