2. 武警黄金第七支队, 烟台 264004;
3. 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所矿物学与成矿学重点实验室, 广州 510640
2. The 7th Gold Detachment of Chinese People's Armed Police Force, Yantai 264004, China;
3. CAS Key Laboratory of Mineralogy and Metallogeny, Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510640, China
长江中下游成矿带是我国重要的铜金多金属成矿带之一, 研究程度甚高(常印佛等, 1991; 翟裕生等, 1992;Pan and Dong, 1999; Mao et al., 2006; 毛景文等, 2009), 自西向东依次分布有鄂东、九瑞、安庆-贵池、庐枞、铜陵、宁芜和宁镇等7个矿集区(常印佛等,1991;Yang and Lee, 2011; Deng et al., 2011)。研究表明长江中下游铜金矿床主要成矿时代为140±5Ma (Mao et al., 2006; Xie et al., 2009; Sun et al., 2003), 这些铜金多金属矿床主要与燕山期中酸性钙碱性侵入岩体有关(王强等, 2004;Wang et al., 2006, 2007; Xie et al., 2009, 2012; Li et al., 2009, 2010)。
贵池矿集区相对于长江中下游其他矿集区研究程度相对较低, 除铜山铜矿研究程度较高外(俞沧海和袁小明, 1999;俞沧海, 2001;周曙光, 2003;张智宇等, 2011), 只有零星的研究(陈国光和应祥熙, 2002;董胜, 2006), 这限制了对长江中下游岩浆与成矿系统特征全面理解。抛刀岭金矿床位于安庆-贵池矿集区(图 1a)。该金矿目前处于勘察阶段, 其金资源储量有望接近或达到大型规模, 为贵池矿集区最大金矿床。该矿床含矿岩石主要为矿化英安玢岩(大于95%), 其次为粉砂质碎裂岩。查清该区含矿英安玢岩成岩年龄, 判定其成因类型, 对该区乃至区域成矿研究和找矿实践都有重要借鉴意义。
|
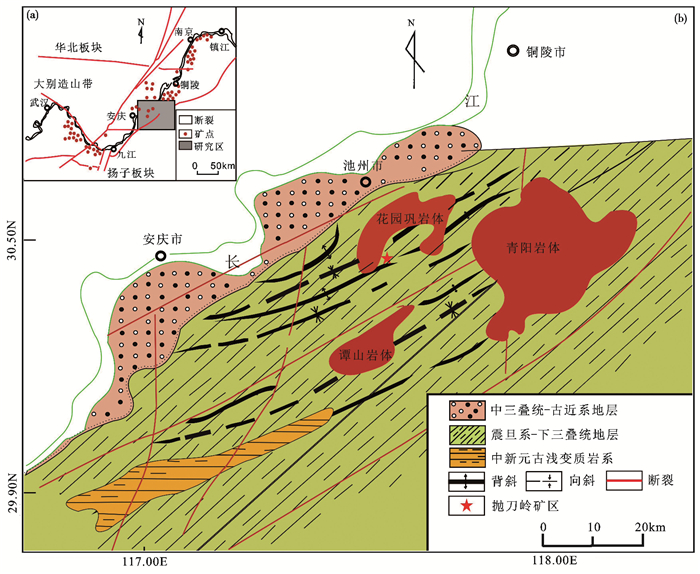
图 1 抛刀岭及周边地区地质简图(据田鹏飞等, 2012修改) Fig. 1 Sketch map of the Paodaoling district, Anqing-Guichi region (after Tian et al., 2012) |
长江中下游地区位于扬子板块北缘, 秦岭大别造山带和华北板块南侧, 西起湖北鄂东, 东至江苏镇江地区, 全长约400km (图 1a)。该区构造演化大体经历前寒武纪基底形成阶段, 震旦纪-早二叠沉积覆盖阶段和中三叠以来的碰撞造山阶段(翟裕生等, 1992);随后进入太平洋构造域, 发生大规模岩浆与地壳伸展活动(Gilder et al., 1991)。该地区中生代发生大规模的岩浆与成矿活动, 是中国东部最重要的成矿带之一(常印佛等,1991)。
研究区抛刀岭金矿位于安庆-贵池矿集区。研究区出露地层从老至新为奥陶系、志留系、泥盆系、石炭系、二叠系、白垩系及第四系, 属扬子地层区之下扬子分区贵池小区, 主要以海相为主的地台沉积, 沉积厚度累计在3189~3358m。其中奥陶系为碳酸盐岩类, 志留-泥盆系发育一套海相碎屑沉积;上二叠系下部为海陆交互的煤系, 上-中部和三叠系仍以海相碳酸盐岩类为主(赵德奎等, 2009)。
据物探、化探和遥感综合解译推测, 本区处于近EW向的深大断裂和NNE向基底断裂的交汇部位(陈国光和应祥熙, 2002)。区内断裂构造广泛发育, 主要以NNE、NE及少数NW向断裂构造为主。断裂构造不仅控制了区域上沉积建造、盖层褶皱、断层及岩浆侵入、火山活动, 而且控制了区域矿产的分布。安庆贵池地区中生代岩浆岩发育, 主要有:青阳岩体(750km2, 139~142Ma)、谭山岩体(140km2, 129~133Ma)、花园巩岩体(220km2, 131Ma)(Wu et al., 2012)。花园巩岩体为A型钾长花岗岩(邢凤鸣和徐祥, 1995;Wu et al., 2012), 分布于抛刀岭金矿的北侧(图 1b、图 2)。

|
图 2 抛刀岭金矿地质简图 1-第四系;2-五通组石英砾岩、砂岩;3-茅山组粉砂岩夹页岩;4-坟头组砂质页岩;5-高家边组;6-钾长花岗岩;7-英安玢岩;8-断层;9-采样位置 Fig. 2 Sketch map of the Paodaoling gold deposit 1-Quaternary System; 2-quartz conglomerate, sandstone of Wutong Formation; 3-silty sandstone and shale of Maoshan Formation; 4-sandy shale of Fentou Formation; 5-Gaojiabian Formation; 6-potassic granite; 7-trachyte andesitic porphyries; 8-fault; 9-sampling location |
矿区位于自来山背斜之北西翼, 岩层倾向NW, 倾角45°~55°。出露地层主要为志留系高家边组(S1g), 其次为坟头组(S2f) 和茅山组(S3m), 岩性主要为粉砂质页岩、砂岩、砂质页岩等(图 2)。
区内断裂构造比较发育, 以NE向为主, 是主要控岩、控矿构造, 主要有F1、F2、F3三条。F1断裂贯穿全区走向NE35°, 倾向NW, 倾角70°~78°, 控制着含矿岩体的西部边界;F3断裂早期为压扭性, 后期表现为张性, 沿断裂带发育有3~7m宽的角砾岩, 为含矿岩体的东部边界。NW向断裂规模较小。区内岩浆岩受F1和F3断裂构造控制, 呈带状分布于其间, 出露面积约0.6km2, 为浅成次火山岩。该岩体是金矿体赋存的主要围岩, 普遍发育绢云母化、黄铁矿化和硅化等, 与金矿化关系密切。
含矿岩体主要矿物成分:斑晶含量20%~35%, 少数可达50%左右, 主要为斜长石, 少量黑云母、普通角闪石、石英, 大部分斑晶已经碳酸盐化和绿泥石化(图 3)。斜长石:自形晶, 板状, 粒径0.25~2.5mm, 聚片双晶发育, 可见卡钠符合双晶, An=24~42, 为更-中长石(图 3c)。部分晶粒蚀变为绢云母(图 3d)。石英一般3%~8%, 黑云母3%~10%, 黑云母斑晶与斜长石斑晶具互为消长的关系。石英大多呈溶蚀的卵圆形或港湾状外貌, 有的保留高温石英的假像(图 3f)。基质为变余霏细结构, 少量包含霏细结构, 主要有微晶斜长石、石英、钾长石, 少量黑云母、角闪石、微量榍石、磷灰石、锆石等组成。金属矿物主要有黄铁矿、少量毒砂等组成。黄铁矿:浅铜黄色, 自形晶, 多数晶粒呈五角十二面体晶型, 少数为立方体晶型, 粒径0.025~0.45mm, 呈浸染状分布(图 3h)。根据镜下分析, 抛刀岭金矿含矿岩石为浅成英安玢岩。

|
图 3 抛刀岭金矿含矿英安玢岩镜下照片 Pl-斜长石; Py-黄铁矿; Bi-黑云母; Cal-方解石; Amp-角闪石; Q-石英 Fig. 3 Micrograph of the Paodaoling trachyte andicitic porphyrite Pl-plagioclase; Py-pyrite; Bi-biotite; Cal-calcite; Amp-hornblende; Q-quartz |
含矿岩石以英安玢岩型(包含英安玢岩质角砾岩) 为主, 约占总量的95%, 粉砂质碎裂岩占型少量。矿石矿物成份主要有黄铁矿, 其次为毒砂、褐铁矿、赤铁矿、胶黄铁矿, 闪锌矿、脆硫锑铅矿, 白铁矿少量, 方铅矿、黄铜矿微量, 偶见蹄金银矿。
4 样品与测试因采集样品时应避免采集无或者少量蚀变样品, 本次在抛刀岭金矿区只采集6件较新鲜岩石样品进行全岩地球化学分析。由于岩体全岩蚀变矿化, 虽尽量采集无或少蚀变的样品, 但镜下观察仍然发现大量矿物发生蚀变作用。所有采集样品统一编号后送至澳实矿物实验室(广州), 由该实验室对样品进行主、微量元素的分析测定, 其中常量元素采用ME-XRF06法, 由X荧光光谱仪测定; 稀土元素采用ME-MS81法, 由等离子体质谱测定; 微量元素采用ME-MS61法, 由等离子体质谱测定, 具体分析流程见Qi et al.(2000)。
英安玢岩锆石单矿物挑选由河北廊坊地质矿产研究所实验室完成。锆石微量元素含量和U-Pb同位素定年在中国科学院地球化学研究所(广州) 同位素地质年代学与地球化学重点实验室利用LA-ICP-MS分析完成。激光剥蚀系统为GeoLas 2005, ICP-MS为Agilent 7500a。激光剥蚀过程中采用氦气作载气、氩气为补偿气以调节灵敏度, 二者在进入ICP之前通过一个T型接头混合。在等离子体中心气流(Ar+He) 中加入了少量氮气, 以提高仪器灵敏度、降低检出限和改善分析精密度(Hu et al., 2008)。每个时间分辨分析数据包括大约20~30s的空白信号和50s的样品信号。对分析数据的离线处理(包括对样品和空白信号的选择、仪器灵敏度漂移校正、元素含量及U-Th-Pb同位素比值和年龄计算) 采用软件ICPMS DataCal (Liu et al., 2008, 2010a) 完成。详细的仪器操作条件和数据处理方法同Liu et al.(2008, 2010a)。
锆石微量元素含量利用多个USGS参考玻璃(BCR-2G, BIR-1G) 作为多外标、Si作内标的方法进行定量计算(Liu et al., 2010a).这些USGS玻璃中元素含量的推荐值据GeoReM数据库(http://georem.mpch-mainz.gwdg.de/)。U-Pb同位素定年中采用锆石标准91500作外标进行同位素分馏校正, 每分析5个样品点, 分析2次91500。对于与分析时间有关的U-Th-Pb同位素比值漂移, 利用91500的变化采用线性内插的方式进行了校正(Liu et al., 2010a).锆石标准91500的U-Th-Pb同位素比值推荐值据Wiedenbeck et al., (1995)。锆石样品的U-Pb年龄谐和图绘制和年龄权重平均计算均采用Isoplot/Ex_ver3 (Ludwig, 2003) 完成。
5 测试结果 5.1 岩石地球化学特征岩石主微量分析结果见表 1。鉴于PDL-2-3样品极高的Fe2O3含量和烧失量(严重的黄铁矿化), 该样分析结果仅作参考。
|
|
表 1 抛刀岭金矿英安玢岩全岩主量(wt%) 和微量(×10-6) 数据 Table 1 Results of major (wt%) and trace (×10-6) elements of Paodaoling ore-bearing trachyandensitic porphyries |
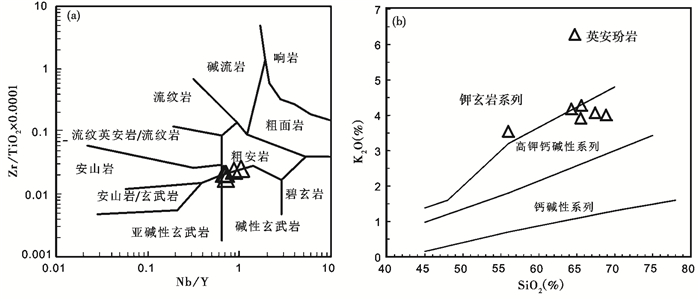
抛刀岭含矿玢岩具集中的SiO2(64.29%~68.86%, 平均为66.34%)、Al2O3 (14.16%~15.65%, 平均为14.93%) 和Fe2O3(5.61%~7.06%, 平均为6.48%) 含量;K2O+Na2O为3.71%~4.41%, 平均为4.14%;TiO2为0.73%~1.07%, 平均为0.86%;较低的MgO (0.67%~0.76%, 平均0.73%)、Mg#(16.7~20.9, 平均为18.4)、CaO (0.01%~0.07%, 平均为0.03%) 含量。岩石总体有表现为富硅、铝、钾, 贫钠、碱、钙、镁的特征。由于抛刀岭岩体受后期热液蚀变作用较大, 如斜长石蚀变, 绢云母化, 钾化, 全岩具有较高的烧失量(5.01%~10.05%)(表 1)。因此在判别岩石性质时不能用受后期热液作用影响较大的元素, 而是采用不活动性元素来进行判别。在Zr/TiO2×0.0001-Nb/Y岩石判别图解中(图 4a), 样品落入粗面安山岩与碱性玄武岩区域内。在SiO2对K2O的判别图上, 岩石总体为高钾钙碱性系列(图 4b)。结合矿物斑晶组成(斜长石、角闪石、黑云母等矿物) 抛刀岭含矿岩石可定名为英安玢岩。活动元素的含量也进一步显示, 抛刀岭英安玢岩可能受到严重的钾化而导致贫Ca、Na、Sr、Ba等地球化学特征(如斜长石绢云母化、绿泥石化等, 图 3b, c)。
|
图 4 抛刀岭金矿含矿岩石地球化学判别图解 (a)-全岩Zr/TiO2×0.0001-Nb/Y判别图解(据Winchester and Floyd, 1976);(b)-岩石系列SiO2-K2O图解(据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) Fig. 4 Discrimination diagrams of gold-bearing rocks in the Paodaoling gold deposit (a)-whole-rock Zr/TiO2×0.0001vs. SiO2 diagram (after Winchester and Floyd, 1976); (b)-SiO2 vs. K2O diagram (after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) |
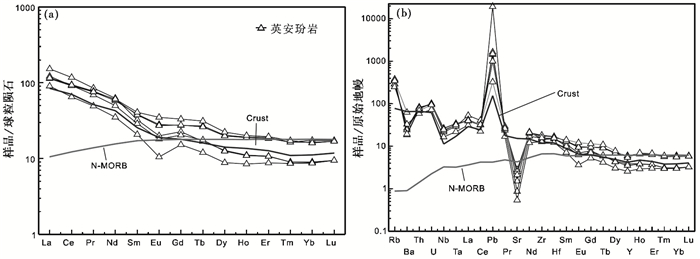
微量元素上, 抛刀岭金矿含矿玢岩显示贫Sr (31.2×10-6~59.3×10-6) 富Y (16.0×10-6~27.3×10-6) 和Yb (1.50×10-6~2.97×10-6)。稀土元素球粒陨石标准化的稀土配分曲线(图 5a) 所示, 样品具有相似的分布模式, 且与地壳稀土元素一致, 为右倾的平滑曲线。花岗闪长玢岩的∑REE=101.8×10-6~174.1×10-6, 平均为143.0×10-6, (La/Yb)N=6.49~17.32, 平均为10.33, δEu为0.74~0.95, 平均为0.83, ,显示其经历不同程度的斜长石结晶分离作用。在微量元素原始地幔标准化图解中(图 5b), 显示明显的K、Pb、Th、U等大离子亲石元素富集(除Sr和Ba相对于地壳有负异常), 亏损Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf、Ti等高场强元素。虽然抛刀岭岩体受到后期的热液蚀变作用可能引起活动性元素的富集或亏损(如K、Pb、Th、Sr、Ba), 但是高场强元素一般不受到影响。抛刀岭英安玢岩表现出Nb、Ta负异常, 与平均地壳和岛弧火山岩显示相似的微量元素配分特征, 而与N-MORB有明显差异, 指示其元素有一定的陆壳物质的加入, 岩石的Nb/Ta (13~14) 也和典型的壳源岩浆比较接近。
|
图 5 抛刀岭金矿英安玢岩稀土元素配分图(a) 及微量元素蛛网图(b)(球粒陨石标准值据Sun and McDonough, 1989; 原始地幔及其他地质储库标准值据McDonough and Sun, 1995) Fig. 5 REE chondrite normalized diagram (a) and trace elements primitive normalized diagram (b) of the Paodaoling trachyte andicitic porphyrites (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989; McDonough and Sun, 1995) |
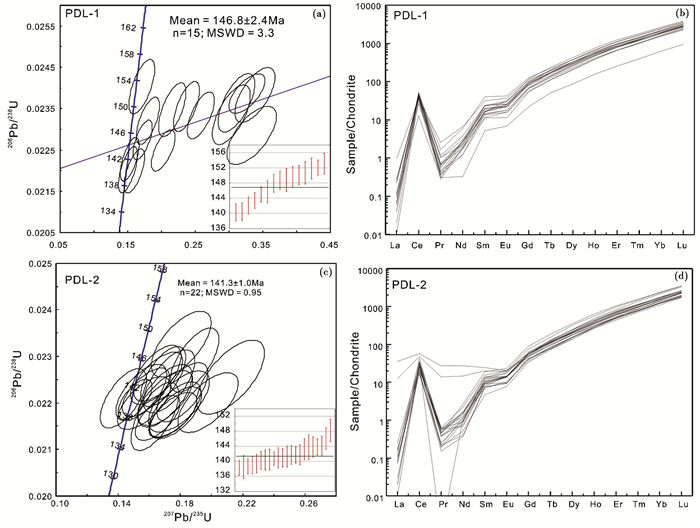
锆石U-Pb同位素、稀土元素数据见表 2和表 3。PDL-1样品15颗锆石206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为146.8±2.4Ma (2σ);样品PDL-2锆石Th/U比值范围为0.28~0.55, 平均0.38;PDL-2样品锆石几乎都落在协和线之上(图 6a), 表明锆石受后期热液流体作用影响较小, 能更好的反映岩浆的结晶年龄。PDL-2样品21颗锆石206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为141.3±1.0Ma (2σ)(图 6c)。虽然PDL-1样品可能遭受了后期的Pb丢失事件, 但是与年龄数据较好的PDL-2样品在误差范围内显示一致的年龄, 表明抛刀岭金矿含矿英安玢岩的成岩年龄为141~146Ma, 为晚侏罗-早白垩世(燕山期) 形成。其中两件样品共发现数颗捕获或残留锆石, 没有显示集中的年龄范围, 可能是原岩残留锆石或岩浆在侵位上升过程中捕获得到。
|
|
表 2 抛刀岭金矿锆石U-Pb年龄数据 Table 2 Zircon U-Pb age of Paodaoling gold deposit |
|
|
表 3 抛刀岭金矿锆石稀土元素含量(×10-6) Table 3 Zircon REE elements content of Paodaoling gold deposit (×10-6) |
|
图 6 抛刀岭金矿英安玢岩锆石年龄图(a, c) 及锆石稀土配分图解(b, d, 粒陨石标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 6 Zircon U-Pb ages (a, c) and REE distribution patterns (b, d) of zircons from the porphyrites in the Paodaoling gold deposit (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
锆石稀土表现为轻稀土亏损、重稀土富集、明显的Ce正异常和Eu负异常(图 6b, d)。这些特征表明本文所分析的锆石为典型的岩浆成因锆石。样品PDL-1锆石Th/U为0.31~0.86, 平均为0.55, U-Pb协和线分析表明大部分样品落在协和线右侧, 可能表示该样品受到后期热液蚀变导致铅丢失。
5.3 锆石稀土元素特征抛刀岭锆石稀土∑REE为230.3×10-6~1028×10-6。球粒陨石标准化图解上表现为轻稀土亏损, 重稀土富集, Ce正异常和Eu负异常典型的岩浆成因特征。两件抛刀岭锆石Ce4+/Ce3+变化范围分别为66.80~472.9, 171.2~1299;EuN/EuN*变化范围为0.46~0.65, 0.50~0.85。与智利地区岩浆岩对比, 两件抛刀岭锆石较高的Ce4+/Ce3+和EuN/EuN*特征, 落在含矿岩石变化范围内, 显示较高的氧逸度特征(图 7)。
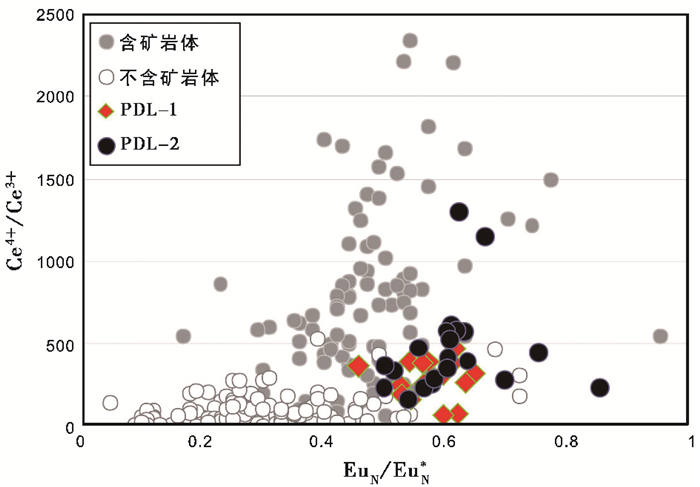
|
图 7 抛刀岭含矿玢岩锆石Ce4+/Ce3+与EuN/EuN*特征 Fig. 7 Characteristics of Ce4+/Ce3+ and EuN/EuN* from zircons in the Paodaoling gold-bearing porphyrites |
长江中下游地区中生代岩浆作用强烈, 并发生大规模的Cu-Au-Fe成矿作用。长江中下游地区在中生代岩浆形成时间可以分为两段:145~136Ma, 131~124Ma (周涛发等, 2008), 并具有分区性和演化趋势(Zhou et al., 2008), 其中与铜金矿有关的岩体主要形成时代为140±5Ma, 而130~120Ma的岩浆活动主要为双峰式火山岩加A型花岗岩组合(Li et al., 2011, 2012), 发育大型铁矿, 如著名的宁芜铁矿矿集区, 以及庐枞盆地的泥河铁矿和罗河铁矿。
抛刀岭金矿含矿玢岩主要形成于146~141Ma, 与长江中下游早期岩浆活动相对应, 因此我们有理由相信抛刀岭金矿的成矿时代也可以与长江中下游铜金成矿的主体时代类比, 形成于晚侏罗-早白垩世。同时, 其东南部铜山岩体年龄145.1±1.2Ma (张智宇等, 2011) 也表明, 贵池矿集区的铜金矿床可以和长江中下游其他地区铜金矿床进行类比。
6.2 抛刀岭含矿玢岩成因与成矿背景抛刀岭含矿玢岩形成时代与岩体产出状态都可以与长江中下游早期岩浆活动进行类比。目前对于长江中下游146~135Ma含矿岩体都表现为高Sr低Yb等埃达克质特征。对于这些埃达克岩浆岩成因主要有:
(1) 由壳幔物质相互作用的产物(陶奎元等, 1998;陈江峰和江博明, 1999;杜杨松等, 2004, 2007;谢建成等, 2012;Li et al., 2009;Xie et al., 2008, 2011), 是富集岩石圈地幔部分熔融产生的玄武质岩浆经过与地壳岩石同化混染后又经过分离结晶作用形成;(2) 拆沉或加厚下地壳物质部分熔融的产物(许继峰等, 2001; Xu et al., 2002; Robert et al., 2002;朱光等, 2003; Wang et al., 2004, 2006, 2007);(3) 俯冲洋壳部分熔融(Ling et al., 2009; Deng et al., 2012; Liu et al., 2010b)。目前最新的研究结果表明, 长江中下游含矿埃达克岩的地区化学特征与俯冲洋壳成因相一致, 因此长江中下游146~135Ma应该属于俯冲背景下。
与同时代的埃达克岩地球化学特征不同的是, 抛刀岭金矿英安玢岩显示高Si、Y和Yb, 低Mg、Sr等特征, 指示其岩浆源区并没有石榴石残留, 且没有发生明显壳幔相互作用。同时, 其微量、稀土元素配分趋势与地壳一致, 而明显富集大离子亲石元素和亏损高场强元素, 不同于MORB等其他地幔储库的地球化学特征, 显示其源区有大量的壳源组分的加入。在Pearce et al.(1984)花岗岩判别图解中, 岩石主要落于岛弧花岗岩区域(图 8a, b)。
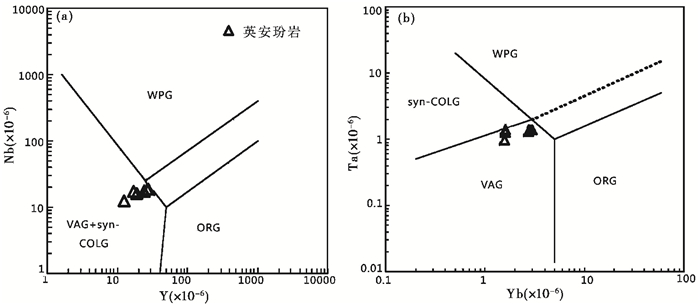
|
图 8 抛刀岭金矿英安玢岩Y-Nb (a) 和Yb-Ta图解(b)(底图据Pearce et al., 1984) WAP-板内花岗岩;VAG-岛弧花岗岩;Syn-CLOG-同碰撞花岗岩;ORG-造山花岗岩 Fig. 8 Y-Nb and Yb-Ta diagram of the Paodaoling ore-bearing porphyries (after Pearce et al., 1984) |
在(La/Yb)N vs. (Yb)N图解中(图 9), 抛刀岭岩体全部落入经典岛弧花岗岩中, 而非埃达克岩类区域, 排除拆沉或洋壳熔融成因。因此, 抛刀岭含矿玢岩更有可能来自俯冲带地幔楔熔融并发生结晶分异的结果。
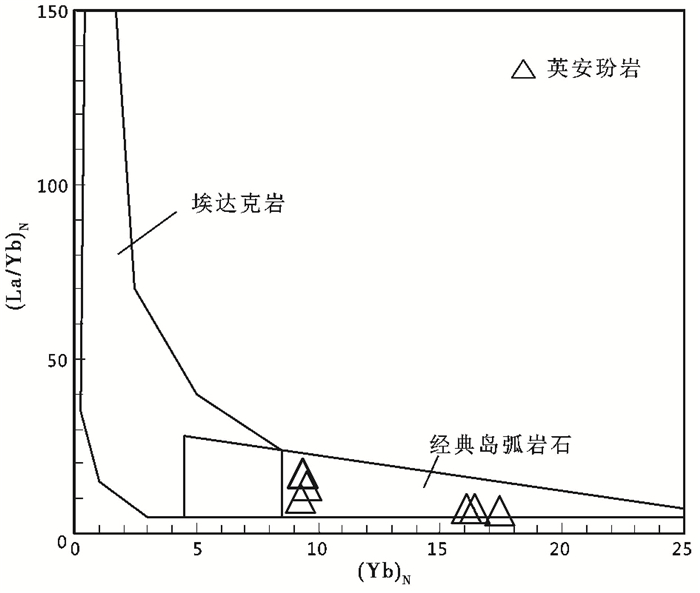
|
图 9 YbN-(La/Yb)N判别图解(底图据Defant and Drummond, 1990) Fig. 9 The YbN-(La/Yb)N discrimination diagram (after Defant and Drummond, 1990) |
锆石的氧逸度特征也进一步佐证抛刀岭金矿玢岩的源区特征。锆石是中酸性岩浆岩中常见的副矿物而且在后期热液蚀变以及物理化学过程中不易发生改变。而且, 锆石结晶过程中, Ce4+比Ce3+优先进入, 这意味着Ce4+/Ce3+比值对氧逸度的变化很敏感, 可以忠实地反映其结晶时岩浆氧化还原状态。可以使用Ce4+和Ce3+在矿物熔体与结晶矿物之间分配系数的晶格张力模型对所测数据进行Ce4+/Ce3+计算。Ballard et al.(2002)通过LA-ICP-MS对智利北部Chuquicamata-E1 Abra斑岩铜矿带中14个不含矿和七个含矿的钙碱性侵入体进行了全岩与锆石微量元素分析, 认为锆石中Ce4+/Ce3+与EuN/EuN*与岩浆中氧化还原度有关系。同样的方法随后被成功地应用于玉龙斑岩铜矿(Liang et al., 2006) 和华南地区中生代含矿与不含矿岩体(Li et al., 2012) 的研究中。本文同样根据Ballard et al.(2002)的方法计算了抛刀岭锆石Ce4+/Ce3+与EuN/EuN*特征(表 3)。从锆石Ce4+/Ce3+和Eu异常特征看, 抛刀岭含矿玢岩锆石落在与智利地区含矿埃达克岩一样的区域范围, 显示较高的氧逸度特征。研究表明, 俯冲带具有比板内和MORB更高的氧逸度特征(Mungall, 2002; Sun et al., 2004, 2011; Ling et al., 2009; Sillitoe, 1997; Wang et al., 2011)。抛刀岭的锆石氧逸度特征进一步证明该地区应该在太平洋俯冲背景下。研究表明, 控制铜金矿床成矿的一个关键因素就是岩体的氧逸度特征。高氧逸度熔体更有成矿的潜力。岩浆的氧逸度控制着熔体中硫的氧化状态:在低氧逸度情况下, 岩浆中的硫主要以S2-的形式存在;而在高氧逸度情况下, 它主要以SO和SO2的形式存在。S2-向SO或SO2转换能阻止不混溶的硫化物相的饱和, 从而能从正在分馏的熔体中提取Cu-Au (Sun et al., 2004)。这时高氧逸度岩浆中铜元素在分异和分馏中富集, 进入岩浆-热液流体中, 从而成矿。同时, 从铜金的洋壳、陆壳和地幔储库丰度统计, Sun et al.(2010, 2011) 发现铜金在俯冲洋壳或岩石圈地幔的丰度远远高于地壳, 因此抛刀岭含矿熔体可能受到地幔或者洋壳熔体的加入, 使其更具有成矿潜力, 经过岩浆演化使金富集成矿。
目前长江中下游中生代岩浆与成矿活动的构造背景还存在较大争论。有人认为中生代该地区处于拉张背景, 与太平洋俯冲无关, 可能是加厚陆壳拆沉导致的陆壳伸展环境(Li, 2000; Wang et al., 2004, 2006, 2007)。大规模的岩浆与成矿作用主要与拆沉下地壳与地幔相互作用的结果。而Ling et al.(2009)等通过综合研究长江中下游岩浆岩、沉积盆地、构造应力等认为长江中下游在早白垩世受到Izanagi板块和太平洋板块中间的洋脊俯冲从而形成, 而Liu et al.(2010b)通过对比长江中下游含矿埃达克岩与郯庐南段不含矿埃达克岩的地球化学特征认为, 长江中下游埃达克岩主要与洋壳俯冲有关。
从抛刀岭含矿玢岩的岩石源区分析, 抛刀岭含矿玢岩可能形成于俯冲背景下地幔楔部分熔融并发生结晶分异的结果。结合锆石年代学特征, 该区甚至整个长江中下游地区146~135Ma时处于古太平洋俯冲背景下。随后发生的双峰式火山岩以及A型花岗岩(如花园巩岩体) 则是可能是在板片拉张背景下形成(Li et al., 2012)。
7 结论抛刀岭金矿英安玢岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为晚侏罗-早白垩世, 与长江中下游铜金成矿主成矿期一致。含矿英安玢岩显示与陆壳相似的地球化学特征, 且具有较高的氧逸度特征, 显示其与同时代的埃达克形成于同样的构造背景, 即古太平洋俯冲。因此, 抛刀岭金矿乃至整个长江中下游地区铜金矿床与太平洋俯冲有关, 其高氧逸度特征是铜金成矿的关键所在。
| [] | Ballard JR, Palin JM, Campbell IH. 2002. Relative oxidation states of magmas inferred from Ce (Ⅳ)/Ce (Ⅲ) in zircon: Application to porphyry copper deposits of northern Chile. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 144: 347–364. DOI:10.1007/s00410-002-0402-5 |
| [] | Chang YF, Liu XP, Wu YC. 1991. The Copper-Iron Belt of the Lower-Middle Research of the Changjiang River. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 294-312. |
| [] | Chen GG, Ying XX. 2002. Geological characteristics of the Puzhuang gold deposit in Guichi, Anhui Province. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 23(3): 213–216. |
| [] | Chen JF, John BM. 1999. Nd, Sr, Pb isotope tracing and crust evolution of Southeast China. Geochimica, 28(2): 127–140. |
| [] | Defant MJ, Drummond MS. 1990. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature, 347(6294): 662–665. DOI:10.1038/347662a0 |
| [] | Deng J, Wang QF, Xiao CH, Yang LQ, Liu H, Gong QJ, Zhang J. 2011. Tectonic-magmatic-metallogenic system, Tongling ore cluster region, Anhui Province, China. International Geology Review, 53(5-6): 449–476. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2010.501538 |
| [] | Deng JH, Yang XY, Sun WD, Huang Y, Chi YY, Yu LF, Zhang QM. 2012. Petrology, geochemistry, and tectonic significance of Mesozoic shoshonitic volcanic rocks, Luzong volcanic basin, eastern China. International Geology Review, 54(6): 714–736. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2011.580628 |
| [] | Dong S. 2006. Regional geochemical characteristics of Guichi area in Anhui Province and their ore-prospecting significance. Geochemical and Geochemical Exploration, 30(3): 215–223. |
| [] | Du YS, Qin XL, Tian SH. 2004. Mesozoic magmatic to hydrothermal process in the Tongguanshan ore field, Tongling, Anhui Province, China: Evidence from xenoliths and their hosts. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(2): 339–350. |
| [] | Du YS, Li ST, Cao Y, Qing XL, Lou YE. 2007. UAFC-related origin of the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous intrusions in the Tongguanshan ore field, Tongling, Anhui Province, East China. Geoscience, 21(1): 71–77. |
| [] | Gao S, Liu XM, Yuan HL, Hattendorf B, Gunther D, Chen L, Hu SH. 2002. Determination of forty two major and trace elements in USGS and NIST SRM glasses by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Geostandards Newsletter-the Journal of Geostandards and Geoanalysis, 26(2): 181–196. DOI:10.1111/ggr.2002.26.issue-2 |
| [] | Gilder SA, Keller GR, Luo M, Goodell PC. 1991. Timing and spatial-distribution of rifting in China. Tectonophysics, 197: 225–243. DOI:10.1016/0040-1951(91)90043-R |
| [] | Hu ZC, Gao S, Liu YS, Hu SH, Chen HH, Yuan HL. 2008. Signal enhancement in laser ablation ICP-MS by addition of nitrogen in the central channel gas. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 23(8): 1093–1101. DOI:10.1039/b804760j |
| [] | Li H, Zhang H, Ling MX, Wang FY, Ding X, Zhou JB, Yang XY, Tu XL, Sun WD. 2011. Geochemical and zircon U-Pb study of the Huangmeijian A-type granite: Implications for geological evolution of the Lower Yangtze River belt. International Geology Review, 53(5-6): 499–525. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2010.496202 |
| [] | Li H, Ling MX, Li CY, Zhang H, Ding X, Yang XY, Fan WM, Li YL, Sun WD. 2012. A-type granite belts of two chemical subgroups in central eastern China: Indication of ridge subduction. Lithos. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.09.021 |
| [] | Li JW, Zhao XF, Zhou MF, Ma CQ, de Souza ZS, Vasconcelos P. 2009. Late Mesozoic magmatism from the Daye region, eastern China: U-Pb ages, petrogenesis, and geodynamic implications. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 157(3): 383–409. DOI:10.1007/s00410-008-0341-x |
| [] | Li WD, Mao JR, Zhu YH, Xie HG. 1998. Mesozoic Volcanic Rocks and Deposits in Southeast China. Beijing: Seismic Press: 1-156. |
| [] | Li XH. 2000. Cretaceous magmatism and lithospheric extension in Southeast China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 18(3): 293–305. DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00060-7 |
| [] | Li XH, Long WG, Li QL, Liu Y, Zheng Y F, Yang YH, Chamberlain KR, Wan DF, Guo CH, Wang XC, Tao H. 2010. Penglai zircon megacrysts: A potential new working reference material for microbeam determination of Hf-O isotopes and U-Pb age. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 34(2): 117–134. DOI:10.1111/j.1751-908X.2010.00036.x |
| [] | Liang HY, Campbell IH, Allen CM, Sun WD, Liu CQ, Yu HX, Xie YW, Zhang YQ. 2006. Zircon Ce4+/Ce3+ ratios and ages for Yulong ore-bearing porphyries in eastern Tibet. Mineralium Deposita, 41: 152–159. DOI:10.1007/s00126-005-0047-1 |
| [] | Ling MX, Wang FY, Ding X, Hu YH, Zhou JB, Zartman RE, Yang XY, Sun WD. 2009. Cretaceous ridge subduction along the Lower Yangtze River Belt, eastern China. Economic Geology, 104(2): 303–321. DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.104.2.303 |
| [] | Liu YS, Hu ZC, Gao S, Günther D, Xu J, Gao CG, Chen HH. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34–43. DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 |
| [] | Liu YS, Hu ZC, Zong KQ, Gao CG, Gao S, Xu J, Chen HL. 2010a. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(15): 1535–1546. DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4 |
| [] | Liu SA, Li SG, He YS, Huang F. 2010b. Geochemical contrasts between early Cretaceous ore-bearing and ore-barren high-Mg adakites in central-eastern China: Implications for petrogenesis and Cu-Au mineralization. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(24): 7160–7178. DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2010.09.003 |
| [] | Ludwig KR. 2003. ISOPLOT 3.0: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication, 4: 1–70. |
| [] | Mao JW, Wang YT, Lehmann B, Yu JJ, Du AD, Mei YX, Li YF, Zang WS, Stein HJ, Zhou TF. 2006. Molybdenite Re-Os and albite40Ar/39Ar dating of Cu-Au-Mo and magnetite porphyry systems in the Yangtze River Valley and metallogenic implications. Ore Geology Reviews, 29(3-4): 307–324. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.11.001 |
| [] | Mao JW, Shao YJ, Xie GQ, Zhang JD, Chen YC. 2009. Mineral deposit model for porphyry-skarn polymetallic copper deposits in the Tongling ore cluster district of Middle-Lower Yangtze Valley metallogenic belt. Mineral Deposits, 28(2): 109–119. |
| [] | McDonough WF, Sun SS. 1995. The composition of the earth. Chemical Geology, 120(3-4): 223–253. DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4 |
| [] | Mungall JE. 2002. Roasting the mantle: Slab melting and the genesis of major Au and Au-rich Cu deposits. Geology, 30: 915–918. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0915:RTMSMA>2.0.CO;2 |
| [] | Pan YM, Dong P. 1999. The Lower Changjiang (Yangzi/Yangtze River) metallogenic belt, east central China: Intrusion-and wall rock-hosted Cu-Fe-Au, Mo, Zn, Pb, Ag deposits. Ore Geology Reviews, 15(4): 177–242. DOI:10.1016/S0169-1368(99)00022-0 |
| [] | Pearce JA, Harris NBW, Tindle AG. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25: 956–983. DOI:10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 |
| [] | Peccerillo R, Taylor SR. 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58: 63–81. DOI:10.1007/BF00384745 |
| [] | Qi L, Hu J, Gregoire DC. 2000. Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Talanta, 51: 507–513. DOI:10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5 |
| [] | Robert PR, Xiao L, Shimizu N. 2002. Experimental constrains on the origin of potassium rich adakites in eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 18(3): 293–302. |
| [] | Sillitoe RH. 1997. Characteristics and controls of the largest porphyry copper-gold and epithermal gold deposits in the circum-Pacific region. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 44: 373–388. DOI:10.1080/08120099708728318 |
| [] | Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in Oceanic Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345 |
| [] | Sun WD, Xie Z, Chen JF, Zhang X, Chai ZF, Du AD, Zhao JS, Zhang CH, Zhou TF. 2003. Os-Os dating of copper and molybdenum deposits along the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Economic Geology, 98(1): 175–180. |
| [] | Sun WD, Arculus RJ, Kamenetsky VS, Binns RA. 2004. Release of gold-bearing fluids in convergent margin magmas prompted by magnetite crystallization. Nature, 431: 975–978. DOI:10.1038/nature02972 |
| [] | Sun WD, Ding X, Hu YH, Li XH. 2007. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the west Pacific. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 262(3-4): 533–542. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.08.021 |
| [] | Sun WD, Ling MX, Yang XY, Fan W M, Ding X, Liang HY. 2010. Ridge subduction and porphyry copper-gold mineralization: An overview. Science China (Earth Sciences), 53(4): 475–484. DOI:10.1007/s11430-010-0024-0 |
| [] | Sun WD, Zhang H, Ling MX, Ding X, Chung SL, Zhou JB, Yang XY, Fan WM. 2011. The genetic association of adakites and Cu-Au ore deposits. International Geology Review, 53(5-6): 691–703. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2010.507362 |
| [] | Tian PF, Yang XY, Yuan WM, Liu HT, Xue B. 2012. Fission track dating on the Paodaoling gold deposit in the middle-lower Yangtze River metallogenic belt: Its significance to tectonic setting. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(3): 400–409. |
| [] | Tao KY, Mao JR, Yang ZL, Zhao Y, Xing GF, Xue HM. 1998. Mesozoic Preto-tectonic associations and record of the geodynamic processes in Southeast China. Earth Science Frontiers, 5(4): 183–192. |
| [] | Wang Q, Zhao ZH, Bao ZW, Xu JF, Liu W, Li CF, Bai ZH, Xiong XL. 2004. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Tongshankou and Yinzu adakitic intrusive rocks and the associated porphyry copper-molybdenum mineralization in Southeast Hubei, East China. Resource Geology, 54(2): 137–152. DOI:10.1111/rge.2004.54.issue-2 |
| [] | Wang Q, Zhao ZH, Xu JF, Bai ZH, Wang JX, Liu CX. 2004. The geochemical comparison between the Tongshankou and Yinzu adakitic intrusive rocks in Southern Hubei: (Delaminated) lower crustal melting and the genesis of porphyry copper deposit. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(2): 351–360. |
| [] | Wang Q, Wyman DA, Xu JF, Zhao ZH, Jian P, Xiong XL, Bao ZW, Li CF, Bai ZH. 2006. Petrogenesis of Cretaceous adakitic and shoshonitic igneous rocks in the Luzong area, Anhui Province (eastern China): Implications for geodynamics and Cu-Au mineralization. Lithos, 89(3-4): 424–446. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2005.12.010 |
| [] | Wang Q, Wyman DA, Xu JF, Zhao ZH, Jian P, Zi F. 2007. Partial melting of thickened or delaminated lower crust in the middle of eastern China: Implications for Cu-Au mineralization. Journal of Geology, 115(2): 149–161. DOI:10.1086/510643 |
| [] | Wang FY, Ling MX, Ding X, Hu YH, Zhou JB, Yang XY, Liang HY, Fan WM, Sun WD. 2011. Mesozoic large magmatic events and mineralization in SE China: Oblique subduction of the Pacific plate. International Geology Review, 53: 704–726. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2010.503736 |
| [] | Wiedenbeck M, Allé P, Corfu F, Griffin WL, Meier M, Oberli F, von Quadt A, Roddick JC, Spiegel W. 1995. Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace element and REE analyses. Geostandards Newsletter, 19(1): 1–23. DOI:10.1111/ggr.1995.19.issue-1 |
| [] | Winchester JA, Floyd PA. 1976. Geochemical magma type discriminations: Application to altered and metamorphosed basic igneous rocks. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 28: 459–469. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(76)90207-7 |
| [] | Wu FY, Ji WQ, Sun DH, Yang YH, Li XH. 2012. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions of the Mesozoic granites in southern Anhui Province, China. Lithos. |
| [] | Xie GQ, Mao JW, Li RL, Bierlein FP. 2008. Geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotopic studies of Late Mesozoic granitoids in the southeastern Hubei Province, Middle-Lower Yangtze River belt, Eastern China: Petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Lithos, 104(1-4): 216–230. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.008 |
| [] | Xie GQ, Mao J, Zhao HJ. 2011. Zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic intrusions in the southeast Hubei Province, Middle-Lower Yangtze River belt (MLYRB), East China. Lithos, 125(1-2): 693–710. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.04.001 |
| [] | Xie JC, Yang XY, Sun WD, Du JG, Xu W, Wu LB, Wang KY, Du XW. 2009. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on formation of the Tongling metal deposits, Middle Yangtze metallogenic belt, east-central China. International Geology Review, 51(5): 388–421. DOI:10.1080/00206810802712004 |
| [] | Xie JC, Yang XY, Xiao YL, Du JG, Sun WD. 2012. Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic intrusive rocks from the Tongling ore cluster region: The metallogenic significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(3): 423–459. |
| [] | Xing FM, Xu X. 1995. Characteristics of Mesozoic igneous rocks along the Yangtze River in Anhui Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 11(4): 409–422. |
| [] | Xu JF, Wang Q, Xu YG, Zhao ZH, Xiong XL. 2001. Geochemistry of Anjishan intermediate-acid intrusive rocks in Ningzhen area: Constraint to origin of the magma with HREE and Y depletion. Acta Geologica Sinica, 17(4): 576–584. |
| [] | Xu JF, Shinjo R, Defant MJ, Wang Q, Rapp RP. 2002. Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of east China: Partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust?. Geology, 30(12): 1111–1114. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1111:OOMAIR>2.0.CO;2 |
| [] | Yang XY, Lee IS. 2011. Review of the stable isotope geochemistry of Mesozoic igneous rocks and Cu-Au deposits along the Middle-Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt, China. International Geology Review, 53(5-6): 741–757. DOI:10.1080/00206814.2010.533881 |
| [] | Yu CH, Yuan XM. 1999. The petrochemical and geochemical characteristics of the Tongshan intrusive, Guichi. Geology of Anhui, 9(3): 194–198. |
| [] | Yu CH. 2001. Study on the genesis of Tongshan copper ore deposit in Guichi. Geology and Prospecting, 37(2): 112–116. |
| [] | Zhai YS, Yao SZ, Lin XD, Zhou XR, Wan TF, Jin FQ, Zhou ZG. 1992. Metallogeny of Iron and Copper Deposits in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Region. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-194. |
| [] | Zhang ZY, Du YS, Zhang J, Pang ZH. 2011. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronology, petrochemical and geochemical characteristics of Tongshan intrusion in Guichi, Anhui Province. Geological Review, 57(3): 366–378. |
| [] | Zhao DK, Wang MS, Zhu YS, Fang M. 2009. Geological features and genesis of the Paodaoling gold ore deposit, Guichi, Anhui Province. Geology of Anhui, 19(2): 107–110. |
| [] | Zhou SG. 2003. Matter source of the Tongshan deposit and its mineralization. Mineral Resources and Geology, 17(5): 610–612. |
| [] | Zhou TF, Fan Y, Yuan F, Lu SM, Shang SG, David C, Sebastien M, Zhao GC. 2008. Geochronology of the volcanic rocks in the Lu-Zong basin and its significance. Science in China (Series D), 51(10): 1470–1482. DOI:10.1007/s11430-008-0111-7 |
| [] | Zhou TF, Fan Y, Yuan F. 2008. Advances on petrogensis and metallogeny study of the mineralization belt of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River area. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(8): 1665–1678. |
| [] | Zhu G, Liu GS, Niu ML, Song CZ, Wang DX. 2003. Transcurrent movement and genesis of the Tan-Lu fault zone. Geological Bulletin of China, 22(3): 200–207. |
| [] | 常印佛, 刘湘培, 吴言昌. 1991. 长江中下游铜铁成矿带. 北京: 地质出版社: 294-312. |
| [] | 陈国光, 应祥熙. 2002. 安徽省贵池铺庄金矿地质特征. 地球学报, 23(3): 213–216. |
| [] | 陈江峰, 江博明. 1999. Nd, Sr, Pb同位素示踪和中国东南大陆地壳演化. 地球化学, 28(2): 127–140. |
| [] | 董胜. 2006. 安徽省贵池地区区域地球化学特征及找矿意义. 物探与化探, 30(3): 215–223. |
| [] | 杜杨松, 秦新龙, 田世洪. 2004. 安徽铜陵铜官山矿区中生代岩浆-热液过程:来自岩石包体及其寄主岩的证据. 岩石学报, 20(2): 339–350. |
| [] | 杜杨松, 李顺庭, 曹毅, 秦新龙, 楼亚儿. 2007. 安徽铜陵铜官山矿区中生代侵入岩的形成过程-岩浆底侵、同化混染和分离结晶. 现代地质, 21(1): 71–77. |
| [] | 毛景文, 邵拥军, 谢桂青, 张建东, 陈毓川. 2009. 长江中下游成矿带铜陵矿集区铜多金属矿床模型. 矿床地质, 28(2): 109–119. |
| [] | 陶奎元, 毛建仁, 杨祝良, 赵宇, 邢光福, 薛怀民. 1998. 中国东南部中生代岩石构造组合和复合动力学过程的记录. 地学前缘, 5(4): 183–192. |
| [] | 田朋飞, 杨晓勇, 袁万明, 刘海涛, 薛斌. 2012. 长江中下游成矿带抛刀岭金矿裂变径迹研究及大地构造意义. 地质学报, 86(3): 400–409. |
| [] | 王强, 赵振华, 许继峰, 白正华, 王建新, 刘成新. 2004. 鄂东南铜山口、殷祖埃达克质(adakitic) 侵入岩的地球化学特征对比:(拆沉) 下地壳熔融与斑岩铜矿的成因. 岩石学报, 20(2): 351–360. |
| [] | 谢建成, 杨晓勇, 肖益林, 杜建国, 孙卫东. 2012. 铜陵矿集区中生代侵入岩成因及成矿意义. 地质学报, 86(3): 423–459. |
| [] | 邢凤鸣, 徐祥. 1995. 安徽沿江地区中生代岩浆岩的基本特点. 岩石学报, 11(4): 409–422. |
| [] | 许继峰, 王强, 徐义刚, 赵振华, 熊小林. 2001. 宁镇地区中生代安基山中酸性侵入岩的地球化学:亏损重稀土和钇的岩浆产生的限制. 岩石学报, 17(4): 576–584. |
| [] | 俞沧海, 袁小明. 1999. 贵池铜山岩体岩石化学与地球化学特征. 安徽地质, 9(3): 194–198. |
| [] | 俞沧海. 2001. 贵池铜山铜矿床成因探讨. 地质与勘探, 37(2): 12–16. |
| [] | 翟裕生, 姚书振, 林新多, 周珣若, 万天丰, 金福全, 周宗桂. 1992. 长江中下游地区铜(金) 成矿规律. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-194. |
| [] | 张智宇, 杜杨松, 张静, 庞振山. 2011. 安徽贵池铜山岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学与岩石地球化学特征研究. 地质论评, 57(3): 366–378. |
| [] | 赵德奎, 汪梅生, 朱永胜, 方梅. 2009. 安徽省责池撼刀岭金矿地质特征及成因. 安徽地质, 19(2): 107–110. |
| [] | 周曙光. 2003. 安徽铜山矿床成矿物质来源及成矿作用探讨. 矿床与地质, 17(5): 610–612. |
| [] | 周涛发, 范裕, 袁峰. 2008. 长江中下游成矿带成岩成矿作用研究进展. 岩石学报, 24(8): 1665–1678. |
| [] | 朱光, 刘国生, 牛曼兰, 宋传中, 王道轩. 2003. 郯庐断裂带的平移运动与成因. 地质通报, 22(3): 200–207. |
 2012, Vol. 28
2012, Vol. 28


