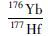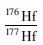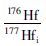2. 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
目前国际上一种代表性观点(亦或普遍)认为古元古代中期到中元古代晚期(2.1~1.2Ga)是哥伦比亚(Columbia, 或称为Nuna)超大陆汇聚、增生和裂解的时期(Zhao et al., 2002, 2003a, 2004; Ernst et al., 2010)。Columbia超大陆的汇聚可能是在2.1~1.8Ga发生的全球性碰撞造山事件中完成, 而裂解可能开始于1.6Ga, 结束于1.3~1.2Ga, 但全球不同块体的裂解历史有较大的差异, 其间发生了大量的中元古代造山后-非造山阶段的非造山岩浆活动及镁铁质岩墙群的侵入(Zhao et al., 2003a, 2004, 2006; Hou et al., 2008; Goldberg, 2010)。
华北克拉通(NCC)2.0~1.8Ga的碰撞造山带包括中部造山带、孔兹岩带和内蒙古缝合带, 它们记录了Columbia超大陆的汇聚(Zhao et al., 2003a, b, 2004, 2005; Santosh, 2010)。然而NCC是否与Columbia超大陆其他块体一样经历了中元古代的裂解过程仍然存在争议(Zhai et al., 2000; Lu et al., 2008; Rogers and Santosh, 2002; Zhao et al., 2003a), 而NCC缺少中元古代时期(1.6~1.0Ga)构造-岩浆活动的可靠同位素年龄是引发争议的主要原因之一。一些研究者认为在1.6Ga以前Columbia超大陆的裂解活动在NCC就已经结束, 所以NCC没有加入到超大陆随后的裂解活动中(Rogers and Santosh, 2002; Hou et al., 2008; Lu et al., 2008)。但是NCC与劳伦古陆、西伯利亚和印度大陆在古元古代晚期到中元古代早期具有相同的古地磁极性, 说明这些大陆在这个时期是一起运动的(Halls et al., 2000; Meert and Stuckey, 2002; Ernst et al., 2000; Piper et al., 2011)。NCC中元古代中期的裂解过程可以与其他加入到Columbia超大陆并最终裂解的克拉通的裂解过程相对比。
目前在NCC北缘已发现有中元古代与Columbia超大陆裂解有关的辉绿岩(1.37Ga, 锆石SHRIMP)、花岗岩(1.31Ga, 锆石LA-ICP-MS)和正长岩(1.35Ga, 锆石LA-ICP-MS)等非造山岩浆岩类(Gao et al., 2008; Su et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2009, 2012; Shi et al., 2012), 但是在NCC南缘目前尚无类似的报道。最近, 我们在华北克拉通南缘的河南省卢氏县潘河地区厘定了一组走向近东西的中元古代黑云母正长岩-霞石正长岩脉群。这种硅不饱和霞石正长岩和硅饱和黑云母正长岩时空关系密切的岩石组合在区域上属首次发现。正长岩类的形成通常与板内伸展构造有关, 是研究超大陆裂解过程的重要线索(Abdalla et al., 1996; Cliff, 1997; Mingram et al., 2000)。我们对该岩脉群进行了岩相学、年代学、地球化学和Hf同位素分析。华北克拉通南缘中元古代正长岩的厘定, 为探讨华北克拉通Columbia超大陆裂解过程提供了新的资料。
2 地质概况和岩石学特征河南省卢氏县潘河地区的大地构造属于华北克拉通南缘。华北南缘结晶基底为新太古界太华群中深变质岩系, 盖层为古元古界熊耳群、中元古界官道口群、新元古界栾川群和陶湾群。区内出露的地层主要是中元古界官道口群的碳酸盐岩和碎屑岩, 由老到新依次为:龙家园组、巡检司组及杜关组(图 1)。
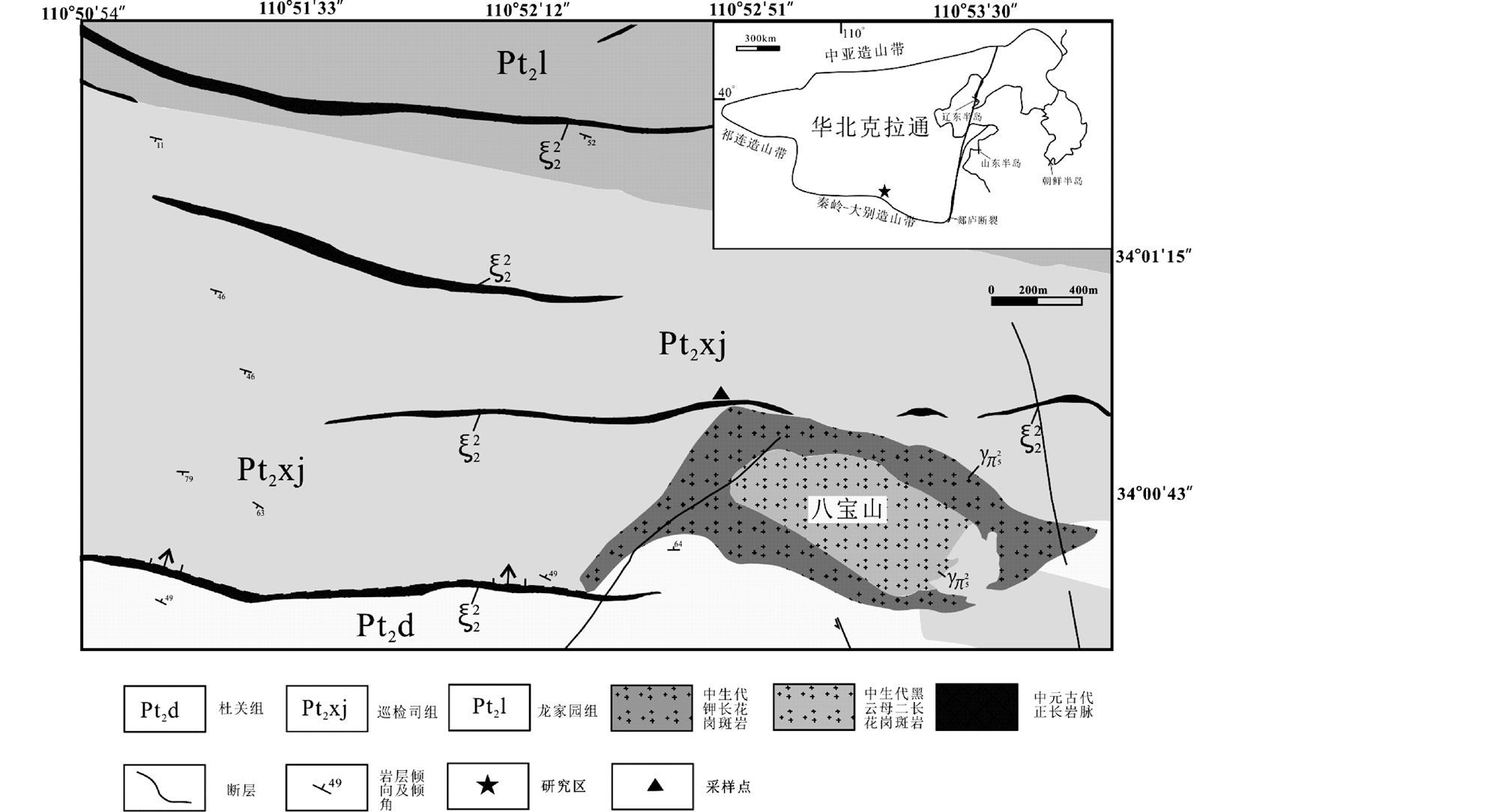
|
图 1 潘河正长岩岩体地质图(据Peng et al., 2010) Fig. 1 Simplified geological map of the Panhe syenites(after Peng et al., 2010) |
本次研究的黑云母正长岩和霞石正长岩呈脉状侵位于中元古界官道口群白云岩中。岩脉呈近东西向展布, 单个岩脉长约2~2.5km, 出露面积约0.1~0.12km2。在该区域发现的硅不饱和的霞石正长岩都是与硅饱和的黑云母正长岩共生, 两者界线明显, 正长岩中未见暗色包体或围岩捕掳体, 有些黑云母正长岩单独产出(图 1、图 2a)。

|
图 2 潘河正长岩野外和岩相学特征 (a)-共生的黑云母正长岩与霞石正长岩;(b)-肉红色黑云母正长岩;(c)-霞石正长岩;(d)-黑云母正长岩中的正长石(Or)、钠长石(Ab)和黑云母(Bt)集合体, 有些正长石发生绢云母化;(e)-黑云母正长岩中正长石发生泥化、绢云母化(Ser)和碳酸盐(Cb)化;(f)-霞石正长岩发生强烈绢云母化. Q-石英; Ab-钠长石; Bt-黑云母; Or-正长石; Ser-绢云母; Cb-碳酸盐矿物 Fig. 2 Photos showing the field crops and micropetrography of the Panhe syenites |
黑云母正长岩呈肉红色, 半自形粒状结构, 块状构造(图 2b), 主要矿物为正长石(45%~55%)、钠长石(35%~45%)和黑云母(3%~5%)。正长石颗粒较大, 约2~4mm, 呈板状, 发育卡斯巴双晶, 但是由于受到后期构造挤压的影响大多数已发生变形, 有应力消光的现象。钠长石, 粒径2~3mm, 呈板条状, 具有明显的聚片双晶。所有长石均见有白云母化和绢云母化的现象, 并且有些正长石有泥化和碳酸盐化的现象。黑云母分布于长石的粒间, 构成填隙结构, 大多数已蚀变成白云母和绢云母并析出不透明的细小铁质矿物。副矿物主要为锆石、磁铁矿等(图 2d, e)。
霞石正长岩强烈绢云母化, 仅可见少量正长石残余, 正长石绢云母化相对较弱(图 2c, f)。在镜下还见到一些浸染状的磁铁矿, 副矿物主要是磷灰石。由于霞石正长岩蚀变较严重, 在镜下未见到霞石残晶, CIPW标准矿物计算结果显示该岩石为霞石正长岩。
3 分析方法样品岩石化学的主量和微量元素组成分别在中国科学院同位素地球化学国家重点实验室Rigaku ZSX 100e型荧光光谱仪、PE Elan 6000型电感耦合等离子体-质谱仪(ICP-MS)上完成。详细分析方法及流程见刘颖等(1996)、梁细荣等(2003)和韦刚健等(2002)。
锆石U-Pb测定及锆石原位Lu-Hf同位素分析在中国科学院同位素地球化学国家重点实验室完成。锆石U-Pb分析所用仪器为Agligent公司生产的四级杆ICP-MS Agligent 7500a, 激光剥蚀系统为德国Lamda Physik公司的GeoLas 2005深紫外(DUV)193 nm ArF准激光剥蚀系统。采用单点剥蚀的方法(激光剥蚀斑束直径为30μm, 频率为8Hz), 标准锆石TEM2作为外标进行校正。详细实验流程和数据处理方法见涂湘林等(2011)。Lu-Hf同位素测试使用Thermo公司制造的Neptune型多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱(LA-MC-ICP-MS), 加载德国Lamda Physik公司制造的Geolas193nm准分子激光取样系统。激光束直径为32μm, 剥蚀频率为8Hz, 能量密度为15~20J/cm2, 剥蚀时间约60s。采用蓬莱锆石Penglai作为外标(Li et al., 2010)。详细的分析流程参见Wu et al.(2006)和谢烈文等(2008)。
4 分析结果 4.1 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄本文选取蚀变相对较弱的黑云母正长岩样品(LSB-118, 地理坐标N34°01′33″, E110°52′23″)进行锆石分选和LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年。选出的锆石颗粒较小(50~150μm), 自形程度较高, 呈长柱状或短柱状, 长宽比约1:1, 振荡环带构造发育, 具明显的岩浆锆石特征(吴元保和郑永飞, 2004)(图 3)。

|
图 3 潘河正长岩锆石阴极发光图 Fig. 3 Cathodoluminescence(CL)images of zircons of the Panhe syenite |
对黑云母正长岩(LSB-118)中的锆石共进行了27个测点分析(表 1), 锆石Th/U比值为0.62~1.02, 与典型的岩浆锆石特征相似(吴元保和郑永飞, 2004)。27个分析点中分析除LSB-118-1和LSB-118-2略微偏离谐和线处(可能是由于放射性Pb丢失), 其余25个测点均位于谐和线上或非常接近谐和线(图 4)。测得锆石207Pb/206Pb的加权平均年龄为1417±89Ma(MSWD=15), 与下交点年龄(1469±8Ma, MSWD=1.4)一致, 可以代表锆石的结晶年龄。
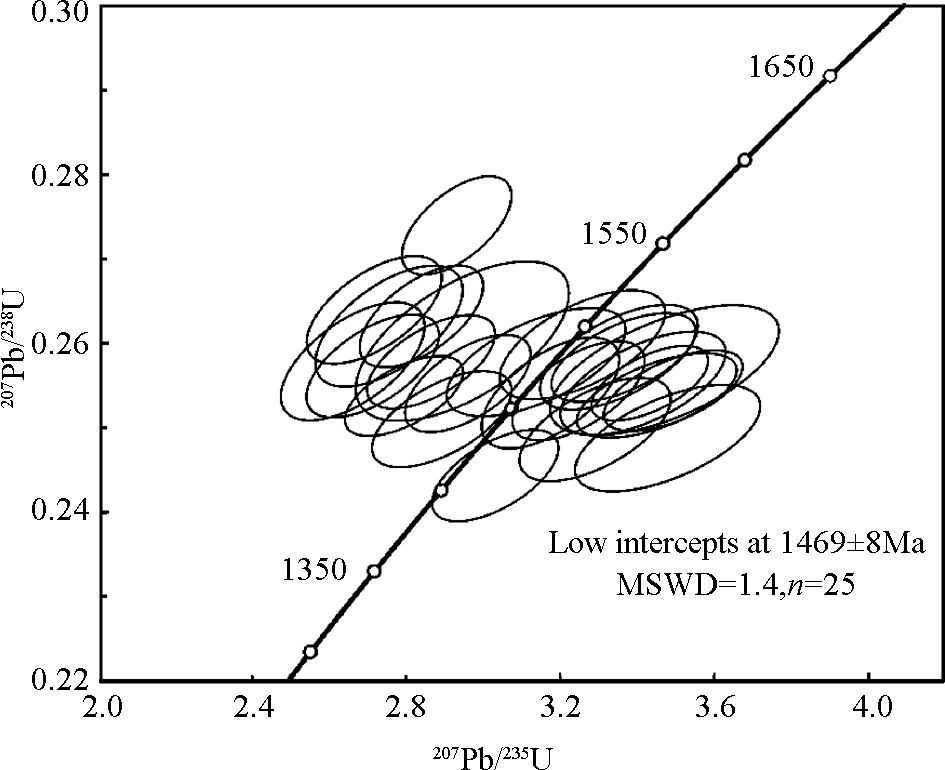
|
图 4 潘河正长岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄谐和图 Fig. 4 U-Pb concordia plots for zircons of the Panhe syenite |
|
|
表 1 潘河正长岩岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测试结果 Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb results for the Panhe syenites |
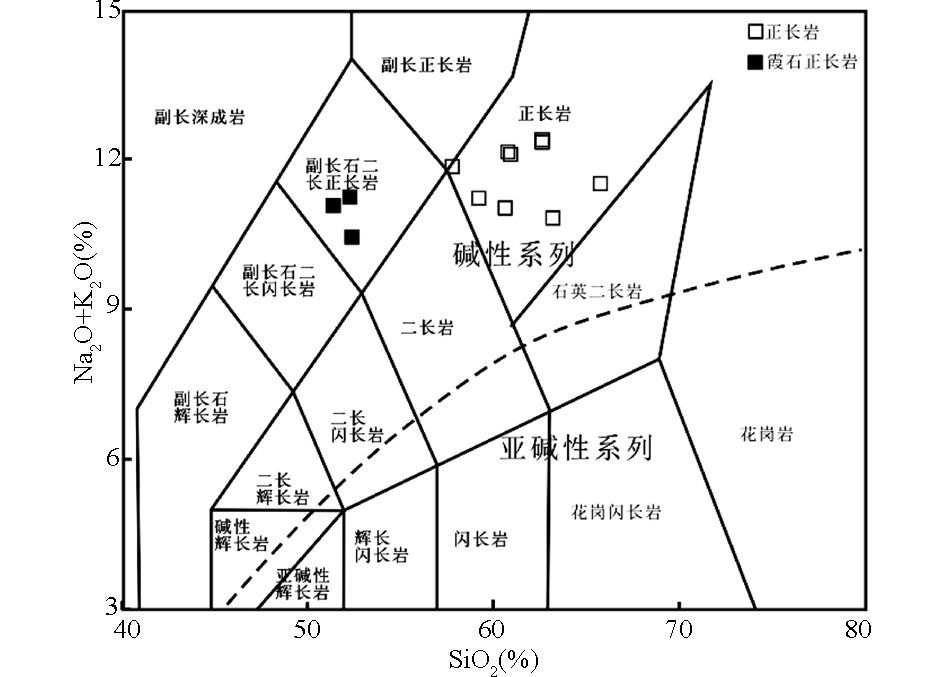
黑云母正长岩SiO2变化于57.7%~65.7%之间(表 2)。岩体碱含量较高, K2O+Na2O总量8.32%~13.0%, K2O/Na2O介于1.04~2.52之间。低的TiO2(0.14%~0.77%)、Fe2O3T(1.91%~4.07%)、MgO(0.48%~3.23%)(主要位于0.48%~1.93%)。霞石正长岩具有相对较低的SiO2含量(51.3%~52.2%), 具有高的K2O(7.10%~8.39%), 中等到低的Na2O(3.01%~4.05%), K2O/Na2O介于1.75~2.78之间, 相对较高的TiO2(0.98%~1.20%)、Fe2O3T(5.07%~5.89%)、MgO(1.79%~2.28%)。在TAS岩石分类图解上(图 5)样品都位于碱性系列。投点均主要落入正长岩和副长石二长正长岩范围, 与岩石的实际矿物组成的定名基本一致。岩石的铝含量均较高(Al2O3=18.7%~20.0%), ACNK(Al2O3/(CaO+ Na2O+K2O)摩尔分数比)=0.98~1.32, 在ANK-ACNK图解(图 6)中, 为过铝质岩类。CaO的含量较高(0.21%~1.34%), 可能是与有些岩石发生碳酸盐化有关。
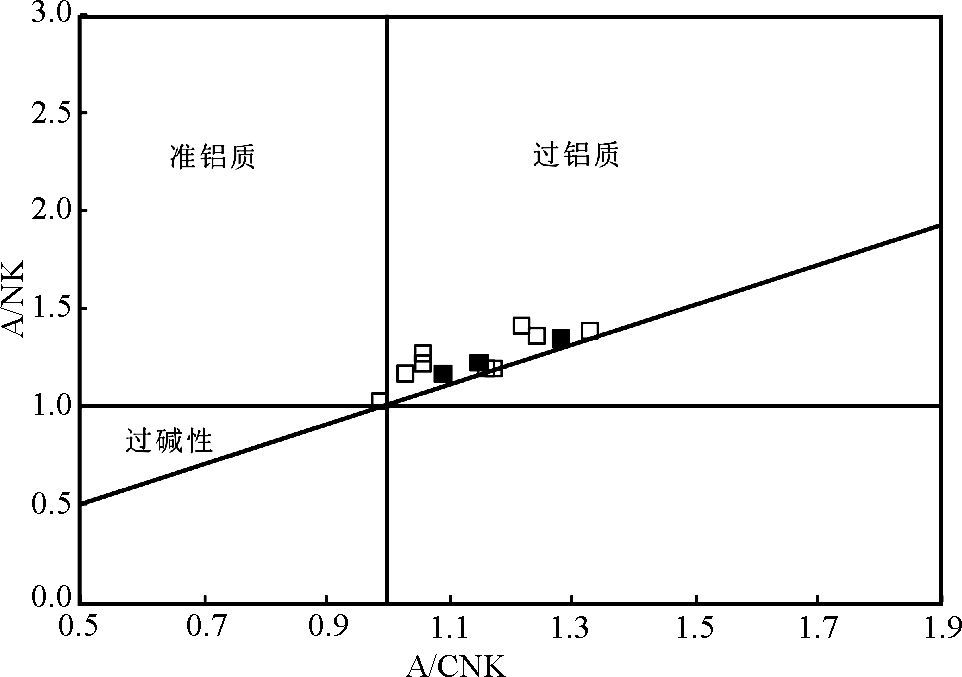
|
图 6 潘河正长岩ANCK-ANK图解(据Maniar and Piccoli, 1989) Fig. 6 ANCK-ANK diagram or the Panhe syenites(after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989) |
|
|
表 2 潘河正长岩岩体主量(wt%)、微量及稀土元素(×10-6)分析表 Table 2 The analyzed data of major(wt%), rare earth and trace elements(×10-6)for the Panhe syenites |
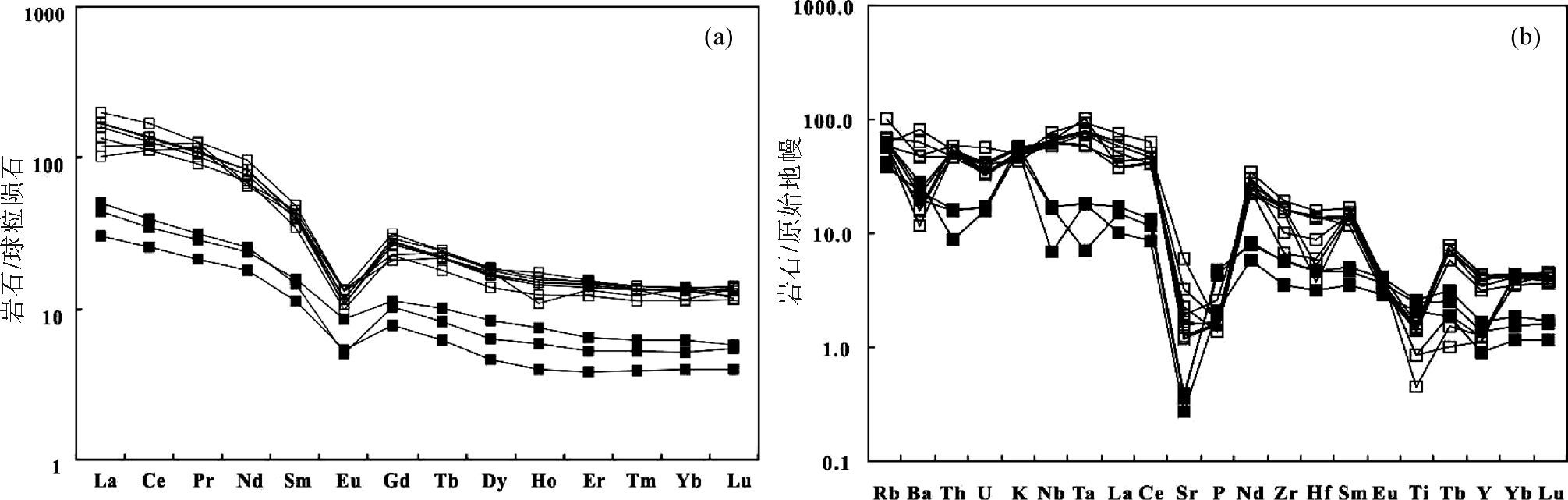
|
图 7 潘河正长岩球粒陨石标准化REE配分模式图及原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle normalized trace elements spider diagram for the Panhe syenites(normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
黑云母正长岩显著富集稀土元素, ∑REE介于663×10-6~1149×10-6之间, 在球粒陨石标准化配分模式图上呈向右倾斜的平滑曲线(图 7a), 轻重稀土分馏较为显著, LREE/HREE在15.5~22.4之间, (La/Yb)N=14.5~34.5。(La/Sm)N为3.33~6.65, (Gd/Yb)N比值为1.72~2.74, 表明轻稀土分馏程度较重稀土显著。岩石具有明显的Eu负异常(δEu=0.2~0.3)。
霞石正长岩的稀土元素总量相对较低, ∑REE介于107×10-6~184×10-6之间, 在球粒陨石标准化分布模式图上呈向右倾斜的平滑曲线(图 7a), 轻重稀土分馏较弱, LREE/HREE在9.78~14.4之间, (La/Yb)N=13.5~20.7。(La/Sm)N为3.74~5.14, (Gd/Yb)N比值为2.23~2.5, 表明轻稀土分馏程度较重稀土显著。岩石Eu异常较弱(δEu=0.92~0.98)。
在微量元素原始地幔标准化图解(图 7b)上, 两种正长岩表现为Rb、Ba、Th等大离子亲石元素强烈富集, Nb、Ta、Nd、Tb等高场强元素的强烈富集, 而Sr、Ti、P、Eu等元素显著亏损, 可能由于斜长石、磷灰石和Fe-Ti氧化物的分离结晶造成的。
与黑云母正长岩相比, 霞石正长岩的稀土元素含量相对较低, 但其Co(8.53×10-6~13.2×10-6)和Ni(54.5×10-6~112×10-6)含量显著的高于黑云母正长岩, 表明霞石正长岩与幔源岩浆亲缘关系更密切。
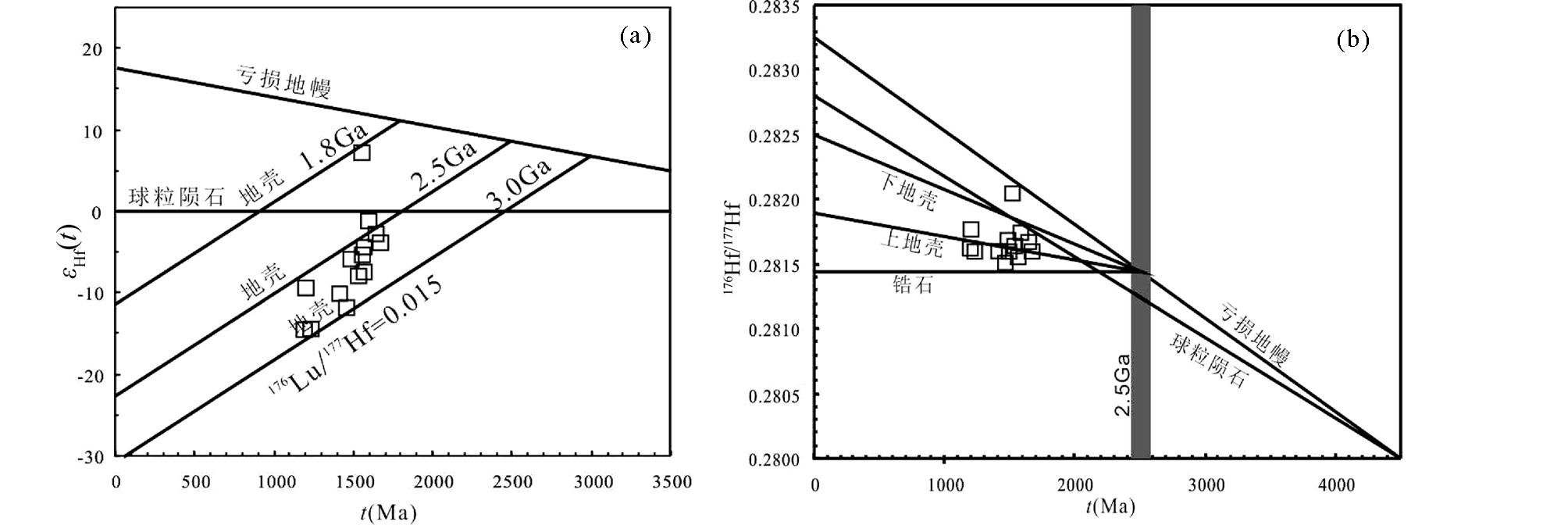
4.3 Hf同位素锆石Hf同位素分析共测试了14个点, 结果见表 3。176Hf/177Hf初始比值为0.281510~0.282042, 平均值为0.281686, εHf(t)值介于-14.79~8.16, 主要集中于-14.79~-1.17之间, 二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)为2.93~1.74Ga。在εHf(t)-t图解和176Hf/177Hf-t图解(图 8)中, 样品投点主要落在3.0~2.5Ga演化曲线之间, 少量落在2.5~1.8Ga演化曲线之间。较低的εHf(t)值、较大的变化范围和较高的Hf模式年龄表明正长岩成岩物质可能来源于富集岩石圈地幔的部分熔融, 在部分熔融、上升、侵位过程中可能存在下地壳物质的同化混染或岩浆混合作用。
|
|
表 3 潘河正长岩岩体锆石Hf同位素分析测试结果 Table 3 Hf isotope composition of zircons for the Panhe syenites |
|
图 8 潘河正长岩的锆石Hf同位素特征 Fig. 8 Hf isotopic compositions of zircons for the syenite from Panhe |
正长岩的成因模式有:(1)由于幔源岩浆和挥发分注入到下地壳底部导致下地壳岩石的部分熔融(Lubala et al., 1994), 或者封闭体系中地壳岩石在加厚的大陆地壳压力下部分熔融(Huang and Wyllie, 1981);(2)可能是和俯冲相关的交代地幔部分熔融(Sutcliffe et al., 1990; Lynch et al., 1993)或者碱性玄武质岩浆分离结晶的产物(Brown and Becker, 1986; Thorpe and Tindle, 1992);(3)可能是岩浆混合, 特别是幔源基性岩浆和酸性岩浆混合后分异的产物(Barker et al., 1975; Sheppard, 1995; Zhao et al., 1995), 或者幔源硅不饱和碱性岩浆和下地壳部分熔融形成的花岗质岩浆混合的产物(Dorais, 1990)。越来越多的研究表明, 硅不饱和正长岩和硅饱和正长岩共生组合形成于开放体系, 硅不饱和的岩浆经过地壳物质的混染和结晶分异(AFC)或引发地壳物质重熔形成硅饱和的岩浆(Brooks and Gill, 1982; Fitton, 1987; Foland et al., 1993;Harris et al., 1999; Marks et al., 2003)。
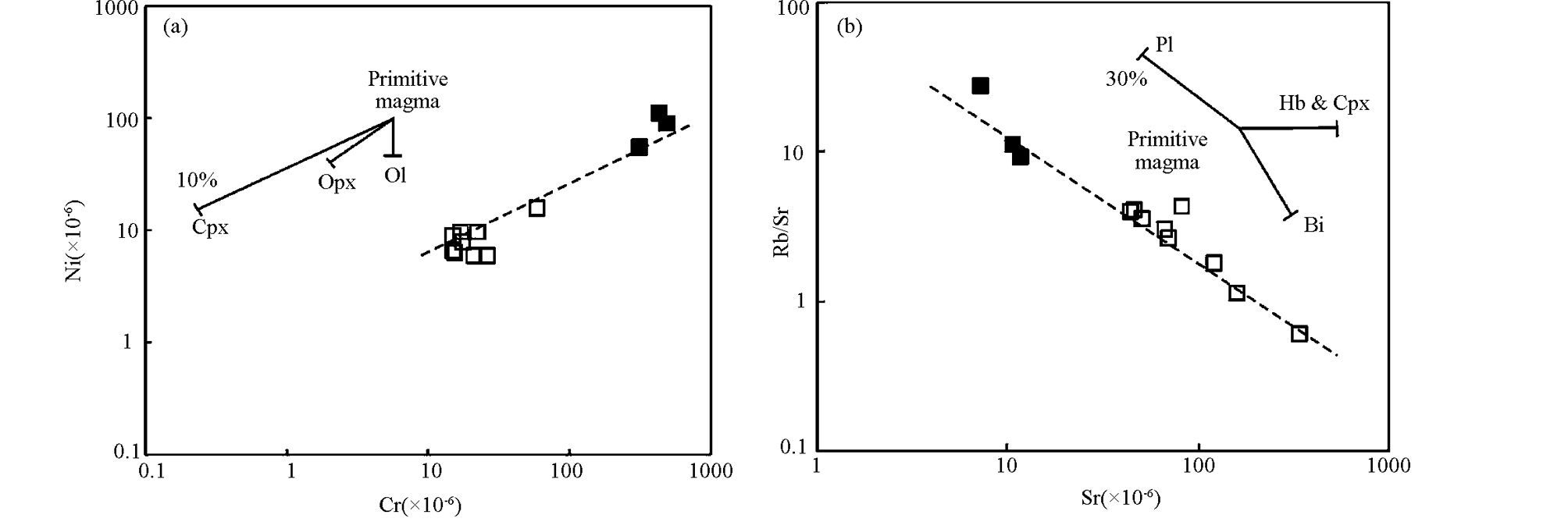
正长岩具有高的K2O+Na2O含量以及低的TiO2、Fe2O3T、MgO。在主量元素Harker变异图解上(图 9), TiO2、Fe2O3T、MgO和SiO2负相关, 暗示霞石正长岩和正长岩在形成过程中可能有橄榄石、单斜辉石和Ti-Fe氧化物的分离结晶。并且V、Co随着SiO2增加而减少, 可能是由于正长岩的演化过程中有单斜辉石的分离结晶。同时在Cr-Ni图解中(图 10a), 也显示了单斜辉石的分离结晶, Sc和Co含量较低也说明有辉石的结晶分异。Sr和Eu的负异常说明正长岩在形成过程中有斜长石的结晶分异。同时在Rb/Sr-Sr图解中(图 10b)也显示了斜长石的分异。也就是说, 正长岩的形成可能经历了单斜辉石和斜长石的结晶分异。在Zr/Nb-Zr图解上(图 11), Zr/Nb比值随着Zr的增加没有改变, 说明正长岩可能是由于玄武质岩浆的结晶分异作用而形成的。

|
图 9 主量元素和微量元素对SiO2变化图解 Fig. 9 Major and trace element vs.SiO2 diagrams for the Panhe syenites |
|
图 10 潘河正长岩Cr-Ni和Sr-Rb/Sr图解(分配系数据Rollison, 1993) Fig. 10 Cr-Ni and Sr-Rb/Sr diagrams for the Panhe syenites(partition coefficients after Rollison, 1993) |

|
图 11 潘河正长岩Zr-Zr/Nb图解(底图据Geng et al., 2009) Fig. 11 Zr-Zr/Nb diagram for the Panhe syenites(after Geng et al., 2009) |
锆石Hf同位素分析结果显示, 潘河地区的正长岩εHf(t)值主要集中于-14.79~-1.17之间, 二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)为2.93~1.74Ga。在εHf(t)-t图解和176Hf/177Hf-t图解(图 8)中, 样品投点主要落在3.0~2.5Ga演化曲线之间, 少量落在2.5~1.8Ga演化曲线之间。根据现有的有关太华群变质岩中锆石Hf同位素数据(时毓等, 2011;第五春荣等, 2010;Xu et al., 2009; Yu et al., 2013; Huang et al., 2012), εHf(1560Ma)的变化范围在-27~-14, 因此潘河正长岩不可能由太古代变质岩重熔形成。较低的εHf(t)值和较高的Hf模式年龄表明正长岩成岩物质可能来源于富集岩石圈地幔的部分熔融, 这种源于富集地幔的碱性玄武质岩浆经过强烈的结晶分异形成碱性正长岩类。εHf(t)变化范围较大可能是有地壳物质的加入。
在NCC内其它地区古元古-中古元代中期岩浆岩的锆石Hf同位素组成亦具有相似的特征。龙王A型花岗岩(1602±6.6Ma, 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb法), εHf(t)=-5.26~-1.11, 模式年龄tDM2=2.6~2.4Ga(包志伟等, 2009)。晋宁A型花岗岩(1318±7Ma, 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb法), εHf(t)=-8.6~-3.6, 模式年龄tDM2=2.6~2.3Ga(Shi et al., 2012)。
前人研究表明(包志伟等, 2009), 华北克拉通存在1.9~1.7Ga地幔富集事件, 可能与克拉通东西地块的拼合后加厚地壳或岩石圈的拆沉作用有关。约1.8Ga NCC进入造山后-非造山阶段, 非造山岩浆岩可能与地壳-岩石圈减薄及软流圈地幔上涌有关(Crawford and Windley, 1990)。古元古代末期具有富集地幔特征且结晶年龄与模式年龄存在巨大差别的镁铁质岩墙在华北克拉通中-南部地区的广泛分布是岩石圈上地幔及下地壳的拆沉导致地幔迅速富集证据之一。富集地幔部分熔融形成的玄武质岩浆的底侵、上涌和强烈的结晶分异, 并且在上升和分异演化过程中同熔或引发地壳物质的部分熔融形成中元古代的正长岩类。即霞石正长岩可能源于富集地幔部分熔融形成的玄武质岩浆强烈分异的产物, 而黑云母正长岩则可能有较多地壳物质的加入, 可能与AFC过程有关。
5.3 地球动力学背景及其与哥伦比亚超大陆裂解的关系碱性正长岩通常形成于板内伸展构造背景, 板内伸展或裂谷作用过程可能与Columbia超大陆的裂解过程有关。
在NCC广泛分布的1.78~1.68Ga的镁铁质岩墙群, 斜长岩-碱性花岗岩和奥长花岗岩组合(Halls et al., 2000; Peng et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2004; Zhang et al., 2007)以及1.62Ga的富钾火山岩系(Lu and Li, 1991), 可能与NCC古元古代晚期的撞后拉伸过程密切相关。NCC南缘河南省栾川县龙王A型花岗岩和河南省卢氏县麻坪霓辉正长岩(~1.6Ga)形成于华北克拉通南缘熊耳群火山岩规模喷溢和镁铁质岩墙群侵位之后, 可能是区内最早的板内非造山岩浆岩(包志伟等, 2009;柳晓艳, 2011), 可能标志着华北南缘自1.6Ga由碰撞后转入非造山演化阶段。NCC北缘的辉绿岩岩床(1.35Ga)(Zhang et al., 2009)和钾质斑脱岩(1.37Ga)(Gao et al., 2008; Su et al., 2008)及~1.31Ga的A型花岗岩(Shi et al., 2012)等产出, 可能代表着Columbia超大陆中元古代最终裂解的时间。而华北克拉通南缘潘河地区~1.5Ga的碱性正长岩的厘定, 进一步说明中元古代中期整个华北克拉通处于板内伸展构造环境。因此, 我们认为华北克拉通作为一个整体可能于~1.6Ga进入板内伸展阶段, 其裂解过程可能持续至中元古代(~1.3Ga), 与Columbia超大陆整体裂解过程在时代上基本一致。
6 结论对华北南缘潘河正长岩系统的岩石学和地球化学研究表明, 岩体形成于1469±8Ma。正长岩的主量元素、微量元素和Hf同位素地球化学特征的初步研究表明, 岩体来源于富集地幔并且有地壳物质参与, 可能经历了斜长石和单斜辉石的分离结晶作用。岩体形成于板内伸展构造环境, 其形成可能与Columbia超大陆的裂解过程有关, 即~1.5Ga时NCC仍处在Columbia超大陆的裂解体制之中。
致谢 野外工作中得到了卢氏县北方矿业有限公司的大力支持;锆石定年、主微量和Hf同位素分析得到中国科学院同位素地球化学重点实验室张潺婵、刘颖、胡光黔以及涂相淋等的支持;中国地质科学院地质力学研究所赵越研究员和中国科学院广州地球化学研究所杨武斌博士提出了建设性的评审意见;在此一并表示感谢。| [] | Abdalla JA, Said AA, Visona D. 1996. New geochemical and petrographic data on the garbbro-syenite Suite between Hargesya and Berbera-Shiikh (northern Somalia). Journal of African Earth Sciences, 23(3): 363–373. DOI:10.1016/S0899-5362(97)00007-9 |
| [] | Bao ZW, Wang Q, Zi F, Tang GJ, Du FJ, Bai GD. 2009. Geochemistry of the Paleproterozoic Longwangchuang A-type granites on the southern margin of North China Craton: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Geochimica, 38(6): 509–522. |
| [] | Barker F, Wones DR, Sharp WN, Desborough GA. 1975. The Pikes Peak batholith, Colorado front range, and a model for the origin of the gabbro-anorthosite-syenite-potassic granite suite. Precambrian Research, 2(2): 97–160. DOI:10.1016/0301-9268(75)90001-7 |
| [] | Brooks CK, Gill RCO. 1982. Compositional variation in the pyroxenes and amphiboles of the Kangerdlugssuaq intrusion, East Greenland: Further evidence for the crustal contamination of syenite magma. Mineralogical Magazine, 45(377): 1–9. |
| [] | Brown PE, Becker SM. 1986. Fractionation, hybridisation and magma-mixing in the Kialineq centre East Greenland. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 92(1): 57–70. DOI:10.1007/BF00373963 |
| [] | Cliff SJ. 1997. The petrology of the layered gabbro intrusion, eastern gabbro, Coldwell alkaline complex, Northwestern Ontario, Canada: Evidence for multiple phases of intrusion in a ring dyke. Lithos, 40(2-4): 243–259. DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(97)00030-3 |
| [] | Crawford MB, Windley BF. 1990. Leucogranites of the Himalaya/Karakoram: Implications for magmatic evolution within collisional belts and the study of collision-relates leucogranite petrogenesis. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 44(1-2): 1–19. DOI:10.1016/0377-0273(90)90008-4 |
| [] | Diwu CR, Sun Y, Lin CL, Wang HL. 2010. LA-(MC)-ICPMS U-Pb zircon geochronology and Lu-Hf isotope compositions of the Taihua complex on the southern margin of the North Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(23): 2557–2571. DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-3273-6 |
| [] | Dorais MJ. 1990. Compositional variations in pyroxenes and amphiboles of the Belknap Mountain complex, New Hampshire: Evidence for the origin of silica-saturated alkaline rocks. American Mineralogist, 75(9-10): 1092–1105. |
| [] | Ernst RE, Buchan KL, Hamilton MA, Okrugin AV, Tomshin MD. 2000. Integrated paleomagnetism and U-Pb geochronology of mafic dikes of the eastern Anabar shield region, Siberia: Implication for Mesoproterozoic paleolatitude of Siberia and comparison with Laurentia. The Journal of Geology, 108(4): 381–401. DOI:10.1086/314413 |
| [] | Ernst RE, Bell K. 2010. Large igneous provinces (LIPs) and carbonatites. Mineralogy and Petrology, 98(1-4): 55–76. DOI:10.1007/s00710-009-0074-1 |
| [] | Fitton JG. 1987. The Cameroon line, West Africa: A comparison between oceanic and continental alkaline volcanism. In: Fitton JG and Upton BGJ (eds.).Alkaline Igneous Rocks.Oxford: Blackwell: 273–291. |
| [] | Foland KA, Landoll JD, Henderson CMB, Chen JF. 1993. Formation of cogenetic quartz and nepheline syenites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 57(3): 697–704. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(93)90380-F |
| [] | Gao LZ, Zhang CH, Shi XY, Song B, Wang ZQ, Liu YM. 2008. Mesoproterozoic age for Xiamaling Formation in North China Plate indicated by zircon SHRIMP dating. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(17): 2665–2671. |
| [] | Geng HY, Sun M, Yuan C, Xiao WJ, Xian WS, Zhao GC, Zhang LF, Wong K, Wu FY. 2009. Geochemical, Sr-Nd and zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopic studies of Late Carboniferous magmatism of the West Junggar, Xinjiang: Implications for ridge subduction?. Chemical Geology, 266(3-4): 364–389. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.07.001 |
| [] | Goldberg AS. 2010. Dyke swarms as indicators of major extensional events in the 1.9~1.2Ga Columbia supercontinent. Journal of Geodynamics, 50(3-4): 176–190. DOI:10.1016/j.jog.2010.01.017 |
| [] | Halls HC, Li JH, Davis D, Hou G, Zhang BX, Qian XL. 2000. A precisely dated Proterozoic palaeomagnetic pole from the North China craton, and its relevance to palaeoconental reconstruction. Geophysical Journal International, 143(1): 185–203. DOI:10.1046/j.1365-246x.2000.00231.x |
| [] | Harris C, Marsh JS, Milner SC. 1999. Petrology of the alkaline core of the Messum igneous complex, Namibia: Evidence for the progressively decreasing effect of crustal contamination. Journal of Petrology, 40(9): 1377–1397. DOI:10.1093/petroj/40.9.1377 |
| [] | Hou GT, Santosh M, Qian XL, Lister GS, Li JH. 2008. Tectonic constraints on 1.3~1.2Ga final breakup of Columbia supercontinent from a giant radiating dyke swam. Gondwana Research, 14(3): 561–566. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2008.03.005 |
| [] | Huang WL, Wyllie PJ. 1981. Phase relationships of S-type granite with H2O to 35kbar: Muscovite granite from Harney Peak, South Dakota. Journal of Geophysical Research, 86(B11): 10515–10529. DOI:10.1029/JB086iB11p10515 |
| [] | Huang XL, Simon AW, Yang QJ, Zhong JW. 2012. Geochronology and petrogenesis of gray gneisses from the Taihua Complex at Xiong’er in the southern segment of the Trans-North China Orogen: Implications for tectonic transformation in the Early Paleoproterozoic. Lithos, 134-135: 236–252. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.01.004 |
| [] | Li XH, Long WG, Li LQ, Liu Y, Zheng YF, Yang YH, Chamberlain KR, Wan DF, Guo CH, Wang XC, Tao H. 2010. Penglai zircon megacrysts: A potential new working reference material for microbeam determination of Hf-O isotopes and U-Pb age. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 34(2): 117–134. DOI:10.1111/j.1751-908X.2010.00036.x |
| [] | Liang XR, Wei GJ, Li XH, Liu Y. 2003. Precise measurement of 143Nd/144Nd and Sm/Nd ratios using multiple collectors inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (MC-ICP-MS). Geochimica, 32(1): 91–96. |
| [] | Liu XY. 2011. Chronological, petrological, and geochemical characteristics of the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic alkali-rich intrusive rocks along the southern part of the North China Craton. Master’s Degree Thesis. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (in Chinese with English summary) |
| [] | Liu Y, Liu HC, Li XH. 1996. Simultaneous and precise determination of 40 trace elements in rock samples using ICP-MS. Geochimica, 25(6): 552–558. |
| [] | Lu SN, Zhao GC, Wang HC, Hao GJ. 2008. Precambrian metamorphic basement and sedimentary cover of the North China Craton: A review. Precambrian Research, 160(1-2): 77–93. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.017 |
| [] | Lubala RT, Frick C, Rogers JH, Walraven F. 1994. Petrogenesis of syenites and granites of the Schiel alkaline complex, northern Transvaal, South Africa. The Journal of Geology, 102(3): 307–316. DOI:10.1086/629673 |
| [] | Lynch DJ, Musselman TE, Gutmann JT, Patchett PJ. 1993. Isotopic evidence for the origin of Cenozoic volcanic rocks in the Pinacate volcanic field, northwestern Mexico. Lithos, 29(3-4): 295–302. DOI:10.1016/0024-4937(93)90023-6 |
| [] | Maniar PD, Piccoli PM. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101(5): 635–643. DOI:10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2 |
| [] | Marks M, Vennemann T, Siebel W, Markl G. 2003. Quantification of magmatic and hydrothermal processes in a peralkaline syenite-alkali granite complex based on textures, phase equilibria, and stable and radiogenic isotopes. Journal of Petrology, 44(7): 1247–1280. DOI:10.1093/petrology/44.7.1247 |
| [] | Meert JG, Stuckey W. 2002. Revisiting the paleomagnetism of the 1.476Ga St. Francois Mountains igneous province, Missouri.Tectonics, 21(2): 1–1. |
| [] | Mingram B, Trumbull RB, Littman S, Gerstenberger H. 2000. A petrogenetic study of anorogenic felsic magmatism in the Cretaceous Paresis ring complex, Namibia: Evidence for mixing of crust and mantle-derived components. Lithos, 54(1-2): 1–22. DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00033-5 |
| [] | Peng P, Zhai MG, Ernst RE, Guo JH, Liu F, Hu B. 2008. A 1.78Ga large igneous province in the North China Craton: The Xiong’er Volcanic Province and the North China dyke swarm. Lithos, 101(3-4): 260–280. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.07.006 |
| [] | Peng P, Zhai MG, Li QL, Wu FY, Hou QL, Li Z, Li TS, Zhang YB. 2010. Neoproterozoic (~900Ma) Sariwon sills in North Korea: Geochronology, geochemistry and implications for the evolution of the south-eastern margin of the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 243–254. |
| [] | Piper JDA, Zhang JS, Huang B, Roberts AP. 2011. Palaeomagnetism of Precambrian dyke swarms in the North China Shield: The ~1.8Ga LIP event and crustal consolidation in late Palaeoproterozoic times. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(6): 504–524. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.010 |
| [] | Rogers JJW, Santosh M. 2002. Configuration of Columbia, a Mesoproterozoic supercontinent. Gondwana Research, 5(1): 5–22. DOI:10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70883-2 |
| [] | Rollison HR. 1993. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation. London: Longman, 1-352 |
| [] | Santosh M. 2010. Assembling North China Craton within the Columbia supercontinent: The role of double-sided subduction. Precambrian Research, 178(1-4): 149–167. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2010.02.003 |
| [] | Sheppard S. 1995. Hybridization of shoshonitic lamprophyre and calc-alkaline granite magma in the Early Proterozoic Mt. Bundey Igneous suite, Northern Territory.Australian Journal of Earth Sciences: An International Geoscience Journal of the Geological Society of Australia, 42(2): 173–185. |
| [] | Shi Y, Yu JH, Xu XS, Tang HF, Qin JS, Chen LH. 2011. U-Pb ages and Hf isotope compositions of zircons of Taihua Group in Xiaoqinling area, Shaanxi Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(10): 588–597. |
| [] | Shi YR, Liu DY, Kröner A, Jian P, Miao LC, Zhang FQ. 2012. Ca. 1318Ma A-type granite on the northern margin of the North China Craton: Implications for intraplate extension of the Columbia supercontinent.Lithos, 148: 1–9. |
| [] | Su WB, Zhang SH, Huff WD, Li HK, Ettensohn FR, Chen XY, Yang HM, Han YG, Song B, Santosh M. 2008. SHRIMP U-Pb ages of K-bentonite beds in the Xiamaling Formation: Implications for revised subdivision of the Meso- to Neoproterozoic history of the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 14(3): 543–553. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2008.04.007 |
| [] | Sun SS, McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.).Magmatism in Oceanic Basins.Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313–345. DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 |
| [] | Sutcliffe RH, Smith AR, Doherty W, Barnett RL. 1990. Mantle derivation of Archean amphibole-bearing granitoid and associated mafic rocks: Evidence from the southern Superior province, Canada. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 105(3): 255–274. DOI:10.1007/BF00306538 |
| [] | Thorpe RS, Tindle AG. 1992. Petrology and petrogenesis of a tertiary bimodal dolerite-peralkaline/sublkline trachyte/rhyolite dyke association from Lundy, Bristol Channel, UK. Geological Journal, 27(2): 101–117. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1034 |
| [] | Tu XL, Zhang H, Deng WF, Ling MX, Liang HY, Liu Y, Sun WD. 2001. Application of RESOlution in-situ laser ablation ICP-MS in trace element analyses. Geochimica, 40(1): 83–98. |
| [] | Wang YJ, Fan WM, Zhang YH, Guo F, Zhang HF, Peng TP. 2004. Geochemical, 40Ar/39Ar geochronological and Sr-Nd isotopic constraints on the origin of Paleoproterozoic mafic dikes from the southern Taihang Mountains and implications for the ca. 1800Ma event of the North China Craton.Precambrian Research, 135(1-2): 55–77. |
| [] | Wei GJ, Liang XR, Li XH, Liu Y. 2003. Precise measurement of Sr isotopic composition of liquid and solid base using (LA) MC-ICP MS. Geochimica, 31(3): 295–299. |
| [] | Wu FY, Yang YH, Xie LW, Yang JH, Xu P. 2006. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology. Chemical Geology, 234(1-2): 105–126. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.003 |
| [] | Wu YB, Zheng YF. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on the interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15): 1554–1569. DOI:10.1007/BF03184122 |
| [] | Xie LW, Zhang YB, Zhang HH, Sun JF, Wu FY. 2008. In situ simultaneous determination of trace elements, U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopes in zircon and baddeleyite. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(10): 1565–1573. |
| [] | Xu XS, GriffinWL, Ma X, O’Reilly SY, He ZY, Zhang CL. 2009. The Taihua group on the southern margin of the North China craton: Further insights from U-Pb ages and Hf isotope compositions of zircons. Mineralogy and Petrology, 97(1-2): 43–59. DOI:10.1007/s00710-009-0062-5 |
| [] | Yu XQ, Liu JL, Li CL, Chen SQ, Dai YP. 2013. Zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotope analysis on the Taihua Complex: Constraints on the formation and evolution of the Trans-North China Orogen. Precambrian Research, 230: 31–44. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.12.008 |
| [] | Zhai MG, Bian AG, Zhao TP. 2000. The amalgamation of the supercontinent of North China Craton at the end of Neo-Archaean and its breakup during Late Palaeoproterozoic and Meso-Proterozoic. Science in China (Series D), 43(Suppl.): 219–232. |
| [] | Zhang SH, Liu SW, Zhao Y, Yang JH, Song B, Liu XM. 2007. The 1.75~1.68Ga anorthosite-mangerite-alkali granitoid-rapakivi granite suite from the northern North China Craton: Magmatism related to a Paleoproterozoic orogen. Precambrian Research, 155(3-4): 287–312. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.02.008 |
| [] | Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Yang ZY, He ZF, Wu H. 2009. The 1.35Ga diabase sills from the northern North China Craton: Implications for breakup of the Clumbia (Nuna) supercontinent. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 288(3-4): 588–600. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2009.10.023 |
| [] | Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Santosh M. 2012. Mid-Mesoproterozoic bimodal magmatic rocks in the northern North China Craton: Implications for magmatism related to breakup of the Columbia supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 222-223: 339–367. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2011.06.003 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Cawood PA, Wilde SA, Sun M. 2002. Review of the global 2.1~1.8Ga orogens: Implications for a pre-Rodinia supercontinent. Earth-Science Reviews, 59(1-4): 125–162. DOI:10.1016/S0012-8252(02)00073-9 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA. 2003a. Assembly, accretion and breakup of the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic Columbia supercontinent: Records in the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 6(3): 417–434. DOI:10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70996-5 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA. 2003b. Major tectonic units of the North China Craton and their Paleoproterozoic assembly. Science in China (Series D), 46(1): 23–38. DOI:10.1360/03yd9003 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA, Li SD. 2004. A Paleo-Mesoproterozoic supercontinent: Assembly, growth and breakup. Earth-Science Reviews, 67(1-2): 91–123. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.02.003 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA, Li SD. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited. Precambrian Research, 136(2): 177–202. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA, Li SZ, Zhang J. 2006. Some key issues in reconstructions of Proterozoic supercontinents. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 28(1): 3–19. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.06.010 |
| [] | Zhao JX, Shiraishi K, Ellis DJ, Sheraton JW. 1995. Geochemical and isotopic studies of syenites from the Yamato Mountains, East Antarctica: Implications for the origin of syenitic magmas. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(7): 1363–1382. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(95)00050-A |
| [] | 包志伟, 王强, 资锋, 唐功建, 杜凤军, 白国典. 2009. 龙王A型花岗岩地球化学特征及其地球动力学意义. 地球化学, 38(6): 509–522. |
| [] | 第五春荣, 孙勇, 林慈銮, 王洪亮. 2010. 河南鲁山地区太华杂岩LA-(MC)-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素组成. 科学通报, 55(21): 2112–2123. |
| [] | 刘颖, 刘海臣, 李献华. 1996. 用ICP-MS准确测定岩石样品中40余种微量元素. 地球化学, 25(6): 552–558. |
| [] | 梁细荣, 韦刚建, 李献华, 刘颖. 2003. 利用MC-ICP MS精确测定143Nd/144Nd和Sm/Nd比值. 地球化学, 32(1): 91–96. |
| [] | 柳晓艳. 2011. 华北克拉通南缘古-中元古代碱性岩岩石地球化学与年代学研究及其地质意义. 硕士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质科学院 |
| [] | 时毓, 于津海, 徐夕生, 唐红峰, 邱检生, 陈立辉. 2011. 陕西小秦岭地区太华群的锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成. 岩石学报, 27(10): 588–597. |
| [] | 涂湘林, 张红, 邓文峰, 凌明星, 梁华英, 刘颖, 孙卫东. 2011. RESOlution激光剥蚀系统在微量元素原位微区分析中的应用. 地球化学, 40(1): 83–98. |
| [] | 韦刚健, 梁细荣, 李献华, 刘颖. 2002. (LA) MC-ICPMS方法精确测定液体和固体样品的Sr同位素组成. 地球化学, 31(3): 295–299. |
| [] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589–1604. |
| [] | 谢烈文, 张艳斌, 张辉煌, 孙金凤, 吴福元. 2008. 锆石/斜锆石U-Pb和Lu-Hf同位素以及微量元素成分的同时原位测定. 科学通报, 53(2): 220–228. |
 2013, Vol. 29
2013, Vol. 29