2. 中国地质科学院地质研究所, 大陆构造与动力学国家重点实验室, 北京 100037
2. State Key Laboratory for Continental Tectonics and Dynamics, Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100037, China
在与俯冲和碰撞相关的变质作用中,流体扮演了非常重要的角色,它对认识碰撞造山中的变质作用、岩浆作用及高压-超高压岩石的形成和保存等有重要的意义(Miller et al., 2002; Li et al., 2004; Hermann et al., 2006; Wu et al., 2006,2008,2009; Sun et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2009; Zheng et al., 2003,2007,2011)。流体作用的产物在超高压岩石中常以浅色矿物为主的岩脉产出,尤其以石英脉最为明显(Wu et al., 2009; 刘小驰等,2009; Zheng et al., 2007,2011; Cao et al., 2013)。石英脉经常出现在榴辉岩相变质岩石中,是流体与岩石反应的产物,为俯冲带流体活动的机制提供至关重要的信息(Liati and Gebauer, 1999; Rubatto et al., 1999; Philippot and Rumble, 2000; Franz et al., 2001; Widmer and Thompson, 2001; Rubatto and Hermann, 2003; Sp and ler and Hermann, 2006; 刘小驰等,2009; Wu et al., 2006,2008,2009; Zheng et al., 2003,2007,2011; Sheng et al., 2012)。
详细的岩石学和流体包裹体研究表明,在高压-超高压岩石中,形成岩脉的流体有两种来源:来自大规模迁移的外部流体和局部活动的内部流体(Henry et al., 1996; Cartwright and Barnicoat, 1999; Scambelluri et al., 1998; Zheng et al., 2003,2007; John et al., 2008; Jamtveit et al., 2000; Chen et al., 2012)。在造山带形成过程中,石英脉可形成于不同的阶段:进变质阶段(Liati and Gebauer, 1999; Rubatto et al., 1999; Molina et al., 2004; Wu et al., 2009)、峰期变质阶段(Rubatto and Hermann, 2003)和退变质阶段(Franz et al., 2001; Rubatto and Hermann, 2003; Li et al., 2004; Sp and ler and Hermann, 2006; Wu et al., 2009; Zheng et al., 2007,2011)。在碰撞造山的过程中,特别是在压力的降低或温度的升高时会分别发生降压脱水作用和升温脱水作用,使得超高压岩石中的含水矿物发生分解或者名义上不含水矿物的羟基发生出溶作用形成流体(Li et al., 2001; Li et al., 2004)。
锆石是榴辉岩和石英脉中常见的副矿物(吴元保郑永飞,2004; Wu et al., 2006; Zheng et al., 2007; 刘小驰等,2009),利用锆石的U-Pb体系可以精确地确定流体活动的年代。锆石中Lu-Hf体系非常的稳定(Cherniak and Watson, 2003),可以示踪寄主岩石来源和演化过程(Zheng et al., 2006),根据锆石的Lu/Hf比值,确定锆石是否与石榴石共生,以进一步限定锆石的形成条件(Zheng et al., 2005; Wu et al., 2006; 刘小驰等,2009)。综合石英脉中锆石的U-Pb定年、Lu-Hf同位素信息,可以为高级变质岩石中流体的来源、活动的时间以及形成条件等方面提供重要的制约。本文对东昆仑温泉地区榴辉岩中石英脉的锆石的形态特征、U-Pb定年、Lu-Hf同位素综合研究,不但为东昆仑榴辉岩峰期变质过程中流体的活动提供证据,同时也确定了流体的性质和来源,对理解流体活动在造山过程中的作用有重要意义。
2 区域地质概况及样品特征
昆仑造山带是中国中央造山带的重要组成部分之一,位于青藏高原北部,以阿尔金断裂为界分为东昆仑造山带和西昆仑造山带,其中东昆仑造山带以北为柴达木盆地,以南为巴颜喀拉-松藩甘孜地体(Bian et al., 2004; 陈能松等,2006)。东昆仑中央断裂带(东昆中断裂)是东昆仑造山带中一条非常重要的构造界线,从北至南可把东昆仑分为昆北地体和昆南地体两部分(图 1)(李怀坤等,2006; 许志琴等,2006; Meng et al., 2013)。
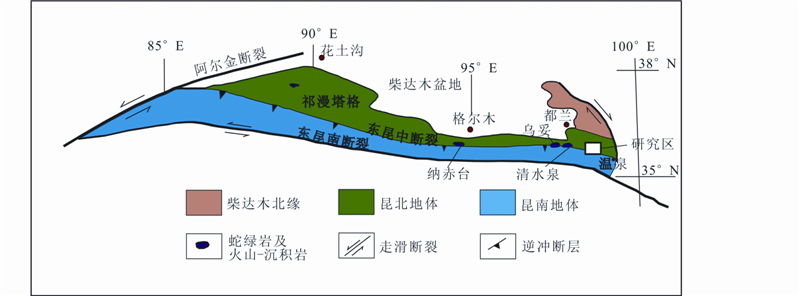 | 图 1 东昆仑地区构造单元划分图(据姜春发等,1992; Meng et al., 2013修改) Fig. 1 Geological map of the East Kunlun orogen and its tectonic division(after Jiang et al., 1992; Meng et al., 2013) |
昆北地体由元古代金水口群、早古生代纳赤台群和晚泥盆世契盖苏群组成(陈能松等,2006)。金水口群被认为是本区最古老的变质岩系,原岩主要为杂砂岩、泥质岩,其次为碳酸盐岩,含少量中基性到基性火山岩,形成于古-中元古代,该群遭受早古生代角闪岩相至麻粒岩相的区域变质作用(陈能松等, 1999,2006,2007;张建新等,2003;李怀坤等,2006;刘彬等,2012)和区域混合岩化作用,形成一些条痕状、条带状、眼球状混合岩及少量混合花岗岩;纳赤台群为一套绿片岩相变质的火山岩、碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩(姜春发等,1992),被大量志留纪-泥盆纪的花岗闪长岩和花岗岩侵入(莫宣学等,2007;许志琴等,2007;刘彬等,2012),存在零星分布的早古生代蛇绿岩,如祁漫塔格地区的鸭子泉蛇绿岩(姜春发等,1992;崔美慧等,2011);晚泥盆世契盖苏群由碎屑岩和陆相火山岩组成(姜春发等,1992),代表了造山后期的磨拉石建造。
昆南地体由元古代的苦海群、万宝沟群、早古生代的纳赤台群以及志留-泥盆纪的牦牛山组红色磨拉石建造组成。苦海群主要为角闪岩、长英质片麻岩和大理岩,其原岩为碎屑岩、中-基性火山岩和碳酸盐岩,经历了早古生代的角闪岩相变质作用(王国灿等,2004; Liu et al., 2005);万宝沟群从下而上可分为五个组,依次为下碎屑岩组、火山岩组、绿色片岩组、碳酸盐岩组和上碎屑岩组,经历了绿片岩相变质作用(姜春发等,1992;潘裕生等,1996);纳赤台群主要为灰黑色、灰绿色变砂岩夹千枚岩以及大透镜状灰岩,经历了低级变质作用(姜春发等,1992),还有少量的石英岩和石英片岩(陈有炘等,2011),存在部分早古生代蛇绿岩残片,比如清水泉和乌妥地区的蛇绿岩(高延林等,1988; Yang et al., 1996; 朱云海等,1999; 冯建赟等,2010);晚泥盆世牦牛山组红色磨拉石建造标志着早古生代造山作用的结束(潘裕生等,1996;李荣社等,2007;许志琴等,2007;张耀玲等,2010)。
研究区位于东昆仑山最东端,距都兰东南方向约100km,温泉乡西北方向40km(图 2),在东昆中断裂与温泉断裂交汇处的北西侧(王秉璋等,2001)。区内发育不同类型的高级变质岩,主要为元古代片麻岩,超镁铁岩和榴辉岩相邻产出于片麻岩之中(解玉月,1998; 王秉璋等,2001; Meng et al., 2013);在片麻岩的北部和南部分别为泥盆纪花岗岩和石炭纪-二叠纪的沉积岩(Meng et al., 2013)。
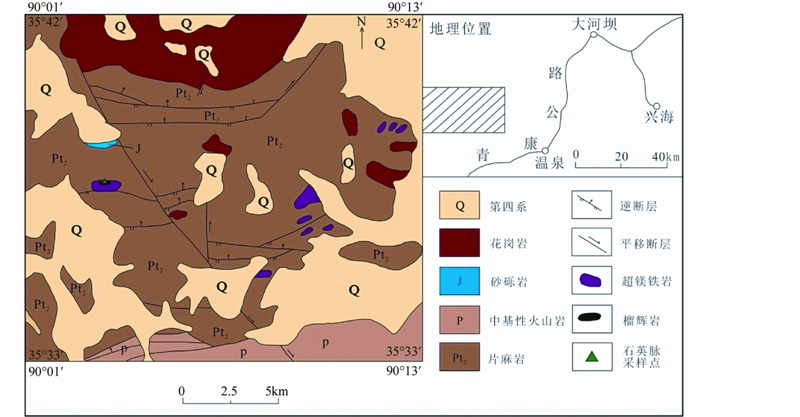 | 图 2 东昆仑温泉地区地质简图(据王秉璋等,2001修改)Fig. 2 Geological sketch map of Wenquan area in East Kunlun(after Wang et al., 2001) |
榴辉岩中有石英脉产出(图 3a),脉宽约为3~8cm,主要有以下三个特征:(1)石英脉与寄主榴辉岩有明显的边界(图 3a,c);(2)在石英脉中没有发现超高压变质的指示性矿物(图 3d);(3)石英脉主要由石英组成,含量约为98%,含有少量方解石(图 3d),进一步说明该石英脉为流体形成。这些特征说明石英脉并非形成于俯冲阶段,有可能形成于峰期变质阶段或早期折返阶段。寄主榴辉岩为黑绿色,块状构造,半自形柱状、粒状结构,主要由石榴石(40%)、绿辉石(10%)、后成合晶(20%)、石英(15%~20%)和金红石(5%~10%)组成。石榴石,粒状,半自形结构,颗粒大小为0.5~3mm,内部含有金红石和石英包体;绿辉石,粒状,半自形-他形结构,可见两组解理,粒径为0.03~0.50mm;后成合晶分散在石榴石和绿辉石之间(图 3b),主要由单斜辉石和斜长石组成,粒径为5~10μm。榴辉岩的原岩为中基性侵入岩,其形成年龄为934Ma(Meng et al., 2013),榴辉岩相峰期变质年龄为451Ma。
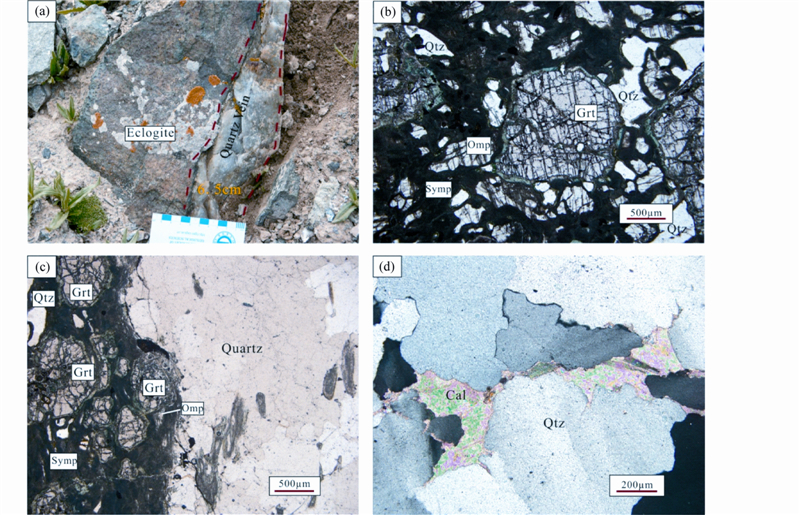 | 图 3 东昆仑温泉地区榴辉岩中石英脉 (a)-榴辉岩和石英脉接触关系,脉宽约6.5cm;(b)-单偏光下榴辉岩;(c)-单偏光下榴辉岩和石英脉;(d)-正交光下石英脉,主要由石英(95%)组成,方解石充填在石英颗粒的间隙,含量约为5%.矿物名称缩写:Qtz-石英;Omp-绿辉石;Symp-后成合晶;Grt-石榴石;Cal-方解石Fig. 3 Quartz vein in eclogite from Wenquan area in East Kunlun(a)-contact relationship between eclogite and quartz vein,quartz vein width of about 6.5cm;(b)-eclogite(-);(c)-eclogite and quartz vein(-);(d)-quartz vein(+)mainly composed of quartz(95%) and calcite(5%)fills in the gap. Abbreviations: Qtz-quartz; Omp-omphacite; Symp-symplectite; Grt-garnet; Cal-calcite |
3 分析方法
锆石的分选由河北廊坊区调院完成,岩石样品经过破碎、淘洗并用重液分选出锆石,在双目镜下挑选出晶形和透明度较好的锆石颗粒作为测定对象,将待测锆石粘在双面胶上,用无色透明的环氧树脂固定,待环氧树脂充分固化后,对其表面进行抛光至锆石内部结构暴露,再进行锆石反射光和透射光照相、阴极发光(CL)显微图像研究以及LA-ICP-MS分析。测试点的选取首先根据锆石反射光和透射光显微照片进行初选,再与CL照片进行对比,尽量避开内部裂隙、包裹体以及不同成因的区域,以获得相对精确的年龄信息。
锆石的LA-ICP-MS测试由天津地质矿产研究所同位素实验室完成:利用193nm激光器对锆石进行剥蚀,通常采用的激光剥蚀的斑束直径为35或50μm,激光能量密度为13~14J/cm2,频率为8~10Hz,激光剥蚀物质以He为载气送入Neptune,利用动态变焦扩大色散可以同时接受质量数相差很大的U-Pb同位素从而进行锆石U-Pb同位素原位测定。利用TEMORA作为外部锆石年龄标准。采用中国地质大学刘勇胜博士研发的ICPMSDataCal和Kenneth R. Ludwig的Isoplot程序进行数据处理,采用208Pb校正法对普通铅进行校正。采用NIST612玻璃标样作为外标计算锆石样品的Pb、U、Th含量(李怀坤等,2009)。
锆石Lu-Hf同位素在中国地质科学院测定,用176Lu/175Lu=0.02669(DeBievre and Taylor, 1993)和176Yb/172Yb=0.5886(Chu et al., 2002)进行同量异位干扰校正计算测试样品的176Lu/177Hf和176Hf/177Hf比值。εHf的计算采用176Lu衰变常数为1.867×10-11y-1(Sderlund et al., 2004),球粒陨石现今的176Hf/177Hf=0.282772,176Lu/177Hf=0.0332(Blichert-Toft and Albarède,1997);Hf亏损地幔单阶段模式年龄tDM1的计算采用现今的亏损地幔176Hf/177Hf=0.2835和176Lu/177Hf=0.0384(Griffin et al., 2000),两阶段模式年龄tDM2依据大陆上地壳平均组成fLu/Hf=-0.55(Griffin et al., 2000)。
4 结果 4.1 锆石特征
石英脉(K12-2-4.2)中的锆石为自形-半自形,无色透明,长柱状,长度介于50~200μm,长宽比为21~31,核边结构不明显,具有较好的振荡环带或弱分带(图 4a),晶型较好,明显与变质锆石不同,与热液成因的锆石特征类似(Rubatto et al., 1999; Rubatto and Hermann, 2003; Zheng et al., 2007; 吴元保和郑永飞,2004)。
 | 图 4 东昆仑温泉地区石英脉(a)及榴辉岩(b)中代表性锆石阴极发光图像 Fig. 4 Representative CL images of analyzed zircon for quartz vein(a) and eclogite(b)from Wenquan area in East Kunlun |
榴辉岩(K11-17-4.7)中的锆石为他形,无色透明,粒状-短柱状,长度介于50~100μm,长宽比为11~21(图 4b)。CL图像显示锆石具有弱的扇形分带结构,部分具有核边结构,边部较窄,这些特征表明锆石可能形成于变质作用的过程中。
4.2 锆石U-Pb同位素
对石英脉中的锆石测试了30个点(表 1),所有的锆石点都具有较低的Pb含量(5×10-6~23×10-6)和U含量(50×10-6~353×10-6),Th/U比值也较低(0.0003~0.053)(除一点为0.1126),为典型的热液锆石(Rubatto,2002)。大部分锆石的206U/238Pb年龄集中在441~459Ma(除一点为363Ma)(图 5a,b),其加权平均年龄为449.9±1.9Ma(2σ,n=29,MSWD=1.07),这组年龄代表石英脉的形成年龄。
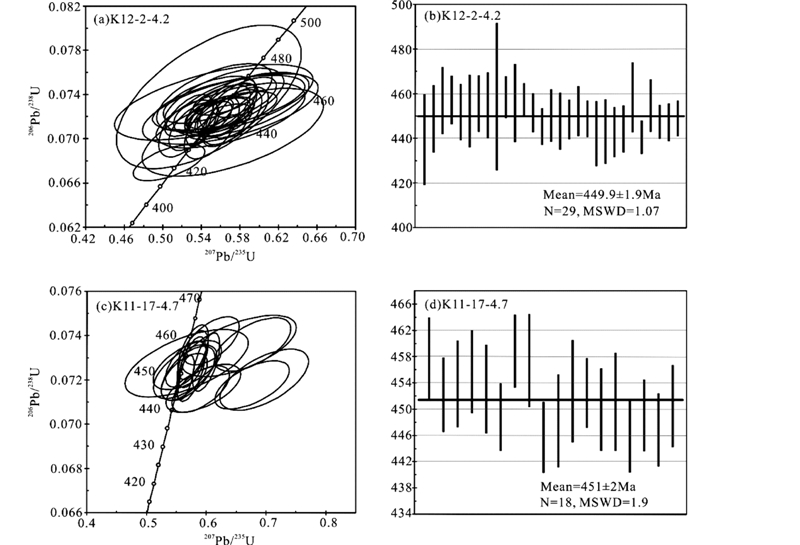 | 图 5 东昆仑温泉地区石英脉(a、b)及榴辉岩(c、d)中锆石U-Pb年龄谐和曲线图 Fig. 5 Zircon U-Pb age concordia diagram for quartz vein(a,b) and eclogite(c,d)from Wenquan area in East Kunlun |
| 表 1 锆石U-Pb同位素定年测试数据结果 Table 1 U-Pb isotope data of zircons |
榴辉岩中的锆石共测试了19粒(表 1),所有的锆石点都具有较低的Pb含量(5×10-6~42×10-6),其U含量为71×10-6~627×10-6,Th/U比值为0.003~0.317,一致低的Th/U说明在榴辉岩相变质作用中存在含水流体。所有锆石的206U/238Pb年龄集中在446~459Ma(除一点为431Ma)(图 5c,d),其加权平均年龄为451±2Ma(2σ,n=18,MSWD=1.9),这组年龄可能代表榴辉岩的峰期变质年龄。
4.3 锆石Lu-Hf同位素
石英脉中的锆石共分析了15颗Lu-Hf同位素数据(表 2),176Lu/177Hf比值为0.000006~0.000029,平均值为0.000012,176Hf/177Hf比值为0.2828450~0.2830796,平均值为0.2829592。利用LA-ICP-MS测得各个相对锆石的U-Pb年龄,计算其εHf(t)值为12.66~20.93,平均值为16.5(图 6a)。寄主榴辉岩中共测试了15个锆石Lu-Hf同位素数据(有一点数据异常除外),176Lu/177Hf比值为0.000004~0.000120,平均值为0.000027,176Hf/177Hf比值为0.2828361~0.2830221,平均值为0.2829286。利用LA-ICP-MS测得各个相对锆石的U-Pb年龄,计算其εHf(t)值为12.19~18.85,平均值为15.5(图 6b)。
| 表 2 锆石Lu-Hf同位素数据结果Table 2 Lu-Hf isotope data of zircons |
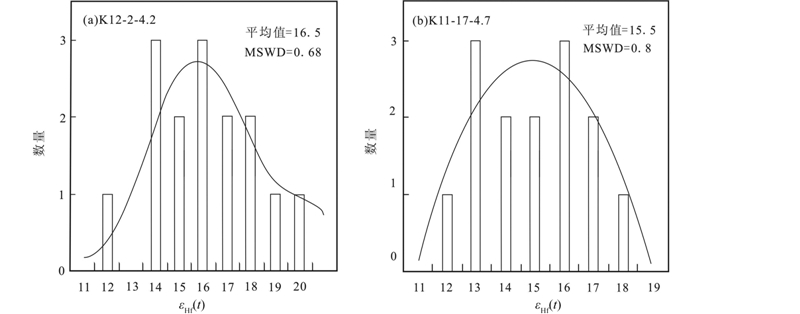 | 图 6 东昆仑温泉地区石英脉(a)及榴辉岩(b)中锆石Lu-Hf同位素εHf(t)值频率分布图Fig. 6 Histograms of zircon εHf(t)values of Lu-Hf isotope for quartz vein(a) and eclogite(b)from Wenquan area in East Kunlun |
5 讨论 5.1 流体活动的时间
目前大别地区超高压榴辉岩中石英脉的研究程度较高,大量研究认为在超高压峰期变质阶段流体活动受到限制(Rumble et al., 2000; Fu et al., 2001; Zheng et al., 2003; Wu et al., 2006),其超高压峰期变质时间达5~10Myr(Zheng et al., 1998; Wu et al., 2006)。温泉地区的榴辉岩中并未发现柯石英或金刚石等超高压的代表性矿物,属于高压榴辉岩(Meng et al., 2013)。由于在进变质、峰期变质和退变质作用过程中矿物都存在结构水,因此不能排除流体活动发生在峰期变质阶段,尽管流体的流量是很小的。本文测得榴辉岩中锆石的加权平均年龄为451±2Ma(图 5c,d),即榴辉岩相峰期变质的年龄。Meng et al.(2013)利用LA-ICP-MS测得榴辉岩的峰期变质年龄为430Ma,这两组数据在实验误差范围内(5%)一致,因此推测温泉地区榴辉岩相峰期变质年龄在430~451Ma,石英脉中锆石的加权平均年龄为450±2Ma(图 5a,b)。
结合前人对锆石学的研究,榴辉岩相变质条件下形成的锆石一般呈他形到半自形,无分带、弱分带到扇形分带,部分锆石具有残留岩浆核(Corfu et al., 2003; Hoskin and Schaltegger, 2003; 吴元保和郑永飞,2004)。本文榴辉岩中的锆石为他形,粒状-短柱状,具有弱的扇形分带结构,部分具有核边结构,边部较窄,这些特征表明锆石可能形成于变质作用的过程中。变质流体活动过程中形成的岩脉中的锆石一般为规则的外形,无分带到明显的面状分带或者振荡环带(Corfu et al., 2003; Hoskin and Schaltegger, 2003; 吴元保和郑永飞,2004)。本文石英脉中的锆石为自形-半自形,长柱状,核边结构不明显,具有较好的振荡环带或弱分带(图 4),晶型较好,明显与变质锆石不同,与热液成因的锆石特征类似。石英脉的寄主岩石为榴辉岩,石英脉中的锆石和榴辉岩中的锆石明显不同,这排除了在流体活动的过程中从榴辉岩中捕获锆石的可能性,因此有充分的证据可以说明石英脉中的锆石是从流体活动过程中形成的。
通常情况下U较Th在流体中有更高的溶解度,其活动性强于Th,石英脉中形成的锆石比寄主榴辉岩中的锆石具有更低的Th/U比值(吴元保和郑永飞,2004; Wu et al., 2006,2009; 刘小驰等,2009)。本文榴辉岩中变质锆石的Th/U比值的变化范围是0.003~0.053,石英脉中结晶的锆石的Th/U比值的变化范围为0.003~0.317(表 1),石英脉中锆石的Th/U比值整体比榴辉岩中的略小或者两者几乎一致,表明其形成条件的相似性。
锆石一般有较高的Hf含量,其Lu/Hf比值较低,相反,一些诸如石榴石、褐帘石、独居石等富集REE的矿物通常具有较高的Lu/Hf比值(Zheng et al., 2005; Wu et al., 2006)。若锆石与石榴石同时形成,则锆石的Lu/Hf比值将会更低,但如果锆石在石榴石分解之后形成,则其Lu/Hf比值会相应的增大。本文中锆石的Lu/Hf比值都相对较低(表 2),故从这一角度说明该石英脉并非形成于折返阶段。
结合以上对温泉地区榴辉岩和石英脉中锆石的U-Pb定年、Th/U比值以及Lu/Hf比值的综合研究,推测此次流体活动发生在榴辉岩相峰期变质阶段。
5.2 流体的来源和特征
在大别-苏鲁地区,普遍认为在当陆壳俯冲到地幔深度时的峰期变质阶段中很难有流体活动(Rumble et al., 2000; Fu et al., 2001; Zheng et al., 2003,2007; Frezzotti et al., 2007)。但是,在减压的过程中会有大量流体从含水矿物的分解(Li et al., 2004; Wu et al., 2006)以及名义上无水矿物(绿辉石、石榴石和金红石)羟基的出溶作用中产生(Zheng et al., 2003,2007; Chen et al., 2007; Frezzotti et al., 2007; Sheng et al., 2007)。经实验研究,榴辉岩中辉石、石榴石和金红石在地幔压力下有大量的水储存在结构水的羟基中(Skogby et al., 1990; Rossman,1996; Sheng et al., 2007),辉石的羟基含水量为600×10-6~1300×10-6(Ingrin and Skogby, 2000),金红石的羟基中含水量为4300×10-6~9600×10-6,石榴石的羟基含水量为92×10-6~1735×10-6(Zhang et al., 2001),使得绿辉石以及金红石等成为在俯冲至地幔过程中最重要的再生水矿物(Zheng et al., 2003),这种流体可以溶解围岩榴辉岩中的元素并且可以运输短暂的距离(Rubatto and Hermann, 2003)。
温泉地区榴辉岩与石英脉具有明显的边界,且接触界线较为平直(图 3c),推测在榴辉岩相峰期变质阶段未发生流体活动之前,此处岩石破裂,裂隙处压力突然降低导致榴辉岩中绿辉石、石榴石等矿物结构中的羟基发生出溶作用,进而产生流体进入到裂隙形成石英脉。另外,在寄主榴辉岩中含有15%~20%的石英(图 3b),绿辉石和石榴石中也发现石英包体,在榴辉岩相峰期变质条件下,这部分石英也可能发生溶解,进入裂隙参与岩脉的形成。因此,温泉地区榴辉岩中的石英脉是榴辉岩中石英溶解以及绿辉石和石榴石结构中羟基发生出溶共同作用的结果。
高级变质作用中锆石的生长机制主要有3种:1)在深熔作用中从熔体中结晶的(Vavra et al., 1999);2)矿物分解释放的Si和Zr进而形成锆石(Bingen et al., 2004);3)在含水流体中结晶的(Vavra et al., 1999; Rubatto and Hermann, 2003; Wu et al., 2006)。绿辉石是榴辉岩相中的典型矿物,在高压榴辉岩中绿辉石和石榴石都是含锆的矿物(锆含量分别可达到1.8×10-6和4.7×10-6; Sassi et al., 2000; Rubatto and Hermann, 2003),尽管这两种矿物分解可以促进在榴辉岩相变质作用下锆石的生长,但若缺少流体,这些都是无意义的,所有变质锆石的生长都只能发生在流体相中(Fraser et al., 1997; Zheng et al., 2004; Corfu et al., 2003; Wu et al., 2006)。
在流体中U比Th流动性更强,故极低的Th/U比值的锆石往往是在含水流体中结晶的。熔体中形成的长英质脉体一般包含石英和长石(Chen et al., 2012),但此次研究的石英脉却没有发现长石,这些证据说明锆石形成于流体而并非熔体。至于形成方解石的Ca(图 3d),可能来自绿辉石;流体中的CO2,可能与其他热液流体蚀变有关(Rayner et al., 2005)。
由于锆石富集Hf的能力比Lu强,通常利用Hf同位素的组成能够识别流体的来源。石英脉中的锆石的εHf(t)值为12.66~20.93,寄主榴辉岩中εHf(t)值为12.19~18.85(图 6),176Lu/177Hf比值和176Hf/177Hf比值见表 2。从数据中我们可以看出,石英脉中锆石的Hf同位素组成与寄主榴辉岩相似,但是有小的变化。这些相似性表明形成石英脉的流体为内部来源,并经历了短距离的运移。Zheng et al.(2007)在大别山东部的石英脉中通过氧同位素的研究也得出了相似的结论。榴辉岩中锆石的εHf(t)平均值为15.5,如此高的εHf(t)值表明榴辉岩的原岩(中-基性辉长岩)源于亏损的地幔(Wu et al., 2006; Zheng et al., 2005,2006; 吴福元等,2007)。
6 结论
本文综合了锆石的U-Pb定年和Lu-Hf同位素的研究,详细解释了高压条件下流体活动的时代、条件以及来源。通过对石英脉的野外接触关系、矿物组成、锆石内部结构、Th、U含量和Th/U比值以及Hf同位素的分析,得出以下认识:
(1)测得榴辉岩的峰期变质年龄为451±2Ma,石英脉中锆石的年龄为450±2Ma,两者在误差范围内一致的年龄说明在榴辉岩相峰期变质阶段可以出现内部流体活动。
(2)认为锆石更可能形成于含水流体而非熔体,对比寄主榴辉岩的锆石和石英脉中锆石的Hf同位素组成,其相似性说明形成石英脉的流体来自榴辉岩的内部,推测流体来源于寄主榴辉岩中石英的溶解以及绿辉石和石榴石分子结构中羟基的出溶作用。
致谢 河北廊坊区调院在锆石的分选;国土资源部大陆动力学实验室在锆石制靶;中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所同位素实验室在Lu-Hf同位素分析;天津地质矿产研究所同位素实验室在锆石U-Pb年代学测试以及数据处理等方面给予了大力的帮助;张泽明和吴元保两位老师提出了建设性修改意见;在此一并表示衷心的感谢。
| [1] | Blichert-Toft J and Albarède F. 1997. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 148(2): 243-258 |
| [2] | Bian QT, Li DH, Pospelov I, Yin LM, Li HS, Zhao DS, Chang CF, Luo XQ, Gao SL, Astrankhantsev O and Chamov N. 2004. Age, geochemistry and tectonic setting of Buqingshan ophiolites, North Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J. Asian Earth Sci., 23(4): 577-596 |
| [3] | Bingen B, Austrheim H, Whitehouse MJ and Davis WJ. 2004. Trace element signature and U-Pb geochronology of eclogite-facies zircon, Bergen Arcs, Caledonides of W Norway. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 147(6): 671-683 |
| [4] | Cao YT, Liu L, Chen DL, Wang C, Yang WQ, Kang L and Zhu XH. 2013. The felsic vein within the garnet pyroxenite from Shenglikou, North Qaidam: Episodic fluid flow during the exhumation of the rock. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(Suppl.): 439-440 |
| [5] | Cartwright I and Barnicoat AC. 1999. Stable isotope geochemistry of Alpine ophiolites: A window to ocean-floor hydrothermal alteration and constraints on fluid-rock interaction during high-pressure metamorphism. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 88(2): 219-235 |
| [6] | Chu NC, Taylor RN, Chavagnac V, Nesbitt RW, Boella RW, Milton JA, German CR, Bayon C and Burton K. 2002. Hf isotope ratio analysis using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: An evaluation of isobaric interference corrections. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 17(12):1567-1574 |
| [7] | Chen DL, Liu L, Sun Y, Sun WD, Zhu XH and Guo CL. 2012. Felsic veins within UPH eclogite at xitieshan in North Qaidam, NW China: Partial melting during exhumation. Lithos, 136: 187-200 |
| [8] | Chen NS, Zhu J, Wang GC, Hou GJ, Zhang KX, Zhu YH and Bai YS. 1999. Metamorphic petrological features of high-grade metamorphic microlithons in Qingshuiquan region, eastern section of Eastern Kunlun orogenic zone. Earth Science, 24(2): 8-12 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] | Chen NS, Li XY, Wang XY, Chen Q, Wang QY and Wan YS. 2006. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age of Neoproterozoic metagranite in the North Kunlun unit on the southern margin of the Qaidam block in China. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(11): 1311-1314 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [10] | Chen NS, Sun M, Wang QY, Zhao GC, Chen Q and Shu GM. 2007. EMP chemical ages of monazites from Central Zone of Eastern Kunlun Orogen: Records of the multi-tectonometamorphic events. Chinese Sci. Bull., 52(11): 1297-1306 (in Chinese) |
| [11] | Chen RX, Zheng YF, Gong B, Zhao ZF, Gao TS, Chen B and Wu YB. 2007. Origin of retrograde fluid in ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks: Constraints from mineral hydrogen isotope and water content changes in eclogite-gneiss transitions in the Sulu orogen. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(9): 2299-2325 |
| [12] | Chen YX, Pei XZ, Li RB, Liu ZQ, Li ZC, Zhang XF, Chen GC, Liu ZG, Ding SP and Guo JF. 2011. Zircon U-Pb age of Xiaomiao Formation of Proterozoic in the eastern section of the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Geoscience, 25(3): 510-521 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [13] | Cherniak DJ and Watson EB. 2003. Diffusion in zircon. In: Hanchar JM and Hoskin PWO (eds.). Zircon, 53(1): 113-143 |
| [14] | Corfu F, Hanchar JM, Hoskin PWO and Kinny P. 2003. Atlas of zircon textures. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53: 468-500 |
| [15] | Cui MH, Meng FC and Wu XK. 2011. Early Ordovician island arc of Qimantag Mountain, eastern Kunlun: Evidences from geochemistry, Sm-Nd isotope and geochronology of intermediate-basic igneous rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(11): 3365-3379 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [16] | DeBievre P and Taylor PDP. 1993. Table of the isotopic composition of the elements. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, Ion Process, 123:149 |
| [17] | Feng JY, Pei XZ, Yu SL, Ding SP, Li RB, Sun Y, Zhang YF, Li ZC, Chen YX, Zhang XF and Chen GC. 2010. The discovery of the mafic-ultramafic mélange in Kekesha area of Dulan County, East Kunlun region, and its LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age. Geology in China, 37(1): 28-38 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Fraser G, Ellis D and Eggins S. 1997. Zirconium abundance in granulite-facies minerals, with implications for zircon geochronology in highgrade rocks. Geology, 25(7): 607-610 |
| [19] | Franz L, Romer RL, Klemd R, Schmid R, Oberhnsli R, Wagner T and Dong S. 2001. Eclogite-facies quartz veins within metabasites of the Dabie Shan: Pressure-temperature-time-deformation path, composition of the fluid phase and fluid flow during exhumation of high-pressure rocks. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 141(3): 322-346 |
| [20] | Frezzotti ML, Ferrando S, Dallai L and Compagnoni R. 2007. Intermediate alkali-alumino-silicate aqueous solutions released by deeply subducted continental crust: Fluid evolution in UHP OH-rich topaz-kyanite quartzites from Donghai (Sulu, China). Journal of Petrology, 48(6): 1219-1241 |
| [21] | Fu B, Touret JLR and Zheng YF. 2001. Fluid inclusions in coesite-bearing eclogites and jadeite quartzite at Shuanghe, Dabie Shan, China. J. Metamor. Geol., 19(5): 529-545 |
| [22] | Gao YL, Wu XN and Zuo GC. 1988. The characters and tectonic significance of ophiolite first discovered in the East Kunlun area. Bulletin of Xi'an Institute Geological Mineral Resource, CAS, 21: 17-28 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [23] | Griffin WL, Pearson NJ, Belousova E, Jackson SE, Achterbergh E, O'Reilly SY and Shee SR. 2000. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LA-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1): 133-147 |
| [24] | Henry C, Burkhard M and Goffe B. 1996. Evolution of synmetamorphic veins and their wallrocks through a Western Alps transect: No evidence for large-scale fluid flow. Stable isotope, major and trace-element systematics. Chemical Geology, 127(1-3): 81-109 |
| [25] | Hermann J, Spandler C, Hack A and Korsakov AV. 2006. Aqueous fluids and hydrous melts in high-pressure and ultrahigh-pressure rocks: Implications for element transfer in subduction zones. Lithos, 92(3-4): 399-417 |
| [26] | Hoskin PWO and Schaltegger U. 2003. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 27-62 |
| [27] | Ingrin J and Skogby H. 2000. Hydrogen in nominally anhydrous upper-mantle minerals: Concentration levels and implications. Eur. J. Mineral, 12(3): 543-570 |
| [28] | Jiang CF, Yang JS, Feng BG, Zhu ZZ, Zhao M, Chai YC, Shi XD, Wang HD and Hu JQ. 1992. Opening-Closing Tectonics of Kunlun Mountains. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-224 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [29] | Jamtveit B, Austrheim H and Malthe-Sorenssen A. 2000. Accelerated hydration of the Earth's deep crust induced by stress perturbations. Nature, 408: 75-78 |
| [30] | John T, Klemd R, Gao J and Garbe-Schonberg CD. 2008. Trace-element mobilization in slabs due to non steady-state fluid-rock interaction: Constrains from an eclogite-facies transport vein in blueschist(Tianshan, China). Lithos, 103: 1-24 |
| [31] | Li HK, Lu SN, Xiang ZQ, Zhou HY, Guo H, Song B, Zheng JK and Gu Y. 2006. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon age of the granulite from the Qingshuiquan area, Central Eastern Kunlun Suture Zone. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(6): 311-321 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Li HK, Geng JJ, Hao S, Zhang YQ and Li HM. 2009. The study of zircon U-Pb dating by means LA-MC-ICPMS. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 29(Suppl.): 600-601 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [33] | Li RS, Ji WH, Zhao ZM, Chen SJ, Meng Y, Yu PS and Pan XP. 2007. Progress in the study of the Early Paleozoic Kunlun orogenic belt. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(4): 373-382 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [34] | Li XP, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Chen FK, Gong B and Li YL. 2004. Low-T eclogite in the Dabie terrane of China: Petrological and isotopic constraints on fluid activity and radiometric dating. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 148(4): 443-470 |
| [35] | Li YL, Zheng YF, Fu B, Zhou JB and We CS. 2001. Oxygen isotope composition of quartz-vein in ultrahigh pressure eclogite from Dabieshan and implications for transport of high-pressure metamorphic fluid. Physics and Chemistry of Earth (A), 26: 695-704 |
| [36] | Liati A and Gebauer D. 1999. Constraining the prograde and retrograde P-T-t path of Eocene HP rocks by SHRIMP dating of different zircon domains: Inferred rates of heating-burial, cooling and exhumation for central Rhodope, northern Greece. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 135(4): 340-354 |
| [37] | Liu B, Ma CQ, Zhang JY, Xiong FH, Huang J and Jiang HA. 2012. Petrogenesis of Early Devonian intrusive rocks in the east part of Eastern Kunlun Orogen and implication for Early Palaeozoic orogenic processes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(6): 1785-1807 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [38] | Liu XC, Wu YB, Gong HJ, Yang SH, Wang J, Peng M and Jiao WF. 2009. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope composition of a quartz vein in ultrahigh-pressure eclogite from the western Dabie orogen. Chinese Sci. Bull., 54(10): 1449-1454 (in Chinese) |
| [39] | Liu YJ, Genser J, Neubauer F, Jin W, Ge XH, Handler R and Takasu A. 2005. 40Ar/39Ar mineral ages from basement rocks in the Eastern Kunlun Mountains, NW China and their tectonic implications. Tectonophysics, 398(3-4): 199-224 |
| [40] | Meng FC, Zhang JX and Cui MH. 2013. Discovery of Early Paleozoic eclogite from the East Kunlun, western China and its Tectonic significance. Gondwana Research, 23(2): 825-836 |
| [41] | Miller JA, Buick IS, Cartwright I and Barnicoat A. 2002. Fluid processes during the exhumation of high-P metamorphic belts. Mineralogical Magazine, 66(1): 93-119 |
| [42] | Mo XX, Luo ZH, Deng FJ, Yu XH, Liu CD, Chen HW, Yuan WM and Liu YH. 2007. Granitoids and crustal growth in the East-Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(3): 403-414 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [43] | Molina JF, Poli S, Austrheim H, Glodny J and Rusin A. 2004. Eclogite-facies vein systems in the Marun-Keu complex (Polar Urals, Russia): Textural, chemical and thermal constraints for patterns of fluid flow in the lower crust. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 147(4): 484-504 |
| [44] | Pan YS, Zhou WM, Xu RH, Wang DA, Zhang YQ, Xie YW, Chen TE and Luo H. 1996. Geological characteristics and evolution of the Kunlun Mountains region during the Early Paleozoic. Science in China (Series D), 39(4): 337-347 |
| [45] | Philippot P and Rumble D. 2000. Fluid rock interactions in HP and UHP rocks. International Geology Review, 42(4): 312-327 |
| [46] | Rayner N, Stern RA and Carr SD. 2005. Grain-scale variations in trace element composition of fluid-altered zircon, Acasta Gneiss Complex, northwestern Canada. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 148(6): 721-734 |
| [47] | Rossman GR. 1996. Studies of OH in nominally anhydrous minerals. Phys. Chem. Miner., 23(4-5): 299-304 |
| [48] | Rubatto D, Gebauer G and Compagnoni R. 1999. Dating of eclogite-facies zircons: The age of Alpine metamorphism in the Sesia-Lanzo Zone (Western Alps). Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 167(3-4): 141-158 |
| [49] | Rubatto D. 2002. Zircon trace element geochemistry: Partitioning with garnet and the link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism. Chemical Geology, 184(1-2): 123-138 |
| [50] | Rubatto D and Hermann J. 2003. Zircon formation during fluid circulation in eclogites (Monviso, Western Alps): Implications for Zr and Hf budget in subduction zones. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(12): 2173-2187 |
| [51] | Rumble D, Wang QC and Zhang RY. 2000. Stable isotope geochemistry of marbles from the coesite UHP terrains of Dabieshan and Sulu, China. Lithos, 52(1-4): 79-95 |
| [52] | Sassi R, Harte B, Carswell DA and Han YJ. 2000. Trace element distribution in central Dabie eclogites. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 139(3): 298-315 |
| [53] | Scambelluri M, Pennacchioni G and Philippot P. 1998. Salt-rich aqueous fluids formed during eclogitization of metabasites in the Alpine continental crust (Austroalpine Mt. Emilius unit, Italian western Alps). Lithos, 43(3): 151-167 |
| [54] | Sheng YM, Xia QK, Dallai L, Yang XZ and Hao YT. 2007. H2O contents and D/H ratios of nominally anhydrous minerals from ultrahigh-pressure eclogites of the Dabie orogen, eastern China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(8): 2079-2103 |
| [55] | Sheng YM, Zheng YF and Chen RX. 2012. Fluid action on zircon growth and recrystallization during quartz veining within UHP eclogite: Insights from U-Pb ages, O-H isotopes and trace elements. Lithos, 136-139: 126-144 |
| [56] | Skogby H, Bell DR and Rossman GR. 1990. Hydroxide in pyroxene: Variations in the natural environment. Am. Mineral., 75: 764-774 |
| [57] | Spandler C and Hermann J. 2006. High-pressure veins in eclogite from New Caledonia and their significance for fluid migration in subduction zones. Lithos, 89(1-2): 135-153 |
| [58] | Sderlund U, Patchett PJ, Vervoort JD and Isachsen CE. 2004. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219(3-4): 311-324 |
| [59] | Sun XM, Tang Q, Sun WD, Xu L, Zhai W, Liang JL, Liang YS, Zhang ZM, Zhou B and Wang FY. 2007. Monazite, iron oxide and barite exsolutions in apatite aggregates from CCSD drillhole eclogites and their geological implications. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(11): 2896-2905 |
| [60] | Vavra G, Schmid R and Gebauer D. 1999. Internal morphology, habit and U-Th-Pb microanalysis of amphibolite-togranulite facies zircons: Geochronology of the Ivrea Zone (Southern Alps). Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 134(4): 380-404 |
| [61] | Wang BZ, Zhang SQ, Zhang ZY and Wang J. 2001. Proterozoic ophiolite in the Zhanahere area in the east section of the East Kunlun. Regional Geology of China, 20(1): 52-57 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [62] | Wang GC, Wang QH, Jian P and Zhu YH. 2004. Zircon SHRIMP ages of Precambrian metamorphic basement rocks and their tectonic significance in the eastern Kunlun Mountains, Qinghai Province, China. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(4): 481-490 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [63] | Widmer T and Thompson AB. 2001. Local origin of high-pressure vein material in eclogite facies rocks of the Zermatt-Saas zone, Switzerland. American Journal of Science, 301(7): 627-656 |
| [64] | Wu FY, Li XH, Zheng YF and Gao S. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematic and the applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185-220 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [65] | Wu YB and Zheng YF. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(16): 1589-1604 (in Chinese) |
| [66] | Wu YB, Zheng YF, Zhao ZF, Gong B, Liu XM and Wu FY. 2006. U-Pb. Hf and O isotope evidence foe two episodes of fluid-assisted zircon growth in marble-hosted eclogites from the Dabie orogen. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 70(14): 3743-3761 |
| [67] | Wu YB, Gao S, Zhang HF, Yang SH, Jiao WF, Liu YS and Yuan HL. 2008. Timing of UHP metamorphism in the Hong'an area, western Dabie Mountains, China: Evidence from zircon U-Pb age, trace element, and Hf isotope composition. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 155(1): 123-133 |
| [68] | Wu YB, Gao S, Zhang HF, Yang SH, Liu XC, Jiao WF, Liu YS, Yuan HL, Gong HJ and He MC. 2009. U-Pb age, trace-element, and Hf-isotope compositions of zircon in a quartz vein from eclogite in the western Dabie Mountains: Constraints on fluid flow during early exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure rocks. American Mineralogist, 94(2-3): 303-312 |
| [69] | Xie YY. 1998. Features of ophiolite with different period in the eastern section of Middle Kunlun Fault and its original environment. Qinghai Geology, 7(1): 27-36 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [70] | Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Li HB and Yao JX. 2006. The Early Palaeozoic terrene framework and the formation of the high-pressure (HP) and ultra-high pressure (UHP) metamorphic belts at the Central Orogenic Belt (COB). Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(12): 1973-1806 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [71] | Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Li HB, Zhang JX and Wu CL. 2007. Orogenic Plateau: Terrane Amalgamation, Collision and Uplift in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-458 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [72] | Yang JS, Robinson PT, Jiang CF and Xu ZQ. 1996. Ophoilites of the Kunlun Mountains, China and their tectonic implications. Tectonophysics, 258(1-4): 215-231 |
| [73] | Zhang JF, Jin ZM, Green HW and Jin SY. 2001. Hydroxyl in continental deep subduction zone: Evidence from UHP eclogites of the Dabie Mountains. Chin. Sci. Bull., 46(7): 592-595 |
| [74] | Zhang JX, Meng FC, Wan YS, Yang JS and Dong AG. 2003. Early Paleozoic tectono-thermal event of the Jinshuikou Group on the southern margin of Qaidam: Zircon U-Pb SHRIMP age evidence. Geological Bulletin of China, 22(6): 397-4048 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [75] | Zhang L, Zhong Z, Zhang H, Sun WD and Xiang H. 2009. The formation of foliated (garnet bearing) granites in the Tongbai-Dabie orogenic belt: Partial melting of subducted continental crust during exhumation. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 27(9): 789-803 |
| [76] | Zhang YL, Zhang XJ, Hu GD, Shi YR and Lu L. 2010. Zircon U-Pb ages for rhyolitic tuffs of the Naocangjiangou formation in the East Kulun orogenic belt and their implication. Journal of Geomechanics, 16(1): 21-27, 50 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [77] | Zhang ZM, Shen K, Sun WD, Liu YS, Liu JG, Shi C and Wang JL. 2008. Fluids in deeply subducted continental crust: Petrology, mineral chemistry and fluid inclusion of UHP metamorphic veins from the Sulu orogen, eastern China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(13): 3200-3228 |
| [78] | Zheng YF, Fu B, Li YL, Xiao YL and Li SG. 1998. Oxygen and hydrogen isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure eclogites from the Dabie Mountains and the Sulu terrane. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 155(1-2): 113-129 |
| [79] | Zheng YF, Fu B, Gong B and Li Y. 2003. Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie-Sulu orogen in China: Implications for geodynamics and fluid regime. Earth-Science Reviews, 62(1-2): 105-161 |
| [80] | Zheng YF, Wu YB, Chen FK, Gong B, Li L and Zhao ZF. 2004. Zircon U-Pb and oxygen isotope evidence for a large-scale 18O depletion event in igneous rocks during the Neoproterozoic. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(20): 4145-4165 |
| [81] | Zheng YF, Wu YB, Zhao ZF, Zhang SB, Xu P and Wu FY. 2005. Metamorphic effect on zircon Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope system in ultrahigh-pressure eclogite-facies metagranite and metabasite. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 240(2): 378-400 |
| [82] | Zheng YF, Zhao ZF, Wu YB, Zhang SB, Liu XM and Wu FY. 2006. Zircon U-Pb age, Hf and O isotope constraints on protolith origin of ultrahigh-pressure eclogite and gneiss in the Dabie orogen. Chemical Geology, 231(1-2): 135-158 |
| [83] | Zheng YF, Gao TS, Wu YB, Gong B and Liu XM. 2007. Fluid flow during exhumation of deeply subducted continental crust: Zircon U-Pb age and O-isotope studies of a quartz vein within ultrahigh-pressure eclogite. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 25(2): 267-283 |
| [84] | Zheng YF, Xia QX, Chen RX and Gao XY. 2011. Partial melting, fluid supercriticality and element mobility in ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks during continental collision. Earth-Science Reviews, 107(3-4): 342-374 |
| [85] | Zhu YH, Zhang KX, Yuan P, Chen NS, Wang GC and Hou GJ. 1999. Determination of different ophiolitic belts in eastern Kunlun orogenic zone and their tectonic significance. Earth Science, 24(2): 134-138 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [86] | 陈能松, 朱杰, 王国灿, 侯光久, 张克信, 朱云海, 拜永山. 1999. 东昆仑造山带东段清水泉高级变质岩片的变质岩石学研究. 地球科学, 24(2): 8-12 |
| [87] | 陈能松, 李晓彦, 王新宇, 陈强, 王勤燕, 万渝生. 2006. 柴达木地块南缘昆北单元变质新元古代花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄. 地质通报, 25(11): 1311-1314 |
| [88] | 陈能松, 孙敏, 王勤燕, 赵国春, 陈强, 舒桂明. 2007. 东昆仑造山带昆中带的独居石电子探针化学年龄: 多期构造变质事件记录. 科学通报, 52(11): 1297-1306 |
| [89] | 陈有炘, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 刘战庆, 李佐臣, 张晓飞, 陈国超, 刘智刚, 丁仨平, 郭俊锋. 2011. 东昆仑造山带东段元古界小庙岩组的锆石U-Pb年龄. 现代地质, 25(3): 510-521 |
| [90] | 崔美慧, 孟繁聪, 吴祥珂. 2011. 东昆仑祁漫塔格早奥陶世岛弧: 中基性火成岩地球化学、Sm-Nd同位素及年代学证据. 岩石学报, 27(11): 3365-3379 |
| [91] | 冯建赟, 裴先治, 于书伦, 丁仨平, 李瑞保, 孙雨, 张亚峰, 李佐臣, 陈有炘, 张晓飞, 陈国超. 2010. 东昆仑都兰可可沙地区镁铁-超镁铁质杂岩的发现及其LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄. 中国地质, 37(1): 28-38 |
| [92] | 高延林, 吴向农, 左国朝. 1988. 东昆仑山清水泉蛇绿岩特征及其大地构造意义. 中国地质科学院西安地质矿产研究所所刊, 21: 17-28 |
| [93] | 姜春发, 杨经绥, 冯秉贵, 朱志直, 赵民, 柴耀楚. 1992. 昆仑开合构造. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-224 |
| [94] | 李怀坤, 陆松年, 相振群, 周红英, 郭虎, 宋彪, 郑健康, 顾瑛. 2006. 东昆仑中部缝合带清水泉麻粒岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究. 地学前缘, 13(6): 311-321 |
| [95] | 李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 张永清, 李惠民. 2009. 用激光烧蚀多接收器等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS) 测定锆石 U-Pb 同位素年龄. 矿物学报, 29(增刊): 600-601 |
| [96] | 李荣社, 计文化, 赵振明, 陈守建, 孟勇, 于浦生, 潘小平. 2007. 昆仑早古生代造山带研究进展. 地质通报, 26(4): 373-382 |
| [97] | 刘彬, 马昌前, 张金阳, 熊富浩, 黄坚, 蒋红安. 2012. 东昆仑造山带东段早泥盆世侵入岩的成因及其对早古生代造山作用的指示. 岩石学报, 28(6): 1785-1807 |
| [98] | 刘小驰, 吴元保, 弓虎军, 杨赛红, 汪晶, 彭敏, 焦文放. 2009. 西大别超高压榴辉岩中石英脉锆石年龄和Hf同位素组成. 科学通报, 54(10): 1449-1454 |
| [99] | 莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 喻学惠, 刘成东, 谌宏伟, 袁万明, 刘云华. 2007. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长. 高校地质学报, 13(3): 403-414 |
| [100] | 潘裕生, 周伟明, 许荣华, 王东安, 张玉泉, 谢应雯, 陈挺恩, 罗辉. 1996. 昆仑山早古生代地质特征与演化. 中国科学(D辑), 26(4): 302-307 |
| [101] | 王秉璋, 张森琦, 张志勇, 王瑾. 2001. 东昆仑东端扎那合惹地区元古宙蛇绿岩. 中国区域地质, 20(1): 52-57 |
| [102] | 王国灿, 王青海, 简平, 朱云海. 2004. 东昆仑前寒武纪基底变质岩系的锆石SHRIMP年龄及其构造意义. 地学前缘, 11(4): 481-490 |
| [103] | 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185-220 |
| [104] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589-1604 |
| [105] | 解玉月. 1998. 昆中断裂东段不同时代蛇绿岩特征及形成环境. 青海地质, 7(1): 27-36 |
| [106] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 姚建新. 2006. 中央造山带早古生代地体构架与高压/超高压变质带的形成. 地质学报, 80(12): 1973-1806 |
| [107] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 张建新,吴才来. 2007. 造山的高原——青藏高原地体的拼合、碰撞造山及隆升机制. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-458 |
| [108] | 张建新, 孟繁聪, 万渝生, 杨经绥, 董国安. 2003. 柴达木盆地南缘金水口群的早古生代构造热事件: 锆石U-Pb SHRIMP年龄证据. 地质通报, 22(6): 397-404 |
| [109] | 张耀玲, 张绪教, 胡道功, 石玉若, 陆露. 2010. 东昆仑造山带纳赤台群流纹岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄. 地质力学学报, 16(1): 21-27, 50 |
| [110] | 朱云海, 张克信, 陈能松, 王国灿, 侯光久. 1999. 东昆仑造山带不同蛇绿岩带的厘定及其构造意义. 地球科学, 24(2): 26-30 |
 2014, Vol. 30
2014, Vol. 30


