2. 自然资源部深地动力学重点实验室, 中国地质科学院地质研究所, 北京 100037;
3. 桂林理工大学地球科学学院, 桂林 541004
2. MNR Key Laboratory of Deep-Earth Dynamics, Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100037, China;
3. School of Earth Sciences, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin 541004, China
Brögger (1921)在研究与挪威Fen碱性杂岩体密切相关的交代蚀变岩时首次提出了“霓长岩(fenite)”这个术语。尔后,世界上其他地方也先后报道了霓长岩,大量关于霓长岩的研究相继问世(McKie, 1966; Woolley, 1982; Yardley and Lloyd, 1995)。霓长岩是碳酸岩(或碱性岩)流体对围岩的交代蚀变作用的产物,主要由碱性长石和碱性镁铁质矿物组成,形成霓长岩的交代蚀变作用即霓长岩化作用(fenitization)(McKie, 1966; Morogan, 1989; Cooper et al., 2016)。霓长岩与碳酸岩(或碱性岩)及围岩的性质密切相关,常见于碳酸岩(或碱性岩)与围岩的接触部位。霓长岩化作用是碳酸岩相关矿床(如REE、Nb等)常见的蚀变类型(Le Bas, 2008; Elliott et al., 2018),它往往发生于开放体系,促使围岩和交代流体发生组分迁移以达到新的物理化学平衡(Woolley, 1982)。一般而言,控制霓长岩化作用的主要因素包括:(1)碳酸岩(或碱性岩)的侵位条件;(2)交代流体的性质及组分;(3)围岩的岩石学及地球化学特征;(4)物理化学条件(如温度、压力、氧逸度、岩石孔隙率等)(杨学明等, 2000; 王凯怡, 2015)。
碳酸岩在所有火成岩中REE含量较高且轻重REE分异较大,REE平均含量为3000×10-6~10000×10-6,高于原始地幔500~1000倍(Nelson et al., 1988)。碳酸岩常常与碱性岩密切共生而形成碳酸岩-碱性岩杂岩体,其高度富集REE、Ba、Sr、Nd等元素(Chakhmouradian, 2006; Xu et al., 2015),碳酸岩型REE矿床也是世界上最重要的REE矿床类型(Weng et al., 2015)。碳酸岩岩浆黏度较小(15×10-3~5×10-3Pa·s;Dobson et al., 1996)且具有较低的密度(2.2g/cm3; Treiman and Schedl, 1983),在碳酸岩岩浆演化过程中,大量富含REE及挥发份的流体可直接从碳酸岩岩浆中分异出来(Veksler et al., 1998)。然而,由于碳酸岩容易遭受后期地质事件的改造(如变质作用、构造活动等),使其在某些岩石学特征上往往难以与沉积变质大理岩相区别。此外,碳酸岩岩浆在侵位过程中往往存在组分迁移,初始岩浆与侵位后固结的碳酸岩体在成分上可能存在较大差异,而与碳酸岩密切相关的霓长岩却能保持相对稳定。因此,霓长岩可作为指示碳酸岩存在的有效“指南”(杨学明等, 2000; 王凯怡, 2015)。显然,霓长岩的存在为鉴别碳酸岩体的存在,厘定碳酸岩岩浆(或流体)的地球化学性质及源区特征提供了理想的对象,对霓长岩的岩石学、矿物化学和同位素特征等方面的综合研究对于寻找碳酸岩相关的矿产资源(主要为REE)及剖析矿床成因机制有着重要的地质意义(Woolley, 1982; Rubie and Gunter, 1983; 王凯怡, 2015)。
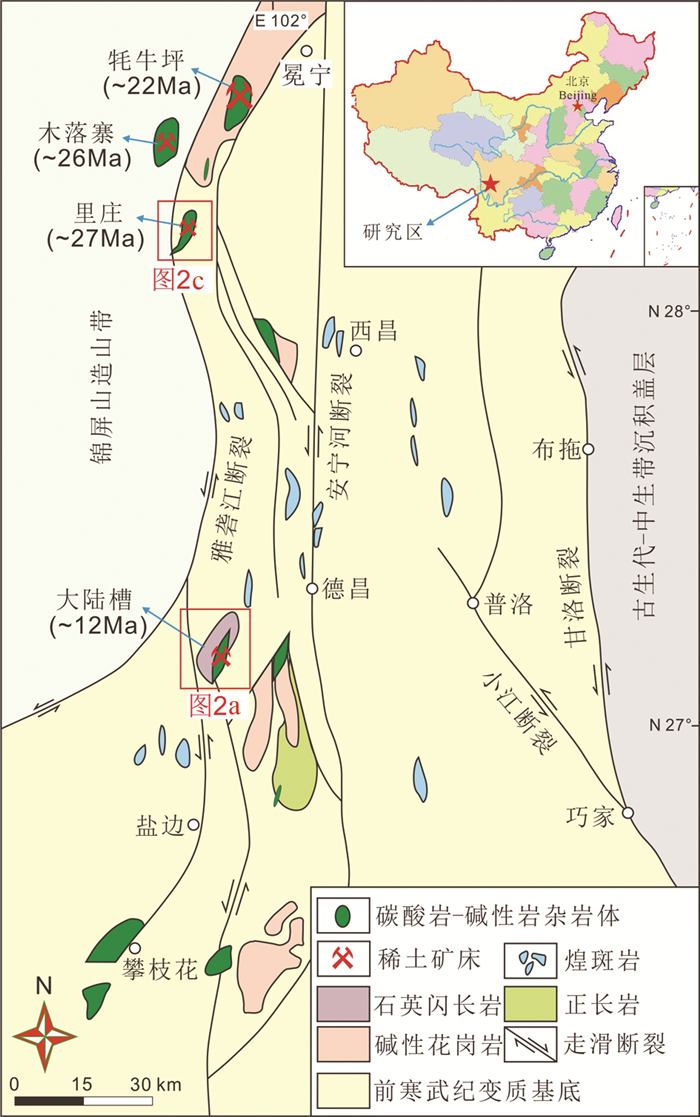
川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带是中国最重要的轻稀土矿带之一,包括牦牛坪超大型、大陆槽大型、木落寨与里庄中小型REE矿床以及一系列矿点(图 1; 侯增谦等, 2008)。这些REE矿床与碳酸岩-碱性岩杂岩体密切相关,它们有着不同的矿化式样,如牦牛坪脉状、大陆槽角砾岩型及里庄浸染型矿化(侯增谦等, 2008; Liu and Hou, 2017; Liu et al., 2019)。前人对该矿带REE矿床的地质特征(侯增谦等, 2008)、岩石学(Hou et al., 2006, 2015; Xu et al., 2008, 2012)、矿物学(Liu et al., 2015b, c; Guo and Liu, 2019)、地质年代学(Ling et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2015a)、同位素地球化学(Hou et al., 2015; Tian et al., 2015; Liu and Hou, 2017)及成矿流体(Xie et al., 2009, 2015; Shu and Liu, 2019; Zheng and Liu, 2019)等方面进行了大量研究,已取得丰硕的研究成果。在这些REE矿床的碳酸岩体与围岩的接触部位广泛发育霓长岩化蚀变带,蚀变带周围往往伴随有萤石-重晶石-方解石-氟碳铈矿(主要的REE矿物)矿脉,尤其以矿带南部的大陆槽角砾岩型和北部的里庄浸染型REE矿床为显著。然而,前人对该矿带的霓长岩及霓长岩化作用缺乏深入的研究,仅散见于早期地质报告及少许文献(杨光明等, 1998①; 李小渝, 2005)。迄今为止,霓长岩的矿物组成、岩石学及地球化学特征等方面尚无系统的报道,与霓长岩化关系密切的角砾岩化事件缺乏足够的讨论,这直接导致霓长岩化作用与REE矿化的关系尚不清楚。
① 杨光明, 常诚, 左大华, 刘学良. 1998.四川省德昌县DL稀土矿床成矿条件研究.中国地质大学(武汉)对外开放资料. 1-89
|
图 1 川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带区域地质简图(据袁忠信等, 1995) REE矿床的年代学数据来自正长岩的锆石U-Pb定年(Liu et al., 2015a) Fig. 1 Sketch map showing regional geology of the Mianing-Dechang REE belt, western Sichuan Province (modified after Yuan et al., 1995) The geochronology data of REE deposits are taken from zircon U-Pb ages for syenites (Liu et al., 2015a) |
本文在详细的野外地质填图及室内综合分析的基础之上,重点选取了矿带南部的大陆槽及矿带北部的里庄REE矿床的霓长岩进行深入的研究。此次研究旨在通过对大陆槽及里庄矿床霓长岩的岩相学及地球化学分析,探讨霓长岩化过程中交代流体的性质、组分迁移规律及其对REE矿化的暗示,从而为揭示川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带的成因机制提供有用信息。
1 地质背景川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带在构造上位于扬子克拉通西缘,扬子克拉通的基底由太古代的高级变质岩、元古代的变质沉积岩和覆盖于其上的显生宙的碳酸盐岩沉积序列组成(从柏林, 1988; 骆耀南等, 1998),中二叠世溢流的玄武岩以及少量橄榄岩覆盖于扬子克拉通的西部并形成面积达50万平方千米的大火成岩省(Xu et al., 2001)。伴随着印度-亚洲大陆的大规模碰撞,扬子克拉通西缘卷入新生代的碰撞造山活动,形成了青藏高原东缘的锦屏山造山带及一系列新生代走滑断裂(Yin and Harrison, 2000; 钟大赉等, 2000; 莫宣学等, 2003)。这些断裂系统吸纳和调节了印度-亚洲大陆碰撞所产生的应力应变,从西到东分别包括嘉黎和高黎贡走滑断裂,巴塘-丽江断裂,哀牢山-红河断裂,鲜水河及小江走滑断裂(图 1; 侯增谦等, 2008)。
青藏高原东部晚碰撞阶段(40~26Ma)属于构造转换阶段,由一系列新生代走滑断裂、走滑剪切和逆冲推覆构造所主导(Hou et al., 2009)。毗邻的三江特提斯构造带则历经了原-古-中-新特提斯洋闭合所引发的增生造山过程及印度-亚洲大陆汇聚所导致的碰撞造山过程,并形成了中国最具经济价值的金属成矿省(杨立强等, 2011; 李龚健等, 2013; Wang et al., 2014c; Deng et al., 2014a, b; 邓军等, 2016)。该区域的主要成矿事件除新生代走滑断裂系统控制的REE成矿作用之外(Hou et al., 2006, 2015; Liu and Hou, 2017),还包括新生代走滑断裂控制的斑岩型Cu-Mo-Au成矿作用,与左旋韧性剪切有关的造山型Au成矿作用,由新生代逆掩断层和后续走滑断裂控制的Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu成矿作用及由新生代走滑断裂控制的REE成矿作用(Hou et al., 2003; Deng and Wang, 2016; Deng et al., 2017a, b, 2018; Wang et al., 2014a, b, 2016, 2018; Zhang et al., 2014, 2017)。在碰撞期间复活的以雅砻江断裂和安宁河断裂为界的碳酸岩-碱性岩杂岩体呈近南北向展布并与新生代REE成矿作用密切相关,导致了川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带的形成(田世洪等, 2008; 侯增谦等, 2008)。最新的锆石年代学(正长岩,U-Pb年龄)研究显示,该REE矿带形成于约12~27Ma,其中牦牛坪为22.81±0.31Ma及21.3±0.4Ma,大陆槽为12.13±0.19Ma及11.32±0.23Ma,木落寨为26.77±0.32Ma,里庄为27.41±0.35Ma(Liu et al., 2015a)。
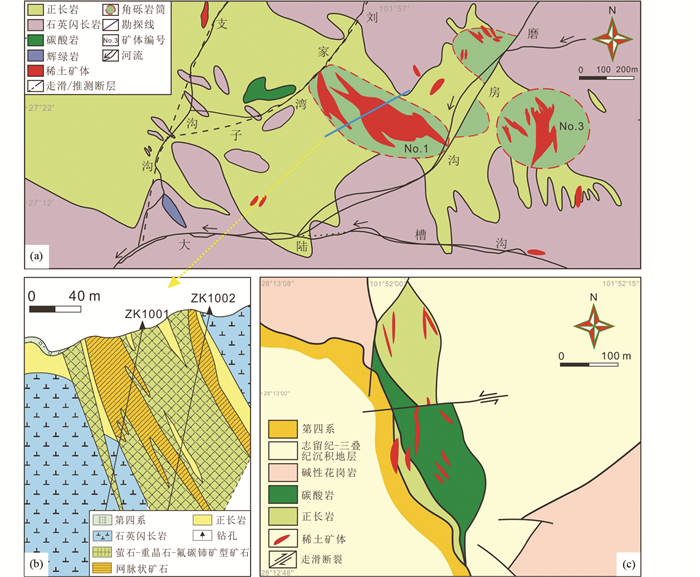
2 大陆槽和里庄矿床地质特征川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带呈近南北向展布,长约270km,宽约15km,其REE成矿作用与新生代碳酸岩-正长岩杂岩体密切相关(图 1; 侯增谦等, 2008)。大陆槽和里庄REE矿床分处矿带“一南一北”,均受新生代走滑断裂的控制(图 2a, c)。矿区内均发育角砾岩(图 3f, g),围岩遭受不同程度的破碎,暗示矿区曾经历过频繁的角砾岩化事件。在大陆槽和里庄矿床的REE矿脉附近往往发育霓长岩化蚀变带,带内蚀变作用强烈,野外产状清晰,是研究整个矿带霓长岩的地球化学特征的典型对象。大陆槽和里庄详细的矿床地质特征见表 1并分述于下。
|
图 2 大陆槽及里庄矿床地质简图 大陆槽矿床地质简图(a)及No.1号矿体勘探线剖面图(b)(据杨光明等, 1998);(c)里庄矿床地质简图(据侯增谦等, 2008) Fig. 2 Sketch geological maps of the Dalucao and Lizhuang deposits Sketch geological map (a) and geological cross-sections along exploration line of No.1 orebody (b) of the Dalucao deposit (modified after Yang et al., 1998); (c) sketch geological map of the Lizhuang deposit (modified after Hou et al., 2008) |

|
图 3 大陆槽及里庄REE矿床的野外照片 大陆槽正长岩岩体(a)和霓长岩(b、c);里庄矿床的霓长岩化蚀变带(d、e)和围岩角砾(f);大陆槽矿床的围岩角砾(g)和角砾状矿石(h);(i)里庄矿床浸染状矿石.矿物缩写:Py-黄铁矿; Fl-萤石; Bsn-氟碳铈矿; Brt-重晶石 Fig. 3 Field photographs of the Dalucao and Lizhuang REE deposit Syenite (a) and fenite (b, c) in the Dalucao deposit; fenitization belt (d, e) and breccia (f) in the Lizhuang deposit; breccia (g) and brecciated ore (h) in the Dalucao deposit; (i) disseminated ore in the Lizhuang deposit. Minerals abbreviation: Py-pyrite; Fl-fluorite; Bsn-bastnäsite; Brt-barite |
|
|
表 1 川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带大陆槽和里庄矿床地质特征总结 Table 1 Summary of geological characteristics of the Dalucao and Lizhuang deposits in the Mianning-Dechang REE belt, western Sichuan Province |
大陆槽矿床由两个大透镜体和诸多小矿体组成,与REE成矿作用有关的两个角砾岩筒产于正长岩之中,主要包括两套成矿系统。第一套成矿系统发育于两个角砾岩筒中,形成具有工业价值的No.1和No.3号矿体。No.1号矿体的矿物组合主要为萤石+重晶石+天青石+方解石+石英+氟碳铈矿,而No.3号矿体的矿物组合则为萤石+天青石+黄铁矿+白云母+方解石+石英+氟碳铈矿(Liu et al., 2015b)。第二套成矿系统发育于两个角砾岩筒之间,受磨房沟走滑断裂的影响而发生错动。大陆槽矿床的矿石类型主要为角砾状矿石和风化状矿石(Liu et al., 2015b)。角砾状矿石具有典型的碎屑支撑结构,碎屑主要由棱角状-次圆状正长岩和碳酸岩角砾组成,基质主要由细粒方解石、石英和氟碳铈矿组成(图 3h)。风化状矿石含有细粒稀土矿物(如氟碳铈矿、独居石等),黏土矿物(如伊利石、高岭石、蒙脱石等),少量热液脉石矿物(如萤石、重晶石、方解石等)及岩浆矿物(如锆石)(Liu et al., 2015c)。大陆槽矿床的岩浆-热液演化过程可划分为岩浆期,伟晶岩期及热液期。岩浆期是碳酸岩-正长岩杂岩体的形成期;伟晶岩期主要见于大陆槽No.1号矿体,形成粗粒萤石、石英、方解石等矿物(Liu and Hou, 2017; Shu and Liu, 2019);热液期以矿脉穿插于碳酸岩-正长岩杂岩体为特征。野外及镜下研究均发现,萤石、重晶石、方解石等常形成稳定的矿物组合,而氟碳铈矿往往充填于这些脉石矿物的裂隙之中。因此,热液期可近一步划分为萤石-重晶石-方解石及氟碳铈矿两个阶段,前者大量沉淀细粒的脉石矿物,后者则以氟碳铈矿的大量结晶为特征。
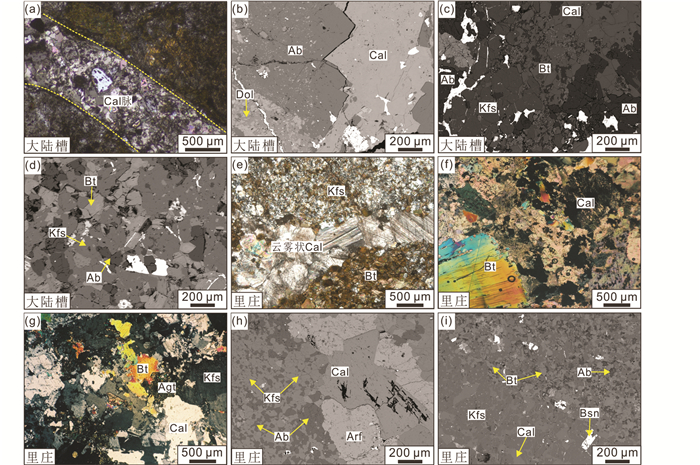
大陆槽矿床的主要蚀变类型为霓长岩化作用,霓长岩化蚀变带往往分布于碳酸岩-正长岩杂岩体与矿脉的接触部位,主要见于大陆槽矿床No.3号矿体。矿区内的正长岩岩体均遭受了不同程度的蚀变作用,然而最强烈的蚀变却产于角砾岩附近。大陆槽矿床新鲜正长岩中的矿物多呈半自形中-细粒结构,矿物组合为钾长石+黑云母+石英+方解石,偶见天青石及少量副矿物(如黄铁矿)。霓长岩中的矿物多呈他形细粒结构,主要由细粒长石、鳞片状黑云母、霓辉石以及少量副矿物组成。大陆槽矿床的霓长岩中尚未发现钠铁闪石,霓长岩化蚀变以钾长石被钠长石交代、霓辉石被黑云母交代为特征,且霓辉石、钠长石和黑云母呈浸染状分布于霓长岩中(图 4b-d)。新生矿物颗粒较细,常沿着正长岩原岩残余矿物的边缘及裂隙进行交代,残余长石类矿物往往发生浑浊化,局部可见典型的交代残余结构及变晶结构。野外手标本(图 3c)及镜下研究(图 4a)均发现,大陆槽霓长岩往往被热液脉切割,这是由于碳酸岩流体侵入正长岩间隙并引起交代蚀变,而碳酸岩流体则冷却沉淀而形成热液脉,显示出碳酸岩流体运移并交代正长岩围岩的典型特征。该热液脉主要由方解石组成,此外还包括少量的萤石、重晶石、天青石及细粒的氟碳铈矿等矿物。
|
图 4 大陆槽(a-d)及里庄(e-i) REE矿床霓长岩的显微照片 大陆槽霓长岩中含方解石脉(a)、原生黑云母(b)和霓长岩(c、d);里庄霓长岩中含方解石脉(e)、原生黑云母(f)和霓长岩(g-i).矿物缩写:Cal-方解石; Bt-黑云母; Ab-钠长石; Kfs-钾长石; Dol-白云石; Agt-霓辉石; Arf-钠铁闪石 Fig. 4 Microphotographs of fenites in the Dalucao and Lizhuang REE deposit Fenite containing calcite vein (a), primary biotite (b) and fenite (c, d) in the Dalucao deposit; fenite containing calcite vein (e), primary biotite (f) and fenite (g-i) in the Lizhuang deposit. Minerals abbreviation: Cal-calcite; Bt-biotite; Ab-albite; Kfs-K-feldspar; Dol-dolomite; Agt-aegirine-augite; Arf-arfvedsonite |
里庄REE矿体长约30~100m,厚约2~12m,赋存于碳酸岩和正长岩的构造破碎带或裂隙之中。矿区碳酸岩-正长岩杂岩体在地表出露宽约100m,长400m,主要呈NNW向展布,侵入厚逾1000m的志留系-三叠系碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩中(图 2c; 侯增谦等, 2008)。与大陆槽REE矿床不同,里庄矿床的矿石类型主要为浸染状矿石及角砾状矿石(Liu and Hou, 2017)。浸染状矿石是主要的矿石类型,整体呈红棕色、浸染状构造,主要由方解石、萤石、重晶石及氟碳铈矿等矿物组成(图 3i)。氟碳铈矿为黄褐色,单晶呈自形-半自形柱状、板状及他形粒状,以稀疏浸染状或斑杂状嵌于脉石矿物颗粒之间。角砾状矿石整体呈褐色,具有典型的碎屑支撑结构,碎屑主要由棱角状-圆状碳酸岩、正长岩角砾以及矿物角砾组成,基质主要由细粒方解石组成。里庄矿床的岩浆-热液演化过程与大陆槽矿床总体类似,所不同的是里庄矿床并无伟晶岩产出,其演化过程可划分为岩浆期及热液期,前者形成碳酸岩及与之相关的正长岩,后者形成热液矿脉。在矿脉中,氟碳铈矿往往呈长柱状叠加与早期的方解石、重晶石和萤石等脉石矿物之上或充填于早期脉石矿物的空隙之中,表明大规模的REE矿化发生于热液阶段的最晚期。
里庄矿床与成矿作用有关的蚀变也主要为霓长岩化作用,碳酸岩流体沿围岩裂隙运移并交代裂隙两侧岩石,形成了一系列长宽不等的霓长岩化带(图 3d, e)。同时在碳酸岩和正长岩的接触带附近,碳酸岩包裹了一些正长岩的黑色角砾,这些角砾也发生了强烈的霓长岩化蚀变。与大陆槽矿床类似,镜下研究发现里庄霓长岩也往往被以方解石为主的热液脉切割(图 4e),而细粒氟碳铈矿往往充填于脉中矿物的空隙之中。里庄霓长岩中的矿物多呈他形细粒结构,主要由细粒的钾长石和钠长石、黑云母、霓辉石及钠铁闪石组成。霓长岩化以钾长石蚀变为碎片状钠长石和黑云母为特征,被交代的正长岩中大量出现了霓长岩化产生的矿物(如钠长石、黑云母、钠铁闪石等)(图 4g-i),原生矿物残留较少,结构构造几乎消失殆尽,表明里庄矿床的霓长岩化作用相对大陆槽更为强烈。基于详细的野外观察、岩相学分析及前人研究(侯增谦等, 2008; Liu and Hou, 2017),现已识别出大陆槽及里庄霓长岩(包括正长岩原岩)中的主要矿物的生成顺序(图 5)。

|
图 5 大陆槽(a)及里庄(b) REE矿床正长岩及相关的霓长岩中主要矿物的生成顺序 Fig. 5 Paragenesis sequence of the most common minerals in syenites and associated fenites from the Dalucao (a) and Lizhuang (b) REE deposits |
本次研究选择了大陆槽和里庄REE矿床的霓长岩为研究对象,它们的原岩均为与碳酸岩体在空间上密切相关的正长岩。这些霓长岩是碳酸岩流体对正长岩进行交代蚀变而形成,因此在矿物组成与化学成分上与正长岩原岩有着千丝万缕的联系。此次共选取了15件霓长岩样品,样品的前期处理(包括粉碎、磨片等)是在河北省区域地质矿产调查研究所实验室进行的。其中,6件用于全岩主微量元素测试,并引用Hou et al. (2006)中的正长岩的主微量元素测试数据进行对比研究;其余样品用于电子探针成分分析,以确定霓长岩的主要矿物组成及化学特征。
3.2 主微量元素分析在中国地质科学院国家地质测试中心进行了主微量元素测试分析。利用Axios波长色散X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)进行主量元素分析,其中FeO采用容量滴定法(国家标准GB/T 14506.14—2010监控),烧失量(LOI)采用重量法(国家标准GB/T 14506.2—2010和JY/T 1253—1999监控)分析完成。在25mL瓷坩埚中将两种围岩的粉末样品与5.3g Li2B4O7,0.4g LiF和0.3g NH4NO3混合。将粉末混合物转移到铂合金坩埚中,在样品干燥之前,加入1mL LiBr溶液。然后样品在自动火焰熔融机中熔化,冷却的玻璃用于XRF主量元素分析,分析误差 < 2%。微量元素(包括REE元素)采用高分辨率等离子质谱仪(ICP-MS)对进行分析,测试过程中将GBW07120、GBW07103、GBW07105、GBW07187等标准样品与待测样品共同分析,测试精度优于10%。将称取的50mg样品粉末与0.5mL HNO3和1mL纯净的HF混合并发生溶解,然后转于15mL的Savillex Teflon螺旋容器中,在190℃的环境下放置一天,干燥后,再次用0.5mL的HNO3进行溶解,再使其干燥。尔后,将样品与5mL的HNO3混合均匀,置于130℃的烤炉中密封3小时。冷却后,将混合好的溶液转移至塑料瓶中并稀释至50mL以供分析。通过电感耦合等离子体的放射性光谱分析方法对所得溶液进行微量元素分析。详细的主微量元素测试方法见Liu et al. (2015b)。
3.3 电子探针分析在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所电子探针实验室采用JXA-8230电子探针仪对霓长岩中的相关矿物进行了电子探针和背散射图像(BSE)分析。硅酸盐和氧化物采用15kV的加速电压,硫化物采用20kV的加速电压,电流大小为20mA,束斑直径选择5μm或1μm(由矿物颗粒大小而定)。标样采用天然矿物或合成化合物,分析精度约为0.01%。脉石矿物的修正采用了生产厂家提供的ZAF修正程序。进行试验测试时,采用了下列标准矿物和晶体:硬玉,AlKα,TAP;硬玉,NaKα,TAP;黄玉,FKα,TAP;镁橄榄石,MgKα,TAP;硬玉,SiK,PETJ;钾长石,K Kα,PETG;硅灰石,CaKα;赤铁矿,FeKα,LIF;金红石,TiKα,LIF;磷灰石,PKα,MnO,Mn Kα,LIFH;PETJ;Cr2O3,CrKα,LIFH;NaCl;ClKα,PETH;NiO,NiKα,LIF;V2O5,VKα,LIFH。
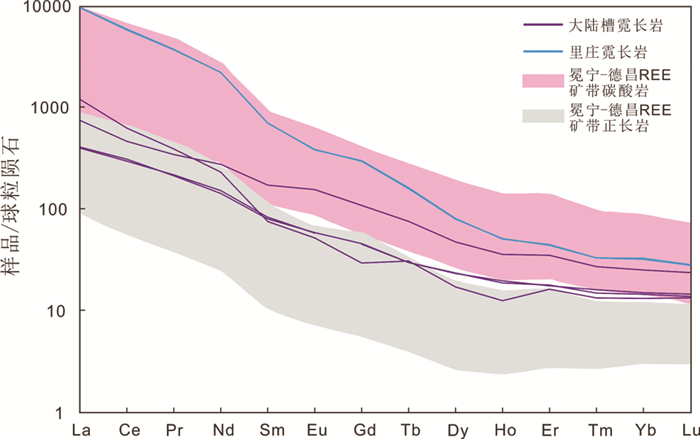
4 分析结果 4.1 主微量元素分析大陆槽和里庄REE矿床霓长岩的主微量元素分析结果见表 2,现分述如下:大陆槽霓长岩SiO2含量为50.2%~65.0%,Al2O3含量为15.7%~17.1%,TiO2含量为0.15%~0.78%,Fe2O3T含量为2.42%~6.76%,MnO含量为0.07%~0.14%,MgO含量为0.03%~3.58%,CaO含量为2.09%~5.73%,K2O+Na2O含量为7.96%~12.4%。里庄霓长岩SiO2含量为37.0%~37.8%,Al2O3含量为10.4%,TiO2含量为1.32%~1.33%,Fe2O3T含量为5.73%~5.86%,MnO含量为0.31%~0.32%,MgO含量为3.82%~3.86%,CaO含量为12.8%,K2O+Na2O含量为8.63%~8.66%。相比于正长岩原岩,大陆槽和里庄霓长岩均相对富集REE、Sr、Ba等元素。大陆槽和里庄霓长岩的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素图解都表现出典型的轻稀土元素富集的右倾型特征,具有相同的变化趋势且均不显示Eu的负异常(图 6)。大陆槽和里庄霓长岩的地球化学特征,尤其是SiO2、Al2O3、碱质(K2O+Na2O)以及镁铁含量(Fe2O3T+MgO)等主量元素的特征,也与世界上其他REE矿床(如白云鄂博)的霓长岩基本一致(图 7; Le Bas, 2008; Elliott et al., 2018)。
|
|
表 2 川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带大陆槽和里庄矿床正长岩与霓长岩主量(wt%)及微量元素(×10-6)分析结果 Table 2 Major (wt%) and trace element (×10-6) data of syenites and fenites from the Dalucao and Lizhuang deposits in the Mianning-Dechang REE belt, western Sichuan Province |
|
图 6 大陆槽及里庄REE矿床霓长岩的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) 冕宁-德昌REE矿带碳酸岩及正长岩数据引自Hou et al. (2015) Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns for fenites from the Dalucao and Lizhuang deposits (normalized values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) The data of carbonatites and syenites in the Mianning-Dechang REE belt are taken from Hou et al. (2015) |

|
图 7 大陆槽和里庄霓长岩的地球化学成分图解 (a) Na2O+K2O与SiO2的相关性图解;(b) Al2O3、Na2O+K2O及Fe2O3T+MgO的三角图解.白云鄂博霓长岩数据来自Le Bas (2008),与碳酸岩相关的霓长岩的数据范围来自Elliott et al. (2018)的统计分析 Fig. 7 Geochemical composition diagrams of fenites from Dalucao and Lizhuang deposits (a) correlation diagram of Na2O+K2O and SiO2; (b) triangular diagram of Al2O3, Na2O+K2O and Fe2O3T+MgO. The data of Bayan Obo fenites are taken from Le Bas (2008); the data of carbonatite-related fenites in the world are taken from the statistic data of Elliott et al. (2018) |
针对大陆槽和里庄REE矿床霓长岩中普遍存在的矿物(如长石、黑云母和霓辉石)进行了电子探针分析,测试结果见表 3。结果表明,大陆槽和里庄霓长岩中的霓辉石FeOT含量较高(26.0%~27.2%),长石Na2O和K2O含量较高,CaO含量极低,An(钙长石)-Ab(钠长石)-Or(钾长石)三角投图(图 8)显示长石主要为透长石和钠长石,属于碱性长石系列。云母MgO含量为16.1%~17.2%,FeOT范围为12.7%~15.2%,TiO2范围为0.74%~1.15%。黑云母的化学组成可反映岩浆-热液体系冷却结晶时的物理化学状况(Nachit et al., 2005),岩浆期后热液及蚀变形成的黑云母的Ti含量低于原生黑云母(Zhang et al., 2016)。将大陆槽和里庄霓长岩中的黑云母的化学分析结果在10TiO2-(FeO+MnO)-MgO图解(Nachit et al., 2005)(图 9a)和Mg-(Fe2++Mn)-(AlⅥ+Fe3++Ti)图解(Foster, 1960)(图 9b)上进行投影,结果显示黑云母的成因类型为交代型且具有相对富镁、贫铁等特征,属于镁质黑云母。上述结果表明,大陆槽和里庄霓长岩具有典型的富碱质(Na2O+K2O)、富镁铁(MgO+FeOT)等地球化学特征。
|
|
表 3 川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带大陆槽和里庄矿床霓长岩中主要矿物电子探针结果(wt%) Table 3 Electron microprobe analyses (wt%) of main minerals within fenites from the Dalucao and Lihuzang deposits in the Mianning-Dechang REE belt, western Sichuan Province |
|
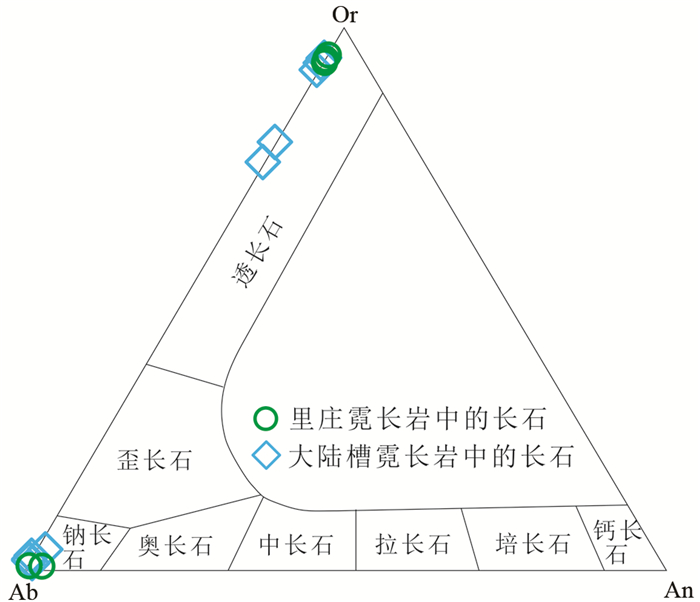
图 8 大陆槽及里庄REE矿床霓长岩中的长石Or-Ab-An分类图解 Fig. 8 Or-Ab-An diagram of feldspars from fenites in the Dalucao and Lizhuang REE deposits |

|
图 9 大陆槽及里庄矿床霓长岩中的黑云母地球化学成分图解(a, 据Nachit et al., 2005; b, 据Foster, 1960) Fig. 9 Geochemical composition diagrams of biotites from fenites in the Dalucao and Lizhuang deposits (a, after Nachit et al., 2005; b, after Foster, 1960) |
霓长岩中的矿物组合及其地球化学特征,与导致霓长岩化作用的交代流体的组分及物理化学性质密切相关。与碳酸岩相关的霓长岩化作用的交代流体中的CO2组分相对较高,CO2也往往是控制霓长岩矿物稳定性的重要因素之一(王凯怡, 2015)。与Morogan (1989)在研究与瑞典Alnö碳酸岩相关的霓长岩时所指出的类似,川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带的霓长岩化蚀变的交代流体中也含有较高的CO2组分,这已经被前人所报道的大量含CO2的“双眼皮”流体包裹体所证实(Xie et al., 2009, 2015; Shu and Liu, 2019),这也可从大陆槽和里庄霓长岩中往往含有热液方解石脉这一地质事实得到佐证(图 4a, e)。这是因为霓长岩中的热液方解石脉是碳酸岩流体运移并交代围岩而沉淀形成的,而碳酸岩流体往往被认为来自地幔且富含大量CO2及挥发份(Groves et al., 1988; Veksler et al., 1998),这种流体有利于REE形成络合物并活化迁移(Morogan, 1989)。
一般而言,霓长岩中长石类矿物通常是碱性长石,它们常具有较低的结构态和较高的有序度(杨学明等, 2000)。对大陆槽和里庄霓长岩的全岩标准长石成分在An-Ab-Or三角图上投影,结果表明大多数的长石成分接近Ab-Or连线,主要为透长石和钠长石,表明它们与富碱质的流体处于平衡(Morogan and Martin, 1985)。运用相关性图解也能直观表示不同的矿床(大陆槽、里庄和白云鄂博)霓长岩的碱质(Na2O+K2O)相对于SiO2的关系(图 7a),结果显示,相比川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带,白云鄂博矿床的霓长岩化程度最强,霓长岩的碱质含量最高。云母是霓长岩中的重要镁铁质矿物,霓长岩中的云母往往属于黑云母-金云母系列,并且随霓长岩化作用的增强,云母中的镁含量逐渐增加,而全铁含量逐渐减少(王凯怡, 2015)。对大陆槽和里庄矿床霓长岩中的云母进行投图,显示其具有相对富镁、贫铁等特征,属交代型镁质黑云母,黑云母的生成则表明交代流体含有羟基(杨学明等, 2000)。全岩微量元素分析显示,大陆槽和里庄霓长岩中较高含量的REE、Sr、Ba等元素(表 1)指示了交代流体中富含REE、Sr、Ba等,这也可从大陆槽和里庄矿床发育重晶石、天青石及氟碳铈矿等热液矿物得到证明。此外,大陆槽和里庄的霓长岩具有与碳酸岩相似的REE配分型式(图 6),从地球化学层面上暗示了引发霓长岩化作用的流体出溶于碳酸岩岩浆的客观事实。霓长岩的REE型式及其与碳酸岩REE型式的相似性可反映霓长岩化蚀变的强度,从蚀变强-弱,霓长岩的REE型式与碳酸岩的相似性逐渐降低。里庄霓长岩REE配分曲线相比于大陆槽霓长岩显著接近于碳酸岩的范围(图 6),表明里庄霓长岩化蚀变强度相比于大陆槽可能更高。
通过对大陆槽和里庄霓长岩的矿物组成及其地球化学特征分析,不难发现,尽管霓长岩化作用不同阶段的交代流体成分可能是变化的,但总体而言均含有较高的CO2组分,并且富含碱质、Fe、Mg以及REE、Sr、Ba等元素。当然,霓长岩化初始阶段可能具有相对较高的温度和氧逸度,但随着流体的演化而逐渐降低(Morogan and Woolley, 1988; 王凯怡, 2015)。
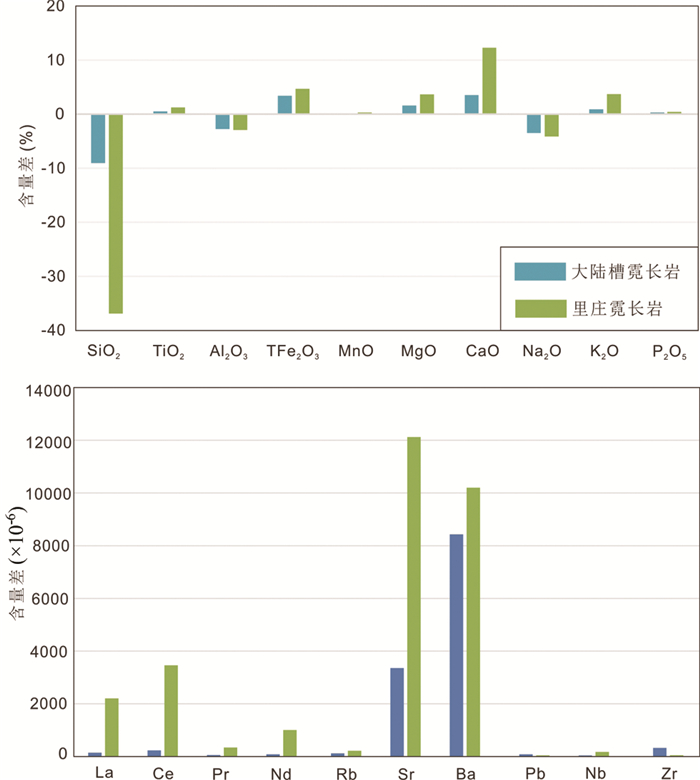
5.2 组分迁移霓长岩化作用属于一种特殊的蚀变类型,从本质上而言,它是碳酸岩或碱性岩流体与围岩之间发生组分迁移的客观反映。流体-围岩反应实质是特定物理化学条件下(包括温度、压力、pH、氧逸度、岩石孔隙率、构造应力等参数),元素在流体与岩石之间活化、迁移与沉淀的全过程。流体与围岩进行化学组分的交换伴随着元素的迁移,将导致蚀变前后矿物种类发生变化(Verma et al., 2005)。其中,主量元素的迁移将体现于矿物组合的变化,而微量元素的迁移则可反映蚀变过程中的微观作用(Whitbread and Moore, 2004)。一般来说,与未受蚀变作用的原岩的全岩平均地球化学组分相比,在霓长岩化过程中带入或带出的主要元素的数量越高,霓长岩化的蚀变程度越高(王凯怡, 2015)。对于川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带的霓长岩化作用,可对蚀变后所生成的霓长岩与未受蚀变的正长岩原岩的全岩主微量数据进行直观的对比分析,并使用柱状图清晰地反映霓长岩化蚀变过程中元素的带入带出情况(王凯怡, 2015; Drüppel et al., 2005)。X轴表示各主量(以氧化物形式)和微量元素,因二者含量变化往往相差巨大,故分别作图表示之。Y轴表示元素的带入带出情况,“0”位置处代表未受蚀变的正长岩原岩的成分,通过对比研究拟定带入(即含量增加,取平均值)为正值(0轴之上),带出(即含量减少,取平均值)为负值(0轴之下),将各个元素含量变化的数值标示于Y轴(图 10)。
|
图 10 大陆槽及里庄正长岩发生霓长岩化蚀变后元素含量的变化情况 Fig. 10 Diagrams illustrating the element changes of syenites by equilibration with fenitizing fluids in the Dalucao and Lizhuang deposits |
大陆槽和里庄矿床霓长岩化作用的强度不同,主微量元素含量变化的幅度亦有所不同,这表明对于不同碳酸岩流体所导致的霓长岩化作用,元素带入带出的种类及数量可能存在差异(Le Bas, 2008)。然而,大陆槽和里庄霓长岩化作用均存在相似的元素迁移规律,亦即:主量元素中,Fe、Mg及Ca等元素的含量增加,Si及Al等元素的含量降低;微量元素中,REE、Sr、Ba等元素的含量显著增加。由于正长岩原岩含有极高的碱质(K2O+Na2O可达12.55%;表 1),对比研究显示出霓长岩化过程中K、Na等碱金属含量变化较小,甚至出现轻微降低的现象。根据霓长岩中大量出现蚀变的碱性长石矿物(主要为钾长石和透长石)这一地质事实可以推断,交代流体含有相当数量的Na和K,在霓长岩化蚀变过程中,这些碱金属很可能被流体带入围岩。以上分析表明,交代流体中含有的Fe2O3T、MgO、CaO以及REE、Sr、Ba等组分在流体-围岩反应过程中被带入围岩。显然,Fe2O3T、MgO等组分的带入与霓长岩化过程中镁铁矿物(如镁质黑云母、霓辉石)的大量生成密切相关,而REE及Sr、Ba等微量元素含量的增加也促使霓长岩更具备碳酸岩的微量元素特征及REE配分型式。相反,尽管Al通常在热液过程中被认为相对不活动而常被当做参照元素(Condie and Sinha, 1996; Klammer, 1997),但Al2O3和其他组分(如SiO2)却从正长岩围岩中被逐出,这与前人研究的瑞典Alnö碳酸岩相关的霓长岩的组分迁移特征一致(Morogan and Woolley, 1988; Morogan, 1989)。事实上,霓长岩化作用愈强,这些组分的迁移程度愈加明显,正如Le Bas (2008)曾明确指出在霓长岩化增强的同时伴随有Ba元素的显著增加。
5.3 霓长岩化作用对REE矿化的暗示霓长岩作为碳酸岩(或碱性岩)流体对围岩交代蚀变的产物,对于剖析碳酸岩型REE矿床的成因机制有着重要意义。例如,Liu et al. (2018)在研究白云鄂博霓长岩时,指出了两期霓长岩化作用的特征及与REE矿化事件的对应关系。尽管碳酸岩的成因存在争议,但已有研究表明川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带的碳酸岩来自于由海相沉积物交代的次大陆岩石圈地幔的部分熔融(Hou et al., 2015)。碳酸岩岩浆在侵位过程中释放出高通量且富REE及CO2的流体,流体沿着构造裂隙运移并交代围岩而引起霓长岩化蚀变作用,尤以大陆矿带南部的大陆槽角砾岩型和里庄浸染型REE矿床为显著,这也反映了大陆槽和里庄矿床相对较高的碳酸岩含量(刘琰等, 2017)。同时,大陆槽和里庄矿区的碳酸岩和/或霓长岩周围往往产出大量的角砾岩,角砾岩的存在指示了富含挥发份的高压流体从碳酸岩岩浆中快速释放的过程(Verplanck et al., 2014; Croll et al., 2015)。事实上,在高压环境下,大量的岩石破碎物可以喷出物的形式瞬间喷出,这已经被Lorenz et al. (1994)的实验所证明。Kresten (1988)证明了碳酸岩和/或霓长岩的角砾岩化过程实际上是体积增加的结果,这也解释了角砾岩化作用之后碳酸岩和/或霓长岩周围为何脉状裂隙往往十分发育。类似地,在大陆槽和里庄碳酸岩与围岩的接触带同样发育角砾岩(图 3f, g),这些角砾岩主要由碳酸岩及正长岩碎屑组成,基质主要为细粒的方解石及碱性长石,这可能是由矿区主断裂及其次级断裂不断演化导致的多期次角砾岩化事件所造成。角砾岩化事件往往伴随着压力的瞬间降低,使围岩破碎化并形成大量的裂隙,超高压富含挥发性的碳酸岩流体通过裂隙释放并运移,并与围岩发生交代蚀变,即霓长岩化作用(Elliott et al., 2018)。大量的裂隙可构成开放性的渗透网络,有利于岩浆流体的运移及与后期大气降水的混合。显然,角砾岩化作用促进了流体与围岩的反应,提高了霓长岩化作用的强度,并且为热液矿脉的穿插及REE矿物的沉淀提供了空间。
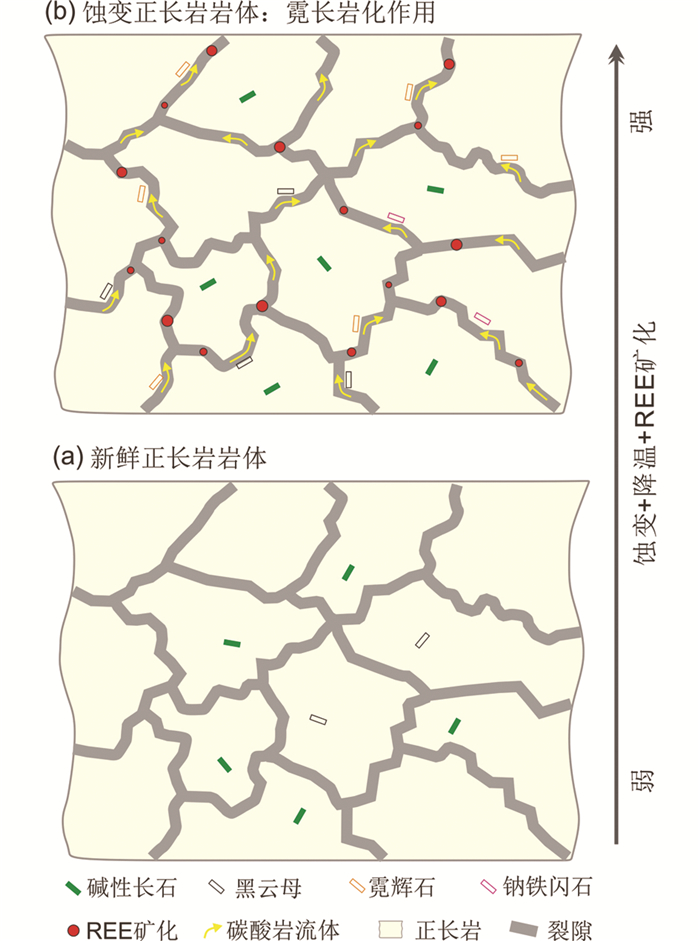
REE往往被认为是相对稳定且性质相似的元素组合(Yang et al., 2015)。然而,已有研究表明REE在热液蚀变过程中可以是较为活动的,如花岗质岩石的热液蚀变过程(Parsapoor et al., 2009; Nishimoto and Yoshida, 2010)和霓长岩化蚀变作用(杨学明等, 2000; Le Bas, 2008; 王凯怡, 2015)。在不同类型的热液蚀变过程中REE的活动习性有所差异,其往往受控于原岩种类、蚀变矿物特征、热液流体中REE含量,以及热液流体的性质等(Michard, 1989; Haas et al., 1995)。对大陆槽和里庄矿床的霓长岩及新鲜正长岩进行的对比研究发现,霓长岩中的REE、Sr、Ba等元素含量均有所增加,表明霓长岩化作用对REE的迁移有着重要影响。在交代蚀变过程中,流体与围岩存在广泛的REE交换,但总体结果是REE由流体向围岩发生了渗透,导致蚀变形成的霓长岩REE含量升高(图 10)且具有与碳酸岩相似的REE配分形式(图 6)。这可能是由于碳酸岩流体和围岩之间形成了化学活动梯度,促使相关化学组分(如REE)发生迁移。详细的岩相学观察显示,大陆槽和里庄矿床霓长岩往往被热液脉切割,而热液脉的组成矿物除方解石外,亦包括少量的萤石、重晶石、天青石等脉石矿物,细粒氟碳铈矿则叠加于脉石矿物之上或充填与它们的裂隙之中(图 4a, e),这表明热液脉石矿物的沉淀及大规模REE矿化同时或晚于霓长岩化作用。氟碳铈矿与萤石、重晶石、方解石等密切共生这一地质事实表明,在成矿流体的运移过程中,F-,CO32-,SO42-等配体与REE形成络合物并使之迁移沉淀(Agangi et al., 2010; Williams-Jones et al., 2012; Migdisov and Williams-Jones, 2014)。川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带霓长岩化的过程可用图 11简要表示,在流体-围岩反应过程中,流体含有的Fe2O3T、MgO、CaO等组分被带入正长岩围岩,导致霓长岩中大量镁铁矿物(如镁质黑云母、霓辉石)的生成(图 11b)。相反,SiO2和其他组分(如Al2O3)从正长岩围岩中被逐出。被逐出的SiO2一部分将进入流体,随着蚀变过程的不断进行,流体中SiO2的含量逐渐增加,这将导致流体的粘度相对增加,流体运移更为缓慢。组分的反复迁移,元素的带入带出(尤其是REE、Sr、Ba等)显然不利于络合物的稳定,这将有助于热液矿物(包括REE矿物)的沉淀。此外,矿区频繁发生的角砾岩化事件促进流体与围岩的反应并提高了霓长岩化作用的强度,开放性裂隙网络可为热液矿脉的穿插及REE矿物的沉淀提供足够的空间。随着体系物理化学性质的不断改变(如温度、pH值、氧逸度等),萤石、重晶石、方解石等脉石矿物的大量沉淀将导致REE络合物的活性急剧降低并使之发生分解,造成氟碳铈矿在热液晚期以较低的温度大量沉淀。当然,这一过程不可能是一蹴而就的,随着成矿流体的不断运移,霓长岩化蚀变作用持续进行,流体与围岩的组分交换反复发生。这些过程伴随着多期次的热液活动及构造事件,REE逐步富集矿化并形成角砾型(大陆槽)及浸染状矿石(里庄),最终完成REE活化→迁移→沉淀的成矿过程。
|
图 11 川西冕宁-德昌REE矿带霓长岩化作用示意图 Fig. 11 Schematic diagram illustrating the process of fenitization in the Mianning-Dechang REE belt, western Sichuan Province |
(1) 大陆槽和里庄矿床广泛发育霓长岩化作用,霓长岩主要由长石、黑云母、霓辉石等组成。长石Na2O和K2O含量较高,CaO含量极低,主要为透长石和钠长石,属碱性长石系列;黑云母具有相对富镁、贫铁等特征,属交代型镁质黑云母。
(2) 霓长岩化作用的交代流体含有较高的CO2组分,且富含碱质、Mg、Fe及REE、Sr、Ba等元素。霓长岩化过程中流体与围岩发生组分迁移,总体而言:流体含有的Fe2O3T、MgO、CaO等组分在交代过程中被带进了围岩,SiO2和Al2O3等组分从正长岩中逐出;微量元素中,霓长岩中的REE及Sr、Ba等元素含量显著增加。
(3) 与碳酸岩密切相关的角砾岩化事件提高了霓长岩化蚀变的强度,并且为矿脉的穿插及REE矿物的沉淀提供了空间。霓长岩化过程中流体-围岩的组分迁移将削弱络合物的稳定性,伴随着多期次的热液活动及构造事件,最终完成REE活化→迁移→沉淀的成矿过程。
致谢 野外工作期间得到中国地质科学院矿产资源综合利用研究所朱志敏研究员及四川省地矿局川西北地质队吕丰强、刘大明工程师的悉心帮助,在此谨表谢忱。
欣逢翟裕生院士九十华诞,先生才学渊博,德厚流光,为中国矿床事业做出了巨大贡献。“高山仰止,景行行止”,谨以此文恭表祝福!
Agangi A, Kamenetsky VS and McPhie J. 2010. The role of fluorine in the concentration and transport of lithophile trace elements in felsic magmas:Insights from the Gawler Range Volcanics, South Australia. Chemical Geology, 273(3-4): 314-325 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.03.008 |
Brögger WC. 1921. Die Eruptivgesteine des Kristianiagebietes, Ⅳ. Das Fengebiet in Telmark, Norwegen. Norske Videnskapsselskapets Skrifter I. Matematisk-naturvidenskapelig Klasse, 9: 408 |
Chakhmouradian AR. 2006. High-field-strength elements in carbonatitic rocks:Geochemistry, crystal chemistry and significance for constraining the sources of carbonatites. Chemical Geology, 235(1-2): 138-160 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.06.008 |
Condie KC and Sinha AK. 1996. Rare earth and other trace element mobility during mylonitization:A comparison of the Brevard and Hope Valley shear zones in the Appalachian Mountains, USA. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 14(2): 213-226 DOI:10.1046/j.1525-1314.1996.05899.x |
Cong BL. 1988. Formation and Evolution of the Panxi Paleorift. Beijing: Science Press, 1-427 (in Chinese)
|
Cooper AF, Palin JM and Collins AK. 2016. Fenitization of metabasic rocks by ferrocarbonatites at Haast River, New Zealand. Lithos, 244: 109-121 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.11.035 |
Croll R, Swinden S, Hall M, Brown C, Beer G, Scheepers J, Redelinghuys T, Wild G and Trusler GE. 2015. Mkango Resources Limited Songwe REE project Malawi. Ni 43-101 Pre-feasibility Report, MSA Group
|
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ and Santosh M. 2014a. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China. Earth-Science Reviews, 138: 268-299 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.05.015 |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ, Li CS and Wang CM. 2014b. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region, SW China. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 419-437 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.002 |
Deng J and Wang QF. 2016. Gold mineralization in China:Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Research, 36: 219-274 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.003 |
Deng J, Wang QF and Li GJ. 2016. Superimposed orogeny and composite metallogenic system:Case study from the Sanjiang Tethyan belt, SW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2225-2247 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Selvaraja V, Jeon H, Wu B and Yang LF. 2017a. Insights into ore genesis of the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan Province, China:Evidence from Zn and in-situ S isotopes. Ore Geology Reviews, 90: 943-957 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.036 |
Deng J, Wang QF and Li GJ. 2017b. Tectonic evolution, superimposed orogeny, and composite metallogenic system in China. Gondwana Research, 50: 216-266 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.02.005 |
Deng J, Wang CM, Zi JW, Xia R and Li Q. 2018. Constraining subduction-collision processes of the Paleo-Tethys along the Changning-Menglian suture:New zircon U-Pb ages and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf-O isotopes of the Lincang Batholith. Gondwana Research, 62: 75-92 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.10.008 |
Dobson DP, Jones AP, Rabe R, Sekine T, Kurita K, Taniguchi T, Kondo T, Kato T, Shimomura O and Urakawa S. 1996. In-situ measurement of viscosity and density of carbonate melts at high pressure. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 143(1-4): 207-215 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(96)00139-2 |
Drüppel K, Hoefs J and Okrusch M. 2005. Fenitizing processes induced by ferrocarbonatite magmatism at swartbooisdrif, NW Namibia. Journal of Petrology, 46(2): 377-406 |
Elliott HAL, Wall F, Chakhmouradian AR, Siegfried PR, Dahlgren S, Weatherley S, Finch AA, Marks MAW, Dowman E and Deady E. 2018. Fenites associated with carbonatite complexes:A review. Ore Geology Reviews, 93: 38-59 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.12.003 |
Foster MD. 1960. Interpretation of the Composition of Trioctahedral Micas. Washington DC: US Government Printing Office, 24-29
|
Groves DI, Golding SD, Rock NMS, Barley ME and McNaughton NJ. 1988. Archaean carbon reservoirs and their relevance to the fluid source for gold deposits. Nature, 331(6513): 254-257 |
Guo DX and Liu Y. 2019. Occurrence and geochemistry of bastnäsite in carbonatite-related REE deposits, Mianning-Dechang REE belt, Sichuan Province, SW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 107: 266-282 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.02.028 |
Haas JR, Shock EL and Sassani DC. 1995. Rare earth elements in hydrothermal systems:Estimates of standard partial molal thermodynamic properties of aqueous complexes of the rare earth elements at high pressures and temperatures. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(21): 4329-4350 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(95)00314-P |
Hou ZQ, Ma HW, Zaw K, Zhang YQ, Wang MJ, Wang Z, Pan GT and Tang RL. 2003. The Himalayan Yulong porphyry copper belt:Product of large-scale strike-slip faulting in Eastern Tibet. Economic Geology, 98(1): 125-145 |
Hou ZQ, Tian SH, Yuan ZX, Xie YL, Yin SP, Yi LS, Fei HC and Yang ZM. 2006. The Himalayan collision zone carbonatites in western Sichuan, SW China:Petrogenesis, mantle source and tectonic implication. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 244(1-2): 234-250 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.01.052 |
Hou ZQ, Tian SH, Xie YL, Yuan ZX, Yang ZS, Yin SP, Fei HC, Zou TR, Li XY and Yang ZM. 2008. Mianning-Dechang Himalayan REE belt associated with carbonatite-alkalic complex in eastern Indo-Asian collision zone, Southwest China:Geological characteristics of REE deposits and a possible metallogenic model. Mineral Deposits, 27(2): 145-176 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hou ZQ, Cook NJ and Zaw K. 2009. Metallogenesis of the Tibetan Collisional Orogen. Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1-3): 1 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2009.07.002 |
Hou ZQ, Liu Y, Tian SH, Yang ZM and Xie YL. 2015. Formation of carbonatite-related giant rare-earth-element deposits by the recycling of marine sediments. Scientific Reports, 5: 10231 DOI:10.1038/srep10231 |
Klammer D. 1997. Mass change during extreme acid-sulphate hydrothermal alteration of a Tertiary latite, Styria, Austria. Chemical Geology, 141(1-2): 33-48 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00056-9 |
Kresten P. 1988. The chemistry of fenitization:Examples from Fen, Norway. Chemical Geology, 68(3-4): 329-349 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(88)90030-7 |
Le Bas MJ. 2008. Fenites associated with carbonatites. The Canadian Mineralogist, 46(4): 915-932 DOI:10.3749/canmin.46.4.915 |
Li GJ, Wang QF, Yu L, Hu ZC, Ma N and Huang YH. 2013. Closure time of the Ailaoshan Paleo-Tethys Ocean:Constraints from the zircon U-Pb dating and geochemistry of the Late Permian granitoids. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(11): 3883-3900 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li XY. 2005. Geological characteristics of Dalucao REE deposit in Dechang County, Sichuan Province. Mineral Deposits, 24(2): 151-160 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ling XX, Li QL, Liu Y, Yang YH, Liu Y, Tang GQ and Li XH. 2016. In situ SIMS Th-Pb dating of Bastnaesite:Constraint on the mineralization time of the Himalayan Mianning-Dechang rare earth element deposits. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 31(8): 1680-1687 DOI:10.1039/C6JA00093B |
Liu S, Fan HR, Yang KF, Hu FF, Rusk B, Liu X, Li XC, Yang ZF, Wang QW and Wang KY. 2018. Fenitization in the giant Bayan Obo REE-Nb-Fe deposit:Implication for REE mineralization. Ore Geology Reviews, 94: 290-309 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.02.006 |
Liu Y, Hou ZQ, Tian SH, Zhang QC, Zhu ZM and Liu JH. 2015a. Zircon U-Pb ages of the Mianning-Dechang syenites, Sichuan Province, southwestern China:Constraints on the giant REE mineralization belt and its regional geological setting. Ore Geology Reviews, 64: 554-568 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.03.017 |
Liu Y, Chen ZY, Yang ZS, Sun X, Zhu ZM and Zhang QC. 2015b. Mineralogical and geochemical studies of brecciated ores in the Dalucao REE deposit, Sichuan Province, southwestern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 70: 613-636 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.03.006 |
Liu Y, Zhu ZM, Chen C, Zhang SP, Sun X, Yang ZS and Liang W. 2015c. Geochemical and mineralogical characteristics of weathered ore in the Dalucao REE deposit, Mianning-Dechang REE Belt, western Sichuan Province, southwestern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 71: 437-456 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.06.009 |
Liu Y and Hou ZQ. 2017. A synthesis of mineralization styles with an integrated genetic model of carbonatite-syenite-hosted REE deposits in the Cenozoic Mianning-Dechang REE metallogenic belt, the eastern Tibetan Plateau, southwestern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 137: 35-79 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.01.010 |
Liu Y, Chen C, Shu XC, Guo DX, Li ZJ, Zhao HX and Jia YH. 2017. The formation model of the carbonatite-syenite complex REE deposits in the east of Tibetan Plateau:A case study of Dalucao REE deposit. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(7): 1978-2000 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu Y, Chakhmouradian AR, Hou ZQ, Song WL and Kynicky J. 2019. Development of REE mineralization in the giant Maoniuping deposit (Sichuan, China):Insights from mineralogy, fluid inclusions, and trace-element geochemistry. Mineralium Deposita, 54: 701-718 DOI:10.1007/s00126-018-0836-y |
Lorenz V, Zimanowski B and Fröhlich G. 1994. Experiments on explosive basic and ultrabasic, ultramafic and carbonatite volcanism. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Kimberlite Conference. Araxa: CPRM Special Publication, 270-282
|
Luo YN, Yu RL, Hou LW, Lai SM, Fu DM, Chen MX, Fu XF, Rao RB and Zhou SS. 1998. Longmenshan-Jinpingshan Intracontinental Orogenic Belt. Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technology Press, 1-171 (in Chinese)
|
McKie D. 1966. Fenitization. In: Tuttle OF and Gittins J (eds.). Carbonatites. New York: Interscience Publishers, 261-294
|
Michard A. 1989. Rare earth element systematics in hydrothermal fluids. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53(3): 745-750 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(89)90017-3 |
Migdisov AA and Williams-Jones AE. 2014. Hydrothermal transport and deposition of the rare earth elements by fluorine-bearing aqueous liquids. Mineralium Deposita, 49(8): 987-997 DOI:10.1007/s00126-014-0554-z |
Mo XX, Zhao ZD, Deng JF, Dong GC, Zhou S, Guo TY, Zhang SQ and Wang LL. 2003. Response of volcanism to the India-Asia collision. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(3): 135-148 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Morogan V and Martin RF. 1985. Mineralogy and partial melting of fenitized crustal xenoliths in the Oldoinyo Lengai carbonatitic volcano, Tanzania. American Mineralogist, 70(11-12): 1114-1126 |
Morogan V and Woolley AR. 1988. Fenitization at the Alnö carbonatite complex, Sweden:Distribution, mineralogy and genesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 100(2): 169-182 DOI:10.1007/BF00373583 |
Morogan V. 1989. Mass transfer and REE mobility during fenitization at Alnö, Sweden. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 103(1): 25-34 DOI:10.1007/BF00371362 |
Nachit H, Ibhi A, Abia EH and Ohoud MB. 2005. Discrimination between primary magmatic biotites, reequilibrated biotites and neoformed biotites. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 337(16): 1415-1420 DOI:10.1016/j.crte.2005.09.002 |
Nelson DR, Chivas AR, Chappell BW and McCulloch MT. 1988. Geochemical and isotopic systematics in carbonatites and implications for the evolution of ocean-island sources. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 52(1): 1-17 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(88)90051-8 |
Nishimoto S and Yoshida H. 2010. Hydrothermal alteration of deep fractured granite:Effects of dissolution and precipitation. Lithos, 115(1-4): 153-162 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.11.015 |
Parsapoor A, Khalili M and Mackizadeh MA. 2009. The behaviour of trace and rare earth elements (REE) during hydrothermal alteration in the Rangan area (Central Iran). Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34(2): 123-134 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.04.005 |
Rubie DC and Gunter WD. 1983. The role of speciation in alkaline igneous fluids during fenite metasomatism. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 82(2-3): 165-175 DOI:10.1007/BF01166611 |
Shu XC and Liu Y. 2019. Fluid inclusion constraints on the hydrothermal evolution of the Dalucao Carbonatite-related REE deposit, Sichuan Province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 107: 41-57 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.02.014 |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345
|
Tian SH, Hou ZQ, Yang ZS, Chen W, Yang ZM, Yuan ZX, Xie YL, Fei HC, Yin SP, Liu YC, Li Z and Li XY. 2008. Geochronology of REE deposits in Mianning-Dechang REE metallogenic belt:Constraints on duration of hydrothermal activities and tectonic model for carbonatite-alkalic complexes in southwestern Sichuan. Mineral Deposits, 27(2): 177-187 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Tian SH, Hou ZQ, Su AN, Qiu L, Mo XX, Hou KJ, Zhao Y, Hu WJ and Yang ZS. 2015. The anomalous lithium isotopic signature of Himalayan collisional zone carbonatites in western Sichuan, SW China:Enriched mantle source and petrogenesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 159: 42-60 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2015.03.016 |
Treiman AH and Schedl A. 1983. Properties of carbonatite magma and processes in carbonatite magma chambers. Journal of Geology, 91(4): 437-447 DOI:10.1086/628789 |
Veksler IV, Petibon C, Jenner GA, Dorfman AM and Dingwell DB. 1998. Trace element partitioning in immiscible silicate-carbonate liquid systems:An initial experimental study using a centrifuge autoclave. Journal of Petrology, 39(11-12): 2095-2104 DOI:10.1093/petroj/39.11-12.2095 |
Verma SP, Torres-Alvarado IS, Satir M and Dobson PF. 2005. Hydrothermal alteration effects in geochemistry and Sr, Nd, Pb, and O isotopes of magmas from the Los Azufres geothermal field (Mexico):A statistical approach. Geochemical Journal, 39: 141-163 DOI:10.2343/geochemj.39.141 |
Verplanck PL, Van Gosen BS, Seal RR and McCafferty AE. 2014. A Deposit Model for Carbonatite and Peralkaline Intrusion-Related Rare Earth Element Deposits. Washington: U.S. Geological Survey, 1-58
|
Wang CM, Deng J, Carranza EJM and Santosh M. 2014a. Tin metallogenesis associated with granitoids in the southwestern Sanjiang Tethyan Domain:Nature, deposit types, and tectonic setting. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 576-593 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.005 |
Wang CM, Deng J, Carranza EJM and Lai XR. 2014b. Nature, diversity and temporal-spatial distributions of sediment-hosted Pb-Zn deposits in China. Ore Geology Reviews, 56: 327-351 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.06.004 |
Wang CM, Bagas L, Lu YJ, Santosh M, Du B and McCuaig TC. 2016. Terrane boundary and spatio-temporal distribution of ore deposits in the Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen:Insights from zircon Hf-isotopic mapping. Earth-Science Reviews, 156: 39-65 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.02.008 |
Wang CM, Bagas L, Chen JY, Yang LF, Zhang D, Du B and Shi KX. 2018. The genesis of the Liancheng Cu-Mo deposit in the Lanping Basin of SW China:Constraints from geology, fluid inclusions, and Cu-S-H-O isotopes. Ore Geology Reviews, 92: 113-128 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.11.012 |
Wang KY. 2015. Fenites associated with carbonatites. Chinese Journal of Geology, 50(1): 203-212 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang QF, Deng J, Li CS, Li GJ, Yu L and Qiao L. 2014c. The boundary between the Simao and Yangtze blocks and their locations in Gondwana and Rodinia:Constraints from detrital and inherited zircons. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 438-448 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.10.002 |
Weng ZH, Jowitt SM, Mudd GM and Haque N. 2015. A detailed assessment of global rare earth element resources:Opportunities and challenges. Economic Geology, 110(8): 1925-1952 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.110.8.1925 |
Whitbread MA and Moore CL. 2004. Two lithogeochemical approaches to the identification of alteration patterns at the Elura Zn-Pb-Ag deposit, Cobar, New South Wales, Australia:Use of Pearce element ratio analysis and Isocon analysis. Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 4(2): 129-141 DOI:10.1144/1467-7873/03-031 |
Williams-Jones AE, Migdisov AA and Samson IM. 2012. Hydrothermal mobilisation of the rare earth elements:A tale of "Ceria" and "Yttria". Elements, 8(5): 355-360 DOI:10.2113/gselements.8.5.355 |
Woolley AR. 1982. A discussion of carbonatite evolution and nomenclature, and the generation of sodic and potassic fenites. Mineralogical Magazine, 46(338): 13-17 DOI:10.1180/minmag.1982.046.338.03 |
Xie YL, Hou ZQ, Yin SP, Dominy SC, Xu JH, Tian SH and Xu WY. 2009. Continuous carbonatitic melt-fluid evolution of a REE mineralization system:Evidence from inclusions in the Maoniuping REE deposit, western Sichuan, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1-3): 90-105 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2008.10.006 |
Xie YL, Li YX, Hou ZQ, Cooke DR, Danyushevsky L, Dominy SC and Yin SP. 2015. A model for carbonatite hosted REE mineralization:The Mianning-Dechang REE belt, western Sichuan Province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 70: 595-612 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.10.027 |
Xu C, Campbell IH, Kynicky J, Allen CM, Chen YJ, Huang ZL and Qi L. 2008. Comparison of the Daluxiang and Maoniuping carbonatitic REE deposits with Bayan Obo REE deposit, China. Lithos, 106(1-2): 12-24 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2008.06.005 |
Xu C, Taylor RN, Li WB, Kynicky J, Chakhmouradian AR and Song WL. 2012. Comparison of fluorite geochemistry from REE deposits in the Panxi region and Bayan Obo, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 57: 76-89 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.06.007 |
Xu C, Kynicky J, Chakhmouradian AR, Li XH and Song WL. 2015. A case example of the importance of multi-analytical approach in deciphering carbonatite petrogenesis in South Qinling orogen:Miaoya rare-metal deposit, central China. Lithos, 227: 107-121 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.03.024 |
Xu YG, Chung SL, Jahn BM and Wu GY. 2001. Petrologic and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Permian-Triassic Emeishan fflood basalts in southwestern China. Lithos, 58(3-4): 145-168 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(01)00055-X |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Zhao K and Liu JT. 2011. Tectono-thermochronology and gold mineralization events of orogenic gold deposits in Ailaoshan orogenic belt, Southwest China:Geochronological constraints. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2519-2532 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yang LQ, Deng J, Dilek Y, Qiu KF, Ji XZ, Li N, Taylor RD and Yu JY. 2015. Structure, geochronology, and petrogenesis of the Late Triassic Puziba granitoid dikes in the Mianlue Suture Zone, Qinling Orogen, China. GSA Bulletin, 127(11-12): 1831-1854 DOI:10.1130/B31249.1 |
Yang XM, Yang XY, Fan HR, Guo F, Zhang ZF and Zheng YF. 2000. Petrological characteristics of fenites and their geological significance. Geological Review, 46(5): 481-490 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Yardley BWD and Lloyd GE. 1995. Why metasomatic fronts are really metasomatic sides. Geology, 23(1): 53-56 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0053:WMFARM>2.3.CO;2 |
Yin A and Harrison TM. 2000. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Science, 28: 211-280 DOI:10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211 |
Yuan ZX, Shi ZM, Bai G, Wu CY, Chi RA and Li XY. 1995. The Maoniuping Rare Earth Ore Deposit, Mianning County, Sichuan Province. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1-150 (in Chinese)
|
Zhang J, Deng J, Chen HY, Yang LQ, Cooke D, Danyushevsky L and Gong QJ. 2014. LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of pyrite from the Chang'an gold deposit, Sanjiang region, China:Implication for ore-forming process. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 557-575 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.11.003 |
Zhang J, Wang H, Li SH and Li TJ. 2017. Paleogene magmatism and gold metallogeny of the Jinping terrane in the Ailaoshan ore belt, Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen (SW China):Geology, deposit type and tectonic setting. Ore Geology Reviews, 91: 620-637 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.08.032 |
Zhang W, Lentz DR, Thorne KG and McFarlane C. 2016. Geochemical characteristics of biotite from felsic intrusive rocks around the Sisson Brook W-Mo-Cu deposit, west-central New Brunswick:An indicator of halogen and oxygen fugacity of magmatic systems. Ore Geology Reviews, 77: 82-96 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.02.004 |
Zheng X and Liu Y. 2019. Mechanisms of element precipitation in carbonatite-related rare-earth element deposits:Evidence from fluid inclusions in the Maoniuping deposit, Sichuan Province, southwestern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 107: 218-238 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.02.021 |
Zhong DL, Ding L, Liu FT, Liu JH, Zhang JJ, Ji JQ and Chen H. 2000. Multi-oriented and layered structures of lithosphere in erogenic belt and their effects on Cenozoic magmatism:A case study of western Yunnan and Sichuan, China. Science in China (Series D), 43(Suppl.): 122-133 |
从柏林. 1988. 攀西古裂谷的形成与演化. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-427.
|
邓军, 王庆飞, 李龚健. 2016. 复合造山和复合成矿系统:三江特提斯例析. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2225-2247. |
侯增谦, 田世洪, 谢玉玲, 袁忠信, 杨竹森, 尹淑苹, 费红彩, 邹天人, 李小渝, 杨志明. 2008. 川西冕宁-德昌喜马拉雅期稀土元素成矿带:矿床地质特征与区域成矿模型. 矿床地质, 27(2): 145-176. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2008.02.002 |
李龚健, 王庆飞, 禹丽, 胡兆初, 马楠, 黄钰涵. 2013. 哀牢山古特提斯洋缝合时限:晚二叠世花岗岩类锆石U-Pb年代学与地球化学制约. 岩石学报, 29(11): 3883-3900. |
李小渝. 2005. 四川德昌大陆槽稀土矿床地质特征. 矿床地质, 24(2): 151-160. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.02.007 |
刘琰, 陈超, 舒小超, 郭东旭, 李自静, 赵海璇, 贾玉衡. 2017. 青藏高原东部碳酸岩-正长岩杂岩体型REE矿床成矿模式——以大陆槽REE矿床为例. 岩石学报, 33(7): 1978-2000. |
骆耀南, 俞如龙, 侯立玮, 赖绍民, 付德明, 陈茂勋, 付小方, 饶荣标, 周世枢. 1998. 龙门山-锦屏山陆内造山带. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社, 1-171.
|
莫宣学, 赵志丹, 邓晋福, 董国臣, 周肃, 郭铁鹰, 张双全, 王亮亮. 2003. 印度-亚洲大陆主碰撞过程的火山作用响应. 地学前缘, 10(3): 135-148. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.013 |
田世洪, 侯增谦, 杨竹森, 陈文, 杨志明, 袁忠信, 谢玉玲, 费红彩, 尹淑苹, 刘英超, 李政, 李小渝. 2008. 川西冕宁-德昌REE成矿带成矿年代学研究:热液系统维系时限和构造控矿模型约束. 矿床地质, 27(2): 177-187. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2008.02.003 |
王凯怡. 2015. 与碳酸岩共生的霓长岩. 地质科学, 50(1): 203-212. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2015.01.012 |
杨立强, 邓军, 赵凯, 刘江涛. 2011. 哀牢山造山带金矿成矿时序及其动力学背景探讨. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2519-2532. |
杨学明, 杨晓勇, 范宏瑞, 郭范, 张兆峰, 郑永飞. 2000. 霓长岩岩石学特征及其地质意义评述. 地质论评, 46(5): 481-490. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.05.006 |
袁忠信, 施泽民, 白鸽, 吴澄宇, 池汝安, 李小渝. 1995. 四川冕宁牦牛坪轻稀土矿床. 北京: 地震出版社, 1-150.
|
钟大赉, 丁林, 刘福田, 刘建华, 张进江, 季建清, 陈辉. 2000. 造山带岩石层多向层架构造及其对新生代岩浆活动制约——以三江及邻区为例. 中国科学(D辑), 30(增): 1-8. |
 2019, Vol. 35
2019, Vol. 35


