沉积岩为容矿岩石的贱金属硫化物矿床作为金属Pb-Zn-Cu的最主要来源之一,例如密西西比河谷型(Mississippi Valley-Type, MVT)铅锌矿床,提供了世界上重要的铅锌资源, 以及沉积岩容矿的层状铜矿床(Sediment-hosted Stratiform Copper, SSC)世界上资源量仅次于斑岩铜矿,一直是地学界关注研究和工业界找矿勘查的重点(Leach et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2014a)。MVT铅锌矿床一般是指赋存于台地碳酸盐岩中,成因上与岩浆活动无明显直接联系的层控、后生的铅锌矿床,在中低温条件下由盆地卤水沉淀形成(Leach et al., 2001;Wang et al., 2014a)。其典型成矿环境多集中于造山带前陆盆地中,极少数存在于大陆伸展环境中,由此建立了典型的铅锌矿床成矿模式,并在世界范围内沉积岩为容矿岩石的贱金属硫化物矿床的勘查中实现了重大突破(Leach et al., 2001;Bradley and Leach, 2003)。然而SSC铜矿床一般赋存于盆地内碳酸盐岩和碎屑岩中,成矿物质和流体具有多样性,仍有同生和后生的争论,大多数学者倾向于在中低温条件下主要由盆地卤水沉淀成矿,甚至有岩浆热液和变质流体参与成矿(Annels, 1984; Kirkham, 1989; Brown, 1978, 1997)。近年来中国学者通过对青藏高原典型铅锌铜矿床研究发现,以沉积岩为容矿岩石的贱金属硫化物矿床,不仅可产于造山带前陆盆地中, 还可产于褶皱-逆冲带中(侯增谦等,2008;宋玉财等,2011)。因此,经典的铅锌铜成矿模型遇到了新的挑战,尚需从新的视角进行研究,给予其特定内涵和合理阐释。
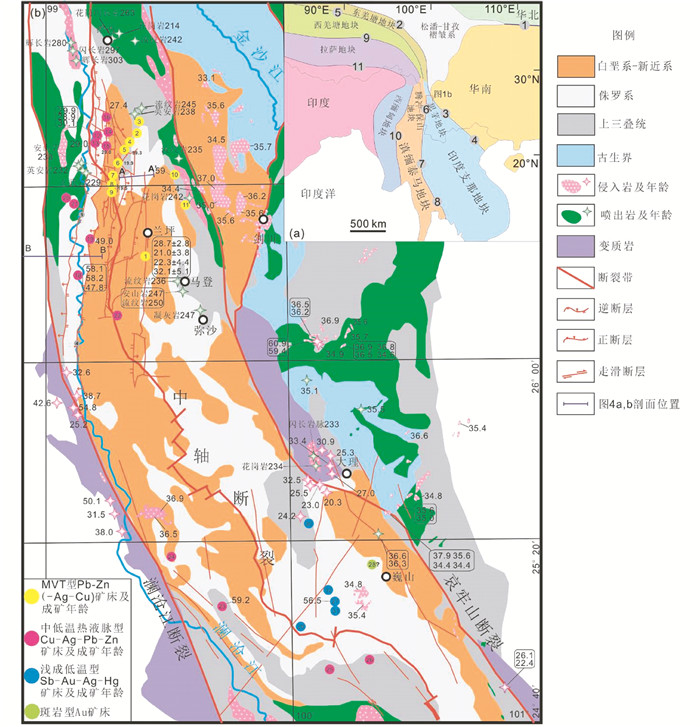
三江特提斯兰坪盆地是一个典型的中新生代陆内盆地,位于欧亚板块和印度板块结合部位,盆地内富集许多重要的喜马拉雅期矿床,如金顶巨型Zn-Pb矿床、白秧坪超大型Ag-Cu-Pb-Zn矿集区,笔架山超大型Sb矿床和金满中型Cu矿床等,由于其特殊的构造位置与丰富多样的矿藏,是解析上述问题的有利研究区,尤其值得关注(图 1)。前人对兰坪盆地内发育的矿床做了大量的研究(He et al., 2009;Xue et al., 2007;杨立飞等,2016)。然而,侧重于单个矿床或某一类矿床的构造流体与成矿作用的研究,对于整个兰坪盆地构造-流体-成矿方面的综合研究较少(张锦让和温汉捷,2012;Chi et al., 2007;Wang et al., 2014a;Song et al., 2016)。这些矿床明显受逆冲构造控制(何龙清等,2004;侯增谦等,2008), 与已有的经典的受台地碳酸盐岩控制的MVT铅锌矿床成矿模式尚存在差异(Leach et al., 2001),加之盆地内矿床类型多样,很难用一个成矿模式进行解释。
|
图 1 三江特提斯构造格架(a)和兰坪盆地矿床分布区地质简图(b)(据范金伟等,2014;Wang et al., 2014b修编 缝合带:1-秦岭-祁连-大别; 2-金沙江; 3-哀牢山; 4-松马; 5-龙木错-双湖; 6-昌宁-孟连; 7-清迈-茵他侬; 8-文冬-劳勿; 9-班公湖-怒江; 10-山边; 11-雅鲁藏布江 Fig. 1 Tectonic framework in the Sanjiang Tethys (a) and simplified geological map of the Lanping basin showing the distribution of major deposits(modified after Fan et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2014b) Sutures: 1-Qinling-Qilian-Dabie; 2-Jinshajiang; 3-Ailaoshan; 4-Song-Ma; 5-Longmu Tso-Shuanghu; 6-Changning-Menglian; 7-Chiang Mai-Inthanon; 8-Bentong-Raub; 9-Bangonghu-Nujiang; 10-Shan Boundary; 11-Indus-Yalung-Zangbu |
本文在梳理前人研究成果的基础上,根据笔者参加两轮973项目的研究成果,综合考虑三江特提斯复合造山与作用,解析兰坪盆地演化过程,总结主要金属矿床的地质特征和成矿流体特征,讨论兰坪盆地的构造-流体-成矿过程,希望为今后的找矿工作提供理论基础与指导。
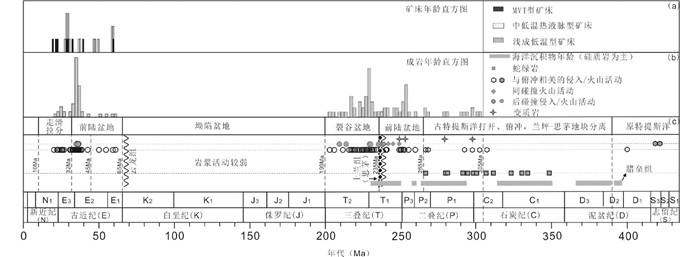
1 兰坪盆地演化过程特提斯-喜马拉雅、滨西太平洋和古亚洲是中国三大成矿域,三江特提斯因其复合造山与成矿而深受地质学家的关注(Liu et al., 2010, 2012a, b, c, 2015; Zhang et al., 2015a; Wang et al., 2016b, c, 2017; Deng et al., 2015a, 2017; Qiu et al., 2016)。滇西兰坪盆地位于青藏高原东南缘,华南板块西缘,三江造山带南部中段,东以哀牢山缝合带为界,西以昌宁-孟连缝合带为界,北起维西,南至云县,与思茅盆地相接,盆地内出露的地层主要为中上三叠统、侏罗系、白垩系和古近系(图 2)。兰坪地块演化过程十分复杂,包括三江特提斯地区内的基底的形成、裂谷盆地及坳陷盆地等转化过程。

|
图 2 兰坪盆地及邻区地层柱状图(据Wang et al., 2015b修编) Fig. 2 Generalized strata histogram in the Lanping basin and its adjacent areas(modified after Wang et al., 2015b) |
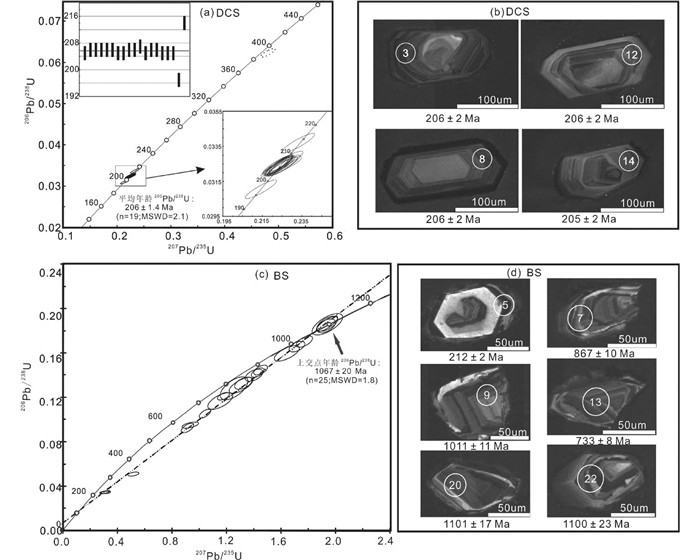
前寒武纪盆地基底属性和形成。前寒武纪的基底岩石在兰坪盆地内出露较少,研究亦相对较少。部分残留的前寒武纪结晶基底赋存于思茅地块中,主要由片麻岩、角闪岩、黑云斜长角闪岩、绢云片岩和大理岩组成,被古生代-新生代巨厚地层所覆盖。前人报道了研究区斜长角闪岩的全岩Sm-Nd的等时线年龄1437±17Ma(钟大赉, 1998; Wang et al., 2000),代表了其形成年龄。本次对盆地西侧片麻质花岗岩中进行研究,利用锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年,上交点年龄测试结果为1067±20Ma (N=25;MSWD=1.8),代表了变质事件的年龄(电子版附表 1、图 3)。Wang et al. (2016a)和杜斌等(2016)结合三江地区构造事件,沉积序列,古生物地理学,以古地磁为结果的古纬度,以及Nd-Hf同位素填图,认为昌宁-孟连缝合带是冈瓦纳与华夏古陆的重要边界,表明思茅地块具有华夏古陆的属性。昌宁-孟连和金沙江-哀牢山古特提斯洋从中泥盆世开始打开,思茅地块从华夏古陆分离出来(Wang et al., 2015a)。昌宁-孟连洋于晚石炭世-晚二叠世(305~265Ma)和金沙江-哀牢山洋于晚石炭世-晚二叠世(305~250Ma)分别向东、西俯冲于思茅地块之下(莫宣学等, 1993; 钟大赉, 1998; Jian et al., 2009; Deng et al., 2014a, b; Wang et al., 2015b),形成了大量同期的与俯冲有关的岩浆岩,如景洪地区的花岗闪长岩和半坡-南林山地区的基性-超基性侵入体(Zhao et al., 1994; Hennig et al., 2009; Jian et al., 2009; 李钢柱等, 2012; Deng et al., 2014a;李龚健,2014)。
|
图 3 兰坪盆地西侧花岗质岩石锆石U-Pb谐和图解 (a、b)二长花岗岩;(c、d)片麻质花岗岩 Fig. 3 Zircon U-Pb dating results of the granitoids in the western margin of the Lanping basin (a, b)monzogranite; (c, d)gneissic granite |
|
|
附表 1 兰坪盆地西南侧花岗质岩石锆石LA-ICP-MS测年结果 Appendix 1 LA-ICP-MS dating results of zircons from the granitoids in the northwestern margin of the Lanping basin |
中二叠世-中三叠世前陆盆地阶段。兰坪盆地东西两侧昌宁-孟连洋、金沙江-哀牢山古特提斯洋在二叠纪末闭合(刘本培等,1993;Deng et al., 2014a, b; Wang et al., 2015b),中三叠统上兰组与下伏上二叠统羊八寨组呈角度不整合接触或超覆不整合接触是该期碰撞造山的产物。早-中三叠世兰坪盆地是一个复合前陆盆地,由西部昌宁-孟连古特提斯洋弧后碰撞形成的景谷-景洪边缘前陆盆地,以及东部金沙江-哀牢山古特提斯洋发育的弧后前陆盆地共同构成(潘桂棠等,2001)。伴随发生了该期同碰撞有关变质变形和岩浆侵入喷发事件(Peng et al., 2008; Hennig et al., 2009; 毕丽莎, 2014; Yang et al., 2014)。
晚三叠世裂谷盆地。晚三叠世(235~203Ma)后碰撞导致思茅地块中兰坪裂谷盆地的形成(孔会磊等, 2012; 聂飞等, 2012; Dong et al., 2013; Peng et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2015b)。盆地内沉积有早三叠世砂岩和粉砂岩、中三叠世砂质板岩和砾岩、晚三叠世泥岩和砂岩。盆地内出露有三合洞组发育同生角砾灰岩及纹层状硅质岩, 以及攀天阁组和忙怀组“双峰式”酸性-基性火山岩,均反映了裂谷盆地的特征。同时形成了大量同期的与后碰撞有关的岩浆岩,具有代表性的是巨型的临沧岩体(Peng et al., 2008; Hennig et al., 2009; 范金伟等, 2014; Yang et al., 2014)。本次对盆地西南侧临沧岩体的二长花岗岩中进行研究,利用锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年,平均年龄测试结果为206±1Ma(N=19;MSWD=2.1),亦代表了该期构造-岩浆事件(附表 1、图 3)。
侏罗纪-白垩纪坳陷盆地。兰坪地区从晚三叠世裂谷盆地演化为坳陷盆地。对于该时期的盆地变化的动力学机制仍存争议,尚待进一步工作与讨论(Deng et al., 2014a; Wang et al., 2014a)。该断陷盆地沉积物主要来源于中侏罗统花开左组、下白垩统景星组及中白垩统虎头寺组,为海相-湖相红色碎屑岩和少量碳酸盐岩(陶晓风等,2002)。
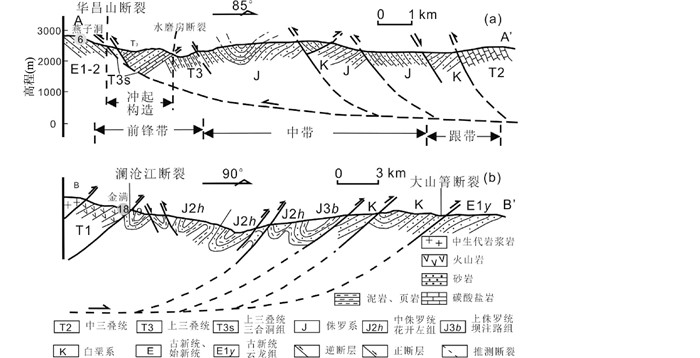
古新世-早渐新世前陆盆地。受印度-亚洲大陆对接碰撞的影响,盆地两侧的中生代地层作为构造岩片,由盆地两侧向中央推进,推覆于古近系地层之上,形成近平行的东、西两大逆冲推覆构造系统,分别为东部的金沙江造山带和西部的澜沧江造山带(图 4)。侏罗纪-白垩纪坳陷盆地范围进一步缩小,部分地区反转成山,仅在推覆带前缘形成陆相前陆盆地,陶晓风等(2002)称之为挤压推覆前陆盆地。盆地内充填以始新统宝相寺组和渐新统金丝厂组磨拉石砾岩为前陆盆地的代表岩石(陶晓风等,2002)。兰坪盆地发育有古新统云龙组和始新统果朗组,为湖泊相-盐湖相-河流相-沼泽相的粉砂岩、石英砂岩、灰质泥岩和页岩(陶晓风等,2002;侯增谦等,2008;Yang et al., 2014)。兰坪前陆盆地西侧发育有古近纪-早始新世与大陆汇聚有关的岩浆岩(65~45Ma),东侧发育有中始新世-早渐新世(45~32Ma)与岩石圈拆沉有关的岩浆岩(Hou et al., 2007; Lu et al., 2012, 2013; Deng et al., 2014b; Chen et al., 2015; Deng et al., 2015b)。
|
图 4 兰坪盆地逆冲推覆构造剖面图 (a)东部;(b)西部(据何龙清等,2004修改;AA′和BB′剖面位置见图 1) Fig. 4 Structural sections of thrust-nappe systems in Lanping basin (a) eastern part; (b) western part (modified after He et al., 2004; for locations of AA′ and BB′ in the Fig. 1) |
晚渐新世-中新世走滑拉分盆地(32~10Ma)。晚渐新世以来,印度板块继续发生NNE向推挤,同时太平洋俯冲使扬子陆块向西推进,形成了大规模NNW向断裂走滑,如红河和高黎贡断裂等以大型右行走滑断裂,盆地分化为多个走滑拉分盆地(潘桂棠等, 2001, 2016;陶晓风等,2002;杨立飞等,2016)。盆地充填了以双河组、三营组为代表的陆相碎屑岩沉积(陶晓风等,2002)。新生代盆地沉积中,尽管现今是菱形或不规则形分布,但均是被后期改造的结果,盆地有边缘相及拉分盆地的特点尚需进一步证实。
2 盆地成矿系统特征三江特提斯兰坪盆地产有与碰撞造山盆地卤水-热液型的成矿作用有关的Pb-Zn-Cu-Ag-Au-Sb-Hg矿产资源。密西西比河谷型(MVT)Pb-Zn多金属成矿系统,以金顶超大型铅锌矿床为代表。中低温热液脉型Cu-Ag多金属成矿系统,以金满-连城铜钼矿床为代表。浅成低温热液Sb-Au-Hg-As多金属成矿系统,以笔架山锑矿床为代表。典型矿床地质特征列于电子版附表 2。
|
|
附表 2 兰坪盆地矿床地质特征 Appendix 2 Deposit characteristics of the Lanping basin |
兰坪Pb-Zn多金属矿床主要分布于盆地东缘,主要包括金顶和白秧坪东矿集区(河西、三山及一系列小型矿床/点)。
金顶锌铅矿床位于三江特提斯兰坪盆地中部。金顶矿床具一百多个矿体,主要分布在跑马坪、北厂、架崖山、峰子山、南厂、白草坪以及西坡7个矿段。如图 5a所示,近水平发育的系列逆冲断层和构造圈闭而成的构造穹隆控制金顶矿床。矿石可归纳为砂岩型矿石和灰岩角砾岩型。其中,砂岩型矿化主要沿景星组砂岩分布,而灰岩角砾岩型矿化则与三合洞组灰岩角砾密切相关。矿石主要呈浸染状、块状、角砾状和脉状等(图 6)。矿石矿物有方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铁矿、白铁矿、黄铜矿、褐铁矿、菱锌矿和水锌矿等。脉石矿物以天青石、方解石和石膏为主,少量石英、重晶石和沥青。金顶矿区有机质丰富,并且有机质富集处,矿化强烈。金顶矿床的砂岩型及灰岩角砾岩型成矿过程主要有3个阶段: ① 白铁矿-闪锌矿阶段;② 黄铁矿-闪锌矿-方铅矿阶段;③ 方铅矿-闪锌矿-黄铁矿-方解石-石膏阶段(Deng et al., 2016)。流体包裹体类型单一,以发育气液两相水溶液包裹体为主。前人对流体包裹体进行研究,均一温度集中在54~309℃(峰值190~80℃),盐度为1.6%~18.0% NaCleqv(曾荣,2007)。
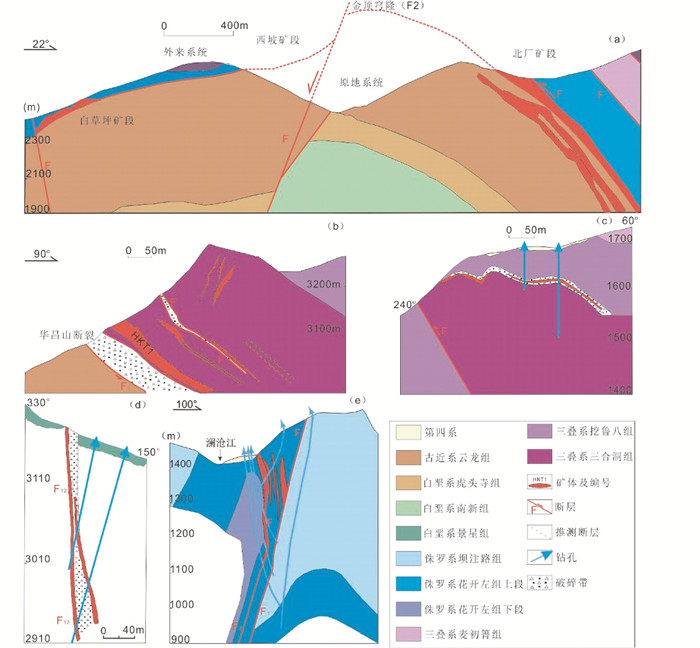
|
图 5 兰坪盆地受逆冲推覆构造控制矿床的地质剖面图(据薛伟, 2010;肖昌浩, 2013; Song et al., 2016修编) (a)金顶矿床;(b)华昌山矿床;(c)笔架山矿床;(d)白秧坪矿床;(e)金满矿床 Fig. 5 Geological sections of thrust-controlled deposits in the Lanping basin (modified after Xue, 2010; Xiao, 2013; Song et al., 2016) (a) Jinding deposit; (b) Huachangshan deposit; (c) Bijiashan deposit; (d) Baiyangping deposit; (e) Jinman deposit |

|
图 6 兰坪盆地典型矿床的矿石特征 (a)石英砂岩发生浸染状闪锌矿+白铁矿矿化,金顶矿床;(b)角砾型矿石, 金顶矿床;(c)砂岩中可见石英黄铜矿脉,金满矿床;(d)碳酸盐硫化物脉,硫化物主要为黄铜矿、辉铜矿,金满矿床;(e)硅质砂岩中石英硫化物矿化,硫化物主要为斑铜矿、辉铜矿,连城矿床;(f)砂岩中可见辉钼矿化,石英碳酸盐脉后期穿插,连城矿床;(g)砂岩中可见辉铜矿脉,白秧坪矿床;(h)砂岩中可见方解石硫化物脉,硫化物主要为辉铜矿、斑铜矿和黄铜矿,白秧坪矿床;(i)砂岩中可见方解石硫化物脉,硫化物主要为闪锌矿、方铅矿,李子坪矿床;(j)砂岩中可见脉状闪锌矿,李子坪矿床;(k)辉锑矿和黄锑华矿石,笔架山矿床(肖昌浩,2013);(l)辰砂矿石,见有石膏脉,笔架山矿床(肖昌浩,2013) Fig. 6 Characteristics of ores from typical deposits in the Lanping basin (a) disseminated marcasite and sphalerite in sandstone ore, Jinding deposit; (b) brecciated limestone-hosted ore, Jinding deposit; (c) quartz-chalcopyrite vein in sandstone, Jianman deposit; (d) carbonate-sulfide vein (major chalcopyrite and chalcocite), Jinman deposit; (e) quartz-sulfide mineralization (major bornite and chalcocite) in siliceous sandstone, Liancheng deposit; (f) quartz-molybdenite vein in sandstone, cut by later quartz-carbonate vein, Liancheng deposit; (g) chalcocite veins in sandstone, Baiyangping deposit; (h) calcite-sulfide (major chalcocite, bornite and chalcopyrite) vein in sandstone, Baiyangping deposit; (i) calcite-sulfide (major sphalerite and galena) vein in sandstone, Liziping deposit; (j) vein-like sphalerite in sandstone, Liziping deposit; (k) stibnite and cervanite ore, Bijiashan deposit (Xiao, 2013); (l) cinnabar ore with gypsum veins, Bijiashan deposit (Xiao, 2013) |
兰坪盆地内华昌山断裂控制河西、东至岩、下区吾、燕子洞和三山等一系列Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu矿床,矿体出现在断裂带内及两侧的裂隙发育部位(图 5b;侯增谦等,2008)。矿体以脉状、透镜状和似层状为主,主要赋存在华昌山断裂构造破碎带中,产状与华昌山断裂基本一致。矿石构造为角砾状构造、网脉状构造、细脉状构造、块状构造和浸染状构造。矿石矿物包括方铅矿、车轮矿、闪锌矿和菱锌矿,以及铜矿物有黝铜矿系列、辉铜矿、黑铜矿、黄铜矿、斑铜矿、孔雀石、蓝铜矿和铜蓝等。脉石矿物方解石、天青石、菱铁矿、白云石、重晶石、萤石、石英和黏土矿物。围岩蚀变较弱,组合简单,分布不均匀,主要为重晶石化、方解石化、萤石化、天青石化、白云石化和硅化。流体包裹体类型单一,以发育气液两相水溶液包裹体为主。前人对流体包裹体进行研究,均一温度集中在100~240℃(主要温度小于185℃),盐度小于3%~21% NaCleqv(徐启东和李建威, 2003;陈开旭等, 2004)。
2.2 中低温热液脉型Cu-Ag成矿系统兰坪Cu-Ag多金属矿床主要分布于盆地西缘。金满Cu-Ag、连城Cu-Mo矿床及30余个小型脉状Cu矿床主要赋存于侏罗系花开佐组的杂色碎屑岩中,矿体受逆冲断裂平行的次级断裂控制;白秧坪西矿集区Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu多金属矿集区的矿床受逆冲断裂平行的次级断裂控制(图 1、图 5)。
金满Cu矿床的岩石因强烈挤压而出现褶皱构造,同时发育平行于逆冲推覆构造带一系列逆断层。如图 5c所示,金满矿床矿体主要分布在金满褶皱东翼近核部,受发育于侏罗系花开佐组砂岩和页岩/板岩层间的近南北向压性F2断层控制,断层倾向NWW,倾角60°~90°。矿石以脉状和网脉状为主。矿石矿物黄铜矿、砷黝铜矿、斑铜矿和蓝辉铜矿,少量辉砷钴矿,形成顺序从早至晚依次为黄铜矿、斑铜矿和砷黝铜(图 6)。矿脉石矿物以石英、铁白云石和方解石为主(杨立飞等,2016)。成矿后的表生氧化作用形成了褐铁矿和铜蓝等次生矿物。本次流体包裹体测温实验在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所国家重点实验室流体包裹体室完成,所使用的测温仪器是英国产Linkam THMS G600显微冷热台,温度范围:-196~+600℃,精度为±0.1℃。本次研究显示流体包裹体类型单一,以发育气液两相水溶液包裹体为主(图 7)。本次对流体包裹体进行研究,均一温度集中在210~270℃,盐度变化范围为0.88%~20.51% NaCleqv,集中分布于11%~19% NaCleqv(电子版附表 3)。
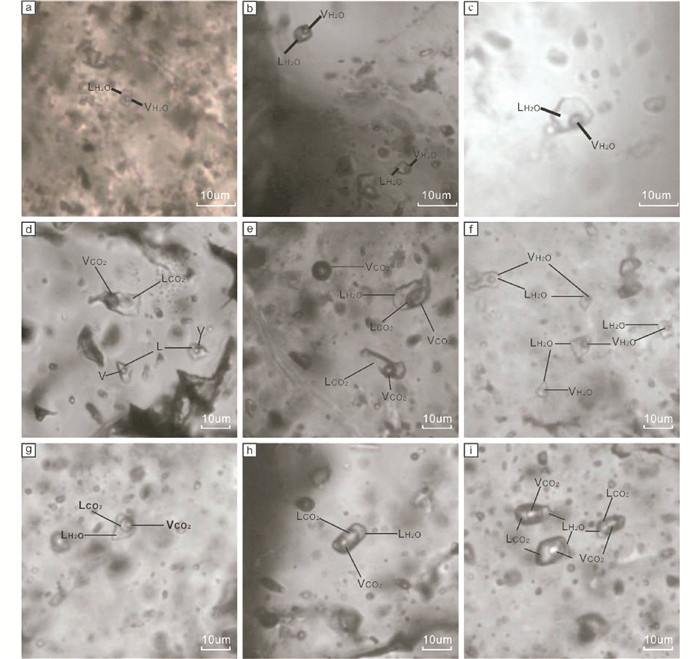
|
图 7 金满-连城和白秧坪矿床流体包裹体显微照片 (a)水溶液型两相包裹体,富隆厂矿床;(b)水溶液型两相包裹体,李子坪矿床;(c)水溶液型两相包裹体,李子坪矿床;(d) CO2型三相包裹体和水溶液型两相包裹体,金满矿床;(e)纯CO2型单相、CO2型两相和CO2型三相包裹体,金满矿床;(f)水溶液型两相包裹体,连城矿床;(g-i) CO2型三相包裹体,连城矿床 Fig. 7 Photos of fluid inclusions at the Jinman-Liancheng and Baiyangping deposits (a) two-phase H2O inclusions, Fulongchang deposit; (b) two-phase H2O inclusions, Liziping deposit; (c) two-phase H2O inclusions, Liziping deposit; (d) two-phase CO2 and two-phase H2O inclusions, Jinman deposit; (e) single-phase, two-phase and three-phase CO2 inclusions, Jinman deposit; (f) two-phase H2O inclusions, Liancheng; (g-i) three-phase CO2 inclusions, Liancheng deposit |
|
|
附表 3 兰坪盆地矿床流体包裹体特征 Appendix 3 Fluid inclusion characteristics of deposits in the Lanping basin |
如图 5d所示,富隆厂和白秧坪矿床受西倾主逆冲断裂派生的NE向次级断裂控制,次级断裂倾向NW,倾角70°~87°(范世家等, 2006)。矿体赋存于赋矿景星组地层中。矿石构造为脉状和网脉状、块状、角砾状、浸染等。矿石矿物包括黝铜矿、砷黝铜矿、汞银矿、辉银矿、辉砷钴矿和方铅矿,少量黄铜矿、黄铁矿和闪锌矿,脉石矿物以菱铁矿、铁白云石和方解石为主,少量重晶石和见石英(图 6)。围岩蚀变较强,主要有硅化、碳酸盐化和重晶石化。白秧坪和富隆厂矿床成矿阶段亦可分为两个阶段:① 碳酸盐-以铜为主多金属硫化物阶段;② 碳酸盐-以铅锌为主多金属硫化物阶段。成矿后期发育热液活动,表现为石英-碳酸盐脉,但与成矿关系甚微。本次研究显示流体包裹体类型单一,以发育气液两相水溶液包裹体为主(图 7)。本次对流体包裹体进行研究,均一温度变化范围为140~367℃,大多数包裹体均一温度小于300℃,在140~270℃中分布较为均匀,平均值为206℃,盐度变化范围为3.5%~19.9% NaCleqv,集中分布于10%~13% NaCleqv(附表 3)。
2.3 浅成低温热液型Sb-Au-Hg-As成矿系统在兰坪盆地的南部巍山-永平地区展布有锑、金、汞、砷低温多金属矿床(图 1、附表 3),其中展布有笔架山锑、石磺厂砷和黑龙潭汞等浅成低温热液型矿床或矿点。除笔架山外,其他规模较小,研究程度较低(董方浏, 2003; 王勇,2002;肖昌浩,2013)。如图 5e所示,笔架山矿体赋存于逆冲断裂上盘,呈似层状薄层状和透镜状,沿笔架山背斜轴部北西向破碎带分布,产出在轴部和两翼的上三叠统三合洞组灰岩与挖鲁八组泥岩、页岩接触带的层间破碎带内,部分矿体充填在三合洞组灰岩裂隙和溶洞中(肖昌浩,2013)。矿石构造为块状、浸染状、角砾状和晶簇状,矿石矿物包括辉锑矿,少量方铅矿、闪锌矿、雌黄和辰砂,脉石矿物以萤石、石膏和方解石为主(图 6)。矿区围岩蚀变较弱,主要有硅化、萤石化、碳酸盐化和石膏化等。笔架山矿床的热液活动期次有2个阶段: ① 萤石-辉锑矿-自然硫-黄铁矿-方铅矿-闪锌矿-石英-方解石-辰砂阶段, ② 萤石-石英-方解石-石膏阶段。其中, 第② 阶段为主成矿阶段。流体包裹体类型单一,以发育气液两相水溶液包裹体为主。前人对流体包裹体进行研究,均一温度集中在145~200℃,盐度小于6% NaCleqv(董方浏,2003; 佟子达等,2016)。
3 讨论 3.1 成矿作用持续时限众多已发表前人年代学数据列于附表 2。大量现有矿床的年龄数据包括蚀变矿物绢云母和伊利石的40Ar-39Ar和K-Ar年龄(毕先梅和莫宣学,2004;王彦斌等,2005;赵海滨,2006)、石英中流体包裹体Rb-Sr年龄(李小明,2001)、含矿脉石方解石和石英的40Ar-39Ar和Sm-Nd年龄(薛春纪等,2003;毕先梅和莫宣学,2004;何明勤等,2004;徐晓春等,2004;Zou et al., 2015;张锦让等,2016)、矿石矿物闪锌矿Rb-Sr年龄(王晓虎等,2011)、辉钼矿和黄铁矿Re-Os年龄(王光辉等,2009;唐永永等,2013;张锦让等,2016)和热液锆石和磷灰石U-Pb年龄(Li and Song, 2006)。数据变化较大,年龄质量参差不齐,有必要对兰坪盆地成矿作用的持续时间重新进行梳理和分析。
MVT Pb-Zn成矿系统的成矿年龄鉴于测试难度较大,数据相对较少。金顶矿床的沥青的Re-Os等时线年龄为68±5Ma,黄铁矿Re-Os测得等时线年龄为65±10Ma,指示金顶古油气成藏时代和成矿前热液事件的年龄(高炳宇等,2012; 唐永永等,2013)。金顶超大型铅锌矿床的架崖山矿段采用磷灰石裂变径迹分析,测定的结果为21.0±3.8Ma、22.3±4.4Ma、28.7±2.8Ma和32.1±5.1Ma(李小明等, 2000; Li and Song, 2006)。Yalikun et al.(2017)使用古地磁方法产生代表铅锌矿化的平均年龄为23±3Ma。区域地质特征显示,始新统宝相寺组砂岩中出现铅锌矿化现象,表明矿化是发在始新统宝相寺组沉积之后。结合区域地质和热事件分析,金顶成矿时代应该在21~32Ma之间,与前人的理解一致(唐永永等,2013;王安建等,2009)。在白秧坪东矿集区,华昌山断裂控制三山Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu矿床,王晓虎等(2016)对灰山、黑山矿段含Pb-Zn矿的方解石,运用Sm-Nd法定年,获得年龄数据为29.5±1.7Ma,与研究区其他MVT Pb-Zn成矿系统矿床年龄比较吻合。
中低温热液脉型Cu-Ag成矿系统的研究,前人已经进行了大量测试,存在不同的理解和认识。在金满和连城矿床,因连城矿床的矿石富含辉钼矿,而使成矿年龄的更趋精准,如辉钼矿Re-Os法测得等时线年龄为47.8±1.8Ma和48.14±0.87Ma(王光辉等,2009;张锦让等,2016),代表Cu-Mo矿床主成矿时代。在金满矿床,刘家军等(2003)利用石英流体包裹体40Ar/39Ar快中子活化法测得与铜矿化有关的石英的等时线年龄为58.05±0.54Ma;同样,徐晓春等(2004)通过石英Ar-Ar快中子活化法测定成矿年龄为56.7±1.0Ma。Li and Song(2006)通过磷灰石裂变径迹测定年龄46.1±5.8Ma。另外,张锦让等(2016)对金满铜多金属矿床主成矿阶段含矿方解石脉,运用Sm-Nd法定年,获得年龄数据为58.2±5.3Ma。其他学者通过蚀变围岩中极低级变质矿物伊利石K-Ar年龄47.2~35.4Ma和绢云母Ar-Ar法定年36.8±0.8Ma,可能代表了晚期或其他构造-热事件对矿床的叠加或改造的年龄(毕先梅和莫宣学,2004;王彦斌等,2005;赵海滨,2006)。区域地质特征显示,古新统云龙组砂岩中出现有金属矿化,因此~56Ma作为矿化的下限年龄。脉状热液脉型Cu-Ag多金属矿床的成矿时代晚于逆冲推覆系统的起始时间,大于56Ma很可能作为其他热液事件的年龄,尚不能作为约束成矿事件(张锦让等,2016)。因此,金满和连城矿床很可能发生的铜矿化的时间集中于56 Ma至46Ma。在白秧坪西矿集区,王晓虎等(2011)对富隆厂、吴底厂和李子坪矿段含Pb-Zn矿的方解石,运用Sm-Nd法定年,获得年龄数据为29.9±1.1Ma;同样,Zou et al.(2015)利用Sm-Nd法在白秧坪和吴底厂矿段获得较为一致年龄数据(30.1±1.9Ma和27.4±1.8Ma)。王晓虎等(2011)同时报道了富隆厂、吴底厂和李子坪矿段闪锌矿的Rb-Sr年龄分别为28.99±0.13Ma、28.93±0.62Ma和29.01±0.04Ma。这些数据年龄基本可以代表白秧坪多金属矿集区铅锌的成矿年龄,集中于30~29Ma。另外,何明勤等(2006)利用石英Ar-Ar快中子活化法测得白秧坪矿段与铜矿化有关的石英的等时线年龄为55.90±0.29Ma;同样,薛春纪等(2003)通过石英Ar-Ar快中子活化法测定成矿年龄为62.78±0.60Ma。因此,白秧坪矿集区很可能发生的铜和铅锌矿化的时间集中于~55Ma和~30Ma。
巍山地区浅成低温热液Sb-Au-Hg-As矿床尚未开展成矿年龄的测试。肖昌浩(2013)报道了莲花山富钾斑岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄为34.11±0.36Ma,约束了莲花山斑岩型金矿点围岩的成岩年龄,同时,间接约束了浅成低温热液矿床的成矿的下限。
综上所述,兰坪盆地三大成矿系统成矿年龄主要集中于三个时期(图 8):早始新世(56~46Ma)早期脉状热液脉型Cu-Ag多金属矿化,中-晚始新世(40~32Ma)富钾斑岩远端的浅成低温热液Sb-Au-Hg-As矿化,和渐新世-中新世(32~21Ma)MVT Pb-Zn矿化和晚期脉状热液脉型Pb-Zn多金属矿化。
兰坪盆地流体包裹体均一温度和盐度直方图显示了不同成矿系统的流体特征(图 9)。
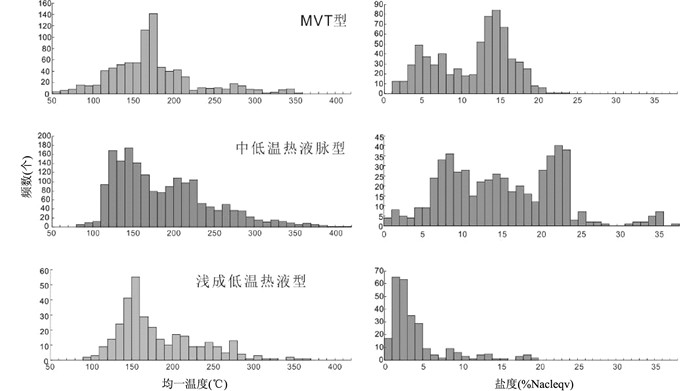
|
图 9 兰坪盆地不同成矿系统的流体包裹体均一温度和盐度直方图 数据据王勇,2002;徐启东和李建威,2003;杨伟光等,2003;陈开旭等,2004;王建飞等,2014;赵海滨,2006;Xue et al., 2007; 曾荣,2007;He et al., 2009;王光辉,2010;薛伟,2010;张锦让和温汉捷,2010;唐永永等,2011;王晓虎等,2011;李彬,2012a;尹静,2012;张锦让等,2012;王哲,2013;杨雁波,2013;Feng et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2015c; Zhang et al., 2015b; 佟子达等,2016;Song et al., 2016;本文 Fig. 9 Histograms of homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions from different ore systems in the Lanping basin Data from Wang, 2002; Xu and Li, 2003; Yang et al., 2003; Chen et al., 2004; Wang et al., 2004; Zhao, 2006; Xue et al., 2007; Zeng et al., 2007; He et al., 2009; Wang, 2010; Xue et al., 2010; Zhang and Wen, 2010; Tang et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2011; Li, 2012a; Yin, 2012; Zhang et al., 2012; Wang, 2013; Yang, 2013; Feng et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2015c; Zhang et al., 2015b; Tong et al., 2016; Song et al., 2016; this study |
兰坪盆地MVT Pb-Zn成矿系统中金顶矿床成矿流体的温度和盐度具有较大的变化范围,图 9显示具有较低温度、较高盐度和较高温度、较低盐度并富CO2流体的混合的成矿流体。低温和高盐度的流体与形成MVT型矿床的盆地卤水具有相似特征,可能成矿流体演化的晚期或在成矿期大气降水也有一定贡献(Leach et al., 2001;Bradley and Leach, 2003;Tang et al., 2014),对此观点,众多的学者也取得一致的意见(薛春纪等,2006;侯增谦等,2008; 唐永永等,2011;Deng et al., 2016)。然而对于较高温度和较低盐度流体来源,尚存在一定争议,如薛春纪等(2006)认为金顶成矿流体相对富含Co、Ni可能指示了成矿作用与深部岩浆或地幔流体具有一定关系,唐永永等(2011)结合铅同位素、稀有气体、以及超压流体包裹体研究,认为金顶铅锌矿脉状方解石的形成很可能与深源流体或隐伏岩浆岩有关。然而研究区范围内未发现出露岩浆岩,隐伏岩浆岩仅是一种推测。随着地质工作的不断深入,深部信息的揭露,将会提供岩浆岩是否与成矿有关的证据。白秧坪东矿集区Pb-Zn矿床的成矿流体相对较为单一,显示为低温和中-高盐度特征,主要有两种观点和认识,其一为单一的盆地卤水来源,其二为盆地卤水与深循环大气降水混合来源(杨伟光等,2003;何龙清等,2005;赵海滨,2006; Feng et al., 2014)。无论何种解释,对于兰坪盆地MVT Pb-Zn成矿系统的成矿流体均充分肯定了盆地卤水对成矿的重要贡献。
中低温热液脉型Cu-Ag成矿系统中金满和连城矿床成矿流体具有多样性,温度和盐度变化范围较广的特点,基本可以排除唯一成矿流体来源的可能性(图 9)。金满和连城矿床的低温和高盐度的流体作为成矿的重要组成部分,来自于盆地热卤水体系(刘家军等,2000)。除此之外,还有另一种富CO2、低盐度和中等温度的成矿流体,其来源尚存在一定争议。一种观点认为来自深部下地壳或上地幔岩浆流体(王光辉,2010;Chi and Xue, 2011;杨立飞等,2016),另一种观点认为成矿流体可能为变质流体来源(侯增谦等,2008; 宋玉财等,2011)。作者更倾向于后一种观点,金满和连城矿床56~46Ma铜矿化的时间,恰好三江特提斯发生印度-亚洲大陆碰撞,为其变质流体的形成提供良好的构造环境,而兰坪盆地及两侧尚未发现出露同时代的岩浆岩,较难解释深部存在隐伏岩体。因此,也有学者称这些中低温热液脉型矿床为造山型矿床(侯增谦等,2008)。在白秧坪西矿集区Pb-Zn-Cu-Ag矿床,如图 9所示,成矿流体显示低温(主体<200℃)和高盐度(主体>20% NaCleqv)特征,反映来源于盆地卤水,与前人研究成果一致(杨伟光等,2003;赵海滨,2006; 薛伟,2010)。因此,中低温热液脉型Cu-Ag成矿系统的成矿流体以盆地卤水为主,并不排除富CO2的变质流体对成矿的重要贡献。
巍山地区浅成低温热液Sb-Au-Hg-As成矿系统具有高温到低温演化的趋势,斑岩型矿床成矿流体以岩浆为主,随着温度减低,远端的浅成低温热液矿床成矿流体以大气降水为主(董方浏, 2003; 王勇,2002;肖昌浩,2013),此与国内外成矿系统流体的大气降水为主来源的特征类似(Wang et al., 2008)。然而,值得关注的问题在于,位于盆地内浅成低温热液矿床是否受到盆地卤水贡献。佟子达等(2016)认为盆地卤水可能参与了成矿,从其低盐度的特征来看,此种解释尚待进一步斟酌。
综上所述,兰坪盆地MVT Pb-Zn成矿系统以盆地卤水为主,浅成低温热液Sb-Au-Hg-As成矿系统以大气降水为主,中低温热液脉型矿床的成矿流体Cu-Ag可能受富CO2的变质流体和盆地卤水贡献。
3.3 构造-流体-成矿系统兰坪盆地的构造与流体-成矿的关系众说纷纭,关键在于对兰坪盆地的演化过程尚存在争议,比如前陆盆地控矿(Wang et al., 2001)、走滑拉分盆地控矿(牟传龙等,1999)和逆冲挤压和走滑拉分控制的盆地控矿等(周江羽等,2011)。从上述的构造演化解析可以看出,兰坪盆地的演化经历了6个阶段,对流体-成矿的作用不能用单一阶段来认识。结合成矿的时代,认为古新世-早渐新世前陆盆地和晚渐新世-中新世走滑拉分盆地对成矿起到关键作用(陶晓风等, 2002)。值得注意的是,古新世-早渐新世前陆盆地位于碰撞造山带内部而非外围,而且近EW双向对冲形成的两套逆冲推覆构造系统叠覆于前陆盆地两侧,明显有别于典型的前陆盆地,矿床不是形成在典型的前陆盆地环境中。同时其还受后期走滑拉分构造控制而变得更加复杂(侯增谦等,2008;宋玉财等,2011;Wang et al., 2014a)。
印度-亚洲大陆岩石圈挤压褶皱阶段,在兰坪盆地西侧发育古新世-早始新世阶段(56~46Ma)中低温热液脉型Cu-Ag成矿系统。兰坪地块受到强烈挤压,形成近平行的东、西两大逆冲推覆构造系统,表现为发育褶皱-逆冲带和挤压构造为特点的新生代盆地(图 4;侯增谦等,2008)。在此阶段,由于陆陆碰撞和大陆板片的俯冲导致地壳的缩短加厚,发生了重要的变质作用和岩浆作用,如龚俊峰等(2006)汇报了研究区49Ma左右变质年龄。陆陆碰撞引发的变质作用主要发生在西藏地区的新特提斯印度-雅鲁藏布缝合带,以及前期已形成的古-中特提斯缝合带,并伴随着与之有关的Cu-Au矿床的形成。例如在西藏地区的发现有该时期的与变质流体有关的金矿床(Jiang et al., 2009)。在三江兰坪盆地西部边缘,逆冲推覆构造系统的逆冲断裂带上盘的构造岩片内发育派生的垂直断裂-裂隙系统、顺层层间破碎带和切割逆冲断裂的平移断层,这些构造常常成为流体积聚和硫化物沉积的重要空间。在古新世-早始新世时期(55~40Ma),在逆冲推覆构造系统中,产生富含CO2、低盐度和NaCl-H2O变质流体,流体沿途萃取Cu和S等成矿金属和元素,通过主逆冲断裂和平移断层垂向沟通网络,流经浅部褶皱翼部和核部,流入平行于逆冲带的断裂进行交代和开放空间充填,形成金满和连城中低温热液脉型Cu矿床;进入主逆冲断裂上盘发育的各级次级断裂和平移断层,形成与主逆冲断裂呈斜交的次级断裂控制着白秧坪Cu-Ag(-Co)矿床(图 10a)。
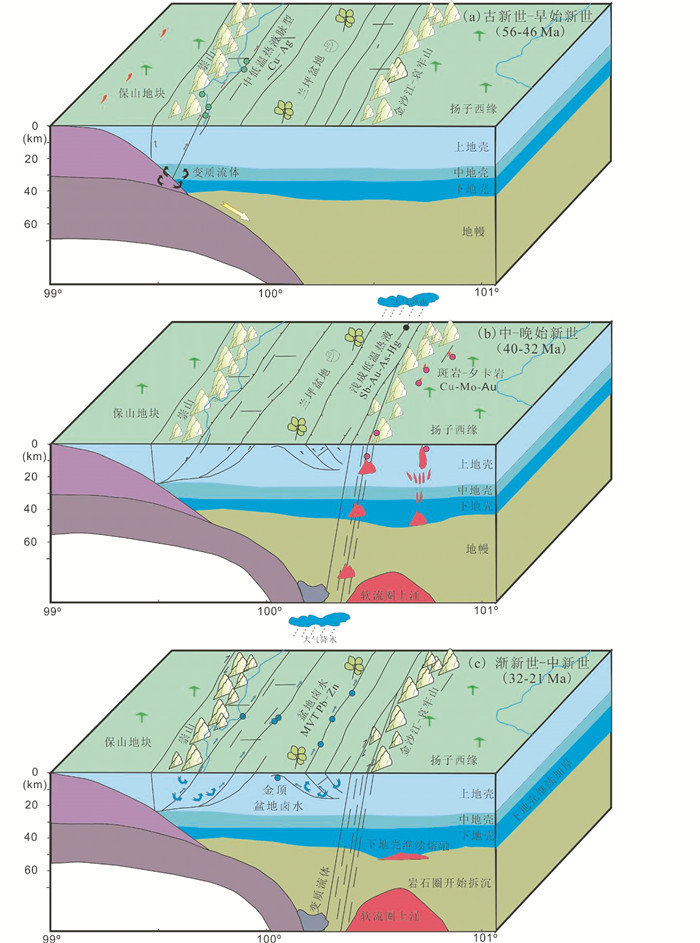
|
图 10 兰坪盆地构造-流体-成矿过程 (a)古新世-早始新世阶段(56~46Ma)中低温热液脉型Cu-Ag成矿系统; (b)中-晚始新世阶段(40~32Ma)斑岩型-夕卡岩型铜钼金矿床远端的浅成低温热液Sb-Au-Hg-As成矿系统; (c)渐新世-中新世(32~21Ma)MVT Pb-Zn成矿系统 Fig. 10 Tectonic-fluid-metallogenic process of the Lanping basin (a) Paleocene-Eocene (56~46Ma) mesothermal vein type Cu-Ag mineral system; (b) Middle-Late Eocene (40~32Ma) epithermal Sb-Au-Hg-As mineral system, as distal member of porphyry-skarn Cu-Mo-Au deposit; (c) Oligocene-Miocene (32~21Ma) Mississippi Valley-Type Pb-Zn mineral system |
印度-亚洲大陆岩石圈拆沉伸展阶段,扬子西缘形成了大规模的与岩石圈拆沉有关的富钾斑岩及其有关斑岩型-夕卡岩型铜钼金矿床(Lu et al., 2012, 2013; Deng et al., 2014a)。而在兰坪盆地,仅仅在其东南缘见有该时期的少量分布的富钾斑岩,斑岩型-夕卡岩型铜钼金矿床尚未报道。受富钾斑岩的影响,在其远端,形成以大气降水为主、受构造控制的中-晚始新世(40~32Ma)浅成低温热液Sb-Au-Hg-As成矿系统(图 10b)。
印度-亚洲大陆挤压走滑阶段,在兰坪盆地西侧发育渐新世-中新世(32~21Ma)MVT Pb-Zn成矿系统,以及叠加改造中低温热液脉型Cu-Ag成矿系统。在盆地东侧形成的造山型金矿亦发生在此时期(Deng et al., 2015b)。前人已有很多报道,认为MVT Pb-Zn在褶皱-逆冲带中形成(如侯增谦等,2008;宋玉财等,2011;江彪,2014;Wang et al., 2014a)。然而,在渐新世-中新世,“三江”东缘地区产生大规模的区域走滑和可能的块体旋转,形成一系列走滑断裂,位于兰坪盆地东侧的巨型的红河剪切带是最好的佐证(Cao et al., 2009, 2011; Deng et al., 2014b)。兰坪盆地两侧断层走滑活动可能是控制其成矿的主导因素之一,促使深部的成矿流体得以沿其侧向和向上流动。富含高盐度的热卤水流入容矿构造,富集成矿,如前期形成的逆冲断裂及其两侧破碎带,构造圈闭而成的构造穹隆等均是矿液存储的有利空间。在此阶段形成的河西-三山式Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu矿床,金顶MVT Zn-Pb矿床以及白秧坪晚阶段Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu矿床(图 10c)。
4 结论(1) 利用锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb同位素定年获得兰坪盆地西侧片麻质花岗岩和二长花岗岩的上交点年龄和加权平均年龄为1067±20Ma和206±1Ma,分别代表了基底岩石前寒武纪时期变质事件的年龄,以及昌宁-孟连古特提斯洋后碰撞造山事件的年龄。
(2) 解析了兰坪盆地的前寒武盆地基底形成、中二叠世-中三叠世前陆盆地、晚三叠世裂谷盆地、侏罗纪-白垩纪坳陷盆地、古新世-早渐新世前陆盆地和晚渐新世-中新世走滑拉分盆地等复杂的转化过程。
(3) 划分了兰坪盆地3个与碰撞造山盆地有关的Pb-Zn-Cu-Ag-Sb-Au-Hg-As成矿系统。其中兰坪盆地MVT Pb-Zn成矿系统以盆地卤水为主,浅成低温热液Sb-Au-Hg-As成矿系统以大气降水为主,中低温热液脉型矿床的成矿流体Cu-Ag可能受富CO2的变质流体和盆地卤水共同影响。
(4) 兰坪盆地三大成矿系统成矿年龄主要集中于三个时期:早始新世(56~46Ma)早期脉状热液脉型Cu-Ag多金属矿化,中-晚始新世(40~32Ma)富钾斑岩远端的浅成低温热液Sb-Au-Hg-As矿化,和渐新世-中新世(32~21Ma)MVT Pb-Zn矿化及晚期热液脉型Pb-Zn多金属叠加矿化。
致谢 论文的完成得益于邓军教授、刘俊来教授、杨天南研究员和毕献武研究员等老师的指导;野外工作得到云南省地质矿产勘查开发局、云南省地质调查局和各矿山工作人员的大力支持和帮助;实验过程中得到了西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室和中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所流体包裹体实验室第五春荣、龚化栋、陈伟十和熊欣等老师的指导;同时,对审稿人的悉心审阅,提出许多宝贵意见;在此一并表示感谢。| [] | Annels AE. 1984. The geotectonic environment of Zambian copper-cobalt mineralization. Journal of the Geological Society, 141(2): 279–289. DOI:10.1144/gsjgs.141.2.0279 |
| [] | Bi LS. 2014. Metamorphism and deformation characteristics of metamorphic rocks in Shangyun-Huimin section of Changning-Menglian suture. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-68 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Bi XM, Mo XX. 2004. Transition from diagenesis to low-grade metamorphism and related minerals and energy resources. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(1): 287–294. |
| [] | Bradley DC, Leach DL. 2003. Tectonic controls of Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc mineralization in orogenic forelands. Mineralium Deposita, 38(6): 652–667. DOI:10.1007/s00126-003-0355-2 |
| [] | Brown AC. 1978. Stratiform copper deposits:Evidence for their post-sedimentary origin. Mineral Science and Engineering, 10: 172–181. |
| [] | Brown AC. 1997. World-class sediment-hosted stratiform copper deposits:Characteristics, genetic concepts and metallotects. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 44(3): 317–328. DOI:10.1080/08120099708728315 |
| [] | Cao SY, Liu JL, Leiss B, Neubauer F and Genser J. 2009. Timing of initiation of left-lateral shearing along the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone:Microstructural and geochronological constraints from high temperature mylonites in Diancang Shan, SW China. In:EGU General Assembly 2009. Vienna, Austria:EGU, 8773 |
| [] | Cao SY, Liu JL, Leiss B, Neubauer F, Genser J, Zhao CQ. 2011. Oligo-Miocene shearing along the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone:Constraints from structural analysis and zircon U/Pb geochronology of magmatic rocks in the Diancang Shan massif, SE Tibet, China. Gondwana Research, 19(4): 975–993. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.10.006 |
| [] | Chen KX, Yao SZ, He LQ, Wei JQ, Yang AP, Huang HL. 2004. Ore-forming fluid in Baiyangping silver-polymetallic mineralization concentration field in Lanping, Yunnan Province. Geological Science and Technology Information, 23(2): 45–50. |
| [] | Chen M, Huang ZL, Luo TY, Yan ZF, Long HS. 2010. SHRIMP dating and its geological significance of zircon in volcanic from Laochang large silver-lead-zinc deposit in western Yunnan Province, China. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 30(4): 456–462. |
| [] | Chen XC, Hu RZ, Bi XW, Zhong H, Lan JB, Zhao CH, Zhu JJ. 2015. Petrogenesis of metaluminous A-type granitoids in the Tengchong-Lianghe tin belt of southwestern China:Evidences from zircon U-Pb ages and Hf-O isotopes, and whole-rock Sr-Nd isotopes. Lithos, 212-215: 93–110. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.11.010 |
| [] | Chi GX, Xue CJ, Lai JQ, Qing HR. 2007. Sand injection and liquefaction structures in the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan, China:Indicators of an overpressured fluid system and implications for mineralization. Economic Geology, 102(4): 739–743. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.102.4.739 |
| [] | Chi GX, Xue CJ. 2011. Abundance of CO2-rich fluid inclusions in a sedimentary basin-hosted Cu deposit at Jinman, Yunnan, China:Implications for mineralization environment and classification of the deposit. Mineralium Deposita, 46(4): 365–380. DOI:10.1007/s00126-011-0337-8 |
| [] | Chung SL, Searle MP, Yeh MW. 2008. The age of the potassic alkaline igneous rocks along the Ailao Shan-Red River Shear Zone:Implications for the onset age of left-lateral shearing:A discussion. The Journal of Geology, 116(2): 201–204. DOI:10.1086/527458 |
| [] | Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ, Li CS, Wang CM. 2014a. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region, SW China. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 419–437. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.002 |
| [] | Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ, Santosh M. 2014b. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China. Earth-Science Reviews, 138: 268–299. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.05.015 |
| [] | Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Carranza EJM, Lu YJ. 2015a. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China:Constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry. Mineralium Deposita, 50(8): 987–1006. DOI:10.1007/s00126-015-0584-1 |
| [] | Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ, Zhao Y. 2015b. Structural control and genesis of the Oligocene Zhenyuan orogenic gold deposit, SW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 42–54. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.08.002 |
| [] | Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Selvaraja V, Jeond H, Wu B and Yang LF. 2016. Insights into ore genesis of the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan Province, China:Evidence from Zn and in-situ S isotopes. Ore Geology Reviews, doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.036 |
| [] | Deng J, Wang QF and Li GJ. 2017. Tectonic evolution, superimposed orogeny, and composite metallogenic system in China. Gondwana Research, doi:10.1016/j.gr.2017.02.005 |
| [] | Dong FL. 2003. Study on metallogenic condition and potentiality of copper-gold-polymetallic deposits in Weishan-Yongping mineralization district, Yunnan. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-131 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Dong FL, Mo XX, Hou ZQ, Wang Y, Bi XM, Zhou S. 2005. 40Ar/39Ar ages of Himalayan alkaline rocks in Lanping Basin, Yunnan Province, and their geological implications. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 24(2): 103–109. |
| [] | Dong GC, Mo XX, Zhao ZD, Zhu DC, Goodman R, Kong HL, Wang S. 2013. Zircon U-Pb dating and the petrological and geochemical constraints on Lincang granite in western Yunnan, China:Implications for the closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 62: 282–294. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.10.003 |
| [] | Du B, Wang CM, He XY, Yang LF, Chen JY, Shi KX, Luo Z, Xia JS. 2016. Advances in research of bulk-rock Nd and zircon Hf isotopic mappings:Case study of the Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2555–2570. |
| [] | Duan XD, Liu GC, Feng QL. 2012. Ladinian radiolarian Fauna from the Changning-Menglian belt and its tectonic significance. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 37(S2): 67–72. |
| [] | Fan JW, Yang TN, Liang MJ, Shi PL. 2014. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of volcanic rocks on the western margin of Lanping Basin in western Yunnan and their tectonic implications. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 33(3): 471–490. |
| [] | Fan SJ, Wang AJ, Liu HB, Xiu QY, Cao DH, Li RP, Gao H, Chen QS. 2006. A discussion on the helium and argon isotopic evidences for genesis of the Baiyangping copper-cobalt deposit in the Lanping Basin. Geological Review, 52(5): 628–635. |
| [] | Feng CX, Bi XW, Liu S, Hu RZ. 2014. Fluid inclusion, rare earth element geochemistry, and isotopic characteristics of the eastern ore zone of the Baiyangping polymetallic ore district, northwestern Yunnan Province, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 85: 140–153. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.01.019 |
| [] | Flower MFJ, Hoàng N, Lo CH, Chí CT, Cu'ò'ng NQ, Liu FT, Deng JF, Mo XX. 2013. Potassic magma genesis and the Ailao Shan-Red River Fault. Journal of Geodynamics, 69: 84–105. DOI:10.1016/j.jog.2012.06.008 |
| [] | Gao BY, Xue CJ, Chi GX, Li C, Qu WJ, Du AD, Li ZX, Gu H. 2012. Re-Os dating of bitumen in the giant Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan and its geological significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(5): 1561–1567. |
| [] | Gong JF, Ji JQ, Sang HQ, Han BF, Li BL, Chen JJ. 2006. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of high-pressure granulite xenolith and its surrounding granite in central Himalaya. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(11): 2677–2686. |
| [] | Guo ZF, Hertogen J, Liu JQ, Pasteels P, Boven A, Punzalan L, He HY, Luo XJ, Zhang WH. 2005. Potassic magmatism in western Sichuan and Yunnan Provinces, SE Tibet, China:Petrological and geochemical constraints on petrogenesis. Journal of Petrology, 46(1): 33–78. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egh061 |
| [] | He LQ, Chen KX, Yu FM, Wei JQ, Yang AP, Li H. 2004. Nappe tectonics and their ore-controlling of Lanping basin in Yunnan Province. Geology and Prospecting, 40(4): 7–12. |
| [] | He LQ, Chen KX, Wei JQ, Yu FM. 2005. Geological and geochemical characteristics and genesis of ore deposits in eastern ore belt of Baiyangping area, Yunnan Province. Mineral Deposits, 24(1): 61–70. |
| [] | He LQ, Song YC, Chen KX, Hou ZQ, Yu FM, Yang ZS, Wei JQ, Li Z, Liu YC. 2009. Thrust-controlled, sediment-hosted, Himalayan Zn-Pb-Cu-Ag deposits in the Lanping foreland fold belt, eastern margin of Tibetan Plateau. Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1-3): 106–132. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2008.11.001 |
| [] | He MQ, Liu JJ, Li CY, Li ZM, Liu YP. 2004. The Study of Fluid Metallogenic Mechanism in Large Scale Pb-Zn-Cu Deposits Concentrating Area of Lanping Basin:Taking Baiyangping Cu-Co Polymetallic Deposit As Example. Beijing: Geologival Publishing House: 1-101. |
| [] | He MQ, Liu JJ, Li CY, Li ZM, Liu YP, Yang AP, Sang HQ. 2006. 40Ar-39Ar dating of ore quartz from the Baiyangping Cu-Co polymetallic mineralized concentration area, Lanping, Yunnan. Chinese Journal of Geology, 41(4): 688–693. |
| [] | He WY, Mo XX, Yu XH, Li Y, Huang XK, He ZH. 2011. Geochronological study of magmatic intrusions and mineralization of Machangqing porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposit, western Yunnan Province. Earth Science Frontiers, 18(1): 207–215. |
| [] | Hennig D, Lehmann B, Frei D, Belyatsky B, Zhao XF, Cabral AR, Zeng PS, Zhou MF, Schmidt K. 2009. Early Permian seafloor to continental arc magmatism in the eastern Paleo-Tethys:U-Pb age and Nd-Sr isotope data from the southern Lancangjiang Zone, Yunnan, China. Lithos, 113(3-4): 408–422. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.031 |
| [] | Heppe K, Helmcke D, Wemmer K. 2007. The Lancang River zone of southwestern Yunnan, China:A questionable location for the active continental margin of Paleotethys. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 30(5-6): 706–720. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.04.002 |
| [] | Hou ZQ, Zaw K, Pan GT, Mo X X, Xu Q, Hu YZ, Li XZ. 2007. Sanjiang Tethyan metallogenesis in S.W. China:Tectonic setting, metallogenic epochs and deposit types. Ore Geology Reviews, 31(1-4): 48–87. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2004.12.007 |
| [] | Hou ZQ, Song YC, Li Z, Wang ZL, Yang ZM, Yang ZS, Liu YC, Tian SH, He LQ, Chen KX, Wang FC, Zhao CX, Xue WW, Lu HF. 2008. Thrust-controlled, sediments-hosted Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu deposits in eastern and northern margins of Tibetan orogenic belt:Geological features and tectonic model. Mineral Deposits, 27(2): 123–144. |
| [] | Huang XL, Niu YL, Xu YG, Chen LL, Yang QJ. 2010. Mineralogical and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of post-collisional potassic and ultrapotassic rocks from western Yunnan, SW China. Journal of Petrology, 51(8): 1617–1654. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egq032 |
| [] | Jia LQ, Mo XX, Dong GC, Xu WY, Wang L, Guo XD, Wang ZH, Wei SG. 2013. Genesis of lamprophyres from Machangqing, western Yunnan:Constraints from geochemistry, geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(4): 1247–1260. |
| [] | Jian P, Liu DY, Sun XM. 2003. SHRIMP dating of Baimaxueshan and Ludian granitoid batholiths, northwestern Yunnan Province, and its geological implications. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 24(4): 337–342. |
| [] | Jian P, Liu DY, Kr ner A, Zhang Q, Wang YZ, Sun XM, Zhang W. 2009. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in southwest China (Ⅱ):Insights from zircon ages of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks and generation of the Emeishan CFB province. Lithos, 113(3-4): 767–784. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.006 |
| [] | Jiang B. 2014. Mineralization of sedimentary-rock-hosted lead-zinc deposits of the Lanping-Simao basin in southern part of Sanjiang area. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-195 (in Chinese with English summary) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272020375_Tin_metallogenesis_associated_with_granitoids_in_the_southwestern_Sanjiang_Tethyan_Domain_Nature_deposit_types_and_tectonic_setting |
| [] | Jiang SH, Nie FJ, Hu P, Lai XR, Liu YF. 2009. Mayum:An orogenic gold deposit in Tibet, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1-3): 160–173. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2009.03.006 |
| [] | Kirkham RV. 1989. Distribution, settings, and genesis of sediment-hosted stratiform copper deposits. In:Boyle RW, Brown AC, Jefferson CW, Jowett EC and Kirkham RV (eds.). Sediment-Hosted Stratiform Copper Deposits. Geological Association of Canada, Special Paper, 36:3-38 http://www.academia.edu/28302141/Genesis_of_sediment-hosted_stratiform_copper_cobalt_mineralization_at_Luiswishi_and_Kamoto_Katanga_Copperbelt_Democratic_Republic_of_Congo_ |
| [] | Kong HL, Dong GC, Mo XX, Zhao ZD, Zhu DC, Wang S, Li R, Wang QL. 2012. Petrogenesis of Lincang granites in Sanjiang area of western Yunnan Province:Constraints from geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotope. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(5): 1438–1452. |
| [] | Leach DL, Bradley DC, Lewchuk MT, Symons DT, de Marsily G, Brannon J. 2001. Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc deposits through geological time:Implications from recent age-dating research. Mineralium Deposita, 36(8): 711–740. DOI:10.1007/s001260100208 |
| [] | Leach DL, Sangster DF, Kelley KD, Large RR, Garven G, Allen CR, Gutzmer J and Walters SG. 2005. Sediment-hosted lead-zinc deposits:A global perspective. In:Economic Geology, 100th Anniversary Volume. Littleton, CO:Societyof Economic Geologists Littleton:561-607 |
| [] | Li B. 2012. Characterics and evolution of geological fluids of Jinding Pb-Zn deposit in Lanping basin. Master Degree Thesis. Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology, 1-80(in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Li GJ. 2014. Tethys tectonic evolution and metallogenesis of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang Region, SW China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-179(in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Li GZ, Su SG, Duan XD. 2012. Precise ID-TIMS zircon U-Pb age, whole-rock geochemistry and plate tectonic setting of the Banpo Complex in the southern Lancangjiang arc terrane, Sanjiang area, SW China. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(4): 96–109. |
| [] | Li JB. 2012. Volcanic rocks and geochronology of the dapingzhang copper deposit, Yunnan Province. Master Degree Thesis, Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology, 1-92(in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Li XM, Tan KX, Gong WJ, Gong GL. 2000. Study on the metallogenic epoch of the Jinding lead-zinc deposit with apatite fission track analysis. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 24(3): 282–286. |
| [] | Li XM. 2001. Metallogenic age of Jinman copper deposit in western Yunnan Province, China. Geoscience, 15(4): 405–408. |
| [] | Li XM, Song YG. 2006. Cenozoic evolution of tectono-fluid and metallogenic process in Lanping Basin, western Yunnan Province, Southwest China:Constraints from apatite fission track data. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 25(6): 396–401. |
| [] | Liang HY, Xie YW, Zhang YQ, Campbell I. 2004. The potassic alkaline intrusions constrain the coppermineralization:Case study from Machangqing copper deposit. Progress in Natural Science, 14(1): 116–120. |
| [] | Liu BP, Feng QL, Fang NQ, Jia JH, He FX. 1993. Tectonic evolution of palaeo-tethys poly-island-ocean in Changning-Menglian and Lancangjiang belts, southwestern Yunnan, China. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 18(5): 529-539–671. |
| [] | Liu HY, Xia B, Zhang YQ. 2003. The SHRIMP U-Pb age of Matouwan diopside granite porphyry in Yunnan Province. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 24(6): 552–554. |
| [] | Liu JJ, Li CY, Pan JY, Liu XF, Zhang Q, Liu YP. 2000. Ore-forming material sources of the copper deposits from sandstone and shale in Lanping-Simao Basin, western Yunnan and their genetic implications. Geology and Prospecting, 36(4): 16–19. |
| [] | Liu JJ, Li ZM, Zhang Q, Liu YP, Li CY, He MQ, Sang HQ. 2003. 40Ar-39Ar fast neutron activation age of quartz from the Jinman copper mine, West Yunnan. Chinese Journal of Geology, 38(4): 529–531. |
| [] | Liu JL, Wang AJ, Xia HR, Zhai YF, Gao L, Xiu QY, Zhang ZC, Zhao ZD, Cao DH. 2010. Cracking mechanisms during galena mineralization in a sandstone-hosted lead-zinc ore deposit:Case study of the Jinding giant sulfide deposit, Yunnan, SW China. Mineralium Deposita, 45(6): 567–582. DOI:10.1007/s00126-010-0294-7 |
| [] | Liu JL, Tran MD, Tang Y, Nguyen QL, Tran TH, Wu WB, Chen JF, Zhang ZC, Zhao ZD. 2012a. Permo-Triassic granitoids in the northern part of the Truong Son belt, NW Vietnam:Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications. Gondwana Research, 22(2): 628–644. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.10.011 |
| [] | Liu Y, Deng J, Shi GH, Sun X, Yang LQ. 2012b. Genesis of the Xuebaoding W-Sn-Be crystal deposits in Southwest China:Evidence from fluid inclusions, stable isotopes and ore elements. Resource Geology, 62(2): 159–173. DOI:10.1111/rge.2012.62.issue-2 |
| [] | Liu Y, Deng J, Shi GH, Sun DS. 2012c. Geochemical and morphological characteristics of coarse-grained tabular beryl from the Xuebaoding W-Sn-Be deposit, Sichuan Province, western China. International Geology Review, 54(14): 1673–1684. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2012.667904 |
| [] | Liu Y, Zhu ZM, Chen C, Zhang SP, Sun X, Yang ZS, Liang W. 2015. Geochemical and mineralogical characteristics of weathered ore in the Dalucao REE deposit, Mianning-Dechang REE Belt, western Sichuan Province, southwestern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 71: 437–456. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.06.009 |
| [] | Lu YJ, Kerrich R, Cawood PA, McCuaig TC, Hart CJR, Li ZX, Hou ZQ, Bagas L. 2012. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of potassic felsic intrusions in western Yunnan, SW China:Constraints on the relationship of magmatism to the Jinsha suture. Gondwana Research, 22(2): 737–747. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.11.016 |
| [] | Lu YJ, Kerrich R, Kemp AIS, McCuaig TC, Hou ZQ, Hart CJR, Li ZX, Cawood PA, Bagas L, Yang ZM, Cliff J, Belousova EA, Jourdan F, Evans NJ. 2013. Intracontinental Eocene-Oligocene porphyry Cu mineral systems of Yunnan, western Yangtze Craton, China:Compositional characteristics, sources, and implications for continental collision metallogeny. Economic Geology, 108(7): 1541–1576. DOI:10.2113/econgeo.108.7.1541 |
| [] | Mao XC, Wang LQ, Li B, Wang BD, Wang DB, Yin FG, Sun ZM. 2012. Discovery of the Late Silurian volcanic rocks in the Dazhonghe area, Yunxian-Jinggu volcanic arc belt, western Yunnan, China and its geological significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(5): 1517–1528. |
| [] | Mo XX, Lu FX, Shen SY, Zhu QW, Hou ZQ, Yang KH. 1993. Volcanism and Metallogenesis of Sanjiang Tethy. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-267. |
| [] | Mou CL, Wang J, Yu Q, Zhang LS. 1999. The evolution of the sedimentary basin in Lanping area during Mesozoic-Cenozoic. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 19(3): 30–36. |
| [] | Nie F, Dong GC, Mo XX, Zhu DC, Dong ML, Wang X. 2012. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb chronology of the Triassic granites in the Changning-Menglian suture zone and their implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(5): 1465–1476. |
| [] | Pan GT, Wang LQ, Li XZ, Wang JM, Xu Q. 2001. The tectonic framework and spatial allocation of the archipelagic arc-basin systems on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 21(3): 1–26. |
| [] | Pan GT, Lu SN, Xiao QH, Zhang KQ, Yin FG, Hao GJ, Luo MS, Ren F, Yuan SH. 2016. Division of tectonic stages and tectonic evolution in China. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(6): 1–23. |
| [] | Peng TP, Wang YJ, Fan WM, Liu DY, Shi YM, Miao LC. 2006. SHRIMP ziron U-Pb geochronology of Early Mesozoic felsic igneous rocks from the southern Lancangjiang and its tectonic implications. Science in China (Series D), 49(10): 1032–1042. DOI:10.1007/s11430-006-1032-y |
| [] | Peng TP, Wang YJ, Zhao GC, Fan WM, Peng BX. 2008. Arc-like volcanic rocks from the southern Lancangjiang zone, SW China:Geochronological and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Lithos, 102(1-2): 358–373. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.08.012 |
| [] | Peng TP, Wilde SA, Wang YJ, Fan WM, Peng BX. 2013. Mid-Triassic felsic igneous rocks from the southern Lancangjiang Zone, SW China:Petrogenesis and implications for the evolution of Paleo-Tethys. Lithos, 168-169: 15–32. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.01.015 |
| [] | Qiu KF, Taylor RD, Song YH, Yu HC, Song KR, Li N. 2016. Geologic and geochemical insights into the formation of the Taiyangshan porphyry copper-molybdenum deposit, Western Qinling Orogenic Belt, China. Gondwana Research, 35: 40–58. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.014 |
| [] | Ru SS, Li F, Wu J, Li JB, Wang DW, Huang YC. 2012. Geochemistry and chronology of granodiorite porphyry in the Dapingzhang Cu polymetallic deposit. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 31(4): 531–540. |
| [] | Song YC, Hou ZQ, Yang TN, Zhang HR, Yang ZS, Tian SH, Liu YC, Wang XH, Liu YX, Xue CD, Wang GH, Li Z. 2011. Sediment-hosted Himalayan base metal deposits in Sanjiang region:Characteristics and genetic types. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 30(3): 355–380. |
| [] | Song YC, Hou ZQ, Cheng Y, Yang TN, Xue CJ. 2016. Fluid inclusion and isotopic constraints on the origin of ore-forming fluid of the Jinman-Liancheng vein Cu deposit in the Lanping Basin, western Yunnan, China. Geofluids, 16(1): 56–77. DOI:10.1111/gfl.2016.16.issue-1 |
| [] | Tang YY, Bi XW, He LP, Wu LY, Feng CX, Zou ZC, Tao Y, Hu RZ. 2011. Geochemical characteristics of trace elements, fluid inclusions and carbon-oxygen isotopes of calcites in the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Lanping, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2635–2645. |
| [] | Tang YY, Bi XW, Wu LY, Wang L, Zou ZC, He LP. 2013. Re-Os isotopic dating of pyrite from jinding Zn-Pb ore deposit and its geological significance. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 33(3): 287–294. |
| [] | Tang YY, Bi XW, Fayek M, Hu RZ, Wu LY, Zou ZC, Feng CX, Wang XS. 2014. Microscale sulfur isotopic compositions of sulfide minerals from the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan Province, southwest China. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 594–607. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.021 |
| [] | Tao XF, Zhu LD, Liu DZ, Wang GZ, Li YG. 2002. The formation and evolution of the Lanping basin in western Yunnan. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 29(5): 521–525. |
| [] | Tong ZD, Zhang J, Li TJ. 2016. Geology and fluid inclusion of the Bijiashan Sb deposit in western Yunnan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2379–2391. |
| [] | Wan SK, Xia B, Zhang YQ. 2005. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of Laojunshan syenite. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 29(4): 522–526. |
| [] | Wang AJ, Cao DH, Gao L, Wang GS, Guan Y, Xiu QY, Liu JL. 2009. A probe into the genesis of Jinding super-large lead-zinc ore deposit. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(1): 43–54. |
| [] | Wang CM, Cheng QM, Zhang ST, Deng J, Xie SY. 2008. Magmatic-hydrothermal superlarge metallogenic systems:A case study of the Nannihu ore field. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 19(4): 391–403. DOI:10.1016/S1002-0705(08)60072-2 |
| [] | Wang CM, Deng J, Carranza EJM, Lai XR. 2014a. Nature, diversity and temporal-spatial distributions of sediment-hosted Pb-Zn deposits in China. Ore Geology Reviews, 56: 327–351. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.06.004 |
| [] | Wang CM, Deng J, Carranza EJM, Santosh M. 2014b. Tin metallogenesis associated with granitoids in the southwestern Sanjiang Tethyan Domain:Nature, deposit types, and tectonic setting. Gondwana Research, 26: 576–593. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.005 |
| [] | Wang CM, Deng J, Lu YJ, Bagas L, Kemp AIS, McCuaig TC. 2015a. Age, nature, and origin of Ordovician Zhibenshan granite from the Baoshan terrane in the Sanjiang region and its significance for understanding Proto-Tethys evolution. International Geology Review, 57(15): 1922–1939. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2015.1043358 |
| [] | Wang CM, Deng J, Santosh M, Lu YJ, McCuaig TC, Carranza EJM, Wang QF. 2015b. Age and origin of the Bulangshan and Mengsong granitoids and their significance for post-collisional tectonics in the Changning-Menglian Paleo-Tethys Orogen. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113: 656–676. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.05.001 |
| [] | Wang CM, Bagas L, Lu YJ, Santosh M, Du B, McCuaig TC. 2016a. Terrane boundary and spatio-temporal distribution of ore deposits in the Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen:Insights from zircon Hf-isotopic mapping. Earth Science Reviews, 156: 39–65. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.02.008 |
| [] | Wang CM, Deng J, Bagas L and Wang Q. 2017. Zircon Hf-isotopic mapping for understanding crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the Eastern Qinling Orogen. Gondwana Research, doi:10.1016/j.gr.2017.04.008 |
| [] | Wang GH, Song YC, Hou ZQ, Wang XH, Yang ZS, Yang TN, Liu YX, Jiang YF, Pan XF, Zhang HR, Liu YC, Li Z, Xue CD. 2009. Re-Os dating of molybdenite from Liancheng vein copper deposit in Lanping basin and its geological significance. Mineral Deposits, 28(4): 413–424. |
| [] | Wang GH. 2010. The study of genesis of Jinman-Liancheng vein deposits in Lanping basin, western Yunnan. Master Degree Thesis. Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology, 1-77 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Wang JF, Xu D, Yin GH. 2014. Ore-forming fluid characteristics and mineralization of Jinding Lead-zinc deposit in Yunnan Province. Geoscience, 28(4): 701–710. |
| [] | Wang JH, Yin A, Harrison TM, Grove M, Zhang YQ, Xie GH. 2001. A tectonic model for Cenozoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 188(1-2): 123–133. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00315-6 |
| [] | Wang JH, Yin A, Harrison TM, Grove M, Zhou JY, Zhang YQ, Xie GH. 2003. Thermochronological constraints on two pulses of Cenozoic high-K magmatism in eastern Tibet. Science in China (Series D), 46(7): 719–729. DOI:10.1360/03yd9063 |
| [] | Wang XH, Hou ZQ, Song YC, Yang TN, Zhang HR. 2011. Baiyangping Pb-Zn-Cu-Ag polymetallic deposit in Lanping Basin:Metallogenic chronology and regional mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2625–2634. |
| [] | Wang XH, Hou ZQ, Song YC, Zhang JR. 2015c. Geological, fluid inclusion and isotopic studies of the Baiyangping Pb-Zn-Cu-Ag polymetallic deposit, Lanping basin, Yunnan Province, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 111: 853–871. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.08.009 |
| [] | Wang XH, Song YC, Zhang HR, Liu YC, Pan XF, Guo T. 2016. Geochemical characteristics and metallogenic age of the east ore belt in Baiyangping polymetallic ore concentration area. Journal of Geomechanics, 22(2): 294–309. |
| [] | Wang Y. 2002. Study on the characteristics of metallogenic fluids and fluid-geological mapping in the Weixi-Yongping coppe-gold -polymetallic mineralization district, Yunnan. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-144 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Wang YB, Chen W, Zeng PS. 2005. Constraints of sericite 40Ar-39Ar ages on the metallogenic epoch of the Jinman vein copper deposit in the Lanping basin, northwestern Yunnan. Geological Bulletin of China, 24(2): 181–184. |
| [] | Wang YH, Zhang FF, Liu JJ, Que CY. 2016b. Carboniferous magmatism and mineralization in the area of the Fuxing Cu deposit, Eastern Tianshan, China:Evidence from zircon U-Pb ages, petrogeochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Hf-O isotopic compositions. Gondwana Research, 34: 109–128. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.007 |
| [] | Wang YH, Xue CJ, Liu JJ, Zhang FF. 2016c. Geological, geochronological, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-O-Hf isotopic constraints on origins of intrusions associated with the Baishan porphyry Mo deposit in eastern Tianshan, NW China. Mineralium Deposita, 51(7): 953–969. DOI:10.1007/s00126-016-0646-z |
| [] | Wang YJ, Zhang AM, Fan WM, Peng TP, Zhang FF, Zhang YH, Bi XW. 2010. Petrogenesis of Late Triassic post-collisional basaltic rocks of the Lancangjiang tectonic zone, Southwest China, and tectonic implications for the evolution of the eastern Paleotethys:Geochronological and geochemical constraints. Lithos, 120(3-4): 529–546. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.09.012 |
| [] | Wang Z. 2013. The ore-forming fluid and mineralization mechanism in super giant Jinding lead-zinc deposit. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-119 (in Chinese with English summary) https://es.scribd.com/document/51333525/2011FinalProgram |
| [] | Wei JQ, Wang XD, Zhuang X, Liu YH. 2008. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of diorite among Jicha serpentine and Eza grabbro from Lancangjiang belt, Yunnan Province and its geological significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(6): 1297–1301. |
| [] | Xiao CH. 2013. The study on minerogenic series of epithermal deposits in mid-southern segment of the Sanjiang Orogenic Belt, Southwest China. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-153 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Xiao XN, Yu XH, Mo XX, Yang GL, Li Y, Huang XK. 2009. Geochemistry, zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating and origin of alkali-rich porphyries in Beiya area, North Erhai Lake, western Yunnan, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(12): 1786–1803. |
| [] | Xu QD, Li JW. 2003. Migration of ore-forming fluids and its relation to zoning of mineralization in northern Lanping Cu-polymetallic metallogenic area, Yunnan Province:Evidence from fluid inclusions and stable isotopes. Mineral Deposits, 22(4): 365–376. |
| [] | Xu XC, Huang Z, Xie QQ, Yue SC, Liu Y. 2004. Ar-Ar isotopic ages of Jinman and Shuixie copper polymetallic deposits in Yunnan Province, and their geological implications. Geological Journal of China Universities, 10(2): 157–164. |
| [] | Xu XW, Cai XP, Zhang BL, Liang GH, Du SJ, Wang J. 2006. Genetic types of Beiya gold deposit in western Yunnan. Mineral Deposits, 25(Suppl.): 201–204. |
| [] | Xue CJ, Chen YC, Wang DH, Yang JM, Yang WG, Zeng R. 2003. Geology and isotopic composition of helium, neon, xenon and metallogenic age of the Jinding and Baiyangping ore deposits, northwest Yunnan, China. Science in China (Series D), 46(8): 789–800. DOI:10.1007/BF02879523 |
| [] | Xue CJ, Zeng R, Gao YB, Zhu HP, Zhao SH, Li YQ. 2006. Fluid processes of a heavy metallogenesis at Jinding, Lanping, SW-China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(4): 1031–1039. |
| [] | Xue CJ, Zeng R, Liu SW, Chi GX, Qing HR, Chen YC, Yang JM, Wang DH. 2007. Geologic, fluid inclusion and isotopic characteristics of the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, western Yunnan, South China:A review. Ore Geology Reviews, 31(1-4): 337–359. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.04.007 |
| [] | Xue W. 2010. Study on the ore-forming fluid of the baiyangping poly-metallic deposit in the Lanping Basin, northwestern Yunnan, China. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-82 (in Chinese with English summary) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009281915000264 |
| [] | Yalikun Y, Xue CJ and Symons DTA. 2017. Paleomagnetic age and tectonic constraints on the genesis of the giant Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan, China. Mineralium Deposita, doi:10.1007/s00126-017-0733-9 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00126-017-0733-9 |
| [] | Yang LF, Shi KX, Wang CM, Wu B, Du B, Chen JY, Xia JS, Chen J. 2016. Ore genesis of the Jinman copper deposit in the Lanping Basin, Sanjiang Orogen:Constraints by copper and sulfur isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2392–2406. |
| [] | Yang TN, Liang MJ, Fan JW, Shi PL, Zhang HR, Hou ZH. 2014. Paleogene sedimentation, volcanism, and deformation in eastern Tibet:Evidence from structures, geochemistry, and zircon U-Pb dating in the Jianchuan basin, SW China. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 521–535. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.014 |
| [] | Yang WG, Yu XH, Li WC, Dong FL, Mo XX. 2003. The characteristics of metallogenic fluids and metallo-genic mechanism in Baiyangping silver and polymetallic mineralization concentration area in Yunnan Province. Geoscience, 17(1): 27–33. |
| [] | Yang YB. 2013. The study on characteristics, sources and evolution of Meso-Neozoic metallogenic fluid in Lanping basin. Master Degree Thesis. Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology, 1-90 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Yin J. 2012. The characteristics of isotope geochemistry and the evolution of metallogenic fluid in Jinding Pb-Zn deposit, Yunnan. Master Degree Thesis. Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology, 1-80 (in Chinese with English summary) http://researchonline.jcu.edu.au/view/year/2011.html |
| [] | Yu SY, Li KQ, Shi YP, Zhang HH. 2003. A study on the granodiorite in the middle part of Lincang granite batholith. Yunnan Geology, 22(4): 426–442. |
| [] | Yu XH, Xiao XN, Yang GL, Mo XX, Zeng PS, Wang JL. 2008. Zircon SHRIMP dating of several granites and geological significance in southern part of "Sanjiang" area, western Yunnan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(2): 377–383. |
| [] | Zeng PS, Mo XX, Yu XH. 2002. Nd, Sr and Pb isotopic characteristics of the alkaline-rich porphyries in western Yunnan and its compression strike-slip setting. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 21(3): 231–241. |
| [] | Zeng PS, Hou ZQ, Gao YF, Du AD. 2006. The Himalayan Co-Mo-Au mineralization in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone:Constraints from Re-Os dating of molybdenite. Geological Review, 52(1): 72–84. |
| [] | Zeng R. 2007. The large-scale fluid ore-forming process in the Lanping basin:Taking the Jinding and Baiyangping deposits as the example. Ph. D. Dissertation. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 1-109 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Zhang C, Qi XX, Tang GZ, Zhao YH , Ji FB. 2014. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb dating for the alkaline porphyries and its constraint on the mineralization in Chang’an Cu-Mo-Au ore concentration region, Ailaoshan orogenic belt, western Yunnan. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(8): 2204–2216. |
| [] | Zhang FF, Wang YH, Liu JJ, and Wang JP. 2015a. Zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os geochronology, Hf isotope analyses, and whole-rock geochemistry of the Donggebi Mo deposit, eastern Tianshan, Northwest China, and their geological significance. International Geology Review, 57(4): 446–462. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2015.1013067 |
| [] | Zhang JR , Wen HJ. 2010. The preliminary study of fluid inclusions in Liancheng Cu-Mo deposit. Mineral Deposits, 29(Suppl.): 623–624. |
| [] | Zhang JR , Wen HJ. 2012. Sulfur and lead isotope compositions and tracing of copper deposits on the western border of the Lanping Basin, Yunnan Province. Geochimica, 41(2): 166–181. |
| [] | Zhang JR, Wen HJ, Qin CJ , Wang JS. 2012. Fluid inclusion and stable isotopes study of Liancheng Cu-Mo polymetallic deposit in Lanping basin, Yunnan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(5): 1373–1386. |
| [] | Zhang JR, Wen HJ, Qiu YZ, Zhang YX , Li C. 2013. Ages of sediment-hosted Himalayan Pb-Zn-Cu-Ag polymetallic deposits in the Lanping basin, China: Re-Os geochronology of molybdenite and Sm-Nd dating of calcite. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 73: 284–295. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.041 |
| [] | Zhang JR, Wen HJ, Qiu YZ, Zou ZC, Du SJ , Wu SY. 2015b. Spatial-temporal evolution of ore-forming fluids and related mineralization in the western Lanping basin, Yunnan Province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 67: 90–108. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.11.017 |
| [] | Zhang JR, Wen HJ, Qiu YZ , Zou ZC. 2016. Ages of the Cu-Ag-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposits in western Lanping basin, Yunan province. Geological Journal of China Universities, 22(2): 219–230. |
| [] | Zhao HB. 2006. Study on the characteristics and metallogenic conditions of copper-polymetallic deposits in middle-northern Lanping Basin, western Yunnan. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-123 (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Zhao J, Zhong DL , Wang Y. 1994. A preliminary study on deformation sequence and metamorphism in lancang metamorphic belt of West Yunnan. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 29(4): 27–40. |
| [] | Zhong DL. 1998. Paleoteyan Ogenic Belt in Western Yunnan and Sichuang. Beijing: Science Press: 1-231. |
| [] | Zhou JY, Wang JH, Horton BK, Yin A , Spurlin MS. 2011. The closure of Paleogene basins of east-central Tibet in response to tectonic, sedimentation, magmatism and paleoclimate. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(2): 172–178. |
| [] | Zhu WG, Zhong H, Wang LQ, He DF, Ren T, Fan HP , Bai ZJ. 2011. Petrogenesis of the basalts and rhyolite porphyries of the Minle copper deposit, Yunnan: Geochronological and geochemical constraints. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2694–2708. |
| [] | Zi JW, Cawood PA, Fan WM, Tohver E, Wang YJ , McCuaig TC. 2012a. Generation of Early Indosinian enriched mantle-derived granitoid pluton in the Sanjiang Orogen (SW China) in response to closure of the Paleo-Tethys. Lithos, 140-141: 166–182. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.02.006 |
| [] | Zi JW, Cawood PA, Fan WM, Wang YJ, Tohver E, McCuaig TC , Peng TP. 2012b. Triassic collision in the Paleo-Tethys Ocean constrained by volcanic activity in SW China. Lithos, 144-145: 145–160. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.020 |
| [] | Zou ZC, Hu RZ, Bi XW, Wu LY, Feng CX , Tang YY. 2015. Absolute and relative dating of Cu and Pb-Zn mineralization in the Baiyangping area, Yunnan Province, SW China: Sm-Nd geochronology of calcite. Geochemical Journal, 49(1): 103–112. DOI:10.2343/geochemj.2.0334 |
| [] | 毕丽莎. 2014. 滇西昌宁-孟连缝合带南段上允-惠民一带变质杂岩的变质变形特征. 硕士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-68 http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ201501010034.htm |
| [] | 毕先梅, 莫宣学. 2004. 成岩-极低级变质-低级变质作用及有关矿产. 地学前缘, 11(1): 287–294. |
| [] | 陈开旭, 姚书振, 何龙清, 魏君奇, 杨爱平, 黄惠兰. 2004. 云南兰坪白秧坪银多金属矿集区成矿流体研究. 地质科技情报, 23(2): 45–50. |
| [] | 陈觅, 黄智龙, 罗泰义, 严再飞, 龙汉生. 2010. 滇西澜沧老厂大型银铅锌多金属矿床火山岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其地质意义. 矿物学报, 30(4): 456–462. |
| [] | 董方浏. 2003. 云南巍山-永平矿化集中区铜金多金属矿床成矿条件及成矿潜力研究. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-131 |
| [] | 董方浏, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 王勇, 毕先梅, 周肃. 2005. 云南兰坪盆地喜马拉雅期碱性岩40Ar/39Ar年龄及地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 24(2): 103–109. |
| [] | 杜斌, 王长明, 贺昕宇, 杨立飞, 陈晶源, 石康兴, 罗政, 夏锦胜. 2016. 锆石Hf和全岩Nd同位素填图研究进展:以三江特提斯造山带为例. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2555–2570. |
| [] | 段向东, 刘桂春, 冯庆来. 2012. 昌宁孟连构造带拉丁期放射虫动物群及构造演化意义. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 37(S2): 67–72. |
| [] | 范金伟, 杨天南, 梁明娟, 史鹏亮. 2014. 滇西兰坪盆地西缘火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其大地构造意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 33(3): 471–490. |
| [] | 范世家, 王安建, 刘汉斌, 修群业, 曹殿华, 李瑞萍, 高辉, 陈其慎. 2006. 论兰坪盆地白秧坪铜(钴)矿床成因的氦氩同位素证据. 地质评论, 52(5): 628–635. |
| [] | 高炳宇, 薛春纪, 池国祥, 李超, 屈文俊, 杜安道, 李足晓, 顾浩. 2012. 云南金顶超大型铅锌矿床沥青Re-Os法测年及地质意义. 岩石学报, 28(5): 1561–1567. |
| [] | 龚俊峰, 季建清, 桑海清, 韩宝福, 李宝龙, 陈建军. 2006. 喜马拉雅中段哲古拉花岗岩中高压麻粒岩包体及其主岩的40Ar/39Ar年代学研究. 岩石学报, 22(11): 2677–2686. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2006.11.006 |
| [] | 何龙清, 陈开旭, 余凤鸣, 魏君奇, 杨爱平, 李航. 2004. 云南兰坪盆地推覆构造及其控矿作用. 地质与勘探, 40(4): 7–12. |
| [] | 何龙清, 陈开旭, 魏君奇, 余凤鸣. 2005. 云南白秧坪地区东矿带矿床地质地球化学特征及成因分析. 矿床地质, 24(1): 61–70. |
| [] | 何明勤, 刘家军, 李朝阳, 李志明, 刘玉平. 2004. 兰坪盆地铅锌铜大型矿集区的流体成矿作用机制——以白秧坪铜钴多金属地区为例. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-101. |
| [] | 何明勤, 刘家军, 李朝阳, 李志明, 刘玉平, 杨爱平, 桑海清. 2006. 云南兰坪白秧坪铜钴多金属矿集区矿石中石英的40Ar-39Ar年龄. 地质科学, 41(4): 688–693. |
| [] | 和文言, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 李勇, 黄行凯, 和中华. 2011. 滇西马厂箐斑岩型铜钼(金)矿床成岩成矿时代研究. 地学前缘, 18(1): 207–215. |
| [] | 侯增谦, 宋玉财, 李政, 王召林, 杨志明, 杨竹森, 刘英超, 田世洪, 何龙清, 陈开旭, 王富春, 赵呈祥, 薛万文, 鲁海峰. 2008. 青藏高原碰撞造山带Pb-Zn-Ag-Cu矿床新类型:成矿基本特征与构造控矿模型. 矿床地质, 27(2): 123–144. |
| [] | 贾丽琼, 莫宣学, 董国臣, 徐文艺, 王梁, 郭晓东, 王治华, 韦少港. 2013. 滇西马厂箐煌斑岩成因:地球化学、年代学及Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf同位素约束. 岩石学报, 29(4): 1247–1260. |
| [] | 简平, 刘敦一, 孙晓猛. 2003. 滇西北白马雪山和鲁甸花岗岩基SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 地球学报, 24(4): 337–342. |
| [] | 江彪. 2014. 三江南段兰坪-思茅盆地沉积岩容矿型铅锌成矿作用. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-195 |
| [] | 孔会磊, 董国臣, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 朱弟成, 王硕, 李荣, 王乔林. 2012. 滇西三江地区临沧花岗岩的岩石成因:地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束. 岩石学报, 28(5): 1438–1452. |
| [] | 李彬. 2012. 兰坪金顶铅锌矿区古地质流体特征及其演化. 硕士学位论文. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 1-80 |
| [] | 李峰, 甫为民, 李雷. 1997. 滇西红层铜矿区域成矿物质来源. 云南地质, 16(3): 233–244. |
| [] | 李龚健. 2014. 三江特提斯复合造山带构造演化与典型矿床成矿过程研究. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-179 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201505033.htm |
| [] | 李钢柱, 苏尚国, 段向东. 2012. 三江地区澜沧江带南段半坡杂岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学特征及板块构造环境. 地学前缘, 19(4): 96–109. |
| [] | 李进宝. 2012. 云南省大平掌铜多金属矿床火山岩建造及年代学研究. 硕士学位论文. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 1-92 |
| [] | 李小明, 谭凯旋, 龚文君, 龚革联. 2000. 利用磷灰石裂变径迹法研究金顶铅锌矿成矿时代. 大地构造与成矿学, 24(3): 282–286. |
| [] | 李小明. 2001. 滇西金满铜矿床成矿年龄测定. 现代地质, 15(4): 405–408. |
| [] | 梁华英, 谢应雯, 张玉泉, CampbellI. 2004. 富钾碱性岩体形成演化对铜矿成矿制约——以马厂箐铜矿为例. 自然科学进展, 14(1): 116–120. |
| [] | 刘本培, 冯庆来, 方念乔, 贾进华, 何馥香. 1993. 滇西南昌宁-孟连带和澜沧江带古特提斯多岛洋构造演化. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 18(5): 529-539–671. |
| [] | 刘红英, 夏斌, 张玉泉. 2003. 云南马头湾透辉石花岗斑岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄研究. 地球学报, 24(6): 552–554. |
| [] | 刘家军, 李朝阳, 潘家永, 刘显凡, 张乾, 刘玉平. 2000. 兰坪-思茅盆地砂页岩中铜矿床成矿物质来源研究. 地质与勘探, 36(4): 16–19. |
| [] | 刘家军, 李志明, 张乾, 刘玉平, 李朝阳, 何明勤, 桑海清. 2003. 滇西金满脉状铜矿床的40Ar-39Ar快中子活化年龄. 地质科学, 38(4): 529–531. |
| [] | 毛晓长, 王立全, 李冰, 王保弟, 王冬兵, 尹福光, 孙志明. 2012. 云县-景谷火山弧带大中河晚志留世火山岩的发现及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 28(5): 1517–1528. |
| [] | 莫宣学, 路凤香, 沈上越, 朱勤文, 侯增谦, 杨开辉. 1993. 三江特提斯火山作用与成矿. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-267. |
| [] | 牟传龙, 王剑, 余谦, 张立生. 1999. 兰坪中新生代沉积盆地演化. 矿物岩石, 19(3): 30–36. |
| [] | 聂飞, 董国臣, 莫宣学, 朱弟成, 董美玲, 王霞. 2012. 滇西昌宁-孟连带三叠纪花岗岩地球化学、年代学及其意义. 岩石学报, 28(5): 1465–1476. |
| [] | 潘桂棠, 王立全, 李兴振, 王洁民, 徐强. 2001. 青藏高原区域构造格局及其多岛弧盆系的空间配置. 沉积与特提斯地质, 21(3): 1–26. |
| [] | 潘桂棠, 陆松年, 肖庆辉, 张克信, 尹福光, 郝国杰, 骆满生, 任飞, 袁四化. 2016. 中国大地构造阶段划分和演化. 地学前缘, 23(6): 1–23. |
| [] | 彭头平, 王岳军, 范蔚茗, 刘敦一, 石玉若, 苗来成. 2006. 澜沧江南段早中生代酸性火成岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年及构造意义. 中国科学(D辑), 36(2): 123–132. |
| [] | 汝珊珊, 李峰, 吴静, 李进宝, 汪德文, 黄应才. 2012. 云南大平掌铜多金属矿区花岗闪长斑岩地球化学特征及年代学研究. 岩石矿物学杂志, 31(4): 531–540. |
| [] | 宋玉财, 侯增谦, 杨天南, 张洪瑞, 杨竹森, 田世洪, 刘英超, 王晓虎, 刘燕学, 薛传东, 王光辉, 李政. 2011. "三江"喜马拉雅期沉积岩容矿贱金属矿床基本特征与成因类型. 岩石矿物学杂志, 30(3): 355–380. |
| [] | 唐永永, 毕献武, 和利平, 武丽艳, 冯彩霞, 邹志超, 陶琰, 胡瑞忠. 2011. 兰坪金顶铅锌矿方解石微量元素、流体包裹体和碳-氧同位素地球化学特征研究. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2635–2645. |
| [] | 唐永永, 毕献武, 武丽艳, 王雷, 邹志超, 和利平. 2013. 金顶铅锌矿黄铁矿Re-Os定年及其地质意义. 矿物学报, 33(3): 287–294. |
| [] | 陶晓风, 朱利东, 刘登忠, 王国芝, 李佑国. 2002. 滇西兰坪盆地的形成及演化. 成都理工学院学报, 29(5): 521–525. |
| [] | 佟子达, 张静, 李腾建. 2016. 滇西笔架山锑矿床地质特征与流体包裹体研究. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2379–2391. |
| [] | 万哨凯, 夏斌, 张玉泉. 2005. 老君山正长岩锆石SHRIMP定年. 大地构造与成矿学, 29(4): 522–526. |
| [] | 王安建, 曹殿华, 高兰, 王高尚, 管烨, 修群业, 刘俊来. 2009. 论云南兰坪金顶超大型铅锌矿床的成因. 地质学报, 83(1): 43–54. |
| [] | 王光辉, 宋玉财, 侯增谦, 王晓虎, 杨竹森, 杨天南, 刘燕学, 江迎飞, 潘小菲, 张洪瑞, 刘英超, 李政, 薛传东. 2009. 兰坪盆地连城脉状铜矿床辉钼矿Re-Os定年及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 28(4): 413–424. |
| [] | 王光辉. 2010. 滇西兰坪盆地金满-连城脉状铜矿床成因研究. 硕士学位论文. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 1-77 |
| [] | 王建飞, 许东, 尹光候. 2014. 云南金顶铅锌矿成矿流体特征与成矿作用. 现代地质, 28(4): 701–710. |
| [] | 王晓虎, 侯增谦, 宋玉财, 杨天南, 张洪瑞. 2011. 兰坪盆地白秧坪铅锌铜银多金属矿床:成矿年代及区域成矿作用. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2625–2634. |
| [] | 王晓虎, 宋玉财, 张洪瑞, 刘英超, 潘小菲, 郭涛. 2016. 白秧坪铅锌多金属矿集区东矿带成矿地球化学作用与成矿年龄. 地质力学学报, 22(2): 294–309. |
| [] | 王勇. 2002. 云南巍山-永平铜金多金属矿化集中区成矿流体特征及流体地质填图研究. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-144 |
| [] | 王彦斌, 陈文, 曾普胜. 2005. 滇西北兰坪盆地金满脉状铜矿床绢云母40Ar-39Ar年龄对成矿时代的约束. 地质通报, 24(2): 181–184. |
| [] | 王哲. 2013. 云南金顶铅锌矿床成矿流体与矿化机制研究. 硕士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-119 |
| [] | 魏君奇, 王晓地, 庄晓, 刘云华. 2008. 澜沧江缝合带吉岔蛇纹岩中闪长岩和俄咱辉长岩中锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 24(6): 1297–1301. |
| [] | 肖昌浩. 2013. 三江中南段低温热液矿床成矿系列研究. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-153 |
| [] | 肖晓牛, 喻学惠, 莫宣学, 杨贵来, 李勇, 黄行凯. 2009. 滇西洱海北部北衙地区富碱斑岩的地球化学、锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及成因. 地质通报, 28(12): 1786–1803. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.12.012 |
| [] | 徐启东, 李建威. 2003. 云南兰坪北部铜多金属矿化区成矿流体流动与矿化分带——流体包裹体和稳定同位素依据. 矿床地质, 22(4): 365–376. |
| [] | 徐晓春, 黄震, 谢巧勤, 岳书仓, 刘因. 2004. 云南金满、水泄铜多金属矿床的Ar-Ar同位素年代学及其地质意义. 高校地质学报, 10(2): 157–164. |
| [] | 徐兴旺, 蔡新平, 张宝林, 梁光河, 杜世俊, 王杰. 2006. 滇西北衙金矿矿床成因类型. 矿床地质, 25. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.06.005 |
| [] | 薛春纪, 陈毓川, 王登红, 杨建民, 杨伟光, 曾荣. 2003. 滇西北金顶和白秧坪矿床:地质和He、Ne、Xe同位素组成及成矿时代. 中国科学(D辑), 33(4): 315–322. |
| [] | 薛春纪, 曾荣, 高永宝, 朱和平, 赵世华, 李永强. 2006. 兰坪金顶大规模成矿的流体过程-不同矿化阶段流体包裹体微量元素约束. 岩石学报, 22(4): 1031–1039. |
| [] | 薛伟. 2010. 滇西北兰坪盆地白秧坪多金属矿床成矿流体研究. 硕士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-82 |
| [] | 杨立飞, 石康兴, 王长明, 吴彬, 杜斌, 陈晶源, 夏锦胜, 陈晶. 2016. 西南三江兰坪盆地金满铜矿床成因研究:来自铜和硫同位素的联合约束. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2392–2406. |
| [] | 杨伟光, 喻学惠, 李文昌, 董方浏, 莫宣学. 2003. 云南白秧坪银多金属矿集区成矿流体特征及成矿机制. 现代地质, 17(1): 27–33. |
| [] | 杨雁波. 2013. 兰坪盆地中新生代成矿流体特征、来源与演化研究. 硕士学位论文. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 1-90 |
| [] | 尹静. 2012. 兰坪金顶铅锌矿床同位素地球化学特征及成矿流体演化. 硕士学位论文. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 1-80 |
| [] | 俞赛赢, 李昆琼, 施玉萍, 张惠华. 2003. 临沧花岗岩基中段花岗闪长岩类研究. 云南地质, 22(4): 426–442. |
| [] | 喻学惠, 肖晓牛, 杨贵来, 莫宣学, 曾普胜, 王晋璐. 2008. 滇西"三江"南段几个花岗岩的锆石SHIRMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 24(2): 377–383. |
| [] | 曾普胜, 莫宣学, 喻学惠. 2002. 滇西富碱斑岩带的Nd、Sr、Pb同位素特征及其挤压走滑背景. 岩石矿物学杂志, 21(3): 231–241. |
| [] | 曾普胜, 侯增谦, 高永峰, 杜安道. 2006. 印度-亚洲碰撞带东段喜马拉雅期铜-钼-金矿床Re-Os年龄及成矿作用. 地质论评, 52(1): 72–84. |
| [] | 曾荣. 2007. 兰坪盆地流体大规模成矿过程-以金顶和白秧坪矿床为例. 博士学位论文. 西安: 长安大学, 1-109 |
| [] | 张超, 戚学祥, 唐贯宗, 赵宇浩, 吉风宝. 2014. 滇西哀牢山构造带长安铜钼金矿集区碱性斑岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb定年及其对成矿作用的约束. 岩石学报, 30(8): 2204–2216. |
| [] | 张锦让, 温汉捷. 2010. 连城铜钼矿床流体包裹体初步研究. 矿床地质, 29. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.06.015 |
| [] | 张锦让, 温汉捷. 2012. 云南兰坪盆地西缘脉状铜多金属矿床硫、铅同位素组成及成矿示踪. 地球化学, 41(2): 166–181. |
| [] | 张锦让, 温汉捷, 秦朝建, 王加昇. 2012. 兰坪盆地连城Cu-Mo多金属矿床流体包裹体和稳定同位素地球化学研究. 岩石学报, 28(5): 1373–1386. |
| [] | 张锦让, 温汉捷, 裘愉卓, 邹志超. 2016. 兰坪盆地西缘沉积岩容矿脉状Cu-Ag-Pb-Zn多金属矿床成矿时代. 高校地质学报, 22(2): 219–230. |
| [] | 赵海滨. 2006. 滇西兰坪盆地中北部铜多金属矿床成矿特征及地质条件. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-123 |
| [] | 赵靖, 钟大赉, 王毅. 1994. 滇西澜沧变质带的变形序列与变质作用初步研究. 地质科学, 29(4): 27–40. |
| [] | 钟大赉. 1998. 滇川西部古特提斯造山带. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-231. |
| [] | 周江羽, 王江海, HortonBK, YinA, SpurlinMS. 2011. 青藏高原中东部古近纪盆地封闭的构造-沉积-岩浆活动和古气候响应. 地质学报, 85(2): 172–178. |
| [] | 朱维光, 钟宏, 王立全, 何德锋, 任涛, 范宏鹏, 柏中杰. 2011. 云南民乐铜矿床中玄武岩和流纹斑岩的成因:年代学和地球化学制约. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2694–2708. |
 2017, Vol. 33
2017, Vol. 33