世界上四分之三的铜和十五分之一的金产自于斑岩成矿系统(Sillitoe,2010),97%的大型-超大型斑岩Cu(-Mo,Au)矿床产于岛弧和陆缘弧环境(Sillitoe,1972; Mitchell,1973; Richards,2003; Cooke et al., 2005; 陈华勇和肖兵,2014)。但近年来的大量研究表明,斑岩型矿床还可以产于与俯冲无关的大陆碰撞造山带环境和陆内环境(侯增谦和杨志明,2009; 陈衍景,2013; Stöcklin,1974; Hezarkhani and Williams-Jones, 1998; Hezarkhani, 2006a,b; Zarasv andi et al., 2005,2007; Shafiei et al., 2009; 周涛发等,2008; 毛景文等,2014; Zhou et al., 2015; Hou et al., 2015; Pirajno and Zhou, 2015)。
长江中下游成矿带是我国东部重要铜铁金多金属成矿带,吸引了众多研究者关注。迄今已提出了著名的“玢岩铁矿”(宁芜研究项目编写小组,1978)、“层控矽卡岩型矿床”(常印佛和刘学圭,1983; 常印佛等,1991)和复合叠加成矿(翟裕生等,1992; 常印佛等,2012)等理论。长期以来,该成矿带以层控矽卡岩型矿床(常印佛等,1991)和玢岩型铁矿床(宁芜研究项目编写小组,1978)闻名于世。近年来,随着沙溪、舒家店等大型斑岩型铜金矿床的勘探发现,成矿带中斑岩型矿床的重要性日益提高(周涛发等,2012),已开始引起研究者的重视,但迄今对这些斑岩型矿床尚未进行系统性的总结研究,对其成因也有很大争议,有研究认为成矿带内的斑岩型矿床为陆内环境岩浆活动的产物(侯增谦和杨志明,2009; 吕庆田等,2014; 周涛发等,2008),但也有学者认为它们是古太平洋俯冲环境的产物(吴利仁等,1982; 汪洋等,2004; Ling et al., 2009,2011; Liu et al., 2010; 孙卫东等,2010; 谢建成等,2012; Wu et al., 2012),因此,有必要加强该成矿带斑岩型矿床的成因研究。特别是近年来,长江中下游成矿带浅部矿床基本发现殆尽,资源保障程度逐渐降低,深部找矿是该成矿带未来资源勘查的主要方向,而带内已发现的斑岩型铜(金)矿床具有埋藏较深的特点,因此,综合研究长江中下游成矿带内斑岩型矿床的特征与成因不仅具有重要的科学意义,而且也将促进该类型矿床的找矿突破,开拓整个成矿带深部找矿工作的新局面。
本文在前人研究和作者已有成果(Zhou et al., 2015)的基础上,通过对长江中下游成矿带内的典型斑岩型矿床的地质特征、成岩成矿时代、岩石化学、矿床地球化学和成矿流体特征的进一步总结、研究,初步建立长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床成岩成矿模式,并与世界范围内典型的岩浆环境斑岩型矿床对比,阐明长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床的独特性,进一步丰富陆内环境斑岩型矿床的成矿理论。
2 地质背景
长江中下游成矿带位于扬子板块北缘的长江断裂坳陷带内,北西以襄樊-广济断裂和郯(郯城)-庐(庐江)断裂为界,南东以阳新-常州断裂为界,总体上呈南西狭窄、北东宽阔的“V”字型地带(图 1)。区内的基底为晚太古代-新元古代变质核杂岩构成的崆岭-董岭式基底和部分巨厚海相浊积复理石沉积岩夹海相火山岩以及晚元古代花岗岩组成的江南基底(董树文等,2011),上覆为一套连续的震旦系-早三叠系被动大陆边缘沉积,直到中三叠世进入板内变形阶段,发育巨厚的陆相沉积岩系和火山岩系。
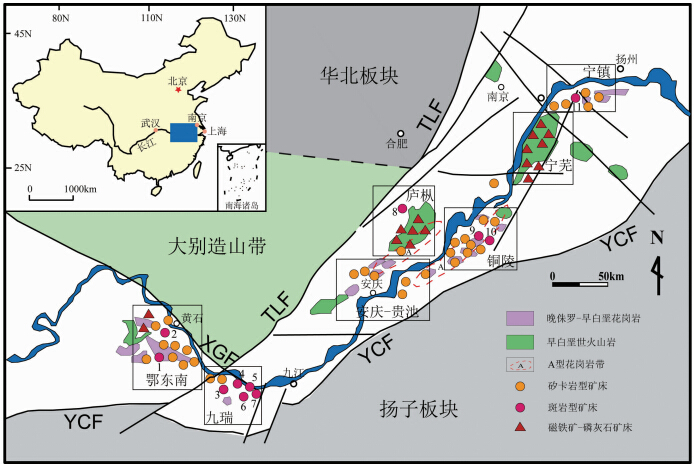 | 图 1 长江中下游成矿带岩浆岩及矿床分布简图(据常印佛等,1991; Mao et al., 2011)红色圆圈代表的斑岩型矿床:1-铜山口铜钼矿床;2-鸡冠嘴铜金矿床;3-丰山洞铜金矿床;4-武山铜钼矿床;5-丁家山铜矿床;6-洋鸡山金矿床;7-城门山铜钼矿床;8-沙溪铜金矿床;9-冬瓜山铜金矿床;10-舒家店铜矿床;11-安基山铜矿床Fig. 1 Sketch Geological map of mgmatic rocks and deposits in the MLYB(modified after Chang et al., 1991; Mao et al., 2011)Red circles with numbers are porphyry deposits: 1-Tongshankou Cu-Mo deposit; 2-Jiguanzui Cu-Au deposit; 3-Fengsh and ong Cu-Au deposit; 4-Wushan Cu-Mo deposit; 5-Dingjiashan Cu deposit; 6-Yangjishan Au deposit; 7-Chengmenshan Cu-Mo deposit; 8-Shaxi Cu-Au deposit; 9-Dongguashan Cu-Au deposit; 10-Shuajiadian Cu deposit; 11-Anjishan Cu deposit |
自晋宁期以来,长期的构造作用、岩浆活动和成矿作用形成了成矿带内断隆区和断凹区的次级构造格局及丰富多样的铁、铜、金多金属等矿床组合,金属矿床计有200余处,集中产于几个各具特点的矿集区中(图 1),自西向东为鄂东南、九瑞、安庆-贵池、庐枞、铜陵、宁芜和宁镇等矿集区,其中,庐枞、宁芜矿集区位于断陷火山盆地区(断凹区),铜陵、安庆-贵池、九瑞、宁镇、鄂东南等矿集区位于次级隆起区(断隆区)。断隆区和断凹区的成岩作用差别十分明显,断隆区岩浆岩为高钾钙碱性岩石组合,由辉石二长闪长岩、闪长岩、石英闪长岩和花岗闪长岩等组成;断凹区侵入岩为高钠钙碱性系列岩石,以辉石闪长岩和二长岩为主;断凹区火山岩为橄榄安粗岩系列岩石,主要为粗安岩、粗面岩、安山岩和玄武岩等,此外,在还出现A型花岗岩和碱性火山岩组合(假白榴石响岩、蓝方石响岩)等(常印佛等,1991; 邢凤鸣和徐祥,1999; 宁芜研究项目编写小组,1978; 毛景文等,2004; 周涛发等, 2008,2011; 范裕等,2008)。
长江中下游地区矿床类型多样(常印佛等,1991; 翟裕生等,1992; Pan and Dong, 1999;唐永成等,1998; 董树文和邱瑞龙,1993; 周涛发等, 2005,2009),其中,由矽卡岩型、斑岩型和玢岩型(磁铁矿-磷灰石型)矿床为主组成的内生铜、铁、金成矿系列是长江中下游成矿带的主要的成矿系列(图 1),与燕山期岩浆作用与流体演化有关,成矿带的成岩成矿特色显著。成矿带内代表性重要斑岩型铜(钼、金)矿床主要有:鄂东南矿集区的铜山口Cu-Mo矿床、鸡冠嘴Cu-Au矿床、九瑞矿集区的城门山Cu-Mo矿床、武山Cu-Mo矿床、丰山洞Cu-Au矿床、丁家山Cu矿和洋鸡山Au矿床、庐枞矿集区外围的沙溪Cu-Au矿床、铜陵矿集区的冬瓜山Cu-Au矿床和舒家店Cu矿床,以及宁镇矿集 区的安基山Cu矿床等(图 1)。 3 斑岩型矿床主要地质特征
本文选取铜山口Cu-Mo矿床、丰山洞Cu-Au矿床、城门山Cu-Mo矿床、沙溪Cu-Au矿床、冬瓜山Cu-Au矿床、舒家店Cu矿床、安基山Cu矿床等代表性的斑岩型矿床,进行成矿带斑岩型矿床地质特征、矿床地球化学特征等综合对比研究(表 1、图 2),可以看出,成矿带内斑岩型矿床具有以下特点:
| 表 1 长江中下游成矿带内典型斑岩型矿床地质-地球化学特征简表 Table 1 Geological and geochemical features of porphyry(-skarn)deposits in the MLYB |
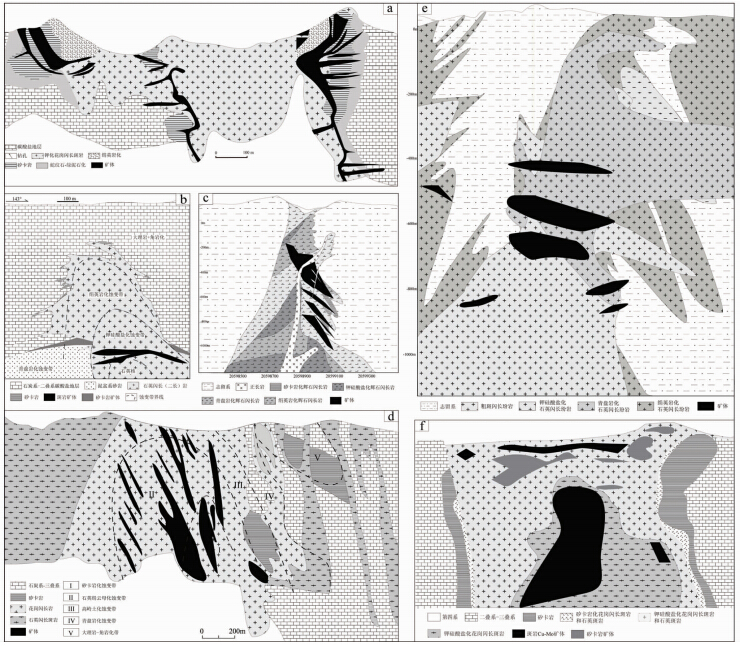 | 图 2 长江中下游成矿带内典型斑岩型矿床地质和矿化蚀变剖面图(a)铜山口矿床地质剖面图(据Anonymous,1984① Anonymous. 1984. Exploration Report of the Tongshankou Cu-Mo Deposit. Huangshi: Geological Team of Southeast Hubei Province,1-109和吕新彪等,1992修改);(b)冬瓜山矿床71线矿化蚀变剖面图(据唐永成等,1998修改);(c)舒家店矿床18线矿化蚀变剖面图;(d)安基山矿床11线地质矿化蚀变剖面图(据李相民等,2009修改);(e)沙溪矿床13号勘探线矿化蚀变剖面图;(f)城门山矿床地质剖面图(据翟裕生等,1992修改)Fig. 2 Cross sections showing geology,mineralization and alteration zoning of porphyry deposits in the MLYB(a)cross-section of the Tongshankou deposit(modified after Lu et al., 1992);(b)cross-section of the Dongguashan deposit Line 71 alteration profile(modified after Tang et al., 1998);(c)cross-section of the Shujiadian deposit Line 18 alteration profile;(d)cross-section of the Anjishan deposit Line 11 alteration profile(modified after Li et al., 2009);(e)cross-section of the Shaxi deposit Line 13 alteration profile;(f)cross-section of the Chengmengshan deposit(modified after Zhai et al., 1992) |
(1)根据是否发育矽卡岩型矿化,成矿带内斑岩型矿床又可分两种类型:斑岩型矿床和斑岩-矽卡岩型矿床。
(2)矿床对于围岩具有明显的选择性,不同性质的围岩对于成矿特点具有直接的影响。斑岩-矽卡岩型矿床的围岩为志留系到三叠系之间的地层,斑岩型矿床的围岩为志留系地层。
(3)成矿带内的斑岩型矿床主要分布于断隆区,在矿田尺度上,常与背斜关系密切,矿化常常发育于背斜核部附近(如沙溪矿床、舒家店矿床),背斜核部常为志留系地层。
(4)含矿斑岩主要为辉石闪长(玢)岩、石英闪长(斑)岩和花岗闪长斑岩。其中,斑岩-矽卡岩型矿床的含矿斑岩主要为高钾钙碱性系列岩石;斑岩型矿床的含矿斑岩主要为钙碱性系列岩石。铜山口、舒家店和安基山含矿斑岩钾含量变化较大,落入钾玄岩区域和低钾系列岩石区域,是钾质蚀变的结果(王世伟等,2011)。
(5)斑岩型矿床发育典型的斑岩型蚀变,蚀变由早期的中心相钾硅酸盐化(钾长石化、黑云母化)和外围的青磐岩化(绿泥石化、绿帘石化)组成,晚期绢英岩化(硅化、绢云母化)常常叠加于两者之上。斑岩-矽卡岩型矿床(如冬瓜山矿床、舒家店矿床)局部发育矽卡岩化(石榴子石化、透辉石化)。矽卡岩型矿化主要分布于岩体与围岩接触带附近,与矽卡岩化关系密切;斑岩型矿化与绢英岩化叠加钾硅酸盐化关系密切。
(6)矿床内发育大量脉体(图 3),成矿早期发育不规则细脉-网脉状(A型脉体;图 3b,c)和板状脉体(B型脉体;图 3a,d-i),成矿晚期发育板状脉体(D型脉体;图 3i-l)(袁峰等,2012; Wang et al., 2015a),其中,钾硅酸盐化蚀变向绢英岩化蚀变转变阶段的脉体为贡献金属量最大的脉体类型。
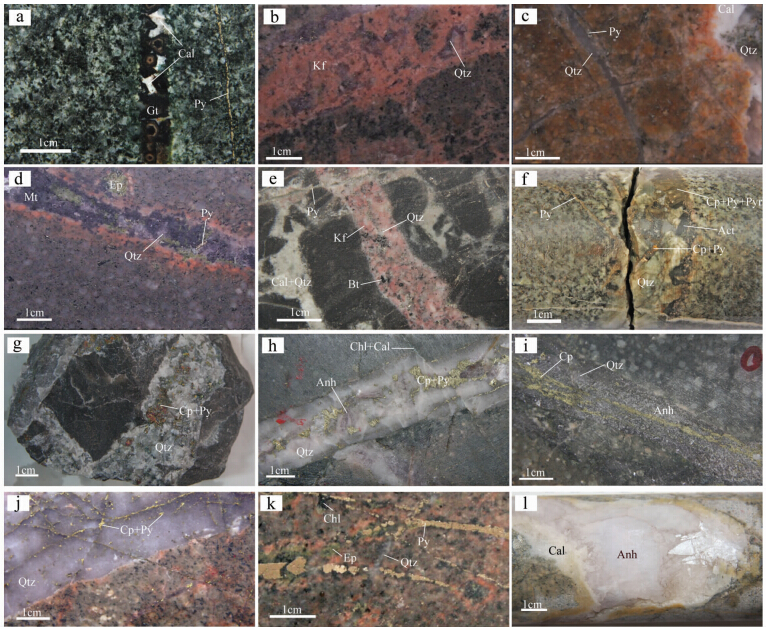 | 图 3 斑岩型矿床的矿化蚀变手标本照片(a)脉状石榴子石矽卡岩化,被晚期碳酸盐化叠加(舒家店);(b)石英-钾长石化(沙溪);(c)石英-黄铁矿脉(黄铁矿呈浸染状分布于脉体中)被晚期石英-碳酸盐买穿切(冬瓜山);(d)石英-磁铁矿脉旁伴随钾长石化,叠加晚期绿帘石化(沙溪);(e)地层中发育石英-钾长石-黑云母脉和石英-碳酸盐脉,两者都被晚期黄铁矿细脉穿切(舒家店);(f)石英-阳起石-黄铜矿-黄铁矿-磁黄铁矿脉,被晚期黄铁矿脉穿切(舒家店);(g)石英-黄铁矿-黄铜矿粗脉,黄铁矿、黄铜矿呈浸染状分布于脉体中(冬瓜山);(h)石英-硬石膏-黄铜矿-黄铁矿粗脉,被晚期绿泥石-碳酸盐细脉穿切(沙溪);(i)石英-硬石膏-黄铜矿脉,黄铜矿在脉体重呈线状分布(沙溪);(j)石英-黄铁矿-黄铜矿脉(黄铁矿、黄铜矿呈浸染状分布于脉体中)被网状黄铜矿-黄铁矿细脉穿切(沙溪);(k)石英-黄铁矿脉被黄铁矿脉穿切,黄铁矿脉旁伴随绿帘石-绿泥石化蚀变(舒家店);(l)晚期硬石膏-碳酸盐粗脉(沙溪)Fig. 3 Vein textures and alteration in porphyry deposits in MLYB(a)garnet vein superimposed on calcite alteration(Shujiadian);(b)quartz-K-feldspar(Shaxi);(c)quartz-pyrite vein(pyrite is disseminated in the vein)is cut by quartz-calcite vein(Dongguashan);(d)quartz-magnetite vein with K-feldspar alteration is superimposed by epidote alteration(Shaxi);(e)quartz-K-feldspar-biotite and quartz-calcite vein in s and stone are cut by pyrite veinlets(Shujiadian);(f)quartz-actinolite-chalcopyrite-pyrite-pyrrhotite vein is cut by later pyrite vein(Shujiadian);(g)quartz-pyrite-chalcopyrite vein, and chalcopyrite and pyrite are disseminated in the vein(Dongguashan);(h)Quartz-anhydrite-chalcopyrite-pyrite vein cut by later chlorite-calcite vein(Shaxi);(i)quartz-anhydrite-chalcopyrite vein; chalcopyrite is continuous in the vein;(j)quartz-pyrite-chalcopyrite vein(chalcopyrite and pyrite are disseminated in the vein)cut by chalcopyrite-pyrite stock vein(Shaxi);(k)quartz-pyrite vein cut by pyrite vein with epidote and chlorite alteration(Shujiadian);(l)anhydrite-calcite vein(Shaxi) |
近年来,对于长江中下游成矿带内的斑岩型矿床已经开展了大量的成岩成矿年代学工作,获得了成矿带中主要岩浆岩的一系列高质量同位素年代数据(Xie et al., 2011; Li et al., 2008,2009,2010; 曾键年等,2013; 吴才来等, 1996,2010; 王世伟等, 2011,2012,2014; 赖小东等,2012; 谢桂青等,2006; Ding et al., 2006; Yang et al., 2011;徐耀明等,2012; 陈志洪等,2011; 李亮和蒋少涌,2009; 陆三明,2007; 徐晓春等,2008; 郭维民等,2013; Wang et al., 2006a; 徐文艺等,1999; 徐兆文等, 2000,2005; 傅斌等,1997; 杨晓勇,2006; 王立本等,1997; 毛景文等,2004; Mao et al., 2006; 蒙义峰等,2004),定年结果(图 4)显示,如果把宁镇矿集区考虑在内,长江中下游成矿带内斑岩的岩浆活动和相关的成矿作用主要发生于149~105Ma之间,可以进一步分为早、中、晚三阶段,对应的时间分别为:149~135Ma、133~125Ma和123~105Ma,其中,早阶段(149~135Ma)和晚阶段(123~105Ma)多为斑岩-矽卡岩型矿化,中阶段(133~125Ma)为典型的斑岩型矿化。Sillitoe and Perelló(2005)对南美安第斯成矿带内的斑岩型矿床研究发现,成矿带内矿床的形成时间相近,同期次斑岩型矿床常呈线状成群分布,可以作为区域寻找斑岩型矿床良好标志。由上述成岩成矿年代学研究可知,长江中下游成矿带内存在三阶段的斑岩型矿床,目前已勘查发现了一批斑岩型矿床,但数量仍然较少(<15个),且主要集中在早阶段,长江中下游成矿带内斑岩型矿床具有良好的找矿潜力。
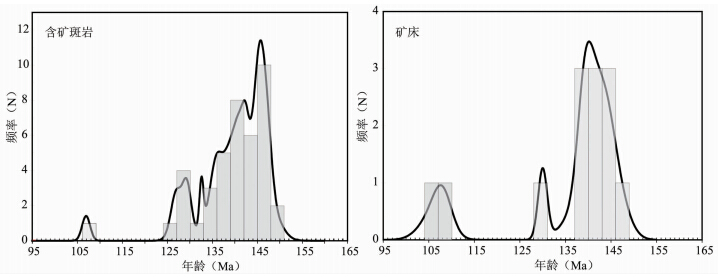 | 图 4 长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床成岩(左图)和成矿年龄(右图)分布图资料来源见文内参考文献,据Zhou et al., 2015Fig. 4 Histogram of the magmatic(left) and metallogenic(right)ages of the MLYB porphyry depositsData source as listed in the text,from Zhou et al., 2015 |
由于长江中下游成矿带晚侏罗-早白垩世时毗邻太平洋板块,一些研究者(吴利仁等,1982; 汪洋等,2004; Ling et al., 2009,2011; Liu et al., 2010; 孙卫东等,2010; 谢建成等,2012; Wu et al., 2012)根据成矿带内存在A型花岗岩和富Nb玄武岩,含矿岩石具有富集大离子亲石元素、亏损高场强元素的特征,以及洋壳更富Cu、Au的理论认识,认为成矿带内含矿岩石是古太平洋俯冲的产物。然而,由本文上述成岩成矿时空格架可知,成矿带内斑岩型矿床形成于149~135Ma、133~125Ma和123~105Ma等三个阶段,且以第一阶段为主,而成矿带内的A型花岗岩主要形成于127~123Ma(周涛发等,2008; 范裕等,2008),粗安质火山岩主要形成于135~123Ma(周涛发等,2011),可见,对应早阶段和晚阶段斑岩型矿床都没有发育同时代的A型花岗岩和粗安质岩石。同时,如果岩石源于被俯冲洋壳流体交代的岩浆,那么岩浆岩应具有岛弧钙碱性岩石的特性,其Sr-Nd同位素应该具有类似于EMⅠ和EMⅡ的特征(Tatsumi et al., 1986; Chauvel et al., 1992; Arculus,1994),这与成矿带内含矿岩石的Sr-Nd组成不同(图 5),因此,成矿带内的含矿斑岩及矿床可能不是洋壳直接俯冲的产物。
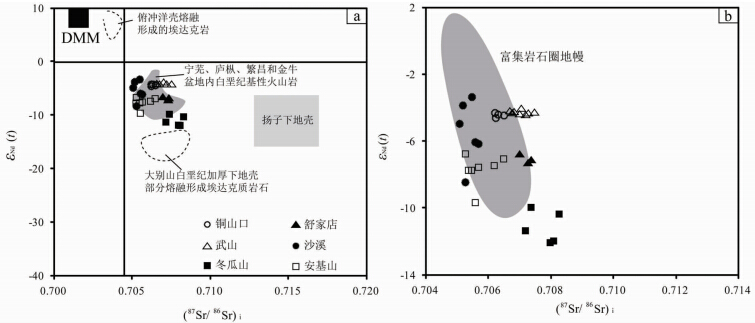 | 图 5 长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床含矿斑岩Sr-Nd同位素组成图解(据Zhou et al., 2015)源自俯冲洋壳的埃达克岩区域据Wang et al.(2006b);白垩纪大别山加厚下地壳部分熔融形成的埃达克岩数据据Wang et al.(2007);庐枞、九瑞和繁昌盆地内白垩纪基性火山岩数据来自Wang et al.(2006a)、赵振华和涂光炽(2003)、Xie et al.(2011)、闫峻等(2005);富集地幔数据来自Xie et al.(2011);样品数据来自Li et al.(2008,2013)、蒋少涌等(2008)、王强等(2003)、Wang et al.(2006a)、赵振华和涂光炽(2003)、Xu et al.(2002)和作者未发表资料Fig. 5 Sr-Nd isotope diagrams for the MLYB porphyry deposits(after Zhou et al., 2015)The field for Cenozoic adakites attributed to melting of subducting oceanic crust is after Wang et al.(2006b). Data for Cretaceous adakitic granites in the Dabie Orogen are after Wang et al.(2007). Mafic volcanic data from the Luzong,Jinniu and Fanchang volcanic basins from Zhao et al.(2003),Yan et al.(2005),Wang et al.(2006a) and Xie et al.(2011). Data of enriched mantle from Xie et al.(2011). Data source from Wang et al.(2003,2006a),Zhao et al.(2003),Jiang et al.(2008),Li et al.(2008,2013),Xu et al.(2002) and our unpublished data |
在Sr/Y-Y、La/Yb-Yb的地球化学判别图解上,长江中下游成矿带含矿斑岩常落入埃达克岩范围,即研究区含矿岩体具有与埃达克岩类似的成分特征,如高Sr/Y和La/Yb等(Mao et al., 2011)。长江中下游成矿带内含矿斑岩的Sr-Nd同位素组成明显不同于俯冲洋壳熔融形成的埃达克岩(图 5a),这些含矿斑岩不是O型埃达克岩,类似于C型埃达克岩(张旗等, 2003,2004)。关于含矿斑岩的这种C型埃达克岩地球化学特征,有研究认为是陆内拆沉或加厚古老下陆壳部分熔融而成的产物(张旗等,2001; 王强等,2003; Wang et al., 2006a,b; Xu et al., 2002; 侯增谦等,2007; 侯增谦和杨志明,2009),是由于岩浆源区存在石榴子石或部分角闪石残留、无斜长石残留的结果。Moyen(2009)研究指出,与石榴子石平衡的熔体往往会具有陡倾的HREE配分模式,具有高Yb/Lu(8~10)和Y/Yb(明显大于10)比值的特征。长江中下游成矿带内的含矿斑岩具有亏损重稀土、富集轻稀土的特征(周涛发等, 2005,2009; Mao et al., 2011),但其Yb/Lu(4.4~8.0)和Y/Yb(6.6~15.9)比值相对较低,因此,本文作者认为成矿带内的含矿斑岩可能不是加厚或拆沉下地壳部分熔融的直接产物。
近年来,也有学者认为该区含矿斑岩为岩浆混合的结果(常印佛等,1991; 邓晋福和吴宗絮,2001; 陈江峰等,1993; 唐永成等,1998; 周涛发等,2000; 秦新龙,2007; 杨小男等,2007; 杜杨松等,2010; Wang et al., 2015b),是由地幔和下地壳物质熔融形成的岩浆混合而成(吴才来等, 2003,2008; 徐夕生等,2004; 郭维民等,2013),其中,一个端元为地幔的基性岩浆,另一个端元为地壳部分熔融的酸性岩浆。由研究区含矿斑岩的Sr-Nd同位素比值(图 5)可知,大部分含矿斑岩的Sr-Nd同位素比值落于富集地幔区域或其与加厚下地壳之间的过渡区域(图 5),指示这些含矿斑岩可能为源自富集地幔的岩浆和加厚下地壳部分熔融形成岩浆混合的产物。长江中下游成矿带内发育与斑岩矿床同时代的基性岩(王彦斌等,2004; Xie et al., 2011; 周涛发等,2011)和基性包体(徐夕生等,2004; Xu et al., 2002)都表明,成矿带内中酸性岩浆侵位过程中伴随有一些基性岩浆的活动,这些都进一步支持可能存在岩浆混合作用。同时,这些含矿斑岩的微量元素和稀土元素特征与长江中下游成矿带火山岩盆地内的基性火山岩相似(郭维民等,2013),都表现为亏损重稀土和高场强元素、富集轻稀土和大离子亲石元素,具有富集地幔的特征。重稀土亏损特征可能是由于岩浆源区存在石榴子石导致的,Ba、Sr等元素的相对较亏损可能是由于存在斜长石的残留或分离结晶导致的,因此,研究区含矿斑岩的埃达克质岩石地球化学特征可能是不同性质的岩浆(酸性+基性)混合造成的。
斑岩型矿床的形成需要富水(>4%; Richards,2011)、富S(>1000×10-6; Chambefort et al., 2008)和高氧逸度(>FMQ+1.3~2; Mungall,2002; Lee et al., 2012)的岩浆。有学者将与俯冲无关的构造环境下的富水岩浆归结于角闪石的分解(Hou et al., 2013a)或残余弧岩浆(Richards,2009)引起的。对于角闪石等含水矿物分解是否能使长英质岩浆富水(>4%)还没有得到实验证实(Hou et al., 2013b),迄今在长江中下游成矿带内也没有发现有中生代弧岩浆的残留,因此,可排除成矿带内含矿岩浆源区富水是角闪石分解或残余弧岩浆造成的。另外,近来有研究指出,基性岩浆的混入可以使混合岩浆富水(Hou et al., 2013b; Ma et al., 2013),因此,含矿岩浆源区富水可能为基性岩浆混入酸性岩浆引起的。在与俯冲无关的构造环境,下地壳并不能提供足够的S和金属(Cameron,1989),由于在变质过程中,金属元素都被释放的流体带走,导致下地壳亏损金属元素(Cameron,1989)。实验岩石学研究证明,长英质岩浆具有比较低的S和金属浓度(Wallace and Carmichael, 1992; Hattori and Keith, 2001; Mungall,2002),因此,单纯的下地壳部分熔融形成的长英质岩浆并不具有提供成矿所需大量S和金属(如Cu、Au)的能力。但是,底侵的或混入到长英质岩浆的镁铁质岩浆具有提供S和Cu(Au)的可能性(Hou et al., 2013b),这已经在Mount Pinatubo和Bingham斑岩矿床的研究中得到证实(Hattori,1993; Keith et al., 1997; Hattori and Keith, 2001),并且得到了越来越多矿床研究成果的支持(如德兴斑岩矿床: Hou et al., 2013b; Aolunhua斑岩矿床: Ma et al., 2013; 冬瓜山矿床: Wang et al., 2015b)。因此,长江中下游成矿带内斑岩型矿床的S和金属(Cu、Au)等可能主要来自基性岩浆。
综上可知,长江中下游成矿带内含矿斑岩可能为源自富集地幔的基性岩浆和加厚下地壳部分熔融的酸性岩浆混合的产物,源自富集地幔的基性岩浆对成矿具有至关重要的作用,它的混入使得混合岩浆富水、硫和金属(Cu、Au)等。 4.3 成岩成矿浅部过程
成岩成矿浅部过程主要反映在浅部构造、岩浆岩、围岩和浅部流体等对成矿流体系统的演化和矿质沉淀所产生的重要影响,是成矿流体系统演化最终能否成矿的关键。常印佛等(1991)曾总结出长江中下游成矿带“一断裂、二序列、三环境、四层位”的区域控矿基本规律。随着富水、硫和金属(Cu、Au)的中酸性岩浆沿长江深断裂带上升侵入到地壳浅部,不断冷凝结晶,浅部构造的性质控制了岩浆在地壳浅部的定位及形态。王庆飞(2005)通过对铜陵矿集区构造、岩浆和矿点的分形统计分析显示盖层褶皱系是岩浆就位的主要场所,北东向高角度逆断层及基底断层是浅部岩浆输运的主要通道,这与成矿带内含矿岩体主要分布于背斜核部附近的地质事实一致。中阶段的沙溪矿床位于长江中下游庐枞盆地的西北外缘(罗河断裂的外部),而罗河断裂为郯庐断裂带的分支(董树文等,2009),这可能表明中阶段沙溪矿床是长江断裂和郯庐断裂联合控制的产物。
斑岩体的浅成-超浅成侵位是引发成矿的重要前提,因为浅成-超浅成侵位是引发中酸性岩浆中挥发相达到饱和或过饱和的主要机制(芮宗瑶等,1984)。当中酸性岩浆中挥发相达到饱和或过饱和时,会出溶大量的岩浆热液,这些流体为斑岩型矿床的形成提供大量的矿化和蚀变的物质。根据Ohmoto and Rye(1979)研究,由上地幔或下地壳物质部分熔融产生的未受污染的酸性火成岩岩浆的δ34S值为-3‰~+3‰之间,从中分离出来的岩浆热液的δ34S值为-3‰~+7‰之间。长江中下游成矿带中斑岩型矿床中金属硫化物的硫同位素组成在δ34S值为-2.6‰~+10.2‰之间(图 6、表 1),主要属于岩浆热液范围。成矿带中部分矿床虽然受到含膏盐地层硫的影响(周涛发等, 2000,2002),但斑岩型矿床的成矿物质(如铜、金等)主要来自岩浆热液。前人(吕新彪等,1992; 方福康,2012; 徐晓春等,2011; 傅斌等,1996; Lan et al., 2009; 黄恩邦等,1990; 张建,1992)关于矿床的氧同位素研究也显示,成矿带内斑岩矿床中成矿流体的氧同位素介于岩浆水和大气水之间(图 7、表 1),也表明为两种流体演化的产物。顾连兴等(2002)通过总结研究长江中下游成矿带内成矿流体特征指出,成矿带内斑岩型矿床早期流体主要为高温(>440℃)、高盐度(52%~58% NaCleqv)的岩浆热液流体,并认为这种流体既可能是岩浆直接出溶,也可能是早期流体沸腾的产物。判定成矿流体是否沸腾可通过包裹体的研究工作得到判定,前人对成矿带内斑岩型矿床内包裹体的研究发现(沙溪矿床: 傅斌等,1997; 城门山矿床: 方福康,2012),岩浆直接出溶产生的是中低盐度的超临界流体,随后上升发生沸腾作用,从而形成高温、高盐度流体相和高温、低密度、低盐度富气相流体相。其中,高温、高盐度流体对运移成矿物质和引发早期矿化和蚀变至关重要。
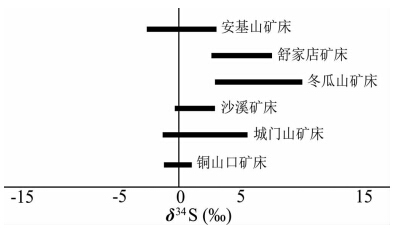 | 图 6 长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床硫同位素组成(据Zhou et al., 2015修改)数据来自周涛发等(2000,2002)、吕新彪等(1992)、赵瑞等(1985)、黄恩邦等(1990)、孟良义等(1988)、席明杰(2009)、方福康(2012)、徐晓春等(2010,2011)、傅斌等(1996)、Lan et al.(2009)、张建(1992)、Wang et al.(2015a)Fig. 6 Sulfur isotopes from ore-bearing porphyries from the MLYB(modified after Zhou et al., 2015)Data from Zhou et al.(1996,2000),Zhao et al.(1985),Meng et al.(1988),Huang et al.(1990),Lu et al.(1992),Zhang(1992),Fu et al.(1996),Lan et al.(2009),Xu et al.(2011),Fang(2012) and Wang et al.(2015a) |
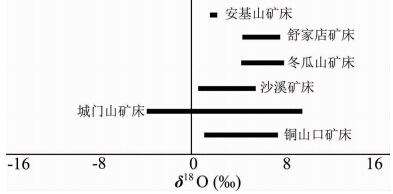 | 图 7 长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床氧同位素组成(据Zhou et al., 2015修改)数据来自吕新彪等(1992)、方福康(2012)、徐晓春等(2011)、傅斌等(1996)、Lan et al.(2009)、黄恩邦等(1990)、张建(1992)和作者未出版资料等Fig. 7 Oxygen isotopes from ore-bearing porphyries from the MLYB(modified after Zhou et al., 2015)Data from Huang et al.(1990),Lu et al.(1992),Zhang(1992),Fu et al.(1996),Xi(2009),Lan et al.(2009),Xu et al.,(2011),Fang(2012),our unpublished data |
随着高温、高盐度流体向上不断运移,会与成矿带中不同时代的围岩不断发生水-岩作用,或与浅部流体发生混合,形成一系列斑岩型矿化和蚀变(华仁民,1994)。根据前人工作(吕新彪等,1992; 周涛发等, 2000,2002; 方福康,2012; 徐晓春等,2011; 傅斌等,1996),形成早期矽卡岩化、钾硅酸盐化和青磐岩化的矿化蚀变的流体主要为岩浆热液,而形成绢英岩化的流体主要为大气降水。对于斑岩型矿床成矿物质的运移沉淀机制,傅斌等(1997)通过对沙溪矿床成矿流体研究认为,大气降水的混入,引起成矿流体性质的改变是导致成矿物质沉淀的主要原因。徐晓春等(2011)通过对冬瓜山矿床流体包裹体地球化学研究,认为矿化蚀变流体中的铜主要以CuCl2-和CuCl-络合物形式运移,铜的卸载和沉淀受温度、pH值、fO2和fS2等因素的控制。方福康(2012)通过对城门山矿床包裹体研究认为,矿床的成矿流体两次沸腾作用导致的温度突降是成矿物质发生沉淀富集的主要因素。可见,长江中下游成矿带内斑岩型矿床中成矿物质的沉淀机制可能有多重因素不同,这是造成斑岩型矿床矿体类型和位置多样性(如接触带内的矽卡岩矿体和岩体内部的斑岩型矿体)的重要原因。 4.4 成矿模式
多年来,众多研究者一直致力于长江中下游成矿带成岩成矿构造背景的探讨,主要分歧在于古太平洋俯冲对于本区的影响。有学者认为古太平洋板片俯冲不仅是控制长江中下游成矿带内燕山期成岩成矿作用的主要动力学因素,也是成岩成矿物质来源的提供者(吴利仁等,1982; 汪洋等,2004; Ling et al., 2009,2011; Liu et al., 2010; 孙卫东等,2010; 谢建成等,2012; Wu et al., 2012; Mao et al., 2011; Li et al., 2013),但另有很多研究却认为,古太平洋板块对包括长江中下游成矿带在内的中国东部燕山期大规模成岩成矿作用的影响主要是动力学机制上的远程力场效应,而不是直接提供成岩成矿物质(侯增谦和杨志明,2009; 常印佛等,1991; 吴言昌等,1999; 吕庆田等,2004; 周涛发等, 2008,2011)。在本文关于成岩成矿深部过程的讨论中已初步排除长江中下游成矿带内燕山期成岩成矿为古太平洋板片俯冲直接作用产物的可能性,但不能排除古太平洋板片远程效应的影响。吕庆田等(2014)通过对长江中下游成矿带开展深部地球物理探测研究发现,从中侏罗世开始,区域构造体制逐渐由特提斯构造域向滨太平洋构造域转换,并逐渐受控于古太平洋板块向华南大陆之下低角度NW向俯冲的远程应力体系,造成长江中下游成矿带发生强烈的陆内构造运动或造山运动(吕庆田等,2014),受华北板块和大别地块的阻挡,长江中下游成矿带的地壳发生强烈的变形,上下地壳拆离,上地壳发生紧闭褶皱、冲断或推覆构造,下地壳和岩石圈地幔发生陆内俯冲,使岩石圈加厚(>100km);晚侏罗世或早白垩世开始,太平洋板块俯冲应力减弱诱发增厚的岩石圈因下地壳发生榴辉岩化使密度反转处于不稳定状态,从而导致岩石圈拆沉等一系列深部过程,继而导致燕山期岩浆作用和成矿作用作用的发生。因此,古太平洋俯冲的远程效应可能为长江中下游成矿带燕山期岩浆活动和成矿作用提供了动力,触发了深部壳幔作用,进而导致岩浆作用和热液成矿作用。
综上所述,长江中下游成矿带斑岩(-矽卡岩)矿床的形成大致经历了如下过程(图 8,Zhou et al,2015):燕山早期开始,长江中下游成矿带由特提斯构造体系向古太平洋构造体系转换,古太平洋NW向俯冲引起的远程挤压使得包括长江中下游地区在内的中国东部产生陆内造山运动,岩石圈加厚,之后随着挤压减弱或方向改变导致富集岩石圈地幔的拆沉和软流圈物质上涌,并引起富集岩石圈地幔发生部分熔融形成基性岩浆,这些基性岩浆上升底侵到下地壳底部,引起下地壳部分熔融形成深部岩浆房。源自富集岩石圈地幔的富含成矿物质、矿化剂及水的基性岩浆上升侵入到深部岩浆房中并发生岩浆混合作用,形成具有埃达克岩地球化学特征的含矿岩浆,并继续上升并侵入到地壳浅部的背斜核部附近志留系至三叠系砂岩或碳酸盐地层中,通过热液系统的水岩作用进一步演化形成长江中下游成矿带三阶段斑岩(-矽卡岩)型铜金钼矿床。
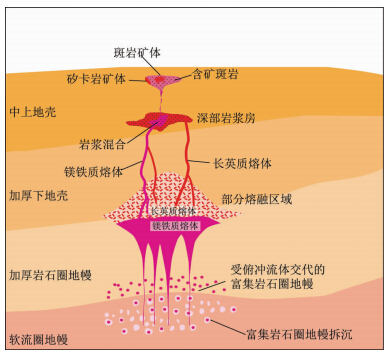 | 图 8 长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床成岩成矿模式示意图(据Zhou et al., 2015) Fig. 8 Schematic diagram of the metallogeny of the MLYB(after Zhou et al., 2015) |
为了进一步明确陆内环境的斑岩型矿床与岩浆弧(陆缘弧和岛弧)环境的斑岩型矿床不同之处,将长江中下游成矿带内的斑岩型矿床与陆缘弧环境(岛弧和陆缘弧)斑岩型矿床(美国西部Bingham Canyon矿床、安第斯山中部Bajo de la Alumbrera矿床)、岛弧环境斑岩型矿床(巴布亚新几内亚Panguna矿床、印度尼西亚Batu Hijau矿床)的斑岩型矿床(表 1)进行对比,可见:
(1)岩浆弧环境的斑岩型矿床常呈线状排列产于俯冲带之上,成矿带平行于造山带且垂直于俯冲带分布(Sillitoe,2010);长江中下游成矿带内的斑岩型矿床则沿长江断裂分布,远离俯冲带,且与古太平洋板块俯冲方向平行或斜交。
(2)岩浆弧环境的斑岩成矿空间上常常伴随有钙碱性或碱性中酸性火山岩(Sillitoe,1973),这些火山岩喷发一般早于斑岩系统约0.5~3Ma,如在Bingham(Waite et al., 1997),Farallón Negro(Sasso and Clark, 1998; Halter et al., 2004),Yerington(Dilles and Wright, 1988; Dilles and Proffett, 1995),Tampakan(Rohrlach and Loucks, 2005)和Yanacocha(Longo and Teal, 2005)等矿床。长江中下游成矿带内并未见与主要(早阶段)斑岩型矿床时代稍早或同期火山岩。
(3)两种环境斑岩矿床的围岩性质各异,显示斑岩型矿床对围岩不具明显的选择性,如岩浆弧环境的围岩常为火山沉积岩,而长江中下游成矿带等陆内环境的斑岩矿床的围岩为砂岩(如:沙溪矿床)和碳酸盐(如:铜山口矿床),因此,后者的斑岩型矿化常与矽卡岩型矿化伴随。
(4)两种环境下各类斑岩型矿床的含矿斑岩主要为钙碱性岩石系列,其中陆缘弧环境的含矿斑岩主要为钙碱性系列,少量为高钾钙碱性系列,岩性以花岗闪长岩和石英二长岩为主(Singer et al., 2005);岛弧环境的含矿斑岩通常为典型的钙碱性系列岩石,岩性以石英闪长岩为主,少数为花岗闪长岩、石英二长岩和正长岩(Misra,2000);长江中下游成矿带含矿斑岩主要为高钾钙碱性系列岩石。
(5)岩浆弧环境的斑岩型矿床的含矿斑岩通常被认为是洋壳流体交代的地幔楔部分熔融(Richards, 2003,2005)形成的;长江中下游成矿带内斑岩型矿床的含矿斑岩可能为源自富集地幔的岩浆和加厚下地壳部分熔融的岩浆混合的产物。
(6)长江中下游成矿带内斑岩型矿床中金属矿物主要有黄铁矿、黄铜矿、磁黄铁矿和斑铜矿,其中,磁黄铁矿常与矽卡岩化关系密切,磁黄铁矿的发育可能说明了围岩的还原性(Kósaka and Wakita, 1978; Perelló et al., 2003),这与岩浆弧环境的斑岩型矿床一致(Sillitoe,2010)。长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床内发育的脉体类型(图 3)与岩浆弧环境的斑岩型矿床基本一致,但各类脉体的比例不尽相同,矿床内贡献金属量最大的脉体类型也不完全相同。岩浆弧环境中贡献金属量最大的脉体常为钾硅酸盐化阶段的脉体,而长江中下游成矿带内的斑岩型矿床中贡献最大的脉体为钾硅酸盐化向绢英岩化过渡阶段的脉体(袁峰等,2012)。
(7)长江中下游成矿带内斑岩型矿床的蚀变类型及蚀变分带与岩浆弧环境的斑岩型矿床基本一致,但长江中下游成矿带内的斑岩型矿床常常不发育浅部的泥化岩帽(advanced argillic liithocaps)以及浅部的高-中硫型矿化蚀变系统。沙溪矿床和舒家店矿床等长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床围岩地层中蚀变不太发育,并常常以脉体的形式产出,而岩浆弧环境斑岩型矿床的围岩常为火山岩和火山沉积岩,后者相对较易蚀变。
(8)不同环境下的斑岩型矿床都是岩浆热液成矿系统演化的产物。岩浆弧环境的斑岩型矿床的成矿物质主要源自俯冲的大洋板片,由大洋板片脱水而将大量H2O、S、Cl和金属输送到地幔楔(Tatsumi et al., 1986; De Hoog et al., 2001; Sillitoe,2010; Richards,2003),含矿岩浆具有形成斑岩型矿床的良好能力;长江中下游成矿带内斑岩型矿床的成矿物质可能主要来自源自富集地幔中产生的基性岩浆。 5 结论
(1)长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床的成岩成矿作用主要形成于149~105Ma之间,主要产于断隆区,可以分为早、中、晚三个阶段,时间分别为149~135Ma、133~125Ma和123~105Ma。本区斑岩型矿床都具有良好的找寻潜力。
(2)长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床的含矿斑岩为高钾钙碱性-钙碱性系列岩石,具有埃达克岩地球化学特征,为陆内源自富集地幔的基性岩浆和加厚下地壳部分熔融的中酸性岩浆混合的产物。源自富集地幔的基性岩浆对成矿具有至关重要的作用,它的混入使得混合岩浆富含水、硫和金属(Cu、Au)等。
(3)长江中下游成矿带斑岩型矿床与岩浆弧环境斑岩型矿床地质特征基本一致,但主要的矿化脉体类型不同,浅部高级泥化岩帽(advanced argillic liithocaps)以及浅部的高-中硫矿化蚀变系统不发育,含矿岩浆源区性质和成矿物质来源差异显著。
致谢 本文的研究工作得到了唐永成、董树文、毛景文、吕庆田、华仁民、邢光福和李建设等专家的指导和帮助;研究工作还得到了铜陵有色金属(集团)公司科技项目的支持。野外工作得到了铜陵有色金属(集团)公司、安徽省地质矿产勘查局327地质队、鄂东南地质大队、华东有色地质勘查研究院和华东冶金地质勘查研究院等单位的大力支持。在此一并表示衷心感谢!| [1] | Arculus RJ. 1994. Aspects of magma genesis in arcs. Lithos, 33(1-3):189-208 |
| [2] | Cameron EM. 1989. Scouring of gold from the lower crust. Geology, 17(1):26-29 |
| [3] | Chambefort I, Dilles JH and Kent AJR. 2008. Anhydrite-bearing andesite and dacite as a source for sulfur in magmatic-hydrothermal mineral deposits. Geology, 36(9):719-722 |
| [4] | Chang YF and Liu XG. 1983. On strate-bound skarn deposits. Mineral Deposits, 2(1):11-20(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [5] | Chang YF, Liu XP and Wu YC. 1991. The Copper-Iron Belt of the Lower and Middle Reaches of the Changjiang River. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-379(in Chinese) |
| [6] | Chang YF, Zhou TF and Fan Y. 2012. Polygenetic compound mineralization and tectonic evolution:Study in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(10):3067-3075(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [7] | Chauvel C, Hofmann AW and Vidal P. 1992. HIMU-EM:The French Polynesian connection. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 110(1-4):99-119 |
| [8] | Chen HY and Xiao B. 2014. Metallogenesis of subduction zone:The progress and future. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(5):13-22(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Chen JF, Zhou TX, Li XM, Foland KA, Huang CY and Lu W. 1993. Sr and Nd isotopic constraints on source regions of the intermediate and acid intrusions from southern Anhui Province. Geochimica,(3):261-268(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Chen YJ. 2013. The development of continental collision metallogeny and its application. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(1):1-17(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | Chen ZH, Xing GF, Guo KY, Zeng Y, Kuang FX, He ZY, Ke X, Yu MG, Zhao XL and Zhang Y. 2011. Zircon U-Pb ages of ore-bearing granitic bodies in northern Jiujiang-Ruichang metallogenic district of the mineralization belt of the Middle-Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River, and its geological significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(7):1146-1158(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] | Chu GZ. 2003. Metallogenic system of Shizishan Cu-Au ore-field in Tongling area and its prospecting significances. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-141(in Chinese) |
| [13] | Cooke DR, Hollings P and Walshe JL. 2005. Giant porphyry deposits:Characteristics, distribution, and tectonic controls. Economic Geology, 100(5):801-818 |
| [14] | De Hoog JCM, Mason PRD and Van Bergen MJ. 2001. Sulfur and chalcophile element s in subduction zones:Constraints from a laser ablation ICP-MS study of melt inclusions from Galunggung Volcano, Indonesia. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(18):3147-3164 |
| [15] | Deng JF and Wu ZX. 2001. Lithospheric thinning event in the Lower Yangtze Craton and Cu-Fe metallogenic belt in the Middle and Lower Yangtze River Reaches. Geology of Anhui, 11(2):86-91(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | Dilles JH and Wright JE. 1988. The chronology of early Mesozoic arc magmatism in the Yerington district of western Nevada and its regional implications. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 100(5):644-652 |
| [17] | Dilles JH and Proffett JM. 1995. Metallogensis of the Yerington batholith, Nevada. Arizona Geological Society Digest, 20:306-315 |
| [18] | Ding X, Jiang SY, Zhao KD, Nakamura E, Kobayashi K, Ni P, Gu LX and Jiang YH. 2006. In-situ U-Pb SIMS dating and trace element(EMPA) composition of zircon from a granodiorite porphyry in the Wushan copper deposit, China. Mineralogy and Petrology, 86(1-2):29-44 |
| [19] | Dong SW and Qiu RL. 1993. Tectonism and Magmatic Activity of Anqing-Yueshan Area, Anhui Province. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-158(in Chinese) |
| [20] | Dong SW, Gao R, Lü QT, Zhang JS, Zhang RH, Xue HM, Wu CL, Lu ZW and Ma LC. 2009. Deep structure and ore-forming in Lujiang-Zongyang Ore Concentrated Area. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 30(3):279-284(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Dong SW, Ma LC, Liu G, Xue HM, Shi W and Li JH. 2011. On dynamics of the metallogenic belt of Middle-Lower Reaches of Yangtze River, eastern China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(5):612-625(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [22] | Du YS, Qin XL and Cao Y. 2010. Sulfide and oxide inclusions in xenoliths and host rocks of Tongling area, Anhui Province. Mineral Deposits, 29(1):71-84(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Fan Y, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Qian CC, Lu SM and Cooke D. 2008. LA-ICP MS zircon U-Pb ages of the A-type granits in the Lu-Zong(Lujiang-Zongyang) area and their significances. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8):1715-1724(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Fang FK. 2012. Studies on the fluid inclusions of the Chengmenshan porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, Jiangxi Province. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-61(in Chinese with English summary) |
| [25] | Fu B, Ren QJ and Hu WX. 1996. Evolution and distribution of hydrothermal fluids in the Shaxi porphyry copper deposit, Anhui Province. Mineral Deposits, 15(1):23-33(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Fu B, Ren QJ, Xing FM, Xu ZW, Hu WX and Zheng YF. 1997. 40Ar-39Ar dating of copper(gold)-bearing porphyry in Shaxi, Anhui Province and its geological significance. Geological Review, 43(3):310-316(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Gu LX, Chen PR, Ni P, Xu ZW, Xiao XJ, Qiu JS, Zhang ZZ and Zhang GH. 2002. Comparative research on ore forming fluids for the main types of hydrothermal copper gold deposits in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Journal of Nanjing University(Natural Sciences), 38(3):392-407(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Guo WM, Lu JJ, Jiang SY, Zhang RQ and Zhao ZJ. 2013. Chronology, Hf isotopes, geochemistry, and petrogenesis of the magmatic rocks in the Shizishan ore field of Tongling, Anhui Province. Science China(Earth Sciences), 56(6):993-1013 |
| [29] | Halter WE, Bain N, Becker K, Heinrich CA, Landtwing M, VonQuadt A, Clark AH, Sasso AM, Bissig T and Tosdal RM. 2004. From andesitic volcanism to the formation of a porphyry Cu-Au mineralizing magma chamber:The Farallón Negro Volcanic Complex, northwestern Argentina. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 136(1-2):1-30 |
| [30] | Hattori K. 1993. High-sulfur magma, a product of fluid discharge from underlying mafic magma:Evidence from Mount Pinatubo, Philippines. Geology, 21(12):1083-1086 |
| [31] | Hattori K and Keith JD. 2001. Contribution of mafic melt to porphyry copper mineralization:Evidence from Mount Pinatubo, Philippines, and Bingham Canyon, Utah, USA. Mineralium Deposita, 36(8):799-806 |
| [32] | Hezarkhani A and Williams-Jones AE. 1998. Controls of alteration and mineralization in the Sungun porphyry copper deposit, Iran:Evidence from fluid inclusions and stable isotopes. Economic Geology, 93(5):651-670 |
| [33] | Hezarkhani A. 2006a. Hydrothermal evolution of the Sar-Cheshmeh porphyry Cu-Mo deposit, Iran:Evidence from fluid inclusions. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 28(4-6):409-422 |
| [34] | Hezarkhani A. 2006b. Petrology of the intrusive rocks within the Sungun porphyry copper deposit, Azerbaijan, Iran. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 27(3):326-340 |
| [35] | Hou ZQ, Pan XF, Yang ZM and Qu XM. 2007. Porphyry Cu-(Mo-Au) deposits no related to oceanic-slab subduction:Examples from Chinese porphyry deposits in continental settings. Geoscience, 21(2):332-351(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [36] | Hou ZQ and Yang ZM. 2009. Porphyry deposits in continental settings of China:Geological characteristics, magmatic-hydrothermal system, and metallogenic model. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(12):1779-1817(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [37] | Hou ZQ, Pan XF, Li QY, Yang ZM and Song YC. 2013a. The giant Dexing porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposit in East China:Product of melting of juvenile lower crust in an intracontinental setting. Mineralium Deposita, 48(8):1019-1045 |
| [38] | Hou ZQ, Zheng YC, Yang ZM, Rui ZY, Zhao ZD, Jiang SH, Qu XM and Sun QZ. 2013b. Contribution of mantle components within juvenile lower-crust to collisional zone porphyry Cu systems in Tibet. Mineralium Deposita, 48(2):173-192 |
| [39] | Hou ZQ, Yang ZM, Lu YJ, Kemp A, Zheng YC, Li QY, Tang JX, Yang ZS and Duan LF. 2015. A genetic linkage between subduction-and collision-related porphyry Cu deposits in continental collision zones. Geology, 43(3):247-250 |
| [40] | Hua RM. 1994. Studies on metal deposition by fluid mixing during ore-forming processes. Advance in Earth Sciences, 9(4):15-22(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [41] | Huang EB, Zhang NT and Luo ZS. 1990. The genesis of the Chengmenshan and Wushan copper deposits. Mineral Deposits, 9(4):291-308(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [42] | Jiang SY, Li L, Zhu B, Jiang YH, Gu LX and Ni P. 2008. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of granodiorite from the Wushan copper deposit, Jiangxi Province and their implications for petrogenesis. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8):1679-1690(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [43] | Keith JD, Whitney JA, Hattori K, Ballantyne GH, Christiansen EH, Barr DL, Cannan TM and Hook CJ. 1997. The role of magmatic sulfides and mafic alkaline magmas in the Bingham and Tintic Mining Districts, Utah. Journal of Petrology, 38(12):1679-1690 |
| [44] | Kósaka K and Wakita K. 1978. Some geologic features of the Mamut porphyry copper deposit, Sabah, Malaysia. Economic Geology, 73(5):618-627 |
| [45] | Lai XD, Yang XY, Sun WD and Cao XS. 2012. Chronological-geochemical characteristics of the Shujiadian intrusion, Tongling ore cluster field:Its significance to metallogenesis. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(3):470-485(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [46] | Lan XH, Yang XY, Yu LF and Zhang QM. 2009. Formation of the adakite-like granitoid complex and porphyry copper-gold deposit in Shaxi from southern Tancheng-Lujiang fault belt:A clue to the West Pacific plate subduction. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 28(1):28-43 |
| [47] | Lee CTA, Luffi P, Chin EJ, Bouchet R, Dasgupta R, Morton DM, Le Roux V, Yin QZ and Jin D. 2012. Copper systematics in arc magmas and implications for crust-mantle differentiation. Science, 336(6077):64-68 |
| [48] | Li JW, Zhao XF, Zhou MF, Vasconcelos P, Ma CQ, Deng XD, Sérgio De Souza Z, Zhao YX and Wu G. 2008. Origin of the Tongshankou porphyry-skarn Cu-Mo deposit, eastern Yangtze craton, eastern China:Geochronological, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints. Mineralium Deposita, 43(3):315-336 |
| [49] | Li JW, Zhao XF, Zhou MF, Ma CQ, Sérgio De Souza Z and Vasconcelos PM. 2009. Late Mesozoic magmatism from Daye region, eastern China:U-Pb ages, petrogenesis and geodynamic implications. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 157(3):383-409 |
| [50] | Li L and Jiang SY. 2009. Petrogenesis and geochemistry of the Dengjiashan porphyritic granodiorite, Jiujiang-Ruichang metallogenic district of the Middle-Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11):2877-2888(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [51] | Li XH, Li WX, Wang XC, Li QL, Liu Y, Tang GQ, Gao YY and Wu FY. 2010. SIMS U-Pb zircon geochronology of porphyry Cu-Au-(Mo) deposits in the Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt, eastern China:Magmatic response to Early Cretaceous lithospheric extension. Lithos, 119(3-4):427-438 |
| [52] | Li XH, Li ZX, Zheng XL, Li WX, Wang XC and Gao YY. 2013. Revisiting the ""C-type adakites"" of the Lower Yangtze River Belt, central eastern China:In-situ zircon Hf-O isotope and geochemical constraints. Chemical Geology, 345:1-15 |
| [53] | Li XM, Sun GX and Qiu SP. 2009. Geological-geophysical model and ore prospecting significance for Anjishan copper deposit. Journal of Geology, 33(1):28-34(in Chinese) |
| [54] | Ling MX, Wang FY, Ding X, Hu YH, Zhou JB, Zartman RE, Yang XY and Sun WD. 2009. Cretaceous ridge subduction along the Lower Yangtze River Belt, eastern China. Economic Geology, 104(2):303-321 |
| [55] | Ling MX, Wang FY, Ding X, Zhou JB and Sun WD. 2011. Different origins of adakites from the Dabie Mountains and the Lower Yangtze River belt in eastern China:Geochemical constraints. International Geology Review, 53(5-6):727-740 |
| [56] | Liu SA, Li SG, He YS and Huang F. 2010. Geochemical contrasts between early Cretaceous ore-bearing and ore-barren high-Mg adakites in central-eastern China:Implications for petrogenesis and Cu-Au mineralization. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(24):7160-7178 |
| [57] | Longo AA and Teal L. 2005. A summary of the volcanic stratigraphy and the geochronology of magmatism and hydrothermal activity in the Yanacocha gold district, northern Peru. In:Rhoden HN, Steininger RC and Vikre PG(eds.). Symposium 2005:Window to the World:Reno/Sparks. Geological Society of Nevada, 2:797-808 |
| [58] | Lu JJ, Guo WM, Chen WF, Jiang SY, Li J, Yan XR and Xu ZW. 2008. A metallogenic model for the Dongguashan Cu-Au deposit of Tongling, Anhui Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8):1857-1864(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [59] | Lu SM. 2007. The magmatism and fluid mineralizationin Shizishan copper-gold ore-field of Tongling, Anhui Province. Ph. D. Dissertation. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology, 1-158(in Chinese with English summary) |
| [60] | Luo JA. 2003. Geological characteristics of Chengmenshan copper deposit and analysis of its ore genesis. Mining Technology, 3(3):55-57(in Chinese) |
| [61] | Luo JA and Yang GC. 2007. Geological characteristics of Chengmenshan copper deposit, Jiangxi and its ore genesis. Mineral Resources and Geology, 21(3):284-288(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [62] | Lü QT, Hou ZQ, Yang ZS and Shi DN. 2004. Upplating process and dynamics evolution mode in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River:Constrain of physical geography information. Science in China(Series D), 34(9):783-794(in Chinese) |
| [63] | Lü QT, Dong SW, Shi DN, Tang JT, Jiang GM, Zhang YQ, Xu T and Sinoprobe-03-CJ Group. 2014. Lithosphere architecture and geodynamic model of Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze Belt:A review from SinoProbe. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(4):889-906(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [64] | Lü XB, Yao SZ and Lin XD. 1992. The geological characteristics and ore-forming mechanism of Tongshankou skarn-prophyry composite type of copper(molybdenum) ore deposit, Hubei. Earth Science, 17(2):171-180(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [65] | Lü YZ. 2012. Genesis and geochemical characteristics of Shujiadian copper deposit in Tongling, Anhui Province, China. Master Degree Thesis. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology, 1-69(in Chinese with English summary) |
| [66] | Ma XH, Chen B and Yang MC. 2013. Magma mixing origin for the Aolunhua porphyry related to Mo-Cu mineralization, eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Gondwana Research, 24(3-4):1152-1171 |
| [67] | Mao JW, Stein H, Du AD, Zhou TF, Mei YX, Li YF, Zang WS and Li JW. 2004. Molybdenite Re-Os precise dating for molybdenite from Cu-Au-Mo deposits in the Middle-Lower Reaches of Yangtze River Belt and its implications for mineralization. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(1):121-131(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [68] | Mao JW, Wang YT, Lehmann B, Yu JJ, Du AD, Mei YX, Li YF, Zang WS, Stein HJ and Zhou TF. 2006. Molybdenite Re-Os and albite 40Ar/39Ar dating of Cu-Au-Mo and magnetite porphyry systems in the Changjiang Valley and metallogenic implications. Ore Geology Reviews, 29(3-4):307-324 |
| [69] | Mao JW, Xie GQ, Duan C, Pirajno F, Ishiyama D and Chen YC. 2011. A tectono-genetic model for porphyry-skarn-stratabound Cu-Au-Mo-Fe and magnetite-apatite deposits along the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley, Eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 43(1):294-314 |
| [70] | Mao JW, Luo MC, Xie GQ, Liu J and Wu SH. 2014. Basic characteristics and new advances in research and exploration on porphyry copper deposits. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(12):2153-2175(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [71] | Meng LY and Huang EB. 1988. The stable isotopic geology of copper, molybdenum ore deposits in Chengmenshan, Jiangxi. Journal of Changchun University of Earth Science, 18(3):269-276(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [72] | Meng YF, Yang ZS, Zeng PS, Xu WY and Wang XC. 2004. Tentative temporal constraints of ore-forming fluid systems in Tongling Metallogenic Province. Mineral Deposits, 23(3):271-280(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [73] | Misra KC. 2000. Understanding Mineral Deposits. Dordrecht:Kluwer Academic Publishers, 353-413 |
| [74] | Mitchell AHG. 1973. Metallogenic belts and angle of dip of Benioff zones. Nature, 245(143):49-52 |
| [75] | Moyen JF. 2009. High Sr/Y and La/Yb ratios:The meaning of the ""adakitic signature"". Lithos, 112(3-4):556-574 |
| [76] | Mungall JE. 2002. Roasting the mantle:Slab melting and the genesis of major Au and Au-rich Cu deposits. Geology, 30(10):915-918 |
| [77] | Ningwu Project Group. 1978. The Porphyrite Iron Deposit of Ningwu. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-320(in Chinese) |
| [78] | Ohmoto H and Rye RO. 1979. Isotopes of sulfur and carbon. In:Barnes H(ed). Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. 2nd Edition. New York:Holt Rinehart and Winston, 509-567 |
| [79] | Pan YM and Dong P. 1999. The Lower Changjiang(Yangzi/Yangtze River) metallogenic belt, east central China:Intrusion-and wall rock-hosted Cu-Fe-Au, Mo, Zn, Pb, Ag deposits. Ore Geology Reviews, 15(4):177-242 |
| [80] | Perelló J, Posso H, Zárate A, Neyra C, Caballero A and Stein H. 2003. Syntectonic Ag-rich porphyry copper mineralization at Pachagón, northern Peru. Abstract of Congreso Geológico Chileno, 10th, Concepción, 2003, CD-ROM, 1 |
| [81] | Pirajno F and Zhou TF. 2015. Intracontinental porphyry and porphyry-skarn mineral systems in eastern China:Scrutiny of a special case ""made-in-China"". Economic Geology, 110(3):603-629 |
| [82] | Qin XL. 2007. Studies on sulfide-metal oxide inclusions from Mesozoic intrusions and their rock xenoliths in Tongling, Anhui Province. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-170(in Chinese with English summary) |
| [83] | Ren QJ, Qiu JS, Xu ZW, Zhang CZ, Fang CQ and Yang RY. 1991. Formation conditions of the mineralized stock in the Shaxi porphyry copper(gold) deposit, Anhui Province. Mineral Deposits, 10(3):232-242(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [84] | Richards JP. 2003. Tectono-magmatic precursors for porphyry Cu-(Mo-Au) deposit formation. Economic Geology, 98(8):1515-1533 |
| [85] | Richards JP. 2005. Cumulative factors in the generation of giant calc-alkaline porphyry Cu deposits. In:Porter TM(ed.). Super Porphyry Copper and Gold Deposits:A Global Perspective. Adelaide:PGC Publishing, 1:7-25 |
| [86] | Richards JP. 2009. Postsubduction porphyry Cu-Au and epithermal Au deposits:Products of remelting of subduction-modified lithosphere. Geology, 37(3):247-250 |
| [87] | Richards JP. 2011. High Sr/Y arc magmas and porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposits:Just add water. Economic Geology, 106(7):1075-1081 |
| [88] | Rohrlach BD and Loucks RR. 2005. Multi-million-year cyclic ramp-up of volatiles in a lower crustal magma reservoir trapped below the Tampakan copper-gold deposit by Mio-Pliocene crustal compression in the southern Philippines. In:Porter TM(ed.). Super Porphyry Copper and Gold Deposits:A Global Perspective. Adelaide:PGC Publishing, 2:369-407 |
| [89] | Rui ZY, Huang CK and Qi GM et al. 1984. The Porphyry Cu(-Mo) Deposits in China. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-350(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [90] | Sasso AM and Clark AH. 1998. The Farallón Negro Group, Northwest Argentina:Magmatic, hydrothermal and tectonic evolution and implication for Cu-Au metallogeny in the Andean back-arc. Society of Economic Geologists Newsletter, 34(1):8-18 |
| [91] | Shafiei B, Haschke M and Shahabpour J. 2009. Recycling of orogenic arc crust triggers porphyry Cu mineralization in Kerman Cenozoic arc rocks, southeastern Iran. Mineralium Deposita, 44(3):265-283 |
| [92] | Shu QA, Chen PL and Cheng JR. 1992. Geology of Iron-copper Deposits in Eastern Hubei Province, China. Beijing:Ministry of Metallurgical Industry Publishing House, 1-532(in Chinese) |
| [93] | Sillitoe RH. 1972. A plate tectonic model for the origin of porphyry copper deposits. Economic Geology, 67(2):184-197 |
| [94] | Sillitoe RH. 1973. The tops and bottoms of porphyry copper deposits. Economic Geology, 68(6):799-815 |
| [95] | Sillitoe RH and Perelló J. 2005. Andean copper province:Tectonomagmatic settings, deposit types, metallogeny, exploration, and discovery. Anniversary Volume in Economic Geology, 100:845-890 |
| [96] | Sillitoe RH. 2010. Porphyry copper systems. Economic Geology, 105(1):3-41 |
| [97] | Singer DA, Berger VI, Menzie WD and Berger BR. 2005. Porphyry copper deposit density. Economic Geology, 100(3):491-514 |
| [98] | Stöcklin J. 1974. Possible ancient continental margins in Iran. In:Burk CA and Drake CL(eds.). The Geology of Continental Margins. Berlin Heidelberg:Springer, 873-877 |
| [99] | Sun WD, Ling MX, Yang XY, Fan WM, Ding X and Liang HY. 2010. Ridge subduction and porphyry copper gold mineralization:An overview. Sci. China(Earth Sci.), 53(4):475-484 |
| [100] | Tang YC, Wu YC and Chu GZ. 1998. Geology of Copper-Gold Polymetallic Deposits in the along-Changjiang Area of Anhui Province. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-351(in Chinese) |
| [101] | Tatsumi Y, Hamilton DL and Nesbitt RW. 1986. Chemical characteristics of fluid phase released from a subducted lithosphere and the origin of arc magmas:Evidence from high-pressure experiments and natural rocks. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 29(1-4):293-309 |
| [102] | Waite KA, Keith JD, Christiansen EH, Whitney JA, Hattori K, Tingey DG and Hook CJ. 1997. Petrogenesis of the volcanic and intrusive rocks associated with the Bingham Canyon porphyry Cu-Au-Mo deposit, Utah. In:John DA and Ballantyne GH(eds.). Geology and Ore Deposits of the Oquirrh and Wasatch Mountains, Utah. Society of Economic Geologists Guidebook Series, 29:69-90 |
| [103] | Wallace P and Carmichael ISE. 1992. Sulfur in basaltic magmas. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 56(5):1863-1874 |
| [104] | Wang LB, Ji KJ and Chen D. 1997. Re-Os isotope ages of molybdenite from the Anjishan copper deposite and the Tongshan copper-molybdenum deposit and their implications. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 16(2):154-159(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [105] | Wang Q, Xu JF, Zhao ZH, Xiong XL and Bao ZW. 2003. Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Tongling area, Anhui Province, China and their constraint on geodynamic process. Science in China(Series D), 46(8):801-815 |
| [106] | Wang Q, Wyman DA, Xu JF, Zhao ZH, Jian P, Xiong XL, Bao ZW, Li CF and Bai ZH. 2006a. Petrogenesis of Cretaceous adakitic and shoshonitic igneous rocks in the Luzong area, Anhui Province(eastern China):Implications for geodynamics and Cu-Au mineralization. Lithos, 89(3-4):424-446 |
| [107] | Wang Q, Xu JF, Jian P, Bao ZW, Zhao ZH, Li CF, Xiong XL and Ma JL. 2006b. Petrogenesis of adakitic porphyries in an extensional tectonic setting, Dexing, South China:Implications for the genesis of porphyry copper mineralization. Journal of Petrology, 47(1):119-144 |
| [108] | Wang Q, Wyman DA, Xu JF, Jian P, Zhao ZH, Li CF, Xu W, Ma JL and He B. 2007. Early Cretaceous adakitic granites in the northern Dabie Complex, central China:Implications for partial melting and delamination of thickened lower crust. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(10):2609-2636 |
| [109] | Wang QF. 2005. Model study of the tectonic-magmatic-metallogenical system in Tongling ore cluster area. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 1-127(in Chinese) |
| [110] | Wang SW, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Fan Y and Lü YZ. 2011. Geochronology and geochemical characteristics of the Shujiadian intrusion in Tongling, China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(5):849-861(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [111] | Wang SW, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Fan Y, Cao XS and Wang B. 2012. Re-Os and 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Shujiadian copper deposit in Tongling, China:Implications for regional metallogenesis. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(10):3170-3180(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [112] | Wang SW, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Fan Y, Yu CH, Ge LH, Shi C and Chi YY. 2014. Emplacement sequences and geochronology of the Shaxi porphyry copper-gold deposit, Anhui Province, East China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(4):979-994(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [113] | Wang SW, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Fan Y, White NC and Lin FJ. 2015a. Geological and geochemical studies of the Shujiadian porphyry Cu deposit, Anhui Province, eastern China:Implications for ore genesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 103:252-275 |
| [114] | Wang SW, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Fan Y, Zhang LJ and Song YL. 2015b. Petrogenesis of Dongguashan skarn-porphyry Cu-Au deposit related intrusion in the Tongling district, eastern China:Geochronological, mineralogical, geochemical and Hf isotopic evidence. Ore Geology Reviews, 64:53-70 |
| [115] | Wang Y, Deng JF and Ji GY. 2004. A perspective on the geotectonic setting of Early Cretaceous adakite-like rocks in the Lower Reaches of Yangtze River and its significance for copper-gold mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(2):297-314(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [116] | Wang YB, Liu DY, Zeng PS, Yang ZS, Meng YF and Tian SH. 2004. SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of Xiaotongguanshan quartz-dioritic intrusions in Tongling district and its petrogenetic implications. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 23(4):298-304(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [117] | Wu CL, Zhou XR, Huang XC, Zhang CH and Huang WM. 1996. 40Ar/39Ar Chronology of intrusive rocks from Tongling. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 15(4):299-306(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [118] | Wu CL, Chen SY, Shi RD and Hao MY, 2003. Origin and features of the Mesozoic intermediate-acid intrusive in the Tongling area, Anhui Province, China. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 24(1):41-48(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [119] | Wu CL, Dong SW, Guo HP, Guo XY, Gao QM, Liu LG, Chen QL, Lei M, Wooden JL, Mazadab FK and Mattinson C. 2008. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of intermediate-acid intrusive rocks from Shizishan, Tongling and the deep processes of magmatism. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8):1801-1812(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [120] | Wu CL, Gao QM, Guo HP, Guo XY, Liu LG, Gao YH, Lei M and Qin HP. 2010. Petrogenesis of the intermediate-acid intrusive rocks and zircon SHRIMP dating in Tongling, Anhui, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(9):2630-2652(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [121] | Wu FY, Ji WQ, Sun DH, Yang YH and Li XH. 2012. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions of the Mesozoic granites in southern Anhui Province, China. Lithos, 150:6-25 |
| [122] | Wu LR, Qi JY, Wang TD, Zhang XQ and Xu YS. 1982. Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the eastern part of China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 56(3):223-234(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [123] | Wu LS and Zou XQ. 1997. Re-Os isotopic age study of the Chengmenshan copper deposit, Jiangxi Province. Mineral Deposits, 16(4):376-381(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [124] | Wu YC, Cao FY and Chang YF. 1999. A preliminary study on this deep-seated structural-magmatic control over the metallogenic system around the Yangtze River Reaches in Anhui Province. Earth Science Frontiers, 6(2):285-296(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [125] | Xi MJ. 2009. The discriminating application of sulfur isotope in the cause of geochemical anormality. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1-64(in Chinese) |
| [126] | Xie GQ, Mao JW, Li RL, Zhang ZS, Zhao WC, Qu WJ, Zhao CS and Wei SK. 2006. Metallogenic epoch and geodynamic framework of Cu-Au-Mo-(W) deposits in southeastern Hubei Province:Constraints from Re-Os molybdenite ages. Mineral Deposits, 25(1):43-52(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [127] | Xie GQ, Mao JW and Zhao HJ. 2011. Zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic intrusions in the Southeast Hubei Province, Middle-Lower Yangtze River belt(MLYRB), East China. Lithos, 125(1-2):693-710 |
| [128] | Xie JC, Chen S, Sun WD and Yang XY. 2012. Geochemistry of Early Cretaceous adakitic rocks in Tongling region of Anhui Province:Constraints for rock-and ore-forming. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(10):3181-3196(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [129] | Xing FM and Xu X. 1999. Magmatic Belt and Mineralization in Yangtze River Reaches of Anhui Province. Hefei:Anhui People Publication House, 1-170(in Chinese) |
| [130] | Xu JF, Shinjo R, Defant MJ, Wang Q and Rapp RP. 2002. Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of East China:Partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust? Geology, 30(12):1111-1114 |
| [131] | Xu WY, Xu ZW, Gu LX, Ren QJ, Fu B and Niu CY. 1999. Heat evolution from intrusion to mineralization in Shaxi porphyry copper(gold) deposits, Anhui Province. Geological Review, 45(4):361-367(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [132] | Xu XC, Lu SM, Xie QQ, Bo L and Chu GZ. 2008. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating for the magmatic rocks in Shizishan ore-field of Tongling, Anhui Province, and its geological implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 82(4):500-509(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [133] | Xu XC, Yin T, Lou JW, Lu SM, Xie QQ and Chu LP. 2010. Origin of Dongguashan stratabound Cu-Au skarn deposit in Tongling:Restraints of sulfur isotope. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(9):2739-2750(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [134] | Xu XC, Lou JW, Xie QQ, Xiao QX, Liang JF and Chu LP. 2011. Thermodynamic study of the paragenesis and fractionation of copper and gold in the Shizishan orefield, Tongling, Anhui Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(5):731-743(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [135] | Xu XS, Fan QC, O'Reilly SY, Jiang SY, Griffin WL, Wang RC and Qiu JS. 2004. U-Pb dating of zircons from quartz diorite and its enclaves at Tongguanshan in Anhui and its petrogenetic implication. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(19):2073-2082 |
| [136] | Xu YM, Jiang SY, Zhu ZY, Zhou W, Kong FB and Sun MZ. 2012. Geochronology, geochemistry and mineralization of the quartz diorite-porphyrite and granodiorite porphyry in the Shanshangwan area of the Jiurui ore district, Jiangxi Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(10):3306-3324(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [137] | Xu ZW, Xu WY, Qiu JS, Fu B and Niu CY. 2000. An investigation of the age and geological-geochemical characteristics of quartz diorite porphyry in Shaxi porphyry copper(gold) deposit. Geology and Prospecting, 36(4):36-40(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [138] | Xu ZW, Lu XC, Ling HF, Lu JJ, Jiang SY, Nie GP, Huang SS and Hua M. 2005. Metallogenetic mechanism and timing of late superimposing fluid mineralization in the Dongguashan diplogenetic stratified copper deposit, Anhui Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(3):405-413(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [139] | Yan J, Chen JF, Xie Z, Yang G, Yu G and Qian H. 2005. Geochemistry of Late Mesozoic basalts from Kedoushan in the Middle and Lower Yangtze regions:Constraints on characteristics and evolution of the lithospheric mantle. Geochimica, 34(5):455-469(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [140] | Yang SY, Jiang SY, Li L, Sun Y, Sun MZ, Bian LZ, Xiong GY and Gao ZQ. 2011. Late Mesozoic magmatism of the Jiurui mineralization district in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt, Eastern China:Precise U-Pb ages and geodynamic implications. Gondwana Research, 20(4):831-843 |
| [141] | Yang XN, Xu ZW, Zhang J, Wang YJ, Xu XS, Jiang SY, Ling HF, Liu LG and Chen DY. 2007. Geoehronology and origin of Nanhongchong pluton in Shizishan ore-field, Anhui Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(6):1543-1551(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [142] | Yang XY. 2006. 40Ar-39Ar dating and geological significance on the Cu-bearing porpyrite of Shaxi from southern Tan-Lu fault belt. J. Mineral. Petrol., 26(2):52-56(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [143] | Yuan F, Zhou TF, Wang SW, Fan Y, Tang C, Zhang QM, Yu CH and Shi C. 2012. Characteristics of alteration and mineralization of the Shaxi porphyry copper deposit, Luzong area, Anhui Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(10):3099-3112(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [144] | Yuan F, Song YL, Wang SW, Zhou TF and Sun WA. 2014. Characteristics of porphyry mineralization in the depth of Dongguashan deposit and its relationship with skarn-type mineralization. Chinese Journal of Geology, 49(2):588-607(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [145] | Zarasvandi A, Liaghat S and Zentilli M. 2005. Geology of the Darreh-Zerreshk and Ali-Abad porphyry copper deposits, Central Iran. International Geology Review, 47(6):620-646 |
| [146] | Zarasvandi A, Liaghat S, Zentilli M and Reynolds PH. 2007. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of alteration and petrogenesis of porphyry copper-related granitoids in the Darreh-Zerreshk and Ali-Abad area, central Iran. Explor. Min. Geol., 16(1-2):11-24 |
| [147] | Zeng JN, Li JW, Chen JH and Lu JP. 2013. SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb dating of Anjishan intrusive rocks in Ningzhen district, Jiangsu, and its geological significance. Earth Science, 38(1):57-67(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [148] | Zhai YS, Yao SZ and Ling XD. 1992. Regularities of Metallogenesis for Copper(Gold) Deposits in the Middle and Lower Reache |
| [149] | Yang XY. 2006. 40Ar-39Ar dating and geological significance on the Cu-bearing porpyrite of Shaxi from southern Tan-Lu fault belt. J. Mineral. Petrol., 26(2):52-56(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [150] | Yuan F, Zhou TF, Wang SW, Fan Y, Tang C, Zhang QM, Yu CH and Shi C. 2012. Characteristics of alteration and mineralization of the Shaxi porphyry copper deposit, Luzong area, Anhui Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(10):3099-3112(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [151] | Zarasvandi A, Liaghat S and Zentilli M. 2005. Geology of the Darreh-Zerreshk and Ali-Abad porphyry copper deposits, Central Iran. International Geology Review, 47(6):620-646 |
| [152] | Zarasvandi A, Liaghat S, Zentilli M and Reynolds PH. 2007. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of alteration and petrogenesis of porphyry copper-related granitoids in the Darreh-Zerreshk and Ali-Abad area, central Iran. Explor. Min. Geol., 16(1-2):11-24 |
| [153] | Zarasvandi A, Liaghat S, Zentilli M and Reynolds PH. 2007. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of alteration and petrogenesis of porphyry copper-related granitoids in the Darreh-Zerreshk and Ali-Abad area, central Iran. Explor. Min. Geol., 16(1-2):11-24 |
| [154] | Zeng JN, Li JW, Chen JH and Lu JP. 2013. SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb dating of Anjishan intrusive rocks in Ningzhen district, Jiangsu, and its geological significance. Earth Science, 38(1):57-67(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [155] | Zhang J. 1992. Geological characters and metallogenic model of Anjishan copper deposit. Jiangsu Geology, 16(3-4):172-179 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [156] | Zhang Q, Wang Y and Wang YL. 2001. Preliminary study on the components of the lower crust in East China Plateau during Yanshanian Period:Constraints on Sr and Nd isotopic compositions of adakite-like rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(4):505-513 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [157] | Zhang Q, Wang Y and Wang YL. 2001. Preliminary study on the components of the lower crust in East China Plateau during Yanshanian Period:Constraints on Sr and Nd isotopic compositions of adakite-like rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(4):505-513 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [158] | Zhang Q, Xu JF, Wang Y, Xiao L, Liu HT and Wang YL. 2004. Diversity of adakite. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(9-10):959-965 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [159] | Zhang Q, Xu JF, Wang Y, Xiao L, Liu HT and Wang YL. 2004. Diversity of adakite. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(9-10):959-965 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [160] | Zhao R, Xie YH, Yao YY and Huo WG. 1985. Sulfur isotope study of the copper ore deposit of Chengmenshan and Wushan. Chinese Journal of Geology, (3):251-258 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [161] | Zhou TF, Yue SC, Yuan F, Liu XD and Zhao Y. 2000. Two series of copper-gold deposits in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Area (MLYRA) and the hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur and lead isotopes of their ore-forming hydrothermal systems. Science in China (Series D), 43(l):208-218 |
| [162] | Zhou TF, Yuan F, Yue SC, Liu XD and Zhao Y. 2002. Water/rock interaction during formation of skarn-type deposits in Yueshan orefield, Anhui Province. Mineral Deposits, 21(1):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [163] | Zhou TF, Yuan F, Yue SC, Liu XD and Zhao Y. 2002. Water/rock interaction during formation of skarn-type deposits in Yueshan orefield, Anhui Province. Mineral Deposits, 21(1):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [164] | Zhou TF, Yuan F, Yue SC, Liu XD, Zhang X and Fan Y. 2007. Geochemistry and evolution of ore-forming fluids of the Yueshan Cu-Au skarn and vein-type deposits, Anhui Province, South China. Ore Geology Reviews, 31(1-4):279-303 |
| [165] | Zhou TF, Fan Y and Yuan F. 2008. Advances on Petrogensis and metallogeny study of the mineralization belt of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River area. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8):1665-1678 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [166] | Zhou TF, Fan Y and Yuan F. 2008. Advances on Petrogensis and metallogeny study of the mineralization belt of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River area. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8):1665-1678 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [167] | Zhou TF, Yuan F, Fan Y, Xie JC and Zhang X. 2009. Textbook for Ore Deposit Practice in Tongling. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1-139 (in Chinese) |
| [168] | Zhou TF, Fan Y, Yuan F, Zhang LJ, Ma L, Qian B and Xie J. 2011. Petrogensis and metallogeny study of the volcanic basins in the Middle and Lower Yangtze metallogenic belt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(5):712-730 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [169] | Zhou TF, Wang SW, Fan Y, Yuan F, Zhang DY and White NC. 2015. A review of the intracontinental porphyry deposits in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt, Eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 65:433-456 |
| [170] | 常印佛, 刘学圭. 1983. 关于层控式矽卡岩型矿床——以安徽省内下扬子坳陷中一些矿床为例. 矿床地质, 2(1):11-20 |
| [171] | 常印佛, 刘学圭. 1983. 关于层控式矽卡岩型矿床——以安徽省内下扬子坳陷中一些矿床为例. 矿床地质, 2(1):11-20 |
| [172] | 常印佛, 周涛发, 范裕. 2012. 复合成矿与构造转换——以长江中下游成矿带为例. 岩石学报, 28(10):3067-3075 |
| [173] | 陈华勇, 肖兵. 2014. 俯冲边界成矿作用研究进展及若干问题. 地学前缘, 21(5):13-22 |
| [174] | 陈江峰, 周泰禧, 李学明, Foland KA, 黄承义, 卢伟. 1993. 安徽南部燕山期中酸性侵入岩源区的锶/钕同位素制约. 地球化学, (3):261-268 |
| [175] | 陈衍景. 2013. 大陆碰撞成矿理论的创建及应用. 岩石学报, 29(1):1-17 |
| [176] | 陈志洪, 邢光福, 郭坤一, 曾勇, 匡福祥, 贺振宇, 柯学, 余明刚, 赵希林, 张勇. 2011. 长江中下游成矿带九瑞矿集区(北部)含矿岩体的锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 地质学报, 85(7):1146-1158 |
| [177] | 陈志洪, 邢光福, 郭坤一, 曾勇, 匡福祥, 贺振宇, 柯学, 余明刚, 赵希林, 张勇. 2011. 长江中下游成矿带九瑞矿集区(北部)含矿岩体的锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 地质学报, 85(7):1146-1158 |
| [178] | 邓晋福, 吴宗絮. 2001. 下扬子克拉通岩石圈减薄事件与长江中下游Cu-Fe成矿带. 安徽地质, 11(2):86-91 |
| [179] | 邓晋福, 吴宗絮. 2001. 下扬子克拉通岩石圈减薄事件与长江中下游Cu-Fe成矿带. 安徽地质, 11(2):86-91 |
| [180] | 董树文, 高锐, 吕庆田, 张季生, 张荣华, 薛怀民, 吴才来, 卢占武, 马立成. 2009. 庐江-枞阳矿集区深部结构与成矿. 地球化学, 30(3):279-284 |
| [181] | 董树文, 马立成, 刘刚, 薛怀民, 施炜, 李建华. 2011. 论长江中下游成矿动力学. 地质学报, 85(5):612-625 |
| [182] | 杜杨松, 秦新龙, 曹毅. 2010. 安徽铜陵中生代侵入岩及其岩石包体中的硫化物-氧化物包裹体研究. 矿床地质, 29(1):71- 84 |
| [183] | 范裕, 周涛发, 袁峰, 钱存超, 陆三明, Cooke D. 2008. 安徽庐江-枞阳地区A型花岗岩的LA-ICP MS定年及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 24(8):1715-1724 |
| [184] | 方福康. 2012. 江西省城门山斑岩铜钼矿成矿流体研究. 硕士学位论文. 北京:中国地质大学, 1-61 |
| [185] | 傅斌, 任启江, 胡文宣. 1996. 安徽沙溪斑岩铜矿床成矿流体演化及分布规律. 矿床地质, 15(1):23-33 |
| [186] | 傅斌, 任启江, 邢凤鸣, 徐兆文, 胡文瑄, 郑永飞. 1997. 安徽沙溪含铜斑岩40Ar-39Ar定年及其地质意义. 地质论评, 43(3):310- 316 |
| [187] | 顾连兴, 陈培荣, 倪培, 徐兆文, 肖新建, 邱检生, 张遵忠, 张光辉. 2002. 长江中、下游燕山期热液铜-金矿床成矿流体. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 38(3):392-407 |
| [188] | 郭维民, 陆建军, 蒋少涌, 章荣清, 招湛杰. 2013. 安徽铜陵狮子山矿田岩浆岩年代学、Hf同位素、地球化学及岩石成因. 中国科学(地球科学), 43(8):1268-1286 |
| [189] | 侯增谦, 潘小菲, 杨志明, 曲晓明. 2007. 初论大陆环境斑岩铜矿. 现代地质, 21(2):332-351 |
| [190] | 侯增谦, 杨志明. 2009. 中国大陆环境斑岩型矿床:基本地质特征、岩浆热液系统和成矿概念模型. 地质学报, 83(12):1779-1817 |
| [191] | 华仁民. 1994. 成矿过程中由流体混合而导致金属沉淀的研究. 地球科学进展, 9(4):15-22 |
| [192] | 黄恩邦, 张迺堂, 罗钊生. 1990. 城门山、武山铜矿床成因. 矿床地质, 9(4):291-308 |
| [193] | 蒋少涌, 李亮, 朱碧, 丁昕, 姜耀辉, 顾连兴, 倪培. 2008. 江西武山铜矿区花岗闪长斑岩的地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素组成及成因探讨. 岩石学报, 24(8):1679-1690 |
| [194] | 赖小东, 杨晓勇, 孙卫东, 曹晓生. 2012. 铜陵舒家店岩体年代学、岩石地球化学特征及成矿意义. 地质学报, 86(3):470-485 |
| [195] | 李亮, 蒋少涌. 2009. 长江中下游地区九瑞矿集区邓家山花岗闪长斑岩的地球化学与成因研究. 岩石学报, 25(11):2877-2888 |
| [196] | 李相民, 孙国曦, 仇慎平. 2009. 安基山铜矿床地质-地球物理模型及其找矿意义. 地质学刊, 33(1):28-34 |
| [197] | 陆建军, 郭维民, 陈卫锋, 蒋少涌, 李娟, 颜晓蓉, 徐兆文. 2008. 安徽铜陵冬瓜山铜(金)矿床成矿模式. 岩石学报, 24(8):1857-1864 |
| [198] | 陆三明. 2007. 安徽铜陵狮子山铜金矿田岩浆作用与流体成矿. 博士学位论文. 合肥:合肥工业大学, 1-158 |
| [199] | 罗建安. 2003. 城门山铜矿地质特征及成因分析. 采矿技术, 3(3):55-57 |
| [200] | 罗建安, 杨国才. 2007. 江西城门山铜矿地质特征及矿床成因. 矿产与地质, 21(3):284-288 |
| [201] | 吕庆田, 侯增谦, 杨竹森, 史大年. 2004. 长江中下游地区的底侵作用及动力学演化模式:来自地球物理资料的约束. 中国科学(D辑), 34(9):783-794 |
| [202] | 吕庆田, 董树文, 史大年, 汤井田, 江国明, 张永谦, 徐涛, SinoProbe-03-CJ项目组. 2014. 长江中下游成矿带岩石圈结构与成矿动力学模型——深部探测 (SinoProbe) 综述. 岩石学报, 30(4):889-906 |
| [203] | 吕新彪, 姚书振, 林新多. 1992. 湖北大冶铜山口矽卡岩-斑岩复合型铜(钼)矿床地质特征和成矿机制. 地球科学, 17(2):171-180 |
| [204] | 吕玉琢. 2012. 安徽铜陵舒家店铜矿床地球化学特征及成因. 硕士学位论文. 合肥工业大学, 1-69 |
| [205] | 毛景文, Stein H, 杜安道, 周涛发, 梅燕雄, 李永峰, 藏文栓, 李进文. 2004. 长江中下游地区铜金(钼)矿Re-Os年龄测定及其对成矿作用的指示. 地质学报, 78(1):121-131 |
| [206] | 毛景文, 罗茂澄, 谢桂青, 刘军, 吴胜华. 2014. 斑岩铜矿床的基本特征和研究勘查新进展. 地质学报, 88(12):2153-2175 |
| [207] | 孟良义, 黄恩邦. 1988. 城门山铜、钼矿床的稳定同位素地质. 长春地质学院学报, 18(3):269-276 |
| [208] | 蒙义峰, 杨竹森, 曾普胜, 徐文艺, 王训成. 2004. 铜陵矿集区成矿流体系统时限的初步厘定. 矿床地质, 23(3):271-280 |
| [209] | 蒙义峰, 杨竹森, 曾普胜, 徐文艺, 王训成. 2004. 铜陵矿集区成矿流体系统时限的初步厘定. 矿床地质, 23(3):271-280 |
| [210] | 秦新龙. 2007. 安徽铜陵中生代侵入岩及其岩石包体中硫化物-金属氧化物包裹体研究. 博士学位论文. 北京:中国地质大学, 1-170 |
| [211] | 任启江, 邱检生, 徐兆文, 张重泽, 方长泉, 杨荣勇. 1991. 安徽沙溪斑岩铜(金)矿床矿化小岩体的形成条件. 矿床地质, 10(3):232-242 |
| [212] | 任启江, 邱检生, 徐兆文, 张重泽, 方长泉, 杨荣勇. 1991. 安徽沙溪斑岩铜(金)矿床矿化小岩体的形成条件. 矿床地质, 10(3):232-242 |
| [213] | 芮宗瑶, 黄崇轲, 齐国明等. 1984. 中国斑岩铜(钼) 矿床. 北京:地质出版社, 1-350 |
| [214] | 孙卫东, 凌明星, 杨晓勇, 范蔚茗, 丁兴, 梁华英. 2010. 洋脊俯冲与斑岩铜金矿成矿. 中国科学(地球科学), 40(2):127-137 |
| [215] | 孙卫东, 凌明星, 杨晓勇, 范蔚茗, 丁兴, 梁华英. 2010. 洋脊俯冲与斑岩铜金矿成矿. 中国科学(地球科学), 40(2):127-137 |
| [216] | 王立本, 季克俭, 陈东. 1997. 安基山和铜山铜(钼)矿床中辉钼矿的铼-锇同位素年龄及其意义. 岩石矿物杂志, 16(2):154-159 |
| [217] | 王强, 许继峰, 赵振华, 熊小林, 包志伟. 2003. 安徽铜陵地区燕山期侵入岩的成因及其对深部动力学过程的制约. 中国科学(D辑), 33(4):323-334 |
| [218] | 王庆飞. 2005. 铜陵矿集区构造-岩浆-成矿系统模型研究. 博士学位论文. 北京:中国地质大学, 1-127 |
| [219] | 王世伟, 周涛发, 袁峰, 范裕, 吕玉琢. 2011. 铜陵舒家店岩体的年代学和地球化学特征研究. 地质学报, 85(5):849-861 |
| [220] | 王世伟, 周涛发, 袁峰, 范裕, 曹晓生, 王彪. 2012. 铜陵舒家店斑岩铜矿成矿年代学研究及其成矿意义. 岩石学报, 28(10):3170-3180 |
| [221] | 王世伟, 周涛发, 袁峰, 范裕, 俞沧海, 葛岭虹, 石诚, 池月余. 2014. 安徽沙溪斑岩型铜金矿床成岩序列及成岩成矿年代学研究. 岩石学报, 30(4):979-994 |
| [222] | 王彦斌, 刘敦一, 曾普胜, 杨竹森, 蒙义峰, 田世洪. 2004. 铜陵地区小铜官山石英闪长岩锆石SHRIMP的U-Pb年龄及其成因指示. 岩石矿物学杂志, 23(4):298-304 |
| [223] | 汪洋, 邓晋福, 姬广义. 2004. 长江中下游地区早白垩世埃达克质岩的大地构造背景及其成矿意义. 岩石学报, 20(2):297-314 |
| [224] | 吴才来, 周珣若, 黄许陈, 张成火, 黄文明. 1996. 铜陵地区中酸性侵入岩年代学研究. 岩石矿物学杂志, 15(4):299-306 |
| [225] | 吴才来, 陈松永, 史仁灯, 郝美英. 2003. 铜陵中生代中酸性侵入岩特征及成因. 地球学报, 24(1):41-48 |
| [226] | 吴才来, 董树文, 国和平, 郭祥炎, 高前明, 刘良根, 陈其龙, 雷敏, Wooden JL, Mazadab FK, Mattinson C. 2008. 铜陵狮子山地区中酸性侵入岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 定年及岩浆作用的深部过程. 岩石学报, 24(8):1801-1812 |
| [227] | 吴才来, 高前明, 国和平, 郭祥炎, 刘良根, 郜源红, 雷敏, 秦海鹏. 2010. 铜陵中酸性侵入岩成因及锆石SHRIMP定年. 岩石学报, 26(9):2630-2652 |
| [228] | 吴利仁, 齐进英, 王听渡, 张秀棋, 徐永生. 1982. 中国东部中生代火山岩. 地质学报, 56(3):223-234 |
| [229] | 吴良士, 邹晓秋. 1997. 江西城门山铜矿铼-锇同位素年龄研究. 矿床地质, 16(4):376-381 |
| [230] | 吴言昌, 曹奋扬, 常印佛. 1999. 初论安徽沿江地区成矿系统的深部构造岩浆控制. 地学前缘, 6(2):285-296 |
| [231] | 席明杰. 2009. 硫同位素在地球化学异常成因判别中的应用. 硕士学位论文. 北京:中国地质科学院, 1-64 |
| [232] | 谢桂青, 毛景文, 李瑞玲, 张祖送, 赵维超, 屈文俊, 赵财胜, 魏世昆. 2006. 鄂东南地区Cu-Au-Mo-(W)矿床的成矿时代及其成矿地球动力学背景探讨:辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄. 矿床地质, 25(1):43-52 |
| [233] | 谢建成, 陈思, 孙卫东, 杨晓勇. 2012. 安徽铜陵早白垩世埃达克质岩地球化学:成岩成矿制约. 岩石学报, 28(10):3181-3196 |
| [234] | 谢建成, 陈思, 孙卫东, 杨晓勇. 2012. 安徽铜陵早白垩世埃达克质岩地球化学:成岩成矿制约. 岩石学报, 28(10):3181-3196 |
| [235] | 徐文艺, 徐兆文, 顾连兴, 任启江, 傅斌, 牛翠祎. 1999. 安徽沙溪斑岩铜(金)矿床成岩成矿热历史探讨. 地质论评, 45(4):361-367 |
| [236] | 徐晓春, 陆三明, 谢巧勤, 柏林, 储国正. 2008. 安徽铜陵狮子山矿田岩浆岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其成因意义. 地质学报, 82(4):500-509 |
| [237] | 徐晓春, 尹滔, 楼金伟, 陆三明, 谢巧勤, 褚平利. 2010. 铜陵冬瓜山层控矽卡岩型铜金矿床的成因机制:硫同位素制约. 岩石学报, 26(9):2739-2750 |
| [238] | 徐晓春, 楼金伟, 谢巧勤, 肖秋香, 梁建锋, 褚平利. 2011. 安徽铜陵狮子山矿田铜、金共生与分离的热力学研究. 地质学报, 85(5):731-743 |
| [239] | 徐夕生, 范钦成, O'Reilly SY, 蒋少涌, Griffin WL, Wang RC, 王汝成, 邱检生. 2004. 安徽铜官山石英闪长岩及其包体锆石U-Pb定年与成因探讨. 科学通报, 49(18):1883-1891 |
| [240] | 徐耀明, 蒋少涌, 朱志勇, 周巍, 孔凡斌, 孙明志. 2012. 九瑞矿集区山上湾矿区石英闪长玢岩和花岗闪长斑岩的年代学、地球化学及成矿意义. 岩石学报, 28(10):3306-3324 |
| [241] | 徐兆文, 徐文艺, 邱检生, 傅斌, 牛翠祎. 2000. 与沙溪斑岩铜(金)矿床有关的石英闪长斑岩地质地球化学特征及形成时代研究. 地质与勘探, 36(4):36-40 |
| [242] | 徐兆文, 陆现彩, 凌洪飞, 陆建军, 蒋少涌, 聂桂平, 黄顺生, 华明. 2005. 安徽冬瓜山层状铜矿床成矿机制及热液叠加改造作用时代研究. 地质学报, 79(3):405-413 |
| [243] | 闫峻, 陈江峰, 谢智, 杨刚, 喻钢, 钱卉. 2005. 长江中下游地区蝌蚪山晚中生代玄武岩的地球化学研究:岩石圈地幔性质与演化的制约. 地球化学, 34(5):455-469 |
| [244] | 杨晓勇. 2006. 郯庐断裂带南段沙溪含铜斑岩体的40Ar-39Ar年代学研究及意义. 矿物岩石, 26(2):52-56 |
| [245] | 杨小男, 徐兆文, 张军, 王云健, 徐夕生, 蒋少涌, 凌洪飞, 刘良根, 陈达源. 2007. 安徽狮子山矿田南洪冲岩体形成时代及成因机制研究. 岩石学报, 23(6):1543-1551 |
| [246] | 袁峰, 周涛发, 王世伟, 范裕, 汤诚, 张千明, 俞沧海, 石诚. 2012. 安徽庐枞沙溪斑岩铜矿蚀变及矿化特征研究. 岩石学报, 28(10):3099-3112 |
| [247] | 袁峰, 宋玉龙, 王世伟, 周涛发, 孙维安. 2014. 铜陵冬瓜山矿床深部斑岩型矿化特征及其与矽卡岩型矿化的关系. 地质科学, 49(2):588-607 |
| [248] | 曾键年, 李锦伟, 陈津华, 陆建培. 2013. 宁镇地区安基山侵入岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 地球科学, 38(1):57-67 |
| [249] | 曾键年, 李锦伟, 陈津华, 陆建培. 2013. 宁镇地区安基山侵入岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 地球科学, 38(1):57-67 |
| [250] | 张建. 1992. 安基山复合型铜矿床成矿地质特征及成矿模式. 江苏地质, 16(3-4):172-179 |
| [251] | 张旗, 王焰, 王元龙. 2001. 燕山期中国东部高原下地壳组成初探:埃达克质岩Sr、Nd同位素制约. 岩石学报, 17(4):505-513 |
| [252] | 张旗, 王焰, 王元龙. 2003. 埃达克岩与构造环境. 大地构造与成矿学. 27(2):101-108 |
| [253] | 张旗, 徐继峰, 王焰, 肖龙, 刘红涛, 王元龙. 2004. 埃达克岩的多样性. 地质通报, 23(9-10):959-965 |
| [254] | 赵瑞, 谢奕汉, 姚御元, 霍卫国. 1985. 城门山及武山铜矿床的硫同位素研究. 地质科学, (3):251-258 |
| [255] | 赵瑞, 谢奕汉, 姚御元, 霍卫国. 1985. 城门山及武山铜矿床的硫同位素研究. 地质科学, (3):251-258 |
| [256] | 周涛发, 岳书仓, 袁峰, 刘晓东, 赵勇. 2000. 长江中下游两个系列铜、金矿床及其成矿流体系统的氢、氧、硫、铅同位素研究. 中国科学(D辑), 30(增刊):122-128 |
| [257] | 周涛发, 袁峰, 岳书仓, 刘晓东, 赵勇. 2002. 安徽月山矿田夕卡岩型矿床形成的水岩作用. 矿床地质, 21(1):1-9 |
| [258] | 周涛发, 袁峰, 岳书仓, 刘晓东, 赵勇. 2002. 安徽月山矿田夕卡岩型矿床形成的水岩作用. 矿床地质, 21(1):1-9 |
| [259] | 周涛发, 范裕, 袁峰. 2008. 长江中下游成矿带成岩成矿作用研究进展. 岩石学报, 24(8):1665-1678 |
| [260] | 周涛发, 范裕, 袁峰. 2008. 长江中下游成矿带成岩成矿作用研究进展. 岩石学报, 24(8):1665-1678 |
| [261] | 周涛发, 范裕, 袁峰, 张乐骏, 马良, 钱兵, 谢杰. 2011. 长江中下游成矿带火山岩盆地的成岩成矿作用. 地质学报, 85(5):712-730 |
| [262] | 周涛发, 范裕, 袁峰, 钟国雄. 2012. 长江中下游成矿带地质与矿产研究进展. 岩石学报, 28(10):3051-3066 |
 2016, Vol. 32
2016, Vol. 32

