2. 造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室,北京大学地球与空间科学学院,北京 100871;
3. 内蒙古第八地质矿产勘查开发院,乌海 016000
2. Key Laboratory of Orogenic Belts and Crustal Evolution, Ministry of Education, School of Earth and Space Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China;
3. The Eighth Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources Exploration and Development, Inner Mongolia Bureau, Wuhai 016000, China
近年来在鄂尔多斯盆地东北部发现的东胜地区中侏罗统直罗组大型砂岩型铀矿显示了良好的铀矿开发前景。前人对该铀矿进行了沉积体系与沉积相(赵宏刚和欧光习,2006;杨仁超等,2007)、铀矿产状及分布(肖新建等,2004;吴仁贵等,2006;赵宏刚和欧光习,2006)、铀矿的成矿期次与成矿年代学(夏毓亮等,2003;夏毓亮和刘汉彬, 2005;林潼等;2007)、赋矿砂岩的成岩作用及地球化学特征(肖新建等,2004;罗静兰等,2005;潘爱芳等,2007)以及铀成矿作用与铀成矿机理(向伟东,2006;罗静兰等, 2005, 2006)等多方位的研究,获得了一批重要成果与认识。对东胜地区砂岩型铀矿可能的物源方向、铀源与母岩性质的研究认为,沉积物质来自盆地北部的花岗岩、中酸性火山岩和变质岩(肖新建,2004;柳益群等,2006;赵俊峰等,2007)。但上述结论基本上属于定性研究结果,截至目前为止,尚缺乏精确的源区岩石的同位素定年结果予以支持;另外,也未见研究区与源区岩石时代及其母岩性质等的对比研究。
华北克拉通是世界上最古老的克拉通之一,最老的基底岩石年龄达3.8Ga(Liu et al., 1992;Song et al., 1996;Wan et al., 2005),其形成和演化历史一直是我国地质学界广泛关注的问题。随着现代分析测试技术的发展,尤其是同位素年代学研究的不断深入,广大地质工作者对华北克拉通早期陆块的形成和演化及最终克拉通化的过程有了更深入的认识(翟明国, 2004, 2010;翟明国和彭澎,2007;赵国春等,2002;赵国春,2009;Zhao et al., 2005, 2010;Kusky et al., 2007;Zhai and Santosh, 2011;Zhai,2011;Wan et al., 2009, 2011)。鄂尔多斯盆地广泛发育中生代碎屑岩沉积,对其碎屑锆石同位素定年的沉积物源示踪研究,不仅可查明鄂尔多斯盆地地质时期的源区位置、母岩地层时代与母岩性质等源区特征,而且对于深入理解华北克拉通的形成与演化,加快鄂尔多斯盆地矿产资源的勘探开发步伐都具有重要的理论意义与实际指导价值。
本文利用LA-(MC)ICP-MS微区原位U-Pb定年、Hf同位素及微量元素分析方法,对鄂尔多斯盆地东胜地区中侏罗统直罗组砂岩型铀矿中的碎屑锆石进行了精细定年和Hf同位素分析,建立了碎屑锆石的U-Pb年龄及Hf模式年龄谱系;通过与物源区地层同位素年代学、母岩性质的对比研究,精确厘定了东胜地区中侏罗统直罗组沉积期的源区位置、母岩的形成时代与母岩性质,并对源区构造演化进行了探讨。
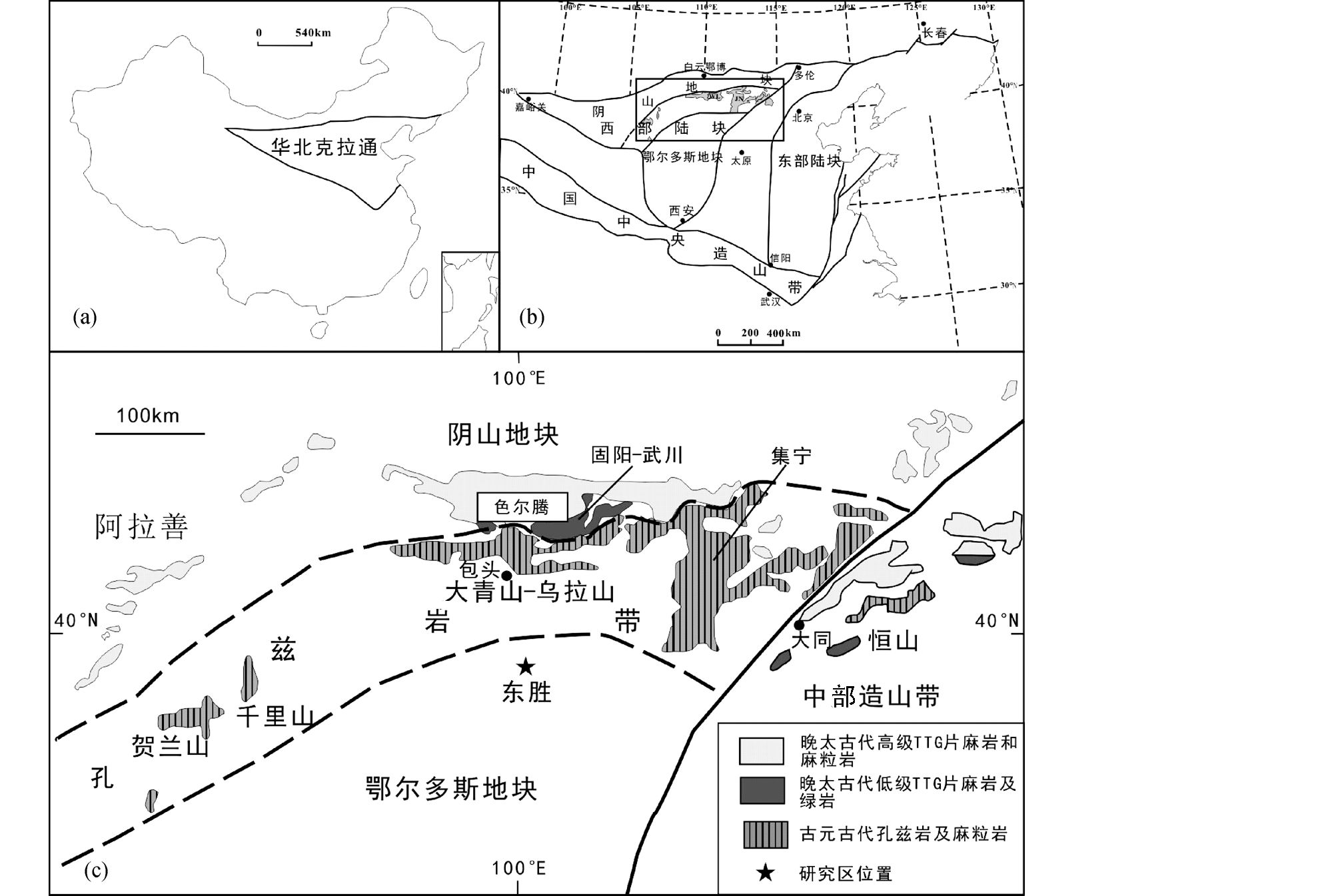
2 区域地质概况依据华北克拉通基底岩石组成、构造样式、变质作用演化和同位素年龄等方面的差异,将华北克拉通基底分为东部陆块、西部陆块和中部造山带三个构造单元(图 1; Zhao et al., 2005;Wilde et al., 2002)。鄂尔多斯盆地隶属于华北克拉通西部陆块的南部,与北部的阴山地块在早元古宙(~1.95Ga)沿孔兹岩带拼合形成西部陆块,此后在古元古代末期(1.85Ga),东、西部陆块拼合成为统一的华北陆块(赵国春,2009;Zhao et al., 2010)。该盆地已成为我国重要的含煤、石油、天然气和铀等能源的盆地,根据现今构造特征,可划分为伊盟隆起、晋西挠褶带、渭北隆起、西缘冲断带、天环坳陷、陕北斜坡等6个构造单元(杨俊杰和裴锡古,1996)。
|
图 1 研究区及周缘地质简图 (a)-华北克拉通在中国大陆的位置;(b)-华北克拉通基底构造单元划分(据Zhao et al., 2005);(c)-鄂尔多斯盆地北部变质基底分布图(据Zhao et al., 2005) Fig. 1 Sketch geological map of the study and adjacent areas (a)-location of the North China Craton; (b)-tectonic subdivision of the North China Craton (after Zhao et al., 2005); (c)-distribution of metamorphic basement to the north of the Ordos basin (after Zhao et al., 2005) |
东胜地区位于鄂尔多斯盆地北部的伊盟隆起区内,南与陕北斜坡相邻。区内地层为一向西南缓倾(倾角1°~3°)的单斜。赋矿地层为中侏罗统直罗组河流相碎屑岩沉积,厚度一般在100~200m,整合或假整合覆盖于中侏罗统延安组煤系地层之上(罗静兰等,2005)。根据岩性、颜色及蚀变特征,直罗组可分为上段(J22z)与下段(J21z)两个岩性段(肖新建等,2004;罗静兰等,2005)。上段(J22z)岩性以紫红色泥岩、泥质粉砂岩与粉砂质泥岩为主,夹紫红-黄褐色细-中细粒砂岩和灰绿色细砂岩与粉砂岩,厚度30~40m。下段可细分为两个亚段:下段上亚段(J21-1z)以灰绿色中粒和中细粒砂岩为主,夹泥质粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩,富含有机质,厚10~30m;下段下亚段(J21-2z)为灰色、浅灰色、灰白色中细粒-中粗粒砂岩与钙质砂岩与灰色、灰绿色泥质粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩,地层中富含有机质、煤屑和还原性物质黄铁矿,厚30~60m。铀矿床产于直罗组下段砂体中,铀矿化受灰绿色蚀变砂岩与灰色砂岩接触带的控制(罗静兰等,2005),多产于灰色砂岩中,少部分产于灰绿色砂岩中。
3 样品与分析方法东胜地区砂岩型铀矿垂向上自上到下依次可划分为黄褐色-紫红色氧化砂岩带(J22z)、灰绿色-绿色蚀变砂岩带(J21-1z)、灰色-浅灰色未蚀变原生砂岩带(J21-2z)以及灰白色中细粒漂白砂岩带(J21-2z)等4个分带。用于碎屑锆石定年的4个砂岩样品兼顾了上、下岩性段的4个带(表 1),完全能满足中侏罗统地层沉积物源的特征分析的需要。
|
|
表 1 碎屑锆石U-Pb定年样品的岩性 Table 1 The lithology of sandstone samples for zircon U-Pb dating |
首先将所选砂岩样品碎至80~100目,利用常规浮选和磁选方法选出锆石单矿物,每个样品均成功分选出1000余粒碎屑锆石。然后在双筒目镜下提纯,并随机整齐排列于双面胶后用环氧树脂灌注成激光样品靶。将其抛光处理后进行锆石样品的反射光和透射光显微照相,并进行锆石阴极发光照相分析,以确定适合分析的锆石颗粒和激光剥蚀位置。
所有测试分析均在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成。LA-ICP-MS采用Geolas200M激光剥蚀系统与E1AN 6100 DRC ICP-MS连接测定,激光剥蚀方式为单点剥蚀。测试过程中用美国国家标准技术研究院研制的人工合成硅酸盐玻璃标准参考物质NIST SRM 610进行仪器最佳化。锆石U-Pb年龄测定采用国际标准锆石91500作为外标校正,每测定4~5个点后测定一次标样;以29Si作内标,测定样品前后各测2次NIST SRM610,保证了标准样品和所测样品的仪器条件完全一致。详细实验过程、仪器参数可参考Yuan et al.(2004) ,普通铅校正采用Anderson (2002) 的方法。
锆石原位Lu-Hf同位素分析在配有193nm激光取样系统的Neptune多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)上与锆石U-Pb定年及微量元素分析一次性剥蚀完成,其原理详见Yuan et al.(2008) 。分别用176Lu/175Lu=0.02669和176Yb/172Yb=0.5886进行同量异位干扰校正计算测定样品的176Lu/177Hf和176Hf/177Hf比值。εHf(t)和模式年龄计算中计算参数如下:衰变常数λ=1.867×10-11(Söderlund et al., 2004),现今球粒陨石和亏损地幔的176Lu/177Hf和176Hf/177Hf分别采用0.0332、0.282772和0.0384、0.28325 (Bichert et a1.,1997)。二阶段模式年龄采用硅铝质地壳的fLu/Hf=-0.72 (Vervoort and Patchett, 1996)进行计算。
4 分析结果 4.1 锆石U-Pb年龄4件样品分离出的碎屑锆石大多无色透明,部分具浅棕色及棕红色色调,均为浑圆状,反映它们经历了风化搬运磨蚀的改造。部分古生代锆石晶形较好,说明其源区较近,阴极发光图像(图 2a,e,r)显示,大部分古生代锆石具有清晰的韵律环带结构,其U、Th含量高(见附表 1,电子版),大多具有较高的Th/U(>0.4)比值(图 3),反映岩浆成因锆石特征(图 2)。古元古代碎屑锆石大都具有不规则面状、扇状或无分带变质结构特征(图 2h-j,m,n),其Th/U比值变化大(图 3),代表存在不同时期的岩浆和变质锆石。此外,还有部分锆石的Th/U比值介于岩浆与变质成因锆石之间(0.1~0.4),可能反映其变质重结晶作用不彻底(吴元保和郑永飞,2004),或受到了后期地质事件改造的结果。另外,古元古代和太古宙锆石均具核-边结构(图 2d,f,g,i,o,p,r),核部具震荡环带,显示为岩浆成因,边部为无特征结构的均匀白色变质边。
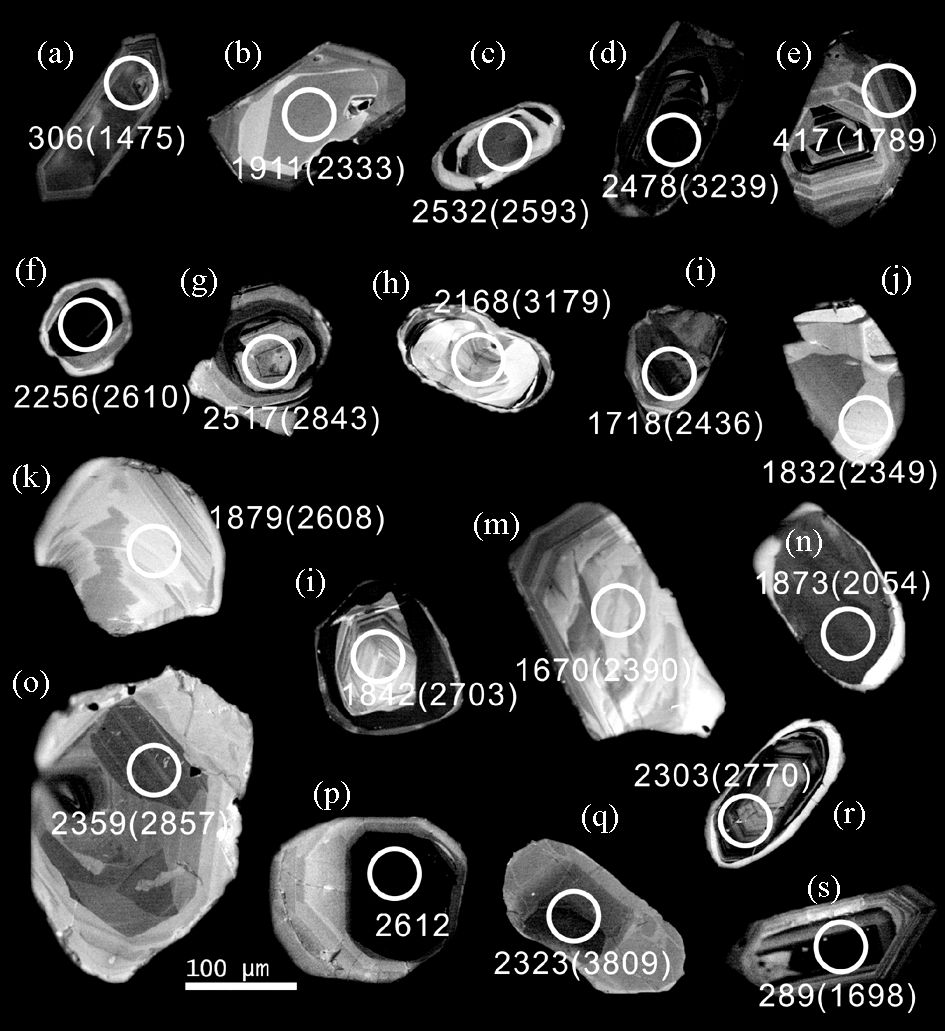
|
图 2 研究区直罗组砂岩中典型碎屑锆石CL图像 图中白色圈为测试位置,数字为锆石U-Pb年龄,括号中数字为Hf同位素两阶段模式年龄(tDM2),单位:Ma;DSL-1(a-f)、DSL-2(g)、DSL-3(h-m)、DSL-4(n-r) Fig. 2 Cathodoluminescence images of typical detrital zircons from sandstones in Zhiluo Formation of the study area Analysis locations are indicated by white circles. Numbers show U-Pb ages of detrital zircons, and numbers in the brackets are Hf isotopic two stages model ages (tDM2). Unit for ages is Ma |
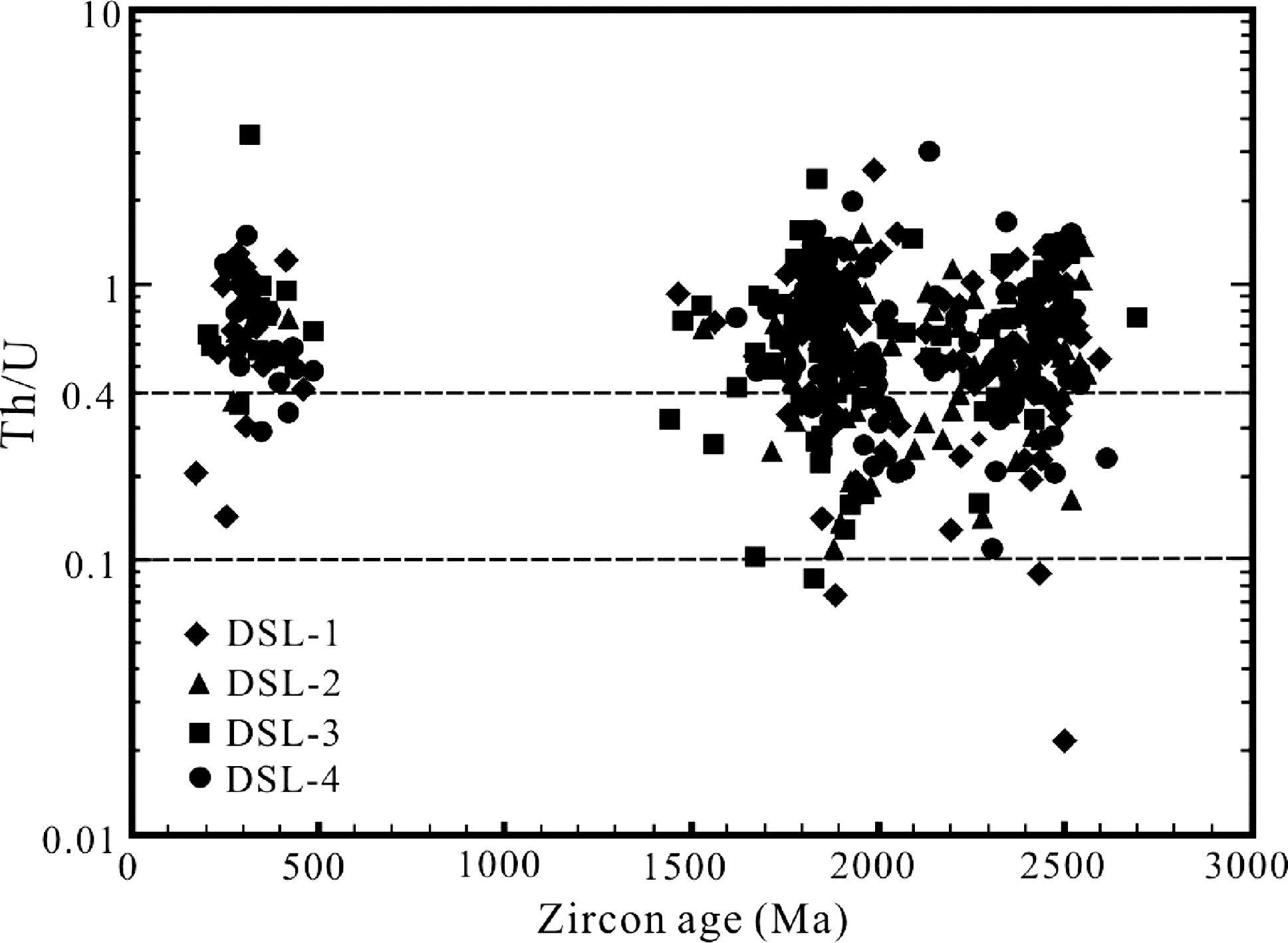
|
图 3 研究区直罗组砂岩碎屑锆石年龄与Th/U关系图 Fig. 3 Zircon ages vs. Th/U diagram of detrital zircons from sandstones in Zhiluo Formation of the study area |
数据分析时,对于放射成因组分积累较少的年轻锆石(<1000Ma)采用206Pb/238U年龄代表锆石的形成时间;而对于放射成因组分积累较多的古老锆石(>1000Ma),则采用207Pb/206Pb年龄(Blank et al., 2003)。
所测4个样品中除DSL-2样品测试115粒锆石以外,其它3个样品均测试的锆石颗粒不少于120粒。选择谐和度在90%~110%之间的锆石年龄,4个样品中分别得到112,103,91,103个谐和年龄数据(见附表 1)。结果显示,4件锆石年龄分布表现出良好的一致性(图 4),总体呈现出2500~2300Ma、2000~1750Ma和400~250Ma三个明显的主峰值年龄段,以及2300~2000Ma、1750~1400Ma的次峰值年龄,少数锆石年龄为500~400Ma、2600~2500Ma(表 2)。其中以2000~1750Ma的年龄为主(平均占总测点数的36.1%),其次是2500~2300Ma的年龄(平均占26.2%)与2300~2000Ma(占13.8%),400~250Ma的年龄占9.7%,而1750~1400Ma的测点数仅占5.9%。相比而言,直罗组下段砂岩中年龄较老的古元古代早期(2500~2300Ma)测点数所占权重较低,中元古代早期与古元古代晚期(2000~1750Ma)测点数所占权重较高。另外,在DSL-3样品中发现1粒年龄为2.69Ga的锆石,DSL-4样品中有1粒2.61Ga的锆石。结合华北克拉通构造演化历史,为讨论方便起见,将所测锆石年龄划分为太古宙(>2500Ma,平均占测点数年龄的4.6%)、古元古代(2500~1800Ma,平均占71%)、中元古代(1800~1440Ma,平均占11.1%)、显生宙(503~173Ma,平均占13.2%)等4个主要阶段。
|
|
附表1 锆石U-Pb年龄 Appendix1 Zircon U-Pb ages |

|
图 4 研究区碎屑锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄协和图(左)与U-Pb年龄分布直方图(右) Fig. 4 Concordant plot of LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages for detrital zircons (left) and corresponding relative probability plot of U-Pb ages for concordant detrital zircons (right) from sandstones in Zhiluo Formation of the study area |
|
|
表 2 研究区碎屑锆石U-Pb各峰值年龄测点百分数统计结果 Table 2 Statistics of U-Pb age peaks of detrital zircons from sandstones in the study area |
剔除Hf同位素信号较差数据外,除少数几颗锆石176Lu/177Hf比值大于0.002外,其它锆石的176Lu/177Hf比值均小于0.002(见附表 2,电子版),说明锆石形成后有较低含量的放射性Hf的积累。鉴于只有少部分锆石的εHf(t)值落在亏损地幔演化线上,而大部分的锆石来自于地壳的再循环物质,所以使用锆石的两阶段模式年龄(tDM2)对地壳生成年龄进行估计(Yang et al., 2009;吴福元等, 2007)。
|
|
附表2 锆石Hf数据 Appendix2 Zircon Hf data |
4件样品中锆石的εHf(t)值由负到正变化范围较大(图 5),表明它们除来自古老地壳的再循环物质外,还存在新生地壳的物质来源。其中,>2.5Ga的锆石的εHf(t)值介于-5.59~9.37之间,且只有2粒锆石的εHf(t)小于零,大多位于亏损地幔线与球粒陨石线所限定的区域内,并有少数点落在亏损地幔演化线上。其tDM2介于3336~2510Ma之间(平均2770Ma),略大于锆石的平均年龄2546Ma。2.5~2.3Ga的锆石εHf(t)值介于-20.33~12.24之间(平均2.26),大部分为正值。tDM2介于3809~2325Ma之间(平均2782Ma),略大于锆石的平均年龄2409Ma。2.3~1.8Ga的锆石也有较大的εHf(t)值变化范围(-13.71~9.24,平均-2.63),且主要为负值,部分位于2.7Ga地壳演化线上及其附近,其tDM2介于3373~2054Ma之间(平均2641Ma)。中元古代锆石(1800~1440Ma)的εHf(t)值介于-15.8~3.69之间(平均-6.48),且主要为负值, tDM2为3094~2078Ma(平均2607Ma)。显生宙锆石(173~503Ma)的εHf(t)变化范围为-25.46~7.24,tDM2变化范围较大,介于2516~732Ma之间。
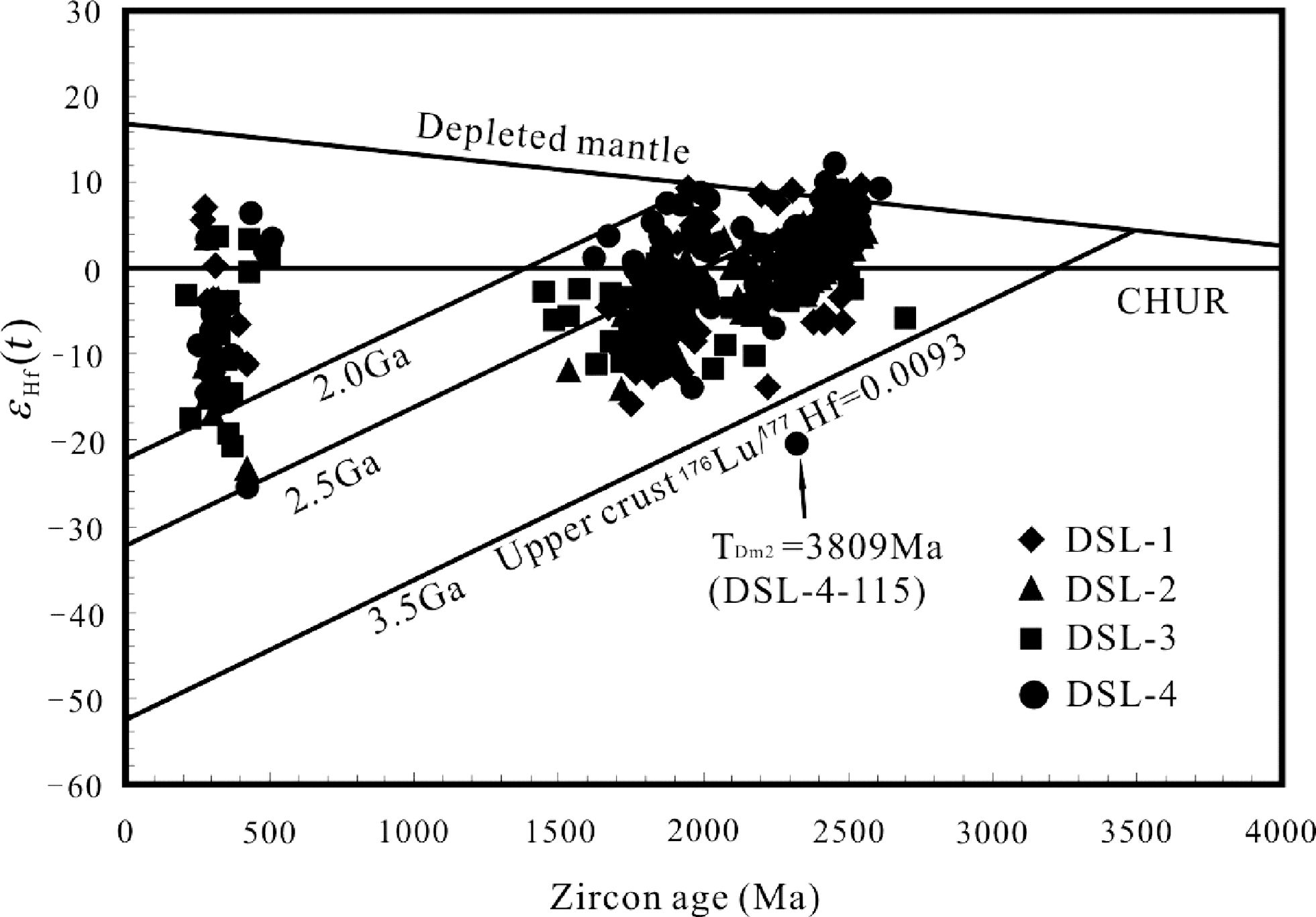
|
图 5 研究区直罗组砂岩碎屑锆石年龄与εHf(t)关系图 Fig. 5 Zircon ages vs. εHf (t) diagram of detrital zircons from sandstones in Zhiluo Formation of the study area |
如图 6所示,本次所测锆石样品中的Hf两阶段模式年龄分布范围较广,从3.8Ga到0.7Ga,但主要集中在3.0~2.3Ga,峰值年龄出现在2.8~2.6Ga。

|
图 6 研究区碎屑锆石Hf两阶段模式年龄直方图 Fig. 6 Histogram of Hf isotopic tDM2 of detrital zircons from sandstones in Zhiluo Formation of the study area |
华北克拉通是世界上最古老的克拉通之一,经历了>3.0Ga的陆核与微陆块的形成、2.9~2.7Ga的地壳增生事件、~2.5Ga的大规模岩浆和变质事件、2.3~1.9Ga的古元古代造山事件、1.8Ga之后的基底隆升、大陆裂谷与非造山岩浆事件(翟明国,2010;Zhai and Santosh, 2011;Zhai,2011)等多阶段的、复杂的构造演化历史。相对于东部陆块,华北克拉通西部陆块基底出露较少,多分布于陆块北部的集宁、大青山-乌拉山、固阳-武川、色尔腾、贺兰山-千里山、阿拉善等地,主要由新太古界和早元古界变质结晶杂岩组成(图 1c)。新太古界主要为2.6~2.5Ga的TTG片麻岩、镁铁质-超镁铁质层状侵入岩和少量表壳岩(Zhao et al., 1999a, b )。早元古界沿集宁-大青山-乌拉山-千里山-贺兰山一线分布,主要为孔兹岩系、TTG片麻岩夹铁镁质麻粒岩和同构造紫苏花岗岩或S型花岗岩,构成一条近东西向孔兹岩带(赵国春等,2002),将北部的晚太古界基底与南部鄂尔多斯地块分开。
东胜直罗组砂岩型铀矿砂岩中,新太古代年龄的碎屑锆石含量较少,仅占锆石总量的4.6%。这些锆石年龄与分布于固阳、武川、色尔腾、阿拉善等地的2.6~2.5Ga TTG片麻岩、镁铁质-超镁铁质层状侵入岩和少量表壳岩的年龄较为一致(Zhao et al., 1999b)。如内蒙古固阳-武川地区麻粒岩2648.5±4.6Ma的单颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄(王惠初等,2001),大青山北西乌兰不浪紫苏斜长麻粒岩单颗粒锆石的2511Ma、代表古老花岗岩侵入体上侵就位时代的不一致上交点年龄(张玉清等,2003),以及阜平、五台地区的TTG片麻岩的 ~2.5Ga年龄(孙敏和关鸿,2001;Liu et al., 2002, 2004;Guan et al., 2002)。由于这些TTG片麻岩和镁铁质侵入岩的原岩的岩浆作用发生的时间极为相近,因此,2.5Ga的变质作用表现为近等压冷却的逆时针P-T轨迹特征,反映变质成因与大规模的地幔岩浆底侵有关(赵国春,2009)。本文得到的新太古代锆石的Hf同位素特征显示其源区物质主要来源于亏损地幔,这一特征与上述推测也有较好的对应关系。因此认为,本研究所获得的新太古代的锆石主体可能来源于阴山地块古老的TTG片麻岩和基性麻粒岩。
研究区所测碎屑锆石年龄以古元古代(2500~1800Ma)的碎屑锆石占主体(约为71%),这些年龄可以分为三组,2500~2300Ma,2300~2000Ma和2000~1800Ma。其中古元古代的年龄(2500~2300Ma)与内蒙古固阳-武川地区的麻粒岩中部分锆石的207Pb /206Pb表面年龄2510~2350Ma(王惠初等,2001)、英云闪长质片麻岩样品中获得的单颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄2494~2384Ma(张维杰等,2000)以及乌拉山-集宁地区钾质花岗岩的锆石表面年龄2494±59Ma~2371±38Ma(吴昌华等,2006)有较好的对应关系。2000~1800Ma的年龄与盆地北部孔兹岩中变质锆石年龄和强过铝质花岗岩的年龄相吻合,如大青山、乌拉山、贺兰山、集宁等地孔兹岩的变质年龄分布在2.0~1.81Ga之间, 峰值变质年龄为1.95Ga(董春艳等, 2007, 2009;Wan et al., 2009;Xia et al., 2006a, b ;吴昌华等,2006),而随后的同构造S型花岗岩的年龄在~1.9Ga(钟长汀等,2007;郭敬辉等,2002)。怀安杂岩带孔兹岩中的很多锆石具有变质成因的核-边结构,核部年龄为~19.5Ga,边部年龄为~18.5Ga (Zhao et al., 2010)。另外,孔兹岩带中由深熔作用形成的石榴石花岗岩的年龄为1892~1836Ma(郭敬辉等,1999)。研究区2300~2000Ma的锆石与孔兹岩中碎屑锆石继承核的年龄(吴昌华等, 1998, 2000, 2006;Xia et al., 2006a;董春艳等,2007)相一致。另外,对鄂尔多斯盆地北部孔兹岩带、阴山地块及中部造山带北部变质基底中已有的锆石年龄数据的统计结果发现,年龄分布较广,但主要集中在2000~1800Ma(图 7)。Xia et al.(2006b)揭示的乌拉山孔兹岩中的碎屑锆石的年龄集中在2.32~1.84Ga,Hf同位素特征显示其来源为亏损地幔和古老地壳物质。董春艳等(2007) 获得的巴彦乌拉-贺兰山地区孔兹岩中锆石两阶段Hf年龄范围为3159~2074Ma,且集中在2.6Ga,Hf同位素特征显示锆石源区主要为古老地壳再循环物质,但在2.0Ga也有亏损地幔的参与。本研究4个样品的两阶段Hf模式年龄峰值集中在2.71~2.27Ga,其中,年龄为2.3~1.8Ga的锆石的两阶段Hf模式年龄集中在3373~2054Ma之间,平均为2641Ma,其Hf同位素特征显示既有地壳来源,又有亏损地幔来源的物质。结合以上讨论,可知东胜砂岩型铀矿直罗组地层中年龄为古元古代的碎屑锆石主要来自于集宁-大青山-乌拉山-千里山-贺兰山一带的孔兹岩,可能有部分来自固阳-武川等地区的片麻岩和麻粒岩。
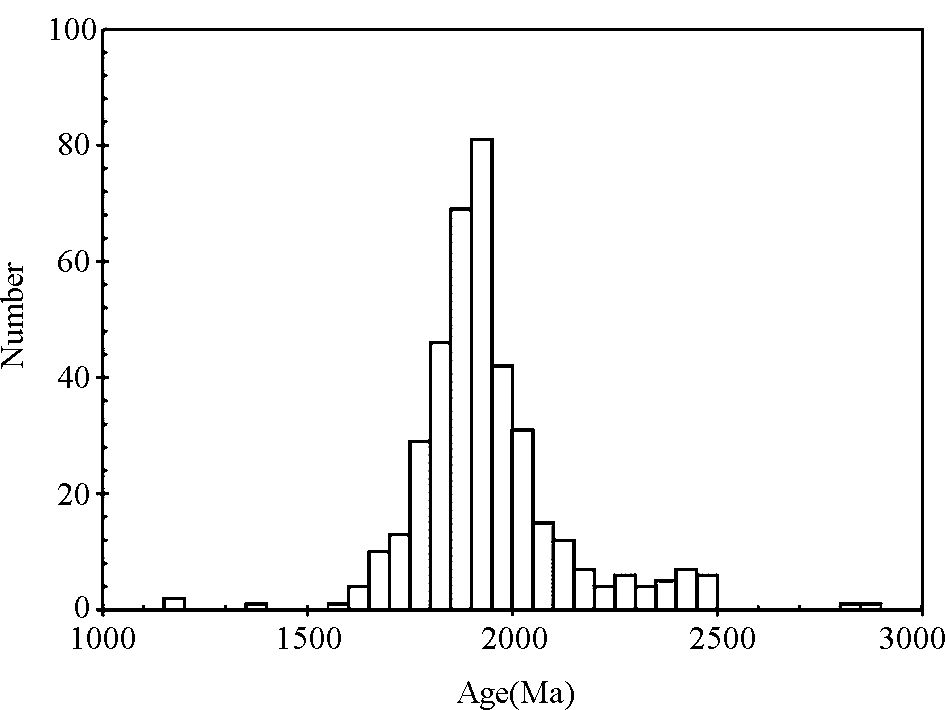
|
图 7 鄂尔多斯盆地北部孔兹岩带锆石年龄谱 锆石年龄数据来自吴昌华等(1997, 1998, 2000, 2006),郭敬辉等(2002) ,钟长汀等(2007) ,董春艳等(2007, 2009),Xia et al.(2006a, b) Fig. 7 Histogram of zircon ages from the Khondalite Belt to the north of Ordos basin |
古元古代末,中元古代初,华北克拉通整体处于伸展构造体制,在恒山、五台、晋冀蒙交界的太古代中-高级变质区广泛发育元古代辉绿岩岩墙群(侯贵廷和穆治国,1994;彭澎等,2004;Peng,2010)。这些主体形成于1780~1760Ma之间的镁铁质岩墙(侯贵廷和穆治国,1994;李江海等,2001;韩宝福等,2007;彭澎等,2004),代表了华北克拉通古元古代最末期的镁铁质岩浆活动(Kröner et al., 2005, 2006),其成因与板内大陆裂谷活动密切相关(侯贵廷等,2003)。另外,在河北承德-蓟县-密云一带存在1765~1650Ma的非造山岩浆岩(郁建华等,1996),εNd(t) 特征显示其为华北克拉通未成熟地壳部分熔融的产物(Zhai et al., 2003),其与基性岩墙群为同一构造体制下的产物(彭澎和翟明国,2002;翟明国,2010)。尽管这一非造山岩浆活动带位于东部陆块,而西部陆块未见报道,但也不排除其在西部陆块存在的可能性。本文获得的1800~1440Ma碎屑锆石的εHf(t)值多为负值(平均为-6.48),除与古老地壳物质熔融形成的锆石类似外,还与韩宝福等(2007) 所获得的镁铁质岩墙中εHf(t)也呈负值有一定的可比性。因此,东胜地区砂岩样品中的1800~1440Ma碎屑锆石很可能来自于这些基性岩石及其同时代中酸性岩浆活动的产物。
样品中显生宙的碎屑锆石年龄(503~173Ma)主要集中在古生代,这一时期正是华北地块北部阴山造山带强烈活动时期,期间发生了多期火山喷发和大规模的中酸性岩浆侵入活动,形成了大面积分布的古生代复式中酸性侵入岩体(彭润民等,2007)。在大青山地区出露的哈拉少岩体含黑云母二长花岗岩中获得的261.1±0.5Ma的锆石U-Pb年龄也是该期活动的具体反映(赵庆英等,2007)。此外,阴山地块也存在大量形成于400~300Ma的花岗岩及火山岩(陈斌和徐备,1996;陈斌等,2001;邵济安,1991)。本文所得到的这一时期锆石的Hf同位素特征显示,其源区主要为古老地壳的熔融再循环物质。因此,东胜地区直罗组砂岩中显生宙的碎屑锆石很可能来自阴山构造带形成于古生代的中酸性火成岩体。
研究表明,鄂尔多斯盆地北部地区大青山自印支-燕山运动以来一直处于隆升状态,伊陕单斜总体上呈向SW倾斜的平缓斜坡(彭云彪,2007)。刘德长等(2006) 根据钻孔数据库中直罗组下伏延安组顶板高程的属性值,利用GIS软件中的地形分析和水系分析扩展模块分析,发现直罗组辫状河的古河道方向是北东-南西向。结合上述讨论可知,鄂尔多斯地块北部的大青山-乌拉山以及集宁地区孔兹岩、TTG片麻岩和麻粒岩,华北克拉通中部造山带北部杂岩和镁铁质岩墙群、阴山地块形成于古生代时期的岩浆岩可能构成了东胜地区中侏罗统直罗组砂岩的主要物源。
5.2 源区构造演化全球前寒武纪基底的锆石Hf模式年龄统计结果显示,地壳有四个主要形成时期,分别为ca. 4.4~4.5Ga,ca. 3.8Ga,ca. 3.4Ga和ca. 2.7~2.8Ga (Pietranik et al., 2008)。对华北克拉通镁铁质火成岩的Nd和Hf模式年龄的统计结果显示,华北克拉通90%以上的陆壳是在前寒武纪形成的,且绝大多数形成于中-新太古代(翟明国,2010)。本研究所测碎屑锆石的Hf同位素两阶段模式年龄(tDM2)虽然分布范围较广,从0.7Ga到3.4Ga,但主要集中在中-晚太古代,其中tDM2大于2.5Ga的锆石占锆石总数的71%,年龄峰值为2.8~2.6Ga。这一年龄峰值与全球大陆地壳增长时期有很好的对应关系,也代表了华北克拉通一次重要的增生事件。此外,也有相当一部分锆石的Hf两阶段模式年龄在2.3~0.7Ga之间,表明地壳增生的长期性和在地质历史时期增长速度的变化。
Wu et al. (2005) 对华北克拉通东、西部陆块和中部造山带三个构造单元的前寒武纪岩石Nd同位素数据综合分析表明,2.8Ga是华北克拉通地幔分离的重要时期,但三个构造单元的形成时代又有一定的差异,东部陆块显示出3.6~3.2Ga和3.0~2.6Ga两个主要的Nd同位素模式年龄段,反映了早太古代的陆壳组成;中部造山带仅存在2.8~2.4Ga的Nd同位素模式年龄段,西部陆块Nd同位素模式年龄(3.2 ~2.4Ga)变化范围较大,并在2.8~2.6Ga存在一峰值。Xia et al. (2006b)对乌拉山地区孔兹岩碎屑锆石的Hf同位素研究认为,~ 2.6Ga是鄂尔多斯地块最主要的地幔分离时期,鄂尔多斯地块在 ~ 2.0Ga有一次重要的未成熟地壳生长事件。董春艳等(2007) 在巴彦克拉-贺兰山地区的孔兹岩样品中所得到的锆石Hf平均大陆地壳二阶段模式年龄总体介于3.0~2.5Ga;年龄2.0Ga左右的锆石显示了较高的正的εHf(t),表明它们主要来自新的地幔添加物源区。以上证据表明,西部陆块地壳主要形成时期在2.8~2.6Ga,并且在2.0Ga有一次重要的地壳生长事件。
与西部陆块相比,东部陆块的基底岩石年龄范围较大,从早太古代一直到晚太古代的岩石均有出露,而阴山地块的基底主要是2.6~2.5Ga的TTG片麻岩,从一个侧面反映了两个陆块在拼合之前的演化是不同的(Xia et al., 2006b)。本研究所获得的Hf同位素两阶段模式年龄(tDM2)主要集中在3.0~2.3Ga(占锆石总数的75.7%),在2.8~2.6Ga(占锆石总数的35.1%)有一峰值(图 6),与西部陆块的Hf和Nd同位素模式年龄都非常接近,而与东部陆块有很大差别,从而进一步证实了华北克拉通东、西部陆块在古元古代拼合之前是独立发展的。值得提出的是,样品DSL-4中有1粒锆石(DSL-4-115)的tDM2高达3809Ma,指示存在3.8Ga地壳物质的涉入。其阴极发光图像特征显示为变质锆石(图 2q),εHf(t)为-20.33,大致位于3.8Ga地壳演化线上(图 6),显示来源于古老地壳物质。另外,在鄂尔多斯盆地乌审召地区6个上古生界砂岩钻井样品中曾获得一个3690±35Ma的锆石U-Pb年龄(罗静兰等,2010),除此之外在西部陆块尚未报道超过3.5Ga的锆石年龄。弄清这些锆石的来源对于理解华北克拉通的演化具有非常重要的意义。目前来看存在两种可能性:其一,由于这一年龄与东部地块存在3.8Ga古老地壳物质较为一致,因此有可能来自东部陆块;另外,也有可能是西部陆块的物质,只是由于前人的研究样品多位于盆地周缘的造山带,该地带出露的古老物质可能已被剥蚀殆尽,但这些古老物质的记录却被完好地保留在盆地的沉积物中,从而可以为盆地演化和地壳生长提供更全面的信息(Bodet and Schörer,2000;Yang et al., 2009)。如果鄂尔多斯盆地内部这些早太古代的锆石确实来源于西部陆块,结合在华北克拉通其他地方发现的>3.3Ga的锆石,则指示华北克拉通可能存在广泛的古老大陆基底(翟明国,2010)。
阴山地块存在大量古生代的岩浆活动(彭润民等,2007;陈斌和徐备,1996;陈斌等,2001;邵济安,1991),但却没有1粒代表该时期锆石的两阶段Hf模式年龄出现,说明这些岩浆物质主要是古老地壳重新活动的产物,基本没有未成熟地壳物质的参与(Yang et al., 2009)。
由Hf模式年龄减去锆石年龄所得到的锆石结晶年龄与地壳滞留时间关系图(图 8)可以看出,地壳滞留时间的变化范围和最大值都随锆石年龄的减小而增大,显示年轻锆石(500~200Ma)可能起源于2.0Ga年前从地幔分离的地壳物质,1.8Ga左右锆石的Hf二阶段模式年龄在2.6Ga左右,均暗示了大陆地壳的长期保存、再造和循环过程。
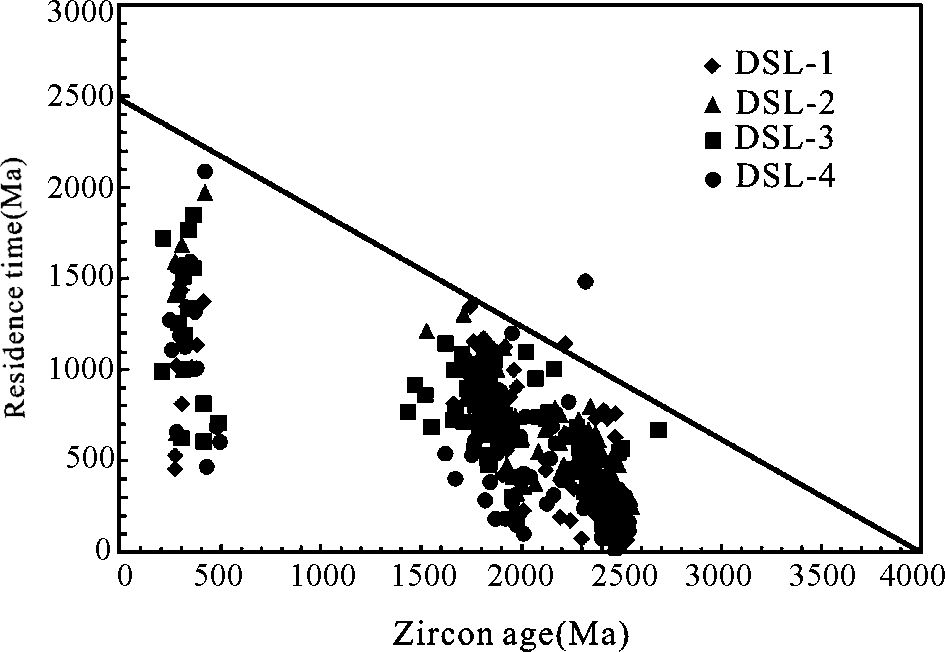
|
图 8 研究区碎屑锆石年龄与地壳存留时间的关系图 地壳存留时间为碎屑锆石的地壳模式年龄(tDM2)与锆石形成年龄之差;斜线表示最大存留年龄的趋势 Fig. 8 Variation of crustal residence time with crystallization age of concordant detrital zircons from sandstones in Zhiluo Formation of the study area |
(1) 东胜地区中侏罗统直罗组砂岩型铀矿的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄呈现2500~2300Ma、2000~1750Ma和500~200Ma三个主峰值年龄段,并以2000~1750Ma年龄段的锆石为主,同时有一定数量2300~2000Ma和1750~1400Ma的锆石。
(2) 研究区与源区同位素年代学对比研究结果显示,东胜地区获得的新太古代锆石的主体(大于2.5Ga)可能来源于阴山地块古老的TTG片麻岩和基性麻粒岩;古元古代锆石(2500~1800Ma)主要来自于集宁-大青山-乌拉山-千里山-贺兰山一带的孔兹岩,部分可能来自固阳-武川等地区的片麻岩和麻粒岩;中元古代锆石(1800~1440Ma)可能主要来自恒山、五台、晋冀蒙交界等地广泛分布的元古代基性岩石和同时期的中酸性岩浆活动的产物;显生宙锆石(503~173Ma)主要来自阴山构造带形成于古生代的火成岩体。
(3) 锆石的二阶段Hf模式年龄介于3.0~2.3Ga,存在2.8~2.6Ga的峰值,与全球大陆地壳增生时期有很好的对应关系。新太古代锆石的Hf同位素特征显示其主要来源于亏损地幔,代表了新太古代的地壳增生事件;古元古代锆石除来自亏损地幔外,另有部分地壳物质的参与,并随时间的推移,地幔物质的参与程度逐渐减少。部分1.9Ga左右的锆石落在亏损地幔线上,证明此时依然存在新生地壳的增生作用;中元古代和显生宙的锆石则主要形成于古老地壳的再循环过程。研究区锆石Hf同位素特征明显不同于东部地块,而与西部陆块相似,证实了华北克拉通东、西部陆块在古元古代拼合之前是独立发展的。
(4) 样品中有1粒锆石的Hf两阶段模式年龄达3.8Ga,指示存在3.8Ga地壳物质的涉入。在鄂尔多斯盆地乌审召地区上古生界砂岩样品中1粒碎屑锆石也曾获得3690±35Ma的U-Pb年龄。如果这些锆石确实来自西部陆块,则指示华北克拉通可能存在广泛的古老大陆。
致谢 感谢西北大学地质系张成立教授在文章修改过程中提出的宝贵意见;感谢西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室各工作人员在实验和数据处理过程中给予的大力支持与热情帮助。两位评审人和编辑部的建设性意见和建议对于提高原稿质量起到非常重要的作用,在此深表谢意。| [] | Anderson T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59–79. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X |
| [] | Blank LP, Kamo SL, Williams IS, Mundil R, Davis DW, Korsch RJ, Foudoulis C. 2003. The application of SHEIMP to Phanerozoic geochronology: A critical appraisal of four zircon standards. Chemical Geology, 200(1-2): 171–188. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(03)00166-9 |
| [] | Blichert-Toft J, Chauvel C, Albarède F. 1997. Separation of Hf and Lu for high-precision isotope analysis of rock samples by magnetic sector-multiple collector ICP MS. Cortrib. Mineral. Petrol., 127: 248–260. DOI:10.1007/s004100050278 |
| [] | Bodet F, Schärer U. 2000. Evolution of the SE-Asian continent from U-Pb and Hf isotopes in single grains of zircon and baddeleyite from large rivers. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(12): 2067–2091. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00352-5 |
| [] | Chen B, Xu B. 1996. The main characteristics and tectonic implications of two kinds of Paleozoic granitoids in Sunidzuqi, central Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 12(4): 546–561. |
| [] | Chen B, Zhao GC, Wilde SA. 2001. Subduction and collision-related granitoids from southern Sonidzuoqi, Inner Mongolia: Isotopic ages and tectonic implications. Geological Review, 47(4): 361–367. |
| [] | Dong CY, Liu DY, Li JJ, Wan YS, Zhou HY, Li CD, Yang YH, Xie LW. 2007. Palaeoproterozoic Khnodalite Belt in the western North China Craton: New evidence from SHRIMP dating and Hf isotope composition of zircons from metamorphic rocks in the Bayan Ul-Helan Mountains area. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(21): 2984–2994. DOI:10.1007/s11434-007-0404-9 |
| [] | Dong CY, Liu DY, Wang YS, Xu ZY, Liu ZH, Yang ZS. 2009. Crustally derived carbonatite from the Daqingshan area: Zircon features and SHRIMP dating. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(3): 388–398. |
| [] | Guan H, Sun M, Wilde SA, Zhou XH, Zhai MG. 2002. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Fuping Complex: Implications for formation and assembly of the North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 113(1-2): 1–18. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(01)00197-8 |
| [] | Guo JH, Shi X, Bian AG, Xu RH, Zhai MG, Li YG. 1999. Pb isotopic composition of feldspar and U-Pb age of zircon from Early Proterozoic granite in Sanggan area, North China craton: Metamorphism, crustal melting and tectono-thermal event. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(2): 199–207. |
| [] | Guo JH, Zhai MG, Xu RH. 2001. Timing of the granulite facies metamorphism in the Sanggan area, North China craton: Zircon U-Pb geochronology. Science in China (Series D), 44(11): 1010–1018. DOI:10.1007/BF02875394 |
| [] | Guo JH, O’brain PJ, Zhai MG. 2002. High-pressure granulites in the Sanggan area, North China Craton: Metamorphic evolution, P-T paths and geotectonic significance. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 20(8): 741–756. DOI:10.1046/j.1525-1314.2002.00401.x |
| [] | Guo JH, Sun M, Chen FK, Zhai MG. 2005. Sm-Nd and SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of high-pressure granulites in the Sanggan area, North China Craton: Timing of Paleoproterozoic continental collision. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 629–642. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.01.017 |
| [] | Han BF, Zhang SB, Wang YM, Song B. 2007. Enriched mantle source for Paleoproterozoic high Mg and low Ti-P mafic dykes in central part of the North China Craton: Constraints from zircon Hf isotopic compositions. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 277–284. |
| [] | Hou GT, Mu ZG. 1994. K-Ar ages and their geological significance of Late Precambrian mafic dyke swarms in North China Craton. Jour. Geol. & Min. Res. North China, 9(3): 267–270. |
| [] | Hou GT, Li JH, Hall HC, Qian XL. 2003. The flow structures and mechanics of Late Precambrian mafic dyke swarms in North China Craton. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(2): 210–216. |
| [] | Kröner A, Wild SA, Li JH, Wang KY. 2005. Age and evolution of a Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic upper to lower crustal section in the Wutaishan/Hengshan/Fuping terrain of northern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 577–595. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.01.001 |
| [] | Kröner A, Wilde SA, Zhao GC, O’Brien PJ, Sun M, Liu DY, Wan YS, Liu SW, Guo JH. 2006. Zircon geochronology and metamorphic evolution of mafic dykes in the Hengshan Complex of northern China: Evidence for late Palaeoproterozoic extension and subsequent high-pressure metamorphism in the North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 146(1-2): 45–67. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.01.008 |
| [] | Kusky TM, Windley BF, Zhai MG. 2007. Tectonic evolution of the North China Block: From orogen to craton to orogen. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 280(1): 1–34. DOI:10.1144/SP280 |
| [] | Li JH, Hou GT, Qian XL, Halls HC, Davis D. 2001. Single-zircon U-Pb age of the initial Mesoproterozoic basic dike swarms in Hengshan Mountain and its implication for the tectonic evolution of the North China Craton. Geological Review, 47(3): 234–237. |
| [] | Lin T, Luo JL, Liu XH, Zhang S. 2007. Characteristics of fluid inclusions in sandstone-type uranium deposit and origin of uranium mineralization in Zhiluo Formation of Dongsheng area. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 28(5): 72–78. |
| [] | Liu DC, Ye FW, Zhao YJ. 2006. Analyzing regional geological setting of DS uranium deposit based on the extensional research of remote sensing information. World Nuclear Geoscience, 23(4): 232–237. |
| [] | Liu DY, Nutman AP, Compston W, Wu JS, Shen QH. 1992. Remnants of >3800Ma crust in the Chinese part of the Sino-Korean craton. Geology, 20(4): 339–342. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0339:ROMCIT>2.3.CO;2 |
| [] | Liu SW, Pan YM, Li JH, Li QG, Zhang J. 2002. Geological and isotopic geochemical constraints on the evolution of the Fuping Complex, North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 117(1-2): 41–56. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00063-3 |
| [] | Liu SW, Pan YM, Xie QL, Zhang J, Li QG. 2004. Archean geodynamics in the Central Zone, North China Craton: Constraints from geochemistry of two contrasting series of granitoids in the Fuping and Wutai complexes. Precambrian Research, 130(1-4): 229–249. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2003.12.001 |
| [] | Liu YQ, Feng Q, Yang RC, Fan AP, Xing XJ. 2006. Discussion on genesis of sandstone-type uranium deposits in Dongsheng Area, Ordos Basin. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(5): 761–769. |
| [] | Luo JL, Zhang FX, Jia H, Liu XH, Li B. 2005. Petrology and diagenesis of uranium-bearing sandstones in Dongsheng area of Ordos Basin and Shihongtan area of Tuha Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 26(4): 39–45. |
| [] | Luo JL, Dai YQ, Liu XH, Lin T, Zhang S. 2006. Petrology of uranium-bearing sandstones and relationship of organic matters, hydrocarbons and coal with uranium: An example from Dongsheng, Ordos Basin and Shihongtan, Tuha Basin. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 36(6): 982–987. |
| [] | Luo JL, Wei XS, Yao JL, et al. 2010. Provenance and depositional facies controlling on the Upper Paleozoic excellent natural gas-reservoir in northern Ordos basin, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(6): 811–82. |
| [] | Peng P, Zhai MG. 2002. Two major Precambrian geological events of North China Block (NCB): Characteristics and property. Advance in Earth Science, 17(6): 818–825. |
| [] | Peng P, Zhai MG, Zhang HF, Zhao TP, Ni ZY. 2004. Geochemistry and geological significance of the 1.8Ga mafic dyke swarms in the North China Craton: An example from the juncture of Shanxi, Hebei and Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(3): 439–456. |
| [] | Peng P. 2010. Reconstruction and interpretation of giant mafic dyke swarms: A case study of 1.78Ga magmatism in the North China craton. In: Kusky TM, Zhai MG and Xiao W (eds.) The Evolution Continents: Understanding Processes of Continental Growth. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 338: 163–178. |
| [] | Peng RM, Zhai YS, Han XF, Wang ZG, Wang JP, Shen CL, Chen XF. 2007. Mineralization response to the structural evolution in the Langshan orogenic belt, Inner Mongolia. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(3): 679–688. |
| [] | Peng YB, Chen AP, Fang XH, Ou GX, Xie QL. 2007. Relationship between hydrocarbon-containing fluid and metallogenesis in Dongsheng sandstone-type uranium deposit. Geochimica, 36(3): 267–274. |
| [] | Pietranik AB, Hawkesworth CJ, Storey CD, Kemp AIS, Sircombe KN, Whitehouse MJ, Bleeker W. 2008. Episodic, mafic crust formation from 4.5 to 2.8 Ga: New evidence from detrital zircons, Slave craton, Canada. Geology, 36(11): 875–878. |
| [] | Shao JA. 1991. Crust Evolution in the Middle Part of the Northern Sino Korean Plate. Beijing: Peking University Press: 11-91. |
| [] | Söderlund U, Patchett PJ, Vervoort JD, Isachsen CE. 2004. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 219(3-4): 311–324. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00012-3 |
| [] | Song B, Nutman AP, Liu DY, et al. 1996. 3800 to 2500 Ma crustal evolution in the Anshan area of Liaoning Province, northeastern China. Precambrian Research, 78(1-3): 79–94. DOI:10.1016/0301-9268(95)00070-4 |
| [] | Sun M, Guan H. 2001. Zircon U-Pb ages of the Fuping Complex and their implications: Some comments on the geochronological study of the Precambrian high-grade metamorphic terrances. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(1): 145–156. |
| [] | Vervoort JD, Patchett PJ. 1996. Behavior of hafnium and neodymium isotopes in the crust: Constraints from Precambrian crustally derived granites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 60(19): 3717–3733. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(96)00201-3 |
| [] | Wan YS, Liu DY, Song B, et al. 2005. Geochemical and Nd isotopic compositions of 3.8Ga meta-quartz dioritic and trondhjemitic rocks from the Anshan area and their geological significance. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 563–575. |
| [] | Wan YS, Wilde SA, Liu DY, et al. 2006. Further evidence for ~1. 85Ga metamorphism in the Central Zone of the North China Craton: SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircon from metamorphic rocks in the Lushan area, Henan Province. Gondwana Research, 9(1-2): 189–197. |
| [] | Wan YS, Liu DY, Dong CY, et al. 2009. The Precambrian Khondalite Belt in the Daqingshan area, North China Craton: Evidence for multiple metamorphic events in the Palaeoproterozoic era. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 323(1): 73–97. DOI:10.1144/SP323.4 |
| [] | Wan YS, Liu DY, Wang SJ, et al. 2011. 2011. ~2.7Ga juvenile crust formation in the North China Craton (Taishan-Xintai area, western Shandong Province): Further evidence of an understated event from U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic composition of zircon. Precambrian Research, 186(1): 169–180. |
| [] | Wang HC, Yuan GB, Xin HT. 2001. U-Pb single zircon ages for granulites in Cunkongshan area, Guyang, Inner Mongolia and enlightenment for its geological signification, China. Progress in Precambrian Research, 24(1): 28–34. |
| [] | Wilde SA, Zhao GC, Sun M. 2002. Development of the North China Craton during the Late Archaean and its Final Amalganmation at 1. 8Ga: Some speculations on its position within a global Palaeoproterozoic Suupercontinent. Gondwana Research, 5(1): 85–94. |
| [] | Wu CH, Zhong CT, Chen QA. 1997. Discussion on the age of Khondalite in Jin-Meng (Shanxi-Nei Mongol) high-grade Terrain. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 13(3): 289–302. |
| [] | Wu CH, Li HM, Zhong CT, Chen QA. 1998. The ages of zircon and rutile (cooling) from Khondalite in Huangtuyao, Inner Mongolia. Geological Review, 44(6): 618–626. |
| [] | Wu CH, Li SM, Zhong CT, Zuo YC. 2000. TIMS U-Pb single zircon ages for the orthogneiss and the paragneiss of Fuping Complex: Implications for existence of the Palaeoproterozoic supracrustal rocks in the central basement of North China Craton. Progress in Precambrian Research, 23(3): 129–139. |
| [] | Wu CH, Sun M, Li HM, Zhao GC, Xia XP. 2006. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon ages of the khondalites from the Wulashan and Jining high-grade terrain in northern margin of the North China Craton: Constraints on sedimentary age of the khondalite. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(11): 2639–2654. |
| [] | Wu FY, Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Sun DY. 2005. Nd isotopic constraints on crustal formation in the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 523–545. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.10.011 |
| [] | Wu FY, Li XH, Zheng YF, Gao S. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185–220. |
| [] | Wu RG, Zhu MQ, Yu DG, Zhou WP. 2006. Geological characteristics of basal-channel sandstone-type uranium deposits in the northern of Ordos Basin. Journal of East China Institute of Technology, 29(1): 1–6. DOI:10.1080/02533839.2006.9671094 |
| [] | Wu YB, Zheng YF. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15): 1554–1569. DOI:10.1007/BF03184122 |
| [] | Xia XP, Sun M, Zhao GC, Luo Y. 2006a. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology of detrital zircons from the Jining Complex, North China Craton and its tectonic significance. Precambrian Research, 144(3-4): 199–212. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2005.11.004 |
| [] | Xia XP, Sun M, Zhao GC, Wu FY, Xu P, Zhang JH, Luo Y. 2006b. U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of detrital zircons from the Wulashan khondalites: Constraints on the evolution of the Ordos Terrane, Western Block of the North China Craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 241(3-4): 581–593. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.11.024 |
| [] | Xia YL, Lin JR, Liu HB, Fan G, Hou YX. 2003. Research on geochronology of sandstone-hosted uranium ore-formation in major uranium-productive basins, northern China. Uranium Geology, 19(3): 129–136. |
| [] | Xiang WD, Fang XY, Li TG, Chen XL, Pang YQ, Cheng HH. 2006. Metallogenic characteristics and model of Dongsheng uranium deposit in Ordos basin, North China. Uranium Geology, 22(5): 257–266. |
| [] | Xiao XJ, Li ZY, Chen AP. 2004. Preliminary study on features of mineralogical zoning of epigenetic alteration at sandstone-type uranium deposit, Dongsheng area, Ordos basin. Uranium Geology, 20(3): 136–140. |
| [] | Yang J, Gao S, Chen C, Tang YY, Yuan HL, Gong HJ, Xie SW, Wang JQ. 2009. Episodic crustal growth of North China as revealed by U-Pb age and Hf isotopes of detrital zircons from modern rivers. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(9): 2660–2673. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2009.02.007 |
| [] | Yang JJ, Pei XG. 1996. Natural Gas Geology in China. Beijing: The Petroleum Industry Press: 3-20. |
| [] | Yang RC, Han ZZ, Fan AP. 2007. Sedimentary microfacies and sequence stratigraphy of sandstone-type uranium deposit in the Dongsheng area of the Ordos basin. Journal of Stratigraphy, 31(3): 261–266. |
| [] | Yu JH, Fu HQ, Zhang FL, et al. 1996. Anorogenic Rapakivi Granites and Related Rocks in Northern of the North China Craton. Beijing: Chinese Science and Technology Press: 1-96. |
| [] | Yuan HL, Gao S, Liu XM, Li HM, Günther D, Wu FY. 2004. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass specrometry. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 28(3): 353–370. DOI:10.1111/ggr.2004.28.issue-3 |
| [] | Yuan HL, Gao S, Dai MN, Zong CL, Günther D, Fontaine GH, Liu XM, Diwu CR. 2008. Simultaneous determinations of U-Pb age, Hf isotopes and trace element compositions of zircon by excimer laser-ablation quadrupole and multiple-collector ICP-MS. Chem. Geol., 247(1-2): 100–118. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.003 |
| [] | Zhang WJ, Li L, Geng MS. 2000. Petrology and dating of Neo-archaean intrusive rocks from Guyang area, Inner Mongolia. Earth Science, 25(3): 221–226. |
| [] | Zhang YQ, Wang T, Jia HY, Zhang ZX. 2003. U-Pb ages of zircons from the Xi Ulanbulang hypersthene-plagioclase granulite in the North Daqing Mountains, central Inner Mongolia. Geology in China, 30(4): 394–399. |
| [] | Zhai MG, Guo JH, Li YG, Liu WJ, Peng P, Shi X. 2003. Two linear granite belts in the central-western North China Craton and their implication for Late Neoarchaean-Palaeoproterozoic continental evolution. Precambrian Research, 127: 267–283. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(03)00191-8 |
| [] | Zhai MG. 2004. 2.1~1.7Ga geological event group and its geotectonic significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(6): 1343–1354. |
| [] | Zhai MG, Peng P. 2007. Paleoproterozoic events in the North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(11): 2665–2682. |
| [] | Zhai MG. 2010. Tectonic evolution and metallogenesis of North China Craton. Mineral Deposits, 29(1): 24–36. |
| [] | Zhai MG. 2011. Cratonization and the Ancient North China Continent: A summary and review. Science China (Earth Sciences), 54(8): 1110–1120. DOI:10.1007/s11430-011-4250-x |
| [] | Zhai MG, Santosh M. 2011. The Early Precambrian odyssey of the North China Craton: A synoptic overview. Gondwana Research, 21(1): 6–25. |
| [] | Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Cawood PA, Lu LZ. 1999a. Thermal evolution of two textural types of mafic granulites in the North China craton: Evidence for both mantle plume and collisional tectonics. Geol. Mag., 136(3): 223–240. DOI:10.1017/S001675689900254X |
| [] | Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Cawood PA, Lu LZ. 1999b. Tectonothermal history of the basement rocks in the western zone of the North China Craton and its tectonic implications. Tectonophysics, 310(1-4): 37–53. DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00152-3 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA. 2003. Major tectonic units of the North China Craton and their Paleoproterozoic assembly. Science in China (Series D), 46(1): 23–38. DOI:10.1360/03yd9003 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA, Li SZ. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited. Precambrian Research, 136(2): 177–202. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002 |
| [] | Zhao GC. 2009. Metamorphic evolution of major tectonic units in the basement of the North China Craton: Key issues and discussion. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(8): 1772–1792. |
| [] | Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Guo JH, Cawood PA, Sun M, Li XP. 2010. Single zircon grains record two Paleoproterozoic collisional events in the North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 177(3-4): 266–276. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2009.12.007 |
| [] | Zhao HG, Ou GX. 2006. The relationship between depositional system and ore-formation of sandstone-type uranium deposits in Dongsheng area, Ordos basin. Uranium Geology, 22(3): 136–142. |
| [] | Zhao JF, Liu CY, Yu L, Huang L, Liu YT, Gao F. 2007. Distributional and sedimentary characteristics of sandstones in Jurassic Zhiluo Formation, Ordos Basin. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 25(4): 535–544. |
| [] | Zhao QY, Liu ZH, Wu XW, Chen XF. 2007. Characteristics and origin of Halaheshao pluton in Daqingshan region, Inner Mongolia. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 27(1): 46–51. |
| [] | Zhong CT, Deng JF, Wan YS, Mao DB, Li HM. 2007. Magma recording of Paleoproterozoic orogeny in central segment of northern margin of North China Craton: Geochemical characteristics and zircon SHRIMP dating of S-type granitoids. Geochimica, 36(6): 633–637. |
| [] | 陈斌, 徐备. 1996. 内蒙古苏左旗地区古生代两类花岗岩类的基本特征和构造意义. 岩石学报, 12(4): 546–561. |
| [] | 陈斌, 赵国春, WildeSA. 2001. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗南两类花岗岩同位素年代学及其构造意义. 地质论评, 47(4): 361–367. |
| [] | 丁万烈. 2003. 绿色蚀变带的地球化学性质及其找矿意义探讨. 铀矿地质, 19(5): 277–282. |
| [] | 董春艳, 刘敦一, 李俊建, 万渝生, 周红英, 李承东, 杨岳衡, 谢烈文. 2007. 华北克拉通西部孔兹岩带形成时代新证据: 巴彦乌拉-贺兰山地区锆石SHRIMP定年和Hf同位素组成. 科学通报, 52(16): 1913–1922. |
| [] | 董春艳, 刘敦, 万渝生, 徐仲元, 刘正宏, 杨振升. 2009. 大青山地区古元古代壳源碳酸岩: 锆石特征及SHRIMP定年. 地质学报, 83(3): 388–398. |
| [] | 郭敬辉, 石昕, 卞爱国, 许荣华, 翟明国, 李永刚. 1999. 桑干地区早元古代花岗岩长石Pb同位素组成和锆石U-Pb年龄: 变质与地壳熔融作用及构造-热事件演化. 岩石学报, 15(2): 199–207. |
| [] | 郭敬辉, 翟明国, 许荣华. 2002. 华北桑干地区大规模麻粒岩相变质作用的时代: 锆石U-Pb年代学. 中国科学(D辑), 32(1): 10–18. |
| [] | 韩宝福, 张磊, 王亚妹, 宋彪. 2007. 华北克拉通中部古元古代高Mg低Ti-P镁铁质岩墙的富晶集地幔源区——锆石Hf同位素的制约. 岩石学报, 23(2): 277–284. |
| [] | 侯贵廷, 穆治国. 1994. 华北克拉通晚前寒武纪镁铁质岩墙群K-Ar年龄及地质意义. 华北地质矿产杂志, 9(3): 267–270. |
| [] | 侯贵廷, 李江海, HallsHC, 钱祥麟. 2003. 华北晚前寒武纪镁铁质岩墙群的流动构造及侵位机制. 地质学报, 77(2): 210–216. |
| [] | 李江海, 侯贵廷, 钱样麟, HallsHC, DavisD. 2001. 恒山中元古代早期基性岩墙群的单颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄及其克拉通构造演化意义. 地质论评, 47(3): 234–237. |
| [] | 林潼, 罗静兰, 刘小洪, 张三. 2007. 东胜地区直罗组砂岩型铀矿包裹体特征与铀矿成因研究. 石油学报, 28(5): 72–78. |
| [] | 刘德长, 叶发旺, 赵英俊. 2006. 基于遥感信息延伸研究的DS铀矿床区域地质背景分析. 世界核地质科学, 23(4): 232–237. |
| [] | 柳益群, 冯乔, 杨仁超, 樊爱萍, 刑秀娟. 2006. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜地区砂岩型铀矿成因探讨. 地质学报, 80(5): 761–769. |
| [] | 罗静兰, 张复新, 贾恒, 刘小洪, 李博. 2005. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜地区和吐哈盆地十红滩地区含铀砂岩岩石学及成岩作用. 石油学报, 26(4): 39–45. |
| [] | 罗静兰, 戴亚权, 刘小洪, 林潼, 张三. 2006. 含铀砂岩中铀与有机质、油气和煤的关系——以鄂尔多斯盆地东胜地区和吐哈盆地十红滩地区为例. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 36(6): 982–987. |
| [] | 罗静兰, 魏新善, 姚泾利, 刘新社, 刘小洪. 2010. 物源与沉积相对鄂尔多斯盆地北部上古生界天然气优质储层的控制. 地质通报, 29(6): 33–42. |
| [] | 彭澎, 翟明国. 2002. 华北陆块前寒武纪两次重大地质事件的特征和性质. 地球科学进展, 17(6): 818–825. |
| [] | 彭澎, 翟明国, 张华峰, 赵太平, 倪志耀. 2004. 华北克拉通1.8Ga镁铁质岩墙群的地球化学特征及其地质意义: 以晋冀蒙交界地区为例. 岩石学报, 20(3): 439–456. |
| [] | 彭润民, 翟裕生, 韩雪峰, 王志刚, 王建平, 沈存利, 陈喜峰. 2007. 内蒙古狼山造山带构造演化与成矿响应. 岩石学报, 23(3): 679–688. |
| [] | 彭云彪, 陈安平, 方锡珩, 欧光习, 解启来. 2007. 东胜砂岩型铀矿床中烃类流体与成矿关系研究. 地球化学, 36(3): 267–274. |
| [] | 邵济安. 1991. 中朝板块北缘中段地壳演化. 北京: 北京大学出版社: 11-91. |
| [] | 孙敏, 关鸿. 2001. 阜平杂岩年龄及其地质意义: 兼论前寒武高级变质地体的定年问题. 岩石学报, 17(1): 145–156. |
| [] | 王惠初, 袁桂邦, 辛后田. 2001. 内蒙古固阳村空山地区麻粒岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及其对年龄解释的启示. 前寒武纪研究进展, 24(1): 28–34. |
| [] | 吴昌华, 钟长汀, 陈强安. 1997. 晋蒙高级地体孔兹岩系的时代. 岩石学报, 13(3): 289–302. |
| [] | 吴昌华, 李惠民, 钟长汀, 陈强安. 1998. 内蒙古黄土窑孔兹岩系的锆石与金红石年龄研究. 地质论评, 44(6): 618–626. |
| [] | 吴昌华, 李塞民, 钟长汀, 左义成. 2000. 阜平片麻岩和湾子片麻岩的单颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄——阜平杂岩并非一统太古宙基底的年代学证据. 前寒武纪研究进展, 23(3): 129–139. |
| [] | 吴昌华, 孙敏, 李惠民, 赵国春, 夏小平. 2006. 乌拉山-集宁孔兹岩锆石激光探针等离子质谱(LA-ICP-MS)年龄——孔兹岩沉积时限的年代学研究. 岩石学报, 22(11): 2639–2654. |
| [] | 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185–220. |
| [] | 吴仁贵, 祝民强, 余达淦, 周万蓬. 2006. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部底河道砂岩型铀矿地质特征. 华东理工学院学报, 29(1): 1–6. |
| [] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589–1064. |
| [] | 夏毓亮, 林锦荣, 刘汉彬, 范光, 侯艳先. 2003. 中国北方主要产铀盆地砂岩型铀矿成矿年代学研究. 铀矿地质, 19(3): 129–136. |
| [] | 向伟东, 方锡珩, 李田港, 陈晓林, 庞雅庆, 程华汉. 2006. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜铀矿床成矿特征与成矿模式. 铀矿地质, 22(5): 257–266. |
| [] | 肖新建, 李子颖, 陈安平. 2004. 东胜地区砂岩型铀矿床后生蚀变矿物分带特征初步研究. 铀矿地质, 20(3): 136–140. |
| [] | 杨俊杰, 裴锡古. 1996. 中国天然气地质学. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 3-20. |
| [] | 杨仁超, 韩作振, 樊爱萍. 2007. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜地区砂岩型铀矿床沉积微相与层序地层. 地层学杂志, 31(3): 261–266. |
| [] | 郁建华, 傅会芹, 张凤兰, 等. 1996. 华北地台北部非造山环斑花岗岩及有关岩石. 北京: 中国科技学术出版社: 1-96. |
| [] | 翟明国. 2004. 华北克拉通2.1~1.7Ga地质事件群的分解和构造意义探讨. 岩石学报, 20(6): 1343–1354. |
| [] | 翟明国, 彭澎. 2007. 华北克拉通古元古代构造事件. 岩石学报, 23(11): 2265–2282. |
| [] | 翟明国. 2010. 华北克拉通的形成演化与成矿作用. 矿床地质, 29(1): 24–36. |
| [] | 张维杰, 李龙, 耿明山. 2000. 内蒙古固阳地区新太古代侵入岩的岩石特征及时代. 地球科学, 25(3): 221–226. |
| [] | 张玉清, 王弢, 贾和义, 张志祥. 2003. 内蒙古中部大青山西乌兰不浪紫苏斜长麻粒岩锆石U-Pb年龄. 中国地质, 30(4): 394–399. |
| [] | 赵国春, 孙敏, WildeSA. 2002. 华北克拉通基底构造单元特征及早元古代拼合. 中国科学(D辑), 32(7): 538–549. |
| [] | 赵国春. 2009. 华北克拉通基底主要构造单元变质作用演化及其若干问题讨论. 岩石学报, 25(8): 1772–1792. |
| [] | 赵宏刚, 欧光习. 2006. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜地区沉积体系与砂岩型铀成矿. 铀矿地质, 22(3): 136–142. |
| [] | 赵俊峰, 刘池洋, 喻林, 黄雷, 刘永涛, 高飞. 2007. 鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗系直罗组砂岩发育特征. 沉积学报, 25(4): 535–544. |
| [] | 赵庆英, 刘正宏, 吴新伟, 陈晓峰. 2007. 内蒙古大青山地区哈拉合少岩体特征及成因. 矿物岩石, 27(1): 46–51. |
| [] | 钟长汀, 邓晋福, 万渝生, 等. 2007. 华北克拉通北缘中段古元古代造山作用的岩浆记录: S型花岗岩地球化学特征及锆石SHRIMP年龄. 地球化学, 36(6): 633–637. |
 2013, Vol. 29
2013, Vol. 29