2. 国土资源部岩浆作用成矿与找矿重点实验室, 西安 710054
2. Key Laboratory for the Study of Focused Magmatism and Giant Ore Deposits, MLR, Xi'an 710054, China
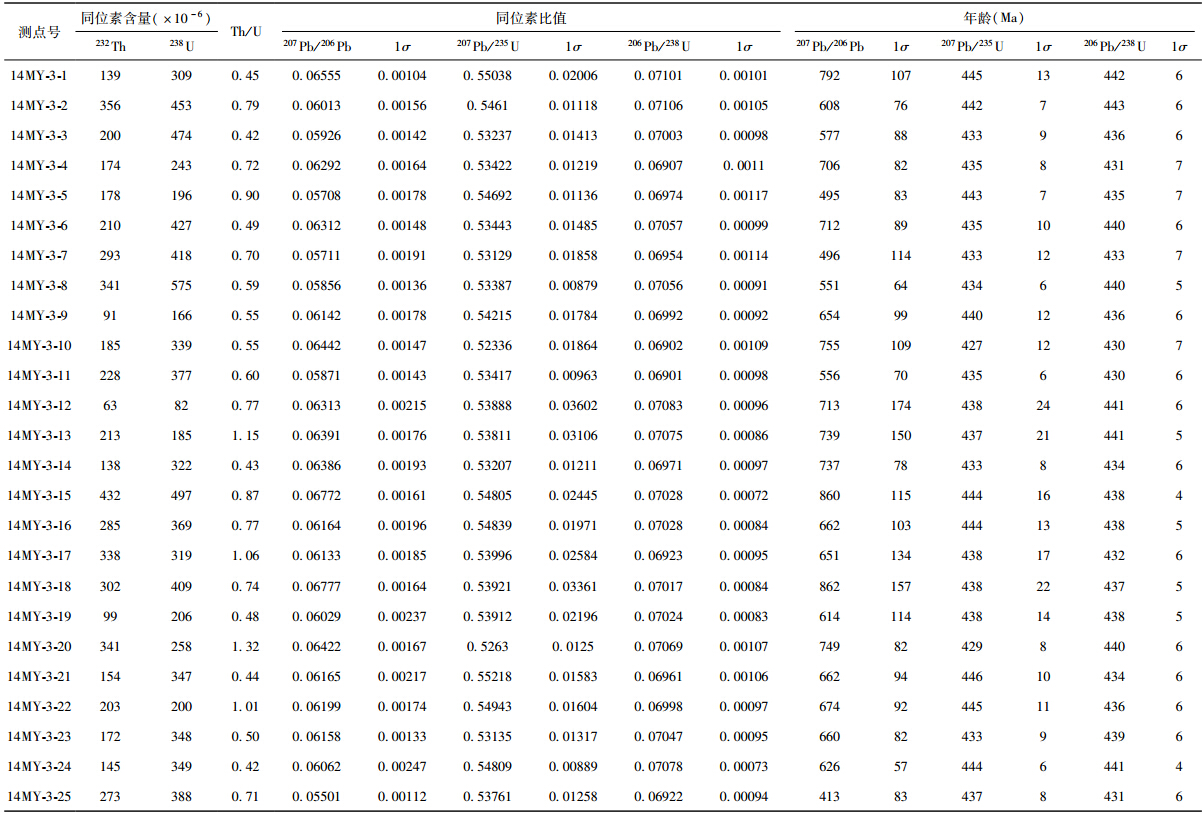
中亚造山带(CAOB)是世界上最大的增生型造山带之一(图 1a,Şengör et al., 1993; Windley et al., 2007; Xiao et al., 2010,2015; Wilhem et al., 2012; Krner et al., 2014; Xiao and Santosh, 2014),也是全球显生宙大陆地壳生长最显著的地区(Jahn et al., 2004; Chen and Arakawa, 2005)。西准噶尔是巨型中亚造山带的一部分,也是中亚-兴蒙巨型构造成矿域的重要组成部分(Shen et al., 2012,2015; 朱永峰,2014)。该地区蛇绿混杂岩分布广泛,主要包括唐巴勒、玛依勒、达尔布特、克拉玛依等多条蛇绿混杂岩带(图 1b),中外学者对其有过较多研究(Kwon et al., 1989; 张弛和黄萱,1992; 白文吉等,1995; Wang et al., 2003; 徐新等,2006; 何国琦等,2007; 朱永峰和徐新,2007; 朱永峰等,2008; 辜平阳等,2009; 刘希军等,2009; 陈博和朱永峰,2010; 陈石和郭召杰,2010; 董连慧等,2010; Xu et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012a,b,c,2013,2015a,b; Chen et al., 2014; Zhu et al., 2015)。另外,该地区发育大量石炭-二叠纪花岗岩类(韩宝福等,2006; Geng et al., 2009; Chen et al., 2010; Yin et al., 2010; Tang et al., 2010; Yin et al., 2015),但目前对其形成环境存在争议(Han et al., 1997; Chen and Arakawa, 2005; Tang et al., 2012; Gao et al., 2014)。
 | 图 1 中亚造山带构造格架图(a,据 Jahnetal et al,2000)及西准噶尔地质简图(b,据新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产局,1993;Yang et al,2013)Fig. 1 Simplified tectonic sketch of the Gentral Asian Orogenic Belt(a,after Jahn et al., 2000) and regional geochemical map of the West Junggar(modified after BGMRX,1993; Yang et al., 2013) |
随着研究的不断深入,在中亚造山带中不断有不同时代碱性洋岛玄武岩(OIB)被识别(Safonova and Santosh, 2014; 杨高学等,2015)。例如在俄罗斯阿尔泰Zasur’ya地区分别发现早寒武世的古海山及晚寒武世洋岛玄武岩(Safonova et al., 2009)。在西准噶尔克拉玛依及达尔布特蛇绿混杂岩中识别出中晚泥盆世碱性玄武岩(杨高学等,2013a; Yang et al., 2015b)。虽然在这些地区均有OIB特征的玄武岩报道,然而对其成因存在不同认识(Wong et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2013)。另外,研究发现志留纪碱性玄武岩在中亚造山带少之又少。但这些碱性洋岛玄武岩的产出,为我们研究深部地幔活动以及岩浆深部过程提供了窗口,也是为探讨壳-幔相互作用提供了物质基础。为此,本文以玛依勒地区枕状玄武岩为研究对象,在精确测定其地质时代的同时探讨源区性质及岩石成因,进一步约束区域构造演化过程。 2 区域地质概况
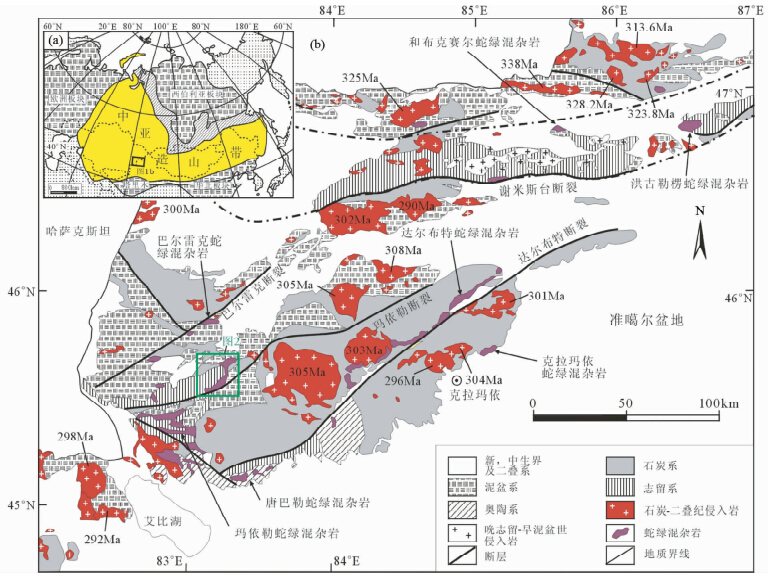
西准噶尔是近年来研究中亚造山带的热点地区之一,主要由一系列的增生杂岩带、古生代岩浆弧构成(Buckman and Aitchison, 2004; Xiao et al., 2008,2009; Han et al., 2010),其主要构造特征为NE-SW向左行走滑断裂非常发育,由北向南依次为巴尔雷克、玛依勒及达尔布特断裂,是一个多米诺式的走滑断裂构造体系(Choulet et al., 2012; 陈宣华等,2015),它们控制着花岗岩类和蛇绿混杂岩的分布(图 1b)。该地区除了出露大量晚古生代中酸性侵入体及岩脉(苏玉平等,2006; 范裕等,2007; Zhou et al., 2008; Chen et al., 2010; Yin et al., 2010; Ma et al., 2012),还发育早古生代花岗岩类(Xu et al., 2013b; Ren et al., 2014)。西准噶尔发育的多条蛇绿混杂岩带的物质组成基本一致,主要为蛇纹石化方辉橄榄岩,二辉橄榄岩,纯橄岩,铬铁矿,辉石岩,辉长岩,块状及枕状玄武岩,硅质岩,凝灰岩及碎屑岩等(Feng et al., 1989; Zhang et al., 1993; 徐新等,2006; 张元元和郭召杰,2010),它们之间均为构造接触,变形强烈,时代跨度大,从震旦纪(杨高学等,2013b)到石炭纪(刘希军等,2009)均有出现。研究区出露的地层主体为奥陶系至石炭系火山-沉积地层(图 2,新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产局,1993),最新在早石炭世海相火山-沉积建造中识别出富Nb岛弧玄武岩(李永军等,2014)。西准噶尔南部中泥盆统与下伏地质体之间发育角度不整合,可能是准噶尔-吐哈陆块与伊犁微地块碰撞过程的地质响应(白建科等,2015)。另外,通过钻进资料研究认为上石炭统与下二叠统之间为角度不整合,是准噶尔残余洋最终关闭的产物(徐新等,2010; Xu et al., 2013a; Li et al., 2015a,b)。
 | 图 2 西准噶尔那伦索一带地质简图年龄数据来自Xu et al., 2012Fig. 2 Simplified tectonic sketch of the Nalunsuo area in West JunggarAge data from Xu et al., 2012 |
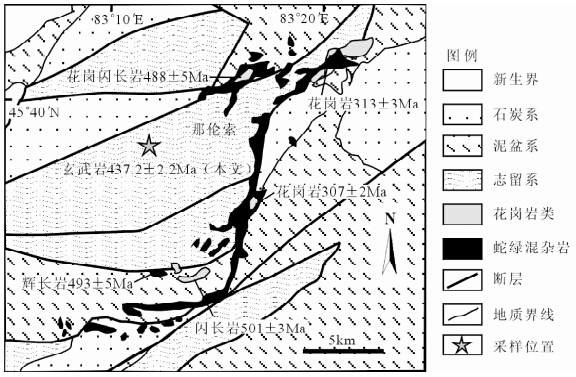
中-上志留统玛依拉山组主要分布于玛依拉山一带,在达尔布特断裂南段的南东侧有少许分布。玛依拉山组是一套海相的正常沉积物与较少的喷发沉积及喷发岩呈相间的互层组合。而本次研究对象枕状玄武岩产于玛依拉山组内部,玛依勒蛇绿混杂岩那伦索岩块的西侧(图 2),出露宽度为1.1km,以溢流相基性火山熔岩为主,玄武岩和火山碎屑岩、硅质岩共生。玄武岩的枕状构造极为发育(图 3a),同时可见扭动及流动构造。在玄武岩枕的边部发育2~5cm不等的冷凝边,表面可见放射状裂纹或凹凸不平的球颗。气孔大小0.1×0.3cm~0.3×0.5cm,杏仁体以灰白色方解石为主,从核心到边部气孔呈放射状分布,由小而密到大而疏(图 3b)。玄武岩岩枕多呈长椭圆形,长轴40~60cm,最大可达1~1.5m,枕状体间破碎角砾岩发育,在均局部偶见块状玄武岩。在枕状熔岩北部和南部,发育一套厚度较大的紫红色-灰紫色硅质岩,局部为整合接触关系,大多被后期断层接触破坏,最厚达150m,单层厚度多为5~15cm,层间褶皱极为发育。
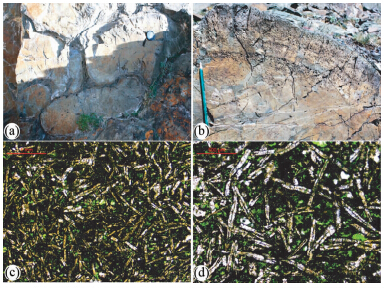 | 图 3 枕状玄武岩野外及镜下特征(a)玄武岩枕;(b)玄武岩枕边部放射状发育的气孔;(c)玄武岩基质特征;(d)斜长石中空骸晶结构Fig. 3 Field and microscopic features of the pillow basalt(a)basalt pillows;(b)radial vesicular structure at the edge of pillow;(c)matrix features of basalt;(d)hollow skeletal crystal structure of plagioclase |
玄武岩为枕状构造,气孔杏仁构造,间隐结构,偶见斑状结构,斑晶矿物主要为单斜辉石和斜长石,斑晶矿物的种类及含量在样品之间存在差异。斜长石斑晶大小为0.1×0.4mm~0.15×0.8mm,无色,长柱状,有溶蚀现象。所有样品基质中含有斜长石微晶,部分样品含有少量的单斜辉石及橄榄石微晶。斜长石微晶,无色,长条状、针状,多数杂乱分布在火山玻璃中(图 3c),也有少数颗粒在局部半定向排列,粒径多为0.02×0.5mm。局部可见杏仁石体发育,为椭圆状、圆状,大小0.5~2.5mm,内充填绿泥石及方解石。最值得关注是大多数样品中斜长石微晶普遍可见中空骸晶结构(图 3d),这是在水下熔岩急剧萃冷条件下迅速结晶的产物。 4 分析方法
首先使用常规的重液浮选和电磁分离方法挑选出锆石,然后在双目镜下根据锆石颜色、自形程度、形态和透明度等特征初步分类,挑选出具有代表性的锆石,用环氧树脂固定,待其充分固化后抛光至锆石露出核部,进行锆石CL显微图像分析。锆石U-Pb同位素测定在国土资源部岩浆作用成矿与找矿重点实验室用德国MicroLas公司生产的GeoLas 200M激光剥蚀系统与Elan 6100DRC ICP-MS联机上进行测定,分析采用的激光斑束直径为30μm,激光脉冲为10Hz,能量为32~36mJ,激光剥蚀样品的深度为20~40μm。锆石年龄测定采用国际标准锆石91500作为外部标准物质。详细分析步骤和数据处理方法参见相关文献(袁洪林等,2003)。采用Glitter(ver4.0,Macquarie University)序对锆石的同位素比值及元素含量进行计算。并按照Andersen Tom的方法(Andersen,2002)。用LAM-ICPMS Common Lead Correction(ver3.15)进行普通铅校正。年龄计算及谐和图采用Isoplot(ver 3.0)完成(Ludwig,1991)。
主量及微量元素在长安大学西部矿产资源与地质工程教育部重点实验室完成。主量元素分析采用X射线荧光光谱(XRF)方法分析完成,XRF溶片法按照国家标准GB/T 14506.28-1993执行。元素分析误差小于2.5%,氧化物总量介于99.75%~100.25%,烧失量(LOI)在烘箱中经1000℃高温烘烤90min后称重获得。微量元素采用Thermo-X7电感耦合等离子体质谱仪进行样品测定,仪器工作参数:Power:1200w,Nebulizer gas:0.64L/min,Auxiliary gas:0.80L/min,Plasma gas:13L/min。
5 分析结果 5.1 锆石U-Pb年代学
玛依勒枕状玄武岩样品(14MY-3)的锆石为无色透明,或浅黄色,大部分锆石晶型较好,多为短柱及等粒状(长宽比在1左右),粒径为30~60μm之间。锆石的CL图像显示大多数锆石具有较好的晶型,并显示明显内部构造及典型的岩浆结晶环带(图 4a)。样品的25个测点Th含量变化为63×10-6~432×10-6,U含量变化为82×10-6~575×10-6,Th/U比值范围为0.42~1.32,均大于0.4(表 1),且Th、U之间具有良好的正相关关系,进一步表明为岩浆成因锆石。样品的典型锆石颗粒CL图像,锆石U-Pb同位素原位分析点见图 4a,其锆石U-Pb年龄测试结果详见表 1。
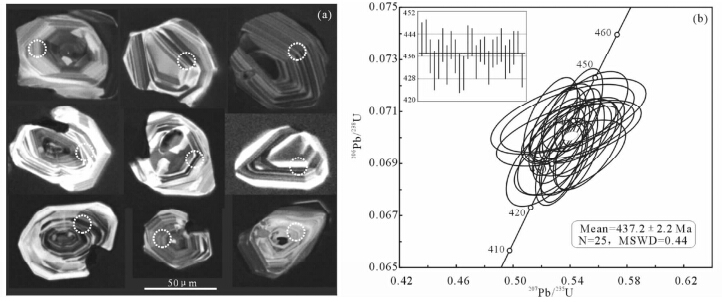 | 图 4 玛依勒枕状玄武岩锆石CL图像(a)及谐和曲线图(b)Fig. 4 CL images(a) and U-Pb concordia plots(b)of zircons for pillow basalt from the Mayile area |
| 表 1 西准噶尔玛依勒枕状玄武岩(14MY-3)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb isotopic of the pillow basalt(14MY-3)in Mayile area form West Junggar |
对样品枕状玄武岩样品14MY-3进行25颗锆石25个点的同位素分析,获得206Pb/238U表面年龄范围在430~443Ma,最大的年龄误差7Ma,所有25个数据点集中分布在谐和曲线附近(图 4b),206Pb/238U年龄的加权平均为437.2±2.2Ma,MSWD=0.44(95%置信度),代表玄武岩岩浆结晶年龄。 5.2 主量元素
西准噶尔玛依勒枕状玄武岩岩石化学分析结果及有关参数列于表 2。从表 2可以看出,枕状玄武岩SiO2含量44.89%~47.81%,平均为46.39%。样品中Fe2OT3含量较高12.97%~15.73%,平均为14.52%。TiO2含量3.28%~4.12%,平均为3.62%,明显高于IAB(0.58%~0.85%)及MORB(1%~1.5%),较加拿大Flin Flon带Long Bay的洋岛玄武岩(TiO2为1.35%~2.29%,Stern et al., 1995)及克拉玛依OIB型枕状玄武岩(TiO2为1.29%~2.48%,朱永峰等,2007)高,而在西藏日喀则洋岛玄武岩(TiO2为3.28%~8.13%,Xia et al., 2008)及东昆仑东段阿尼玛卿蛇绿岩中洋岛玄武岩(2.2%~4.73%; 郭安林等,2006)范围之内。Al2O3含量15.53%~16.87%,MgO为3.49%~6.79%,Mg#为34.4~45.9,低于原生岩浆(Mg#=68~75; Wilson,1989)。CaO含量4%~10.29%,Na2O含量2.27%~4.97%,K2O含量0.28%~2.77%,P2O5含量0.5%~0.7%,均略高于Long Bay的洋岛玄武岩,而与日喀则洋岛玄武岩玄武岩相当。样品烧失量较高(0.48%~1.47%),这与镜下观察到存在绿泥石化等蚀变一致,为正确确定岩石类型,采用抗蚀变元素Zr/TiO2-Nb/Y及Zr/TiO2×SiO2图解进行岩石分类判别(图 5),所有样品均无一例外的落在碱性玄武岩区域。
| 表 2 西准噶尔玛依勒枕状玄武岩主量元素(wt%)、微量元素(×10-6)分析结果及主要参数 Table 2 The concentration of major(wt%),trace elements(×10-6) and parameters for Mayile pillow basalts in West Junggar |
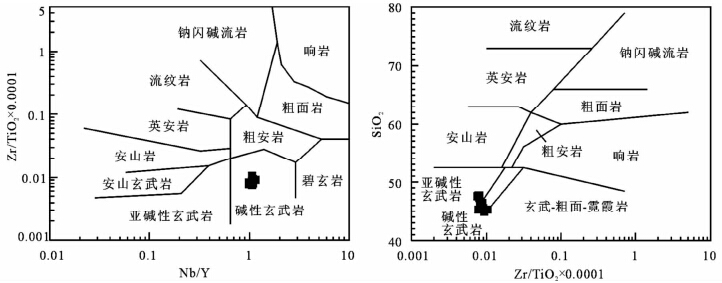 | 图 5 玛依勒枕状玄武岩Zr/TiO2-Nb/Y及Zr/TiO2×SiO2岩石分类图(据Winchester and Floyd, 1977)Fig. 5 Zr/TiO2-Nb/Y and Zr/TiO2×SiO2 diagrams of the pillow basalt in Mayile area from West Junggar(after Winchester and Floyd, 1977) |
枕状玄武岩稀土元素总量较高(∑REE=221.7×10-6~296.7×10-6),明显高于MORB(39.1×10-6),无明显Eu异常(Eu/Eu*=0.96~1.06),表明没有发生斜长石的分离结晶作用。在球粒陨石标准化曲线图(图 6a)上,轻稀土(LREE)明显富集,重稀土(HREE)相对亏损,轻重稀土分馏较为明显((La/Yb)N=5.5~7.3)。各个样品REE配分模式相互平行,只有位置高低差异,具有同源岩浆演化特征。稀土元素球粒陨石标准化模式高于E-MORB,而与典型OIB玄武岩(Sun and McDonough, 1989)、太平洋夏威夷Oahu碱性玄武岩(Clague et al., 2006)及日喀则洋岛玄武岩(Xia et al., 2008)一致(图 6a)。
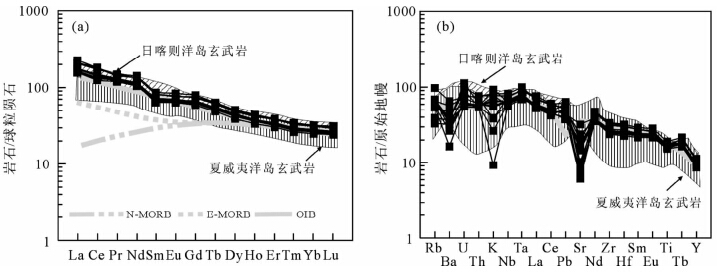 | 图 6 玛依勒枕状玄武岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)及原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)N-MORB、E-MORB、OIB、球粒陨石及原始地幔标准化值均来自Sun and McDonough(1989),日喀则及夏威夷洋岛玄武岩数据分别来自Xia et al.(2008)和Clague et al.(2006)Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace multi-element patterns(b)for pillow basalt in the Mayile areaN-MORB,E-MORB,OIB,Chondrite and primitive mantle values are from Sun and McDonough(1989). Oceanic isl and basalts data of Xigaze and Hawaii values are from Xia et al.(2008) and Clague et al.(2006) |
在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 6b)中,枕状玄武岩相对富集Rb、Th、U和REE元素,相对亏损Ba、K、Sr,没有明显的Nb、Ta负异常,并且含量变化较大,Ti在玄武岩中略显负异常。玄武岩中Nb/Ta比值为14.1~14.5,略低于OIB和原始地幔(分别为17.78,17.5±2.0; Sun and McDonough, 1989)。相容元素Cr和Ni含量(表 2)远低于原生玄武岩岩浆范围(Cr=300×10-6~500×10-6,Ni=300×10-6~400×10-6,Hess,1992),表明成岩过程经历了橄榄石和单斜辉石的分离结晶作用,这与MgO含量较低相吻合。结合主量元素高Fe2OT3、TiO2、P2O5特征,总体显示OIB型玄武岩的地球化学特征。 6 讨论 6.1 时代意义
前人采用不同的测试方法对玛依勒蛇绿混杂岩中的辉石岩、玄武岩等分别进行锆石SHRIMP和全岩Rb-Sr等时线测年(朱宝清等,1987; Jian et al., 2005; 魏荣珠,2010),认为其形成于中或晚志留世,李红生(1994)从玛依勒地区玛依勒组地层中发现中志留世放射虫。另外,杨高学等(2013b)对其中的辉长岩进行锆石LA-ICP-MS测年获得年龄572.2±9.2Ma,该年龄是准噶尔乃至北疆地区报道的最古老的蛇绿混杂岩年龄。本次在玛依勒地区枕状玄武岩进行了锆石U-Pb测年,获得206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为437.2±2.2Ma,这与魏荣珠(2010)采用全岩Rb-Sr同位素获得年龄435.3±6.5Ma和432.5±7.4Ma一致,也与玛依勒蛇绿混杂岩时代相吻合。前人研究认为该套枕状玄武岩及硅质岩应是玛依勒蛇绿混杂岩的组成部分(魏荣珠,2010),但结合野外地质特征,笔者认为将该套岩石组合划归玛依拉山组似乎更为合理,有待进一步研究。
对准噶尔乃至中亚造山带中碱性OIB特征玄武岩进行系统年代学研究发现,其时代为新元古代晚期至二叠纪,甚至延伸到早三叠世,但中古生代志留纪碱性玄武岩报道很少,是没有识别出来,还是整个中亚造山带中的碱性玄武岩在中古生代就存在间歇期。本次获得的年龄恰恰填补了这个“空白”,该问题在本研究中得到了很好解决,表明OIB特征玄武岩在中亚造山带中是连续发育的。 6.2 构造环境
玛依勒枕状玄武岩为碱性玄武岩,发育中空骸晶结构(图 3c,d),具有类似于典型OIB的稀土元素配分形式(图 6a)和原始地幔标准化图解(图 6b)。由于样品所代表的岩浆经历适度演化,并非原生岩浆,加之玄武岩遭受后期弱的碳酸盐化等蚀变,故采用对部分熔融和分离结晶作用不敏感及对蚀变作用具有较高稳定性的元素进行构造环境判别和源区性质分析。本区样品的Th/Ta比值为1.45~1.73,Ta/Hf比值为0.4~0.41,变化范围较小,与冰岛玄武岩、夏威夷Koodau玄武岩(Th/Ta=0.4~1.6,Ta/Hf=0.1~0.3)基本一致(Furman et al., 1992; Frey et al., 1994),与典型俯冲带玄武岩明显不同(Th/Ta=4.1~11,Ta/Hf=0.2~0.4; Kita et al., 2001)。样品的Th/Nb比值为0.1~0.12,Nb/Zr比值为0.15~0.16,均也在大洋板内玄武岩比值范围之内(孙书勤等,2003; 王涛等,2009; Dai et al., 2012; 刘飞等,2013; 王智琳等,2013; Liu et al., 2015),而与岛弧区玄武岩明显不同(分别为0.6~1,0.05~0.09; Kita et al., 2001)。另外,采用TiO2-MnO×10-P2O5×10(图 7a),Nb×2-Zr/4-Y(图 7b),V-Ti/1000(图 7c),Th/Yb-Nb/Yb(图 7d)系列图解进一步判别,发现玛依勒枕状玄武岩属于大洋板内玄武岩,具有典型OIB的亲缘性。有学者研究认为在俯冲带存在少量的富碱岩石(van Bergen et al., 1992),其Nb/Y,Ba/Nb及Pb/Ce分别为0.9~1.4,7~23,0.06~0.13(Portnyagin et al., 2005),而玛依勒枕状玄武岩数据分别为0.98~1.15,2.82~8.61,0.03~0.05,两者区别明显。通过上述地球化学对比及野外有共生硅质岩发育的地质事实,认为玛依勒枕状玄武岩形成于大洋板内的洋岛或海山环境。
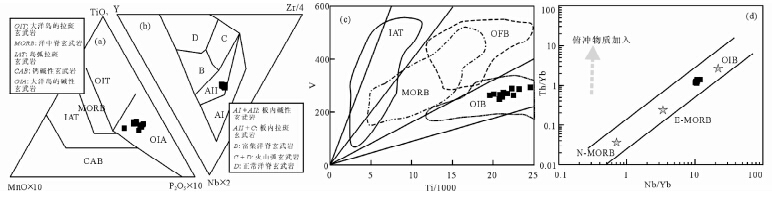 | 图 7 枕状玄武岩构造环境分类图(a)TiO2-MnO×10-P2O5×10图解(Mullen,1983);(b)Nb×2-Zr/4-Y图解(Meschede,1986);(c)V-Ti/1000图解(Shervais,1982);(d)Th/Yb-Nb/Yb图解(Pearce,2008)Fig. 7 Tectonic discrimination diagrams for the pillow basalts |
通常被认为大洋板内洋岛玄武岩在成因上与“热点”或“地幔柱”有关(Kellogg et al., 1999; Montelli et al., 2004; Niu,2009)。一般来自软流圈的岩浆TiO2含量为1.27%左右,而与更深部地幔物质有关的岩浆TiO2含量普遍大于2%(朱弟成等,2008),玛依勒枕状玄武岩TiO2含量为3.28%~4.12%。来自地幔柱的岩浆具有低的La/Ta比值(一般为8~15),La/Sm变化不大(<5; Lassiter and Depaolo, 1997),枕状玄武岩的La/Ta及La/Sm比值分别为11~14,3.4~4.3,表明岩浆源区具有深部地幔成分的印迹,暗示岩浆源区可能与地幔柱有关,同时没有或很少有地壳物质加入,这与没有明显的Nb和Ta负异常,及小于1的(La/Nb)PM和(Th/Ta)PM比值(分别为0.8~1,0.7~0.84)相吻合(Neal et al., 2002)。对微量元素比值进行系统分析,发现其与典型OIB的比值极为接近,并且位于EM Ⅰ型和EM Ⅱ型OIB比值范围内(表 3),表明玛依勒枕状玄武岩来自富集地幔,这与87Sr/86Sr比值(0.7057~0.7067)相一致(魏荣珠,2010)。
| 表 3 不同地幔储库不相容元素的比值对照表 Table 3 Incompatible trace element ratios in different reservoirs |
轻稀土元素和高场强元素含量及比值被广泛的用于判别岩浆源区特征和部分熔融程度等(Zhao and Zhou, 2007)。轻稀土元素La相对于中稀土Sm更不相容,这两者在尖晶石或石榴子石地幔部分熔融过程中均富集在熔体中,而中稀土Sm相对于重稀土(如Yb)的富集则依靠熔融过程中是否有石榴石作为残留相。另外,分离结晶作用对La/Sm和Sm/Yb比值的影响相对较小。因此,利用La/Sm-Sm/Yb图解(图 8a,Aldanmaz et al., 2000)研究部分熔融程度,发现全部样品同样落在尖晶石和石榴石二辉橄榄岩演化曲线之间并靠近富集趋势的OIB,并发生5%±的部分熔融。这与Sm-Sm/Yb图解(图 8b)中所有碱性玄武岩样品落在尖晶石二辉橄榄岩和石榴石二辉橄榄岩演化曲线之上完全一致,表明源区主要组成为尖晶石和石榴石二辉橄榄岩,并发生5%±的部分熔融。
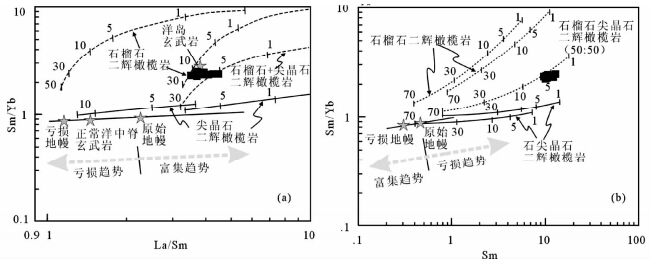 | 图 8 枕状玄武岩源区特征判别图(据Aldanmaz et al., 2000)原始地幔及亏损地幔分别据McKenzie and O’Nions(1991)及Sun and McDonough(1989). 尖晶石二辉橄榄岩(Ol53+Opx27+Cpx17+Sp11)及石榴石二辉橄榄岩(Ol60+Opx20+Cpx10+Gt10)曲线据Aldanmaz et al.(2000). 曲线上数字表示部分熔融程度Fig. 8 Plots of La/Sm-Sm/Yb(a) and Sm-Sm/Yb(b)for pillow basalt(after Aldanmaz et al., 2000) |
玄武岩是造山带内部常见的岩石类型之一,其中洋岛型玄武岩通常在俯冲碰撞过程中,部分物质发生刮削拼贴,与残留洋壳及灰岩、硅质岩等构造增生楔(Kimura et al., 1994; Safonova and Santosh, 2014)。通过对造山带内增生楔中洋岛玄武岩块体的时代及性质研究,不仅可以进行古海山、洋岛及大洋高原的识别,而且还可以进行古洋盆演化及古构造格局恢复(李继亮,2004; 闫臻等,2008; 杨高学等,2015)。
实际上,前人在西准噶尔玛依勒地区的萨雷诺海就有过关于碱性玄武岩的报道,并认为其成因与地幔柱有关,但没有获得准确的时代(Yang et al., 2012a)。此次报道的碱性玄武岩,发育在玛依勒山北部的那伦索一带,获得准确的锆石U-Pb年龄为437.2±2.2Ma,时代为早中志留世,具有典型OIB地球化学特征,其成因可能与大洋板内地幔柱活动有关,但也不排除与大洋岩石圈地幔的盖层效应有关(Niu et al., 2011)。西准噶尔地区除了玛依勒之外,在唐巴勒、达尔布特及克拉玛依蛇绿混杂岩中均有碱性洋岛玄武岩的报道(杨高学等,2015),表明在准噶尔洋发展演化的整个历程中,均有地幔柱活动的印迹。最新研究发现在西准噶尔萨尔托海蛇绿岩的高铝铬铁矿中发育金刚石(Tian et al., 2015),另外,在青藏高原的雅鲁藏布江缝合带及俄罗斯极地乌拉尔地区蛇绿岩中均发育金刚石(Yang et al., 2007,2014,2015c),它们很可能来自深部的地幔过渡带(Mantle transition zone),暗示存在深部地幔岩浆作用。 7 结论
通过对西准噶尔玛依勒地区枕状玄武岩岩相学、同位素年代学及地球化学的系统研究,取得如下主要认识:
(1)玛依勒枕状玄武岩与火山碎屑岩、硅质岩共生,枕状构造极为发育。枕状玄武岩斜长石微晶普遍发育中空骸晶结构,是在水下熔岩急剧萃冷条件下迅速结晶的产物。
(2)通过LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,获得枕状玄武岩206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为437.2±2.2Ma,时代属于早中志留世。
(3)枕状玄武岩属于碱性玄武岩系列,具有典型洋岛玄武岩地球化学特征,来源于富集地幔源区,主要组成为尖晶石和石榴石二辉橄榄岩,并发生了5%±的部分熔融。
(4)枕状玄武岩形成于大洋板内与地幔柱有关的海山/大洋岛屿环境。结合前人研究,认为西准噶尔乃至古亚洲洋在中古生代洋内俯冲的同时,大洋板内可能存在地幔柱活动。
致谢 真诚感谢王强副主编、俞良军编委及两位匿名审稿人对本文认真细致审阅,并提出具体修改意见。| [1] | Aldanmaz E, Pearce JA, Thirlwall MF and Mitchell JG. 2000. Petrogenetic evolution of Late Cenozoic, post-collision volcanism in western Anatolia, Turkey. Journal of Volcanology Geothermal Research, 102(1-2):67-95 |
| [2] | Andersen T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2):59-79 |
| [3] | Bai JK, Chen JL, Yan Z, Tang Z, Xue XY and Li JL. 2015. The timing of opening and closure of the Mayile oceanic basin:Evidence from the angular unconformity between the Middle Devonian and its underlying geological body in the southern West Junggar. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(1):133-142(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [4] | Bai WJ, Robinson P, Yang JS, Zhou MF and Hu XF. 1995. Tectonic evolution of different dating ophiolites in the western Jungger, Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 11(Suppl.):62-72(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Buckman S and Aitchison JC. 2004. Tectonic evolution of Palaeozoic terranes in West Junggar, Xinjiang, NW China. In:Malpas J, Fletcher, CJN, Aitchison JC and Ali J(eds.). Aspects of the Tectonic Evolution of China. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 101-129 |
| [6] | Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Xinjiang(BGMRX). 1993. Regional Geology of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 442-504(in Chinese) |
| [7] | Chen B and Arakawa Y. 2005. Elemental and Nd-Sr isotopic geochemistry of granitoids from the West Junggar foldbelt(NW China), with implications for Phanerozoic continental growth. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(5):1307-1320 |
| [8] | Chen B and Zhu YF. 2010. Petrology and geochemistry of gabbro in Baikouquan, Keramay(Xinjiang, NW China):Implication of magmatic evolution. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(8):2287-2298(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Chen JF, Han BF, Ji JQ, Zhang L, Xu Z, He GQ and Wang T. 2010. Zircon U-Pb ages and tectonic implications of Paleozoic plutons in northern West Junggar, North Xinjiang, China. Lithos, 115(1-4):137-152 |
| [10] | Chen S and Guo ZJ. 2010. Time constraints, tectonic setting of Dalabute ophiolitic complex and its significance for Late Paleozoic tectonic evolution in West Junggar. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(8):2336-2344(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Chen S, Pe-Piper G, Piper DJW and Guo ZJ. 2014. Ophiolitic mélanges in crustal-scale fault zones:Implications for the Late Palaeozoic tectonic evolution in West Junggar, China. Tectonics, 33(12):2419-2443 |
| [12] | Chen XH, Nie LS, Ding WC, Wang XQ, Wang ZH and Ye BY. 2015. The relationship between strike-slip tectonic system and geochemical anomalies in the West Junggar, northwestern China and its implication for mineral exploration. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(2):371-387(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Choulet F, Faure M, Cluzel D, Chen Y, Lin W and Wang B. 2012. From oblique accretion to transpression in the evolution of the Altaid collage:New insights from West Junggar, northwestern China. Gondwana Research, 21(2-3):530-547 |
| [14] | Clague DA, Paduan JB, McIntosh WC, Cousens BL, Davis AS and Reynolds JR. 2006. A submarine perspective of the Honolulu Volcanics, Oahu. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 151(1-3):279-307 |
| [15] | Dai JG, Wang CS and Li Y. 2012. Relicts of the Early Cretaceous seamounts in the central-western Yarlung Zangbo Suture Zone, Southern Tibet. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 53:25-37 |
| [16] | Dong LH, Zhu ZX, Qu X, Wang KZ and Zhao TY. 2010. Spatial distribution, geological features and latest research progress of the main ophiolite zones in Xinjiang, NW-China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(10):2894-2904(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Fan Y, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Tan LG, Cooke D, Meffre S, Yang WP and He LX. 2007. LA-ICP MS zircon age of Tasite pluton in Sawuer region of West Junggar, Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(8):1901-1908(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Feng Y, Coleman RG, Tilton GR and Xiao X. 1989. Tectonic evolution of the West Junggar region, Xinjiang, China. Tectonics, 8(4):729-752 |
| [19] | Frey FA, Garcia MO and Roden MF. 1994. Geochemical characteristics of Koolau Volcano:Implications of intershield geochemical differences among Hawaiian volcanoes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 58(5):1441-1462 |
| [20] | Furman T, Frey FA and Meyer PS. 1992. Petrogenesis of evolved basalts and rhyolites at austurhorn, Southeastern Iceland:The role of fractional crystallization. Journal of Petrology, 33(6):1405-1445 |
| [21] | Gao R, Xiao L, Pirajno F, Wang GC, He XX, Yang G and Yan SW. 2014. Carboniferous-Permian extensive magmatism in the West Junggar, Xinjiang, northwestern China:Its geochemistry, geochronology, and petrogenesis. Lithos, 204:125-143 |
| [22] | Geng HY, Sun M, Yuan C, Xiao WJ, Zhao GC, Zhang LF, Wong K and Wu FY. 2009. Geochemical, Sr-Nd and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic studies of Late Carboniferous magmatism in the West Junggar, Xinjiang:Implications for ridge subduction? Chemical Geology, 266(3-4):364-389 |
| [23] | Gu PY, Li YJ, Zhang B, Tong LL and Wang JN. 2009. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of gabbro in the Darbut ophiolite, western Junggar, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(6):1364-1372(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Guo AL, Zhang GW, Sun YG, Zheng JK, Liu Y and Wang JQ. 2007. Geochemistry and apatial distribution of OIB and MORB in A'nymaqen ophiolite zone:Evidence of Majixueshan ancient ridge-centered hotspot. Science in China(Series D), 50(2):197-208 |
| [25] | Han BF, Wang SG, Jahn BM, Hong DW, Kagami H and Sun YL. 1997. Depleted-mantle source for the Ulungur River A-type granites from North Xinjiang, China:Geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotopic evidence, and implications for Phanerozoic crustal growth. Chemical Geology, 138(3-4):135-159 |
| [26] | Han BF, Ji JQ, Song B, Chen LH and Zhang L. 2006. Late Paleozoic vertical growth of continental crust around the Junggar Basin, Xinjiang, China(Part I):Timing of post-collisional plutonism. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(5):1077-1086(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Han BF, Guo ZJ, Zhang ZC, Zhang L, Chen JF and Song B. 2010. Age, geochemistry, and tectonic implications of a Late Paleozoic stitching pluton in the North Tian Shan suture zone, western China. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 122(3-4):627-640 |
| [28] | He GQ, Liu JB, Zhang YQ and Xu X. 2007. Keramay ophiolitic mélange formed during Early Paleozoic in western Junggar basin. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(7):1573-1576(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Hess PC. 1992. Phase equilibria constraints on the origin of ocean floor basalts. In:Morgan JP, Blackman DK and Sinton JM(eds.). Mantle Flow and Melt Generation at Mid-Ocean Ridges. Geophysical Monograph. Washington, DC:American Geophysical Union, 67-102 |
| [30] | Jahn BM, Wu FY and Chen B. 2000. Granitoids of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and continental growth in the Phanerozoic. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh:Earth Sciences, 91(1-2):181-193 |
| [31] | Jahn BM, Windley BF, Natal'in BA and Dobretsov N. 2004. Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 23(5):599-603 |
| [32] | Jian P, Liu DY, Shi YR and Zhang FQ. 2005. SHRIMP dating of SSZ ophiolites from northern Xinjiang Province, China:Implications for generation of oceanic crust in the central Asian orogenic belt. In:Sklyarov EV(ed.). Structural and Tectonic Correlation across the Central Asian Orogenic Collage:Northeastern Segment. Guidebook and Abstract Volume of the Siberian Workshop IGCP-480. Irkutsk:Institute of the Earth Crust, Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences, 1-246 |
| [33] | Kellogg LH, Hager BH and van der Hilst RD. 1999. Compositional stratification in the deep mantle. Science, 283(5409):1881-1884 |
| [34] | Kimura G, Sakakibara M and Okamura M. 1994. Plumes in central Panthalassa? Deductions from accreted oceanic fragments in Japan. Tectonics, 13(4):905-916 |
| [35] | Kita I, Yamamoto M, Asakawa Y, Nakagawa M, Taguchi S and Hasegawa H. 2001. Contemporaneous ascent of within-plate type and island-arc type magmas in the Beppu-Shimabara graben system, Kyushu Island, Japan. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 111(1-4):99-109 |
| [36] | Kröner A, Kovach V, Belousova E, Hegner E, Armstrong R, Dolgopolova A, Seltmann R, Alexeiev DV, Hoffmann JE, Wong J, Sun M, Cai K, Wang T, Tong Y, Wilde SA, Degtyarev KE and Rytsk E. 2014. Reassessment of continental growth during the accretionary history of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Gondwana Research, 25(1):103-125 |
| [37] | Kwon ST, Tilton GR, Coleman RG and Feng Y. 1989. Isotopic studies bearing on the tectonics of the West Junggar region, Xinjiang, China. Tectonics, 8(4):719-727 |
| [38] | Lassiter JC and Depaolo DJ. 1997. Plume/lithosphere interaction in the generation of continental and oceanic flood basalts:Chemical and isotopic constraints. In:Mahoney JJ and Coffin MF(eds.). Geophysical Monograph. Washington, DC:American Geophysical Union, 100:335-355 |
| [39] | Li D, He DF, Qi XF and Zhang NN. 2015a. How was the Carboniferous Balkhash-West Junggar remnant ocean filled and closed? Insights from the Well Tacan-1 strata in the Tacheng Basin, NW China. Gondwana Research, 27(1):342-362 |
| [40] | Li D, He DF, Santosh M and Ma DL. 2015b. Tectonic framework of the northern Junggar Basin Part Ⅱ:The island arc basin system of the western Luliang Uplift and its link with the West Junggar terrane. Gondwana Research, 27(3):1110-1130 |
| [41] | Li HS. 1994. Middle Silurian radiolarians from Keerhada, Xinjiang. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 11(2):259-272(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [42] | Li JL. 2004. Basic characteristics of accretion-type orogens. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(9-10):947-951(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [43] | Li YJ, Shen R, Wang R, Guo ST, Tong LL and Yang GX. 2014. Discovery and significance of Early Carboniferous Nb-enriched basalts in Barnuke, West Junggar, Xinjiang. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(12):3501-3511(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [44] | Liu F, Yang JS, Chen SY, Liang FH, Niu XL, Li ZL and Lian DY. 2013. Ascertainment and environment of the OIB-type basalts from the Dongbo ophiolite in the western part of Yarlung Zangbo Suture Zone. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(6):1909-1932(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [45] | Liu F, Yang JS, Dilek Y, Xu ZQ, Xu XZ, Liang FH, Chen SY and Lian DY. 2015. Geochronology and geochemistry of basaltic lavas in the Dongbo and Purang ophiolites of the Yarlung-Zangbo suture zone:Plume-influenced continental margin-type oceanic lithosphere in southern Tibet. Gondwana Research, 27(2):701-718 |
| [46] | Liu XJ, Xu JF, Wang SQ, Hou QY, Bai ZH and Lei M. 2009. Geochemistry and dating of E-MORB type mafic rocks from Dalabute ophiolite in West Junggar, Xinjiang and geological implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(6):1373-1389(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [47] | Ludwig KR. 1991. Isoplot:A plotting and regression program for radiogenic-isotope data. File Report 91-445. United States:US Geological Survey |
| [48] | Ma C, Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Zhao GP, Han CM, Zhang JE, Luo J and Li C. 2012. Tracing a subducted ridge-transform system in a Late Carboniferous accretionary prism of the southern Altaids:Orthogonal sanukitoid dyke swarms in Western Junggar, NW China. Lithos, 140-141:152-165 |
| [49] | McKenzie D and O'Nions RK. 1991. Partial melt distributions from inversion of rare earth element concentrations. Journal of Petrology, 32(5):1021-1091 |
| [50] | Meschede M. 1986. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y diagram. Chemical Geology, 56(3-4):207-218 |
| [51] | Montelli R, Nolet G, Dahlen FA, Masters G, Engdahl ER and Hung SH. 2004. Finite-frequency tomography reveals a variety of plumes in the mantle. Science, 303(5656):338-343 |
| [52] | Mullen ED. 1983. MnO-TiO2-P2O5:A minor element discriminant for basaltic rocks of oceanic environments and its implications for petrogenesis. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 62(1):53-62 |
| [53] | Neal CR, Mahoney JJ and Chazey WJ. 2002. Mantle sources and the highly variable role of continental lithosphere in basalt petrogenesis of the Kerguelen plateau and broken ridge LIP:Results from ODP leg 183. Journal of Petrology, 43(7):1177-1205 |
| [54] | Niu YL. 2009. Some basic concepts and problems on the petrogenesis of intra-plate ocean island basalts. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(22):4148-4160 |
| [55] | Niu YL, Wilson M, Humphreys ER and O'Hara MJ. 2011. The origin of intra-plate ocean island basalts(OIB):The lid effect and its geodynamic implications. Journal of Petrology, 52(7-8):1443-1468 |
| [56] | Pearce JA. 2008. Geochemical fingerprinting of oceanic basalts with applications to ophiolite classification and the search for Archean oceanic crust. Lithos, 100(1-4):14-48 |
| [57] | Portnyagin M, Hoernle K, Avdeiko G, Hauff F, Werner R, Bindeman I, Uspensky V and Garbe-Schönberg D. 2005. Transition from arc to oceanic magmatism at the Kamchatka-Aleutian junction. Geology, 33(1):25-28 |
| [58] | Ren R, Han BF, Xu Z, Zhou YZ, Liu B, Zhang L, Chen JF, Su L, Li J, Li XH and Li QL. 2014. When did the subduction first initiate in the southern Paleo-Asian Ocean:New constraints from a Cambrian intra-oceanic arc system in West Junggar, NW China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 388:222-236 |
| [59] | Rollison HR. 2000. Petrological Geochemistry. In:Yang XM, Yang XY and Chen SX(Trans.). Hefei:University of Science and Technology of China Press, 1-275(in Chinese) |
| [60] | Safonova IY, Utsunomiya A, Kojima S, Nakae S, Tomurtogoo O, Filippov AN and Koizumi K. 2009. Pacific super plume-related oceanic basalts hosted by accretionary complexes of Central Asia, Russian Far East and Japan. Gondwana Research, 16(3-4):587-608 |
| [61] | Safonova IY and Santosh M. 2014. Accretionary complexes in the Asia-Pacific region:Tracing archives of ocean plate stratigraphy and tracking mantle plumes. Gondwana Research, 25(1):126-158 |
| [62] | Şengör AMC, Natal'in BA and Burtman VS. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia. Nature, 364(6435):299-307 |
| [63] | Shen P, Shen YC, Pan HD, Li XH, Dong LH, Wang JB, Zhu HP, Dai HW and Guan WN. 2012. Geochronology and isotope geochemistry of the Baogutu porphyry copper deposit in the West Junggar region, Xinjiang, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 49:99-115 |
| [64] | Shen P, Pan HD, Shen YC, Yan YH and Zhong SH. 2015. Main deposit styles and associated tectonics of the West Junggar region, NW China. Geoscience Frontiers, 6(2):175-190 |
| [65] | Shervais JW. 1982. Ti-V plots and the petrogenesis of modern and ophiolitic lavas. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 59(1):101-118 |
| [66] | Stern RA, Syme EC and Lucas SB. 1995. Geochemistry of 1.9Ga MORB- and OIB-like basalts from the Amisk collage, Flin Flon Belt, Canada:Evidence for an intra-oceanic origin. Geocheimtca et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(15):3131-3154 |
| [67] | Su YP, Tang HF, Hou GS and Liu CQ. 2006. Geochemistry of aluminous A-type granites along Darabut tectonic belt in West Junggar, Xinjiang. Geochimica, 35(1):55-67(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [68] | Sun SQ, Wang YL and Zhang CJ. 2003. Discrimination of the tectonic settings of basalts by Th, Nb and Zr. Geological Review, 49(1):40-47(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [69] | Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes. In:Sauders AD and Norry MJ(eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42:313-345 |
| [70] | Tang GJ, Wang Q, Wyman DA, Li ZX, Zhao ZH, Jia XH and Jiang ZQ. 2010. Ridge subduction and crustal growth in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt:Evidence from Late Carboniferous adakites and high-Mg diorites in the western Junggar region, northern Xinjiang(west China). Chemical Geology, 277(3-4):281-300 |
| [71] | Tang GJ, Wang Q, Wyman DA, Li ZX, Zhao ZH and Yang YH. 2012. Late Carboniferous high εNd(t)-εHf(t) granitoids, enclaves and dikes in western Junggar, NW China:Ridge-subduction-related magmatism and crustal growth. Lithos, 140-141:86-102 |
| [72] | Tian YZ, Yang JS, Robinson PT, Xiong FH, Li Y, Zhang ZM, Liu Z, Liu F and Niu XL. 2015. Diamond discovered in high-Al chromitites of the Sartohay ophiolite, Xinjiang Province, China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(2):332-340 |
| [73] | van Bergen MJ, Vroon PZ, Varekamp JC and Poorter RPE. 1992. The origin of the potassic rock suite from Batu Tara volcano(East Sunda Arc, Indonesia). Lithos, 28(3-6):261-282 |
| [74] | Wang T, Wang ZQ, Yan Z, Yan QR, Zhang YL and Xiang ZJ. 2009. Identification of the Ordovician oceanic island basalts and their tectonic significance of the Dabao Formation in southern Qinling:Constraints from geochemistry and geochronology of oceanic island basalt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(12):3241-3250(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [75] | Wang ZH, Sun S, Li JL, Hou QL, Qin KZ, Xiao WJ and Hao J. 2003. Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the northern Xinjiang, China:Geochemical and geochronological constraints from the ophiolites. Tectonics, 22(2), doi:10.1029/2002TC001396 |
| [76] | Wang ZL, Xu DR, Wu CJ, Fu WW, Wang L and Wu J. 2013. Discovery of the Late Paleozoic ocean island basalts(OIB) in Hainan Island and their geodynamic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(3):875-886(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [77] | Wei RZ. 2010. The Mayileshan pillow(Western Junggar, Xinjiang) and their tectonic implications:Constraints from the geological and geochemical characteristics and Rb-Sr isochron ages. Xinjiang Geology, 28(3):229-235(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [78] | Wilhem C, Windley BF and Stampfli GM. 2012. The Altaids of Central Asia:A tectonic and evolutionary innovative review. Earth-Science Reviews, 113(3-4):303-341 |
| [79] | Wilson M. 1989. Igneous Petrogenesis. London:Unwin Hyman, 1-466 |
| [80] | Winchester JA and Floyd PA. 1977. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements. Chemical Geology, 20:325-343 |
| [81] | Windley BF, Alexeiev D, Xiao W, Kroner A and Badarch G. 2007. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Journal of the Geological Society, 164(1):31-47 |
| [82] | Wong K, Sun M, Zhao GC, Yuan C and Xiao WJ. 2010. Geochemical and geochronological studies of the Alegedayi Ophiolitic Complex and its implication for the evolution of the Chinese Altai. Gondwana Research, 18(2-3):438-454 |
| [83] | Xia B, Chen GW, Wang R and Wang Q. 2008. Seamount volcanism associated with the Xigaze ophiolite, southern Tibet. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32(5-6):396-405 |
| [84] | Xiao WJ, Han CM, Yuan C, Sun M, Lin SF, Chen HL, Li ZL, Li JL and Sun S. 2008. Middle Cambrian to Permian subduction-related accretionary orogenesis of Northern Xinjiang, NW China:Implications for the tectonic evolution of Central Asia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 32(2-4):102-117 |
| [85] | Xiao WJ, Kröner A and Windley BF. 2009. Geodynamic evolution of Central Asia in the paleozoic and mesozoic. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(6):1185-1188 |
| [86] | Xiao WJ, Huang BC, Han CM, Sun S and Li JL. 2010. A review of thewestern part of the western Altaids:A key to understanding the architecture of accretionary orogens. Gondwana Research, 18(2-3):253-273 |
| [87] | Xiao WJ and Santosh M. 2014. The western Central Asian Orogenic Belt:A window to accretionary orogenesis and continental growth. Gondwana Research, 25(4):1429-1444 |
| [88] | Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Sun S, Li JL, Huang BC, Han CM, Yuan C, Sun M and Chen HL. 2015. A tale of amalgamation of three permo-triassic collage systems in central Asia:Oroclines, sutures, and terminal accretion. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 43(1):477-507 |
| [89] | Xu QQ, Ji JQ, Zhao L, Gong JF, Zhou J, He GQ, Zhong DL, Wang JD and Griffiths L. 2013a. Tectonic evolution and continental crust growth of northern Xinjiang in northwestern China:Remnant ocean model. Earth-Science Reviews, 126:178-205 |
| [90] | Xu X, He GQ, Li HQ, Ding TF, Liu XY and Mei SW. 2006. Basic characteristics of the Karamay ophiolitic mélange, Xinjiang and its zircon SHRIMP dating. Geology in China, 33(3):470-475(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [91] | Xu X, Zhou KF and Wang Y. 2010. Study on extinction of the remnant oceanic basin and tectonic setting of West Junggar during Late Paleozoic. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(11):3206-3214(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [92] | Xu Z, Han BF, Ren R, Zhou YZ, Zhang L, Chen JF, Su L, Li XH and Liu DY. 2012. Ultramafic-mafic mélange, island arc and post-collisional intrusions in the Mayile Mountain, West Junggar, China:Implications for Paleozoic intra-oceanic subduction-accretion process. Lithos, 132-133:141-161 |
| [93] | Xu Z, Han BF, Ren R, Zhou YZ and Su L. 2013b. Palaeozoic multiphase magmatism at Barleik Mountain, southern West Junggar, Northwest China:Implications for tectonic evolution of the West Junggar. International Geology Review, 55(5):633-656 |
| [94] | Yan Z, Li JL, Yong Y, Xiao WJ, Wang ZQ and Xiang YS. 2008. Tectonic environment of Ordovician carbonate-cherts in the Shihuigou area, North Qilian orogen. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(10):2384-2394(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [95] | Yang GX, Li YJ, Santosh M, Gu PY, Yang BK, Zhang B, Wang HB, Zhong X and Tong LL. 2012a. A Neoproterozoic seamount in the Paleoasian Ocean:Evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the Mayile ophiolitic mélange in West Junggar, NW China. Lithos, 140-141:53-65 |
| [96] | Yang GX, Li YJ, Santosh M, Yang BK, Yan J, Zhang B and Tong LL. 2012b. Geochronology and geochemistry of basaltic rocks from the Sartuohai ophiolitic mélange, NW China:Implications for a Devonian mantle plume within the Junggar Ocean. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 59:141-155 |
| [97] | Yang GX, Li YJ, Gu PY, Yang BK, Tong LL and Zhang HW. 2012c. Geochronological and geochemical study of the Darbut Ophiolitic Complex in the West Junggar(NW China):Implications for petrogenesis and tectonic evolution. Gondwana Research, 21(4):1037-1049 |
| [98] | Yang GX, Li YJ, Santosh M, Yang BK, Zhang B and Tong LL. 2013. Geochronology and geochemistry of basalts from the Karamay ophiolitic mélange in West Junggar(NW China):Implications for Devonian-Carboniferous intra-oceanic accretionary tectonics of the southern Altaids. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 125(3-4):401-419 |
| [99] | Yang GX, Li YJ, Yang BK, Liu ZW, Zhang HW and Tong LL. 2013a. Petrogenesis of alkaline basalt from the Darbut ophiolitic mélange in West Junggar:The product of a Late Devonian mantle plume? Earth Science Frontiers, 20(3):192-203(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [100] | Yang GX, Li YJ, Yang BK, Liu ZW, Tong LL and Zhang HW. 2013b. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the Mayile ophiolitic mélange in West Junggar and implications for source nature. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(1):303-316(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [101] | Yang GX, Li YJ, Xiao WJ and Tong LL. 2015a. OIB-type rocks within West Junggar ophiolitic mélanges:Evidence for the accretion of seamounts. Earth-Science Reviews, 150:477-496 |
| [102] | Yang GX, Li YJ, Santosh M, Xiao WJ, Yang BK, Tong LL and Zhang SL. 2015b. Alkaline basalts in the Karamay ophiolitic mélange, NW China:A geological, geochemical and geochronological study and implications for geodynamic setting. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113(Part 1):110-125 |
| [103] | Yang GX, Li YJ, Tong LL, Yang BK, Zhang SL, Shen R and Duan FH. 2015. New advance in oceanic island basalts of ophiolitic mélange from the West Junggar. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(2):392-405(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [104] | Yang JS, Dobrzhinetskaya LF, Bai WJ, Fang QS, Robinson PT, Zhang JF and Green Ⅱ HW. 2007. Diamond-and coesite-bearing chromitites from the Luobusa ophiolite, Tibet. Geology, 35(10):875-878 |
| [105] | Yang JS, Robinson PT and Dilek Y. 2014. Diamonds in ophiolites. Elements, 10(2):127-130 |
| [106] | Yang JS, Meng FC, Xu XZ, Robinson PT, Dilek Y, Makeyev AB, Wirth R, Wiedenbeck M and Cliff J. 2015c. Diamonds, native elements and metal alloys from chromitites of the Ray-Iz ophiolite of the Polar Urals. Gondwana Research, 27(2):459-485 |
| [107] | Yin JY, Yuan C, Sun M, Long XP, Zhao GC, Wong KP, Geng HY and Cai KD. 2010. Late Carboniferous high-Mg dioritic dikes in Western Junggar, NW China:Geochemical features, petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Gondwana Research, 17(1):145-152 |
| [108] | Yin JY, Chen W, Yuan C, Yu S, Xiao WJ, Long XP, Li J and Sun JB. 2015. Petrogenesis of Early Carboniferous adakitic dikes, Sawur region, northern West Junggar, NW China:Implications for geodynamic evolution. Gondwana Research, 27(4):1630-1645 |
| [109] | Yuan HL, Wu FY, Gao S, Liu XM, Xu P and Sun DY. 2003. Determination of U-Pb age and rare earth element concentrations of zircons from Cenozoic intrusions in northeastern China by laser ablation ICP-MS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(22):2411-2421 |
| [110] | Zhang C and Huang X. 1992. The ages and tectonic settings of ophiolites in West Junggar, Xinjiang. Geological Review, 38(6):507-524(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [111] | Zhang C, Zhai MG, Allen MB, Saunders AD, Wang GR and Huang X. 1993. Implications of Palaeozoic ophiolites from western Junggar, NW China, for the tectonics of central Asia. Journal of the Geological Society of London, 150(3):551-561 |
| [112] | Zhang JE, Xiao WJ, Han CM, Mao QG, Ao SJ, Guo QQ and Ma C. 2011. A Devonian to Carboniferous intra-oceanic subduction system in western Junggar, NW China. Lithos, 125(1-2):592-606 |
| [113] | Zhang YY and Guo ZJ. 2010. New constraints on formation ages of ophiolites in northern Junggar and comparative study on their connection. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(2):421-430(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [114] | Zhao JH and Zhou MF. 2007. Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic mafic intrusions in the Panzhihua district(Sichuan Province, SW China):Implications for subduction-related metasomatism in the upper mantle. Precambrian Research, 152(1-2):27-47 |
| [115] | Zhou TF, Yuan F, Fan Y, Zhang DY, Cooke D and Zhao GC. 2008. Granites in the Sawuer region of the West Junggar, Xinjiang Province, China:Geochronological and geochemical characteristics and their geodynamic significance. Lithos, 106(3-4):191-206 |
| [116] | Zhu BQ, Wang LS and Wang LX. 1987. Paleozoic Era ophiolite of southwest part in western Junggar, Xinjiang, China. Bull. Xi'an Inst. Geol. Min. Res., Chinese Acad. Geol. Sci.,(17):3-64(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [117] | Zhu DC, Mo XX, Wang LQ, Zhao ZD and Liao ZL. 2008. Hotspot-ridge interaction for the evolution of Neo-Tethys:Insights from the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous magmatism in southern Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(2):225-237(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [118] | Zhu YF and Xu X. 2007. Exsolution texture of two-pyroxenes in lherzolite from Baijiantan ophiolitic mélange, western Junggar, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(5):1075-1086(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [119] | Zhu YF, Xu X, Wei SN, Song B and Guo X. 2007. Geochemistry and tectonic significance of OIB-type pillow basalts in western Mts. of Karamay city(western Junggar), NW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(7):1739-1748(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [120] | Zhu YF, Xu X, Chen B and Xue YX. 2008. Dolomite marble and garnet amphibolite in the ophiolitic mélange in western Junggar:Relics of the Early Paleozoic oceanic crust and its deep subduction. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(12):2767-2777(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [121] | Zhu YF. 2014. Geological evolution and division of giant metallogenic belts in core part of Central Asian Metallogenic Region. Mineral Deposits, 33(3):471-485(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [122] | Zhu YF, Chen B and Qiu T. 2015. Geology and geochemistry of the Baijiantan-Baikouquan ophiolitic mélanges:Implications for geological evolution of West Junggar, Xinjiang, NW China. Geological Magazine, 152(1):41-69 |
| [123] | Rollison HR. 2000. 岩石地球化学. 见:杨学明, 杨晓勇, 陈双喜译. 合肥:中国科学技术大学出版社, 1-275 |
| [124] | 白建科,陈隽璐,闫臻,唐卓,徐学义,李继亮. 2015. 西准噶尔南部玛依勒洋盆开启、闭合时限:来自中泥盆统与下伏地质体之间角度不整合关系证据. 岩石学报,31(1):133-142 |
| [125] | 白文吉, Robinson P, 杨经绥, 周美付, 胡旭峰. 1995. 西准噶尔不同时代蛇绿岩及其构造演化. 岩石学报, 11(增刊):62-72 |
| [126] | 陈博, 朱永峰. 2010. 新疆克拉玛依百口泉蛇绿混杂岩中辉长岩岩石学和地球化学研究. 岩石学报, 26(8):2287-2298 |
| [127] | 陈石, 郭召杰. 2010. 达拉布特蛇绿岩带的时限和属性以及对西准噶尔晚古生代构造演化的讨论. 岩石学报, 26(8):2336-2344 |
| [128] | 陈宣华, 聂兰仕, 丁伟翠, 王学求, 王志宏, 叶宝莹. 2015. 西准噶尔走滑断裂系元素分布特征及其成矿意义. 岩石学报, 31(2):371-387 |
| [129] | 董连慧, 朱志新, 屈迅, 王克卓, 赵同阳. 2010. 新疆蛇绿岩带的分布、特征及研究新进展. 岩石学报, 26(10):2894-2904 |
| [130] | 范裕, 周涛发, 袁峰, 谭绿贵, Cooke D, Meffre S, 杨文平, 何立新. 2007. 新疆西准噶尔地区塔斯特岩体锆石LA-ICPMS年龄及其意义. 岩石学报, 23(8):1901-1908 |
| [131] | 辜平阳, 李永军, 张兵, 佟丽莉, 王军年. 2009. 西准噶尔达尔布特蛇绿岩中辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年. 岩石学报, 25(6):1364-1372 |
| [132] | 郭安林, 张国伟, 孙延贵, 郑健康, 刘晔, 王建其. 2006. 阿尼玛卿蛇绿岩带OIB和MORB的地球化学及空间分布特征:玛积雪山古洋脊热点构造证据. 中国科学(D辑), 36(7):618-629 |
| [133] | 韩宝福, 季建清, 宋彪, 陈立辉, 张磊. 2006. 新疆准噶尔晚古生代陆壳垂向生长(I):后碰撞深成岩浆活动的时限. 岩石学报, 22(5):1077-1086 |
| [134] | 何国琦, 刘建波, 张越迁, 徐新. 2007. 准噶尔盆地西北缘克拉玛依早古生代蛇绿混杂岩带的厘定. 岩石学报, 23(7):1573-1576 |
| [135] | 李红生. 1994. 新疆克尔哈达中志留世放射虫. 微体古生物学报, 11(2):259-272 |
| [136] | 李继亮. 2004. 增生型造山带的基本特征. 地质通报, 23(9-10):947-951 |
| [137] | 李永军, 沈锐, 王冉, 郭少婷, 佟丽莉, 杨高学. 2014. 新疆西准噶尔巴尔努克早石炭世富Nb岛弧玄武岩的发现及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 30(12):3501-3511 |
| [138] | 刘飞, 杨经绥, 陈松永, 梁凤华, 牛晓露, 李兆丽, 连东洋. 2013. 雅鲁藏布江缝合带西段东波蛇绿岩OIB型玄武岩的厘定及其形成环境. 岩石学报, 29(6):1909-1932 |
| [139] | 刘希军,许继峰,王树庆,侯青叶,白正华,雷敏. 2009. 新疆西准噶尔达拉布特蛇绿岩E-MORB型镁铁质岩的地球化学、年代学及其地质意义. 岩石学报,25(6):1373-1389 |
| [140] | 苏玉平, 唐红峰, 侯广顺, 刘丛强. 2006. 新疆西准噶尔达拉布特构造带铝质A型花岗岩的地球化学研究. 地球化学, 35(1):55-67 |
| [141] | 孙书勤, 汪云亮, 张成江. 2003. 玄武岩类岩石大地构造环境的Th、Nb、Zr判别. 地质论评, 49(1):40-47 |
| [142] | 王涛, 王宗起, 闫臻, 闫全人, 张英利, 向忠金. 2009. 南秦岭大堡组奥陶纪洋岛玄武岩的识别及其构造意义:来自地球化学和年代学证据. 岩石学报, 25(12):3241-3250 |
| [143] | 王智琳, 许德如, 吴传军, 付王伟, 王力, 吴俊. 2013. 海南岛晚古生代洋岛玄武岩(OIB型)的发现及地球动力学暗示. 岩石学报, 29(3):875-886 |
| [144] | 魏荣珠. 2010. 新疆西准噶尔玛依勒山枕状熔岩地质特征及大地构造意义. 新疆地质, 28(3):229-235 |
| [145] | 新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产局. 1993. 新疆区域地质志. 北京:地质出版社, 442-504 |
| [146] | 徐新, 何国琦, 李华芹, 丁天府, 刘兴义, 梅绍武. 2006. 克拉玛依蛇绿混杂岩带的基本特征和锆石SHRIMP年龄信息. 中国地质, 33(3):470-475 |
| [147] | 徐新, 周可法, 王煜. 2010. 西准噶尔晚古生代残余洋盆消亡时间与构造背景研究. 岩石学报, 26(11):3206-3214 |
| [148] | 闫臻, 李继亮, 雍拥, 肖文交, 王宗起, 向永生. 2008. 北祁连石灰沟奥陶纪碳酸盐岩-硅质岩形成的构造环境. 岩石学报, 24(10):2384-2394 |
| [149] | 杨高学, 李永军, 杨宝凯, 刘振伟, 张洪伟, 佟丽莉. 2013a. 西准噶尔达尔布特蛇绿混杂岩中碱性玄武岩的成因:晚泥盆世地幔柱的产物?地学前缘, 20(3):192-203 |
| [150] | 杨高学, 李永军, 杨宝凯, 刘振伟, 佟丽莉, 张洪伟. 2013b. 西准噶尔玛依勒蛇绿混杂岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及源区特征. 岩石学报, 29(1):303-316 |
| [151] | 杨高学, 李永军, 佟丽莉, 杨宝凯, 张胜龙, 沈锐, 段丰浩. 2015. 西准噶尔蛇绿混杂岩中洋岛玄武岩研究新进展. 地质学报, 89(2):392-405 |
| [152] | 袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 柳小明, 徐平, 孙德有. 2003. 东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析. 科学通报, 48(14):1511-1520 |
| [153] | 张驰, 黄萱. 1992. 新疆西准噶尔蛇绿岩形成时代和环境的探讨. 地质论评, 38(6):507-524 |
| [154] | 张元元, 郭召杰. 2010. 准噶尔北部蛇绿岩形成时限新证据及其东、西准噶尔蛇绿岩的对比研究. 岩石学报, 26(2):421-430 |
| [155] | 朱宝清, 王来生, 王连晓. 1987. 西准噶尔西南地区古生代蛇绿岩. 中国地质科学院西安地质矿产研究所所刊,(17):3-64 |
| [156] | 朱弟成, 莫宣学, 王立全, 赵志丹, 廖忠礼. 2008. 新特提斯演化的热点与洋脊相互作用:西藏南部晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆作用推论. 岩石学报, 24(2):225-237 |
| [157] | 朱永峰, 徐新. 2007. 西准噶尔白碱滩二辉橄榄岩中两种辉石的出溶结构及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 23(5):1075-1086 |
| [158] | 朱永峰, 徐新, 魏少妮, 宋彪, 郭璇. 2007. 西准噶尔克拉玛依OIB型枕状玄武岩地球化学及其地质意义研究. 岩石学报, 23(7):1739-1748 |
| [159] | 朱永峰, 徐新, 陈博, 薛云兴. 2008. 西准噶尔蛇绿混杂岩中的白云石大理岩和石榴角闪岩:早古生代残余洋壳深俯冲的证据. 岩石学报, 24(12):2767-2777 |
| [160] | 朱永峰. 2014. 中亚成矿域核心区地质演化和巨型成矿带划分. 矿床地质, 33(3):471-485 |
 2016, Vol. 32
2016, Vol. 32