2. 辽宁出入境检验检疫局, 辽宁 大连 116001
2. Liaoning Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureau, Dalian 116001, Liaoning Province, China
除草剂广泛应用于防除蔬菜等作物的田间杂草[1]。除草剂施用后可通过迁移、降解等过程进入环境,再通过食物链进入人体。目前,由于除草剂的大量使用已对环境及人类健康造成了很大的危害[2]。因此,加强对蔬菜中各种除草剂残留的测定对保障食品安全具有十分重要的意义。
关于蔬菜中除草剂残留的检测方法较多,如采用气相色谱-质谱法(GC-MS或GC-MS/MS)[3-7]分析敌草隆、鰁草酮、氟乐灵、丁草胺、丙草胺等,液相色谱-串联质谱法(LC-MS/MS)[8-13]测定乙草胺、异丙甲草胺、草毒死、草津净等,酶联免疫法[14]测定蔬菜中的甲草胺残留,液相色谱-紫外法(LC-UV)[15]分析氯代乙酰胺类除草剂,气相色谱-电子捕获检测器(GC-ECD)法测定硝草胺[16]或炔苯酰草胺[17]等。其中液相色谱-紫外法不适用于本研究所选定的15种除草剂的多残留测定,如草毒死[13]、敌草隆等紫外吸收较弱,检测灵敏度较低,同时基质成分对待测组分的干扰较大,因此,该方法不能满足农药残留检测要求。气相色谱-质谱法或液相色谱-质谱法虽然可同时测定该15种除草剂,定性及定量准确性高,但仪器成本较高,不适于普通实验室的常规分析;另外,为提高样品分析速度,色谱-质谱联用法通常需要采用QuEChERS法净化样品,而为保证所有组分的回收率,样品净化时选择性较低,只能去除少量干扰成分,且对色谱柱污染较大,会降低色谱柱的使用寿命。而气相色谱-选择性检测器方法灵敏度高,分析速度快,可适合实验室日常分析,而且通过优化样品净化过程减小基质成分的干扰,可提高目标组分在蔬菜样品中定性及定量的准确性。鉴于此,本研究拟建立GC-ECD法同时测定蔬菜中氟嘧磺隆、草毒死、敌草隆、氯草定、氟乐灵、炔苯酰草胺、乙草胺、甲草胺、异丙甲草胺、吡唑草胺、硝草胺、丁草胺、丙草胺、鰁草酮及吡氟酰草胺15种除草剂的多残留分析方法。
1 材料与方法 1.1 仪器与试剂Agilent 7890B气相色谱仪,配有自动进样器和电子捕获检测器(ECD)等(USA, Agilent公司);KQ-500DE型医用数控超声波清洗器(昆山市超声仪器有限公司);DT5-1离心机(北京时代北利离心机有限公司);R-210旋转蒸发仪(BüCHI公司,瑞士);JJ-2组织捣碎机(金坛市城东新瑞仪器厂);XH-C漩涡混合器(常州朗越仪器制造有限公司);MG-2200氮吹仪(东京理化器械株式会社)。
15种除草剂[氟嘧磺隆(primisulfuron)、草毒死(allidochlor)、敌草隆(diuron)、氯草定(nitrapyrin)、氟乐灵(trifluralin)、炔苯酰草胺(propyzamide)、乙草胺(acetochlor)、甲草胺(alachlor)、异丙甲草胺(metolachlor)、吡唑草胺(metazachlor)、硝草胺(pendimethalin)、丁草胺(butachlor)、丙草胺(pretilachlor)、鰁草酮(oxadiazon)、吡氟酰草胺(diflufenican)]标准品(纯度均≥98.0%)均购自Sigma-Aldrich公司。Florisil PR固相萃取柱和Al2O3萃取柱(1 000 mg/6 mL,Agilent公司),NH2固相萃取柱(500 mg/6 mL,Dikma公司),C18萃取柱(500 mg/6 mL,Agilent公司);DM-1毛细管气相色谱柱(30 m × 0.32 mm,0.25 μm,Dikma公司)。正己烷(色谱纯,Fluka公司),试验用水为“娃哈哈”纯净水(娃哈哈集团,杭州),其他试剂均为分析纯。
供试番茄、黄瓜、青椒、茄子、西葫芦、马铃薯、芸豆及萝卜,购于沈阳当地超市。
1.2 分析方法 1.2.1 样品制备选择番茄、黄瓜、青椒、茄子、西葫芦、马铃薯、芸豆及萝卜8种市售蔬菜样品进行添加回收试验以及实际样品的测定。蔬菜试样混匀缩分后,于4 ℃下储存备用。
提取:称取5 g蔬菜样品(精确至0.001 g)于100 mL具塞三角瓶中,加入20 mL V (乙酸乙酯) : V (二氯甲烷)=80 : 20的混合溶液,超声提取20 min;过滤,收集滤液,残渣依次用15和10 mL上述混合溶液提取,过滤,合并滤液;滤液于40 ℃旋转蒸发至近干,残渣用5 mL正己烷溶解,待净化。
净化:依次用6 mL丙酮、10 mL正己烷活化Florisil PR固相萃取柱;加入待净化溶液,用6 mL V(正己烷) : V(丙酮)=80 : 20的混合溶液洗脱;收集洗脱液用氮气吹至近干,用正己烷溶解并定容至1 mL,待色谱测定。
1.2.2 色谱分析条件DM-1 (30 m × 0.32 mm,0.25 μm)毛细管气相色谱柱。载气:氮气,恒流模式,流速为2 mL/min。尾吹气:氮气,流速为45 mL/min。温度:进样口230 ℃;检测器350 ℃。程序升温条件:初始温度80 ℃,以10 ℃/min升温至170 ℃,再以2 ℃/min升温至190 ℃,再以20 ℃/min升温至280 ℃,保持2 min。进样量1 μL。不分流进样。
1.2.3 标准曲线绘制各除草剂标准品分别用正己烷配成1 mg/mL的标准储备液,各取5 mL用正己烷稀释配制成50 μg/mL的混合标准溶液,再稀释成质量浓度分别为10.0、1.0、0.1、0.01和0.001 μg/mL的系列标准工作溶液,按1.2.2的条件测定。以样品质量浓度为横坐标,峰面积为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线。
1.2.4 添加回收试验在8种供试蔬菜样品中分别添加3个水平的标准品溶液,按本文所建方法测定,每个水平重复5次,计算平均回收率和相对标准偏差。
2 结果与讨论 2.1 方法优化本研究选择的15种除草剂,包含酰胺类、二硝基苯胺类、吡啶类、鰁二唑酮类、取代脲类及磺酰脲类等,各除草剂之间化学性质差异较大。为提高待测除草剂的提取效率,对提取溶剂进行了优化。分别尝试了极性溶剂(甲醇、乙腈、丙酮等)和非极性溶剂(乙酸乙酯、二氯甲烷等)。通过对各除草剂提取效率的比较,最终确定利用V (二氯甲烷) : V (乙酸乙酯)=20 : 80为提取溶剂,提取20 min时,15种待测组分的回收率均达最佳值(图 1)。
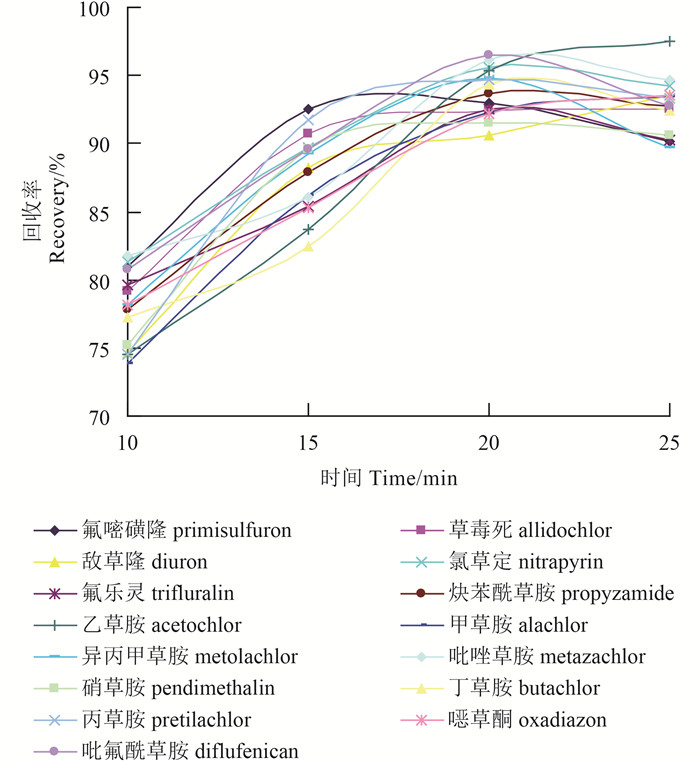
|
提取溶剂为V (二氯甲烷) : V (乙酸乙酯)=20 : 80的混合溶液 The mixed solution of dichloromethane and ethyl acetate (20 : 80, V : V) as the extraction solvent 图 1 15种除草剂不同提取时间的回收率 Fig. 1 Recoveries of 15 herbicides with different extraction time |
由于蔬菜样品基质成分复杂,而且色素含量较高,因此提取后的样品溶液需进一步净化。分别考察了中性氧化铝-SPE、Florisil PR-SPE、C18-SPE及NH2-SPE的净化效果。结果表明:尽管中性氧化铝萃取柱对色素的去除效果较好,但农药的回收率较低。部分待测组分在C18-SPE和NH2-SPE中回收率也小于80%;尽管Florisil PR固相萃取柱去除色素的效果不如中性氧化铝,但待测组分的回收率均大于80%,所以选择Florisil PR固相萃取柱进行净化(表 1)。
|
|
表 1 15种除草剂采用不同固相萃取柱的回收率 Table 1 The recoveries of 15 herbicides purified by different solid phase extraction |
试验中对净化过程中的洗脱溶剂及其用量进行了优化。结果表明:洗脱溶剂中丙酮的含量越高,则回收率越高,但样品中的色素等杂质同时也被洗脱下来。综合比较回收率及净化效果,最终确定以V (正己烷) : V (丙酮)=80 : 20的混合溶液作为洗脱溶剂。15种除草剂的回收率随着洗脱溶液体积的增加而提高,当溶剂为6 mL时,回收率最高,故确定洗脱溶剂用量为6 mL (图 2)。
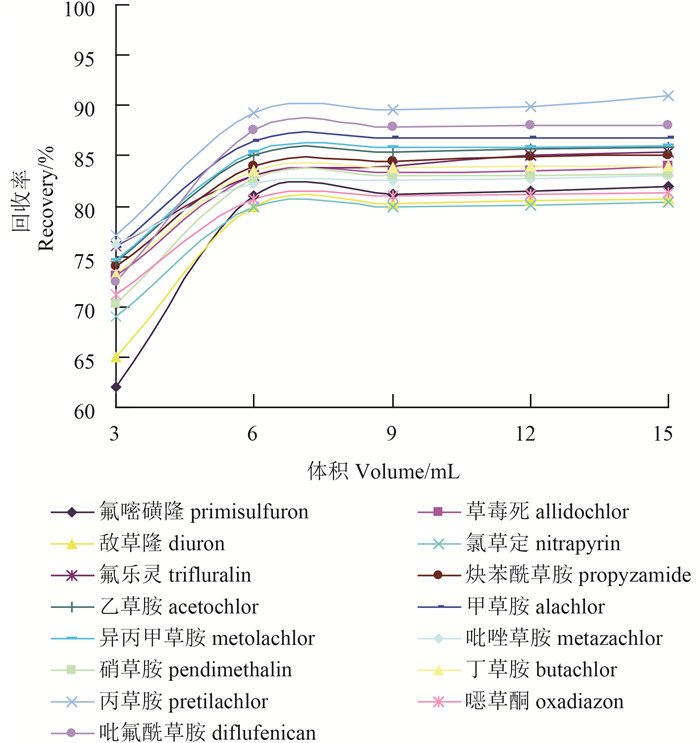
|
洗脱溶剂为V (正己烷) : V (丙酮)=80 : 20的混合溶液 The mixed solution of hexane and acetone (80 : 20, V : V) as the elution solvent 图 2 不同体积洗脱溶剂的回收率 Fig. 2 Recoveries of 15 herbicides eluted by solvents with different volume |
2.2 方法评价
分别采用8种供试蔬菜样品基质进行方法验证(标准品谱图见图 3;以番茄基质为例,空白样品图及添加样品图见图 4),确定了15种除草剂的检测限(S/N=3)、定量限(S/N=5)[18],线性方程以及添加回收率和重现性(表 2及表 3)。15种除草剂在所研究的线性范围内,其质量浓度与峰面积间呈良好的线性关系(线性相关系数均大于0.992)。
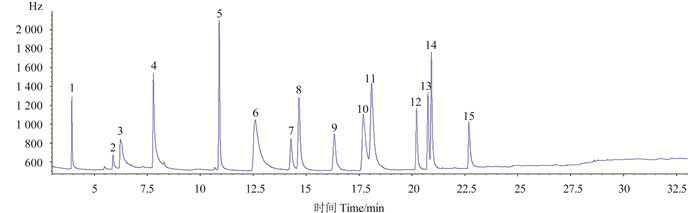
|
1.氟嘧磺隆primisulfuron;2.草毒死allidochlor;3.敌草隆diuron;4.氯草定nitrapyrin;5.氟乐灵trifluralin;6.炔苯酰草胺propyzamide;7.乙草胺acetochlor;8.甲草胺alachlor;9.异丙甲草胺metolachlor;10.吡唑草胺metazachlor;11.硝草胺pendimethalin;12.丁草胺butachlor;13.丙草胺pretilachlor;14. 鰁草酮oxadiazon;15.吡氟酰草胺diflufenican 图 3 15种除草剂标准溶液(0.02 μg/mL)色谱图 Fig. 3 The chromatogram of the 15 herbicides standard solution (0.02 μg/mL) by GC-ECD |

|
1.氟嘧磺隆primisulfuron (0.1 mg/kg);2.草毒死allidochlor (0.005 mg/kg);3.敌草隆diuron (0.02 mg/kg);4.氯草定nitrapyrin (0.002 mg/kg);5.氟乐灵trifluralin (0.005 mg/kg);6.炔苯酰草胺propyzamide (0.01 mg/kg);7.乙草胺acetochlor (0.01 mg/kg);8.甲草胺alachlor (0.02 mg/kg);9.异丙甲草胺metolachlor (0.01 mg/kg);10.吡唑草胺metazachlor (0.01 mg/kg);11.硝草胺pendimethalin (0.01 mg/kg);12.丁草胺butachlor (0.01 mg/kg);13.丙草胺pretilachlor (0.01 mg/kg);14. 鰁草酮oxadiazon (0.002 mg/kg);15.吡氟酰草胺diflufenican (0.001 mg/kg) 图 4 空白样品(a)及添加15种除草剂(b)的色谱图(以番茄为例) Fig. 4 The chromatogram of blank sample (a) and spiked with 15 herbicides (b) (tomato) |
|
|
表 2 15种除草剂的线性范围、线性方程、相关系数、定量限及最大残留限量 Table 2 Linear ranges, regression equations, correlation coefficients, limit of quantitations (LOQ) and maximum residue limits (MRL) of 15 herbicides analysed by GC-ECD |
|
|
表 3 番茄中15种除草剂的平均添加回收率及相对标准偏差 Table 3 Average recoveries and RSDs of 15 herbicides spiked in the real sample (tomato)(n=5) |
目前国内外尚未制定氟嘧磺隆、草毒死、吡唑草胺、丁草胺及丙草胺在蔬菜中的最大残留限量(MRL)值,GB 2763—2014标准中只制定了鰁草酮等7种除草剂在蔬菜中的MRL值,但除鰁草酮外,其他除草剂在蔬菜中的MRL值均大于国外制定的MRL值(表 2)。本研究所测定的15种除草剂中,有11种在国内外蔬菜作物中进行了登记,而氟嘧磺隆、草毒死、丁草胺及丙草胺未查到在蔬菜作物中进行登记(表 4)[19]。鉴于采用本方法所测定除草剂的定量限均低于国内外最大残留限量(表 2),因此认为,本研究所建立的15种除草剂的分析方法可以满足有关标准对15种除草剂的测定要求[18-19]。
|
|
表 4 待测除草剂的登记作物情况 Table 4 The crops registered with the studied herbicides |
添加回收试验结果表明:15种除草剂在番茄样品中的平均添加回收率为77%~113%,相对标准偏差为3.5%~10.8%。而15种除草剂在其他7种蔬菜样品中的平均添加回收率均在75%~117%之间,相对标准偏差在5.1%~11.4%之间,从以上数据可以看出,本方法的准确度和精密度均可满足农药残留分析的要求[24-25]。
通过空白样品测定以及添加试验,比较了不同蔬菜基质成分对待测目标组分测定的影响。结果发现,采用本研究建立的方法,供试8种蔬菜样品中的基质成分对目标组分的定性及定量并无影响。
2.3 实际样品测定采用本研究建立的方法对市售番茄、黄瓜、青椒、茄子、西葫芦、马铃薯、芸豆及萝卜等蔬菜样品进行分析,考查其可行性。结果发现:除在青椒中检测出鰁草酮(0.01 mg/kg)和马铃薯中检测出硝草胺(0.02 mg/kg)外,其余除草剂均未检出或低于目前国际上制定的MRL值(表 2)。
3 结论本研究建立了气相色谱-电子捕获器法同时测定瓜果类蔬菜中15种除草剂残留的分析方法,该方法具有样品处理步骤简单,分析速度快,检测灵敏度高等优势。15种除草剂的定量限均低于当前各国制定的蔬菜中目标除草剂的最大残留限量,因此,该方法可为农产品及食品等领域的农药残留检测提供技术依据。
| [1] | ALEBRAHIM M T, MAJD R, MOHASSEL M H R, et al. Evaluating the efficacy of pre-and post-emergence herbicides for controlling Amaranthus retroflexus L. and Chenopodium album L. in potato[J]. Crop Prot, 2012, 42 :345–350. |
| [2] | EBENEZER V, KI J S. Quantification of toxic effects of the herbicide metolachlor on marine microalgae Ditylum brightwellii (Bacillariophyceae), Prorocentrum minimum (Dinophyceae), and Tetraselmis suecica (Chlorophyceae)[J]. J Microbiol, 2013, 51 :136–139. |
| [3] | ZHAO Y G, SHEN H Y, SHI J W, et al. Preparation and characterization of amino functionalized nano-composite material and its application for multi-residue analysis of pesticides in cabbage by gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2011, 1218 (33):5568–5580. |
| [4] | CERVERA M I, PORTOLÉS T, PITARCH E, et al. Application of gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry for target and non-target analysis of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2012, 1244 :168–177. |
| [5] | GUEDES J A C, DE OLIVEIRA SILVA R, LIMA C G, et al. Matrix effect in guava multiresidue analysis by QuEChERS method and gas chromatography coupled to quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chem, 2016, 199 :380–386. |
| [6] | SATPATHY G, TYAGI Y K, GUPTA R K. A novel optimised and validated method for analysis of multi-residues of pesticides in fruits and vegetables by microwave-assisted extraction (MAE)-dispersive solid-phase extraction (d-SPE)-retention time locked (RTL)-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry with Deconvolution reporting software (DRS)[J]. Food Chem, 2011, 127 (3):1300–1308. |
| [7] | ZHANG H, CHEN Z L, YANG G S, et al. Microwave pretreatment and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry determination of herbicide residues in onion[J]. Food Chem, 2008, 108 (1):322–328. |
| [8] | ANDRADE G C R M, MONTEIRO S H, FRANCISCO J G, et al. Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry and dynamic multiple reaction monitoring method for determining multiple pesticide residues in tomato[J]. Food Chem, 2015, 175 :57–65. |
| [9] | NÚÑEZ O, GALLART-AYALA H, FERRER I, et al. Strategies for the multi-residue analysis of 100 pesticides by liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2012, 1249 :164–180. |
| [10] | SINHA S N, VASUDEV K, RAO M V V. Quantification of organophosphate insecticides and herbicides in vegetable samples using the "Quick Easy Cheap Effective Rugged and Safe" (QuEChERS) method and a high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) technique[J]. Food Chem, 2012, 132 (3):1574–1584. |
| [11] | BAKIRCI G T, HIŞIL Y. Fast and simple extraction of pesticide residues in selected fruits and vegetables using tetrafluoroethane and toluene followed by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chem, 2012, 135 (3):1901–1913. |
| [12] | WANG J F, DU Z X, YU W L, et al. Detection of seven pesticides in cucumbers using hollow fibre-based liquid-phase microextraction and ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2012, 1247 :10–17. |
| [13] |
田宏哲, 周艳明, 赵瑛博, 等. 谷物中草毒死及草净津残留的高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定[J]. 分析测试学报, 2010,29 (8):855–858.
TIAN H Z, ZHOU Y M, ZHAO Y B, et al. Simultaneous determination of allidochlor and cyanazine in grains by HPLC-ESI MS/MS[J]. J Instrum Anal, 2010, 29 (8):855–858. |
| [14] | GABALDóN J A, CASCALES J M, MAQUIEIRA A, et al. Rapid trace analysis of alachlor in water and vegetable samples[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2002, 963 (1-2):125–136. |
| [15] | HU X G, DAI G M, HUANG J J, et al. Molecularly imprinted polymer coated on stainless steel fiber for solid-phase microextraction of chloroacetanilide herbicides in soybean and corn[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2010, 1217 (38):5875–5882. |
| [16] | SŁOWIK-BOROWIEC M, SZPYRKA E, WALORCZYK S. Gas chromatographic determination of pesticide residues in white mustard[J]. Food Chem, 2015, 173 :997–1005. |
| [17] | GELSOMINO A, PETROVIČOVÁ B, TIBURTINI S, et al. Multiresidue analysis of pesticides in fruits and vegetables by gel permeation chromatography followed by gas chromatography with electron-capture and mass spectrometric detection[J]. J Chromatogr A, 1997, 782 (1):105–122. |
| [18] | 食品卫生检验方法理化部分总则:GB/T 5009.1-2003[S].北京:中国标准出版社, 2004. |
| [19] |
食品中农药最大残留限量:GB 2763-2014[S].北京:中国标准出版社, 2014.
Maximum residue limits for pesticides in food:GB 2763-2014[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2014. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/dl/Detail/Standard?id=Standard_GB%202763-2014&type=Free |
| [20] | Trifluralin, acetochlor, metolachlor.[2016-01-30]. https://iaspub.epa.gov/apex/pesticides/f?p=chemicalsearch:1. |
| [21] | Oxadiazon, trifluralin.[2016-01-30]. http://www.mfds.go.kr/eng/eng/index.do?nMenuCode=15 & page=1 & mode=view & boardSeq=67166. |
| [22] | Primisulfuron, allidochlor, diuron, nitrapyrin, propyzamide, acetochlor, alachlor, metolachlor, pendimethalin, diflufenican.[2015-10-25]. http://www.fcg-r.co.jp/pesticide/index.htm. |
| [23] | Propyzamide, pendimethalin.[2015-10-25]. http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/public/?event=pesticide.residue.selection & language=EN. |
| [24] |
测量方法与结果的准确度(正确度与精密度)第2部分:确定标准测量方法重复性与再现性的基本方法:GB/T 6379.2-2004[S].北京:中国标准出版社, 2005.
Accuracy (trueness and precision) of measurement methods and results-part 2:basic method for the determination of repeatability and reproducibility of a standard measurement method:GB/T 6379.2-2004[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2005. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Standard_ISO%205725-2-1994.aspx |
| [25] |
测量方法与结果的准确度(正确度与精密度)第4部分:确定标准测量方法正确度的基本方法:GB/T 6379.4-2006[S].北京:中国标准出版社, 2007.
Accuracy (trueness and precision) of measurement methods and results-part 4:basic methods for the determination of the trueness of a standard measurement method:GB/T 6379.4-2006[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2007. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Standard_ISO%205725-4-1994.aspx |
 2016, Vol. 18
2016, Vol. 18


