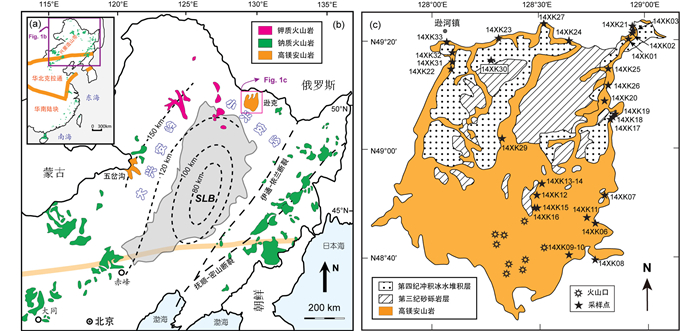
中国东部地区分布有大量的新生代火山岩,这些火山岩南起海南岛的北部,北至黑龙江的小古里河(图 1a),断续分布长达8000余千米,分布面积估计在150000km2以上(包括隐伏于中、新生代盆地中的火山岩)(刘若新, 1992)。东北地区位于我国东部新生代火山岩之最北端,是中国东部新生代火山岩分布面积最大的区域,出露面积达60000km2 (图 1b,陈霞玉等, 2014)。东北地区的新生代火山岩主要是沿着松辽盆地的东侧,西侧和北侧分布的(Liu et al., 2001)。东侧的火山岩主要分布在长白山脉地区,包括镜泊湖小北湖火山群、长白山火山群、龙岗火山群以及宽甸火山群。西侧的火山岩主要靠近大兴安岭-太行山重力梯度带及其西侧,从北往南有小古里河火山岩、诺敏河火山群、柴河-哈拉哈河火山群、五岔沟组火山岩以及阿巴嘎-辉腾梁-赤峰火山群。北侧的火山岩主要分布在小兴安岭地区,包括五大连池-二克山-科洛火山群和逊克火山岩(图 1b)。
|
图 1 中国东部新生代火山岩的分布图(a, 据刘若新,1992)、中国东北新生代火山岩的分布图(b, 据Liu et al., 2001)和小兴安岭逊克地区第四纪高镁安山岩的分布及采样位置图(c, 据黑龙江省地质调查总院, 2014①修改) Fig. 1 Distribution of Cenozoic volcanic rocks in the eastern China (a, after Liu, 1992), distribution of Cenozoic volcanic rocks in the Northeast China (b, after Liu et al., 2001) and distribution and sampling location of Quaternary lavas from the Xunke volcanic field, Lesser Khingan Range (c) |
①黑龙江省地质调查总院.2014.黑龙江省1:50万地质图
近年来,对中国东北地区新生代火山岩的研究主要集中在松辽盆地的东侧(余扬,1987;武殿英,1989;Chen et al., 2003, 2007, 2015;樊祺诚等,2006;张辉煌等,2006;Choi et al., 2006;Wei et al., 2007;闫峻等, 2007;Yan and Zhao, 2008;Zou et al., 2008;Kuritani et al., 2009, 2011;Kuang et al., 2012;Xu et al., 2012;Xu, 2014; Liu et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2015)。而松辽盆地西侧及北侧的新生代火山岩主要分布在大兴安岭及小兴安岭的原始森林中,由于交通不便和森林覆盖等原因,对地质考察造成了困难,因此对西侧及北侧的火山岩研究程度一直比较低。然而,近十几年来随着林区交通的改善和火山地质公园的建立,一些地质学家开始走进大兴安岭及小兴安岭,并关注这些火山群的分布及其岩石成因(代国良和汉景泰, 2005;马保起等, 2006;邵济安等,2008;赵勇伟等, 2008, 2013;樊祺诚等, 2011, 2012;白志达等,2012;赵勇伟和樊祺诚, 2012;Ho et al., 2013;Zhao et al., 2014a, b; Sun et al., 2014, 2015; Yu et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2016)。本文所研究的逊克火山岩位于小兴安岭火山岩区,归为下更新统的大熊山玄武岩,包括石参山和大寿山等火山群。为了解该区的火山活动历史与演化,我们在火山地质考察的基础上,从火山岩岩石学及K-Ar年代学两个方面,对该区的火山岩进行了研究。
1 地质概况小兴安岭位于中亚-兴蒙造山带的东段,处于西伯利亚克拉通、华北克拉通和太平洋板块三大板块的交汇区。地理位置为东经127°42′~130°14′,北纬46°28′~49°21′,处于黑龙江省的东北部。逊克第四纪火山岩位于小兴安岭北段,分布在逊克县城以南的区域,地理坐标为东经127°24′12″~129°17′36″,北纬47°58′15″~49°36′12″。境内地形由沿江平原、丘陵坡地、漫岗低地组成。地势南高北低,自北向南呈阶梯缓延升高,直至南部小兴安岭分水岭。熔岩的分布面积为3000km2,逊克火山岩的野外分布特征及样品采样位置见图 1c。
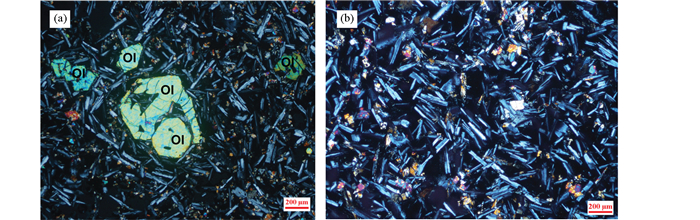
2 逊克火山岩的岩石学特征本次研究共采集了30块逊克火山岩的手标本样品,岩石较新鲜,为灰黑色到黑色,致密块状或气孔状构造。在显微镜下观察,逊克火山岩以无斑隐晶质结构为主,少量岩石具有斑状结构。具有斑状结构的岩石中,斑晶矿物主要为橄榄石(图 2a)和斜方辉石,含量为3%~5%,自形晶-半自形晶。基质主要由斜长石、橄榄石和辉石微晶以及玻璃质组成,表现为填间结构,即板条状斜长石微晶间的填隙物既有辉石等镁铁质矿物,也有玻璃质或隐晶质(图 2b)。其中斜长石微晶的含量为55%~60%,粒状镁铁质矿物微晶含量为20%左右,玻璃质或隐晶质的含量为20%~25%。在野外和显微镜下观察均未发现岩石中含外来捕掳体或捕掳晶。
|
图 2 逊克火山岩的显微照片 (a)正交偏光镜下观察逊克火山岩中的橄榄石斑晶(14XK12);(b)正交偏光镜下观察基质中的填间结构(14XK20) Fig. 2 Representative microphotographs of Xunke volcanic rocks (a) phenocrystic olivine in Xunke volcanic rocks under crossed polarizer (14XK12); (b) matrix interseptal texture of Xunke volcanic rocks under crossed polarizer (14XK20) |
主量元素含量在南京大学内生金属矿床成矿机制研究国家重点实验室配置的ARL9900型X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)上测试完成。根据标样(GBW-07103和GBW07105)测定值,相对误差在元素丰度>1.0%时为±1%,元素丰度 < 1.0%时为±10%,化学分析结果列于表 1。
|
|
表 1 小兴安岭逊克火山岩的主量元素组成(wt%) Table 1 Major element compositions (wt%) of Xunke volcanic rocks, Lesser Khingan Range |
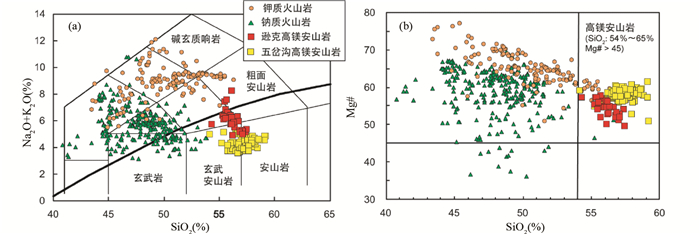
我们将火山岩的主量元素组成投在TAS图上(图 3a)。为了便于比较,来自东北地区的钾质火山岩和钠质火山岩,以及五岔沟地区的新生代火山岩同样投在图 3a中。逊克火山岩的SiO2含量变化为54.3%~57.4%,全碱含量(Na2O+K2O)变化为4.93%~8.27%,跨越拉斑系列和碱性系列,主要岩性为玄武安山岩和玄武质粗面安山岩,还含有少量的安山岩和粗面安山岩,明显不同于东北新生代的板内钾质火山岩(Zhang et al., 1995)和钠质火山岩(Chen et al., 2007)。而位于大兴安岭中段的五岔沟组火山岩的SiO2含量变化为54.1%~59.2%,全碱含量(Na2O+K2O)变化为3.62%~5.28%,其主要岩性为玄武安山岩和安山岩(Ho et al., 2013),与逊克火山岩一起构成东北地区的新生代安山质岩浆作用。此外,小兴安岭逊克火山岩和大兴安岭五岔沟组火山岩的Mg# (Mg2+/(Mg2++Fe2+))分别变化于49.6~57.8和51.0~61.2之间,均属于高镁安山岩的范围(图 3b,Kelemen et al., 1993)。因此,我们首次将逊克火山岩和五岔沟火山岩归类为新生代的板内高镁安山岩。
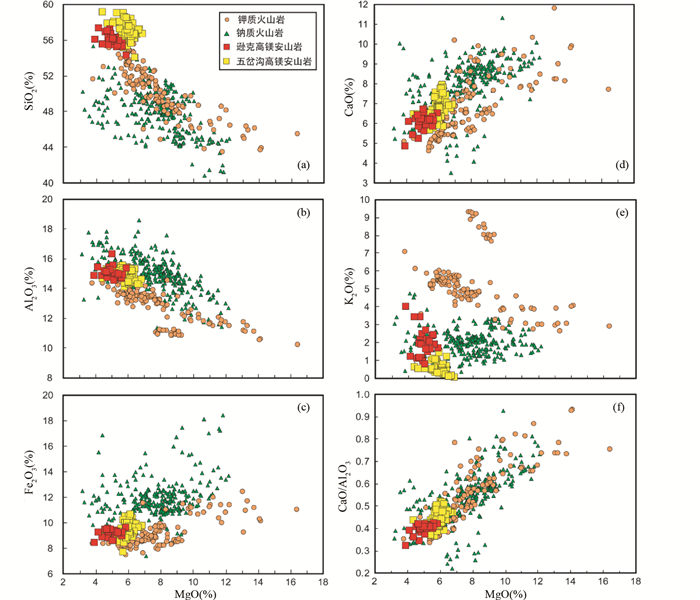
在MgO与其它主量元素的相关图解(图 4)上,逊克高镁安山岩的MgO的变化范围为3.82%~5.80%,与大兴安岭地区的五岔沟组高镁安山岩的MgO (4.36%~6.78%)含量相近,但明显低于东北新生代的钾质玄武岩和钠质玄武岩(图 4)。研究区逊克火山岩的主量元素组成变化范围不大,Al2O3=14.55%~16.32%,Fe2O3=8.42%~9.62%,CaO=4.86%~6.71%,K2O=0.81%~4.02%,CaO/Al2O3=0.33%~0.43%,且它们与MgO之间没有明显的相关关系,表明岩浆从源区到地表过程中演化不明显。尽管逊克火山岩具有较低的MgO含量,但是它们具有较高的Mg#(49.6~57.8),指示这些高镁安山岩的成分可以代表原始岩浆的特征。
|
图 4 中国东北新生代火山岩的主量元素SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3T、CaO、K2O、CaO/Al2O3和MgO之间的相关关系图解 Fig. 4 Variation of SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3T, CaO, K2O, CaO/Al2O3versus MgO for Cenozoic volcanic rocks in Northeast China |
对于中、新生代火山岩来说,K-Ar法和Ar-Ar法是最有效的测年方法之一。本文对逊克高镁安山岩的K-Ar测年工作是在中国地震局地质研究所地震动力学国家重点实验完成的。在详细野外地质考察及岩相学观察的基础上,我们选取了新鲜未蚀变的或蚀变微弱的、具有代表性的岩石样品进行K-Ar定年。先将样品粉碎至40~60目(相当于0.45~0.3mm),然后利用磁选法除去早期结晶的橄榄石或辉石斑晶。由于进行定年的样品比较年轻,为了尽量去除大气Ar的影响,提高放射性成因Ar的相对含量,实验前进行了1h的250℃低温烘烤去气处理。K-Ar法测年分为两部分:钾的测量和氩的测量。K的测量使用HG-5型火焰光度计完成。Ar的测量是在MM1200质谱仪上通过同位素稀释剂法完成的。MM1200质谱仪与全金属萃取系统及纯化系统连接,双真空萃取系统采用电子轰击炉方式加热,包括圣诞树的内真空系统与纯化系统和质谱仪相连通,外真空系统用于电子轰击加热。样品用量在200mg左右,所用稀释剂为99.98%的38Ar。在静态下记录分别40Ar,38Ar,36Ar的量,经线性回归计算其初始值,并根据K-Ar年龄公式计算出样品的表面年龄。年龄计算中采用的衰变常数及其他系数为:40Ar/36Ar=295.5,λ=5.543×10-10,λβ=4.962×10-10,λe=0.581×10-10,40K/K=1.167×10-10 (Steiger and Jäger, 1977)。逊克7个高镁安山岩样品的采样位置见图 1c,测年结果见表 2。
|
|
表 2 小兴安岭逊克高镁安山岩的K-Ar年龄测定结果 Table 2 K-Ar ages of Xunke volcanic rocks, Lesser Khingan Range |
K-Ar年龄测定结果表明,逊克高镁安山岩的喷发时间为更新世(1.12~0.25Ma),属于第四纪岩浆作用的产物,进一步可分为早更新世(1.12~1.00Ma)和中更新世(0.68~0.25Ma)两期火山作用。为了进一步了解东北新生代岩浆作用的时空变化规律,我们统计了整个东北地区出露的新生代火山岩的年龄数据(图 5)。位于松辽盆地西侧(33.17~0.16Ma)和东侧(47.33~0.023Ma)的钠质火山岩的岩浆作用延续时间很长,一直从始新世持续至第四纪(图 5a,b),并在第四纪时达到顶峰。东北新生代的钾质岩浆作用喷发时间比较晚,主要是在上新世和第四纪时期(4.59~0.025Ma)完成的(图 5c),其主要分布在大兴安岭的北段(诺敏河)和松辽盆地的北侧(五大连池-二克山-科洛)(图 1)。东北地区的高镁安山岩的喷发主要分为两期,分别对应于大兴安岭的五岔沟地区和小兴安岭的逊克地区(图 5d)。大兴安岭五岔沟组高镁安山岩为中新世喷发(10.5~8.0Ma),而位于小兴安岭逊克地区的高镁安山岩(1.12~0.25Ma)为更新世喷发。大兴安岭地区高镁安山岩的喷发要早于小兴安岭地区,这可能对中国东北板内高镁安山岩的成因研究具有一定的指示意义。
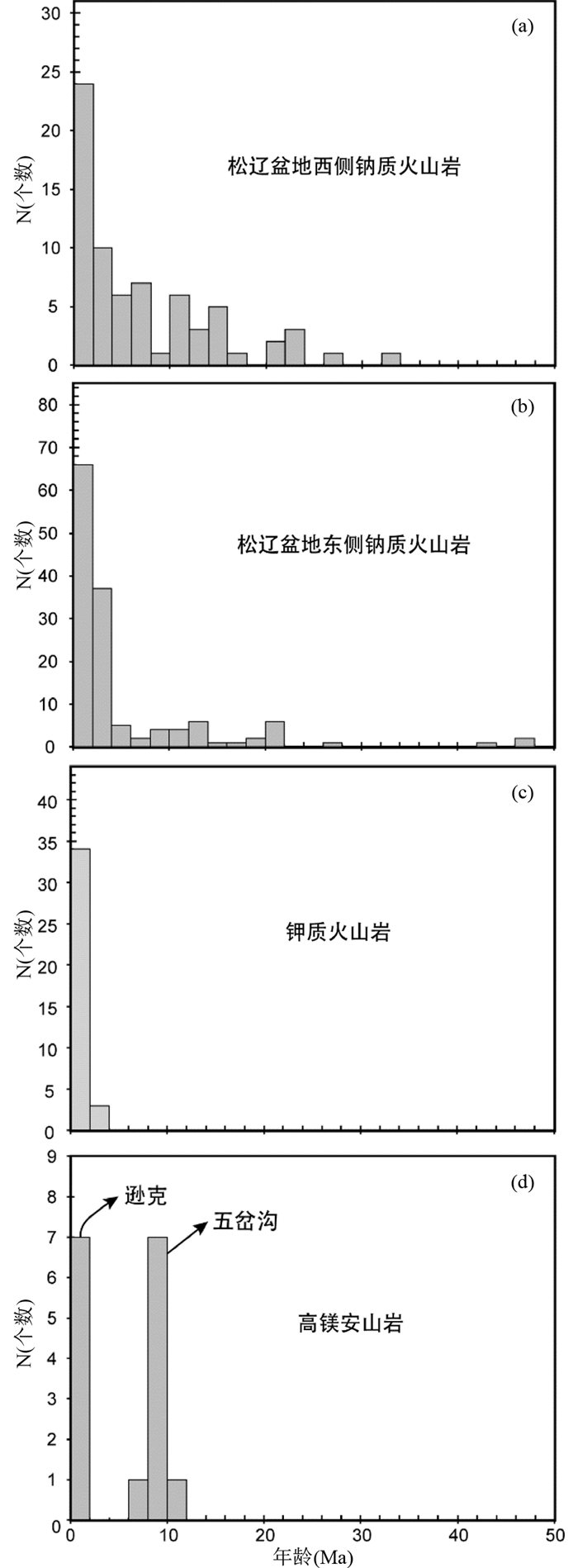
|
图 5 东北新生代火山岩的喷发年龄统计直方图 (a)松辽盆地西侧的钠质火山岩:阿巴嘎(罗修泉和陈启桐,1990;刘若新, 1992;Ho et al., 2008)、辉腾梁(罗修泉和陈启桐,1990;刘若新, 1992;Ho et al., 2008)、赤峰(罗修泉和陈启桐,1990;韩宝福和王式洸,1998)和哈拉哈-柴河(樊祺诚等,2011;Ho et al., 2013);(b)松辽盆地东侧的钠质火山岩:长白山(Liu et al., 2001;樊祺诚等,2006;Wei et al., 2007;Kuritani et al., 2009)、抚顺-密山断裂带(Liu et al., 2001)、伊通-依兰断裂带(Liu et al., 2001)和龙岗地区(Liu et al., 2001);(c)钾质火山岩:五大连池-二克山-科洛(Liu et al., 2001; Zhao et al., 2014)和诺敏河(马保起等,2006;樊祺诚等,2012);(d)高镁安山岩:五岔沟(Ho et al., 2013)和逊克(刘若新,1992;以及本文数据) Fig. 5 Statistical histograms of eruptive ages for Cenozoic volcanic rocks in Northeast China (a) sodic rocks to the west of the Songliao Basin: Abaga (Luo and Chen, 1990; liu, 1992; Ho et al., 2008), Huitengliang (Luo and Chen, 1990; Liu, 1992; Ho et al., 2008), Chifeng (Luo and Chen, 1990; Han and Wang, 1998) and Halaha-Chaihe (Fan et al., 2011; Ho et al., 2013); (b) sodic rocks to the east of the Songliao Basin: Changbaishan (Liu et al., 2001; Fan et al., 2006; Wei et al., 2007; Kuritani et al., 2009), Fushun-Mishan fault belts (Liu et al., 2001), Yitong-Yilan fault belts (Liu et al., 2001) and Longgang (Liu et al., 2001); (c) potassic rocks: Wudalianchi-Erkeshan-Keluo (Liu et al., 2001; Zhao et al., 2014) and Nuominhe (Ma et al., 2006; Fan et al., 2012); (d) high-Mg# andesites: Wuchagou (Ho et al., 2013) and Xunke (Liu, 1992; and this study) |
小兴安岭逊克高镁安山岩所分布的地区具有南高北低的地势特征,并且从地质填图的结果来看火山口的位置都位于南侧,因此推测大面积的岩浆流是从南侧的火山口喷发后向北流动形成的,并形成一些独具特征的火山地貌,如石垄和石海。由于火山区南面的路况不甚理想,交通极其不便,我们在野外工作中没能考察火山口。
(1)石垄
岩浆沿着地势较低的古河道流动时能形成长达数千米的石垄景观。在二皮河东侧的采石场,野外观察到两条东西向的、宽约50m的石垄汇聚成一条宽约100m的石垄(图 6a)。此处出露的火山岩具有块状构造的特征。因此我们推测,尽管逊克火山岩整体上是由大面积的岩浆流由南向北流动形成的,但在局部地区岩浆流有可能沿着古河道从西向东流动的。
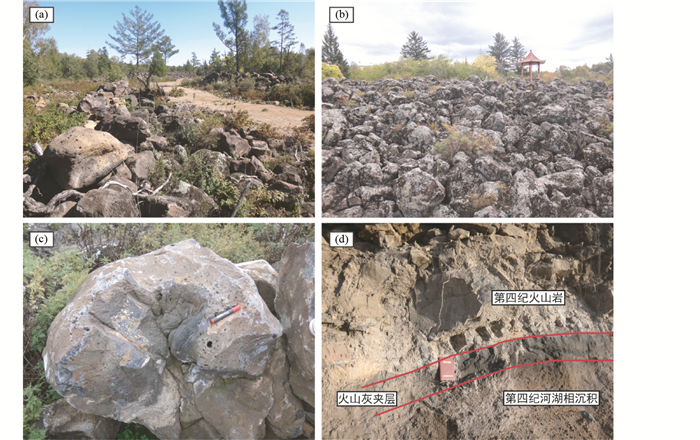
|
图 6 逊克第四纪火山地质特征 (a)二皮河东侧石垄采石场;(b)石景山庄出露大面积的火山岩石海;(c)早期形成的熔岩表层被后期的熔岩流包裹;(d)逊比拉河出露的地层剖面,在第四纪的河湖相沉积与火山岩之间有一薄的火山灰夹层,推测岩浆溢流形成大面积的火山岩之前有岩浆爆发活动 Fig. 6 Geological feathers of Quaternary volcanos in the Xunke area (a) lava quarry in the eastern side of Erpi River; (b) extensive volcanic block lavas in Shijingshanzhuang; (c) the early lava surface layer was encircled by the late magma flow; (d) stratigraphic section near the Xunbila river showing a volcanic ash sandwich between Quaternary fluvial-lacustrine sedimentary strata and volcanic rocks |
(2)石海
岩浆在流动过程中,因表面冷却凝固得早,结成厚厚的硬表壳,岩浆继续运动过程中,由于流动挤压而变形,形成了渣状堆积物,进而大面积熔岩翻转破碎,后面的岩浆继续推挤,向前运动,后浪推前浪,于是能够形成翻花石海。石海即是翻花熔岩。在逊克火山岩东侧的宝山电站-白石电站-乌一电站一带以及石景山庄地质公园内(图 6b)出露大面积非常壮观的石海景观。在宝山电厂附近,还能看到岩浆流动的证据(图 6c),早期形成的熔岩表层被后期的熔岩流包裹。
(3)火山灰
火山碎屑物的发现是岩浆爆发的最直接证据。根据火山碎屑物的大小,可以将其分为火山灰、火山砾、火山渣、火山弹和火山块。火山灰是指由火山喷发出而直径小于2mm的细小火山碎屑物。在逊比拉河北镇大桥南面出露一套第四纪的地层剖面(图 6d)。逊克第四纪火山岩覆盖在第四纪的河湖相沉积物之上,指示了逊克火山岩的喷发较河湖相沉积晚。另外,在第四纪河湖相沉积物与逊克第四纪火山岩之间还夹有一薄层(25~30cm)的火山灰,火山灰呈灰黑色,上覆的火山岩呈致密块状,厚约1.5m,推测岩浆溢流形成大面积的火山岩之前有岩浆爆发的痕迹,但火山喷发的规模较小。
5 东北新生代板内高镁安山岩的首次发现及其重要意义高镁安山岩是指那些与典型岛弧安山岩相比,具有更高的MgO (>5%)和更低的FeOT/MgO ( < 1.5)(Tatsumi et al., 2001),或更高的Mg#(>45)和SiO2(54%~65%)(Kelemen et al., 1993)以及更高的Ni和Cr含量的一类安山岩。经典的高镁安山岩和大陆地壳具有非常相似的元素组成特征(Kelemen et al., 1993; Kelemen, 1995; Rudnick and Fountain, 1995; Taylor and McLennan, 1995),例如它们都亏损高场强元素(Nb,Ta)以及含有较高的Ni含量(20×10-6~200×10-6)。全球新生代高镁安山岩主要形成于汇聚板块边界,并且大都与年轻的、热的洋壳或洋脊的俯冲作用有关(Kelemen, 1995; Kelemen et al., 2003)。因此,研究高镁安山岩的成因对揭示地球的分异演化、地壳的生长与拆沉,洋壳的俯冲与再循环,以及熔体-地幔间的相互作用具有非常重要的意义。
一般地,与年轻的大洋岩石圈俯冲有关的,形成于板块边界的高镁安山岩通常具有亏损的同位素组成特征(Shimoda et al., 1998;Hanyu et al., 2002)。然而,这种成因模式难以解释那些形成于板内环境的高镁安山岩,因为它们具有富集的Sr-Nd同位素组成特征。中国华北克拉通内部出露大量的中生代的高镁安山岩,这些具有同位素富集特征的高镁安山岩通常被解释为拆沉的古老下地壳部分熔融形成的熔体在上升的过程中与岩石圈地幔橄榄岩的相互作用形成的(Gao et al., 2004;王晓蕊等,2005;黄华等,2007;Xu et al., 2008;王超等,2010;王明梁和唐红峰,2014)。大兴安岭五岔沟地区和小兴安岭逊克地区出露的新生代高镁安山岩,是中国东部新生代板内岩浆作用的重要组成部分,它们的首次报道具有十分重要的意义。五岔沟高镁安山岩同样具有富集的Sr-Nd同位素组成特征(Ho et al., 2013),不能用年轻的再循环洋壳的熔融来解释,因此其源区物质组成的性质还需进一步探讨。
致谢 全岩主量元素分析得到南京大学苏贵贞老师的帮助; K-Ar定年得到中国地震局地质研究所郑德文、李大明和武颖老师的帮助; 两位审稿专家对本文提出了建设性的意见和建议; 在此一并表示衷心的感谢。| [] | Bai ZD, Tan QW, Xu GL, Xu DB, Wang Y. 2012. Late Quaternary volcanic activity and neotectonics in the eastern Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 28 (4) :1099–1107. |
| [] | Basu AR, Wang JW, Huang WK, Xie GH, Tatsumoto M. 1991. Major element, REE, and Pb, Nd and Sr isotopic geochemistry of Cenozoic volcanic rocks of eastern China:Implications for their origin from suboceanic-type mantle reservoirs. Earth and Planetary Science Letters , 105 (1-3) :149–169. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(91)90127-4 |
| [] | Chen H, Xia QK, Ingrin J, Jia ZB, Feng M. 2015. Changing recycled oceanic components in the mantle source of the Shuangliao Cenozoic basalts, NE China:New constraints from water content. Tectonophysics , 650 :113–123. DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2014.07.022 |
| [] | Chen JC, Hsu CN, Ho KS. 2003. Geochemistry of Cenozoic volcanic rocks and related ultramafic xenoliths from the Jilin and Heilongjiang provinces, Northeast China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 21 (9) :1069–1084. DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00144-X |
| [] | Chen XY, Chen LH, Chen Y, Zeng G, Liu JQ. 2014. Distribution summary of Cenozoic basalts in central and eastern China. Geological Journal of China Universities , 20 (4) :507–519. |
| [] | Chen Y, Zhang YX, Graham D, Su SG, Deng JF. 2007. Geochemistry of Cenozoic basalts and mantle xenoliths in Northeast China. Lithos , 96 (1-2) :108–126. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.09.015 |
| [] | Choi SH, Mukasa SB, Kwon S, Andronikov AV. 2006. Sr, Nd, Pb and Hf isotopic compositions of Late Cenozoic alkali basalts in South Korea:Evidence for mixing between the two dominant asthenospheric mantle domains beneath East Asia. Chemical Geology , 232 (3-4) :134–151. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.014 |
| [] | Chu ZY, Harvey J, Liu CZ, Guo JH, Wu FY, Tian W, Zhang YL, Yang YH. 2013. Source of highly potassic basalts in Northeast China:Evidence from Re-Os, Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes and PGE geochemistry. Chemical Geology , 357 :52–66. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.08.007 |
| [] | Dai GL, Han JT. 2005. A preliminary petrological study of Late Cenozoic volcanic rocks in Xunke area, upper north of Northeast China. Quaternary Science , 25 (6) :793–794. |
| [] | Fan QC, Hooper PR. 1991. The Cenozoic basaltic rocks of eastern China:Petrology and chemical composition. Journal of Petrology , 32 (4) :765–810. DOI:10.1093/petrology/32.4.765 |
| [] | Fan QC, Sui JL, Wang TH, Li N, Sun Q. 2006. Eruption history and magma evolution of the trachybasalt in the Tianchi volcano, Changbaishan. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 22 (6) :1449–1457. |
| [] | Fan QC, Zhao YW, Li DM, Wu Y, Sui JL, Zheng DW. 2011. Studies on Quaternary volcanism stages of Halaha River and Chaoer River area in the Great Xing'an Range:Evidence from K-Ar dating and volcanic geology features. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 27 (10) :2827–2832. |
| [] | Fan QC, Zhao YW, Sui JL, Li DM, Wu Y. 2012. Studies on Quaternary volcanism stages of Nuomin River area in the Great Xing'an Range:Evidence from petrology, K-Ar dating and volcanic geology features. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 28 (4) :1092–1098. |
| [] | Gao S, Rudnick RL, Yuan HL, Liu XM, Liu YS, Xu WL, Ling WL, Ayers J, Wang XC, Wang QH. 2004. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton. Nature , 432 (7019) :892–897. DOI:10.1038/nature03162 |
| [] | Han BF, Wang SG. 1998. General features and origin of Cenozoic basalts from Chifeng Region, North China. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis , 34 (1) :88–96. |
| [] | Hanyu T, Tatsumi Y, Nakai S. 2002. A contribution of slab-melts to the formation of high-Mg andesite magmas; Hf isotopic evidence from SW Japan. Geophysical Research Letters , 29 (22) :8–1. |
| [] | Ho KS, Liu Y, Chen JC, Yang HJ. 2008. Elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of Late Cenozoic Abaga basalts, Inner Mongolia:Implications for petrogenesis and mantle process. Geochemical Journal , 42 (4) :339–357. DOI:10.2343/geochemj.42.339 |
| [] | Ho KS, Ge WC, Chen JC, You CF, Yang HJ, Zhang YL. 2013. Late Cenozoic magmatic transitions in the central Great Xing'an Range, Northeast China:Geochemical and isotopic constraints on petrogenesis. Chemical Geology , 352 :1–18. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.05.040 |
| [] | Hsu CN, Chen JC. 1998. Geochemistry of Late Cenozoic basalts from Wudalianchi and Jingpohu areas, Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 16 (4) :385–405. DOI:10.1016/S0743-9547(98)00022-1 |
| [] | Huang H, Gao S, Hu ZC, Liu XM, Yuan HL. 2007. Geochemistry of the high-Mg andesites at Zhangwu, western Liaoning:Implication for delamination of newly formed lower crust. Science in China (Series D) , 50 (12) :1773–1786. DOI:10.1007/s11430-007-0121-x |
| [] | Kelemen PB, Shimizu N, Dunn T. 1993. Relative depletion of niobium in some arc magmas and the continental crust:Partitioning of K, Nb, La and Ce during melt/rock reaction in the upper mantle. Earth and Planetary Science Letters , 120 (3-4) :111–134. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(93)90234-Z |
| [] | Kelemen PB. 1995. Genesis of high Mg# andesites and the continental crust. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology , 120 (1) :1–19. DOI:10.1007/BF00311004 |
| [] | Kelemen PB, Hanghøj K, Greene AR. 2003. One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs, with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust. In:Holland HD and Turekian KK (eds.). Treatise on Geochemistry. Amsterdam:Elsevier , 3 :593–659. |
| [] | Kuang YS, Wei X, Hong LB, Ma JL, Pang CJ, Zhong YT, Zhao JX, Xu YG. 2012. Petrogenetic evaluation of the Laohutai basalts from North China Craton:Melting of a two-component source during lithospheric thinning in the Late Cretaceous-Early Cenozoic. Lithos , 154 :68–82. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.06.027 |
| [] | Kuritani T, Kimura JI, Miyamoto T, Wei HQ, Shimano T, Maeno F, Jin X, Taniguchi H. 2009. Intraplate magmatism related to deceleration of upwelling asthenospheric mantle:Implications from the Changbaishan shield basalts, Northeast China. Lithos , 112 (3-4) :247–258. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.02.007 |
| [] | Kuritani T, Ohtani E, Kimura JI. 2011. Intensive hydration of the mantle transition zone beneath China caused by ancient slab stagnation. Nature Geoscience , 4 (10) :713–716. DOI:10.1038/ngeo1250 |
| [] | Kuritani T, Kimura JI, Ohtani E, Miyamoto H, Furuyama K. 2013. Transition zone origin of potassic basalts from Wudalianchi volcano, Northeast China. Lithos , 156-159 :1–12. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.10.010 |
| [] | Le Bas MJ, Le Maitre RW, Streckeisen A, Zanettin B. 1986. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram. Journal of Petrology , 27 (3) :745–750. DOI:10.1093/petrology/27.3.745 |
| [] | Li C, Liu Y, Zhu CH, Zhao HD. 2009. Tectonic environment of the Cenozoic basalts in Jixi basin, Heilongjiang Province. Geology and Resources , 18 (4) :245–249. |
| [] | Lim WH, Chen LH, Liu JQ, Wang XJ, Zhong Y and Zeng G. 2017. Discovery of Cenozoic high-magnesium andesites in the Greater Khingan Range. Geological Journal of China Universities, in press (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [] | Liu CQ, Masuda A, Xie GH. 1994. Major-and trace-element compositions of Cenozoic basalts in eastern China:Petrogenesis and mantle source. Chemical Geology , 114 (1-2) :19–42. DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(94)90039-6 |
| [] | Liu JQ, Han JT, Fyfe WS. 2001. Cenozoic episodic volcanism and continental rifting in Northeast China and possible link to Japan Sea development as revealed from K-Ar geochronology. Tectonophysics , 339 (3-4) :385–401. DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(01)00132-9 |
| [] | Liu JQ, Chen SS, Guo ZF, Guo WF, He HY, You HT, Kim HM, Sung GH, Kim H. 2015. Geological background and geodynamic mechanism of Mt. Changbai volcanoes on the China-Korea border. Lithos , 236-237 :46–73. |
| [] | Liu JQ, Chen LH, Zeng G, Wang XJ, Zhong Y, Yu X. 2016. Lithospheric thickness controlled compositional variations in potassic basalts of Northeast China by melt-rock interactions. Geophysical Research Letters , 43 (6) :2582–2589. DOI:10.1002/2016GL068332 |
| [] | Liu RX. 1992. The Age and Geochemistry of Cenozoic Volcanic Rocks in China. Beijing:Seismological Press, 1-43, 213-227 (in Chinese) |
| [] | Liu YS, Gao S, Kelemen PB, Xu WL. 2008. Recycled crust controls contrasting source compositions of Mesozoic and Cenozoic basalts in the North China Craton. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta , 72 (9) :2349–2376. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2008.02.018 |
| [] | Luo XQ, Chen QT. 1990. Preliminary study on geochronology for Cenozoic basalts from Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica , 9 (1) :37–46. |
| [] | Ma BQ, Lu HF, Wang XD, Guo WS. 2006. Preliminary chronological constraint of the eruption of the Nuomin volcanoes group in the Daxing'anling Mountains. Quaternary Sciences , 26 (2) :295–296. |
| [] | Peng ZC, Zartman RE, Futa K, Chen DG. 1986. Pb-, Sr-and Nd-isotopic systematics and chemical characteristics of Cenozoic basalts, eastern China. Chemical Geology:Isotope Geoscience Section , 59 :3–33. DOI:10.1016/0168-9622(86)90054-0 |
| [] | Rudnick RL, Fountain DM. 1995. Nature and composition of the continental crust:A lower crustal perspective. Reviews of Geophysics , 33 (3) :267–310. DOI:10.1029/95RG01302 |
| [] | Shao JA, Zhang WL, Zhang C. 2008. Mantle enrichment of Wudalianchi volcanic rock belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 24 (11) :2485–2494. |
| [] | Shimoda G, Tatsumi Y, Nohda S, Ishizaka K, Jahn BM. 1998. Setouchi high-Mg andesites revisited:Geochemical evidence for melting of subducting sediments. Earth and Planetary Science Letters , 160 (3-4) :479–492. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00105-8 |
| [] | Steiger RH, Jäger E. 1977. Subcommission on geochronology:Convention on the use of decay constants in geo-and cosmo-chronology. Earth and Planetary Science Letters , 36 (3) :359–362. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(77)90060-7 |
| [] | Sun Y, Ying JF, Zhou XH, Shao JA, Chu ZY, Su BX. 2014. Geochemistry of ultrapotassic volcanic rocks in Xiaogulihe NE China:Implications for the role of ancient subducted sediments. Lithos , 208-209 :53–66. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.08.026 |
| [] | Sun Y, Ying JF, Su BX, Zhou XH, Shao JA. 2015. Contribution of crustal materials to the mantle sources of Xiaogulihe ultrapotassic volcanic rocks, Northeast China:New constraints from mineral chemistry and oxygen isotopes of olivine. Chemical Geology , 405 :10–18. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.04.005 |
| [] | Tatsumi Y, Ishikawa N, Anno K, Ishizaka K, Itaya T. 2001. Tectonic setting of high-Mg andesite magmatism in the SW Japan arc:K-Ar chronology of the Setouchi volcanic belt. Geophysical Journal International , 144 (3) :625–631. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-246x.2001.01358.x |
| [] | Taylor SR, McLennan SM. 1995. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics , 33 (2) :241–265. DOI:10.1029/95RG00262 |
| [] | Wang C, Jin ZM, Gao S, Zhang JF, Zheng S. 2010. Eclogite-melt/peridotite reaction:Experimental constrains on the destruction mechanism of the North China Craton. Science China (Earth Sciences) , 53 (6) :797–809. DOI:10.1007/s11430-010-3084-2 |
| [] | Wang ML, Tang HF. 2014. Reaction experiments between tonalitic melt and mantle olivine and their implications for genesis of high-Mg andesites within cratons. Science China (Earth Sciences) , 56 (11) :1918–1925. |
| [] | Wang XR, Shan G, Liu XM, Yuan HL, Hu ZC, Zhang H, Wang XC. 2006. Geochemistry of high-Mg andesites from the Early Cretaceous Yixian Formation, western Liaoning:Implications for lower crustal delamination and Sr/Y variations. Science in China (Series D) , 49 (9) :904–914. DOI:10.1007/s11430-006-2016-7 |
| [] | Wei HQ, Wang Y, Jin JY, Gao L, Yun SH, Jin BL. 2007. Timescale and evolution of the intracontinental Tianchi volcanic shield and ignimbrite-forming eruption, Changbaishan, Northeast China. Lithos , 96 (1-2) :315–324. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.10.004 |
| [] | Wu DY. 1989. Magma origin of Cenozoic basalts in Yitong County, Jilin Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 5 (2) :65–75. |
| [] | Xu WL, Hergt JM, Gao S, Pei FP, Wang W, Yang DB. 2008. Interaction of adakitic melt-peridotite:Implications for the high-Mg# signature of Mesozoic adakitic rocks in the eastern North China Craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters , 265 (1-2) :123–137. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.09.041 |
| [] | Xu YG, Zhang HH, Qiu HN, Ge WC, Wu FY. 2012. Oceanic crust components in continental basalts from Shuangliao, Northeast China:Derived from the mantle transition zone?. Chemical Geology , 328 :168–184. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.01.027 |
| [] | Xu YG. 2014. Recycled oceanic crust in the source of 90~40Ma basalts in North and Northeast China:Evidence, provenance and significance. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta , 143 :49–67. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2014.04.045 |
| [] | Yan J, Zhao JX, Liu HQ. 2007. Quaternary basalts from Longgang in the North China Craton:Petrologenesis and characteristics of the mantle source. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 23 (6) :1413–1422. |
| [] | Yan J, Zhao JX. 2008. Cenozoic alkali basalts from Jingpohu, NE China:The role of lithosphere-asthenosphere interaction. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences , 33 (1-2) :106–121. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.11.001 |
| [] | Yu X, Lee CTA, Chen LH, Zeng G. 2015. Magmatic recharge in continental flood basalts:Insights from the Chifeng igneous province in Inner Mongolia. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems , 16 (7) :2082–2096. DOI:10.1002/2015GC005805 |
| [] | Yu Y. 1987. Petrology and petrogenesis of the Cenozoic basaltic rocks from Mt. Qixingshan, Jilin Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 3 (3) :55–63. |
| [] | Zhang HH, Xu YG, Ge WC, Ma JL. 2006. Geochemistry of Late Mesozoic-Cenozoic basalts in Yitong-Datun area, Jilin Province and its implication. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 22 (6) :1579–1596. |
| [] | Zhang M, Suddaby P, Thompson RN, Thirlwall MF, Menzies MA. 1995. Potassic volcanic rocks in NE China:Geochemical constraints on mantle source and magma genesis. Journal of Petrology , 36 (5) :1275–1303. DOI:10.1093/petrology/36.5.1275 |
| [] | Zhang ML, Guo ZF, Cheng ZH, Zhang LH, Liu JQ. 2015. Late Cenozoic intraplate volcanism in Changbai volcanic field, on the border of China and North Korea:Insights into deep subduction of the Pacific slab and intraplate volcanism. Journal of the Geological Society , 172 (5) :648–663. DOI:10.1144/jgs2014-080 |
| [] | Zhao YW, Fan QC, Bai ZD, Sun Q, Li N, Sui JL, Du XX. 2008. Preliminary study on Quaternary volcanoes in the Halaha River and Chaoer River area in Daxing'an Mountain range. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 24 (11) :2569–2575. |
| [] | Zhao YW, Fan QC. 2012. Mantle sources and magma genesis of Quaternary volcanic rocks in the Halaha River and Chaoer River area, Great Xing'an Range. Acta Petrologica Sinica , 28 (4) :1119–1129. |
| [] | Zhao YW, Fan QC, Bai ZD, Sui JL. 2013. Quaternary volcanism in the Nuomin River and Kuile River area of the Greater Hinggan Mountains. Science China (Earth Sciences) , 56 (2) :173–181. DOI:10.1007/s11430-012-4544-7 |
| [] | Zhao YW, Fan QC, Zou HB, Li N. 2014a. Geochemistry of Quaternary basaltic lavas from the Nuomin volcanic field, Inner Mongolia:Implications for the origin of potassic volcanic rocks in northeastern China. Lithos , 196-197 :169–180. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.03.011 |
| [] | Zhao YW, Li N, Fan QC, Zou HB, Xu YG. 2014b. Two episodes of volcanism in the Wudalianchi volcanic belt, NE China:Evidence for tectonic controls on volcanic activities. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research , 285 :170–179. DOI:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2014.08.016 |
| [] | Zhou XH, Armstrong RL. 1982. Cenozoic volcanic rocks of eastern China:Secular and geographic trends in chemistry and strontium isotopic composition. Earth and Planetary Science Letters , 58 (3) :301–329. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(82)90083-8 |
| [] | Zou HB, Reid MR, Liu YS, Yao YP, Xu XS, Fan QC. 2003. Constraints on the origin of historic potassic basalts from Northeast China by U-Th disequilibrium data. Chemical Geology , 200 (1-2) :189–201. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(03)00188-8 |
| [] | Zou HB, Fan QC, Yao YP. 2008. U-Th systematics of dispersed young volcanoes in NE China:Asthenosphere upwelling caused by piling up and upward thickening of stagnant Pacific slab. Chemical Geology , 255 (1-2) :134–142. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.06.022 |
| [] | 白志达, 谭庆伟, 许桂玲, 徐德斌, 王妍.2012. 内蒙东部晚第四纪火山活动与新构造. 岩石学报 , 28 (4) :1099–1107. |
| [] | 陈霞玉, 陈立辉, 陈晹, 曾罡, 刘建强.2014. 中国中-东部地区新生代玄武岩的分布规律与面积汇总. 高校地质学报 , 20 (4) :507–519. |
| [] | 代国良, 汉景泰.2005. 逊克晚新生代火山岩岩石学特征初步研究. 第四纪研究 , 25 (6) :793–794. |
| [] | 樊祺诚, 隋建立, 王团华, 李霓, 孙谦.2006. 长白山天池火山粗面玄武岩的喷发历史与演化. 岩石学报 , 22 (6) :1449–1457. |
| [] | 樊祺诚, 赵勇伟, 李大明, 武颖, 隋建立, 郑德文.2011. 大兴安岭哈拉哈河-绰尔河第四纪火山分期:K-Ar年代学与火山地质特征. 岩石学报 , 27 (10) :2827–2832. |
| [] | 樊祺诚, 赵勇伟, 隋建立, 李大明, 武颖.2012. 大兴安岭诺敏河第四纪火山岩分期:岩石学、年代学与火山地质特征. 岩石学报 , 28 (4) :1092–1098. |
| [] | 韩宝福, 王式洸.1998. 赤峰地区新生代玄武岩的基本特征及成因. 北京大学学报(自然科学版) , 34 (1) :88–96. |
| [] | 黄华, 高山, 胡兆初, 柳小明, 袁洪林.2007. 辽西彰武地区中生代高镁安山岩地球化学及其对新生下地壳拆沉作用的指示. 中国科学(D辑) , 37 (10) :1287–1300. |
| [] | 李超, 刘勇, 朱长海, 赵寒冬.2009. 黑龙江鸡西盆地新生代玄武岩大地构造环境探讨. 地质与资源 , 18 (4) :245–249. |
| [] | 林蔚涵, 陈立辉, 刘建强, 王小均, 钟源, 曾罡. 2017.大兴安岭新生代高镁安山岩的确认.高校地质学报, 出版中 |
| [] | 刘若新. 1992.中国新生代火山岩年代学与地球化学.北京:地震出版社, 1-43, 213-227 |
| [] | 罗修泉, 陈启桐.1990. 内蒙古新生代玄武岩年代学初步研究. 岩石矿物学杂志 , 9 (1) :37–46. |
| [] | 马保起, 卢海峰, 旺小东, 郭文生.2006. 大兴安岭诺敏河火山喷发时代的初步研究. 第四纪研究 , 26 (2) :295–296. |
| [] | 邵济安, 张文兰, 张聪.2008. 五大连池火山岩带的地幔富集作用. 岩石学报 , 24 (11) :2485–2494. |
| [] | 王超, 金振民, 高山, 章军锋, 郑曙.2010. 华北克拉通岩石圈破坏的榴辉岩熔体-橄榄岩反应机制:实验约束. 中国科学(地球科学) , 40 (5) :541–555. |
| [] | 王明梁, 唐红峰.2014. 英云闪长质熔体与地幔橄榄石反应的实验研究--对克拉通内部高镁安山岩成因的约束. 中国科学(地球科学) , 44 (3) :405–413. |
| [] | 王晓蕊, 高山, 柳小明, 袁洪林, 胡兆初, 张宏, 王选策.2005. 辽西四合屯早白垩世义县组高镁安山岩的地球化学:对下地壳拆沉作用和Sr/Y变化的指示. 中国科学(D辑) , 35 (8) :700–709. |
| [] | 武殿英.1989. 吉林伊通新生代玄武岩的岩浆起源. 岩石学报 , 5 (2) :65–75. |
| [] | 闫峻, 赵建新, 刘海泉.2007. 华北龙岗第四纪玄武岩:岩石成因和源区性质. 岩石学报 , 23 (6) :1413–1422. |
| [] | 余扬.1987. 吉林双辽七星山新生代玄武岩的特点及其成因探讨. 岩石学报 , 3 (3) :55–63. |
| [] | 张辉煌, 徐义刚, 葛文春, 马金龙.2006. 吉林伊通-大屯地区晚中生代-新生代玄武岩的地球化学特征及其意义. 岩石学报 , 22 (6) :1579–1596. |
| [] | 赵勇伟, 樊祺诚, 白志达, 孙谦, 李霓, 隋建立, 杜星星.2008. 大兴安岭哈拉哈河-淖尔河地区第四纪火山活动初步研究. 岩石学报 , 24 (11) :2569–2575. |
| [] | 赵勇伟, 樊祺诚.2012. 大兴安岭哈拉哈河-绰尔河第四纪火山岩地幔源区与岩浆成因. 岩石学报 , 28 (4) :1119–1129. |
| [] | 赵勇伟, 樊祺诚, 白志达, 隋建立.2013. 大兴安岭诺敏河-奎勒河地区第四纪火山活动研究. 中国科学(地球科学) , 43 (9) :1464–1473. |
 2017, Vol. 33
2017, Vol. 33