文章信息
- 陶月佳, 赵媛, 李冰, 徐远义, 黄允宁
- Tao Yuejia, Zhao Yuan, Li Bing, Xu Yuanyi, Huang Yunning
- 胃癌中EIF4A3的表达及临床意义
- Expression of EIF4A3 in gastric cancer and its clinical significance
- 实用肿瘤杂志, 2022, 37(2): 146-153
- Journal of Practical Oncology, 2022, 37(2): 146-153
基金项目
- 宁夏回族自治区重点研发项目(2019BEG03007);宁夏自然科学基金项目(2020A0597)
-
通信作者
-
徐远义,E-mail:nxxyy@hotmail.com
黄允宁,E-mail:nxhyncc@126.com
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2021-04-19
2. 宁夏回族自治区人民医院胃肠外科,宁夏回族自治区 银川 750002
2. Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750002, China
胃癌是全球常见的恶性肿瘤之一,东亚地区尤为高发。由于早期症状不明显,胃癌发现时多为进展期,导致其预后极差[1]。目前,胃癌患者的治疗方式包括手术、放疗、化疗、生物治疗和靶向治疗等,然而胃癌患者5年生存率仍然很低[2]。因此,发现胃癌新的诊断标志物和探讨其潜在的调控机制对胃癌患者的诊治尤为重要。
真核生物起始因子4A-3(eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-Ⅲ,EIF4A3)是一种Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp盒家族的三磷酸腺苷(adenosine triphosphate,ATP)依赖性RNA解旋酶,在mRNA剪接、转运、翻译和监控中起着重要作用。EIF4A3的功能复杂而重要,其结构和功能异常导致下游生物效应的变化[3]。既往研究表明,EIF4A3在多种常见恶性肿瘤中的转录水平表达上调[4]。本研究拟通过生物信息学分析EIF4A3在不同肿瘤中的表达情况及其与胃癌患者临床病理特征的关系,通过实时荧光定量PCR(quantitative PCR,qPCR)、免疫组织化学和Western blot实验检测EIF4A3在胃癌组织及胃癌细胞株中的表达水平,进一步通过生物信息学分析EIF4A3与肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α)/核因子κB(nuclear factor kappa-B,NF-κB)信号通路中TNF和NF-κB亚单位1(NF-κB subunit 1,NFKB1)的相关性,探讨EIF4A3在胃癌发生和发展中的作用机制,从而为胃癌的诊治寻找潜在的靶点。
1 资料与方法 1.1 一般资料收集2020年1月至2020年11月在宁夏回族自治区人民医院经手术治疗的29例胃癌患者的胃癌组织和癌旁组织样本。所有患者均经病理证实为胃癌,术前未进行放疗、化疗或免疫治疗。患者年龄48~73岁,平均年龄64.5岁,其中男性17例,女性12例。所有患者均书面知情同意。本研究通过宁夏回族自治区人民医院伦理委员会批准。
1.2 生物信息学分析EIF4A3在胃癌和其他肿瘤中的表达水平2021年4月使用Tumor Immune Estimation Resource(TIMER)数据库(https://cistrome.shinyapps.io/timer/)分析EIF4A3 mRNA在不同肿瘤中的表达情况。2021年4月通过用癌症基因组图谱(The Cancer Genome Atlas,TCGA)数据库可视化工具Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis(GEPIA)(https://gepia.camcer-pku.cn/)分析EIF4A3 mRNA在胃癌组织及癌旁组织中的表达情况,阈值由肿瘤组织相对于正常组织mRNA表达的差异表达倍数来定义,参数如下:P < 0.05,差异倍数(fold change,FC) > 2。2021年4月NCBI数据库(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)分析EIF4A3在正常组织中的表达水平。2021年4月UCLCAN数据库(http://ualcan.path.uab.edu/)分析EIF4A3与胃癌患者临床病理特征的关系。2021年4月KM plotter数据库(http://www.kmplot.com/)分析EIF4A3对胃癌患者预后的影响。2021年4月通过Starbase v3.0数据库(http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/)分析EIF4A3与TNF-α/NF-κB信号通路中TNF和NFKB1的相关性。
1.3 细胞培养胃癌细胞株HGC-27、MKN-45和AGS以及正常胃上皮细胞株GES-1购自中国科学院细胞库(上海)。所有细胞使用RPMI-1640培养液(Gibco,美国)加5%胎牛血清(Gibco,美国),1×青霉素/链霉素(碧云天公司,上海)培养,置于含5%CO2 37℃培养箱中。
1.4 免疫组织化学染色石蜡包埋组织切成4 μm切片,用二甲苯和乙醇脱蜡。切片置于柠檬酸钠溶液中进行抗原修复,用PBS冲洗3次,每次10 min,0.3% H2O2阻断内源性过氧化物酶活性,胎牛血清封闭1 h,1∶400 EIF4A3一抗(Proteintech,17504-1-AP,武汉)孵育,4℃过夜。二抗孵育1 h。DAB(ZSGB-BIO,北京)对组织进行显色后,用苏木精(ZSGB-BIO,北京)对比染色。对脱水后的组织封闭,在显微镜下观察并拍照分析。
1.5 细胞免疫荧光将14 mm细胞爬片置于12孔培养板中,将细胞消化和重悬后接种于细胞爬片上,在5%CO2 37℃培养箱中培养48 h后,取出12孔板,去除培养液,PBS洗涤细胞3次,每次10 min。室温下,4%多聚甲醛固定细胞15 min。0.5% TritonX-100通透20 min,胎牛血清封闭1 h,EIF4A3一抗(1∶50)孵育,4℃过夜,山羊抗兔荧光二抗(Proteintech,武汉)37℃温箱中孵育1 h,滴加DAPI(ZSGB-BIO,北京)封固,应用Image-Pro Plus图像分析软件,在200和400倍镜下随机选取5个视野,获得所选视野的平均吸光度值。
1.6 Western blot使用RIPA缓冲液(Beyotime,上海)裂解细胞和人胃癌及癌旁组织,提取蛋白,使用BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(KeyGEN Biotech,南京)测定蛋白浓度。细胞裂解液在SDS-PAGE凝胶上电泳,转移至PVDF膜(Millipore,美国)上。10%脱脂牛奶封闭2 h,EIF4A3抗体(1∶1 000)孵育,4℃过夜。细胞总蛋白以β-tubulin(MultiSciences,杭州)作为内参对照,组织总蛋白以β-actin(Affinity Bioscience,南京)作为内参对照。山羊抗兔IgG二抗(ThermoFisher Scientific,美国)室温孵育PVDF膜1 h,使用ECL(ThermoFisher Scientific,美国)试剂化学发光。最后保存图像结果并计算灰度值。
1.7 RNA提取和RT-qPCR所有RNA提取使用TRIzol试剂(ThermoFisher Scientific,美国),按照说明书进行RNA提取,检测RNA浓度后,使用PrimeScript试剂(TaKaRa,RR036A,日本)反转录成cDNA(反应条件为42℃1 h,72℃10 min)。以100 ng的cDNA为模板,按荧光定量试剂盒SYBR Green Master Mix(TaKaRa,RR820A,日本)说明书步骤,在7500实时PCR系统(Applied Biosystems,美国)进行实时定量反转录聚合酶链反应(反应条件为95℃10 min,95℃15 s,64℃15 s,72℃30 s处检测信号,循环40次; 在65℃~95℃,每升高1℃收集1次荧光信号,作溶解曲线)。同时,以GAPDH作为内参,2-ΔΔct表示目的基因mRNA相对表达水平。ΔCT=CT目的基因-CT管家基因,ΔΔCT=ΔCT实验组-ΔCT对照组。引物由北京生工生物公司合成,序列如下:EIF4A3上游引物为3’-ATCGCACAGTCAGTCCGG-5’,下游引物为3’-AGCCCCTTCTGGATCTGCAC-5’; GAPDH上游引物为3’-TGTGGGCATCAATGGATTGG-5’,下游引物为3’-ACACCATGTATTCCGGGTCAAT-5’。
1.8 统计学分析采用SPSS 23.0统计学软件和GraphPad Prism 8.0软件进行数据分析。实验结果至少来自3个独立实验。组间比较采用独立样本t检验。以P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
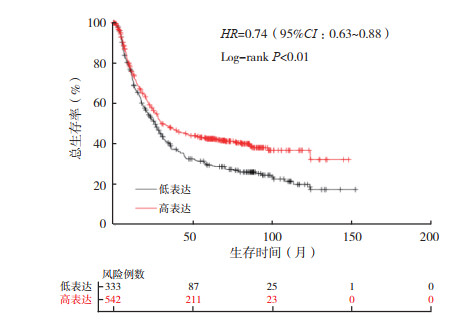
2 结果 2.1 EIF4A3在不同肿瘤中的表达情况通过TIMER数据库中的“Different Expression”模块分析EIF4A3 mRNA在不同肿瘤中的表达水平显示,EIF4A3 mRNA在乳腺癌、胆管癌、食管癌和肝癌等肿瘤中表达上调(均P < 0.05,图 1)。NCBI数据库分析EIF4A3 mRNA在正常组织中的表达水平显示,EIF4A3 mRNA在食管、胃和结肠等组织中低表达(图 2)。通过GEPIA数据库(http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/)“Expression DIY”模块分析EIF4A3在胃癌与癌旁组织中的表达,结果显示EIF4A3在胃癌组织中相对高表达(P < 0.05,图 3)。同时,通过UALCAN数据库分析显示,在年龄、肿瘤分期、肿瘤分级和淋巴结转移的亚组分析中,胃癌患者EIF4A3的转录水平均高于健康对照组(P < 0.01,图 4A~4D)。通过KM plotter数据库分析EIF4A3对胃癌患者总生存的影响,结果显示EIF4A3的表达状态(分类变量)与患者总生存时间相关(HR=0.74,95%CI:0.63~0.88,P < 0.01,图 5)。
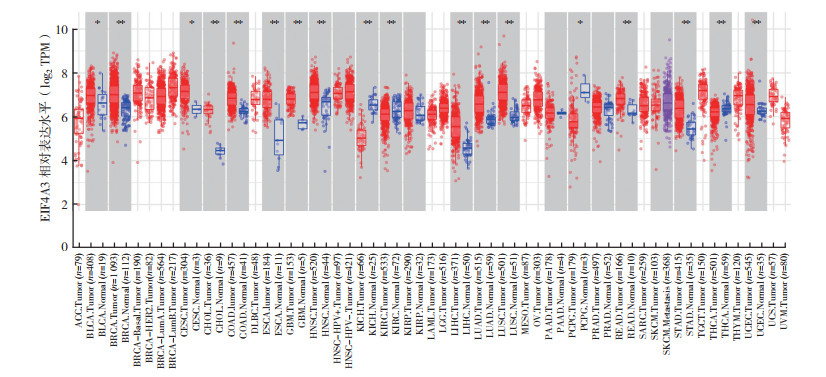
|
| 注 EIF4A3:真核生物起始因子4A-3(eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-Ⅲ); TPM:transcripts per million; ACC:腺样囊性癌(adenoid cystic carcinoma); BLCA:膀胱癌(bladder cancer); BRCA:乳腺癌(breast cancer); CESC:子宫颈鳞状细胞癌(cervical squamous cell carcinoma); CHOL:胆管癌(cholangiocarcinoma); COAD:结肠腺癌(colon adenocarcinoma); DLBC:弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤(lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B-cell lymphoma); ESCA:食管癌(esophageal carcinoma); GBM:多形成性胶质细胞瘤(glioblastoma multiforme); HNSC:头颈鳞状细胞癌(head and neck squamous cell carcinoma); KICH:肾嫌色细胞癌(kidney chromophobe); KIRC:肾透明细胞癌(kidney renal clear cell carcinoma); KIRP:肾乳头状细胞癌(kidney renal papillary carcinoma); LAML:急性髓细胞样白血病(acute myeloid leukemia); LGG:脑-低级别胶质瘤(brain lower grade glioma); LIHC:肝细胞肝癌(liver hepatocellular carcinoma); LUAD:肺腺癌(lung adenocarcinoma); LUSC:肺鳞癌(lung squamous cell carcinoma); OV:卵巢浆液性囊腺癌(ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma); PAAD:胰腺癌(pancreatic adenocarcinoma); PCPG:嗜铬细胞瘤和副神经节瘤(pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma); PRAD:前列腺癌(prostate adenocarcinoma); PEAD:直肠腺癌(rectum adenocarcinoma); SARC:肉瘤(sarcoma); SKCM:皮肤黑色素瘤(skin cutaneous melanoma); STAD:胃腺癌(stomach adenocarcinoma); TGCT:睾丸癌(testicular germ cell tumor); THCA:甲状腺癌(thyroid carcinoma); THYM:胸腺癌(thymoma); UCEC:子宫内膜癌(uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma); UCS:子宫肉瘤(uterine carcinosarcoma); UVM:葡萄膜黑色素瘤(uveal melanoma); *P < 0.05;**P < 0.01 图 1 TIMER数据库中EIF4A3在不同肿瘤中的相对表达水平 Fig.1 Relative expression of EIF4A3 in different tumors in TIMER database |
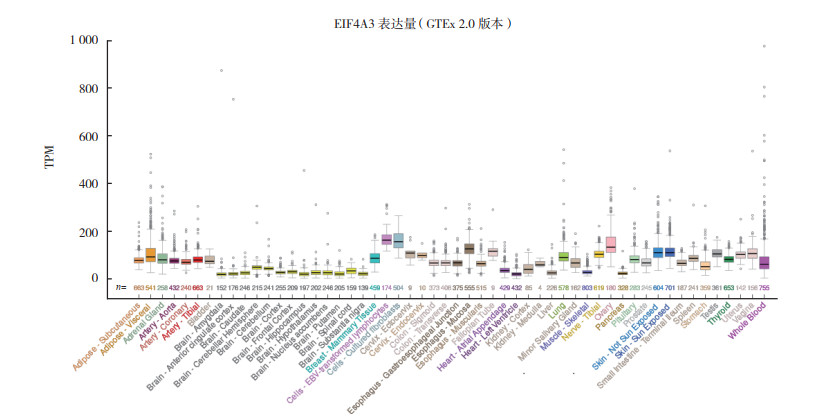
|
| 注 EIF4A3:真核生物起始因子4A-3(eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-Ⅲ); TPM:transcripts per million 图 2 通过NCBI数据库分析EIF4A3在正常组织中的表达情况 Fig.2 Expression of EIF4A3 in normal tissues analyzed by NCBI database |
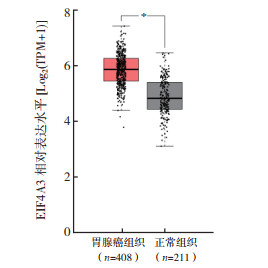
|
| 注 EIF4A3:真核生物起始因子4A-3(eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-Ⅲ); TPM:transcripts per million; *P < 0.05 图 3 GEPIA分析EIF4A3在胃癌中的相对表达水平 Fig.3 Relative expression of EIF4A3 in gastric cancer analyzed by GEPIA |
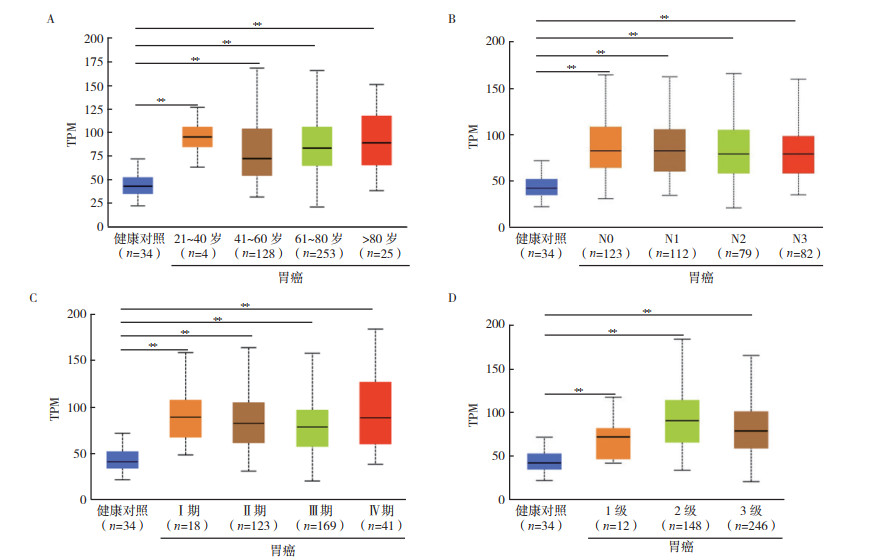
|
| 注 A:年龄亚组胃癌患者中EIF4A3表达水平; B:淋巴结转移亚组胃癌患者中EIF4A3表达水平; C:肿瘤分期亚组胃癌患者中EIF4A3表达水平; D:肿瘤分级亚组胃癌患者中EIF4A3表达水平; TCGA:癌症基因组图谱(The Cancer Genome Atlas); EIF4A3:真核生物起始因子4A-3(eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-Ⅲ); TPM:transcripts per million; **P < 0.01 图 4 TCGA样本中根据年龄、淋巴结转移、肿瘤分期和肿瘤分级分层的胃癌患者亚组中EIF4A3转录水平比较(UALCAN) Fig.4 Comparison of EIF4A3 transcription in patients with gastric cancer stratified by age, lymph node metastasis, tumor stage and grades in TCGA database (UALCAN |
|
| 图 5 KM plotter数据库分析EIF4A3表达对胃癌患者总生存的影响 Fig.5 Influence of EIF4A3 expression on the overall survival of gastric cancer patients analyzed by KM plotter database |
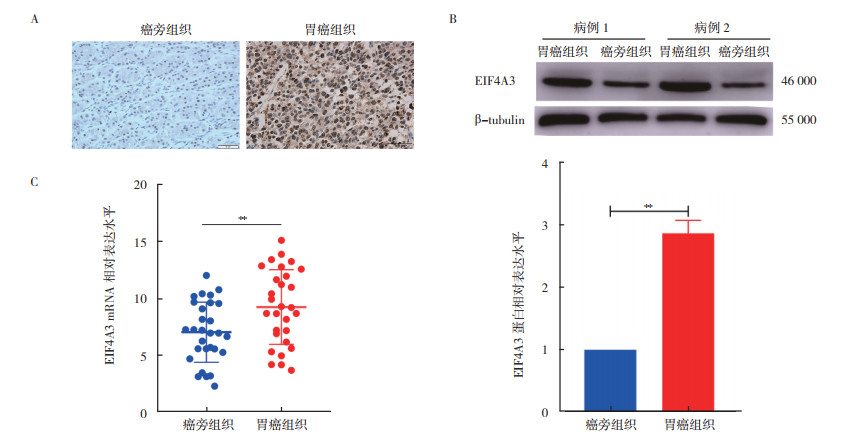
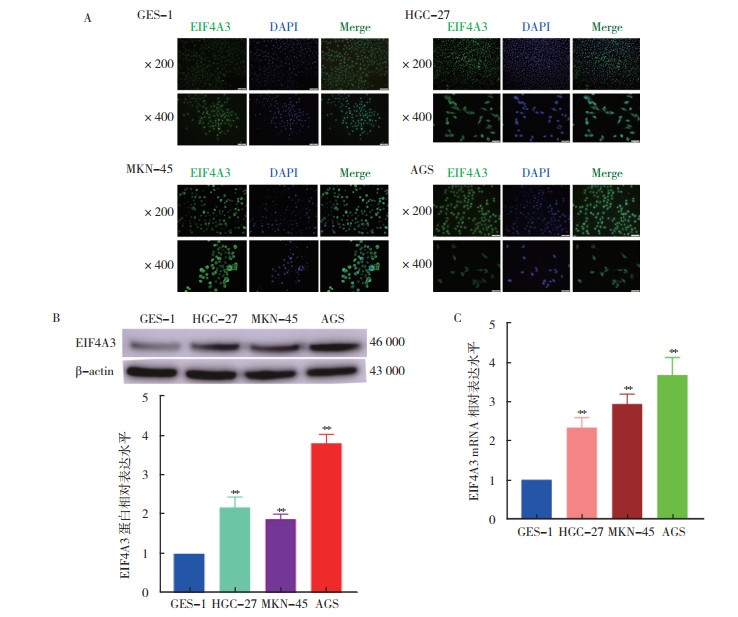
通过免疫组织化学、Western blot和RT-qPCR检测显示,胃癌组织中EIF4A3 mRNA和蛋白表达均较癌旁组织升高(均P < 0.05,图 6)。细胞免疫荧光、Western blot和RT-qPCR检测显示,HGC-27、MKN-45和AGS胃癌细胞中EIF4A3 mRNA和蛋白表达水平均高于正常胃上皮细胞GES-1(均P < 0.05,图 7)。
|
| 注 A:免疫组织化学染色检查结果(EnVision×400);B:Western blot检测结果; C:RT-qPCR检测结果; EIF4A3:真核生物起始因子4A-3(eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-Ⅲ); **P < 0.01 图 6 EIF4A3在胃癌组织中高表达 Fig.6 EIF4A3 highly expressed in gastric cancer |
|
| 注 A:细胞免疫荧光检测结果; B:Western blot检测结果; C:RT-qPCR检测结果; EIF4A3:真核生物起始因子4A-3(eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-Ⅲ); **P < 0.01 图 7 EIF4A3在胃癌细胞株中的表达 Fig.7 Expression of EIF4A3 in gastric cancer cells |
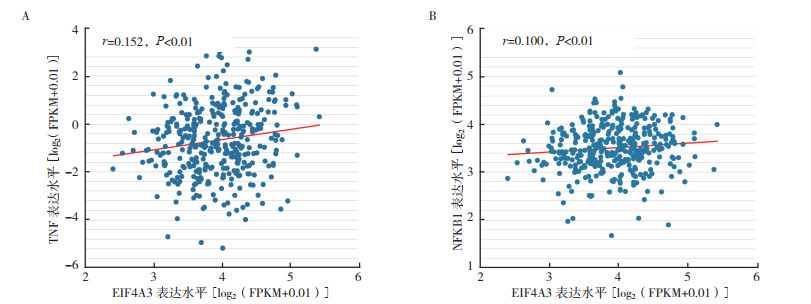
通过Starbase v3.0数据库(http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/)“RNA-RNA CoExpression”模块分析EIF4A3与TNF和NFKB1的相关性显示,EIF4A3与TNF和NFKB1均呈正相关(r=0.152,P < 0.01;r=0.100,P < 0.01;图 8A~8B)。
|
| 注 A:胃腺癌中EIF4A3与TNF表达的相关性; B:胃腺癌中EIF4A3与NFKB1的相关性; NFKB1:核因子κB亚单位1(nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1);FPKM:每千碱基外显子的片段数每绘制的百万片段数(fragments per kilobase of exon per million fragments mapped); EIF4A3:真核生物起始因子4A-3(eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-Ⅲ); TNF:肿瘤坏死因子(tumor necrosis factor) 图 8 Starbase数据库分析胃腺癌中EIF4A3与TNF和NFKB1的相关性 Fig.8 Correlation between EIF4A3 level and the expression of TNF and NFKB1 in gastric adenocarcinoma analyzed by Starbase database |
胃癌发病率高,早期诊断率低,预后差[5]。寻找新的胃癌诊断标志物尤为重要。EIF4A3是外显子连接复合体(exon-junction complex helicase,EJC)的核心成分[6],广泛参与RNA剪接和无义介导的mRNA降解[4]。既往研究表明,EIF4A3在神经肌肉退行性病变中发生突变,并在多种肿瘤中差异表达[7-9]。肝癌组织中EIF4A3表达上调,并且EIF4A3高表达与预后不良相关[10]。EIF4A3在卵巢癌组织中也表达上调[11]。EIF4A3与细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶1(cyclin-dependent kinase 1,CDK1)、CDK2、肿瘤相关转录因子、趋化因子信号通路和剪接体信号通路等的表达密切相关[12-13]。同时,EIF4A3也被报道参与细胞周期调控和凋亡[14],如EIF4A3在细胞周期中发挥作用,通过使用化合物或基因干扰技术抑制细胞中的EIF4A3的表达可减少G2/M期的细胞周期阻滞,进而促进细胞凋亡[15],因此,EIF4A3在癌症进展中发挥着复杂而广泛的作用。EIF4A3通过影响TNF-α/NF-κB信号通路的异常激活,从而促进肿瘤的发生和发展[4]。越来越多的证据表明,TNF-α/NF-κB信号通路与多种癌症相关[16-17],如子宫颈癌和前列腺癌的细胞增殖、迁移、凋亡和血管生成等[18]。
本研究通过生物信息学分析发现,EIF4A3在包括胃癌在内的多种类型肿瘤中表达上调,并且胃癌患者EIF4A3的转录水平在年龄、淋巴结转移、肿瘤分期和肿瘤分级的亚组分析中均高于健康人群。运用RT-qPCR、Western blot、细胞免疫荧光和免疫组织化学方法检测胃癌和癌旁组织以及胃癌细胞株和正常胃上皮细胞中EIF4A3 mRNA和蛋白的表达显示,EIF4A3在胃癌组织和胃癌细胞中均高表达,与生物信息学分析结果一致。进一步生物信息学分析发现,EIF4A3与TNF-α/NF-κB信号通路中的TNF和NFKB1呈正相关(r=0.152,P < 0.01;r=0.100,P < 0.01),提示EIF4A3可能参与TNF-α/NF-κB信号通路的激活。这些结果显示,EIF4A3可能参与胃癌发生和发展的调控。生物信息学分析具有其局限性:(1)胃癌样本中Ⅳ期患者较少,而临床实践中多数胃癌患者是在疾病进展期和预后极差的情况下首次诊断的,因此,本研究成果需在临床样本中得到验证; (2)转录组测序只能检测到转录组静态变化,不能直接提供其表达水平和蛋白质活性的信息。这些问题将在后续研究中得到解决。
综上所述,EIF4A3在胃癌组织和胃癌细胞株中高表达; 其发挥促癌的作用机制可能是通过激活TNF-α/NF-κB信号通路调控胃癌的发生和发展。这为研究EIF4A3在胃癌中的作用机制提供一定的理论基础。明确EIF4A3在胃癌中所起的作用和具体分子机制尚需要进一步的实验,展开更深入的研究,从而为胃癌的早期诊断、临床治疗和预后指导提供思路。
| [1] |
Tan Z. Recent advances in the surgical treatment of advanced gastric cancer: a review[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 3537-3541. DOI:10.12659/MSM.916475 |
| [2] |
柏玉蓉, 陆一丹, 孙杨承, 等. 预防性腹腔热灌注化疗治疗进展期胃癌临床疗效的meta分析[J]. 实用肿瘤杂志, 2021, 36(4): 306-313. |
| [3] |
Lin Y, Zhang J, Cai J, et al. Systematic analysis of gene expression alteration and co-expression network of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-3 in cancer[J]. J Cancer, 2018, 9(4): 4568-4577. |
| [4] |
Zhu Y, Ren C, Yang L. Effect of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A3 in malignant tumors[J]. Oncol Lett, 2021, 21(5): 358. DOI:10.3892/ol.2021.12619 |
| [5] |
樊启林, 刘红利. 晚期胃癌的免疫检查点抑制剂研究进展[J]. 实用肿瘤杂志, 2020, 35(6): 479-485. |
| [6] |
Gehring NH, Lamprinaki S, Kulozik AE, et al. Disassembly of exon junction complexes by PYM[J]. Cell, 2009, 137(3): 536-548. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.042 |
| [7] |
Tang W, Wang D, Shao L, et al. LINC00680 and TTN-AS1 stabilized by EIF4A3 promoted malignant biological behaviors of glioblastoma cells[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2020, 19(3): 905-921. |
| [8] |
Nakao S, Nogami M, Iwatani M, et al. Identification of a selective DDX3X inhibitor with newly developed quantitative high-throughput RNA helicase assays[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 523(3): 795-801. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.12.094 |
| [9] |
Han D, Gao X, Wang M, et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 indicates a poor prognosis of colorectal cancer and promotes tumor growth by recruiting and binding to eIF4A3[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(16): 22159-22173. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.8063 |
| [10] |
Lin Y, Liang R, Mao Y, et al. Comprehensive analysis of biological networks and the eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-3 gene as pivotal in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2020, 121(10): 4094-4107. DOI:10.1002/jcb.29596 |
| [11] |
Zhang S, Leng T, Zhang Q, et al. Sanguinarine inhibits epithelial ovarian cancer development via regulating long non-coding RNA CASC2-EIF4A3 axis and/or inhibiting NF-κB signaling or PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 102(3): 302-308. |
| [12] |
Ryu I, Won YS, Ha H, et al. eIF4A3 phosphorylation by CDKs affects NMD during the cell cycle[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 26(8): 2126-2139. DOI:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.101 |
| [13] |
Zheng X, Huang M, Xing L, et al. The circRNA circSEPT9 mediated by E2F1 and EIF4A3 facilitates the carcinogenesis and development of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 73. DOI:10.1186/s12943-020-01183-9 |
| [14] |
Kanellis DC, Espinoza JA, Zisi A, et al. The exon-junction complex helicase eIF4A3 controls cell fate via coordinated regulation of ribosome biogenesis and translational output[J]. Sci Adv, 2021, 7: eabf7561. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.abf7561 |
| [15] |
Mazloomian A, Araki S, Ohori M, et al. Pharmacological systems analysis defines EIF4A3 functions in cell-cycle and RNA stress granule formation[J]. Commun Biol, 2019, 2(3): 165. |
| [16] |
Bai L, Sun W, Han Z, et al. CircSND1 regulated by TNF-α promotes the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2021, 13(13): 259-275. |
| [17] |
Lei Q, Gu H, Li L, et al. TNIP1-mediated TNF-α/NF-κB signalling cascade sustains glioma cell proliferation[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24(1): 530-538. |
| [18] |
Mu HQ, He YH, Wang SB, et al. MiR-130b/TNF-α/NF-κB/VEGFA loop inhibits prostate cancer angiogenesis[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2020, 22(1): 111-121. |
 2022, Vol. 37
2022, Vol. 37


