2. 上海市水产养殖工程技术研究中心, 上海 201306;
3. 水产动物遗传育种上海市协同创新中心, 上海 201306;
4. 上海鱼跃水产专业合作社, 上海 201611
水草作为生态系统的初级生产者,是水体食物链的基础,可影响水中鱼类、底栖生物、浮游动植物的组成和分布,而且可以起到稳定底质的作用[1]。水草在生长过程中,可有效吸收水体的氮磷[2-4],还可以去除有机物和重金属[5-6],促进水环境的改善,对整个生态系统的结构、功能和系统稳定性具有重要的作用[7]。因此,在污水处理和水体富营养化治理方面,水生植被的生态修复法已成为重要的方法[8-9]。水草在生态养殖方面也起到非常重要的作用,在河蟹生态养殖中,水草的作用尤为明显,俗话说“蟹大小、看水草”,充分肯定了水草在河蟹养殖中的重要性。水草不仅是河蟹隐匿、栖息和脱壳的重要场所,还是河蟹的天然植物性饵料。河蟹养殖池塘的氮、磷通常会超标,有利于藻类的繁殖,藻类的大量繁殖可能会导致水质的严重恶化,水草不仅可以有效降低氮、磷含量,避免藻类的大量繁殖,还可以分泌化感物质抑制藻类的生长,王立新等[10]发现黑藻分泌的化感物质可明显抑制铜绿微囊藻的生长。鲜放鸣等[11]的研究结果表明:金鱼藻、微齿眼子菜和苦草均具有较强的克藻作用。
从水草的生长周期看,只要合理地控制水草种植密度,对生态系统和水质会产生正效应,但是,水草的正常衰亡、机械损坏和高温季节腐烂等会对生态系统和水质会产生负效应。如水生植物茭草(Zizania latifolia)腐烂分解使东太湖形成“茭黄水” [12],菹草(Potamogeton crispus)腐解造成秦皇岛洋河水库的二次污染[13]。但水体中保留适量的植物残体,能够有效地促进系统中氮、磷等营养元素的循环,并在一定程度上去除系统硝态氮,降低水体的氮负荷。强蓉蓉等[14]和潘慧云等[15]认为适量的水生植物残体不会使水质明显恶化,且较低的腐解速率可降低营养盐的循环速度,有利于控制水体富营养化,但较大量的植物残体会造成水体缺氧,植物残体可能会发生厌氧分解,造成水质恶化。目前有关河蟹生态养殖水质净化的研究主要集中在水草种类和密度方面,关于水草腐解对水质影响的研究甚少。水草腐解过程及产生的水质效应会因种类不同而存在差异,本文就河蟹生态养殖池塘中常见的3种水草腐烂分解过程对水质的影响进行研究,以期在深化水质净化、环境保护和河蟹生态养殖池塘中水草残体的管理方面提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验材料试验用的3种水草为轮叶黑藻(Hydrilla verticillata)、伊乐藻(Elodea nuttallii)和金鱼藻(Ceratophyllum demersum),2015年7月取自上海松江区泖港镇田黄村三泖水产养殖基地。三泖水产养殖基地河蟹生态养殖池塘中种植了大量的水草,夏季水草的覆盖率达70%以上。3种水草均为沉水植物,地上部分和地下部分的腐解节律不同,仅取地上离根部10 cm以上部分的茎、叶作为试验材料。将采集的3种水草先在池塘中洗去污泥,在实验室用自来水反复冲洗后,用去离子水漂洗,去除杂质,放置在室外风干,然后于80 ℃的恒温干燥箱中烘干至恒重[16-17]。取水草所在池塘的表层底泥,用200目网筛去除底泥的植物残体和其他杂质,向过滤好的底泥中加入自来水,不断搅拌,配制成底泥匀浆备用。试验所用的容器为10 L不透明的白色带盖塑料桶(桶盖上有圆孔),用自来水浸泡3 d后风干备用。为了防止水草腐解过程中沉入桶底,水草全部装在200目的网袋中进行试验,试验前,网袋进行浸泡处理,避免网袋对试验造成影响。
1.2 试验设计试验于2015年7-9月在三泖水产养殖基地进行。每个塑料桶中加入250 mL底泥匀浆(试验前测定底泥匀浆的TN和TP的质量分数)和5 L去离子水,在阴暗干燥处放置3 d备用。试验设置4个处理,每个处理3个重复,即取烘干至恒重的轮叶黑藻(A)240 g,分别装在24个网袋中,每个网袋10 g,编号为A1-1、A1-2、A1-3,A2-1、A2-2、A2-3……A8-1、A8-2、A8-3,伊乐藻(B)和金鱼藻(C)也按照同样方法处理。除空白对照(CK)桶不放入网袋外,每个桶内均放入1个。
1.3 试验样品的采集与分析试验于第0、3、6、12、20、28、44、60天分别取3种水草和对照组尾数编号相同(如A1-1、A1-2、A1-3,B1-1、B1-2、B1-3,C1-1、C1-2、C1-3,CK1-1、CK1-2、CK1-3)的样品和水样。立刻用仪器测定各水样的DO和pH,水草样品放在80 ℃的恒温干燥箱中烘干至恒重后称重,其他水质指标尽快测定。整个试验结束时测定各桶底泥TN和TP的质量分数。试验前测定去离子水的各指标:DO为4.580 mg/L,pH为7.280,高锰酸盐指数(CODMn)为1.980 mg/L,氨氮(NH4+-N)为0.174 mg/L,亚硝氮(NO2--N)为0.004 mg/L,硝氮(NO3--N)为0.763 mg/L,总磷(TP)为0.011 mg/L,总氮(TN)为0.987 mg/L。底泥匀浆ω(TN)和ω(TP)分别为1.35和0.41 mg/g。
水质指标DO、pH、CODMn、NH4+-N、NO2--N、NO3--N、TP和TN的测定方法参照《水和废水检测方法》(第四版) [18]。其中DO用美国YSI550A溶氧仪测定,pH用pHSJ-3F型pH计测定,高锰酸盐指数(CODMn)用酸性高锰酸钾法测定,氨氮(NH4+-N)采用纳氏试剂光度法测定,亚硝酸盐(NO2--N)采用盐酸萘乙二胺比色法测定,硝酸盐(NO3--N)采用紫外分光光度法测定,总磷(TP)采用钼酸铵分光光度法测定,总氮(TN)采用过硫酸钾氧化紫外分光光度法测定。底泥,采用凯氏法测定ω(TN),SWT法[19]测定ω(TP)。
1.4 数据处理试验数据采用SPSS 20.0和Excel 2003软件进行统计和作图。采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)和LSD法进行方差分析和差异显著性检验(α=0.05)。
2 结果与分析 2.1 3种水草腐解的差异性水草的腐解是个复杂的过程,包括植物组织的水解、矿质成分和可溶性有机物的溶解、各类有机成分的酶解,以及生物降解、微小颗粒的逸散等,很难用表达式来描述,本文用质量损失率来描述。
随着腐解时间的延长,植物残体逐渐减少,3种水草的质量损失率明显升高。3种水草的腐解速率相似,均表现出前期快,中、后期慢的变化特征。经过60 d的腐解,轮叶黑藻和伊乐藻的腐解速率显著高于金鱼藻(P< 0.05),而轮叶黑藻和伊乐藻的腐解速率相近,无显著性差异(P>0.05),见图 1。整个试验阶段,水草腐解速率在0~3 d最快;3~28 d有所降低,且第20天轮叶黑藻和伊乐藻的质量损失已过半,金鱼藻也损失近一半,质量损失率分别为58.3%±0.6%、58.3%±2.1%和41.3%±1.5%;28~60 d分解速率较低。试验结束时,轮叶黑藻、伊乐藻和金鱼藻的质量损失率分别为72.3%±2.1%、71.7%±1.5%和58.3%±0.6%。
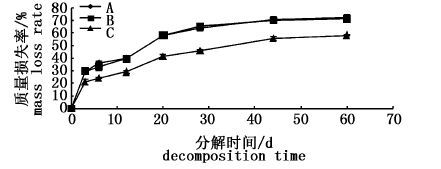
|
图 1 3种水草的质量损失率
Fig. 1 Mass loss rate of the three plants
|
试验组水体DO呈3个变化阶段,即试验初期水草腐解速率较快,消耗了水体大量的DO,DO急剧下降;之后分解速率变缓,DO呈缓慢降低趋势,第12天降到最低值;第12天后,水体DO缓慢升高,第60天达到最高浓度,但低于试验初始含量(图 2)。对照组水体DO变化趋势和试验组相似,但变化幅度远小于试验组,整个试验阶段,对照组水体DO均显著高于试验组(P< 0.05)。轮叶黑藻、伊乐藻和金鱼藻虽种类不同,但腐解过程中,同一时间水体DO无显著性差异(P>0.05),耗氧率基本相当。
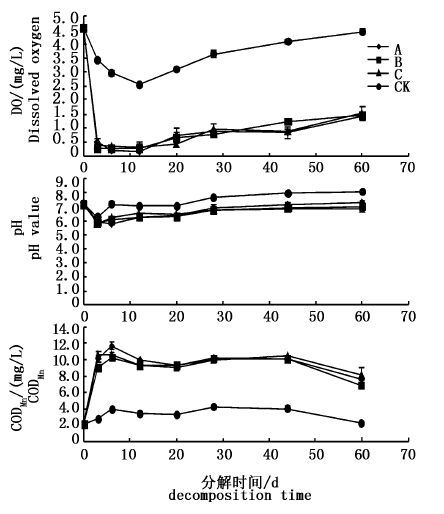
|
图 2 水体中DO、pH和CODMn的动态变化
Fig. 2 Dynamics of DO,pH and CODMn in water
|
3种水草腐解过程中,水体pH变化趋势相似,试验初期,水体的pH呈下降趋势,第3天达到最低,试验组水体由中性变为酸性;之后整体呈缓慢升高趋势,第60天,试验组和对照组水体中pH均接近但低于初始水平(图 2)。对照组水体pH的变化趋势和试验组相似,但变化幅度小于试验组,整个试验阶段,对照组水体pH显著高于试验组(P< 0.05)。同一时间3种水草水体pH除第6天差异显著外(P< 0.05),均无差异显著性(P>0.05)。
3种水草腐解过程中,水体CODMn的变化趋势相似,整体呈先迅速升高,之后缓慢升高,最后缓慢下降的趋势。试验初期水体CODMn上升较快,第3天,试验组水体CODMn均升高4.5倍左右;第6天,轮叶黑藻、伊乐藻和金鱼藻水体CODMn均达到最高,较试验初分别升高约5.4、5.0和4.6倍;第60天,试验组水体CODMn均高于对照组和初始含量(图 2)。对照组水体CODMn变化趋势和试验组相似,但变化幅度远小于试验组,试验组水体CODMn显著高于对照组(P< 0.05)。第3、6天,伊乐藻处理组水体CODMn显著低于轮叶黑藻和金鱼藻处理组(P< 0.05),第6、12天,轮叶黑藻处理组水体CODMn显著高于伊乐藻和金鱼藻处理组(P< 0.05),其他时间3种水草水体CODMn差异不显著(P>0.05)。
2.3 水体中NH4+-N、NO2--N和NO3--N的动态变化试验组水体的NH4+-N呈3个变化阶段,试验前3 d为快速升高阶段,第3天,轮叶黑藻、伊乐藻和金鱼藻处理组水体NH4+-N较初始含量升高5.2、4.8和4.7倍;之后呈缓慢升高阶段,第6天达到最高,分别较第3天增加了4.2%、2.6%和1.3%;第6天后为缓慢下降阶段,试验结束时,试验组水体NH4+-N高于对照组但低于试验初始含量(图 3)。对照组水体NH4+-N变化趋势和试验组相似,但变化幅度远小于试验组。总体上,60 d的腐解,对照组水体NH4+-N显著低于试验组(P< 0.05),轮叶黑藻处理组水体NH4+-N显著高于伊乐藻和金鱼藻处理组(P< 0.05),伊乐藻和金鱼藻处理组水体NH4+-N无显著性差异(P>0.05)。
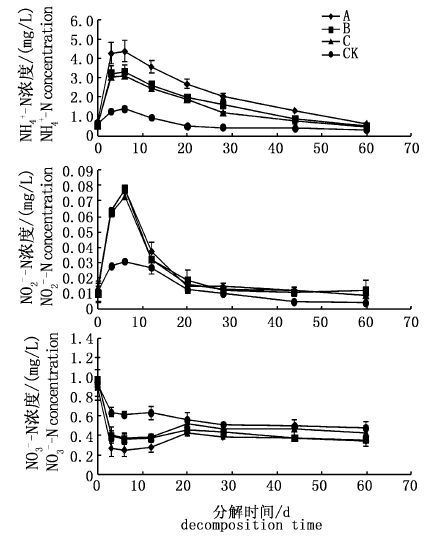
|
图 3 水体中NH4+-N、NO2--N和NO3--N的动态变化
Fig. 3 Dynamics of NH4+-N,NO2--N and NO3--N in water
|
与NH4+-N变化趋势相似,试验组水体NO2--N变化趋势也呈3个阶段,即快速升高、缓慢升高和下降阶段(图 3)。试验前3 d,水体中NO2--N升高迅速,第3天,轮叶黑藻、伊乐藻和金鱼藻处理组水体NO2--N是初始含量的4.9、6.3和2.5倍;第6天,试验组水体NO2--N均达到最高,较第3天,分别增加了21.9%,23.8%和17.7%;第6天到试验结束,试验组水体NO2--N一直呈下降趋势,第60天,试验组水体NO2--N恢复到初始水平,且均略高于对照组。总体上,60 d的腐解,试验组水体NO2--N无显著性差异(P>0.05),但试验组显著高于对照组(P< 0.05)。
NO3--N的变化趋势与NH4+-N和NO2--N相反,试验前3 d,试验组水体NO3--N迅速下降,第3天,轮叶黑藻、伊乐藻和金鱼藻处理组水体NO3--N分别降低了234.7%、147.6%和139.4%;之后缓慢下降,第6天达到最低,较初始含量分别下降了251.8%、169.5%和166.0%;第6天到试验结束,试验组水体NO3--N一直呈缓慢下降趋势,第60天,试验组水体NO3--N约下降到初始含量的一半且小于对照组(图 3)。对照组水体的NO3--N变化趋势和试验组相似,但变化幅度小于试验组。总体上,60 d的腐解,试验组水体的NO3--N显著低于对照组(P< 0.05),但试验组水体NO3--N无差异显著性(P>0.05)。
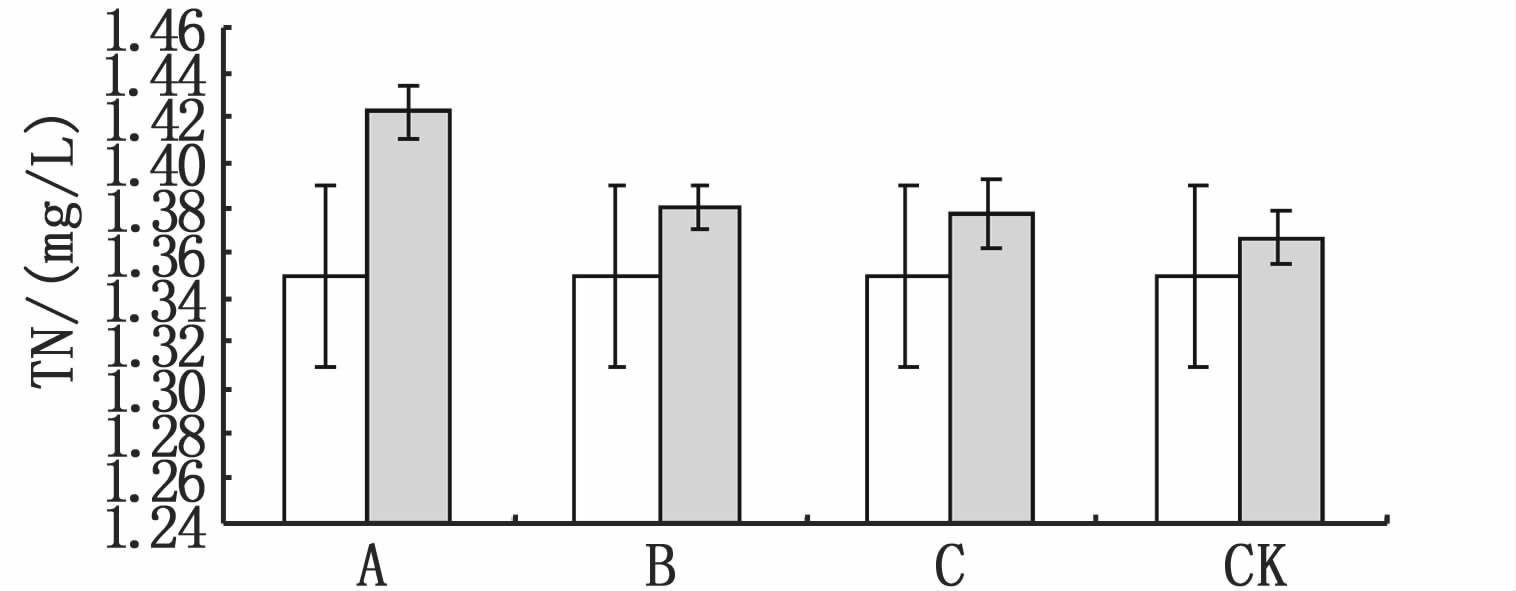
2.4 水体和底泥中TP和TN的变化试验组水体TP的变化趋势呈3个阶段,即快速升高、缓慢升高和缓慢下降阶段。试验的前期,水体的TP快速升高,第3天,轮叶黑藻、伊乐藻和金鱼藻处理组水体TP是初始含量的123.9、124.2和66.2倍;之后缓慢升高,试验第12天,试验组水体TP较第3天分别增加了0.7%、11.7%和44.7%;第12天后,试验组水体TP缓慢降低,第60天下降到最低但均高于初始含量和对照组。对照组水体TP变化幅度较小,整个试验阶段显著低于试验组(P< 0.05,图 4)。总体上,60 d的腐解,金鱼藻处理组水体TP显著低于轮叶黑藻和伊乐藻处理组(P< 0.05),而轮叶黑藻和伊乐藻处理组TP呈交替状态,无显著性差异(P>0.05)。为了探究水草腐解过程中底泥TP的迁移情况,试验初和试验末分别测定了底泥的ω(TP),从图 5中不难发现,试验组和对照组底泥TP的质量分数试验结束后均有增加,表明腐解过程中,水体的磷并未一直停留在水体,而是有部分磷向底泥中转移。
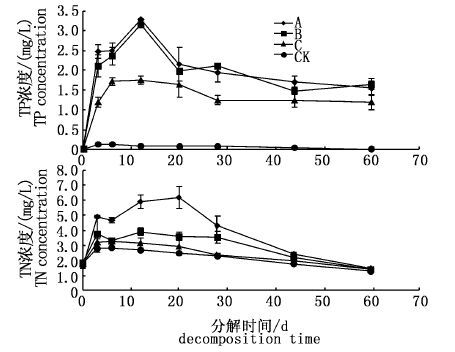
|
图 4 水体TP和TN的动态变化
Fig. 4 Dynamics of TP and TN in water
|
|
图 5 试验初和试验末底泥ω(TP)和ω(TN)的变化
Fig. 5 Initial and final ω(TP) and ω(TN) in sediment
|
水体TN的变化趋势和TP相似,也存在3个阶段,试验的前期轮叶黑藻、伊乐藻和金鱼藻处理组水体TP升高迅速,但存在差异,表现为轮叶黑藻>伊乐藻>金鱼藻;之后在缓慢升高和下降的过程中,伊乐藻和金鱼藻处理组水体TN较接近且均低于轮叶黑藻处理组,试验结束时,3种水草处理组水体TN基本相当且均略低于试验初始含量(图 4)。对照组水体TN的变化趋势和试验组相似,整个试验阶段均低于试验组。总体上,60 d的腐解,轮叶黑藻处理组水体TN显著高于伊乐藻和金鱼藻(P< 0.05),而伊乐藻和金鱼藻处理组水体TN较接近,无明显的显著性差异(P>0.05)。由试验初和试验末底泥ω(TN)图不难发现,较试验初,试验组和对照组底泥的TN均有增加(图 5)。图 4已证明,试验末水体的TN低于试验初,水体的氮可以转化为气体形式逸出,试验末底泥的TN增加,表明水体的氮不仅仅以气体形式转移到空气,还有部分氮向底泥转移。
3 讨论 3.1 水草腐解的过程水草的腐解是个复杂的过程,主要包括糖类、有机酸、蛋白质和矿物质的释放以及木质素、纤维素等的不断降解[20]。一般分为3个过程,第1个过程是水溶性物质的淋溶作用,主要是水草的糖类,有机酸,蛋白质和K、Ca、Mn、Mg等矿物质的释放,此过程是水草质量损失较快的阶段;第2个过程是在微生物的作用下降解水草的有机物,这一步是质量损失的主要阶段;第3个过程是未分解的水草残体中难分解物质木质素、纤维素等的比例不断升高,水草残体的分解受到抑制,分解速率明显减慢的阶段[21]。
本试验发现,轮叶黑藻、伊乐藻和金鱼藻在腐解过程中明显地表现出3个阶段,试验前3 d水草的分解速率较高,质量损失率分别达到29.3%±1.5%、29.7%±2.1%和21.0%±2.0%;第3~28天分解速率下降,但是此阶段质量损失较多,质量损失率分别为64.0%±2.0%、65.3%±0.6%和46.0%±1.0%;第28~60天,水草的分解速率较低,第60天轮叶黑藻、伊乐藻和金鱼藻的质量损失率分别为72.3%±2.1%、71.7%±1.5%和58.3%±0.6%,相对于第28天,3种水草此阶段质量损失并不高。
3.2 水草腐解对水质的影响在试验的初期主要为易分解的物质腐烂分解,分解速率较快,消耗了水体大量的溶解氧,上覆水体的溶解氧迅速下降。试验的中、后期,水草残体难分解物质木质素、纤维素等的比例不断升高,分解速率逐渐下降,耗氧量降低,水体的溶解氧逐渐升高。表明:虽然水草腐解是耗氧过程,但是不会使水体的溶解氧持续降低,主要原因是空气的氧气可以溶入水体,腐解的后期,空气复氧增加的氧气大于腐解消耗的氧气,故水体的溶解氧逐渐上升。对照组的底泥同样取自河蟹养殖池塘,底泥未被完全分解的植物残体和饵料腐烂分解导致对照组水体溶解氧变化趋势和试验组相似,但对照组分解物较试验组少,耗氧量明显小于试验组。空气复氧和水体耗氧的差值较小时,可能导致水质恶化,有研究表明,当水体植物残体生物量较大时,极易在腐解期造成水体缺氧并向水体释放大量的营养盐,造成水质恶化,甚至发黄、发臭[22]。水草腐解初期,体内不稳定的含碳有机物质释放到水体,在微生物的作用下分解释放出CO2,造成水体pH下降[23],试验的中、后期,水草体内的含氮有机物在微生物的作用下产生NH3和胺类物质使水体pH升高[24-25],这与张来甲等[26]对苦草腐烂分解的研究结果一致。对照组分解物生物量小于试验组,分解过程中产生的CO2、NH3和胺类物质的量均低于试验组,导致对照组pH的变化趋势和试验组相似,但幅度较小。水草腐解初期,水体由中性变为酸性,超过了河蟹最适生长pH(7.50~8.50),可使河蟹的免疫系统受到损伤。STEBBING[27]研究发现,pH胁迫可使水生生物的免疫系统受到伤害。CODMn是衡量水体有机物质含量的指标,CODMn越大,说明水体受有机物污染越严重。试验初期,试验组水体溶解氧大量被消耗,在厌氧菌的作用下,水草体内大量的有机物释放到水体,CODMn迅速升高。试验中、后期,一方面水体的有机物不断被分解,另一方面通过物理、化学、生物交换作用等被底泥吸附,CODMn缓慢下降[28]。底泥和水体存在吸附解吸平衡[29],周林飞等[30]研究沉水植物腐解试验时发现,初期水体CODCr较高,当水草残体分解沉降后,底泥的有机物向水体的迁移量很微小,与本试验的研究结果基本一致。
水草腐解的初期,水体的溶解氧大量被消耗,使得整个水体保持低氧或厌氧环境,三氮转化有利于向反硝化反应方向进行[31],试验组水体NO3--N迅速降低而NO2--N和NH4+-N迅速升高。试验的中、后期水体的溶解氧缓慢升高,NO2--N和NH4+-N可被氧化,反应有利于向硝化反应方向进行,试验组水体NO3--N缓慢升高而NO2--N和NH4+-N缓慢下降。对照组底泥未完全分解物质的量较少,虽产生了与试验组NO3--N、NO2--N和NH4+-N相似的变化趋势,但幅度低于试验组。三氮是衡量水体毒性和富营养化程度的重要指标,其中NH4+-N和NO2--N浓度过高对水生生物具有毒害作用[32-33],养殖池塘富氧曝气可以有效降低NH4+-N和NO2--N含量。TN和TP的变化趋势和水草腐解的3个阶段密切相关,水草腐解的前两个阶段向水体释放了大量了氮、磷等营养盐,TN和TP短期内达到较高浓度,第3阶段,水草分解速率降低,再加上氮、磷的转移或转化,TN和TP缓慢降低。有研究表明,水草腐解,体内氮、磷的70%以上会在短期内释放到水体[34],氮、磷的快速升高容易导致水体藻类的大量繁殖,藻类的大量繁殖可能导致水质严重恶化。
3.3 氮、磷元素在水体和底泥中的转移在水体循环过程中,底泥的吸附作用对水体的营养物质具有很强的吸附及截留作用[35-36]。本试验中,3种水草腐解的初期,水体的TP迅速上升,在试验的中、后期逐渐下降,且试验结束时,底泥的ω(TP)升高,表明水草腐解释放的磷并未全部停留在水体,而是发生了转移,有部分磷转移到了底泥。叶春等[37]研究黑藻腐解营养盐释放的试验时也得到同样的结果。磷在水体和底泥的交换是个十分复杂的物理、化学、生物过程,主要包括含磷颗粒的沉降与再悬浮、溶解态磷的吸附与解吸附、磷酸盐的沉淀与溶解等[38-39]。
氮在底泥和水体的迁移和交换过程主要通过硝化和反硝化作用来实现[40]。水体的溶氧充足时,底泥的有机氮经矿化作用生成NH4+-N,NO3--N等无机离子进入水体,提高水体氮的浓度;水体的NO3--N也可以反向扩散进入底泥,在缺氧的条件下,经过反硝化作用还原成N2O和N2等逸出到空气,而且这种脱氮机制的效果明显。本试验的初期,水体的总氮迅速升高,主要是在溶氧充足时有机氮易被氧化成无机氮,因而水体的总无机氮迅速达到一个峰值,随着腐解的进行,水体的溶解氧逐渐被消耗,无机氮的生成效率降低[41]。测定试验初和试验末底泥的ω(TN)发现,试验末底泥的TN高于试验初,证明水草腐解释放的氮有部分转移到底泥。
| [1] | 徐德兰, 刘正文, 雷泽湘, 等.大型水生植物对湖泊生态修复的作用机制研究进展[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 2(2): 14–18. XU D L, LIU Z W, LEI Z X, et al.Advances in the Study of Mechanism of Macrophytes on the Ecological Remediation of Lake[J]. Journal of Yangtze University(Natural Science Edition), 2005, 2(2): 14–18. |
| [2] | 袁东海, 任全进, 高士祥, 等.几种湿地植物净化生活污水COD、总氮效果比较[J]. 应用生态学报, 2004, 15(12): 2337–2341. YUAN D H, REN Q J, GAO S X, et al.Purification efficiency of several wetland macrophytes on COD and nitrogen removal from domestic sewage[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004, 15(12): 2337–2341. |
| [3] | 赵琳, 李正魁, 周涛, 等.伊乐藻-氮循环菌联用对太湖梅梁湾水体脱氮的研究[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(8): 3057–3063. ZHAO L, LI Z K, ZHOU T, et al.Denitrification study of Elodea nuttallii-Nitrogen cycling bacteria restoration in Meilian Bay, Taihu Lake[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(8): 3057–3063. |
| [4] | 吴晓霞, 范长禄, 凌辉, 等.伊乐藻对富营养化水体的净化作用分析[J]. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(4): 787–791. WU X X, FAN C L, LING H, et al.Purification efficiency of elodea canadensis on eutrophic water[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2013, 33(4): 787–791. |
| [5] | 潘义宏, 王宏镔, 谷兆萍, 等.大型水生植物对重金属的富集与转移[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(23): 6430–6441. PAN Y X, WANG H B, GU Z P, et al.Accumulation and translocation of heavy metals by macrophytes[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(23): 6430–6441. |
| [6] | 黄永杰, 刘登义, 王友保, 等.八种水生植物对重金属富集能力的比较研究[J]. 生态学杂志, 2006, 25(5): 541–545. HUANG Y J, LIU D Y, WANG Y B, et al.Heavy metals accumulation by hydrophytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2006, 25(5): 541–545. |
| [7] | HORPPILA J, NURMINEN L.Effects of submerged macrophytes on sediment resuspension and internal phosphorus loading in Lake Hiidenvesi (southern Finland)[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(18): 4468–4474. DOI:10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00405-6 |
| [8] | 颜昌宙, 许秋瑾, 赵景柱, 等.五里湖生态重建影响因素及其对策探讨[J]. 环境科学研究, 2004, 17(3): 44–47. YAN C Y, XU Q J, ZHAO J Z, et al.Study on the key factors and countermeasures of Eco-reconstruction in Lake Wuli[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2004, 17(3): 44–47. |
| [9] | MOSS B.Engineering and biological approaches to the restoration from eutrophication of shallow lakes in which aquatic plant communities and important components[J]. Hydrobiological, 1990, 200/201(1): 367–377. DOI:10.1007/BF02530354 |
| [10] | 王立新, 吴国荣, 王建安, 等.黑藻(Hydrilla verticillata)对铜绿微囊藻(Microcystis aeruginosa)抑制作用[J]. 湖泊科学, 2004, 16(4): 337–342. WANG L X, WU G R, WANG J A, et al.The inhibition of Hydrilla verticillata on Microcystis aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 2004, 16(4): 337–342. |
| [11] | 鲜啟鸣, 陈海东, 邹惠仙, 等.四种沉水植物的克藻效应[J]. 湖泊科学, 2005, 17(1): 75–80. DOI:10.18307/2005.0112 XIAN Q M, CHEN H D, ZOU H X, et al.Allelopahtic eeffes of four submerged maerophyets on Mciorycs aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 2005, 17(1): 75–80. DOI:10.18307/2005.0112 |
| [12] | 李文朝.东太湖茭黄水发生原因与防治对策探讨[J]. 湖泊科学, 1997, 9(4): 364–368. DOI:10.18307/1997.0412 LI W C.“Yellow water” in east Taihu Lake caused by zizania latifolia and its prevention[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 1997, 9(4): 364–368. DOI:10.18307/1997.0412 |
| [13] | 杨红君.菹草腐解对洋河水库水质的影响[J]. 科技信息, 2011: 366–367. YANG H J.Effects of Potamogeton crispus decomposition on the water quality of Yanghe[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2011: 366–367. |
| [14] | 强蓉蓉, 王国祥, 张利民, 等.凤眼莲死亡对湖泊水质的持续性影响分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 2005, 21(1): 24–27. QIANG R R, WANG G X, ZHANG L M, et al.The continuous effects of decaying Eichhornia crassipes on water quality[J]. Environmental Monitoring In China, 2005, 21(1): 24–27. |
| [15] | 潘慧云, 徐小花, 高士祥.沉水植物衰亡过程中营养盐的释放过程及规律[J]. 环境科学研究, 2008, 21(1): 64–68. PAN H Y, XU X H, GAO S X.Study on process of nutrition release during the decay of submerged macrophytes[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 21(1): 64–68. |
| [16] | 李文朝, 陈开宁, 吴庆龙, 等.东太湖水生植物生物质腐烂分解实验[J]. 湖泊科学, 2001, 13(4): 331–336. DOI:10.18307/20010407 LI W C, CHEN K N, WU Q L, et al.Experimental studies on decomposition process of aquatic plant material from east Taihu Lake[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 2001, 13(4): 331–336. DOI:10.18307/20010407 |
| [17] | 唐金艳, 曹培培, 徐驰, 等.水生植物腐烂分解对水质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(1): 83–89. TANG J Y, CAO P P, XU C, et al.Effect of aquatic plants during their decay decomposition on water quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(1): 83–89. |
| [18] | 国家环保总局.水和废水检测分析方法[M].北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. Environmental Protection Agency of China.Methods for the monitoring and analysis of water and wastewater[M].Beijing: Chinese Environmental Science Press, 2002. |
| [19] | 中国科学院南京土壤研究所.土壤理化分析[M].上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1978: 204-262. Institute of Soil Science,Chinese Academy of Sciences.Analysis of soil physico-chemical[M].Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 1978: 204-262. |
| [20] | BEST E P H, DSDDRN J H A, BOON J J, et al.Studies on decomposition of Ceratophyllum demersum litter under laboratory and field conditions: Losses of dry mass and nutrients, qualitative changes in organic compounds and consequences for ambient water and sediments[J]. Hydrobiologia, 1990, 194: 91–114. DOI:10.1007/BF00028411 |
| [21] | CORSTANJE R, REDDY K R, PORTIER K M.Typha latifolia and Cladium jamaicense litter decay in response to exogenous nutrient enrichment[J]. Aquatic Botany, 2006, 84(1): 70–78. DOI:10.1016/j.aquabot.2005.07.013 |
| [22] | GIBBS M, OZKUNDAKCI D.Effects of a modified zeolite on P and N processes and fluxes across the lake sediment-water interface using core incubations[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2011, 661: 21–25. DOI:10.1007/s10750-009-0071-8 |
| [23] | 武海涛, 吕宪国, 杨青, 等.三江平原典型湿地枯落物早期分解过程及影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(10): 331–336. WU H T, LV X G, YANG Q, et al.Dynamics of major elements in Deyeuxia angustifolia litter during its decomposition in Sanjiang Plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2007, 27(10): 331–336. |
| [24] | WANG CHAO, WANG CUN, WANG ZE.Effects of submerged macrophytes on sediment suspension and NH4+-N release under hydrodynamic conditions[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2010, 22(6): 810–815. DOI:10.1016/S1001-6058(09)60120-7 |
| [25] | CARVALHO P, THOMAZ S M, BINI L M.Effect of temperature on decomposition of a potential nuisance species: the submerged aquatic macrophyte Egeria najia Planchon(Hydrocharitanceae)[J]. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 2005, 65(1): 51–60. |
| [26] | 张来甲, 叶春, 李春华, 等.沉水植物腐解对水体水质的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 2013, 26(2): 145–151. ZHANG L J, YE C, LI C H, et al.The effect of submerged macrophytes decomposition on water quality[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 26(2): 145–151. |
| [27] | STEBBING A R D.The stimulation of growth by low levels of inhibitors[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 1982, 22(3): 213–234. DOI:10.1016/0048-9697(82)90066-3 |
| [28] | 朱健, 李捍东, 王平.环境因子对底泥释放COD、TN和TP的影响研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2009, 35(8): 44–49. ZHU J, LI H D, WANG P.The impact of environmental factors of cod, tn, tp from sediment[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2009, 35(8): 44–49. |
| [29] | 薛泉宏, 尉庆丰, 李宝安, 等.黄土性土壤K+吸附、解吸动力学研究[J]. 土壤学报, 1997, 34(2): 113–122. XUE Q H, WEI Q F, LI B A, et al.Study on K+ adsorbing-desorbing kinetics of loessial soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1997, 34(2): 113–122. |
| [30] | 周林飞, 邹飞, 李颖卓.沉水植物腐解对人工湿地水质的持续影响研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(6): 119–123. ZHOU L F, ZOU F, LI Y Z.Continous influence of submerged plant decomposition on water quality in constructed wetland[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(6): 119–123. |
| [31] | BASTVIKEN S K, ERIKSSON P G.Potential denitrification in wetland sediment with different plant species detritus[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2005, 25(2): 183–190. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2005.04.013 |
| [32] | 洪美玲, 陈立侨, 顾顺樟, 等.氨氮胁迫对中华绒螯蟹免疫指标及肝胰腺组织结构的影响[J]. 中国水产科学, 2007, 14(3): 412–418. HONG M L, CHEN L Q, GU S Z, et al.Effects of ammonia exposure on immunity indicators of haemolymph and histological structure of hepatopancreas in Chinese mitten crab(Eriocheir sinensis)[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2007, 14(3): 412–418. |
| [33] | 洪美玲, 陈立侨, 孙新谨, 等.亚硝酸盐急性胁迫对中华绒螯蟹幼体相关免疫指标和应激蛋白(HSP70)表达的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2011, 17(5): 688–693. HONG M L, CHEN L Q, SUN X J, et al.Effects of acute nitrite exposure on immunity indicators and HSP70 expression in Chinese mitten-hand crab(Eriocheir sinensis)[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2011, 17(5): 688–693. |
| [34] | SHILLA D, FUJINO T, SANDERSON B.Decomposition of dominant submerged macrophytes: Implications for nutrient release in Myall Lake, NSW, Australia[J]. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 2006, 14(5): 427–433. DOI:10.1007/s11273-006-6294-9 |
| [35] | 厉恩华, 刘贵华, 李伟.洪湖三种水生植物的分解速率及氮、磷动态[J]. 中国环境科学, 2006, 26(6): 667–671. LI E H, LIU G H, LI W.Decomposition rate and nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics of three kinds of hydrophyte in Lake Honghu[J]. China Environmental Science, 2006, 26(6): 667–671. |
| [36] | HU D, CAI L, CHEN H.Fungal diversity on submerged wood in a tropical stream and an artificial lake[J]. Biodiversity and Conservation, 2010, 19(13): 3799. DOI:10.1007/s10531-010-9927-5 |
| [37] | 叶春, 王博, 李春华, 等.沉水植物黑藻腐解过程中营养盐释放过程[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(10): 2653–2659. YE C, WANG B, LI C H, et al.Nutrient release process during decomposition of submerged macrophytes (Hydrilla verticillata Royle)[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(10): 2653–2659. |
| [38] | 陈永川, 汤利.沉积物-水体界面氮磷的迁移转化规律研究进展[J]. 云南农业大学学报, 2005, 20(4): 527–533. CHEN Y C, TANG L.Study prospect on removing and transformaing characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in sediment-water interface[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 2005, 20(4): 527–533. |
| [39] | 史小丽, 王凤平, 蒋丽娟, 等.温度对外源性~(32)P在水、铜绿微囊藻和底泥中迁移的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(11): 1967–1970. SHI X L, WANG F P, JIANG L J, et al.Effect of temperature on the translocation of exogenous 32P in water column, Microcystis aeruginosa and sediments[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(11): 1967–1970. |
| [40] | 杨龙元, 蔡启铭, 秦伯强, 等.太湖梅梁湾沉积物-水界面氮迁移特征初步研究[J]. 湖泊科学, 1998, 10(4): 41–47. DOI:10.18307/1998.0406 YANG L Y, CAI Q M, QIN B Q, et al.Characteristies of nitrogen removing between sediment-water interfaee in Meiliang Bay,Taihu Lake[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 1998, 10(4): 41–47. DOI:10.18307/1998.0406 |
| [41] | REDDY K R, SACCO P D.Decomposition of water hyacinth in agricultural drainage water[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1981, 10(2): 228–234. |
2. Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Aquaculture, Shanghai 201306, China;
3. Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center for Aquatic Animal Genetics and Breeding, Shanghai 201306, China;
4. Shanghai Yuyue Aquaculture Professional Cooperatives, Shanghai 201611, China
 2016,
Vol. 25
2016,
Vol. 25


