文章信息
- 李国盛, 何融泉, 周华富, 孔晋亮, 陈罡
- Li Guosheng, He Rongquan, Zhou Huafu, Kong Jinliang, Chen Gang
- 血液中低表达的微小RNA let-7b-5p对非小细胞肺癌的诊断价值
- Diagnostic value of lowly expressed microRNA let-7b-5p in blood for non-small-cell lung cancer
- 实用肿瘤杂志, 2023, 38(6): 558-565
- Journal of Practical Oncology, 2023, 38(6): 558-565
基金项目
- 广西医疗卫生适宜技术开发与推广应用项目(S2020031);广西教育科学规划2021年度重点课题B类(2021B167)
-
通信作者
- 陈罡, E-mail: chengang@gxmu.edu.cn
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2022-05-10
2. 广西医科大学第一附属医院心胸外科, 广西 南宁 530021;
3. 广西医科大学第一附属医院肿瘤内科, 广西 南宁 530021;
4. 广西医科大学第一附属医院呼吸与危重症医学科, 广西 南宁 530021
2. Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, the First Affi liated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, China;
3. Department of Medical Oncology, the First Affi liated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, China;
4. Ward of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, China
全球范围内,肺癌是发病率排名第2位(仅次于乳腺癌)且死亡率位列第1位的恶性肿瘤。据预测,2020年,全球新诊断的肺癌患者约220万例,死亡病例高达179万例[1]。得益于手术、放疗和化疗等治疗手段的发展,近年来肺癌预后得到一定提升[2-4]。然而,诊断延误等问题导致肺癌患者生存率较低,尤其是晚期肺癌患者(5年生存率≤15%)[4-5]。更糟糕的是,多数肺癌患者确诊时已为晚期,给治疗带来巨大挑战。非小细胞肺癌(non-small-cell lung cancer,NSCLC)是最常见的肺癌病理亚型,占肺癌总病例的80%以上[5-6],主要为肺腺癌(lung adenocarcinoma,LUAD)和肺鳞癌(lung squamous cell carcinoma,LUSC)。因此,开展NSCLC相关的研究探索可用于早期诊断肺癌的生物标志物尤为重要。
微小RNA(microRNA,miRNA)是一类非编码RNA分子,可参与细胞的增长、分化及凋亡等多种生物学进程[7]。目前已有多种miRNA被指出在肿瘤中发挥重要作用,并具有明显的临床价值。有学者指出,通过检测血浆中外泌体的let-7d-3p和miR-30d-5p表达水平可以早期诊断子宫颈癌[8]。而血清中的miR-1290表达水平则被认为是食管鳞癌患者预后不良的标志,且该分子可以区分食管鳞癌患者和健康人群[9]。let-7b-5p被认为与肿瘤的发生和发展密切相关。例如,该miRNA在多发性骨髓瘤组织及细胞株中均被报道低表达,且其表达上调可抑制肿瘤细胞增殖[10]。let-7b-5p也在肺类癌中低表达[11]。然而,目前let-7b-5p在NSCLC组织中高表达[12]或低表达[13]尚存争议,且未见相关研究揭示其在NSCLC患者血液中存在表达差异以及是否可用于诊断NSCLC患者。因此,有必要进一步探讨let-7b-5p在NSCLC中的表达水平以及诊断价值。
本研究通过检索Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO)、ArrayExpress、The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)和PubMed等数据库,采集来自多中心的样本数据,探索let-7b-5p在NSCLC患者血液中的表达水平。同时,通过受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic, ROC)曲线评判let-7b-5p诊断NSCLC的效能,并综合多种方法探索let-7b-5p在NSCLC中的潜在靶基因和相关靶基因在NSCLC中的诊断价值。
1 资料和方法 1.1 数据获取为获取全球范围内的多中心样本,截至2021年12月22日,通过检索上述GEO、ArrayExpress、Sequence Read Archive、ONCOMINE、TCGA、PubMed、中国知网、万方数据以及重庆维普9个数据库,筛选NSCLC相关的逆转录定量聚合酶链式反应(reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction, RT-qPCR)及高通量数据。检索式关键词为“lung cancer, microRNA”。数据纳入标准:(1)试验组样本获取自NSCLC患者;(2)血液样本;(3)包含miRNA表达数据。排除标准:(1)表达数据缺失;(2)重复样本。最终,4个高通量原始数据集GSE27486、GSE40738、GSE152702及GSE171517(均来自GEO数据库)符合标准,共包含145例NSCLC患者血液样本(NSCLC组)和83位健康人血液样本(对照组)。根据NSCLC亚型将4个原始数据集拆分为7个数据集:4个LUAD相关数据集(LUAD-GSE27486、LUAD-GSE40738、LUAD-GSE152702和LUAD-GSE171517)以及3个LUSC相关数据集(LUSC-GSE40738、LUSC-GSE152702和LUSC-GSE171517)。其中,源自同一个原始数据集的LUAD数据集和LUSC数据集共用该原始数据集中的对照组样本。例如,LUAD-GSE40738和LUSC-GSE40738共用原始数据集GSE40738中的58例对照组样本。基于这些数据,分LUAD和LUSC两种亚型探索NSCLC组与对照组间的let-7b-5p表达差异。为探索let-7b-5p在NSCLC中的潜在靶基因,于2022年1月5日从Genomic Data Commons数据库(该数据库存储TCGA的最新数据)分别下载LUAD和LUSC组织样本的转录组测序数据集。
1.2 NSCLC组和对照组let-7b-5p表达水平差异及let-7b-5p诊断NSCLC的效能评估采用R(v4.1.0)的ggplot2、ggsignif以及meta程序包,通过小提琴图、箱型图以及森林图比较NSCLC组和对照组let-7b-5p表达水平差异。采用Wilcoxon秩和检验和标准化均数差(standardized mean difference, SMD)分析两组间let-7b-5p表达水平差异。SMD的95% CI不包含0提示SMD结果差异具有统计学意义;其余情况下,以P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。通过ROC曲线及综合ROC(summary ROC,SROC)曲线的曲线下面积(area under the curve, AUC)评估let-7b-5p诊断NSCLC的效能。AUC > 0.5且 < 0.7提示低准确度,AUC≥0.7且 < 0.9提示中等准确度,AUC≥0.9提示高准确度。诊断性meta分析的敏感度和特异度也用于检测let-7b-5p诊断NSCLC的效能。除了SROC曲线和诊断性meta分析森林图于Stata(v15.0)软件绘制外,其余计算及绘图过程均借助R(v4.1.0)软件完成。
1.3 let-7b-5p在NSCLC中的潜在靶基因筛选及let-7b-5p潜在靶基因鉴别NSCLC的效能TargetScan通过寻找与每个miRNA种子区相匹配的3种保守性位点(8mer、7mer和6mer)预测miRNA的生物学靶点[14-15]。miRDB基于高通量测序实验数据和计算生物学方法预测miRNA的靶点,预测5种物种(人类、小鼠、大鼠、狗和鸡)的miRNA靶基因供研究者参考[16]。miRTarBase数据库的开发团队手工整理miRNA功能实验相关的文献,于miRTarBase数据库中存放≥36万条miRNA-靶基因的相互作用的信息[17]。2022年1月6日分别从TargetScan (v8.0)、miRDB以及miRTarBase数据库中获取let-7b-5p的预测靶基因。同时,根据TCGA数据库中的LUAD和LUSC组织样本的转录组测序数据集分别计算这2种疾病的上调基因(upregulated genes, UGs)。UGs的筛选借助R(v4.1.0)的limma程序包完成,筛选条件为:log2(fold change)≥1且校正P值< 0.05。运用韦恩图将预测靶基因以及LUAD和LUSC的UGs取交集获取let-7b-5p的潜在靶基因[18],并运用Cytoscape(v3.9.0)软件绘制网络图展示let-7b-5p及其潜在靶基因。通过ROC曲线的AUC评估let-7b-5p的潜在靶基因区分NSCLC组织样本和正常肺组织样本的能力,方法及判定标准同1.2。
2 结果 2.1 NSCLC组和对照组let-7b-5p表达差异LUAD-GSE152702、LUAD-GSE27486以及LUAD-GSE40738数据集显示let-7b-5p在LUAD组的血液中表达低于对照组(均P < 0.05,图 1A)。LUSC-GSE152702数据集显示,与对照组比较,LUSC患者的血液中let-7b-5p表达更低(P < 0.05,图 1A)。进一步亚组分析显示,let-7b-5p在LUAD组(SMD=-0.53,95% CI: -0.84~-0.21)及LUSC组(SMD=-0.47,95% CI: -0.84~-0.09)血液中低表达(图 1B)。LUAD和LUSC汇总分析表明,let-7b-5p在NSCLC组血液中的表达水平较对照组低(SMD=-0.50,95% CI: -0.75~-0.26;图 1B)。
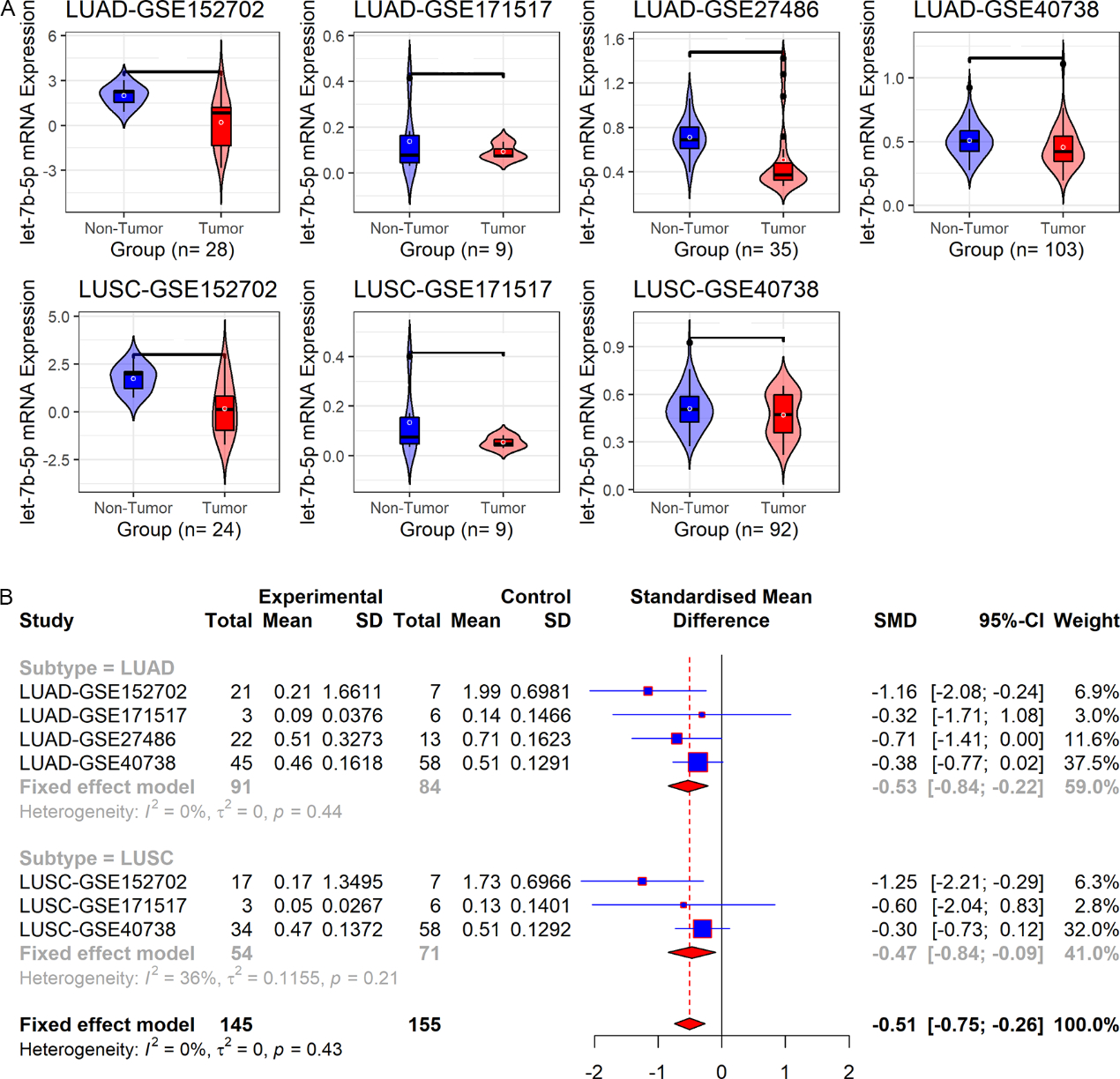
|
| 注 A:小提琴图和箱型图比较let-7b-5p在LUAD组、LUSC组与对照组中的表达差异;B:森林图比较let-7b-5p在LUAD组、LUSC组、NSCLC组与对照组中的表达差异;LUAD:肺腺癌(lung adenocarcinoma);LUSC:肺鳞癌(lung squamous cell carcinoma);NS:not significant(P > 0.05);*P < 0.05;**P < 0.01 图 1 在LUAD-GSE152702、LUAD-GSE171517、LUAD-GSE27486、LUAD-GSE40738、LUSC-GSE152702、LUSC-GSE171517和LUSC-GSE40738数据集中NSCLC组及对照组let-7b-5p表达水平比较 Fig.1 Comparison of let-7b-5p expression between NSCLC group and control group based on the datasets of LUAD-GSE152702, LUAD-GSE171517, LUAD-GSE27486, LUAD-GSE40738, LUSC-GSE152702, LUSC-GSE171517, and LUSC-GSE40738 |
ROC曲线分析显示,let-7b-5p诊断LUAD和LUSC的准确度均为低~中等(LUAD:AUC=0.556~0.844,LUSC:AUC=0.570~0.836;图 2A)。整合LUAD和LUSC数据集的SROC曲线显示,let-7b-5p诊断NSCLC的准确度为中等(AUC=0.79,图 2B);森林图的敏感度和特异度均 > 0.7,表明let-7b-5p可以区分NSCLC患者和健康人(图 2C)。
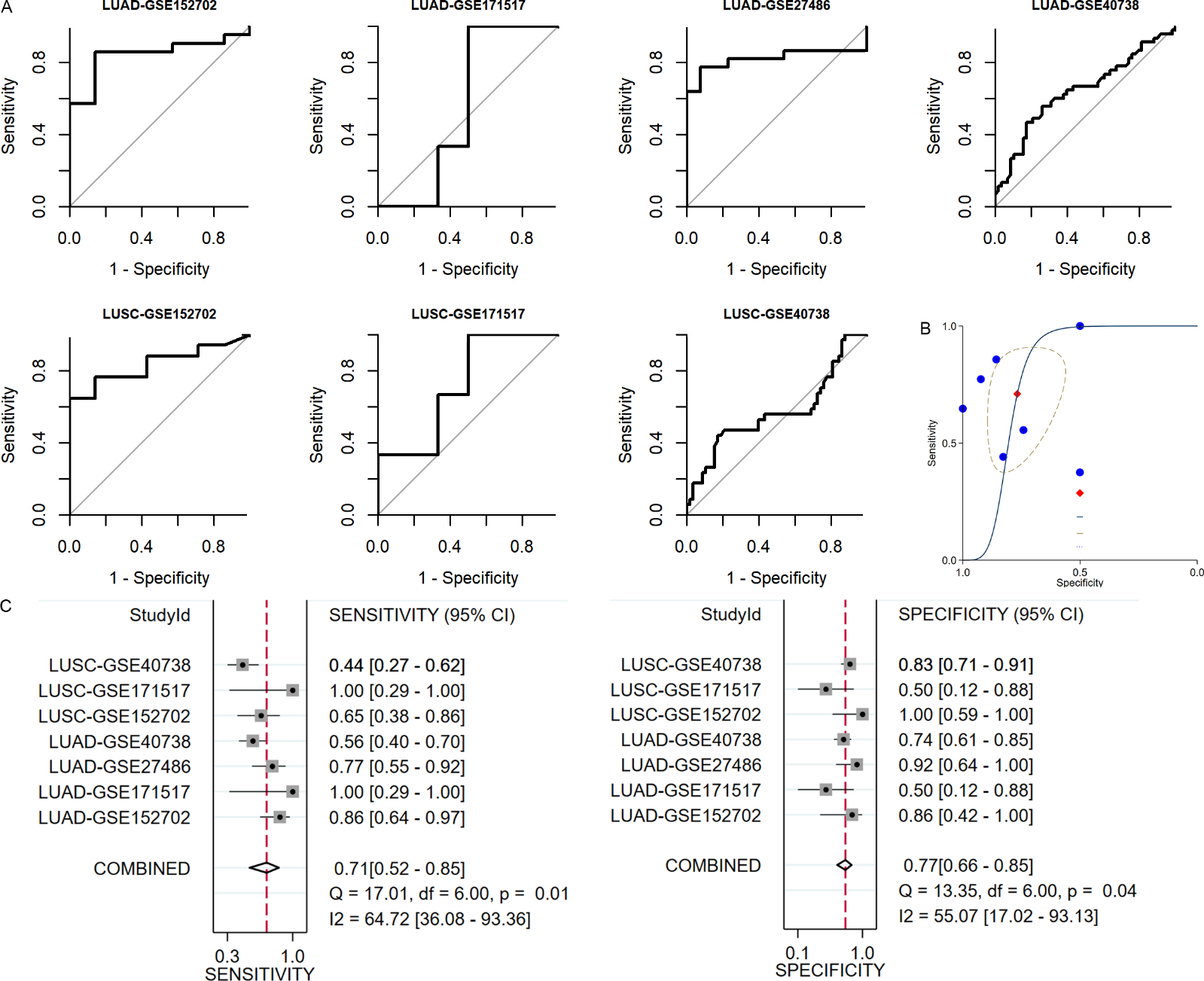
|
| 注 A:ROC曲线评估let-7b-5p诊断LUAD以及LUSC的效能;B:SROC曲线评估let-7b-5p诊断NSCLC的效能;C:敏感度及特异度森林图评估let-7b-5p诊断NSCLC的效能;LUAD:肺腺癌(lung adenocarcinoma);LUSC:肺鳞癌(lung squamous cell carcinoma);AUC:曲线下面积(area under the curve);SROC:综合受试者工作特征(summary receiver operating characteristic) 图 2 在LUAD-GSE152702、LUAD-GSE171517、LUAD-GSE27486、LUAD-GSE40738、LUSC-GSE152702、LUSC-GSE171517以及LUSC-GSE40738数据集中let-7b-5p诊断NSCLC患者的效能评估 Fig.2 Evaluation of the efficacy of let-7b-5p in diagnosing NSCLC patients based on the datasets LUAD-GSE152702, LUAD-GSE171517, LUAD-GSE27486, LUAD-GSE40738, LUSC-GSE152702, LUSC-GSE171517, and LUSC-GSE40738 |
分别从TargetScan、miRDB和miRTarBase数据库中获取1 207、990和1 113个let-7b-5p的预测靶基因。根据TCGA数据库中的LUAD和LUSC测序数据集分别计算出1 286和1 976个UGs。将预测靶基因和LUAD-UGs及LUSC-UGs交集得到10个let-7b-5p的潜在靶基因(图 3A)。这10个潜在靶基因分别为:碱性亮氨酸拉链和W2结构域2(basic leucine zipper and W2 domains 2,BZW2)、细胞分裂周期蛋白25A(cell division cycle 25A,CDC25A)、细胞分裂周期相关基因8(cell division cycle associated 8, CDCA8)、Ⅲ型胶原α-1链(collagen type Ⅲ alpha 1 chain,COL3A1)、外纺锤体极样蛋白1(extra spindle pole bodies like 1,ESPL1)、高迁移率族AT-hook蛋白1(high mobility group AT-hook 1,HMGA1)、胰岛素样生长因子2结合蛋白3(insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3,IGF2BP3)、NME/NM23核苷二磷酸激酶4(NME/NM23 nucleoside diphosphate kinase 4,NME4)、葡萄糖磷酸变位酶2样蛋白1(phosphoglucomutase 2 like 1,PGM2L1)以及核糖核苷酸还原酶调节亚基M2(ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2,RRM2;图 3B)。let-7b-5p在NSCLC的10个潜在靶基因均具有中等至高准确度来区分LUAD与正常肺样本(AUC=0.765~0.980)以及LUSC与正常肺样本(AUC=0.749~0.997;图 4)。
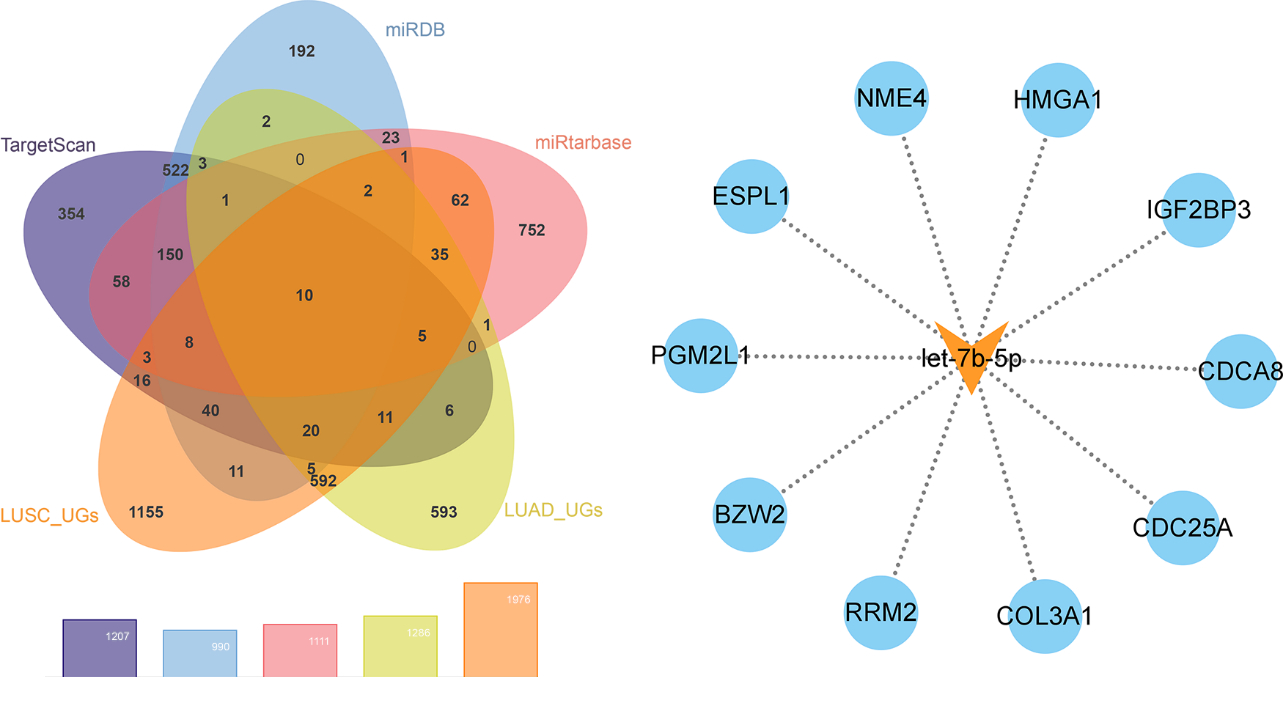
|
| 注 A:韦恩图筛选let-7b-5p在NSCLC中的潜在靶基因;B:let-7b-5p的潜在靶基因;LUSC:肺鳞癌(lung squamous cell carcinoma);UGs:上调基因(upregulated genes);LUAD:肺腺癌(lung adenocarcinoma);HMGA1:高迁移率族AT-hook蛋白1(high mobility group AT-hook 1);ESPL1:外纺锤体极样蛋白1(extra spindle pole bodies like 1);RRM2:核糖核苷酸还原酶调节亚基M2(ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2);CDCA8:细胞分裂周期相关基因8(cell division cycle associated 8);CDC25A:细胞分裂周期蛋白25A(cell division cycle 25A);IGF2BP3:胰岛素样生长因子2结合蛋白3(insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3);BZW2:碱性亮氨酸拉链和W2结构域2(basic leucine zipper and W2 domains 2);PGM2L1:葡萄糖磷酸变位酶2样蛋白1(phosphoglucomutase 2 like 1);NME4:NME/NM23核苷二磷酸激酶4(NME/NM23 nucleoside diphosphate kinase 4);COL3A1:Ⅲ型胶原α-1链(collagen type Ⅲ alpha 1 chain) 图 3 let-7b-5p在NSCLC中的潜在靶基因筛选 Fig.3 Screening of potential target genes of let-7b-5p in NSCLC |
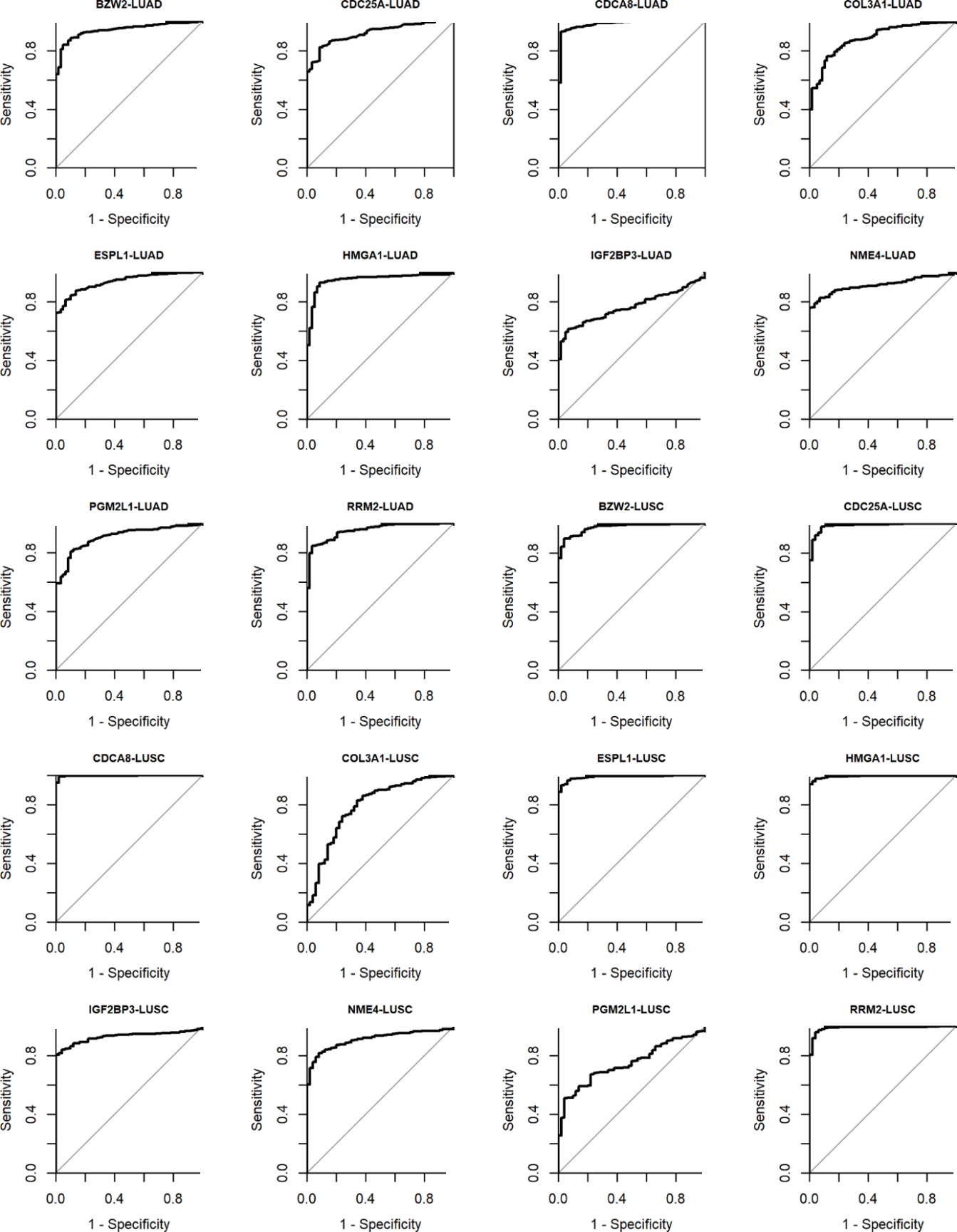
|
| 注 LUAD:肺腺癌(lung adenocarcinoma);BZW2:碱性亮氨酸拉链和W2结构域2(basic leucine zipper and W2 domains 2);AUC:曲线下面积(area under the curve);CDC25A:细胞分裂周期蛋白25A(cell division cycle 25A);CDCA8:细胞分裂周期相关基因8(cell division cycle associated 8);COL3A1:Ⅲ型胶原α-1链(collagen type Ⅲ alpha 1 chain);ESPL1:外纺锤体极样蛋白1(extra spindle pole bodies like 1);HMGA1:高迁移率族AT-hook蛋白1(high mobility group AT-hook 1);IGF2BP3:胰岛素样生长因子2结合蛋白3(insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3);NME4:NME/NM23核苷二磷酸激酶4(NME/NM23 nucleoside diphosphate kinase 4);PGM2L1:葡萄糖磷酸变位酶2样蛋白1(phosphoglucomutase 2 like 1);RRM2:核糖核苷酸还原酶调节亚基M2(ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2);LUSC:肺鳞癌(lung squamous cell carcinoma) 图 4 ROC曲线评估let-7b-5p在NSCLC中的10个潜在靶基因区分LUAD及LUSC与正常肺样本的效能 Fig.4 Efficacy of the 10 potential target genes of let-7b-5p in screening LUAD and LUSC samples from normal lung samples evaluated by ROC curves |
肺癌是发病率和死亡率均排名前列的癌症。≥50%的肺癌患者确诊时已至晚期,患者5年生存率不容乐观[4-5]。目前已有多种治疗手段使早期肺癌患者获益,故探索可用于早期诊断肺癌患者的生物标志物具有重要意义。
本研究首次揭示let-7b-5p在NSCLC患者血液中低表达。let-7b-5p的低表达状态在多种癌组织中被报道,如多发性骨髓瘤以及乳腺癌等[10, 19]。在肺癌相关的研究中,let-7b-5p被明确指出在肺类癌(一种神经内分泌肿瘤)中表达下调[11]。而let-7b-5p在NSCLC组织中高表达还是低表达存在争议[12-13]。此前研究报道显示,血清中检测到let-7b-5p高表达的NSCLC患者具有更好的预后,但在NSCLC患者和健康人的血清样本中未发现let-7b-5存在表达差异[20]。本研究纳入的数据集中,并非所有数据集都可检测到NSCLC组和对照组的let-7b-5表达有差异。这提示上述未发现NSCLC体液中let-7b-5p的低表达的研究可能是由于相关研究仅基于单中心数据所致[20]。为明确健康人和NSCLC患者血液中的let-7b-5p表达水平差异,本研究纳入多中心数据进行研究。考虑到不同NSCLC亚型之间let-7b-5p的表达状态可能存在差异,本研究在LUAD和LUSC患者中分别分析let-7b-5p的表达水平。结果显示,与健康人比较,LUAD患者和LUSC患者的血液中均检测到更低水平的let-7b-5p;LUAD及LUSC亚型的meta分析也支持NSCLC中let-7b-5p低表达的结论。
let-7b-5p在血液中的表达水平具有诊断NSCLC患者的潜力。成功的早期诊断可提升肺癌患者的预后[21]。本研究显示,血液中的let-7b-5p表达水平可以将LUAD患者和LUSC患者从健康人群中区分出来,表明该分子用于筛选NSCLC患者的可行性。事实上,此前已有研究揭示可通过检测血浆中的let-7b-5p筛检鼻咽癌患者(AUC=0.676)[22]。let-7b-5p的潜在靶基因可能也具有诊断NSCLC的效能。通过综合数据库预测以及UGs筛选等方法进行分析,BZW2、CDC25A、CDCA8、COL3A1、ESPL1、HMGA1、IGF2BP3、NME4、PGM2L1及RRM2被鉴定为let-7b-5p在NSCLC中的潜在靶基因。虽然未能采集血液样本直接检测这10个潜在靶基因诊断NSCLC的效能,但这些分子的组织表达水平可以区分NSCLC组织和正常肺组织,表明其可能同let-7b-5p具有类似地筛检NSCLC的能力,但仍需体液样本验证。同时,let-7b-5p的靶基因诊断NSCLC的可观效能一定程度上印证let-7b-5p诊断NSCLC的潜力。
综上所述,本研究首次揭示let-7b-5p在NSCLC患者的血液中低表达,并明确let-7b-5p表达水平可能可用于诊断NSCLC。let-7b-5p的10个潜在靶基因BZW2、CDC25A、CDCA8、COL3A1、ESPL1、HMGA1、IGF2BP3、NME4、PGM2L1及RRM2也具有诊断NSCLC的效能。然而,let-7b-5p在NSCLC中的分子机制及其10个潜在靶基因在NSCLC中的临床意义及潜在分子机制尚需体内外实验进一步探讨。
致谢: 感谢广西医学病理学重点实验室提供技术支持
| [1] |
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel R, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. DOI:10.3322/caac.21660 |
| [2] |
Siegel R, Miller K, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. DOI:10.3322/caac.21590 |
| [3] |
朱潇宽, 虞永峰, 陆舜. 老年晚期非小细胞肺癌一线治疗[J]. 实用肿瘤杂志, 2022, 37(3): 221-226. |
| [4] |
Spella M, Stathopoulos G. Immune resistance in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(3): 384. DOI:10.3390/cancers13030384 |
| [5] |
Siegel R, Miller K, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(1): 7-30. DOI:10.3322/caac.21442 |
| [6] |
Ye Z, Huang Y, Ke J, et al. Breakthrough in targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 133: 111079. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111079 |
| [7] |
林雪芳, 周建维. miR-513a-5p通过靶向调控PAK1抑制子宫颈癌细胞增殖和侵袭[J]. 实用肿瘤杂志, 2023, 38(1): 17-25. |
| [8] |
Zheng M, Hou L, Ma Y, et al. Exosomal let-7d-3p and miR-30d-5p as diagnostic biomarkers for non-invasive screening of cervical cancer and its precursors[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 76. DOI:10.1186/s12943-019-0999-x |
| [9] |
Sun H, Wang L, Zhao Q, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of serum miRNA-1290 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2019, 25(4): 381-387. DOI:10.3233/CBM-190007 |
| [10] |
Xu H, Liu C, Zhang Y, et al. Let-7b-5p regulates proliferation and apoptosis in multiple myeloma by targeting IGF1R[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 2014, 46(11): 965-972. DOI:10.1093/abbs/gmu089 |
| [11] |
Fazio P, Maass M, Roth S, et al. Expression of hsa-let-7b-5p, hsa-let-7f-5p, and hsa-miR-222-3p and their putative targets HMGA2 and CDKN1B in typical and atypical carcinoid tumors of the lung[J]. Tumour Biol, 2017, 39(10): 1010428317728417. |
| [12] |
Hosseini S, Soltani B, Tavallaei M, et al. Clinically significant dysregulation of hsa-miR-30d-5p and hsa-let-7b expression in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol, 2018, 10(2): 98-104. |
| [13] |
Jusufović E, Rijavec M, Keser D, et al. Let-7b and miR-126 are down-regulated in tumor tissue and correlate with microvessel density and survival outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(9): e45577. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0045577 |
| [14] |
McGeary S, Lin K, Shi C, et al. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy[J]. Science, 2019, 366(6472): eaav1741. DOI:10.1126/science.aav1741 |
| [15] |
Lewis B, Burge C, Bartel D. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets[J]. Cell, 2005, 120(1): 15-20. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.035 |
| [16] |
Chen Y, Wang X. miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020, 48(D1): D127-D131. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkz757 |
| [17] |
Huang H, Lin Y, Li J, et al. miRTarBase 2020: updates to the experimentally validated microRNA-target interaction database[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020, 48(D1): D148-154. |
| [18] |
Bardou P, Mariette J, Escudié F, et al. Jvenn: an interactive Venn diagram viewer[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2014, 15: 293. DOI:10.1186/1471-2105-15-293 |
| [19] |
Zou X, Xia T, Li M, et al. microRNA profiling in serum: potential signatures for breast cancer diagnosis[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2021, 30(1): 41-53. DOI:10.3233/CBM-201547 |
| [20] |
Heegaard N, Schetter A, Welsh J, et al. Circulating micro-RNA expression profiles in early stage non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Int J Cancer, 2012, 130(6): 1378-1386. DOI:10.1002/ijc.26153 |
| [21] |
van Hal G, Diab Garcia P. Lung cancer screening: targeting the hard to reach-a review[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2021, 10(5): 2309-2322. DOI:10.21037/tlcr-20-525 |
| [22] |
Zou X, Zhu D, Zhang H, et al. microRNA expression profiling analysis in serum for nasopharyngeal carcinoma diagnosis[J]. Gene, 2020, 727: 144243. DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2019.144243 |
 2023, Vol. 38
2023, Vol. 38


