2. 上海海洋大学 上海水产养殖工程技术研究中心, 上海 201306;
3. 江苏省渔业技术推广中心, 江苏 南京 210036;
4. 安徽省水产技术推广总站, 安徽 合肥 230601
自然界中同一种珍珠贝的贝壳可以表现出多种颜色,所产珍珠颜色也丰富多彩[1]。黑蝶贝(Pinctada margaritifera)所产珍珠的颜色包括孔雀绿、酪乳黄、银冰灰、乳亮白等[2];马氏珠母贝(Pinctada martensii)所产珍珠颜色主要为白色、黄色等[3];企鹅珍珠贝(Pteria penguin)则可以产出深褐色珍珠或其他浅色珍珠[4]。三角帆蚌(Hyriopsis cumingii)作为我国特有的淡水育珠蚌,所产珍珠珠质细腻光滑,所产珍珠颜色主要为白色,红色、黄色、紫色和褐色珍珠稀少[5]。珍珠颜色是让消费者产生第一感官印象的指标,更是评价珍珠质量的重要指标,因此定向培育天然彩色珍珠可显著提高珍珠的价值。研究[6-8]已发现珍珠颜色与供片蚌内壳色显著相关,且珍珠贝的壳色可以稳定遗传给后代。因此,内壳色性状已逐渐成为珍珠贝遗传改良的重要目标性状[9-11]。
三角帆蚌、马氏珠母贝、黑蝶贝均以内壳色为目标性状开展选育工作[12-13],但由于内壳色属于珍珠贝内部性状,难以直接测量,目前主要采用目测法对内壳色进行主观评价。目测法不仅选种速度慢,而且易受主观因素和环境条件的影响[14],大大限制了选育规模和选育效率[15],致使贝类多产性的育种优势难以发挥,依赖于表型性状准确测量的现代育种技术也难以应用[16]。
本团队在三角帆蚌“申紫1号”育种过程中,通过三角帆蚌幼蚌阶段外部观察间接评价内壳色,产生良好选育效果[17],推测该阶段外壳色与内壳色可能存在一定关联性。为了验证上述设想,以紫色品系和白色品系三角帆蚌幼蚌为研究对象,分析不同月龄三角帆蚌内外壳颜色参数相关性,并确定最大相关性出现时期。研究结果为采用三角帆蚌外壳色间接评价内壳色奠定理论基础,并将大大提高三角帆蚌内壳色性状遗传改良效率。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料2016年5月中旬,在上海海洋大学三角帆蚌良种繁育基地,挑选性状优良的三角帆蚌“申紫1号”和白色品系三角帆蚌亲蚌,鉴别雌雄后,将所选亲本挂养于2个温室大棚中分别培育,隔日检查母蚌怀卵情况,选取同一天怀卵的紫色和白色雌性三角帆蚌各3只,按常规方法育苗[18]。当年7月中旬蚌苗出池,选取生长良好的紫色品系三角帆蚌幼蚌600只和白色品系三角帆蚌幼蚌120只,养殖于上海海洋大学崇明竖新养殖基地。养殖密度为每个网箱(45 cm × 45 cm × 10 cm)放入40只幼蚌,吊养水层深度为40 cm[19]。
1.2 实验方法 1.2.1 同时期三角帆蚌内外壳色相关性实验在分析同时期三角帆蚌内外壳色相关性的实验中,于4月龄、4.5月龄、5月龄、5.5月龄、6月龄和8月龄,分别随机取30只紫色品系三角帆蚌,解剖后,测量外壳色和内壳色[20]。
1.2.2 不同时期三角帆蚌外壳色与8月龄三角帆蚌内壳色相关性实验4月龄时,随机取紫色和白色品系三角帆蚌各60只,用防水粘贴标签标记,并测量外壳色,测量后将三角帆蚌放回网箱吊养,在4.5月龄、5月龄、5.5月龄、6月龄持续跟踪测量外壳色,至8月龄时,同时测量外壳色和内壳色。
1.3 颜色参数测量与数据分析采用Lovibond-RT200表面色度计,测量贝壳L*、a*、b*和dE*颜色参数[21]。L*为明度,L*>0颜色偏白,L* < 0颜色偏黑;a*>0颜色偏红,a* < 0颜色偏绿;b*>0颜色偏黄,b* < 0颜色偏蓝。色差值dE*表示所测样品和标准白之间的色差,dE*越大表示色彩越丰富,dE*越小则所测颜色就越单一。根据内外壳颜色前后渐变的特点和壳型特征,经预实验,分别在内外壳前端和后端各选取1个部位作为测量位置,即OF、OB、IF和IB(图 1)。内外壳色各颜色参数均取两个部位测量值的平均值[22]。
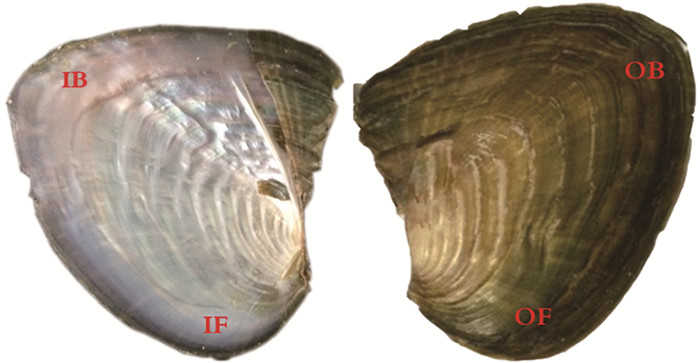
|
IF为左内壳前闭壳肌痕;IB为左内壳外套痕与纵肋交叉部位;OF和OB分别为与IF和IB相对应的外壳部位。 IF, the anterior adductor muscle scar in the left inner shell; IB, the cross site of mantle scar and posterior ridge in the left inner shell; OF and OB are the opposite positions of IF and IB on the outer shell respectively. 图 1 壳色测量位置示意图 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of measured positions of shell color |
采用Excel 2016软件对测量数据进行初步整理,再用SPSS 22.0统计软件中的Pearson法进行相关性分析[23]。
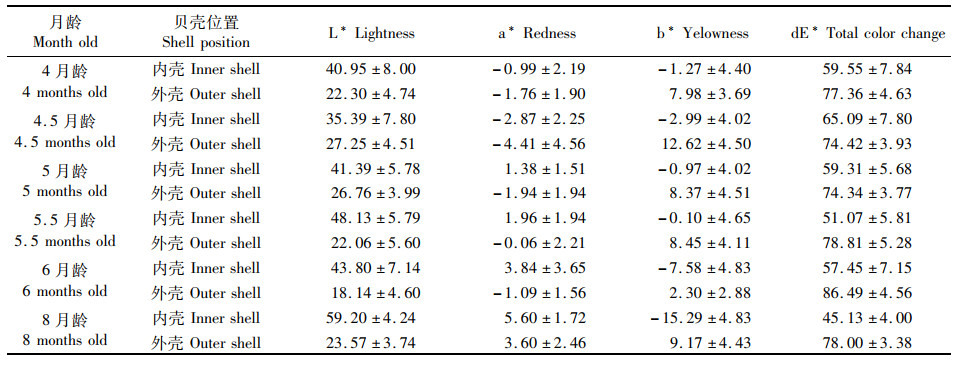
2 结果 2.1 紫色品系三角帆蚌不同月龄幼蚌内外壳色比较分析紫色品系三角帆蚌4~8月龄幼蚌内壳和外壳颜色参数见表 1。各月龄紫色蚌的外壳颜色参数L*值均小于内壳,外壳颜色参数dE*值均大于内壳对应参数值,表明三角帆蚌外壳颜色偏暗,内壳颜色较浅,外壳颜色较内壳颜色丰富。内壳颜色参数a*值于5月龄由负值转向正值,且红色度逐渐加深,外壳颜色参数a*值则于8月龄由负值转向正值;随着月龄增加,内壳和外壳颜色参数b*值则向两个方向发展,内壳蓝色度逐渐加深,外壳黄色度逐渐加深;各时期颜色参数L*和dE*变化趋势不明显。
|
表 1 紫色品系三角帆蚌不同月龄幼蚌内外壳颜色参数 Tab.1 The color parameters of inner shell and outer shell in purple Hyriopsis cumingii at different ages |
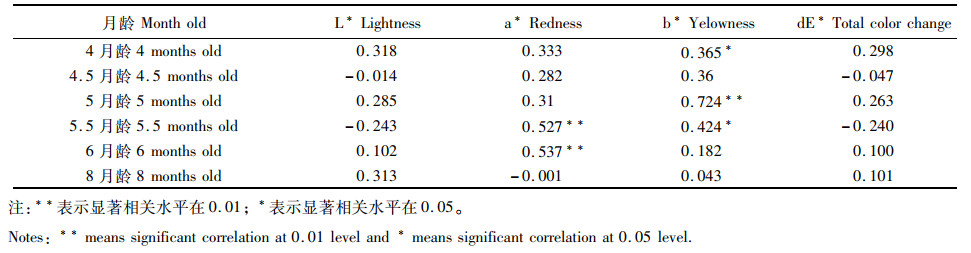
紫色品系三角帆蚌相同月龄幼蚌外壳色与内壳色的相关性分析结果见表 2。5.5月龄和6月龄时的外壳颜色参数a*与同时期内壳颜色的a*呈极显著相关(P < 0.01),相关系数分别为0.527和0.537,相关系数在6月龄时最大。4月龄、5月龄和5.5月龄时期,外壳颜色参数b*与同时期的内壳颜色参数b*呈显著正相关,相关系数分别为0.365、0.724和0.424,其中5月龄时期内外壳色相关系数最大(P < 0.01)。各时期外壳颜色参数L*和dE*与同时期内壳颜色参数L*和dE*均未见显著相关性(P>0.05)。
|
表 2 紫色品系三角帆蚌同期幼蚌内外壳颜色参数的相关性分析 Tab.2 The correlation analysis of the inner shell color parameters and outer shell color parameters of purple Hyriopsis cumingii at same ages |
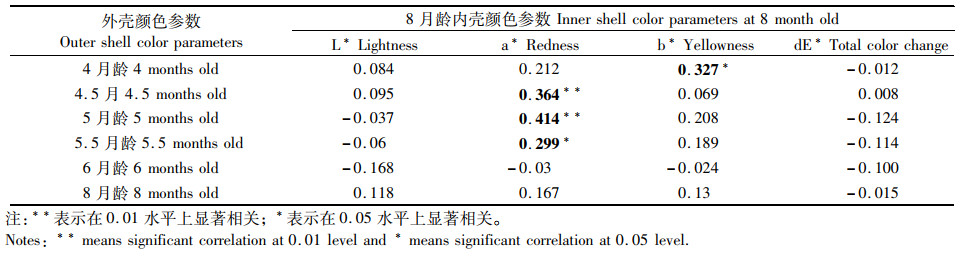
采用三角帆蚌个体标记跟踪法,测量不同时期紫色品系三角帆蚌外壳色,并分析其与8月龄内壳色相关性,结果见表 3。在4.5月龄、5月龄、5.5月龄时,外壳颜色参数a*与8月龄时期的内壳颜色参数a*均呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),相关系数分别为0.364、0.414和0.299,5月龄时期出现最大相关系数,且呈极显著相关(P < 0.01)。在4月龄时,外壳颜色参数b*与8月龄时期的内壳颜色参数b*呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),相关系数为0.327。在6个不同的测量时期,外壳颜色参数L*和dE*与8月龄时期的内壳颜色参数L*和dE*均未见显著相关性(P>0.05)。
|
表 3 紫色品系三角帆蚌不同月龄幼蚌外壳色参数与8月龄幼蚌内壳色参数相关性分析 Tab.3 The correlation analysis between the outer shell color parameters of different aged mussels and inner shell color parameters of 8-month-old mussels in purple Hyriopsis cumingii |
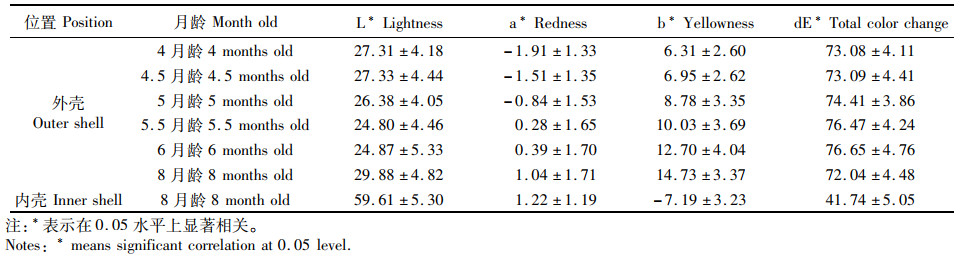
采用三角帆蚌个体标记跟踪法,测量4~8月龄白色品系三角帆蚌外壳颜色参数和8月龄幼蚌内壳颜色参数,结果见表 4。白色品系三角帆蚌8月龄幼蚌内壳颜色参数dE*明显低于紫色品系,与品系特征一致。除5月龄外,不同月龄白色品系三角帆蚌幼蚌外壳颜色参数dE*均低于紫色品系,也反映出品系特征。在4月龄、4.5月龄和5月龄时,外壳颜色参数a*为负,在5.5月龄、6月龄和8月龄时,外壳颜色参数a*为正,且随着月龄的增加而逐渐变大;在这6个不同的测量时期,外壳色的b*均为正值,且随着月龄的增加而逐渐变大,贝壳黄色度不断增加。
|
表 4 白色品系三角帆蚌不同月龄幼蚌外壳色参数和8月龄幼蚌内壳色参数 Tab.4 The outer shell color parameters of different aged mussels and inner shell color parameters of 8-month-old mussels in white Hyriopsis cumingii |
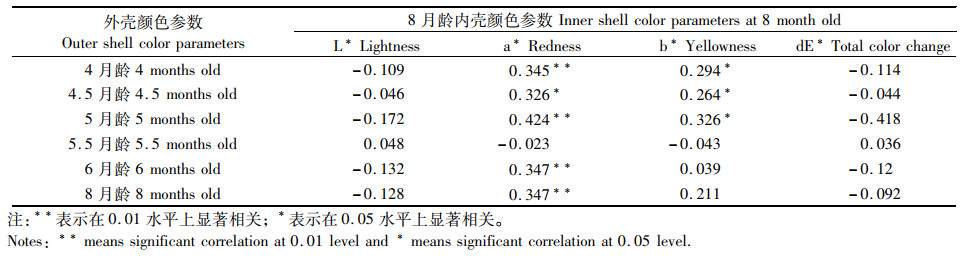
在白色品系三角帆蚌实验中,除5.5月龄外,在4月龄、4.5月龄、5月龄、6月龄和8月龄时,外壳颜色参数a*与8月龄时内壳颜色参数a*均存在显著正相关性(P < 0.05, 表 5),相关系数分别为0.345、0.326、0.424、0.347和0.347,5月龄时呈现最大相关系数。4月龄、4.5月龄、5月龄时,外壳颜色参数b*与8月龄内壳颜色参数b*呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),相关系数分别为0.294、0.264和0.326,5月龄时期呈现最大相关系数。但不同月龄白色品系三角帆蚌外壳颜色参数L*和dE*与8月龄的内壳颜色参数L*和dE*均未见显著相关性(P>0.05)。
|
表 5 白色品系三角帆蚌不同月龄幼蚌外壳色参数与8月龄幼蚌内壳色参数相关性分析 Tab.5 The correlation analysis between the outer shell color parameters of different aged mussels and inner shell color parameters of 8-month-old mussels in white Hyriopsis cumingii |
颜色是影响珍珠价值的重要因素之一,通过改良供片贝内壳色可实现彩色珍珠定向培育,因此,以内壳色为目标性状的育种工作在三角帆蚌、马氏珠母贝、黑蝶贝等育珠贝中普遍开展[2, 11-15],但由于内壳色不易直接观测,选种效率较低且准确性不高。刘越等[24]评估了供片蚌制备小片后可正常损伤恢复的最大组织移取量和最佳位置,建立了通过评价供片蚌育珠效果选择供片蚌的选育技术,该选育方法较为可靠,但受育珠周期较长的限制,选育进展仍较慢。因此,珍珠贝内壳色选育方法亟待提升。
本实验室研究发现三角帆蚌早期发育阶段贝壳是透明或半透明的,该时期可从外观透视内壳色[25],但对外壳色和内壳色关联性未做深入研究。WEN等[26]研究发现三角帆蚌壳长26 mm时,不同色系三角帆蚌外壳色已可明显区分;笔者在三角帆蚌苗种繁育过程中发现紫色品系和白色品系三角帆蚌壳长1 cm时,不同品系的壳色特征开始出现,并逐步明显。本研究发现不同时期三角帆蚌内外壳色变化程度有较大区别,因此内外壳色相关性的最佳时期的确定是开展内壳色早期选育的技术关键。
KY等[27]对3月龄黑蝶贝进行外壳色和内壳色表型组合选育研究,发现黑色外壳色和绿色内壳色表型的黑蝶贝可用于生产孔雀绿颜色珍珠,红色外壳色和黄色内壳色表型的黑蝶贝生产的珍珠颜色趋于多样,取得较好的育珠效果。另外,大溪地养殖业者采用外壳色作为依据评价内壳色已形成惯例[28]。本团队在选育三角帆蚌“申紫1号”过程中,也在壳色透明期开展选种工作,取得良好效果[17]。本研究综合分析三角帆蚌早期不同时期内外壳颜色参数相关性,初步确定5月龄是通过三角帆蚌外壳色间接评价内壳色的最佳时期,对实现三角帆蚌内壳颜色的早期选育工作具有重要意义。另外,尽管内外壳颜色参数存在显著相关性,但也存在相关系数较低的问题,因此,建议育种实践中进行外壳色和内壳色组合选育更佳。
珍珠贝壳色受环境的影响较大,本研究也发现三角帆蚌早期壳色变异较小,该时期受到环境的影响较小,因此,珍珠贝幼体是开展珍珠贝颜色分子机制研究的较好动物模型。早期幼体贝壳呈现较小的颜色多态性,成体贝壳呈现较大的颜色多态性,意味着每种幼体贝壳颜色表型将会发育成几种成体颜色表型。解析幼体贝壳颜色表型与成体贝壳颜色表型的关系,是进一步优化内壳色早期选育技术的关键。另外,研究发现黑蝶贝软体部组织颜色也影响所育珍珠颜色,橘红色外套膜的黑蝶贝与浅色贝壳和珍珠具有相关性。进一步分析发现,这种相关性的分子机制涉及壳基质蛋白基因Shem4和黑色素代谢途径基因的表达情况[29],考虑到软体部颜色对珍珠颜色的影响,深入研究软体部与内外壳色关联性分子机制,对三角帆蚌壳色的选育具有重要意义。
| [1] |
管云雁, 何毛贤. 海产经济贝类壳色多态性的研究进展[J]. 海洋通报, 2009, 28(1): 108-114. GUAN Y Y, HE M X. Progress on shell coloration polymorphism in seashells[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2009, 28(1): 108-114. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2009.01.017 |
| [2] |
MCGINTY E L, EVANS B S, TAYLOR J U U, et al. Xenografts and pearl production in two pearl oyster species, P. maxima and P. margaritifera:effect on pearl quality and a key to understanding genetic contribution[J]. Aquaculture, 2010, 302(3/4): 175-181. |
| [3] |
顾志峰, 王嫣, 石耀华, 等. 马氏珠母贝两个不同地理种群的形态性状和贝壳珍珠质颜色比较分析[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2009, 30(1): 79-86. GU Z F, WANG Y, SHI Y H, et al. Comparison of morphometrics and shell nacre colour between two geographical populations of pearl oyster Pinctada martensii (Dunker)[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2009, 30(1): 79-86. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2009.01.013 |
| [4] |
RUIZ-RUBIO H, ACOSTA-SALMÓN H, OLIVERA A, et al. The influence of culture method and culture period on quality of half-pearls ('mabé') from the winged pearl oyster Pteria sterna, Gould, 1851[J]. Aquaculture, 2006, 254(1/4): 269-274. |
| [5] |
汪桂玲, 白志毅, 刘晓军, 等. 三角帆蚌种质资源研究进展[J]. 水产学报, 2014, 38(9): 1618-1627. WAND G L, BAI Z Y, LIU X J, et al. Research progress on germplasm resources of Hyriopsis cumingii[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2014, 38(9): 1618-1627. |
| [6] |
WADA K T, KOMARU A. Effect of selection for shell coloration on growth rate and mortality in the Japanese pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata martensii[J]. Aquaculture, 1994, 125(1/2): 59-65. |
| [7] |
刘越.三角帆蚌供片蚌对珍珠质量的影响[D].上海: 上海海洋大学, 2013. LIU Y. The effect of donor Hyriopsis cumingii on the quality of pearls[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2013. |
| [8] |
彭建庆.三角帆蚌EST-SSR标记开发及生长性状和内壳色遗传分析[D].上海: 上海海洋大学, 2017. PENG J Q. Development of EST-SSR markers and genetic analysis of growth performance and inner shell color of Hyriopsis cumingii[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2017. |
| [9] |
王鑫.淡水有核养殖珍珠宝石学特征及质量影响因素[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. WANG X. Gemological characteristic and quality influencing factors of freshwater nucleated cultured pearls[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015. |
| [10] |
李清清, 白志毅, 刘晓军, 等. 三角帆蚌生长性状和内壳色与所产无核珍珠质量的相关性分析[J]. 水产学报, 2015, 39(11): 1631-1639. LI Q Q, BAI Z Y, LIU X J, et al. Correlation analysis of non-nucleated pearl quality parameters with growth traits and inner shell color of Hyriopsis cumingii[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2015, 39(11): 1631-1639. |
| [11] |
王照旗, 韩学凯, 白志毅, 等. 三角帆蚌紫色选育系1龄阶段内壳色及生长性状的遗传参数估计[J]. 水产学报, 2014, 38(5): 644-650. WANG Z Q, HAN X K, BAI Z Y, et al. Estimates of genetic parameters for inner shell color and growth straits during one year old stage in the purple strain of Hyriopsis cumingii using microsatellite based parentage assignment[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2014, 38(5): 644-650. |
| [12] |
姜琦, 白志毅, 孙朝虎. 三角帆蚌所育不同颜色珍珠及其相关组织金属元素种类和含量差异分析[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2019, 28(6): 882-889. JIANG Q, BAI Z Y, SUN C H. Analysis of metallic element types and contents in pearls of different colors and their related tissues in Hyriopsis cumingii[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2019, 28(6): 882-889. |
| [13] |
吴曼, 刘宝锁, 黄桂菊, 等. 合浦珠母贝全同胞家系贝壳珍珠质颜色分析[J]. 南方水产科学, 2014, 10(6): 44-50. WU M, LIU B S, HUANG G J, et al. Analysis of shell nacre color in full-sib families of pearl oyster (Pinctada fucata)[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2014, 10(6): 44-50. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2014.06.006 |
| [14] |
张欣.三种珍珠贝贝壳珍珠层颜色特征分析及其颜色与生长性状相关性研究[D].海口: 海南大学, 2012. ZHANG X. Color characteristics analysis of three kinds of pearl oyster and the correlation between color and growth traits[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2012. |
| [15] |
殷浩, 白志毅, 李家乐. 优质紫色淡水有核珍珠的培育方法[J]. 科学养鱼, 2015(10): 38. YIN H, BAI Z Y, LI J L. Cultivation of high quality purple fresh water with nuclear pearls[J]. Scientific Fish Farming, 2015(10): 38. |
| [16] |
张晓娟, 周莉, 桂建芳. 遗传育种生物技术创新与水产养殖绿色发展[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2019, 49(11): 1409-1429. ZHANG X J, ZHOU L, GUI J F. Biotechnological innovation in genetic breeding and sustainable green development in Chinese aquaculture[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2019, 49(11): 1409-1429. |
| [17] |
孙朝虎, 白志毅, 李清清, 等. 三角帆蚌生长和壳色性状早期复合选择的优化研究[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2019, 40(2): 91-97. SUN C H, BAI Z Y, LI Q Q, et al. The optimization of early compound selection for growth traits and shell color in Hyriopsis cumingii[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2019, 40(2): 91-97. |
| [18] |
陈友明, 李家乐, 白志毅. 三角帆蚌人工繁育工艺的改良及效果[J]. 渔业现代化, 2007, 34(5): 26-28. CHEN Y M, LI J L, BAI Z Y. Improvement and effect of artificial breeding process of spinnaker[J]. Fishery Modernization, 2007, 34(5): 26-28. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9580.2007.05.011 |
| [19] |
高吉华, 王伟良, 王岩, 等. 吊养在池塘不同水层中的三角帆蚌的存活和生长[J]. 淡水渔业, 2007, 37(4): 61-64. GAO J H, WANG W L, WANG Y, et al. Survival and growth of freshwater pearl mussel (Hyriopsis cumingii) suspended at different water depth in a commercial pond[J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 2007, 37(4): 61-64. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2007.04.014 |
| [20] |
杜美荣, 方建光, 高亚平, 等. 不同贝龄栉孔扇贝数量性状的相关性和通径分析[J]. 水产学报, 2017, 41(4): 580-587. DU M R, FANG J G, GAO Y P, et al. Correlation and path analysis of quantitative traits of different-age Chlamys farreri[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2017, 41(4): 580-587. |
| [21] |
宋俊霖, 李琪, 孔令锋. 长牡蛎四种壳色选育系壳色性状的量化分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2018, 48(1): 25-30. SONG J L, LI Q, KONG L F. A quantitative analysis of four shell color strains of pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas)[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2018, 48(1): 25-30. |
| [22] |
金武.三角帆蚌生长性状与育珠性状的遗传参数估计[D].上海: 上海海洋大学, 2012. JIN W. Genetic parameters of growth rate and pearl production trait of Hyriopsis cumingii[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2012. |
| [23] |
QU X Y, SU L, LI H X, et al. Assessing the relationship between the abundance and properties of microplastics in water and in mussels[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 621: 679-686. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.284 |
| [24] |
LIU Y, BAI Z Y, LI Q Q, et al. Healing and regeneration of the freshwater pearl mussel Hyriopsis cumingii Lea after donating mantle saibos[J]. Aquaculture, 2013, 392-395: 34-43. DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.01.035 |
| [25] |
刘士力, 李家乐, 张根芳, 等. 三角帆蚌稚蚌形态发育与生长特性[J]. 水产学报, 2009, 33(4): 604-609. LIU S L, LI J L, ZHANG G F, et al. Morphological development and growth characteristics of the juvenile of Hyriopsis cumingii[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2009, 33(4): 604-609. |
| [26] |
WEN H B, GU R B, CAO Z M, et al. Variation of color and ray pattern in juvenile shells in hatchery-produced freshwater triangle pearl mussels, Hyriopsis cumingii, in China[J]. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 2013, 44(1): 154-160. DOI:10.1111/jwas.12013 |
| [27] |
KY C L, LE PABIC L, KOUA M S, et al. Is pearl colour produced from Pinctada margaritifera predictable through shell phenotypes and rearing environments selections?[J]. Aquaculture Research, 2017, 48(3): 1041-1057. DOI:10.1111/are.12947 |
| [28] |
KY C L, NAKASAI S, POMMIER S, et al. The mendelian inheritance of rare flesh and shell colour variants in the black-lipped pearl oyster (Pinctada margaritifera)[J]. Animal Genetics, 2016, 47(5): 610-614. DOI:10.1111/age.12454 |
| [29] |
KY C L, BLAY C, BROUSTAL F, et al. Relationship of the orange tissue morphotype with shell and pearl colouration in the mollusc Pinctada margaritifera[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 5114. |
2. Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Aquaculture, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China;
3. Fisheries Technology Extension Center of Jiangsu Province, Nanjing 210036, Jiangsu, China;
4. Fisheries Technology Extension Center of Anhui Province, Hefei 230601, Anhui, China
 2021,
Vol. 30
2021,
Vol. 30


