2. 贵州省喀斯特山地生态环境国家重点实验室培育基地, 550025:贵阳
-
项目名称
- 贵州省科技支撑计划项目"喀斯特地区蔬菜地农业系统中重金属减控关键技术研究"([2017]2580)
-
第一作者简介
- 赵帅(1997-), 男, 硕士研究生。主要研究方向: 生物炭修复治理土壤重金属污染。E-mail: 1217771794@qq.com
-
通信作者简介
- 王济(1975-), 男, 博士, 教授。主要研究方向: 土壤重金属污染治理与修复。E-mail: wangji@gznu.edu.cn
-
文章历史
-
收稿日期:2020-07-20
修回日期:2021-02-04
2. 贵州省喀斯特山地生态环境国家重点实验室培育基地, 550025:贵阳
2. The State Key Laboratory Incubation Base for Karst Mountain Ecology Environment of Guizhou Province, 550025:Guiyang, China
随着现代社会的快速发展,工矿业和农业生产过程中排放的大量重金属(heavy metals, HMs)污染物进入土壤环境,严重危害土壤生态环境和生物健康[1-2]。生物质材料在缺氧、相对低温的条件下热解制备的高含碳固体物质称之为生物炭(biochar, BC)[3]。生物炭材料因其具有来源广泛、绿色环保、成本低廉等性质,成为治理HMs污染土壤的研究热点[4-5];BC具有高度芳香化和杂环化结构,这使它具备良好的吸附能力,可以有效地修复土壤环境中的HMs污染;它还具有复杂的孔隙结构、巨大的比表面积和丰富的表面基团,可为土壤中的微生物提供一定所需栖息环境和所需元素,提升微生物的活性和繁殖效率,对土壤HMs污染治理起到正面调节作用[6-7]。但当前土壤HMs污染情况复杂多样,原质BC不能满足现有需求且达不到研究效果,因此需要对原质BC材料进行改性处理,提升原质BC某方面性能,例如增大比表面积、孔隙复杂程度和改变表面的官能团物质类别,以此对HMs污染土壤达到更好的治理效果[8]。笔者介绍制备BC所需的生物质来源和生物炭制备技术,以及生物质原料和制备温度对BC性质的影响;讨论BC对HMs的吸附机制,并探析BC对土壤HMs污染物的修复效果;总结BC的改性方法以及改性后结构变化,阐述改性BC的性能提升和对HMs的修复效果。最后对BC修复HMs污染土壤的发展方向和情况进行总结和展望,希望为BC修复HMs污染土壤领域的研究和发展提供借鉴。
1 生物炭来源与制取 1.1 原料来源和制备过程可用于制备BC的材料来源广泛,其中包含农林废弃物、污泥、果壳、家禽粪便等几种类型,不同研究采用的生物质原料和制备过程也有较大差别,表 1对一些研究中所涉及到的BC原料来源和制备过程进行总结。
| 表 1 生物炭的原料来源和制备 Tab. 1 Raw materials sources of biochar and preparations |
BC由生物质原料通过热化学过程(缺氧或无氧条件下)制备。制备BC的工艺可分为快速热裂解、慢速热裂解、气化、水热炭化等几类。由表 2可知,几种制备方法的温度区间在175~1 500 ℃左右,气化法所需温度较高,制备过程须达到700~1 500 ℃高温和较高气压,且BC产率较低,只有10%左右,但是停留时间较短,只需几秒钟到几分钟,此法主要用于获取气相产物;而水热炭化法所需制备温度较低,且BC产量较高,可达到30%~60%,缺点是停留时间较长,需要几个小时时间,含水量高的生物质材料使用此方法进行BC的制备;大多数研究中采用慢速热裂解手段制备所需BC。
BC的物化性质包括产率、灰分、挥发分、表面积、孔径、阳离子交换量等,受原料种类和热解条件影响较大[9-11]。动物粪便和植物秸秆的BC产率相差较大,因为其中的灰分和HMs含量差异显著,挥发分和灰分之间呈正相关关系[7]。研究发现,水葫芦、杨树枝和玉米秸秆BC的表面性质差异较大,水葫芦BC表面积更大,对Pb的吸附效率最高。温度是热解BC时的关键工艺参数,较高温度裂解制备的BC具有较高的pH、灰分含量、生物学稳定性和碳含量,BC的表面积、微孔量及疏水性也较高;较低温度裂解下吸附容量较高[12]。不考虑原料差异所带来的影响,热解温度决定了BC的比表面积和阳离子交换量(cation exchange capacity, CEC),只有在一定的温度范围内热解BC[13],才能使BC的表面积、孔径及阳离子交换量获得最大值[14],提高HMs污染物的去除效率。
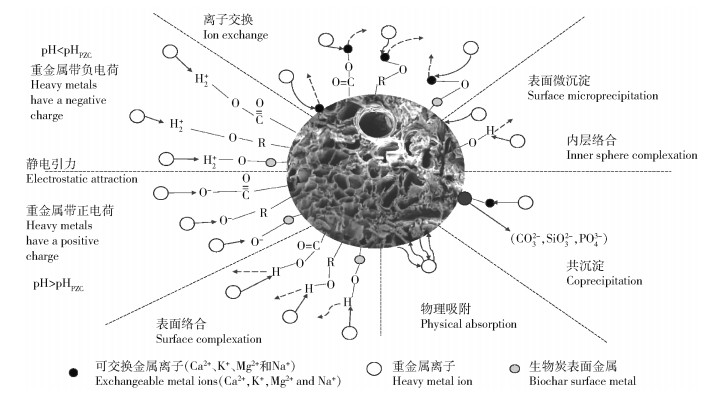
2 生物炭对重金属的吸附机理和修复效果 2.1 吸附机理为了研究BC对HMs的去除效果,需要明确其吸附过程的基本机制。一般可分为表面吸附(物理吸附)、表面络合或沉淀、离子交换和静电引力作用[7]。BC对HMs离子的表面吸附效果取决于BC对HMs离子的化学键力强度,也与HMs离子本身的性质有关,比表面积和孔隙结构也是影响BC吸附能力的关键因素,通常情况下,较大的比表面积和复杂的孔隙结构会强化BC的表面吸附能力;表面络合或沉淀则与BC表面的官能团种类和数量有直接关系,且BC表面的金属和矿物组分(CO32-、SiO32-和PO43-)也会对其产生影响;离子交换作用效果与BC表面的金属种类和性质相关;静电引力作用可分为2种情况:当HMs带负电荷时,会被BC表面带正电的官能团吸引;但带正电荷时就会被BC表面带负电的官能团吸引;详见图 1。
2.2 对污染土壤中重金属的修复效果土壤中HMs具有迁移性、不可降解性、稳定性和毒害性。BC孔隙结构复杂且发达,拥有巨大的比表面积和丰富的官能团,可以有效吸附土壤中的HMs并且降低其在土壤中的迁移性和生物有效性[15-16]。陈再明等[13]发现水稻秸秆BC中的有机碳和无机矿物组分对Pb2+可产生吸附作用,其最大的吸附量可达85.7 mg/g;实验表明,牛粪和稻杆BC可以降低Pb、Zn和Cd的TCLP形态含量[17],其中牛粪BC和稻杆对Pb的作用效果优良,可分别降低56.0%和35.8%的TCLP形态Pb含量,降低Pb的迁移性。在HMs污染土壤中施加BC,不仅可以提高土壤pH、增加CEC和土壤表面可变负电荷,还可降低土壤电动电位(zeta),HMs离子与BC发生键合作用后形成金属氢氧化物、碳酸盐或磷酸盐沉淀[18],明显降低某些HMs的有效态含量[19],减弱HMs生物有效性和毒性[20];徐楠楠等[21]在研究中得到与上述一致的结果,在施加玉米秸秆BC后土壤pH升高,Cd2+与OH-结合形成沉淀物Cd(OH)2;Xu等[22]通过研究发现也得到相似的结果,粪便BC可与大部分Cd形成金属磷酸盐和碳酸盐沉淀。BC还可以强化阳离子的吸附能力,抑制Pb的解吸并促进Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2、Pb2OF2沉淀产生;Dong等[23]通过研究发现BC中的P含量较高,其中溶解产生的可溶性P与Pb能够形成Ca2Pb8(PO4)6(OH)2和Pb10(PO4)6(OH)2沉淀;郭文娟等[24]热解棉花秸秆制备BC,在吸附Cd过程中加入电解质钠盐和钾盐(NaCl、NaNO3和KNO3)后,对BC与Cd2+的离子交换产生竞争,抑制BC对Cd2+的吸附,通过FTIR分析BC,发现水葫芦BC吸收Cd2+的量等于释放其他几种阳离子的量(K+、Ca2+、Na+和Mg2+),Cd2+与BC上的O—H和—CH2中含有的H+也可发生离子交换[25];袁启慧等[26]发现BC与HMs可形成络合物,BC中的CO可与Cd2+络合;因为BC种类繁多,且性质差异较大,所以研究效果存在差异性,在此基础上针对不同土壤环境和污染类型,深入研究BC的制备条件,提高BC性能和修复效率。
3 改性生物炭研究和对重金属修复效果 3.1 改性方法和结构变化不同类型的BC性质有较大差异,从环境污染的角度出发,人们常通过物理、化学2类改性方法来提升BC自身性能。其中化学改性方法应用较为广泛,主要包括酸改性、碱改性、氧化剂改性、金属氧化物改性和碳质材料改性;物理改性主要包括蒸汽和汽化(图 2)。酸改性可以去除BC表面的金属等杂质,并且引入酸性官能团物质,常用到盐酸、硫酸、硝酸、磷酸、草酸和柠檬酸[27];碱改性可以提升BC的表面积,引入含氧官能团,常见的碱性改性剂有NaOH和KOH;通过加入不同的氧化剂,如H2O2、HNO3或KMnO4[28],也能起到引入含氧官能团的作用,还可以活化BC表面官能团并增加其活性点位;而金属氧化物改性可提升BC磁性,磁化介质能够长时间稳定存在于BC中,修复完成后BC和被修复对象易于分离,表面性能和吸附能力得到增强,一般采用金属Fe、Mg、Al和Mn作为金属氧化物;利用碳质材料改性可以提高BC的表面积;利用蒸汽和汽化改性BC,可提高BC的pH和比表面积,使其表面的孔隙结构复杂化,拥有更大的孔隙体积,增强其吸附能力[29]。
大多数研究发现,BC的结构如表面形态、孔径分配、表面积和表面官能团是影响BC吸附能力的关键性质,改性的目的是使BC获得更加突出的结构性能,以便在实际运用中发挥最大效力[31]。无论是化学改性还是物理改性,几乎都能改变原有BC的表面结构,使其表面塌陷或出现褶皱,从而提高BC的比表面积,但是少数研究发现在BC改性后,其孔洞被改性物质堵塞造成孔径和比表面积减小的情况(表 3)。因此对于不同的生物质原料应该选取不同的改性方法,尽量避免出现负面效应。
| 表 3 改性后生物炭结构性质变化 Tab. 3 Changes in structures and properties of biochar after modification |
相比于原质BC,改性BC施加进入HMs污染土壤后,对HMs的修复效果会得到不同程度的加强,提高HMs稳定形态含量,降低植物根际有效态HMs浓度。利用磷酸盐改性竹子生物炭,发现对Cd的吸附能力提升将近10倍,其去除效率可达到85.78%;由表 4可知,利用磷酸改性小麦秸秆,可以提升土壤pH,使Pb沉淀从而达到固定效果;而用聚乙烯亚胺改性玉米秸秆生物炭后,对Cr6+的最大吸附量可达到386.3 mg/g,对Cr6+的最大吸附效率达到95.94%,有着非常优良的吸附效果;通过大量研究结果表明,纳米零价铁BC性能优良,采用羧甲基纤维素来稳定纳米零价铁BC,当制备比例为2.5 g/kg时,对Cr6+的修复效率可达100%。
| 表 4 改性生物炭对重金属的修复效果 Tab. 4 Remediation effects of modified biochar on heavy metals |
研究发现,在BC的结构中引入N、P和S基团能提高BC碱性和表面极性,使其电子结构发生改变,引入基团位点可以产生局部电荷累积的离域效应,局部的电荷密度对电子转移有重要作用,配位机制促进了分子的解离或吸附,可以增强对HMs离子的吸附效果[81]。在杨兰等[82]的研究中,原状Cd污染土壤中,几种改性BC都可以降低Cd的有效态和可交换态含量;在外源高含量Cd污染土壤中,也可以起到同样的效果,说明改性BC对于重金属迁移转化产生积极效应。目前,大多数改性BC应用在水中污染物的吸附或者去除,对土壤中HMs污染物的钝化研究相对较少[83],虽然BC治理土壤HMs污染物有着不错的效果,但对改性BC在热解后是否会产生有害毒素并对土壤造成二次污染的研究不足,是否会破坏土壤中原有的生态系统动态平衡也还不够清楚,未来应建全BC在HMs污染土壤中的应用规范,以期改性BC材料在土壤HMs污染原位修复领域中更加实用。
4 总结及展望1) 原质BC在HMs污染土壤的修复治理中或许不够有效、高效和长效,针对不同类型的BC材料,通过适当的改性方法提升BC的自身性能,并尽可能控制成本和环境影响,提高HMs污染土壤治理成效。
2) 目前多数关于BC治理修复HMs污染土壤的研究还停留在实验室阶段或者小规模实验阶段,缺乏大规模原位实验,实验室条件与大田实验环境差异较大,缺乏自然环境因素对实验的影响。BC施加到土壤后长期暴露在自然环境中会出现老化的现象,老化后BC的修复效果可能会降低,还应探究老化带来的负面效果以及BC的流向问题。
2) BC材料来源广泛且类型和范围无专业划分标准,针对不同材料选取适当制备方法,探究不同类型BC材料的最佳热解条件将会决定BC修复治理土壤HMs的功效最大化能否实现。针对现有研究阶段的不足,利用当地特有的生物质原材料,探析当地主要的HMs污染类型,选取合适的生物质原料进行产业化推广应用,坚持绿色环保的理念合理运用BC材料,以免对环境造成二次污染。
| [1] |
李江遐, 吴林春, 张军, 等. 生物炭修复土壤重金属污染的研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(12): 2075. LI Jiangxia, WU Linchun, ZHANG Jun, et al. Research progress in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by biochar[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(12): 2075. |
| [2] |
谢金亮, 张建锋, 刘永兵, 等. 白云鄂博稀土伴生矿区土壤重金属污染及其环境评价[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 2020, 18(2): 92. XIE Jinliang, ZHANG Jianfeng, LIU Yongbing, et al. Heavy metal pollution and environmental assessment in the soil of the rare earth associated mining area in Bayan Obo[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 18(2): 92. |
| [3] |
CAO Xinde, HARRIS W. Properties of dairy-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use in remediation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(14): 5222. DOI:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.052 |
| [4] |
BUSTIN R M, GUO Yingting. Abrupt changes(jumps) in reflectance values and chemical composition of artificial charcoals and inertinite in coals[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 1999, 38(3/4): 237. |
| [5] |
MUNIR M A M, LIU Guijian, YOUSAF B, et al. Synergistic effects of biochar and processed fly ash on bioavailability, transformation and accumulation of heavy metals by maize (Zea mays L.) in coal-mining contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 2019(240): 124845. |
| [6] |
WANG Shengsen, GAO Bin, ZIMMERMAN A R, et al. Physicochemical and sorptive properties of biochars derived from woody and herbaceous biomass[J]. Chemosphere, 2015(134): 257. |
| [7] |
王重庆, 王晖, 江小燕, 等. 生物炭吸附重金属离子的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(1): 692. WANG Chongqing, WANG Hui, JIANG Xiaoyan, et al. Research advances on adsorption of heavy metals by biochar[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(1): 692. |
| [8] |
黄安香, 杨定云, 杨守禄, 等. 改性生物炭对土壤重金属污染修复研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(12): 5266. HUANG Anxiang, YANG Dingyun, YANG Shoulu, et al. Advance in remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil by modifiedbiochar[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(12): 5266. |
| [9] |
王宏胜, 唐朝生, 巩学鹏, 等. 生物炭修复重金属污染土壤研究进展[J]. 工程地质学报, 2008, 26(4): 1064. WANG Hongsheng, TANG Chaosheng, GONG Xuepeng, et al. Research progress in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils with biochar[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 26(4): 1064. |
| [10] |
马献发, 李伟彤, 孟庆峰, 等. 生物炭对土壤重金属形态特征及迁移转化影响研究进展[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2017, 48(6): 82. MA Xianfa, LI Weitong, MENG Qingfeng, et al. Research advance on biochars of the speciation, mobility and transfer of heavy metals in soils[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2017, 48(6): 82. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2017.06.011 |
| [11] |
王红, 夏雯, 卢平, 等. 生物炭对土壤中重金属铅和锌的吸附特性[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(9): 3944. WANG Hong, XIA Wen, LU Ping, et al. Adsorption characteristics of biochar on heavy metals (Pb and Zn) in soil[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(9): 3944. |
| [12] |
安增莉, 侯艳伟, 蔡超, 等. 水稻秸秆生物炭对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附特性[J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(11): 1851. AN Zengli, HOU Yanwei, CAI Chao, et al. Lead (Ⅱ) adsorption characteristics on different biochars derived from rice straw[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(11): 1851. |
| [13] |
陈再明, 方远, 徐义亮, 等. 水稻秸秆生物碳对重金属Pb2+的吸附作用及影响因素[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(4): 769. CHEN Zaiming, FANG Yuan, XU Yiliang, et al. Adsorption of Pb2+ by rice straw derived-biochar and its influential factors[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2012, 32(4): 769. |
| [14] |
何绪生, 耿增超, 佘雕, 等. 生物炭生产与农用的意义及国内外动态[J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(2): 1. HE Xusheng, GENG Zengchao, SHE Diao, et al. Implications of production and agricultural utilization of biochar and its international dynamic[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2011, 27(2): 1. |
| [15] |
MOHAN D, SARSWAT A, OK Y S, et al. Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent: A critical review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2014(160): 191. |
| [16] |
CUI Liqiang, PAN Genxing, LI Lianqing, et al. The reduction of wheat Cd uptake in contaminated soil via biochar amendment: A two-year field experiment[J]. BioResources, 2012, 7(4): 5666. |
| [17] |
王济, 李丁, 宣斌, 等. 有机物料对土壤Pb有效态作用机理及影响效果研究进展[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 36(2): 107. WANG Ji, LI Ding, XUAN Bin, et al. Review on the mechanism and effect of organic materials on available Pb in soil[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University(Natural Sciences), 2018, 36(2): 107. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-5570.2018.02.019 |
| [18] |
PARK J H, CHOPPALA G, LEE S J, et al. Comparative sorption of Pb and Cd by biochars and its implication for metal immobilization in soils[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2013(224): 1711. DOI:10.1007%2Fs11270-013-1711-1 |
| [19] |
臧晓梅, 缪爱军, 郑浩, 等. 3种修复剂对底泥中不同形态重金属去除效果评估[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(8): 4585. ZANG Xiaomei, LIAO Aijun, ZHENG Hao, et al. Efficiency of three remediation agents on removal of heavy metals or metalloids from sediments[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(8): 4585. |
| [20] |
CAO Xinde, MA Lena, GAO Bin, et al. Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine.[J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2009, 43(9): 3285. DOI:10.1021/es803092k |
| [21] |
徐楠楠, 林大松, 徐应明, 等. 玉米秸秆生物炭对Cd2+吸附特性及影响因素[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(5): 958. XU Nannan, LIN Dasong, XU Yingming, et al. Adsorption of aquatic Cd2+ by biochar obtained from corn stover[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(5): 958. |
| [22] |
XU Xiaoyun, CAO Xinde, ZHAO Ling. Comparison of rice husk-and dairy manure-derived biochars for simultaneously removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions: Role of mineral components in biochars[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 92(8): 955. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.03.009 |
| [23] |
DONG Xiaoling, MA L Q, LI Yuncong. Characteristics and mechanisms of hexavalent chromium removal by biochar from sugar beet tailing[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 190(1/3): 909. |
| [24] |
郭文娟, 梁学峰, 林大松, 等. 土壤重金属钝化修复剂生物炭对镉吸附特性研究[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(9): 3716. GUO Wenjuan, LIANG Xuefeng, LIN Dasong, et al. Adsorption of Cd2+ on biochar from aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(9): 3716. |
| [25] |
HARVEY O R, HERBERT B E, RHUE R D, et al. Metal interactions at the biochar-water interface: Energetics and structure-sorption relationships elucidated by flow adsorption microcalorimetry[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(13): 5550. |
| [26] |
袁启慧, 包立, 张乃明. 钝化剂种类和粒径对复合污染土壤镉铅有效态的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2019, 36(2): 192. YUAN Qihui, BAO Li, ZHANG Naiming. The effect of type and particle size of passivator on effective state of Cd and Pb in compound polluted soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2019, 36(2): 192. |
| [27] |
RAJAPAKSHA A U, CHEN S S, TSANG D C, et al. Engineered/designer biochar for contaminant removal/immobilization from soil and water: Potential and implication of biochar modification[J]. Chemosphere, 2016(148): 276. |
| [28] |
LI Yunchao, SHAO Jingai, WANG Xiaohua, et al. Characterization of modified biochars derived from bamboo pyrolysis and their utilization for target component(furfural) adsorption[J]. Energy and Fuels, 2014, 28(8): 5119. DOI:10.1021/ef500725c |
| [29] |
HASS A, GONZALEZ J M, LIMA I M, et al. Chicken manure biochar as liming and nutrient source for acid Appalachian soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2012, 41(4): 1096. DOI:10.2134/jeq2011.0124 |
| [30] |
WANG Jianlong, WANG Shizong. Preparation, modification and environmental application of biochar: A review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019(227): 1002. |
| [31] |
QIAN Kezhen, KUMAR A, ZHANG Hailin, et al. Recent advances in utilization of biochar[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015(42): 1055. |
| [32] |
王楠, 吴玮, 杨春光, 等. 盐酸改性松针生物炭对磺胺甲噁唑的吸附性能[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(6): 1428. WANG Nan, WU Wei, YANG Chunguang, et al. Adsorption performance of hydrochloric acid-modified pine needle biochar on sulfamethoxazolef[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 14(6): 1428. |
| [33] |
杨奇亮, 吴平霄. 改性多孔生物炭的制备及其对水中四环素的吸附性能研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(12): 3973. YANG Qiliang, WU Pingxiao. Preparation of modified porous biochar and its adsorption properties for tetracycline in water[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(12): 3973. |
| [34] |
CHEN Baoliang, CHEN Zaiming, LÜ Shaofang. A novel magnetic biochar efficiently sorbs organic pollutants and phosphate[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(2): 716. DOI:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.08.067 |
| [35] |
INYANG M, GAO Bin, PULLAMMANAPPALLIL P, et al. Biochar from anaerobically digested sugarcane bagasse[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(22): 8868. DOI:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.088 |
| [36] |
周书葵, 田林玉, 荣丽杉, 等. 3种固定剂联合修复铀尾矿污染土壤[J]. 精细化工, 2020, 37(10): 2105. ZHOU Shukui, TIAN Linyu, RONG Lishan, et al. Remediation of uranium contaminated soil with three combined stabilizers[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2020, 37(10): 2105. |
| [37] |
吴丹萍, 李海红, 张田田. ZnCl2/AlCl3改性生物炭的甲基紫吸附特性研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2020, 48(8): 227. WU Danping, LI Haihong, ZHANG Tiantian. Study on adsorption characteristics of methyl violet by modified biochar[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2020, 48(8): 227. |
| [38] |
王思源, 申健, 李盟军, 等. 不同改性生物炭功能结构特征及其对铵氮吸附的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(5): 1037. WANG Siyuan, SHEN Jian, LI Mengjun, et al. Functional and structural characteristics of different modified biochar and its impacts on ammonium nitrogen adsorption[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(5): 1037. |
| [39] |
郭晓慧, 康康, 于秀男, 等. 磁改性柚子皮与杏仁壳生物炭的理化性质研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(S1): 164. GUO Xiaohui, KANG Kang, YU Xiunan, et al. Study on physicochemical properties of magnetic modified biocharderived from pyrolysis of pomelo peel and apricot keanel shell[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2018, 34(S1): 164. |
| [40] |
胡术刚, 栾小凯, 颜昌宙, 等. 改性生物炭的制备及其对水中镉离子的吸附试验[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(5): 12. HU Shugang, LUAN Xiaokai, YAN Changyu, et al. Preparation of modified biochar and its adsorption for cadmium ions in water[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(5): 12. |
| [41] |
吴鸿伟, 陈萌, 黄贤金, 等. 改性生物炭对水体中头孢噻肟的吸附机制[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(7): 2527. WU Hongwei, CHEN Meng, HUANG Xianjin, et al. Preparation of modified biochar for adsorption of cefotaxime in solution[J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(7): 2527. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2018.07.018 |
| [42] |
马艳茹, 孟海波, 沈玉君, 等. 改性生物炭对沼液氨氮的吸附效果研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2018, 20(11): 135. MA Yanru, MENG Haibo, SHEN Yujun, et al. Research on adsorption effect of ammonia-nitrogen from biogas slurry by modified biochar[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(11): 135. |
| [43] |
孙晓杰, 秦永丽, 伍贝贝, 等. 硅烷偶联剂改性生物炭的疏水性能优化试验[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(12): 68. SUN Xiaojie, QIN Yongli, WU Beibei, et al. Optimization of hydrophobic properties of biochar modified by silane coupling agent[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(12): 68. |
| [44] |
陈友媛, 李培强, 李闲驰, 等. 浒苔生物炭对雨水径流中氨氮的吸附特性及吸附机制[J/OL]. 环境科学: 1-19[2020-08-19]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202004051. CHEN Youyuan, LI Peiqiang, LI Xianchi, et al. Effect of Enteromorpha prolifera biochar on the adsorption characteristics and adsorption mechanisms of ammonia nitrogen in rainfall runoff[J/OL]. Environmental Science: 1-19[2020-08-19]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202004051. |
| [45] |
张悍, 吴亦潇, 万亮, 等. 碱改性米糠炭对水中四环素的吸附性能研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2020, 46(6): 20. ZHANG Han, WU Yixiao, WAN Liang, et al. Study on adsorption performance of alkali-modified rice bran biochar for tetracycline in water[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2020, 46(6): 20. |
| [46] |
何红艳, 邹思佳. 介孔生物炭的合成、改性及其对染料的吸附性能研究[J]. 化学试剂, 2020, 42(10): 1148. HE Hongyan, ZOU Sijia., et al. Preparation and modification of mesoporous biochar and adsorption properties for dyes[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2020, 42(10): 1148. |
| [47] |
叶益辰, 孙雨晴, 萨仁格日乐, 等. 磷酸改性生物炭-LDHs(Mg-Al-NO3)复合材料对双酚A的吸附[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(1): 61. YE Yichen, SUN Yuqing, SA Rengerile, et al. Adsorption of bisphenol a by phosphoric acid modified biochar-LDHs(Mg-Al-NO3) composite[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(1): 61. |
| [48] |
孟庆梅, 孟迪, 张艳丽, 等. 榴莲壳生物炭对磺胺嘧啶的吸附性能[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(11): 4651. MENG Qingmei, MENG Di, ZHANG Yanli, et al. Adsorption characteristics of biochar prepared by durian shell on sulfadiazine[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(11): 4651. |
| [49] |
安强, 乔卢阿里·科阿里, 金琳, 等. 氯化锌改性玉米秸秆生物炭对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附特性研究[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2020, 43(10): 104. AN Qiang, CHORLOUALY K, JIN Lin, et al. Study on adsorption property of Cr(VI) by Corn Stalk Biochar modified byzincchloride[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2020, 43(10): 104. |
| [50] |
李安玉, 李双莉, 余碧戈, 等. 镁浸渍生物炭吸附氨氮和磷: 制备优化和吸附机理[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1683. LI Anyu, LI Shuangli, YU Biyi, et al. Adsorption of ammonia nitrogen and phosphorus by magnesium impregnated biochar: Preparation optimization and adsorption mechanism[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(4): 1683. |
| [51] |
王鹏飞, 郅蒙蒙, 储昭升, 等. 生物质粒径对负载MgO生物炭吸附水体中磷的影响[J/OL]. 环境科学: 1-11[2020-08-19]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202005063. WANG Pengfei, ZHI Mengmeng, CHU Zhaosheng, et al. Effect of biomass particle size on the adsorption of phosphorus from the aqueous solution by MgO-loaded biochar[J/OL]. Environmental Science: 1-11[2020-08-19]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202005063. |
| [52] |
智燕彩, 赖欣, 谭炳昌, 等. 铁锰镁离子改性生物炭对溶液硝态氮的吸附性能研究[J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(7): 1588. ZHI Caiyan, LAI Xin, TAN Bingchang, et al. Adsorption of nitrate by iron, manganese and magnesium ion modified biochars[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 34(7): 1588. |
| [53] |
乔洪涛, 乔永生, 秦瑞红, 等. 微波酸改性生物炭的制备及其对Cd2+的吸附性能研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2020, 48(4): 212. QIAO Hongtao, QIAO Yongsheng, QIN Ruihong, et al. Adsorptive characteristics of Cd2+ in solution by MBC[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2020, 48(4): 212. |
| [54] |
储刚, 赵婧, 刘洋, 等. 氧氟沙星和诺氟沙星在磷酸改性生物炭上的等温吸附行为[J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(3): 462. CHU Gang, ZHAO Jing, LIU Yang, et al. Sorption of ofloxacin and norfloxacin on modified biochars using phosphoric acid treatment[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(3): 462. |
| [55] |
BAHARUM N A, NASIR H M, ISHAK M Y, et al. Highly efficient removal of diazinon pesticide from aqueous solutions by using coconut shell modified biochar[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 13(7): 6106. |
| [56] |
PANDI K, PRABHU S M, CHOI J. Fabrication of lanthanum methanoateon sucrose-derived biomass carbon nanohybrid for the efficient removal of arsenate from water[J]. Chemosphere, 2020(262): 127596. |
| [57] |
ZHANG Xu, GANG D D, SUN Peizhe, et al. Goethite dispersed corn straw-derived biochar for phosphate recovery from synthetic urine and its potential as a slow-release fertilizer[J]. Chemosphere, 2021(262): 127861. |
| [58] |
OGINNI O, YAKABOYLU G A, SINGH K, et al. Phosphorus adsorption behaviors of MgO modified biochars derived from waste woody biomass resources[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 8(2): 103723. |
| [59] |
AJMAL Z, MUHMOOD A, DON R, et al. Probing the efficiency of magnetically modified biomass-derived biochar for effective phosphate removal[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020(253): 109730. |
| [60] |
SONG Jingpeng, ZHANG Shuaishuai, LI Guixianng, et al. Preparation of montmorillonite modified biochar with various temperatures and their mechanism for Zn ion removal[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020(391): 121692. |
| [61] |
WANG Yue, YANG Qixia, CHEN Jiacheng, et al. Adsorption behavior of Cr(VI) by magnetically modified Enteromorpha prolifera based biochar and the toxicity analysis[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020(395): 122658. |
| [62] |
GODLEWAKA P, BOGUSZ A, DOBROWOLSKI R, et al. Engineered biochar modified with iron as a new adsorbent for treatment of water contaminated by selenium[J]. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 2020, 24(11): 824. |
| [63] |
YIN Daixia, WANG Xin, PENG Bo, et al. Effect of biochar and Fe-biochar on Cd and As mobility and transfer in soil-rice system[J]. Chemosphere, 2017(186): 928. |
| [64] |
张学庆, 费宇红, 田夏, 等. 磷改性生物炭对Pb、Cd复合污染土壤的钝化效果[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2017, 39(9): 1017. ZHANG Queqing, FEI Yuhong, TIAN Xia, et al. The passivation effect of Pb, Cd composite polluted soil by phosphorus-modified biochar[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2017, 39(9): 1017. |
| [65] |
KHAN M A, AQADAMIL A A, OTERO M, et al. Heteroatom-doped magnetic hydrochar to remove post-transition and transition metals from water: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption studies[J]. Chemosphere, 2019(218): 1089. |
| [66] |
ZHANG Shihong, ZHANG Han, CAI Ji'an, et al. Evaluation and prediction of cadmium removal from aqueous solution by phosphate-modified activated bamboo biochar[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 32(4). |
| [67] |
周志云, 马文连, 周振, 等. 磷酸改性生物炭和氯混施对土壤铅形态及小麦铅吸收的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(5): 899. ZHOU Zhiyun, MA Wenlian, ZHOU Zhen, et al. Effects of phosphoric-acid-modified biochar combined with chlorine on soil lead form and lead absorption in wheat[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(5): 899. |
| [68] |
YU Zhihong, QIU Weiwen, WANG Fei, et al. Effects of manganese oxide-modified biochar composites on arsenic speciation and accumulation in an indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivar[J]. Chemosphere, 2017(168): 341. |
| [69] |
ISLAM M S, CHEN Yali, WENG Liping, et al. Watering techniques and zero-valent iron biochar pH effects on As and Cd concentrations in rice rhizosphere soils, tissues and yield[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021(100): 144. |
| [70] |
CHEN Dun, WANG Xiaobing, WANG Xiaoli, et al. The mechanism of cadmium sorption by sulphur-modified wheat straw biochar and its application cadmium-contaminated soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020(714): 136550. |
| [71] |
SHI Yueyue, SHAN Rui, LU Lili, et al. High-efficiency removal of Cr(VI) by modified biochar derived from glue residue[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020(254): 119935. |
| [72] |
荣嵘, 张瑞雪, 吴攀, 等. AMD铁絮体改性生物炭对重金属吸附机理研究-以Pb(Ⅱ)为例[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(3): 959. RONG Rong, ZHANG Ruixue, WU Pan, et al. The adsorption mechanisms of heavy metals by the biochar modified by AMD iron floc: Taking Pb(Ⅱ) as an example[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(3): 959. |
| [73] |
陆嫚嫚, 马洁晨, 张学胜, 等. MnOx负载生物质炭对Cu2+、Zn2+的吸附机理研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(10): 2297. LU Manman, MA Jiecheng, ZHANG Xuesheng, et al. The properties and mechanism of Cu2+ and Zn2+ sorption by MnOx-loaded biochar[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(10): 2297. |
| [74] |
徐建玲, 张頔, 聂苗青, 等. PEI功能化秸秆生物炭对水中Cr6+的吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(1): 155. XU Jianling, ZHANG Di, NIE Miaoqing, et al. Adsorption of Cr6+ on polyethyleneimine-functionalized straw biochar from aqueous solution[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 155. |
| [75] |
孙彤, 李可, 付宇童, 等. 改性生物炭对弱碱性Cd污染土壤钝化修复效应和土壤环境质量的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(7): 2571. SUN Tong, LI Ke, FU Yutong, et al. Effect of modified biochar on immobilization remediation of weakly alkaline Cd-contaminated soil and environmental quality[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(7): 2571. |
| [76] |
孟繁健, 朱宇恩, 李华, 等. 改性生物炭负载nZVI对土壤Cr(VI)的修复差异研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(12): 4715. MENG Fanjian, ZHU Yuen, LI Hua, et al. Effects of the remediation of Cr (VI) in soil by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2017, 37(12): 4715. |
| [77] |
周春地, 阳婷, 闵熙泽, 等. 零价铁、铜改性生物炭及其对Cr(Ⅵ)吸附性能的影响[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(10): 4275. |
| [78] |
WU Huihui, WEI Wenxia, XU Congbin, et al. Polyethylene glycol-stabilized nano zero-valent iron supported by biochar for highly efficient removal of Cr (VI)[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020(188): 109902. |
| [79] |
ZHANG Runyuan, ZHANG Nuanqin, FANG Zhanqiang. In situ remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil by cmc-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron composited with biochar[J]. Water Science Technology, 2018, 77(6): 1622. |
| [80] |
梁婷, 李莲芳, 朱昌雄, 等. 铈锰改性生物炭对土壤As的固定效应[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(11): 5114. LIANG Ting, LI Lianfang, ZHU Changxiong, et al. Cerium-manganese modified biochar immobilizes arsenic in farmland soils[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(11): 5114. |
| [81] |
HUANG Xixian, LIU Yunguo, LIU Shaobo, et al. Effective removal of Cr(VI) using β-cyclodextrin-chitosan modified biochars with adsorption/reduction bifuctional roles[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(1): 94. |
| [82] |
杨兰, 李冰, 王昌全, 等. 改性生物炭材料对稻田原状和外源镉污染土钝化效应[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(9): 3562. YANG Lan, LI Bing, WANG Changquan, et al. Effect of modified biochars on soil cadmium stabilization in paddy soil suffered from original or exogenous contamination[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(9): 3562. |
| [83] |
RAJAPAKSHA A U, CHEN S S, TSANG D C W, et al. Engineered/designer biochar for contaminant removal/immobilization from soil and water: Potential and implication of biochar modification[J]. Chemosphere, 2016(148): 276. |
 2021, Vol. 19
2021, Vol. 19