2. 西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室,西安 710069
2. State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Department of Geology, Northwest University, Xi'an 710069, China
近年来,有关华北克拉通早前寒武纪地壳演化备受国内外学者的关注,并获得了大量重要研究成果(Zhai and Santosh, 2011)。但在一些关键科学问题上仍存在不同认识(Zhao et al., 2010;Zhai and Santosh, 2011;Kusky,2011;Liu et al., 2011)。例如,高压麻粒岩峰期变质及其退变质时代仍然有不同认识。目前国内外对高压麻粒岩锆石U-Pb年代学所代表的地质含义,即能否代表峰期变质时代存在不同的认识(Fraser et al., 1997;Roberts and Finger, 1997;Ashwal et al., 1999;Timmerman et al., 2004;张华锋等,2006;翟明国,2009)。怀安地区出露的高压麻粒岩锆石U-Pb年龄集中分布在1950~1800Ma (郭敬辉等,2002;Guo et al., 2005;Kröner et al., 2005;张华锋等, 2005, 2006;Zhao et al., 2008;Wang et al., 2010)。对此,部分学者认为其峰期变质年龄应在1900~1800Ma之间(Zhao et al., 2001, 2005;Guo et al., 2002, 2005);另一部分学者则认为峰期变质在1950~1900Ma之间,1900~1800Ma应为地壳抬升退变年龄(张华锋等, 2006, 2009;翟明国,2009)。前人对孔兹岩等高级变质岩P-T-t研究也获得了相似的认识,认为1900~1800Ma为地壳隆升冷却阶段,~1900Ma之前则为大陆造山构造增厚阶段(金巍和李树勋,1996)。然而,上述争论也是引起国内外学者对华北克拉通古元古代碰撞造山时限不同认识的原因所在。若高压麻粒岩峰期变质在1900~1850Ma,中部带所代表的东、西部陆块的碰撞拼合则很可能发生在~1.85Ga (Zhao et al., 1999);但若峰期变质发生在1950~1900Ma,与孔兹岩系-超高温变质岩峰期变质年龄大体一致(Santosh et al., 2006;翟明国和彭澎,2007;Santosh et al., 2007a, b),就上述提出的1.85Ga则很可能代表的是区域地壳抬升下退变质时代,而非碰撞拼合时限。另外,高压麻粒岩的定义也是目前具有争议性的关键问题(Carswell and O’Brien,1993;刘树文等,1996;O’Brien and Rötzler, 2003;Pattison, 2003)。翟明国(2009)对高压麻粒岩定义做了详细讨论,并认为对石英拉斑玄武质成分的基性麻粒岩,石榴石的出现比紫苏辉石消失与否对高压变质更具有指示意义。若按这一定义,华北克拉通出露的高压麻粒岩则更可能呈面状分布,而非仅局限在中部造山带内,代表华北克拉通早期下地壳岩石。
对于构建反演地壳演化的P-T-t轨迹,除对不同演化阶段的P、T条件分析外,相应时限t的确定也是至关重要的(England and Thompson, 1984;Thompson and England, 1984)。野外观察发现,在怀安蔓菁沟地区与围岩孔兹岩、高压麻粒岩等呈构造接触的岩系中还存在一套经历中压二辉麻粒相和角闪岩相退变质的中性辉石麻粒岩(变石英闪长岩)。为进一步探讨本区区域变质作用时限,即为P-T-t轨迹提供更加详细的时间(t) 过程,本文对其锆石进行U-Pb、Lu-Hf同位素及微量元素等方面的分析研究,探讨其年代学数据所代表的地质含义。
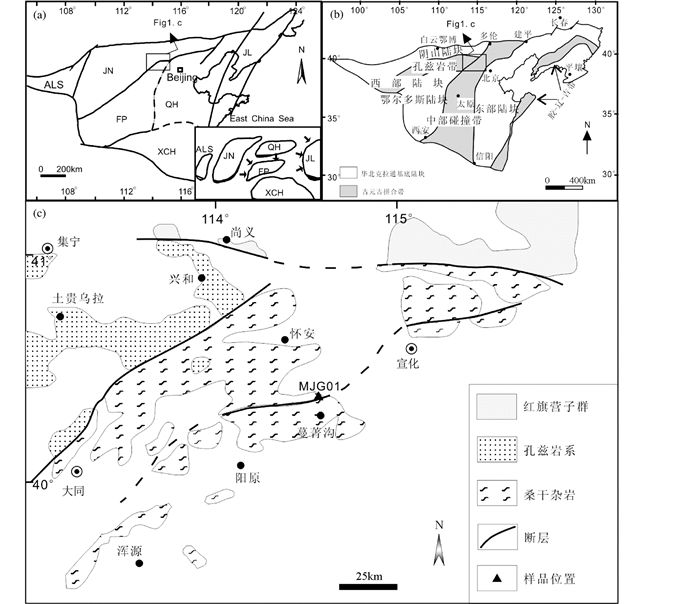
1 地质背景华北克拉通基底构造单元划分及其演化一直存在不同认识(翟明国和卞爱国,2000;Zhai and Liu, 2003;Zhao et al., 2005;Kusky et al., 2007)。翟明国和卞爱国(2000)提出胶辽、迁怀、阜平、集宁、许昌、和阿拉善六个微陆块的划分,并认为在新太古代末发生超大陆的拼合(图 1a);Zhai and Liu (2003)提出了丰镇、晋豫、胶辽活动带(Mobile belt) 的认识,认为其具有显生宙造山带特征;Zhao et al.(2005)提出的华北克拉通基底东、西部陆块二分模式中认为于2.0~1.9Ga沿孔兹岩带碰撞拼合形成西部陆块,在~1.85Ga与东部陆块拼合形成中部造山带,并且认为鄂尔多斯地块与阴山地块的拼合应早于~1.92Ga超高温变质年龄(赵国春,2009)(图 1b);Kusky et al.(2007)则认为东部陆块与西部陆块的碰撞造山发生在~2.5Ga,其提出的冀北古元古造山带(1.93~1.92Ga) 代表区域上由北向南碰撞逆冲。
|
图 1 华北克拉通基底构造单元划分(a、b) 及研究区地质简图(c) (a、b、c分别据翟明国和卞爱国,2000;Zhao et al., 2005;郭敬辉等,1999) ALS-阿拉善陆块;JN-集宁陆块;JL-胶辽陆块;FP-阜平陆块;QH-迁怀陆块;XCH-许昌陆块 Fig. 1 Tectonic division framework of the North China Craton basement (a, b) and the simplified geologic map of the studied area (c) (Fig 1.a, b, c after Zhai and Bian, 2000; Zhao et al., 2005; Guo et al., 1999, respectively) ALS-Alashan Block; JN-Jining Block; JL-Jiaoliao Block; FP-Fuping Block; QH-Qianhuai Block; XCH-Xuchang Block |
研究区位于迁怀陆块的西北缘(图 1a),或Zhao et al. (2005)中部造山带的中北部(图 1b)。区域上出露的地质体主要有太古宙TTG岩系为特征的桑干杂岩(赵宗溥等,1993)、孔兹岩为特征的兴和岩群(卢良兆等,1996) 和变质火山-沉积岩为特征的红旗营子群(胡学文等,1996),并伴有大量的高压麻粒岩、紫苏花岗岩以及钾质花岗岩(翟明国等,1996)。桑干杂岩构成了研究区的主体,由太古宙TTG岩系和少量变质表壳岩、石榴石基性麻粒岩以及紫苏花岗岩组成,并以赤诚-尚义断裂与北部红旗营子群相邻,西部则与孔兹岩带相邻(图 1c)。岩石普遍经历了麻粒岩相变质作用,各类岩石之间多为构造接触。石榴石基性麻粒岩以变形的岩席或岩墙以及小岩体产于太古宙TTG和钾质花岗岩中,时代以古元古代侵入体为主(张华锋等,2005;Peng et al., 2005;张华锋等,2006;Peng et al., 2010)。进一步的变质作用P-T轨迹研究表明,其峰期变质条件在800~850℃和1.2~1.5GPa左右,并经历了中压麻粒岩相(T=800℃,P=0.8GPa) 和角闪岩相(T=650~700℃,P=0.5~0.6GPa) 的退变质作用,显示为近等温减压的变质P-T轨迹(翟明国等,1992;Zhao et al., 2001;Guo et al., 2002);围岩TTG锆石U-Pb年龄多分布于2.55~2.45Ga之间(Zhao et al., 2008;刘富等,2009;Wang et al., 2010;Zhang et al., 2012),野外与其出露特征相似伴生的钾质花岗岩,其锆石U-Pb年龄和较高的εHf(t) 值表明其形成可能与TTG片麻岩相似,为早期加厚新生下地壳部分熔融产物(Zhang et al., 2011);西北部的孔兹岩系为一套麻粒岩相-高角闪岩相的变质沉积岩组合,原岩是一套稳定的克拉通盆地沉积(刘金钟等,1990;Condie et al., 1992),形成时代应为古元古代(金巍等,1991;万渝生等,2000;Wan et al., 2009)。孔兹岩系变质岩石大致显示出近顺时针的变质P-T轨迹,峰期前的角闪岩相进变质(M1=600℃,0.8GPa)、峰期麻粒岩相变质(M2=800~850℃,1~1.2GPa) 和后期的中压麻粒岩相(M3-4=700~750℃,0.6~0.8GPa) 和角闪岩相(M5=500~600℃,0.4GPa) 退变质作用(贺高品等,1991;卢良兆等,1996;刘福来和沈其韩,1999);北部红旗营子群则为一套经历绿片岩-角闪岩相变质火山-沉积岩建造,时代归属曾存在新太古、古元古代争议(王启超,1992;胡学文等,1996),但进一步的碎屑锆石分析表明,其物源包括有前寒武纪地块基底及古生代地层-岩浆系列等,普遍经历的古生代晚期构造变形变质作用可能与西伯利亚和华北板块的拼合有关(刘树文等,2007;Wang et al., 2011)。
野外观察发现,在怀安蔓菁沟地区还出露一套原岩相当于石英闪长岩的辉石麻粒岩,与高压麻粒岩、石榴夕线片麻岩(孔兹岩) 及英云闪长质片麻岩等呈构造接触,矿物组合上与高压麻粒岩明显不同。
2 岩石学特征研究区出露的这套辉石麻粒岩(MJG01,N 40°22′43″、E 114°28′26″),与高压麻粒岩、石榴夕线片麻岩呈构造接触,条带状构造,粒状变晶结构。主要矿物组成为斜长石(55%±)、单斜辉石(15%±)、紫苏辉石(5%±)、石英(10%±)、钾长石(5%±)、角闪石(5%±) 以及少量磁铁矿(1%~2%),副矿物主要为锆石和磷灰石。斜长石、石英分布相对较均匀。斜长石半自形-他形,聚片双晶发育;石英则多呈舌状-弱舌状形态,波状消光;紫苏辉石、单斜辉石因后期退变而不完整,分布不均匀;单偏光下,紫苏辉石以发育浅玫瑰红-浅绿的多色性为特征。镜下可见紫苏辉石+单斜辉石+斜长石±石英±磁铁矿(Opx+Cpx+Pl±Q±Mt) 的典型中压辉石麻粒岩相矿物组合(图 2a) 和单斜辉石+角闪石+斜长石±石英±磁铁矿(Cpx+Hb+Pl±Q±Mt) 的麻粒岩相晚期-角闪岩相退变质矿物组合(图 2b)。呈细粒分布在紫苏辉石、单斜辉石边部的角闪石应为退变质晚期产物(Hb+Pl±Q±Mt)(图 2c)。另外,可见单斜辉石中的角闪石矿物包体(图 2d),可能为辉石麻粒岩峰期变质前的早期角闪石。与其伴生的高压麻粒岩中亦可见二辉麻粒岩相的紫苏辉石+单斜辉石+斜长石±角闪石(Opx+Cpx+Pl±Hb) 和角闪岩相的角闪石+斜长石±磁铁矿(Hb+Pl±Mt) 退变产物(图 2e)。两者所不同的是高压麻粒岩中发育石榴石变斑晶,并可见单斜辉石+斜长石±石英(Cpx+Pl±Q) 矿物包体(图 2g, h),为早期高压麻粒岩相变质组合。

|
图 2 怀安地区辉石麻粒岩(变石英闪长岩, a-f) 及高压麻粒岩(g-h) 显微特征 (a)-中压辉石麻粒岩峰期变质矿物组合:Opx+Cpx+Pl;(b)-麻粒岩晚期-角闪岩相退变质矿物组合:Opx+Cpx→Cpx+Hb+Pl+Mt;(c)-晚期角闪岩相退变质矿物组合:Opx+Cpx→Hb+Pl+Mt;(d)-紫苏辉石中早期角闪石矿物包体;(e)-退变质锆石穿插紫苏辉石边部产出;(f)-退变质锆石分布在紫苏辉石与斜长石之间;(g)-高压麻粒岩中压麻粒岩相退变矿物组合:Opx+Cpx+Pl+Mt及角闪岩相退变矿物组合:Hb+Pl+Mt;(h)-高压麻粒岩相变质矿物组合:Gt+Cpx+Pl. Gt-石榴石;Cpx-单斜辉石;Opx-紫苏辉石;Hb-角闪石;Pl-斜长石;Q-石英;Mt-磁铁矿;Zrn-锆石;(+)/(-)-正交/单偏光 Fig. 2 Microscope features of the pyroxene granulite (meta-quartz-diorite, a-f) and high-pressure granulite (g-h) in Huai'an area (a)-mineral assemblages of the mid-pressure granulite facies metamorphism: Opx+Cpx+Pl; (b)-mineral assemblages of the late granulite to amphibolite retrograde metamorphism: Opx+Cpx→Cpx+Hb+Pl+Mt; (c)-mineral assemblages of the later amphibolite retrograde metamorphismin: Opx+Cpx→Hb+Pl+Mt; (d)-early amphiboles-mineral inclusions in Opx; (e)-metamorphic zircon inserting the edge of Opx; (f)-metamorphic zircon distributed between the Opx and Pl; (g)-mineral assemblages of the mid-pressure granulite retrograde metamorphism: Opx+Cpx+Pl+Mt, and those of the amphibolite retrograde metamorphism: Hb+Pl+Mt, in high-pressure granulite; (h)-mineral assemblages of the high-pressure granulite facies metamorphism: Gt+Cpx+Pl. Gt-garnet; Cpx-clinopyroxene; OPX-orthopyroxene; Hb-hornblende; Pl-plagioclase; Q-quartz; Mt-magnetite; Zrn-zrcon; (+)/(-)-monopolarizer/crossed polarizer |
另外,在紫苏辉石与单斜辉石后期退变矿物组合中可见新生变质锆石,以穿插紫苏辉石边部(图 2e) 以及紫苏辉石与斜长石之间(图 2f) 为特征。这表明变质锆石应形成于紫苏辉石之后。在时间上,应介于中压麻粒岩变质作用晚期至角闪岩相退变过程中形成的变质增生锆石。
综上可知,本文中的辉石麻粒岩发育有紫苏辉石+单斜辉石+斜长石(Opx+Cpx+Pl)、单斜辉石+角闪石+斜长石±石英±磁铁矿(Cpx+Hb+Pl±Q±Mt) 和角闪石+斜长石±石英±磁铁矿(Hb+Pl±Q±Mt) 的矿物共生组合显示岩石经历了中压麻粒岩相变质作用及晚期的角闪岩相退变质作用。而变质锆石则形成于紫苏辉石之后。
3 分析方法锆石的阴极发光图像(CL) 在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所电子探针与电镜实验室完成。锆石U-Pb、微量元素及Lu-Hf同位素均在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成。
3.1 锆石U-Pb及微量元素分析锆石U-Pb定年测试工作在连接Geolas-193型紫外激光剥蚀系统的Agilient 7500a型ICP-MS上进行。激光剥蚀采用单点剥蚀方式,以He作为剥蚀物质的载气,斑束直径为30μm,频率为8Hz。ICP-MS数据采集选用跳峰方式,每测定6个样品点,测定一个锆石91500和一个NIST610。年龄计算以标准锆石91500为外标进行同位素比值分馏校正,原始数据处理采用GLITTER (ver 4.0) 程序,处理后的数据使用ComPb Corr#3 _151软件(Andersen,2002) 进行普通铅校正,锆石的U-Pb年龄结果使用Isoplot程序(Ludwig,2003) 计算。元素浓度计算采用NIST610作外标,Si作内标。有关分析测试方法、流程和相关的仪器工作参数详见(柳小明等,2007)。
3.2 锆石Hf同位素分析锆石Hf同位素分析在相应测年点相邻位置测定,在配备Geolas-193型紫外激光剥蚀系统(LA) 的Nu Plasma HR (Wrexham, UK) 多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(MC-ICP-MS) 上完成。激光斑束直径为44μm,所用的激光剥蚀脉冲频率为10Hz,激光束的能量密度为10J·cm-2,测定时用国际标样91500作外标。干扰校正取推荐值175Lu/176Lu=0.02669(De Biévre and Taylor, 1993),176Yb/172Yb=0.5886(Chu et al., 2002)。计算εHf(t) 值时,Lu衰变常数采用1.867×10-11a-1(Soderlund et al., 2004),球粒陨石的176Hf/177Hf比值为0.282785,176Lu/177Hf的比值为0.0336(Bouvier et al., 2008)。Hf亏损地幔模式年龄的计算采用现今的亏损地幔176Hf/177Hf=0.28325和176Lu/177Hf=0.0384(Griffin et al., 2000)。
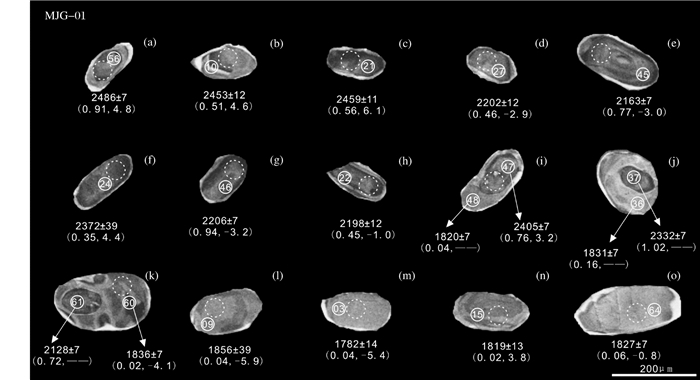
4 分析结果 4.1 锆石U-Pb年龄阴极发光图像显示辉石麻粒岩中锆石较为复杂,主要存在两种类型的锆石颗粒:1) 发育核、边双层结构的锆石。此类型中部分锆石最外层还发育有CL强度较高的白色亮边,但其宽度相对较窄(<10μm);核部锆石多保留较完整的晶形和生长韵律环带,其柱面{110}和锥面{101}保留较好(图 3b-h),显示出岩浆结晶锆石特征;边部锆石无内部结构,CL强度相对核部高(图 3a, i-k),为变质增生边;2) 无生长环带的不规则状锆石(图 3l-o),此类锆石为变质增生的新生锆石颗粒,部分锆石的阴极发光显示边部也发育有很窄的亮边(图 3m, o)。这些极薄的亮边未进行测试分析。
|
图 3 怀安地区辉石麻粒岩锆石CL图像特征 实线圆圈及数字为锆石U-Pb年龄测点、点号,虚线圆圈为Hf同位素分析点;锆石下方数据代表测点207Pb/206Pb年龄,括号内左边为Th/U比,右边为εHf(t) 值,--表示未测试 Fig. 3 Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of representative zircons from the pyroxene granulite in Huai'an area The solid circles with number inside in the CL images represent the analytical spots and number of the zircon U-Pb age, and the dotted circles represent the Hf isotopic analytical spots; The data beneath the CL images represent the 207Pb/206Pb age, and the left of the brackets are the ratios of Th/U, the right represent εHf(t) values; --represents not tested |
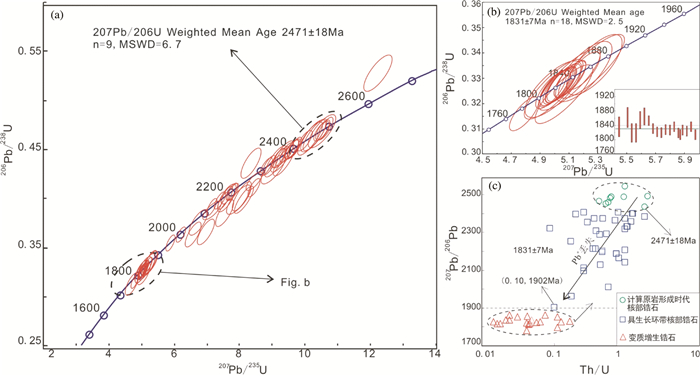
针对上述锆石CL图像观察,我们对该样品不同类锆石颗粒进行了70个点位的LA-ICP-MS定年测试(表 1)。除去五个测点(1, 18, 29, 34, 68) 年龄不谐和外,其余点显示较好的谐和度。对发育较好或残余岩浆环带的核部锆石测试表明,其207Pb/206Pb年龄相对分散,在1902~2542Ma之间分布,且Th、U及Th/U变化较大,Th、U含量分别为7.76×10-6~182× 10-6和46.5×10-6~605×10-6,而Th/U比为0.10~1.92,在年龄与Th/U相关图上两者显示较好正相关性(图 4c)。其中9个岩浆生长韵律环带相对较发育的锆石(02, 10, 21, 25, 26, 33, 40, 56, 69),其207Pb/206Pb年龄最大(2435~2542Ma),在U-Pb谐和图上显示较好的谐和度(图 4a)。Th、U含量分别为38×10-6~122×10-6和48×10-6~170×10-6,并且Th/U比值均大于0.4(0.42~1.92),获得加权平均年龄为2471±18Ma (2σ, MSWD=6.7, n=9)。对变质增生锆石的边部共进行了18个测点的分析,其207Pb/206Pb年龄分布在1782~1865Ma之间(图 4b),加权平均年龄为1831±7Ma (2σ, MSWD=2.5, n=18)。它们的Th含量均小于15×10-6,U含量为21×10-6~120×10-6,Th/U比值变化在0.01~0.16之间,绝大部分小于0.1,与核部锆石相比Th及Th/U比值明显降低。
|
图 4 怀安地区辉石麻粒岩锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果(a、b) 及Th/U比与年龄相关图(c) 图 4c中圆圈图例代表参加计算原岩时代的核部具生长环带锆石;方框图例代表年龄明显变小的核部具生长环带锆石;三角形图例代表幔部变质增生边和变质新生锆石,均为变质增生锆石 Fig. 4 Zircon U-Pb isotope analysis diagrams (a, b) and plots of Th/U ratio versus 207Pb/206Pb age (c) for the pyroxene granulite in Huai'an area In Fig. 4c: the circles represent those zircon cores calculating the forming age of protolith; Rectangles represent the zircon cores with the reducing age; Triangles represent the zircon mantles of metamorphic overgrowth around the magmatic zircon cores, and the metamorphic new-single grains, unified to be the metamorphic overgrowth zircon |
|
|
表 1 怀安地区辉石麻粒岩(变质石英闪长岩) 锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb分析结果 Table 1 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb analytical data for the pyroxene granulite (metamorphic quartz diorite) in Huai'an area |
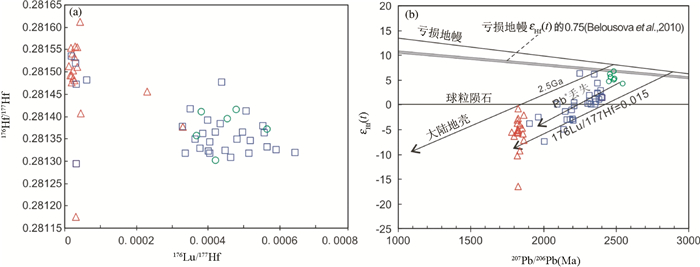
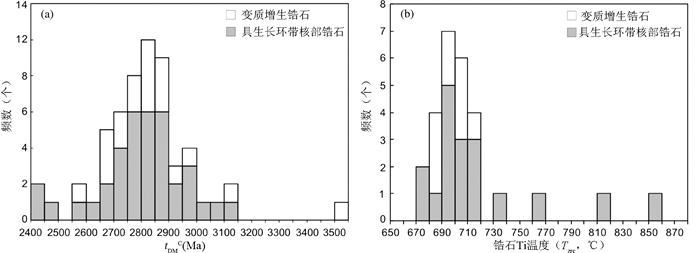
获得的锆石Hf同位素数据表明(表 2),核部具生长环带锆石的176Lu/177Hf比值均 < 0.001,多分布在0.0003~0.0007之间,176Hf/177Hf值多小于0.28145。但变质增生锆石具更低的176Lu/177Hf值,大部分小于0.0001,而176Hf/177Hf值相比增高,多在0.28140以上(图 5a)。计算获得的Hf亏损模式年龄及εHf(t) 值表明,核部锆石单阶段Hf亏损模式年龄tDM分布在2350~2770Ma之间,峰值年龄为2602Ma,两阶段模式年龄tDMC为2439~3126Ma,主要集中在2600~2900Ma (峰值年龄为2782Ma);在εHf(t) 与207Pb/206Pb年龄相关图上两者显示正相关变化关系(图 5b)。上述近似代表岩浆结晶年龄的6个测点(2, 10, 21, 25, 33, 56) 的tDM为2550~2621Ma (峰值年龄为2586Ma),tDMC变化在2596~2716Ma (峰值年龄为2665Ma),εHf(t) 值在4.1~6.7之间,略低于同期亏损地幔εHf(t) 的0.75倍(Belousova et al., 2010, 图 5b)。变质增生锆石的tDM分布在2300~2500Ma之间,tDMC为2555~3536Ma,主要集中在2650~2900Ma (平均为2790Ma, 图 6a),εHf(t) 均为负值(-0.8~-7.2)。
|
图 5 怀安地区辉石麻粒岩锆石176Lu/177Hf与176Hf/177Hf (a) 和εHf(t) 与年龄(b) 相关图 图例如图 4c Fig. 5 Plots of zircons 176Lu/177Hf versus 176Hf/177Hf (a) and εHf(t) versus 207Pb/206Pb age for the pyroxene granulite in Huai'an area (b) Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4c |
|
图 6 怀安地区辉石麻粒岩锆石两阶段Hf模式年龄(tDMC) 及锆石Ti (Tzrc) 温度分布图 Fig. 6 Distribution diagram of the second-stage Hf model ages (tDMC) and the Ti-in-zircon temperature (Tzrc) values for the pyroxene granulite in Huai'an area |
|
|
表 2 怀安地区辉石麻粒岩锆石LA-ICP-MS Lu-Hf同位素分析结果 Table 2 Zircon LA-ICP-MS Lu-Hf isotope analytical data for the pyroxene granulite in Huai'an area |
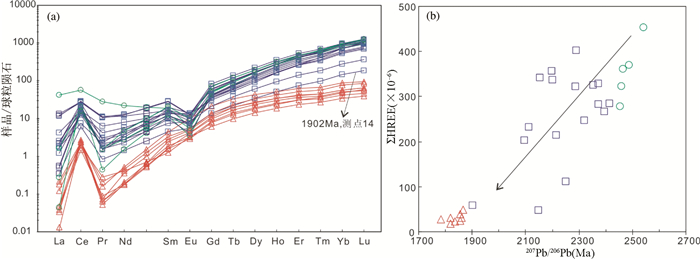
30个测点的锆石微量元素分析表明(表 3),发育生长环带的核部锆石,其∑REE在120×10-6~490×10-6之间,而变质锆石的∑REE明显减少(19.6×10-6~64.8×10-6)。二者均显示出相对富集HREE的特征(图 7a)。但是,变质增生锆石的HREE富集程度((Lu/Gd)N=4.39~13.40) 明显低于核部锆石((Lu/Gd)N=15.03~33.27)。核部锆石具有明显的正Ce异常(δCe=1.55~23.85) 和负Eu异常(δEu=0.14~0.96),与岩浆锆石特征相似(Corfu et al., 2003)。变质增生锆石则无明显的Eu异常(δEu=0.79~1.19,但显示出更加强烈的Ce正异常(δCe=11.25~98.43)。另外,变质锆石的Y含量与核部发育生长环带的锆石相比也明显减少,前者为34.02×10-6~95.56×10-6,后者为164.6×10-6~577.8×10-6。在锆石ΣHREE与207Pb/206Pb年龄相关性图上显示,核部具生长韵律环带的锆石ΣHREE随年龄变小呈现降低趋势(图 7b),与Th/U比值和年龄相关性特征相同(图 4c)。相应获得的微量元素Ti含量分析表明,核部锆石与变质增生锆石两者的Ti含量没有太大差异,后者Ti含量分布相对较集中(图 6b),对应的锆石钛温度值(Tzrc,Ferry and Watson, 2007) 在683~714℃之间,平均值为697±10℃(2σ, n=8)。核部锆石的钛温度值分布在679~857℃,平均值为700±7℃(2σ, n=15)。
|
图 7 怀安地区辉石麻粒岩岩锆石稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a) 及ΣHREE与年龄相关图(b) 图例同图 4c Fig. 7 Zircon chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns diagram (a) of the pyroxene granulite in Huai'an area and Plots of ΣHREE versus 207Pb/206Pb age (b) Symbols are the same as in Fig. 4c |
|
|
表 3 怀安地区辉石麻粒岩锆石LA-ICP-MS微量元素分析结果(×10-6) Table 3 Zircon LA-ICP-MS trace elements analytical data for pyroxene granulite in Huai'an area (×10-6) |
本文生长韵律环带发育的核部锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果显示,207Pb/206Pb年龄分布分散,在1902~2542Ma之间变化,其锆石年龄与Th/U比、ΣHREE和εHf(t) 值之间均显示较好的正相关性特征(图 4c、图 5b、图 7b),反映出这些岩浆锆石受后期变质作用影响而发生过重结晶作用(Pidgeon,1992;Pidgeon et al., 1998),并导致放射成因Pb的丢失(Vavra et al., 1996;Hoskin and Black, 2000)。其中9个岩浆生长韵律环带相对较发育的核部锆石(测点MJG01-02, 10, 21, 25, 26, 33, 40, 56, 69),207Pb/206Pb年龄集中在2435~2542Ma之间,在U-Pb谐和图上显示较好的谐和度(图 4a),获得加权平均年龄为2471±18Ma (MSWD=6.7, n=9)。其Th/U比值(0.42~1.92) 均大于0.4,与岩浆结晶锆石相似(Rubatto and Gebauer, 2000),稀土总量ΣREE (337.6×10-6~489.5×10-6) 以及明显正Ce异常(δCe=1.55~23.85) 和负Eu异常(δEu=0.14~0.96) 也显示岩浆锆石特征(Corfu et al., 2003),并具相对较高的εHf(t) 值(4.1~6.7,图 5b)。与其它核部岩浆锆石相比,这些锆石受后期变质热事件改造程度应较弱,其年龄更为接近锆石的真实形成年龄。因此,2471±18Ma的年龄可近似代表辉石麻粒岩原岩(石英闪长岩) 的形成年龄。
上述近似代表岩浆结晶年龄中的6个测点(2, 10, 21, 25, 33, 56) Hf同位素分析表明,其单阶段模式年龄tDM为2550~2621Ma (峰值年龄为2586Ma),略低于两阶段模式年龄(tDMC=2596~2716Ma,峰值年龄为2665Ma);εHf(t) 值在4.1~6.7之间,略低于同期亏损地幔εHf(t) 的0.75倍(Belousova et al., 2010, 图 5b),表明岩浆的源区具新生下地壳特征,辉石麻粒岩的原岩(石英闪长岩) 应为增生地壳部分熔融形成。这与前人对TTG的研究结果一致,是本区新太古代末地壳增生与改造的响应(刘敦一等,1997;刘富等,2009;Zhang et al., 2012),与华北克拉通其它地区新太古代末地壳增生事件类似(Wu et al., 2005;耿元生等,2010;Jiang et al., 2010;Diwu et al., 2011;Wan et al., 2011;Wang and Liu, 2012;Geng et al., 2012)。
5.2 1.85~1.80Ga退变质作用对变质增生锆石分析表明,其CL图像与上述核部具生长环带锆石相比变亮,具更低的Th/U比值(0.01~0.1) 和∑REE (19.61×10-6~64.75×10-6) 等,与变质锆石特征一致(Rubatto,2002;Whitehouse and Platt, 2003),并且Th/U比(0.01~0.1) 与麻粒岩至角闪岩相过渡变质增生锆石的Th/U比值接近(Vavra et al., 1999)。锆石年龄分布在1782~1865Ma之间,在U-Pb谐和图上显示较好的谐和度,获得1831±7Ma (MSWD=2.5, n=18) 的加权平均年龄(图 4b) 应为变质年龄。另外,相对于核部锆石,此类锆石具有更低的176Lu/177Hf比值(多数小于0.0001),但176Hf/177Hf值明显增高(图 5a)。引起这类锆石明显不同的Hf同位素组成可能与退变质过程中富REE变质矿物分解、重结晶和或变质流体有关(Amelin et al., 2000;Rubatto and Hermann, 2003;Zheng et al., 2005)。在锆石稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图上(图 7a),核部生长环带锆石虽受到后期变质热事件影响,但其REE配分模式相似,而变质增生锆石则明显不同,除具更低的∑REE外,该类锆石Eu负异常明显变弱,但Ce异常有所增大,若锆石Ce异常与体系氧化状态程度有关的话(Hoskin and Schaltegger, 2003;Schulz et al., 2006),该类锆石弱的Eu异常则可能与其高的Ce异常相对应(Rubatto,2002)。另外,变质增生锆石HREE富集程度相对核部锆石明显变低,两者相应的LuN/GdN值分别在4.39~13.40和15.03~33.27之间。HREE矿物/熔体分配系数表明,石榴石为其最富集的矿物相,角闪石次之(Rollinson,1993)。根据矿物组合分析,本文样品在麻粒岩相及其退变过程中并无共生石榴石矿物相,而普遍发育的是Opx+Cpx+Pl→Am+Pl+Mt±Cpx,即麻粒岩-角闪岩相退变质反应,若退变过程中与角闪石平衡共生,对应变质锆石的HREE富集程度将会明显降低。在岩石显微特征观察中可见部分锆石以穿插紫苏辉石边部(图 2e) 或位于紫苏辉石与斜长石之间(图 2f)。这类变质锆石应形成在紫苏辉石之后,属于麻粒岩晚期至角闪岩退变阶段的产物,非麻粒岩相变质峰期产物。因此,变质增生锆石HREE配分特征更可能与退变过程中角闪石的形成有关。
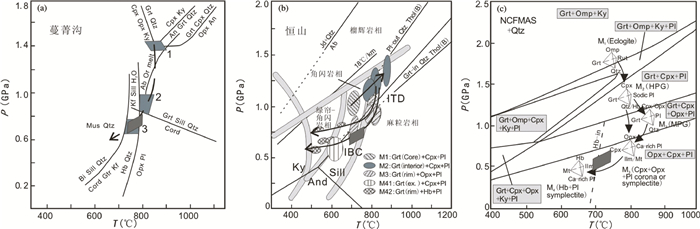
在相应获得的锆石钛温度Tzrc上,核部锆石虽发生变质重结晶作用,但在锆石温度Tzrc上无明显区别。加权平均计算获得700±7℃的平均温度,与早期太古宙岩浆锆石钛温度相近(Watson and Harrison, 2005;Nutman,2006;Hiess et al., 2008;Fu et al., 2008)。后期退变质锆石钛温度分布在683~714℃之间(图 6b),加权平均值为696±8℃。对硅酸岩熔体其aTiO2普遍在0.6~0.9之间(Ghent and Stout, 1984;Watson et al., 2006;Hayden and Watson, 2007),若考虑aTiO2对锆石钛温度的影响,相应的锆石钛温度可能会偏低约50~10℃(Ferry et al., 2007)。此假设成立的话,本文中的变质锆石形成的温度可能在690~750℃之间,这与前人分析的区域麻粒岩所经历的从中压麻粒岩相到角闪岩相退变过程的变质温度相对应(图 8;翟明国等,1992;刘树文等,1996;Zhao et al., 2001;Guo et al., 2002)。Wang et al. (2011)对蔓菁沟处高压麻粒岩进行过研究。其变质锆石Ti温度计算结果分布在682~738℃之间,并获得了1839±22Ma的年龄。该结果与本文结果非常相似。前人将其解释为麻粒岩相变质年龄(Wang et al., 2011)。若同样考虑aTiO2对锆石钛温度的影响,他们获得的锆石Ti温度与区域高压麻粒岩峰期变质温度(800~850℃;翟明国等,1992;刘树文等,1996;Zhao et al., 2001;Guo et al., 2002) 有较大差别(图 8)。因此,我们认为前人获得的1839±22Ma年龄与本文锆石记录的年龄一致,解释为高压麻粒岩晚期退变时代更为合理。
|
图 8 高压麻粒岩变质作用P-T轨迹图(a、b、c分别据翟明国等,1992;Guo et al., 2002;Zhao et al., 2001) 矩形深灰色方框区域代表辉石麻粒岩(麻粒岩相晚期-角闪岩相) 退变质阶段 Fig. 8 Diagrams of the metamorphic P-T conditions for high-pressure granulites (a, b, c after Zhai et al., 1992; Guo et al., 2002; Zhao et al., 2001, respectively) Rectangular region shaded dark grey respects the stage of the late granulit to amphibolite retrograde facies metamorphism for the pyroxene granulite |
综上所述,这类具更低Th/U、176Lu/177Hf值且相对较缓的HREE配分特征的变质锆石应为中压麻粒岩相变质作用晚期至角闪岩相退变质过程中的产物。它们所记录的1831±7Ma的加权平均年龄应近似代表中压麻粒岩相结束,并向角闪岩相退变质过程的年龄,非峰期变质时代。因此,本文数据表明,1850~1800Ma之间发生的构造热事件性质应代表区域地壳抬升和岩石退变质过程。
另外,对第一部分年龄较分散的具生长环带核部锆石(2542~1902Ma),若其放射成因Pb丢失与变质重结晶程度对应的话(Hoskin and Black, 2000),那么记录最小年龄的锆石重结晶程度应最高,并具有最低的Th/U比值和REE含量。我们的数据明显具有上述特征。其中记录最小年龄的测点(1σ,1902Ma;测点14),具有最低的Th/U值(Th/U=0.10,图 4d) 和最低的REE配分曲线(图 7a)。因此可以推测导致核部锆石重结晶的变质热事件时间应在1902Ma左右,早于晚期1850~1800Ma退变质年龄。1900~1850Ma可以作为麻粒岩相变质热事件时限,但因我们测得的数据中缺少1900~1850Ma之间的年龄记录,对这一阶段的变质热事件年龄缺失的原因还有待进一步的研究。在此,笔者推测岩石可能在麻粒岩相变质过程中,因缺乏流体或温度较高,导致变质流体Zr不饱和,从而未能结晶出变质锆石。而岩浆锆石则是发生不同程度的重结晶作用,导致年龄变小。
6 结论(1) 核部具生长环带锆石因后期变质热事件影响而发生重结晶作用,导致不同程度放射成因Pb丢失,相应的锆石年龄分布在2542~1902Ma之间。对近似代表岩浆结晶的锆石其获得的加权平均年龄为2471±18Ma,可解释为辉石麻粒岩原岩(石英闪长岩) 岩浆结晶年龄。相应的锆石Hf同位素特征表明本区新太古代末发生过地壳增生。
(2) 锆石Th/U、Hf和微量元素上均显示与核部岩浆锆石不同特征的边部变质锆石,应为后期麻粒岩-角闪岩相退变产物;锆石钛温度表明其形成温度在683~714℃之间,与麻粒岩到角闪岩相退变质过程的温度高度吻合;其1830.7±6.6Ma的207Pb/206Pb年龄应代表退变质时代。
(3) 1900~1850Ma可能为辉石麻粒岩中压麻粒岩相峰期变质热事件时限,但因测得的数据中缺少1900~1850Ma之间的年龄记录,对这一阶段的变质热事件年龄缺失的原因及该阶段年龄的性质,有待进一步的研究。
致谢 衷心感谢中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所电子探针与电镜实验室全体员工的帮助;感谢西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室在实验过程中给予的大力支持和帮助;吴佳林博士、钟焱博士等协助测试工作一并表示感谢。| [] | Amelin Y, Lee DC, Halliday AN. 2000. Early-middle Archaean crustal evolution deduced from Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotopic studies of single zircon grains. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(24): 4205–4225. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00493-2 |
| [] | Andersen T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59–79. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X |
| [] | Ashwal LD, Tucher RD, Zinner EK. 1999. Slow cooling of deep crustal granulites and Pb-loss in zircon. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(18): 2839–2851. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00166-0 |
| [] | Belousova EA, Kostitsyn YA, GriffinWL, Begg GC, O'Reilly SY, Pearson NJ. 2010. The growth of the continental crust: Constraints from zircon Hf-isotope data. Lithos, 119(3-4): 457–466. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.07.024 |
| [] | Bouvier A, Vervoort JD, Patchett PJ. 2008. The Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotopic composition of CHUR: Constraints from unequilibrated chondrites and implications for the bulk composition of terrestrial planets. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 273(1-2): 48–57. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.06.010 |
| [] | Carswell DA, O'Brien PJ. 1993. High-pressure quartz feldspathic garnet granulites in the Moldanubian zone, Bohemian Massif, in lower Austria: Their P-T conditions for formation, uplift history and geotectonic significance. Journal of Petrology, 3: 13–25. |
| [] | Chu NC, Taylor RN, Chavagnac V, Nesbitt RW, Boella RM, Milton JA, German CR, Bayon G, Burton K. 2002. Hf isotope ratio analysis using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: An evaluation of isobaric interference corrections. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 17(12): 1567–1574. DOI:10.1039/b206707b |
| [] | Condie KC, Boryta MD, Liu JZ, Qian XL. 1992. The origin of khondalites: Geochemical evidence from the Archean to Early Proterozoic granulite belt in the North China craton. Precambrian Research, 59(3-4): 207–223. DOI:10.1016/0301-9268(92)90057-U |
| [] | Corfu F, Hanchar JM, Hoskin PWO, Kinny P. 2003. Altas of zircon textures. Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry, 53(1): 469–500. |
| [] | De Biévre P, Taylor PDP. 1993. Table of the isotopic compositions of the elements. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Processes, 123(2): 149–166. DOI:10.1016/0168-1176(93)87009-H |
| [] | Diwu CR, Sun Y, Guo AL, Wang HL, Liu XM. 2011. Crustal growth in the North China Craton at~2. 5Ga: Evidence from in situ zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotopes and whole-rock geochemistry of the Dengfeng complex. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 149–170. |
| [] | England PC, Thompson AB. 1984. Pressure-temperature-time paths of regional metamorphism, Ⅰ. Heat transfer during the evolution of regions of thickened continental crust. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 894–928. |
| [] | Ferry JM, Watson EB. 2007. New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 154(4): 429–437. DOI:10.1007/s00410-007-0201-0 |
| [] | Fu B, Page FZ, Cavosie AJ, Fournelle J, Kita NT, Lackey JS, Wilde SA, Valley JW. 2008. Ti-in-zircon thermometry: Applications and limitations. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 156(2): 197–215. DOI:10.1007/s00410-008-0281-5 |
| [] | Fraser G, Ellis D, Eggins S. 1997. Zirconium abundance in granulite-facies minerals, with implications for zircon geochronology in high-grade rocks. Geology, 25(7): 607–610. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0607:ZAIGFM>2.3.CO;2 |
| [] | Geng YS, Shen QH, Ren LD. 2010. Late Neoarchean to Early Paleoproterozoic magmatic events and tectonothermal systems in the North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7): 1945–1966. |
| [] | Geng YS, Du LL, Ren LD. 2012. Growth and reworking of the early Precambrian continental crust in the North China Craton: Constraints from zircon Hf isotopes. Gondwana Research, 21(2-3): 517–529. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.07.006 |
| [] | Ghent ED, Stout MZ. 1984. TiO2 activity in metamorphosed politic and basic rocks: Principles and applications to metamorphism in southeastern Canadian cordillera. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 86(3): 248–255. DOI:10.1007/BF00373670 |
| [] | Griffin WL, Pearson NJ, Belousova E, Jackson SE, van Achterbergh E, O'Reilly SY, Shee SR. 2000. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICP MS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1): 133–147. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9 |
| [] | Guo JH, Shi X, Bian AG, Xu RH, Zhai MG, Li YG. 1999. Pb isotopic composition of feldspar and U-Pb age of zircon from early Proterozoic granite in Sanggan area, North China craton: Metamorphism, crustal melting and tectono-thermal event. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(2): 199–207. |
| [] | Guo JH, Zhai MG, Xu RH. 2001. Timing of the granulite facies metamorphism in the Sanggan area, North China craton: Zircon U-Pb geochronology. Science in China (Series D), 44(11): 1010–1018. DOI:10.1007/BF02875394 |
| [] | Guo JH, O'Brien PJ, Zhai MG. 2002. High-pressure granulites in the Sanggan area, North China Craton: Metamorphic evolution, P-T paths and geotectonic significance. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 20(8): 741–756. DOI:10.1046/j.1525-1314.2002.00401.x |
| [] | Guo JH, Sun M, Chen FK, Zhai MG. 2005. Sm-Nd and SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of high-pressure granulites in the Sanggan area, North China Craton: Timing of Paleoproterozoic continental collision. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 629–642. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.01.017 |
| [] | Hayden LA, Watson EB. 2007. Rutile saturation in hydrous siliceous melts and its bearing on Ti-thermometry of quartz and zircon. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 258(3-4): 561–568. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.04.020 |
| [] | He GP, Lu LZ, Ye HW, Jin SQ and Ye TS. 1991. Metamorphic Evolution of Early Precambrian Rocks in the Eastern Hebei and Inner Mongolia Regions. Changchun: Jilin University Press, 9-100 (in Chinese) |
| [] | Hiess J, Nutman AP, Bennett VC, Holden P. 2008. Ti-in-zircon thermometry applied to contrasting Archean metamorphic and igneous systems. Chemical Geology, 247(3-4): 323–338. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.012 |
| [] | Hoskin PWO, Black LP. 2000. Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 18(4): 423–439. |
| [] | Hoskin PWO, Schaltegger U. 2003. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 27–55. DOI:10.2113/0530027 |
| [] | Hu XW, Zhang JM, Quan H. 1996. The isotopic ages of the Hongqiyingzi Group in northern Hebei and its age assignment. Regional Geology of China(2): 186–192. |
| [] | Jiang N, Guo JH, Zhai MG, Zhang SQ. 2010. ~2. 7Ga crust growth in the North China craton. Precambrian Research, 179(1-4): 37–49. |
| [] | Jin W, Li SX, Liu XS. 1991. A study on characteristics of Early Precambrian high-grade metamorphic rock series and their metamophic dynamics. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 7(4): 27–36. |
| [] | Jin W, Li SX. 1996. P-T-t path and crustal thermodynamic model of Late Archaean-Early Proterozoic high grade metamorphic terrain in North China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 12(2): 208–221. |
| [] | Kröner A, Wilde SA, O'Brien PJ, Li JH, Passchier CW, Walte NP, Liu DY. 2005. Field relationships, geochemistry, zircon ages and evolution of a Late Archaean to Palaeoproterozoic lower crustal section in the Hengshan Terrain of northern China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(5): 605–632. |
| [] | Kusky TM, Li JH, Santosh M. 2007. The Paleoproterozoic North Hebei Orogen: North China craton's collisional suture with the Columbia supercontinent. Gondwana Research, 12(1-2): 4–28. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2006.11.012 |
| [] | Kusky TM. 2011. Geophysical and geological tests of tectonic models of the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 26–35. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.01.004 |
| [] | Liu DY, Geng YS, Song B. 1997. The constitute, geochronology and geologic evolution of the Kongling complex, western Hubei. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 18(3): 226–232. |
| [] | Liu F, Guo JH, Lu XP, Diwu CR. 2009. Crustal growth at~2.5Ga in the North China Craton: Evidence from whole-rock Nd and zircon Hf isotopes in the Huai'an gneiss terrane. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(24): 4704–4713. |
| [] | Liu FL, Shen QH. 1999. Retrogressive textures and metamorphic reaction features of Al-rich gneisses in the granulite facies belt from northwestern Hebei Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(4): 505–517. |
| [] | Liu JZ, Chen YP and Qian XL. 1990. Study on original tectonic environment of the Datong-Xinghe Khondalite Suite. In: Lithospheric Geoscience. Beijing: Peking University Press, 61-68 (in Chinese) |
| [] | Liu SW, Shen QH, Geng YS. 1996. Metamorphic evolution of two types of garnet granulites in northwestern Hebei Province and analyses by Gibbs method. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 12(2): 261–275. |
| [] | Liu SW, Lü YJ, Feng YG, Liu XM, Yan QR, Zhang C, Tian W. 2007. Zircon and monazite geochronology of the Hongqiyingzi complex, northern Hebei, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(9): 1086–1100. |
| [] | Liu SW, Santosh M, Wang W, Bai X, Yang PT. 2011. Zircon U-Pb chronology of the Jianping Complex: Implications for the Precambrian crustal evolution history of the northern margin of North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 48–63. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.01.003 |
| [] | Liu XM, Gao S, Diwu CR, Yuan HL, Hu ZC. 2007. Simultaneous in-situ determination of U-Pb age and trace elements in zircon by LAICP-MS in 20μm spot size. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(9): 1257–1264. DOI:10.1007/s11434-007-0160-x |
| [] | Lu LZ, Xu XC and Liu FL. 1996. The Precambrian Khondalite Series in Northern China. Changchun: Changchun Publishing House, 16-69(in Chinese) |
| [] | Ludwig KR. 2003. Mathematical-statistical treatment of data and errors for 230Th/U geochronology. Uranium-Series Geochemistry. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 52(1): 631–656. DOI:10.2113/0520631 |
| [] | Nutman AP. 2006. Comment on 'Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest Earth' II. Science, 311(5762): 779. |
| [] | O'Brien PJ, Rötzler J. 2003. High-pressure granulites: Formation, recovery of peak conditions and implications for tectonics. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 21(1): 3–20. DOI:10.1046/j.1525-1314.2003.00420.x |
| [] | Pattison DRM. 2003. Petrogenetic significance of orthopyroxene-free garnet + clinopyroxene + plagioclase±quartz-bearing metabasites with respect to the amphibolite and granulite facies. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 21(1): 21–34. DOI:10.1046/j.1525-1314.2003.00415.x |
| [] | Peng P, Zhai MG, Zhang HF, Guo JH. 2005. Geochronological constraints on the Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China craton: SHRIMP zircon ages of different types of mafic dikes. International Geology Review, 47(5): 492–508. DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.47.5.492 |
| [] | Peng P, Guo JH, Zhai MG, Bleeker W. 2010. Paleoproterozoic gabbronoritic and granitic magmatism in the northern margin of the North China Craton: Evidence of crust-mantle interaction. Precambrian Research, 183(3): 635–659. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2010.08.015 |
| [] | Pidgeon RT. 1992. Recrystallisation of oscillatory zoned zircon: Some geochronological and petrological implications. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 110(4): 463–472. DOI:10.1007/BF00344081 |
| [] | Pidgeon RT, Nemchin AA, Hitchen GJ. 1998. Internal structures of zircons from Archaean granites from the Darling Range batholith: Implications for zircon stability and the interpretation of zircon U-Pb ages. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 132(3): 288–299. DOI:10.1007/s004100050422 |
| [] | Roberts MP, Finger F. 1997. Do U-Pb zircon ages from granulites reflect peak metamorphic conditions?. Geology, 25(4): 319–322. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0319:DUPZAF>2.3.CO;2 |
| [] | Rollinson HR. 1993. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation. Singapore: Longman, Technical Press, 1-352 |
| [] | Rubatto D and Gebauer D. 2000. Use of cathodoluminescence for U-Pb zircon dating by IOM Microprobe: Some examples from the western Alps. In: Cathodoluminescence in Geoscience. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 373-400 |
| [] | Rubatto D. 2002. Zircon trace element geochemistry: Partitioning with garnet and the link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism. Chemical Geology, 184(1-2): 123–138. DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00355-2 |
| [] | Rubatto D, Hermann J. 2003. Zircon formation during fluid circulation in eclogites (Monviso, Western Alps): Implications for Zr and Hf budget in subduction zones. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(12): 2173–2187. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(02)01321-2 |
| [] | Santosh M, Sajeev K, Li JH. 2006. Extreme crustal metamorphism during Columbia supercontinent assembly: Evidence from North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 10(3-4): 256–266. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2006.06.005 |
| [] | Santosh M, Tsunogae T, Li JH, Liu SJ. 2007a. Discovery of sapphirine-bearing Mg-Al granulites in the North China Craton: Implications for Paleoproterozoic ultrahigh temperature metamorphism. Gondwana Research, 11(3): 263–285. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2006.10.009 |
| [] | Santosh M, Wilde SA, Li JH. 2007b. Timing of Paleoproterozoic ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism in the North China Craton: Evidence from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology. Precambrian Research, 159(3-4): 178–196. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.06.006 |
| [] | Schulz B, Klemd R, Brätz H. 2006. Host rock compositional controls on zircon trace element signatures in metabasites from the Austroalpine basement. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(3): 697–710. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2005.10.001 |
| [] | Soderlund U, Patchett JP, Vervoort JD, Isachsen CE. 2004. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219(3-4): 311–324. DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00012-3 |
| [] | Timmermann H, Štědrá V, Gerdes A, Noble SR, Parrish RR, Dörr W. 2004. The problem of dating high-pressure metamorphism: A U-Pb isotope and geochemical study on eclogites and related rocks of the Mariánske Lázně Complex, Czech Republic. Journal of Petrology, 45(7): 1311–1338. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egh020 |
| [] | Thompson AB, England PC. 1984. Pressure-temperature-time paths of regional metamorphism, Ⅱ. Their inference and interpretation using mineral assemblages in metamorphic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 929–955. |
| [] | Vavra G, Gebauer D, Schmid R, Compston W. 1996. Multiple zircon growth and recrystallization during polyphase Late Carboniferous to Triassic metamorphism in granulites of the Ivrea Zone (Southern Alps): An ion microprobe (SHRIMP) study. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 122(4): 337–358. DOI:10.1007/s004100050132 |
| [] | Vavra G, Schmid R, Gebauer D. 1999. Internal morphology, habit and U-Th-Pb microanalysis of amphibolite-to-granulite facies zircon: Geochronology of the Ivrea Zone (Southern Alps). Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 134(4): 380–404. DOI:10.1007/s004100050492 |
| [] | Wan YS, Geng YS, Liu FL, Shen QH, Liu DY, Song B. 2000. Age and composition of the Khondalite Series of the North China Craton and its adjacent area. Progress in Precambrian Research, 23(4): 221–237. |
| [] | Wan YS, Liu DY, Dong CY, Xu ZY, Wang ZJ, Wilde SA, Yang YH, Liu ZH, Zhou HY. 2009. The Precambrian Khondalite Belt in the Daqingshan area, North China Craton: Evidence for multiple metamorphic events in the Palaeoproterozoic era. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 323: 73–97. DOI:10.1144/SP323.4 |
| [] | Wan YS, Liu DY, Wang SJ, Yang EX, Wang W, Dong CY, Zhou HY, Du LL, Yang YH, Diwu CR. 2011. ~2. 7Ga juvenile crust formation in the North China Craton (Taishane-Xintai area, western Shandong Province): Further evidence of an understated event from U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic composition of zircon. Precambrian Research, 186(1-4): 169–180. |
| [] | Wang AD, Liu YC. 2012. Neoarchean (2. 5~2.8Ga) crustal growth of the North China Craton revealed by zircon Hf isotope: A synthesis. Geoscience Frontiers, 3(2): 147–173. |
| [] | Wang F, Chen FK, Siebel W, Li SQ, Peng P, Zhai MG. 2011. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic composition of the Hongqiyingzi Complex, northern Hebei Province: New evidence for Paleoproterozoic and late Paleozoic evolution of the northern margin of the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 122–136. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.02.003 |
| [] | Wang J, Wu YB, Gao S, Peng M, Liu XC, Zhao LS, Zhou L, Hu ZC, Gong HJ, Liu YS. 2010. Zircon U-Pb and trace element data from rocks of the Huai'an Complex: New insights into the Late Paleoproterozoic collision between the Eastern and Western Blocks of the North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 178(1-4): 59–71. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2010.01.007 |
| [] | Wang QC. 1992. On the age of Hongqiyingzi Group and geological thermal events in undergone. Chinese Journal of Geology(Suppl.): 17–24. |
| [] | Watson EB, Harrison TM. 2005. Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest Earth. Science, 308(5723): 841–844. DOI:10.1126/science.1110873 |
| [] | Watson EB, Wark DA, Thomas JB. 2006. Crystallization thermometers for zircon and rutile. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 151(4): 413–433. DOI:10.1007/s00410-006-0068-5 |
| [] | Whitehouse MJ, Platt JP. 2003. Dating high-grade metamorphism-constraints from rare-earth elements in zircon and garnet. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 145(1): 61–74. DOI:10.1007/s00410-002-0432-z |
| [] | Wu FY, Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Sun DY. 2005. Nd isotopic constraints on crustal formation in the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 523–545. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.10.011 |
| [] | Zhai MG, Guo JH, Yan YH, Han XL, Li YG. 1992. Discovery and preliminary study of Archaean high-pressure basic granulites in North China. Science in China (Series B)(12): 1325–1330. |
| [] | Zhai MG, Li YG, Guo JH, Zhang WH, Yan YH. 1996. Two linear granite zones in Shanxi-Hebei-Nei Mongol juncture region and their implication for Early Precambrian continental evolution. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 12(2): 299–314. |
| [] | Zhai MG, Bian AG, Zhao TP. 2000. The amalgamation of the supercontinent of North China Craton at the end of Neo-Archaean and its breakup during Late Palaeoproterozoic and Meso-Proterozoic. Science in China (Series D), 43(Suppl.): 219–232. |
| [] | Zhai MG, Liu WJ. 2003. Palaeoproterozoic tectonic history of the North China craton: A review. Precambrian Research, 122(1-4): 183–199. DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00211-5 |
| [] | Zhai MG, Peng P. 2007. Paleoproterozoic events in the North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(11): 2665–2682. |
| [] | Zhai MG. 2009. Two kinds of granulites (HT-HP and HT-UHT) in North China Craton: Their genetic relation and geotectonic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(8): 1753–1771. |
| [] | Zhai MG, Santosh M. 2011. The Early Precambrian odyssey of the North China Craton: A synoptic overview. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 6–25. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.02.005 |
| [] | Zhang HF, Zhai MG, Peng P, Guo JH. 2005. Geochronology, geochemistry and implications of the high pressure granulites in the Sanggan area, North China Craton. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology Geochemistry, 24(Suppl.1): 138–139. |
| [] | Zhang HF, Zhai MG, Peng P. 2006. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age of the Paleoproterozoic high-pressure granulites from the Sanggan area, the North China craton and its geologic implications. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(3): 190–199. |
| [] | Zhang HF, Luo ZB, Zhou ZG, Liu CF. 2009. Palaeoproterozoic collisional time in the Sanggan area of the North China Craton: Constraints from age of regional ductile shearing and post-collisional super peraluminous granites. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 29(1): 60–67. |
| [] | Zhang HF, Zhai MG, Santosh M, Diwu CR, Li SR. 2011. Geochronology and petrogenesis of Neoarchean potassic meta-granites from Huai'an Complex: Implications for the evolution of the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 20(1): 82–105. DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.01.009 |
| [] | Zhang HF, Zhai MG, Santosh M, Li SR. 2012. Low-Al and high-Al trondhjemites in the Huai'an Complex, North China Craton: Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopes, and implications for Neoarchean crustal growth and remelting. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 49: 203–213. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.11.004 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Cawood PA, Lu LZ. 1999. Thermal evolution of two textural types of mafic granulites in the North China Craton: Evidence for both mantle plume and collisional tectonics. Geological Magazine, 136(3): 223–240. DOI:10.1017/S001675689900254X |
| [] | Zhao GC, Cawood PA, Wilde SA, Lu LZ. 2001. High-pressure granulites (retrograded eclogites) from the Hengshan Complex, North China Craton: Petrology and tectonic implications. Journal of Petrology, 42(6): 1141–1170. |
| [] | Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA, Li SZ. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited. Precambrian Research, 136(2): 177–202. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002 |
| [] | Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Sun M, Guo JH, Kröner A, Li SZ, Li XP, Zhang J. 2008. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Huai'an complex: Constraints on Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic magmatic and metamorphic events in the Trans-North China Orogen. American Journal of Science, 308(3): 270–303. DOI:10.2475/03.2008.04 |
| [] | Zhao GC. 2009. Metamorphic evolution of major tectonic units in the basement of the North China Craton: Key issues and discussion. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(8): 1772–1792. |
| [] | Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Guo JH, Cawood PA, Sun M, Li XP. 2010. Single zircon grains record two Paleoproterozoic collisional events in the North China Craton. Precambrian Research, 177(3-4): 266–276. DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2009.12.007 |
| [] | Zhao ZP, Zhai MG, Wang KY, Yan YH, Guo JH and Liu YG. 1993. Precambrian Crustal Evolution of the Sino-Korean Paraplatform. Beijing: Science Press, 284-384 (in Chinese) |
| [] | Zheng YF, Wu YB, Zhao ZF, Zhang SB, Xu P, Wu FY. 2005. Metamorphic effect on zircon Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systems in ultrahigh-pressure eclogite-facies metagranite and metabasite. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 240(2): 378–400. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.09.025 |
| [] | 耿元生, 沈其韩, 任留东. 2010. 华北克拉通晚太古代末-古元古代初的岩浆事件及构造热体制. 岩石学报, 26(7): 1945–1966. |
| [] | 郭敬辉, 石昕, 卞爱国, 许荣华, 翟明国, 李永刚. 1999. 桑干地区早元古代花岗岩长石Pb同位素组成和锆石U-Pb年龄:变质与地壳熔融作用及构造-热事件演化. 岩石学报, 15(2): 199–207. |
| [] | 郭敬辉, 翟明国, 许荣华. 2002. 华北桑干地区大规模麻粒岩相变质作用的时代:锆石U-Pb年代学. 中国科学(D辑), 31(1): 10–18. |
| [] | 贺高品, 卢良兆, 叶慧文, 靳是琴, 叶挺松. 1991.冀东和内蒙古东南部早前寒武纪变质作用演化.长春:吉林大学出版社, 9-100 |
| [] | 胡学文, 张江满, 权桓. 1996. 冀北红旗营子群同位素年龄及其时代归属. 中国区域地质(2): 186–192. |
| [] | 金巍, 李树勋, 刘喜山. 1991. 内蒙大青山地区早前寒武纪高级变质岩系特征和变质动力学. 岩石学报, 7(4): 27–36. |
| [] | 金巍, 李树勋. 1996. 华北晚太古代-早元古代高级变质区的变质P-T-t轨迹及其地壳热动力学演化模式. 岩石学报, 12(2): 208–221. |
| [] | 刘敦一, 耿元生, 宋彪. 1997. 冀西北地区晚太古代大陆地壳的增生和再造--同位素年代学证据. 地球学报, 18: 226–232. |
| [] | 刘富, 郭敬辉, 路孝平, 第五春荣. 2009. 华北克拉通2. 5Ga地壳生长事件的Nd-Hf同位素证据:以怀安片麻岩地体为例.科学通报, 54(17): 2517–2526. |
| [] | 刘福来, 沈其韩. 1999. 冀西北麻粒岩相带富铝片麻岩的退变结构及其变质反应性质. 岩石学报, 15(4): 505–517. |
| [] | 刘金钟, 陈亚平, 钱祥麟. 1990.大同-兴和孔兹岩系原始构造环境的研究.见:岩石圈地球科学.北京:北京大学出版社, 61-68 |
| [] | 刘树文, 沈其韩, 耿元生. 1996. 冀西北两类石榴基性麻粒岩的变质演化及Gibbs方法分析. 岩石学报, 12(2): 261–275. |
| [] | 刘树文, 吕勇军, 凤永刚, 柳小明, 闫全人, 张臣, 田伟. 2007. 冀北红旗营子杂岩的锆石、独居石年代学及地质意义. 地质通报, 26(9): 1086–1100. |
| [] | 柳小明, 高山, 第五春荣, 袁洪林, 胡兆初. 2007. 单颗粒锆石的20μm小斑束原位微区LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄和微量元素的同时测定. 科学通报, 52(2): 228–235. |
| [] | 卢良兆, 徐学纯, 刘福来. 1996.中国北方早前寒武纪孔兹岩系.长春:长春出版社, 16-69 |
| [] | 万渝生, 耿元生, 刘福来, 沈其韩, 刘敦一, 宋彪. 2000. 华北克拉通及邻区孔兹岩系的时代及对太古宙基底组成的制约. 前寒武纪研究进展, 23(4): 221–237. |
| [] | 王启超. 1992. 红旗营子群的时代归属及所经历的地质热事件. 地质科学(增刊): 17–24. |
| [] | 翟明国, 郭敬辉, 阎月华, 韩秀伶, 李永刚. 1992. 中国华北太古宙高压基性麻粒岩的发现及初步研究. 中国科学(B辑)(12): 1325–1330. |
| [] | 翟明国, 李永刚, 郭敬辉, 张雯华, 阎月华. 1996. 晋冀内蒙交界地区麻粒岩地体中两条花岗岩带及其对早前寒武纪地壳生长的意义. 岩石学报, 12(2): 299–314. |
| [] | 翟明国, 卞爱国. 2000. 华北克拉通新太古代末超大陆拼合及古元古代末-中元古代裂解. 中国科学(D辑), 30(增刊): 129–137. |
| [] | 翟明国, 彭澎. 2007. 华北克拉通古元古代构造事件. 岩石学报, 23(11): 2665–2682. |
| [] | 翟明国. 2009. 华北克拉通两类早前寒武纪麻粒岩(HT-HP和HT-UHT) 及其相关问题. 岩石学报, 25(8): 1753–1771. |
| [] | 张华锋, 翟明国, 彭澎, 郭敬辉. 2005. 华北桑干地区高压麻粒岩的年代学、地球化学及其地质意义. 岩石矿物化学通报, 24(增刊): 138–139. |
| [] | 张华锋, 翟明国, 彭澎. 2006. 华北克拉通桑干地区高压麻粒岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地质含义. 地学前缘, 13: 190–199. |
| [] | 张华锋, 罗志波, 周志广, 柳长峰. 2009. 华北克拉通中北部古元古代碰撞造山时限:来自强过铝花岗岩和韧性剪切时代的制约. 矿物岩石, 29(1): 60–67. |
| [] | 赵国春. 2009. 华北克拉通基底主要构造单元变质作用演化及其若干问题讨论. 岩石学报, 25(8): 1772–1792. |
| [] | 赵宗溥, 翟明国, 王凯怡, 阎月华, 郭敬辉, 刘宇光. 1993.中朝准地台前寒武纪地壳演化.北京:科学出版社, 284-384 |
 2012, Vol. 28
2012, Vol. 28



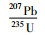
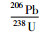
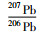
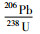
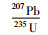
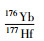
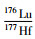
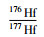
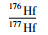
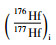
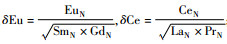 ;锆石钛温度
;锆石钛温度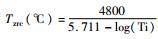 -273(
-273(