东北地区位于华北板块和西伯利亚板块所夹持的中亚造山带东段(Şengör et al., 1993;Şengör and Naial’in,1996),区域上广泛分布着巨量花岗岩(吴福元等,1999),传统上将其视为海西期造山作用的产物(黄汲清等,1977),即它们主要形成于海西期(吉林省地质矿产局,1988;内蒙古自治区地质矿产局,1991;黑龙江省地质矿产局,1993)。然而,随着新的定年技术的应用和高精度年代学资料的积累,人们普遍认识到该区花岗岩主要形成于印支期和燕山期,少量花岗岩形成于加里东期和海西期(Wu et al., 2011;Wang et al., 2012;Yu et al., 2013)。对东北地区燕山期花岗岩年代学资料的进一步研究表明,该期花岗岩的形成时代集中分布在早-中侏罗世和早白垩世(孙德有等, 2001, 2005;Wu et al., 2002, 2005a, b,2011;Zhang et al., 2004;葛文春等,2005;程瑞玉等,2006;隋振民等,2007;Gao et al., 2007;许文良等,2008a;张彦龙等,2008;Sun et al., 2008;Wilde et al., 2010),但对于是否存在晚白垩世花岗岩目前还没有得到证实,这与东亚大陆东缘的俄罗斯远东地区、朝鲜半岛以及日本西南部广泛存在的晚白垩世花岗岩(Kagami et al., 1988;Yuhara et al., 2000, 2003;Sato et al., 2002;Zhang et al., 2012b)形成了鲜明的对比。那么,东北地区是否存在晚白垩世花岗岩?如果存在,它们的空间展布、岩石组合、源区性质及其构造属性如何?这些问题至今没有得到很好的解决。鉴于此,本文报道了黑龙江东部三江盆地北缘晚白垩世花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb定年、岩石地球化学分析以及锆石Hf同位素分析结果,这对揭示东北地区晚白垩世花岗岩的存在以及重塑该区构造演化历史具有重要意义。
1 地质背景与样品描述东北地区具有多块体拼合的构造属性(图 1a),其中额尔古纳、兴安、松嫩、佳木斯、兴凯等古地块在古生代已完成拼合(叶茂等,1994;Jia et al., 2004;张兴洲和马志红,2010),最东部的那丹哈达(完达山)地体属于锡霍特阿林中生代增生杂岩带的一部分,它们于侏罗纪拼贴到布列亚-佳木斯-兴凯地块的东缘(水谷伸治郎等,1989;邵济安等, 1991, 1992, 邵济安和唐克东,1995;程瑞玉等,2006),之后东北地区作为一个整体共同经历了古太平洋域的构造演化过程。三江盆地位于佳木斯地块和那丹哈达地体的衔接部位,向北与俄罗斯境内的中阿穆尔盆地相连(图 1a)。已有资料表明,三江盆地的基底可以区分出性质不同的3个区(黑龙江省地质矿产局,1993):西部区主要由元古宙的兴东群、麻山群、黑龙江群变质岩系和加里东期花岗岩组成;中部区主要由上古生界和早中生代花岗岩组成;东部区由上三叠统-下侏罗统深海相硅质岩、泥质页岩、浊积岩及晚印支期花岗岩组成。其中西部区和东部区的基底组成分别与佳木斯地块和那丹哈达地体的基底组成类似,指示该盆地具有复合基底性质(黑龙江省地质矿产局,1993;张兴洲和马志红,2010;Zhang et al., 2012a)。自中晚侏罗世以来,该盆地接受了数千米的海相、海陆交互相和陆相沉积,形成了以砂砾岩、砂岩和泥岩为主的含煤碎屑岩建造,它们角度不整合于基底之上(黑龙江省地质矿产局,1993;Zhang et al., 2012a)。本文研究的花岗质岩石分布于三江盆地北缘的勤得利-抚远镇一带(图 1b),由于区内覆盖严重,加之后期构造的影响,岩体的连续性遭到严重破坏,本文暂按该区花岗质岩石的空间分布将其分为勤得利岩体和抚远岩体。
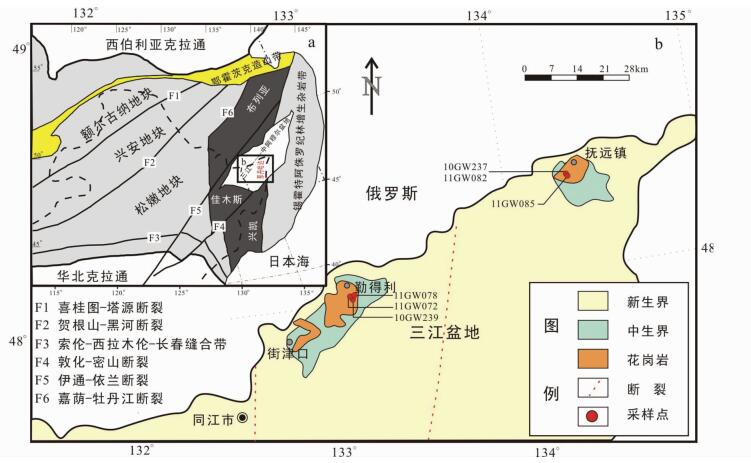
|
图 1 东北及邻区构造简图(a, 据Zhang et al., 2012a)和研究区地质简图(b, 据黑龙江省地质矿产局,1993) Fig. 1 Tectonic sketch map of NE China and adjacent areas (a, after Zhang et al., 2012a) and geological sketch map of the studied area (b, after BGMRH, 1993) |
勤得利岩体 位于勤得利镇西侧,呈北北东向展布的岩株状产出(图 1b),南侧和东北侧侵入到上三叠统-下侏罗统大岭桥组,西侧为第四系覆盖(黑龙江省地质矿产局,1993)。岩体岩性均为含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩,按结构不同可区分出中细粒、中粗粒和斑状含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩3种类型。其中斑状含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩具似斑状结构,斑晶总量约5%~15%,斑晶成分主要为斜长石,基质具细粒半自形粒状结构。上述3种岩石类型均呈块状构造,主要矿物组成类似,为斜长石(50%~60%)+碱性长石(5%~15%)+石英(20%~25%)+角闪石(3%~5%)+黑云母(±10%),其中斜长石常见聚片双晶和环带结构,碱性长石多见条纹结构。副矿物主要为磷灰石、锆石和磁铁矿,偶见褐帘石和榍石,其中磷灰石常呈自形柱状产出。
抚远岩体 位于抚远镇及其附近,呈北北东向展布的岩株状产出(图 1b),侵入到上三叠统-下侏罗统大岭桥组或大佳河组,北侧为第四系覆盖(黑龙江省地质矿产局,1993)。岩体岩性与勤得利岩体一致,为含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩,按结构可区分出中细粒和斑状含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩2种类型,它们与勤得利岩体同类岩石具有近乎一致的矿物组合和组构特征。
野外观察,可见中细粒和中粗粒含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩呈渐变过渡关系,但未见它们与斑状含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩直接接触。为了保证样品的代表性,分别对上述2个岩体不同位置、不同结构类型的含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩进行了系统采样,其中用于锆石U-Pb定年和锆石Lu-Hf同位素测试的样品6件,用于地球化学分析的样品13件。
2 分析方法 2.1 锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素分析用于锆石分选的样品每件样品重约0.5kg,在野外和室内系统岩相学研究的基础上,将每件样品破碎、筛选、清洗和烘干后,采用磁选和重液分选出锆石晶体,然后在双目镜下挑选透明度和晶形较好、无明显裂痕的锆石颗粒置于双面胶上,灌上环氧树脂制靶,固化后打磨抛光使锆石内部结构露出,用于阴极发光图像的采集和锆石微区原位单点U-Pb定年及Lu-Hf同位素分析。锆石的分选工作由河北省廊坊区调院矿物分离实验室完成,锆石的制靶、反射光和透射光照相以及锆石U-Pb同位素定年在中国地质大学(北京)科学研究院地质过程与矿产资源研究室完成。用于锆石U-Pb测试的仪器为美国New Wave Research Inc.公司生产的激光剥蚀进样系统(UPI93SS)和美国AGILENT科技有限公司生产的Agilent 7500a型四级杆等离子质谱仪联合构成的激光等离子质谱仪(LA-ICP-MS)。本次分析激光器工作频率为10Hz,质谱仪有效采集时间为45s,测试点束斑直径为36μm,锆石U-Pb及年龄标准选用标准锆石91500,使用锆石中含量稳定的29Si作为内标,监控标样为TEM (416±5Ma)和HQ (160±1Ma);数据处理采用Glitter 4.4程序,普通铅校正方法同Anderson (2002)。锆石Hf同位素分析在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所LA-MC-ICP-MS实验室完成。实验中采用Neptune多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱仪测定锆石的Hf同位素比值,激光束斑直径为60μm,仪器状态监控和样品外部校正采用哈佛大学国际标准锆石91500(176Hf/177Hf比值取0.282310±0.000035),详细测试流程以及仪器参数等见Wu et al.(2006)。
2.2 全岩主量元素和微量元素分析全岩主量元素和微量元素分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试中心完成。其中主量元素分析采用X-荧光光谱法(XRF),痕量元素分析采用电感耦合等离子质谱法(ICP-MS)。对国际标样BCR-2(玄武岩)、BHVO-1(玄武岩)和AGV-1(安山岩)的分析结果表明,主量元素分析精度和准确度优于5%,微量元素的分析精度和准确度一般优于10%(Rudnick et al., 2004)。
3 分析结果 3.1 锆石U-Pb定年结果6件样品的锆石U-Pb分析数据列于表 1。所测定锆石主要呈自形-半自形晶,阴极发光图像上具明显震荡环带(图 2),Th/U比值介于0.32~1.09之间,表明它们为岩浆成因(Pupin,1980;Koschek,1993)。由于所测定的岩石形成于中生代,其结果以206Pb/238U年龄计算,单点分析年龄误差为1σ,加权平均年龄误差为2σ。
|
|
表 1 晚白垩世花岗质岩石锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb分析结果 Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data for the Late Cretaceous granitoids |
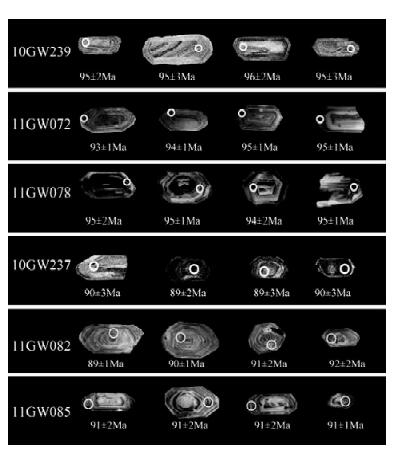
|
图 2 三江盆地北缘晚白垩世花岗质岩石的代表性锆石阴极发光图像 Fig. 2 CL images of representative zircons from the Late Cretaceous granitoids in the northern margin of the Sanjiang basin |
勤得利岩体 进行了3个样品的测定。样品10GW239采自于勤得利农场西1km (位置:47°57′59.2″N,133°07′48.1″E),岩石类型为斑状含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩,24个分析点给出的206Pb/238U表面年龄介于93~97Ma之间(表 1),其加权平均年龄为95.1±0.9Ma (MSWD=0.12,n=24)(图 3a);样品11GW072采自于勤得利西山石场(位置:47°58′42.2″N,133°07′29.9″E),岩石类型为中细粒含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩,24个分析点给出的206Pb/238U表面年龄介于92~99Ma之间(表 1),其加权平均年龄为94.8±0.7Ma (MSWD=2.8,n=24)(图 3b);样品11GW078采自于勤得利大理石场(位置:47°58′49.5″N,133°08′02.3″E),岩石类型为中粗粒含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩,25个分析点给出的206Pb/238U表面年龄介于93~98Ma之间(表 1),其加权平均年龄为94.7±0.4Ma (MSWD=0.85,n=25)(图 3c)。上述3个样品定年结果在误差范围内基本一致,代表了岩体的成岩年龄(94.7~95.1Ma)。
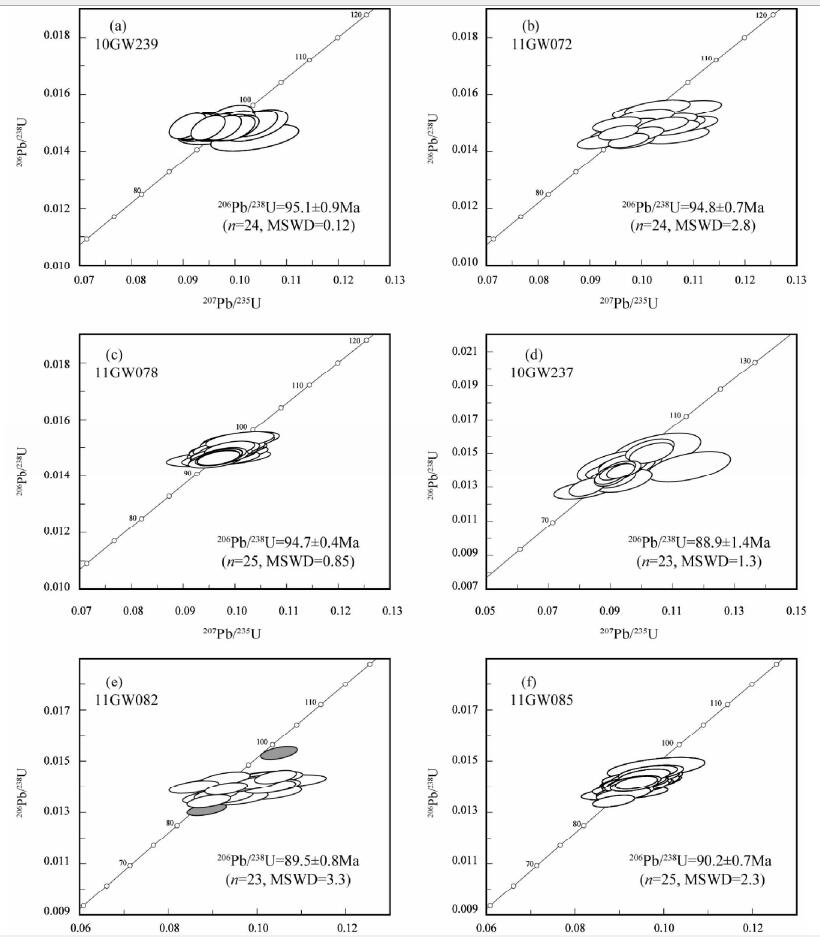
|
图 3 晚白垩世花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图 Fig. 3 Zircon U-Pb concordia diagrams for the Late Cretaceous granitoids |
抚远岩体 进行了3个样品的测定。样品10GW237采自于抚远镇采石场(位置:48°21′27.3″N,134°19′43.8″E),岩石类型为中细粒含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩,除一个分析点(11GW237-19)的206Pb/238U表面年龄为179±4Ma (可能为捕获锆石)外,其余23个分析点给出的206Pb/238U表面年龄介于82~92Ma之间(表 1),其加权平均年龄为88.9±1.4Ma (MSWD=1.3,n=23)(图 3d);样品11GW082(位置:48°21′27.3″N,134°19′43.8″E),岩石类型为中细粒含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩,23个分析点给出的206Pb/238U表面年龄介于86~92Ma之间(表 1),其加权平均年龄为89.5±0.8Ma (MSWD=3.3,n=23)(图 3e);样品11GW085采自抚远镇东发采石场(位置:48°21′16.8″N,134°20′23.0″E),岩石类型为斑状含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩,25个分析点给出的206Pb/238U表面年龄介于86~94Ma之间(表 1),其加权平均年龄为90.2±0.7Ma (MSWD=2.3,n=25)(图 3f)。上述3个样品定年结果在误差范围内基本一致,代表了岩体的成岩年龄(88.9~90.2Ma)。
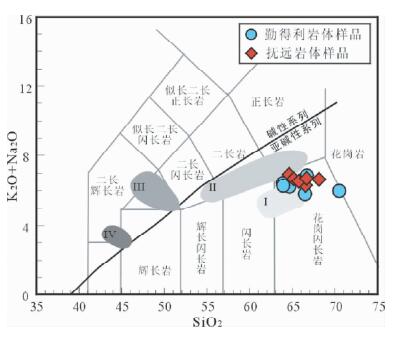
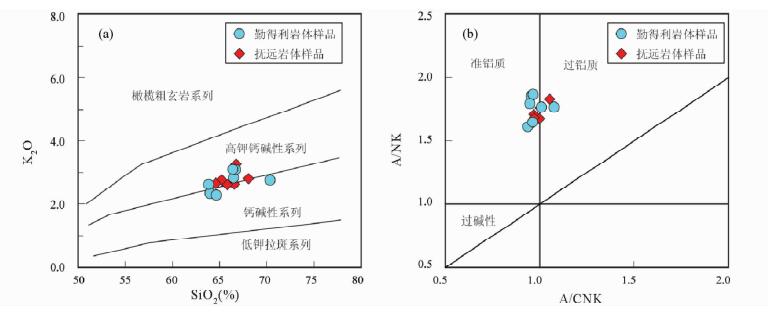
3.2 地球化学特征 3.2.1 主量元素主量和微量元素分析结果及有关参数列于表 2。由表 2可以看出,本文研究的13个花岗质岩石样品的主量元素特征较为一致:它们的SiO2含量主要介于63.9%~68.1%之间(样品10GW239的SiO2含量为70.4%),Na2O=3.03%~4.25%,K2O=2.28%~3.27%,Na2O+K2O=5.85%~6.90%,Na2O/K2O=1.06~1.73,Al2O3=14.2%~16.7%,A/CNK值=0.94~1.08(均小于 < 1.1)。在TAS图解(图 4)中,该区晚白垩世花岗质岩石均投影在花岗闪长岩范围内,并属于亚碱性系列。在K2O-SiO2图解上,具有高钾-中钾钙碱性系列的过渡特征(图 5a),在A/NK-A/CNK图解中,呈现出准铝质-弱过铝质特征(图 5b)。结合样品的岩性为含角闪石黑云母花岗闪长岩,实际矿物中出现角闪石和黑云母,副矿物出现磷灰石、磁铁矿、榍石等,可以判定它们属于准铝质-弱过铝质的高钾-中钾钙碱性I型花岗岩。
|
|
表 2 晚白垩世花岗质岩石主量元素(wt%)和微量元素(×10-6)分析结果 Table 2 Major (wt%) and trace element (×10-6) data for the Late Cretaceous granitoids |
|
图 4 研究区及邻区晚白垩世火成岩的TAS图解(据Irvine and Baragar, 1971) I-绥芬河安山岩-英安岩组合(数据引自Ji et al., 2007);II-延吉屯田营安山岩-英安岩组合(数据引自Xu et al., 2013);III-松辽盆地橄榄粗安岩(数据王璞珺等,2009)和双鸭山二长辉长岩(数据张磊等,2009);IV-辽东曲家屯碱性玄武岩(数据王薇等,2006) Fig. 4 Total alkali versus SiO2 diagram for the Late Cretaceous granitoids in the study area and adjacent areas (after Irvine and Baragar, 1971) I-Suifenhe andesite-dacite association (after Ji et al., 2007); II-Tuntianying andesite-dacite association in Yanji area (after Xu et al., 2013); III-ugearite in Songliao basin (after Wang et al., 2009) and Shuangyashang monzogabbro (after Zhang et al., 2009); IV-Qujiatun alkaline basalts in eastern Liaoning Province (after Wang et al., 2006) |
|
图 5 晚白垩世花岗质岩石的SiO2-K2O图解(a, 据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976)和A/CNK-A/NK图解(b, 据Maniar and Piccoli, 1989) Fig. 5 SiO2 versus K2O diagram (a, after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) and A/CNK versus A/NK diagram (b, after Maniar and Piccoli, 1989) for the Late Cretaceous granitoids |
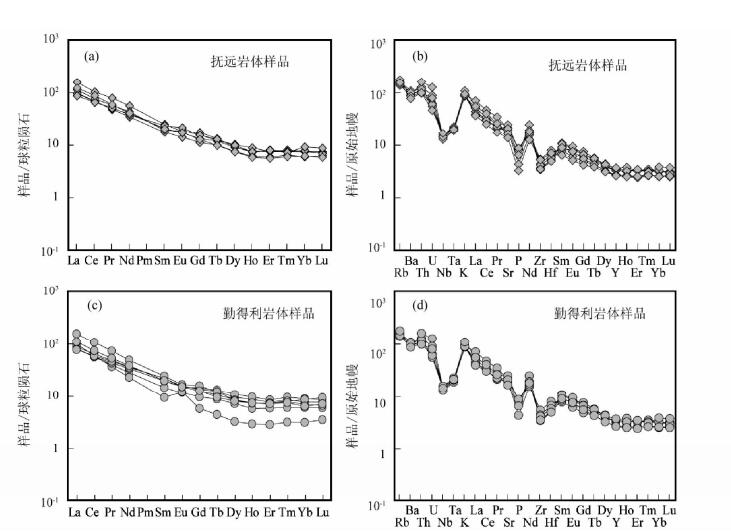
研究区晚白垩世2个岩体的稀土元素组成总体相似(表 2),除了个别样品(10GW239)外,其它12个样品具有类似的稀土元素(REE)配分型式--即富含轻稀土元素(LREE)、贫重稀土元素(HREE)、较弱的铕异常(图 6a, c)。它们的稀土总量介于105×10-6~194×10-6之间,LREE/HREE介于8.13~15.5之间,(La/Yb)N介于8.61~21.0之间,δEu=0.82~1.11。在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图上,该区晚白垩世花岗质岩石总体上表现出大离子亲石元素(Rb、Ba、K)的富集和高场强元素(Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf)及P的亏损(图 6b, d)。
|
图 6 晚白垩世花岗质岩石的稀土配分模式(a、c,球粒陨石值据Boynton, 1984)和微量元素蛛网图(b、d, 原始地幔值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, c, chondrite-normalized values after Boynton, 1984) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns (b, d, primitive mantle-normalized values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) for the Late Cretaceous granitoids |
本文对勤得利岩体的样品11GW072、11GW078和抚远岩体的样品11GW082进行了Hf同位素分析,结果列于表 3。样品11GW072(锆石U-Pb年龄均为94.8Ma)25个分析点给出的176Hf/177Hf值在0.282840~0.282970之间,εHf(t)值介于+4.44~+9.00之间,二阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM2)介于583~875Ma之间;样品11GW078(锆石U-Pb年龄均为94.7Ma)25个分析点给出的176Hf/177Hf值在0.282849~0.282943之间,εHf(t)值介于+4.72~+8.06之间,二阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM2)介于643~857Ma之间;样品11GW082(锆石U-Pb年龄均为89.5Ma)25个分析点给出的176Hf/177Hf值在0.282849~0.282947之间,εHf(t)值介于+4.65~+8.07之间,二阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM2)介于639~858Ma之间。
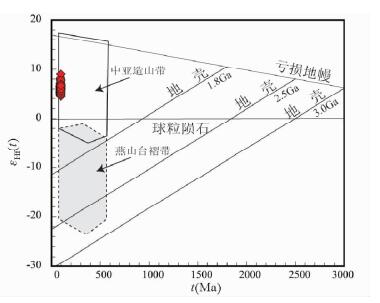
从测定结果来看,研究区不同样品晚白垩世花岗质岩石中锆石的同位素组成比较一致,它们的176Hf/177Hf值在0.282840~0.282970之间,εHf(t)值介于+4.44~+9.00之间,二阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM2)介于583~875Ma之间,这与典型中亚造山带东段显生宙火成岩中锆石的Hf同位素组成类似(图 7),而明显不同于华北克拉通显生宙火成岩中锆石的Hf同位素组成(Yang et al., 2006)。
|
|
表 3 晚白垩世花岗质岩石锆石Hf同位素分析结果 Table 3 Zircon Lu-Hf isotopic data for the Late Cretaceous granitoids |
|
图 7 晚白垩世花岗质岩石的锆石εHf(t)-t(Ma)图解(据Yang et al., 2006) Fig. 7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, c, chondrite-normalized values after Boynton, 1984) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns (b, d, primitive mantle-normalized values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) for the Late Cretaceous granitoids |
Wu et al.(2011)对东北地区花岗质岩石的形成时代所进行的系统总结表明,该区中生代花岗质岩石主要形成于晚三叠世、早中侏罗世和早白垩世,而对于是否存在晚白垩世花岗质岩石却没有得到证实。本文研究的勤得利岩体和与其类似的抚远岩体先前并没有同位素年代学资料,前人主要通过岩体与地层的接触关系以及与饶河地区的蚂蚁河岩体、太平村岩体等综合对比研究,将这2个岩体厘定为晚印支期,并将这些岩体划归为饶河晚印支期花岗岩带,其主要依据是该期花岗岩侵入到上三叠统-下侏罗统的大佳河组和大岭桥组中,并在蚂蚁河岩体中取得了189Ma的K-Ar法年龄(黑龙江省地质矿产局,1993)。但是,太平村岩体和蚂蚁河岩体是目前东北地区最具代表性的S型花岗岩,其岩浆锆石的U-Pb定年结果为115~131Ma (程瑞玉等,2006),而抚远和勤得利岩体则是典型的I型花岗岩,它们之间并不具有可比性,致使该岩带在形成时代上失去了有效的约束。
本文所测定的勤得利岩体和抚远岩体中的锆石多呈自形-半自形晶,普遍发育振荡环带结构(图 3),Th/U比值较高(表 1),这表明它们的岩浆成因,所获得的年龄代表了岩体的形成时代。定年结果表明,抚远岩体的3个样品成岩年龄在88.9~90.2Ma之间,勤得利岩体的3个样品成岩年龄在94.7~95.1Ma之间,它们均形成于晚白垩世(88.9~95.1Ma),而非前人认为的晚印支期(黑龙江省地质矿产局,1993)。上述定年结果揭示出,在三江盆地北缘东段存在晚白垩世花岗质岩浆作用,这也得到了东北地区东部存在同期岩浆作用的证实--如位于黑龙江东部鸡西盆地内的辉绿玢岩(96~101Ma)(朱占平等,2009)、双鸭山盆地内的二长辉长岩(97.5Ma)(张磊等,2009)、松辽盆地内的橄榄粗安岩(88.0Maa)(王璞珺等,2009)以及绥芬河英安岩(93.2Ma)(Ji et al., 2007)、延吉屯田营安山岩-英安岩(Xu et al., 2012)、辽东曲家屯碱性玄武岩(81.6Ma) (王薇等,2006)等,这表明,东北地区东部可能广泛存在晚白垩世岩浆作用。
4.2 晚白垩世花岗质岩石的源区性质首先,本文研究的晚白垩世花岗质岩石具有高硅、富钾和贫镁、铁、钙以及过渡族元素的地球化学属性,揭示出这些花岗质岩石的原始岩浆起源于陆壳物质的部分熔融(Taylor and McLennan, 1985;Hofmann,1988;吴福元等,2007;张旗等,2008)。其次,该区晚白垩世花岗质岩石均显示出准铝质-弱过铝质的高钾-中钾钙碱性I型花岗岩的成因类型(图 5a, b),指示岩浆源区应是基性或中基性火成岩(Chappell and White, 1974;Roberts and Clemens, 1993)。第三,本文研究的花岗岩具有中等富集的右倾型稀土配分模式(图 6a, c)、铕异常(0.82~1.11)不明显、重稀土分馏中等且相对含量较高,暗示源区与熔体平衡的残留相应主要为角闪石或辉石。第四,该区晚白垩世花岗质岩石中锆石Hf的εHf(t)值介于+4.44~+9.00之间,锆石Hf二阶段模式年龄在583~875Ma之间,反映岩浆源区是在新元古代时期从亏损地幔增生的年轻陆壳物质,这与中亚造山带显生宙花岗质岩石的岩浆源区相类似(吴福元等,1999;Jahn et a1.,2000;Wu et al., 2000, 2002, 2003;Yang et al., 2006;Zhang et al., 2006;隋振民等,2007;Xu et al., 2009; 张彦龙等,2010)。综合上述特征,可以得出该区晚白垩世花岗质岩石的源区岩石应为新增生的年轻陆壳物质,原始岩浆起源于深部陆壳基性火成岩的部分熔融。
4.3 晚白垩世花岗质岩石形成的构造背景与区域构造演化对东北地区晚中生代火成岩及其构造背景的研究一直是该区构造演化研究中最受关注的热点问题之一(殷长建等,2000;许文良等,2008b;Pei et al., 2011a, b;Wu et al., 2011),然而,与早白垩世相比(Fan et al., 2003;Wu et al., 2005b, 2011;Guo et al., 2007; Li et al., 2007;章凤奇等,2009;Yu et al., 2009;Wilde et al., 2010),对该区晚白垩世火成岩构造背景的讨论却很少(王薇等,2006;Ji et al., 2007;王璞珺等,2009;张磊等,2009)。本文研究的晚白垩世花岗质岩石均为准铝质-弱过铝质的高钾-中钾钙碱性I型花岗岩的成岩类型,虽然该类花岗岩可以形成于不同的构造背景--如板块俯冲或板块碰撞后背景(Roberts and Clemens, 1993),但区域上同期火成岩的组合与空间变异特征、古太平洋板块的运动轨迹以及区域构造演化历史等为讨论该区晚白垩世构造属性提供了有效约束。
首先,除了在研究区存在晚白垩世钙碱性花岗岩外,在研究区南侧的绥芬河和延吉一带还存在着与俯冲背景相关的同期钙碱性安山岩-英安岩组合(图 4;Ji et al., 2007;Xu et al., 2013),它们与俄罗斯远东的锡霍特阿林地体、韩国的Gyeongsang盆地及日本西南部广泛发育的与俯冲背景相关的晚白垩世火成岩组合(Kagami et al., 1988;Iijumi et al., 2000;Sato et al., 2002, Kirillova,2003;Matsumoto et al., 2007;Zhang et al., 2012b)共同构成了东亚大陆东缘晚白垩世火成岩带,进而揭示出晚白垩世俯冲环境的存在(Otsuki,1992;Kinoshita, 1995, 2002;Kirillova,2003)。
其次,在该火山岩带西侧的松辽盆地、双鸭山盆地以及辽东、辽西等地存在与伸展环境有关的同期碱性玄武岩、橄榄粗安岩以及偏碱性的二长辉长岩(图 4;许文良等,1999;王薇等,2006;王璞珺等,2009;张磊等,2009),同时代火成岩的这种空间变异揭示出晚白垩世岩浆活动的动力源应来源于东部,即古太平洋板块向东亚大陆的俯冲作用造成了东亚大陆东缘晚白垩世岩浆作用的形成。
第三,来自于地层、古生物和古地磁等方面的对比研究表明,在日本海张开之前,中国境内的那丹哈达地体、俄罗斯远东地区的锡霍特阿林地体与日本西南部的美侬地体等曾是一个连在一起的超级地体,该超级地体于晚侏罗世-早白垩世与其西侧先期拼合的佳木斯、兴凯等复合地块完成拼合,之后它们作为东亚大陆东缘的一部分整体演化(水谷伸治郎等,1989;Kojima,1989;邵济安等, 1991, 1992;邵济安和唐克东,1995;Mizutani and Kojima 1992;程瑞玉等,2006),这与上述地体均存在与俯冲背景相关的晚白垩世火成岩组合相一致。
第四,对古太平洋板块(Izanagi-Kula)运动轨迹的研究表明,在晚白垩世初期(约90Ma)该板块的运动方向和俯冲角度都发生了重大变化,即古太平洋板块由早白垩世近于正北的低角度高斜度俯冲作用转变为晚白垩世北西向的高角度正向俯冲作用(Engebretson et al., 1985;Maruyama et al., 1997;Zhou and Li, 2000),这也得到了日本西南部存在晚白垩世加积楔的印证(Taira et al., 1988;Taira,2001)。
综上所述,我们可以得出,该区晚白垩世花岗质岩石形成于古太平洋板块向东亚大陆下俯冲的构造背景,该期岩浆事件标志着古太平洋板块由斜向俯冲作用转换为正向俯冲作用的开始。
5 结论(1)三江盆地北缘勤得利岩体和抚远岩体中的花岗质岩石均形成于晚白垩世(88.9~95.1Ma),而非前人认为的晚印支期。
(2)三江盆地北缘晚白垩世花岗质岩石均为准铝质-弱过铝质的高钾-中钾钙碱性I型花岗岩的成因类型,原始岩浆起源于新增生的深部陆壳基性火成岩的部分熔融。
(3)三江盆地北缘晚白垩世花岗质岩石形成于古太平洋板块向东亚大陆下俯冲的构造背景,该期岩浆事件标志着古太平洋板块由斜向俯冲作用转换为正向俯冲作用的开始。
致谢 感谢中国地质大学苏犁教授和中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所杨进辉研究员在锆石CL图像采集、锆石U-Pb测试和锆石Hf同位素测试过程中给予的帮助;感谢核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心在主、微量元素分析过程中给予的支持;感谢许文良教授和审稿专家提出的宝贵意见和建议。| [] | Anderson T. 2002. Correction of common Lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59–79. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X |
| [] | Boynton WV. 1984. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. In: Henderson P (ed.). Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 63-114 |
| [] | Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Heilongjiang Province (BGMRH). 1993. Regional Geology of Heilongjiang Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-734. |
| [] | Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Inner Monggolia Autonomous Region. 1991. Regional Geology of Inner Monggolia Autonomous Region. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-725. |
| [] | Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Jilin Province. 1988. Regional Geology of Jilin Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-698. |
| [] | Chappell BW, White AJR. 1974. Two contrasting granite types. Pacific Geology, 8: 173–174. |
| [] | Cheng RY, Wu FY, Ge WC, Sun DY, Liu XM, Yang JH. 2006. Emplacement age of the Raohe Complex in eastern Heilongjiang Province and the tectonic evolution of the eastern part of Northeastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(2): 353–376. |
| [] | Engebretson DC, Cox A, Gordon RG. 1985. Relative motions between oceanic and continental plates in the Pacific basins. Geological Society of America, Special Paper, 206: 1–59. DOI:10.1130/SPE206 |
| [] | Fan WM, Guo F, Wang YJ, Ge L. 2003. Late Mesozoic calc-alkaline volcanism of post-orogenic extension in the northern Da Hinggan Mountains, northeastern China. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 121(1-2): 115–135. DOI:10.1016/S0377-0273(02)00415-8 |
| [] | Gao FH, Xu WL, Yang DB, Pei FP, Liu XM, Hu ZC. 2007. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating from granitoids in southern basement of Songliao basin: Constraints on ages of the basin basement. Science in China (Series D), 50(7): 995–1004. DOI:10.1007/s11430-007-0019-7 |
| [] | Ge WC, Wu FY, Zhou CY, Zhang JH. 2005. Zircon U-Pb ages and its significance of the Mesozoic granites in the Wulanhaote region, central Da Hinggan Mountain. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(3): 749–762. |
| [] | Guo F, Nakamura E, Fan WM, Kobayashi K, Li CW. 2007. Generation of Palaeocene adakitic andesites by magma mixing, Yanji area, NE China. Journal of Petrology, 48: 661–692. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egl077 |
| [] | Hofmann AW. 1988. Chemical differentiation of the Earth: The relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 90(3): 297–314. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(88)90132-X |
| [] | Huang TK, Ren JS, Jiang CF, Zhang ZM, Xu ZQ. 1977. An outline of the tectonic characteristics of China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 51(2): 117–135. |
| [] | Iijumi S, Imaoka T, Kangmi H. 2000. Sr-Nd isotope ratios of gabbroic and dioritic rocks in a Cretaceous-Paleogene granite terrain, southwest Japan. The Island Arc, 9(1): 113–127. DOI:10.1046/j.1440-1738.2000.00265.x |
| [] | Irvine TH, Baragar WRA. 1971. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 8(5): 523–548. DOI:10.1139/e71-055 |
| [] | Jahn BM, Wu FY, Chen B. 2000. Massive granitoid generation in central Asia: Nd isotopic evidence and implication for continental growth in the Phanerozoic. Episodes, 23: 82–92. |
| [] | Ji WQ, Xu WL, Yang DB, Pei PF, Jin K, Liu XM. 2007. Chronology and geochemistry of volcanic rocks in the Cretaceous Suifenhe Formation in eastern Heilongjiang, China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(2): 266–277. DOI:10.1111/acgs.2007.81.issue-2 |
| [] | Jia DC, Hu RZ, Lu Y, Qiu XL. 2004. Collision belt between the Khanka block and the North China block in the Yanbian Region, Northeast China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 23(2): 211–219. DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00123-8 |
| [] | Kagami H, Honma H, Shirahase T, Nureki T. 1988. Rb-Sr whole rock isochron ages of granites from northern Shikoku and Okayama, Southwest Japan: Implications for the migration of the Late Cretaceous to Paleogene igneous activity in space and time. Geochemical Journal, 22(2): 69–79. DOI:10.2343/geochemj.22.69 |
| [] | Kinoshita O. 1995. Migration of igneous activities related to ridge subduction in Southwest Japan and the East Asian continental margin from the Mesozoic to the Paleogene. Tectonophysics, 245(1-2): 25–35. DOI:10.1016/0040-1951(94)00211-Q |
| [] | Kinoshita O. 2002. Possible manifestations of slab window magmatisms in Cretaceous southwest Japan. Tectonophysics, 344(1-2): 1–13. DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(01)00262-1 |
| [] | Kirillova GL. 2003. Cretaceous tectonics and geological environments in East Russia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 21(8): 967–977. DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00093-7 |
| [] | Kojima S. 1989. Mesozoic terrane accretion in Northeast China, Sikhote-Alin and Japan regions. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 69: 213–232. DOI:10.1016/0031-0182(89)90165-X |
| [] | Koschek G. 1993. Origin and significance of the SEM cathodoluminescence from zircon. Journal of Microscopy, 171(3): 223–232. DOI:10.1111/jmi.1993.171.issue-3 |
| [] | Li CW, Guo F, Fan WM, Gao XF. 2007. Ar-Ar geochronology of Late Mesozoic volcanic rocks from the Yanji area, NE China and tectonic implications. Science in China (Series D), 50(4): 505–518. DOI:10.1007/s11430-007-2046-9 |
| [] | Maniar PD, Piccoli PM. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 101(5): 635–643. DOI:10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2 |
| [] | Maruyama S, Isozaki Y, Kimura G, Terabayashi M. 1997. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands: Plate tectonic synthesis from 750Ma to the present. The Island Arc, 6(1): 121–142. DOI:10.1111/iar.1997.6.issue-1 |
| [] | Matsumoto A, Ohta Y, Hoshizumi H, Takahashi Y, Nishioka Y, Miyake Y, Tsunoda K, Shimizu M. 2007. K-Ar age determinations of age-unknown rocks in Japanese Islands: Volcanic and plutonic rocks in the areas associated with Geological Map Project. Bulletin of Geological Survey of Japan, 58(1-2): 33–43. DOI:10.9795/bullgsj.58.33 |
| [] | Mizutani S, Shao JA, Zhang QL. 1989. The Nadanhada terrane in relation to Mesozoic tectonics on continental margins of East Asia. Acta Geologica Sinica, 63(3): 204–215. |
| [] | Mizutani S, Kojima S. 1992. Mesozoic radiolarian biostratigraphy of Japan and collage tectonics along the eastern continental margin of Asia. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 96(1-2): 3–22. DOI:10.1016/0031-0182(92)90056-B |
| [] | Otsuki K. 1992. Oblique subduction, collision of microcontinents and subduction of oceanic ridge: Their implications on the Cretaceous tectonics of Japan. The Island Arc, 1(1): 51–63. DOI:10.1111/iar.1992.1.issue-1 |
| [] | Peccerillo A, Peccerillo R A. 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63–81. DOI:10.1007/BF00384745 |
| [] | Pei FP, Xu WL, Yang DB, Yu Y, Meng E, Zhao QG. 2011a. Petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic granitoids in southern Jilin Province, northeastern China: Geochronological, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic evidence. Lithos, 125(1-2): 27–39. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.01.004 |
| [] | Pei FP, Xu WL, Yang DB, Yu Y, Wang W, Zhao QG. 2011b. Geochronology and geochemistry of Mesozoic mafic-ultramafic complexes in the southern Liaoning and southern Jilin provinces, NE China: Constraints on the spatial extent of destruction of the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(2): 636–650. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.10.015 |
| [] | Pitcher WS. 1997. The Nature and Origin of Granite. 2nd Edition. London: Chapman & Hall. |
| [] | Pupin JP. 1980. Zircon and granite petrology. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 73(3): 207–220. DOI:10.1007/BF00381441 |
| [] | Roberts MP, Clemens JD. 1993. Origin of high-potassium, calc-alkaline, I-type granitoids. Geology, 21(9): 825–828. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0825:OOHPTA>2.3.CO;2 |
| [] | Rudnick RL, Gao S, Ling WL, Liu YS, McDonough WF. 2004. Petrology and geochemistry of spinel peridotite xenoliths from Hannuoba and Qixia, North China Craton. Lithos, 77(1-4): 609–637. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.03.033 |
| [] | Sato K, Vrublevsky AA, Rodionov SM, Romanovsky NP, Nedachi M. 2002. Mid-Cretaceous episodic Magmatism and tin mineralization in Khingan-Okhotsk volcano-plutonic belt, Far East Russia. Resource Geology, 52(1): 1–14. DOI:10.1111/rge.2002.52.issue-1 |
| [] | ŞengörAMC, Naial'inBA, BurtmanVS. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia. Nature, 364(6435): 299–307. |
| [] | Şengör AMC and Natal'in BA. 1996. Paleotectonics of Asia: fragments of a synthesis. In: Yin A and Harrison M (eds.). The Tectonic Evolution of Asia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 486-640 |
| [] | Shao JA, Tang KD, Wang CY, Zang QJ, Zhang YP. 1991. The tectonic characteristics and evolution of Nadanhada Terrane. Science in China (Series B), 21(7): 744–751. |
| [] | Shao JA, Wang CY, Tang KD. 1992. A new approach to the tectonics in the Ussuri (Wusuli) Region. Geological Review, 38(1): 33–39. |
| [] | Shao JA, Tang KD. 1995. Terranes in Northeast China and Evolution of Northeast Asia Continental Margin. Beijing: Seismic Press: 1-185. |
| [] | Sui ZM, Ge WC, Wu FY, Zhang JH, Xu XC, Cheng RY. 2007. Zircon U-Pb ages, geochemistry and its petrogenesis of Jurassic granites in northeastern part of the Da Hinggan Mts. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 461–480. |
| [] | Sun DY, Wu FY, Lin Q, Lu XP. 2001. Petrogenesis and crust-mantle interaction of early Yanshanian Baishishan pluton in Zhangguangcai Range. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(2): 227–235. |
| [] | Sun DY, Wu FY, Gao S, Lu XP. 2005. Confirmation of two episodes of A-type granite emplacement during Late Triassic and Early Jurassic in the central Jilin Province, and their constraints on the structural pattern of eastern Jilin-Heilongjiang area, China. Earth Science Frontiers, 12(2): 263–275. |
| [] | Sun DY, Suzuki K, Kajizuka I, Kamikubo H, Lu XP, Wu FY. 2008. CHIME dating of monazite from the Dongqing pluton in SE Jilin, China. The Journal of Earth and Planetary Sciences (Nagoya University), 55: 23–37. |
| [] | Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London: Geological Society of Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345 |
| [] | Taira A, Katto J, Tashiro M, Okamura M, Kodama K. 1988. The Shimanto belt in Shikoku, Japan: Evolution of Cretaceous to Miocene accretionary prism. Modern Geology, 12: 5–46. |
| [] | Taira A. 2001. Tectonic evolution of the Japanese island arc system. The Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 29: 109–134. DOI:10.1146/annurev.earth.29.1.109 |
| [] | Taylor SR, McLennan SM. 1985. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publication: 1-132. |
| [] | Wang F, Xu WL, Meng E, Cao HH, Cao FH. 2012. Early Paleozoic amalgamation of the Songnen-Zhangguangcai Range and Jiamusi massifs in the eastern segment of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Geochronological and geochemical evidence from granitoids and rhyolites. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 49: 234–248. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.09.022 |
| [] | Wang PJ, Gao YF, Ren YG, Liu WZ, Zhang JG. 2009. 40Ar/39Ar age and geochemical features of mugearite from the Qingshankou Formation: Significances for basin formation, hydrocarbon generation and petroleum accumulation of the Songliao Basin in Cretaceous. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(5): 1178–1190. |
| [] | Wang W, Xu WL, Ji WQ, Yang DB, Pei FP. 2006. Late Mesozoic and Paleogene basalts and deep-derived xenocrysts in eastern Liaoning Province, China: Constraints on nature of lithospheric mantle. Geological Journal of China Universities, 12(1): 30–40. |
| [] | Wilde SA, Wu FY and Zhao GC. 2010. The Khanka Block, NE China, and its significance for the evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and continental accretion. In: Kusky TM, Zhai MG and Xiao WJ (eds.). The Evolving Continents: Understanding Processes of Continental Growth. London: Geological Society, Special Publications, 338(1): 117-137 |
| [] | Wu FY, Sun DY, Lin Q. 1999. Petrogenesis of the Phanerozoic granites and crustal growth in Northeast China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(2): 18l–189. |
| [] | Wu FY, Jahn BM, Wilde SA, Sun DY. 2000. Phanerozoic crustal growth: U-Pb and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from the granites in northeastern China. Tectonophysics, 328(1-2): 87–113. |
| [] | Wu FY, Sun DY, Li HM, Jahn BM, Wilde SA. 2002. A-type granites in northeastern China: Age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis. Chemical Geology, 187(1-2): 143–173. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00018-9 |
| [] | Wu FY, Jahn BM, Wilde SA, Lo CH, Yui TF, Lin Q, Ge WC, Sun DY. 2003. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (II): Isotopic geochemistry and implications for crustal growth in the Phanerozoic. Lithos, 67(3-4): 191–204. DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(03)00015-X |
| [] | Wu FY, Yang JH, Wilde SA, Zhang XO. 2005a. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Jurassic granites in the Liaodong Peninsula, NE China. Chemical Geology, 221(1-2): 127–156. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.04.010 |
| [] | Wu FY, Lin JQ, Wilde SA, Zhang ZO, Yang JH. 2005b. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 233(1-2): 103–119. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.019 |
| [] | Wu FY, Yang YH, Xie LW, Yang JH, Xu P. 2006. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology. Chemical Geology, 234(1-2): 105–126. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.003 |
| [] | Wu FY, Li XH, Yang JH, Zheng YF. 2007. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(6): 1217–1238. |
| [] | Wu FY, Sun DY, Ge WC, Zhang YB, Grant ML, Wilde SA, Jahn BM. 2011. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(1): 1–30. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014 |
| [] | Xu WL, Zheng CQ, Wang DY. 1999. The discovery of mantle-and lower crust-derived xenoliths in Mesozoic trachybasalts from western Liaoning, and their geological implications. Geological Review, 45(Suppl.): 444–449. |
| [] | Xu WL, Pei FP, Gao FH, Yang DB, Bu YJ. 2008a. Zircon U-Pb age from basement granites in Yishu graben and its tectonic implications. Earth Sciences, 33(2): 145–150. |
| [] | Xu WL, Ge WC, Pei FP, Meng E, Yu Y, Yang DB. 2008b. Geochronology frame and tectonic implications for Mesozoic volcanism in Northeast China. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 27(Suppl.): 286–287. |
| [] | Xu WL, Ji WQ, Pei FP, Meng E, Yu Y, Yang DB, Zhang XZ. 2009. Triassic volcanism in eastern Heilongjiang and Jilin provinces, NE China: Chronology, geochemistry, and tectonic implications. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34(3): 392–402. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.07.001 |
| [] | Xu WL, Pei FP, Wang F, Meng E, Ji WQ, Yang DB and Wang W. 2013. Spatial-temporal relationships of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in NE China: Constraints on tectonic overprinting and transformations between multiple tectonic systems. Earth-Science Review, under review |
| [] | Yang JH, Wu FY, Shao JA, Simon AW, Xie LW, Liu XM. 2006. Constraints on the timing of uplift of the Yanshan fold and thrust belt, North China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 246(3-4): 336–352. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.04.029 |
| [] | Ye M, Zhang SH, Wu FY. 1994. The classification of the Paleozoic tectonic units in the area crossed by M-S GGT. Journal of Changchun University of Earth Sciences, 24(3): 241–245. |
| [] | Yin CJ, Peng YJ, Jin K. 2000. Mesozoic volcanism in the eastern part of Northeast China and Transpacific plate. Regional Geology of China, 19(3): 303–311. |
| [] | Yuhara M, Kangmi H, Nagao K. 2000. Geochronological characterization and petrogenesis of granitoids in the Ryoke Belt, southwest Japan Arc: Constraints from K-Ar, Rb-Sr and Sm-Nd systematics. The Island Arc, 9(1): 64–80. DOI:10.1046/j.1440-1738.2000.00262.x |
| [] | Yuhara M, Miyazaki T, Kangmi H, Yuhara M. 2003. Rb-Sr and K-Ar geochronology and petrogenesis of the Aji granite in the eastern Sanuki district, Ryoke Belt, southwest Japan. Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 98(1): 19–30. DOI:10.2465/jmps.98.19 |
| [] | Yu JJ, Wang F, Xu WL, Gao FH, Tang J. 2013. Late Permian tectonic evolution at the southeastern margin of the Songnen-Zhangguangcai Range Massif, NE China: Constraints from geochronology and geochemistry of granitoids. Gondwana Research. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.11.015 |
| [] | Yu Y, Xu WL, Pei FP, Yang DB, Zhao QG. 2009. Chronology and geochemistry of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Linjiang area, Jilin Province and their tectonic implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(2): 245–257. DOI:10.1111/acgs.2009.83.issue-2 |
| [] | Zhang FQ, Cheng XG, Chen HL, Dong CW, Yu X, Xiao J, Xu Y, Pang YM, Shu P. 2009. Zircon chronological and geochemical constraints on the Late Mesozoic volcanic events in the southeastern margin of the Songliao Basin, NE China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(1): 39–54. |
| [] | Zhang FQ, Chen HL, Yang SF, Feng ZQ, Wu HY, Batt GE, Zhao XQ, Sun MD, A MN, Wang SH, Yang JG. 2012a. Late Mesozoic-Cenozoic evolution of the Sanjiang Basin in NE China and its tectonic implications for the West Pacific continental margin. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 49: 287–299. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.017 |
| [] | Zhang JH, Ge WC, Wu FY, Liu XM. 2006. Mesozoic bimodal volcanic suite in Zhalantun of the Da Hinggan Range and its geological significance: Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic constraints. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(1): 58–69. DOI:10.1111/acgs.2006.80.issue-1 |
| [] | Zhang L, Han BF, Zhu YF, Xu Z, Chen JF, Song B. 2009. Geochronology, mineralogy, crystallization process and tectonic implications of the Shuangyashan monzogabbro in eastern Heilongjiang Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(3): 577–587. |
| [] | Zhang Q, Wang Y, Pan GQ, Li CD, Jin WJ. 2008. Sources of granites: Some crucial questions on granite study (4). Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(6): 1193–1204. |
| [] | Zhang XZ, Ma ZH. 2010. Evolution of Mesozoic-Cenozoic basins in the eastern Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China. Geology and Resources, 19(3): 191–196. |
| [] | Zhang YB, Wu FY, Wilde SA, Zhai MG, Lu XP, Sun DY. 2004. Zircon U-Pb ages and tectonic implications of "Early Paleozoic" granitoids at Yanbian, Jilin Province, northeast China. The Island Arc, 13(4): 484–505. DOI:10.1111/iar.2004.13.issue-4 |
| [] | Zhang YB, Zhai MG, Hou QL, Li TS, Liu F, Hu B. 2012b. Late Cretaceous volcanic rocks and associated granites in Gyeongsang Basin, SE Korea: Their chronological ages and tectonic implications for cratonic destruction of the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 47: 252–264. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.011 |
| [] | Zhang YL, Ge WC, Liu XM, Zhang JH. 2008. Isotopic characteristics and its significance of the Xinlin Town pluton, Great Hinggan Mountains. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 38(2): 177–186. |
| [] | Zhang YL, Ge WC, Gao Y, Chen JS, Zhao L. 2010. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes of granites in Longzhen area and their geological implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(4): 1059–1073. |
| [] | Zhu ZP, Liu L, Ma R, Qiu ZK, Ma SH. 2009. 40Ar/39Ar isotopic dating and geological significance of mafic rocks from the Jixi basin, Heilongjiang Province. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 39(2): 238–243. |
| [] | Zhou XM, Li XW. 2000. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China: Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas. Tectonophysics, 326(3-4): 269–287. DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00120-7 |
| [] | 程瑞玉, 吴福元, 葛文春, 孙德有, 柳小明, 杨进辉. 2006. 黑龙江省东部饶河杂岩的就位时代与东北东部中生代构造演化. 岩石学报, 22(2): 353–376. |
| [] | 葛文春, 吴福元, 周长勇, 张吉衡. 2005. 大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区中生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义. 岩石学报, 21(3): 749–762. |
| [] | 黑龙江省地质矿产局. 1993. 黑龙江省区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-734. |
| [] | 黄汲清, 任纪舜, 姜春发, 张之孟, 许志琴. 1977. 中国大地构造基本轮廓. 地质学报, 51(2): 117–135. |
| [] | 吉林省地质矿产局. 1988. 吉林省区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-698. |
| [] | 内蒙古自治区地质矿产局. 1991. 内蒙古自治区区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-725. |
| [] | 邵济安, 唐克东, 王成源, 藏启家, 张允平. 1991. 那丹哈达地体的构造特征及演化. 中国科学(B辑), 21(7): 744–751. |
| [] | 邵济安, 王成源, 唐克东. 1992. 乌苏里地区构造新探索. 地质论评, 38(1): 33–39. |
| [] | 邵济安, 唐克东. 1995. 中国东北地体与东北亚大陆边缘演化. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-185. |
| [] | 水谷伸治郎, 邵济安, 张庆龙. 1989. 那丹哈达地体与东亚大陆边缘中生代构造的关系. 地质学报, 63(3): 204–215. |
| [] | 隋振民, 葛文春, 吴福元, 张吉衡, 徐学纯, 程瑞玉. 2007. 大兴安岭东北部侏罗纪花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及成因. 岩石学报, 23(2): 461–480. |
| [] | 孙德有, 吴福元, 林强, 路孝平. 2001. 张广才岭燕山早期白石山岩体的成因与壳幔相互作用. 岩石学报, 17(2): 227–235. |
| [] | 孙德有, 吴福元, 高山, 陆孝平. 2005. 吉林中部晚三叠世和早侏罗世两期铝质A型花岗岩的厘定及对吉黑东部构造格局的制约. 地学前缘, 12(2): 263–275. |
| [] | 王璞珺, 高有峰, 任延广, 刘万洙, 张建光. 2009. 松辽盆地青山口组橄榄粗安岩: 40Ar/39Ar年龄、地球化学及其成盆、成烃和成藏意义. 岩石学报, 25(5): 1178–1190. |
| [] | 王薇, 许文良, 纪伟强, 杨德彬, 裴福萍. 2006. 辽东中生代晚期和古近纪玄武岩及深源捕虏晶--对岩石圈地幔性质的制约. 高校地质学报, 12(1): 30–40. |
| [] | 吴福元, 孙德有, 林强. 1999. 东北地区显生宙花岗岩的成因与地壳增生. 岩石学报, 15(2): 181–189. |
| [] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 郑永飞. 2007. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题. 岩石学报, 23(6): 1217–1238. |
| [] | 许文良, 郑常青, 王冬艳. 1999. 辽西中生代粗面玄武岩中地幔和下地壳捕虏体的发现及其地质意义. 地质论评, 45(增刊): 444–449. |
| [] | 许文良, 裴福萍, 高福红, 杨德彬, 卜永吉. 2008a. 伊舒地堑基底花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年代学及其构造意义. 地球科学, 33(2): 145–150. |
| [] | 许文良, 葛文春, 裴福萍, 孟恩, 于洋, 杨德彬. 2008b. 东北地区中生代火山作用的年代学格架及其构造意义. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 27(增刊): 286–287. |
| [] | 叶茂, 张世红, 吴福元. 1994. 中国满洲里-绥芬河地学断面域古生代构造单元及其地质演化. 长春地质学院学报, 24(3): 241–245. |
| [] | 殷长建, 彭玉鲸, 靳克. 2000. 中国东北东部中生代火山活动与泛太平洋板块. 中国区域地质, 19(3): 303–311. |
| [] | 章凤奇, 程晓敢, 陈汉林, 董传万, 余星, 肖骏, 徐岩, 庞彦明, 舒萍. 2009. 松辽盆地东南缘晚中生代火山事件的锆石年代学与地球化学制约. 岩石学报, 25(1): 39–54. |
| [] | 张磊, 韩宝福, 朱永峰, 徐钊, 陈家富, 宋彪. 2009. 黑龙江省东部双鸭山二长辉长岩的年代学、矿物学、结晶过程及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 25(3): 577–587. |
| [] | 张旗, 王焰, 潘国强, 李承东, 金惟俊. 2008. 花岗岩源岩问题--关于花岗岩研究的思考之四. 岩石学报, 24(6): 1193–1204. |
| [] | 张兴洲, 马志红. 2010. 黑龙江东部中-新生代盆地演化. 地质与资源, 19(3): 191–196. |
| [] | 张彦龙, 葛文春, 柳小明, 张吉衡. 2008. 大兴安岭新林镇岩体的同位素特征及其地质意义. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 38(2): 177–186. |
| [] | 张彦龙, 葛文春, 高妍, 陈井胜, 赵磊. 2010. 龙镇地区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素及地质意义. 岩石学报, 26(4): 1059–1073. |
| [] | 朱占平, 刘立, 马瑞, 邱增凯, 马胜晖. 2009. 黑龙江省鸡西盆地基性岩40Ar/39Ar同位素定年及其地质意义. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 39(2): 238–243. |
 2013, Vol. 29
2013, Vol. 29

