2. 伊犁师范学院化学与生物科学学院, 新疆伊宁 835000
2. College of Chemistry and Biology, Xinjiang Yili Normal University, Yining 835000, Xinjiang, China
噻霉酮 (图式1) 化学名称为 1,2-苯并异噻唑啉 -3-酮,属于有机杂环类杀菌剂,对真菌、细菌性 病害有很强的抑杀作用,具有高效、安全、低毒 和低残留等特点[1]。虽然该农药对农作物具有良好 的保护和治疗作用,但若其残留过多会对食用者 产生潜在危害。关于噻霉酮的检测方法报道较 少,主要以液相色谱法[2, 3, 4]为主,但该法的灵敏度 低、选择性差,属于半定性分析。GB 2763—2014 中规定了噻霉酮在黄瓜中的临时限量为 0 . 1 mg/kg[5],目前国内外尚未见食品中噻霉酮的标准 检测方法。液相色谱-串联质谱仪具有灵敏度高、 选择性强和定性准确等特点,在农药残留分析方 面应用广泛[6, 7, 8, 9, 10],但未见其用于分析噻霉酮的报 道。QuEChERS 技术是一种快速、简单、廉价、 高效、耐用和安全的样品前处理方法,已广泛用 于食品中农药残留的检测[11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16]。本研究采用改进的 QuEChERS 前处理方法,结合液相色谱-串联质谱 仪建立了果蔬及其制品中噻霉酮残留的分析方 法。
|
图式 1 噻霉酮 Scheme 1 benziothiazolinone |
1260-6460A 液相色谱-串联质谱仪 (美国 Agilent 公司);Sigma3-18 K 台式冷冻离心机 (Sigma 公司);EYELA MMV-1000 W 振荡器 (东 京理化公司);GM200 刀式混合研磨仪 (Retsch 公 司);N-EVAP-112 水浴氮吹仪 (Organomation 公 司);MiIIi-Q Advangtage A10 超纯水系统 (Millipore 公司);MS3 型涡旋振荡器 (IKA 公司)。
99% 噻霉酮 (benziothiazolinone) 标准品 (德国Dr.Ehrenstorfer 公司);乙睛、甲醇、丙酮、甲酸 和正己烷均为色谱纯 (德国 MERCK 公司);试验 用水为 Milli-Q 超纯水 (符合 GB/T 6682—2008 一 级水要求);C18 和 PEP 吸附剂均购自 Agela 公 司;分析样品为实验室送检和市售样品。
1.2 QuEChERS 前处理新鲜果蔬取可食部分,切碎混匀,用混合研 磨仪制成匀浆,备用;番茄酱搅拌均匀后直接称 样。葡萄干样品先于 -20 ℃ 下静置 6 h 以上,将 样品中水分冻成固态冰,迅速取出用混合研磨仪 加工成粉末状,备用。
称取新鲜果蔬样品 2 g (精确至 0.01 g) 于 50 mL 具塞离心管中,加入 1 g 氯化钠、5 mL 含 0 . 1 % 乙酸的乙腈,涡旋 3 0 s 后,振荡提取 15 min,于 5 000 r/min 下离心 2 min;取 3 mL 上 清液于 15 mL 具塞离心管中,加入吸附剂 C18 和 PEP 粉各 50 mg,摇匀并涡旋 30 s,于 5 000 r/min 下离心 1 min;取 2.5 mL 上清液于 10 mL 试管 中,于 40 ℃ 水浴中氮吹至干,用 1 mL 的 V (甲醇): V (水) = 1:9 溶解,涡旋 30 s 混匀,经 0.22 μm 滤 膜过滤,待分析。
分别称取 2 g 含水量较少的番茄酱和葡萄干样 品 (精确至 0.01 g) 于 50 mL 具塞离心管中,加入 5 mL 水,静置 30 min;加入 2 g 氯化钠及10 mL 含 0.1% 乙酸的乙腈,涡旋 30 s 后,振荡提取 15 min,于 5 000 r/min 下离心 2 min;取 7.0 mL 上清液于 15 mL 具塞离心管中,加入吸附剂 C18 和 P E P 粉各 5 0 m g ,摇匀并涡旋 3 0 s ,于 5000 r/min 下离心 1 min;取 5.0 mL 上清液于 10 mL 试管中,于 40 ℃水浴中氮吹至干,用 1 mL 的 V (甲醇):V (水) = 1:9 溶解,涡旋 30 s 混匀,经 0.22 μm 滤膜过滤,待分析。
1.3 液相色谱-串联质谱 (LC-MS/MS) 检测条件JADE-PAK CB-C18 色谱柱 (100 mm × 2.1 mm,3 μm);柱温 30 ℃;进样量 10.0 μL。流动相:A 相为 0.1% 的甲酸水 (含 2 mmol/mL 乙酸铵),B 相为甲醇,流速 0 . 2 5 m L / m i n;梯度洗脱程序: 0~3.5 min (B 相 10%~50%),3.5~5.5 min (B 相 50%~90%),5.5~7.5 min (B 相 90%),7.51~10 min (B 相 10%)。
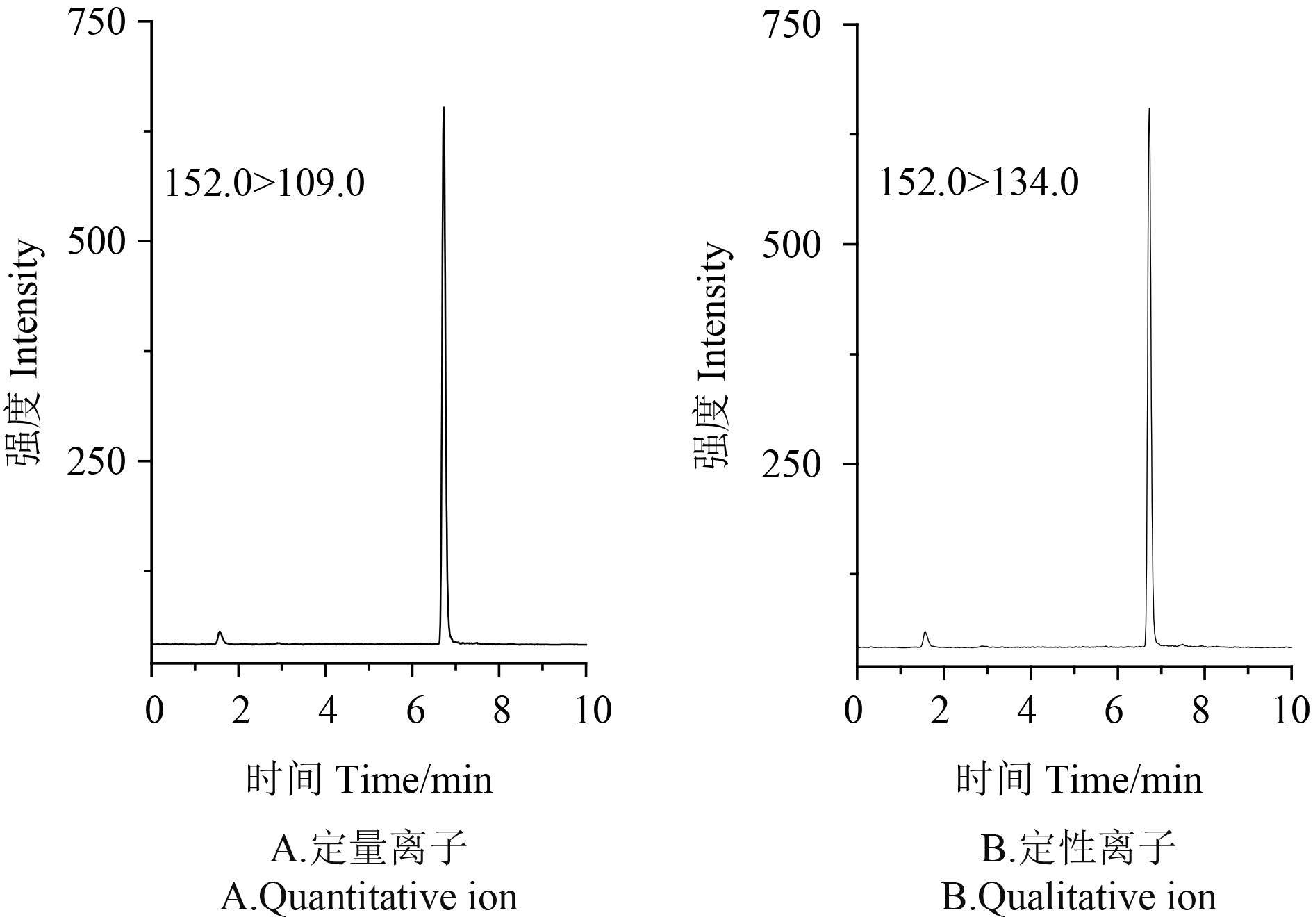
电离模式:电喷雾正离子源模式 (ESI+);多重 反应监测 (MRM);干燥气温度 300 ℃;干燥气流 量 1 0 . 0 L / m i n;鞘气温度 2 5 0 ℃;鞘气流速 9.0 L/min,毛细管电压 4 kV;碎裂电压:122 V; 驻留时间 50 ms;监测离子对分别为 m/z 152.0 > 109.0 (定量离子对) 和 m/z 152.0 > 134.0 (定性离子 对)。
1.4 标准溶液的配制及标准曲线的绘制标准储备溶液:准确称取噻霉酮标准品 10 mg (精确至 0.01 mg),用甲醇溶解并定容至 10 mL,配成 1 000 mg/L 的标准储备液,于 4 ℃ 储存,备 用。
基质匹配标准曲线的绘制:准确称取 2 g 待测 果蔬样品 (精确到 0.01 g),按 1.2 节的前处理及 1.3 节的条件分析,当农药的定性和定量离子信噪 比均小于 3 时,样品确定为空白基质;空白基质 按照 1.2 节前处理,获得基质空白提取液,逐步用 基质空白提取液将标准储备液稀释至 10、20、 50、100、200 和 500 ng/mL,以峰面积 (y) 对农药 的质量浓度 (x) 作线性回归,绘制标准曲线。
1.5 基质效应采用相对响应值法[17],根据公式 (1) 计算噻霉酮的基质效应 (ME)。当基质效应大于 1 时,表现为基质增强效应;当基质效应小于 1 时,为基质抑制效应。
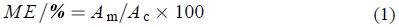
式中,ME 表示基质效应;Am 表示空白基质标准响应值;Ac 表示纯溶剂标准响应值。
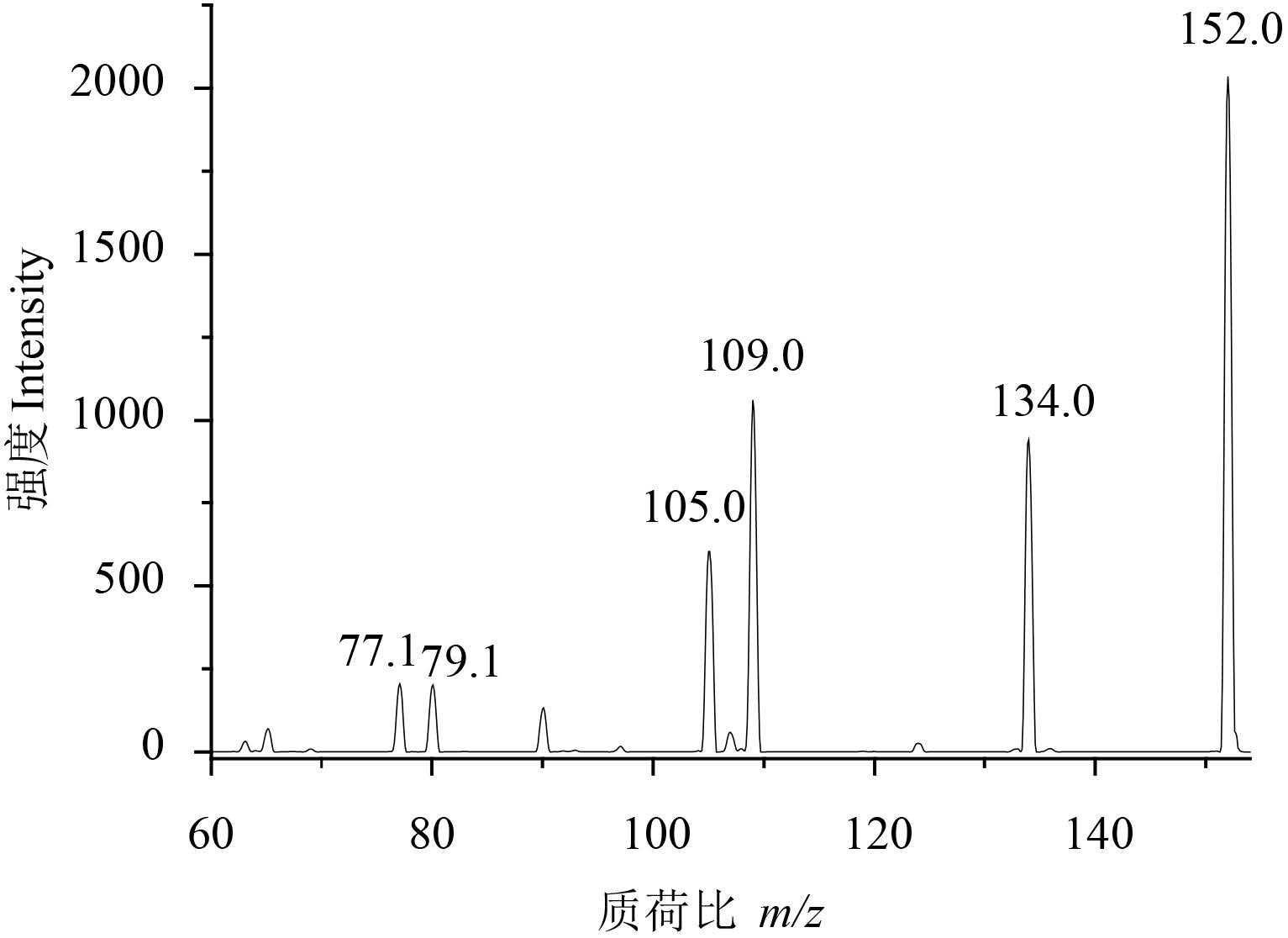
2 结果与讨论 2.1 检测条件的优化配制 1.0 mg/L 的噻霉酮标准溶液,分别采用 电喷雾正离子模式 (ESI+) 和负离子模式 (ESI-) 对 其进行母离子扫描。结果发现:噻霉酮在正离子 模式下信号丰度远高于负离子模式下的,从而确 定噻霉酮的母离子为 [M + H]+,即m/z 152.0。进 一步对子离子、碎裂电压、碰撞能量等参数进行 优化,获得噻霉酮子离子全扫描质谱图见图 1。结 合样品基质效应的影响,最终选取离子丰度最高、本底干扰最小的 m/z 152.0 > 109.0 作为定量离 子对,m/z 152.0 > 134.0 为定性离子对。
|
图 1 噻霉酮的子离子扫描质谱图 Fig. 1 Chromatogram of product ion scan for benziothiazolinone |
本研究选择常规的 JADE-PAK CB-C18 柱作为 分析柱,比较了不同浓度的甲酸水溶液、乙酸铵 水溶液、甲酸-乙酸铵水溶液、纯水所组成的水 相,乙腈和甲醇组成的有机相。通过不同水相与 有机相组合的分析发现,选择 0.1% 甲酸水 (含 2 mmol/L 乙酸铵) -甲醇为流动相时,噻霉酮离子 化效益较好。同时通过设计梯度洗脱程序,噻霉 酮的保留时间和峰形均十分理想,能够有效降低 基质干扰。标准溶液典型色谱图见图 2。
|
图 2 10 ng/mL 噻霉酮标准溶液的色谱图 Fig. 2 Chromatograms of 10 ng/mL benziothiazolinone standard solution |
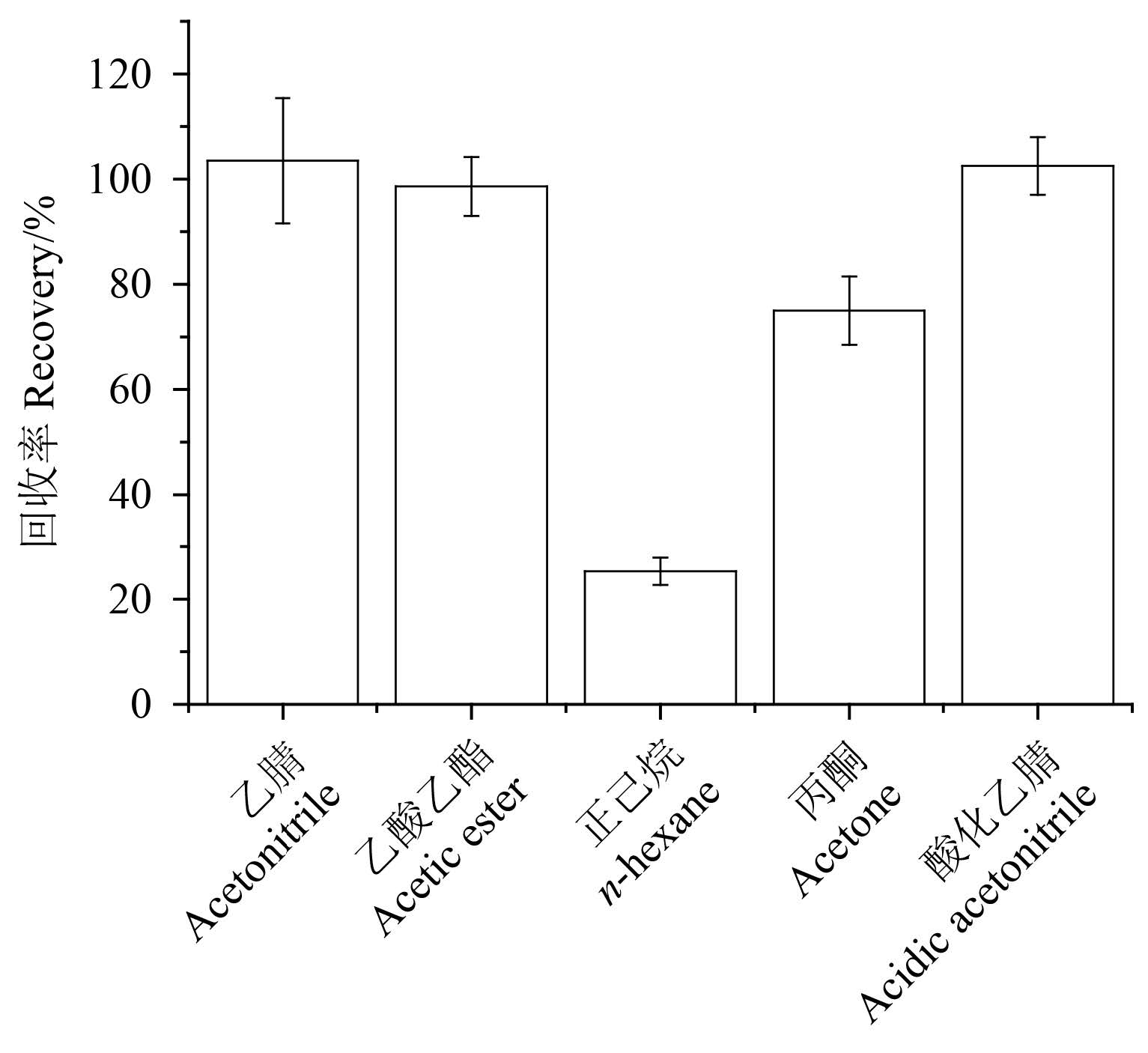
以苹果为分析样品,比较了乙腈、含 0.1% 乙 酸的乙腈、正己烷、乙酸乙酯、丙酮对噻霉酮的 提取效果。结果 (图 3) 表明:用正己烷和丙酮提 取时,回收率达不到检测要求;以乙腈、含 0.1% 乙酸的乙腈、乙酸乙酯为提取剂时,回收率均可满足检测方法的要求。但乙酸乙酯提取时样品的 基质效应相对较大,后续吸附剂净化效果不明 显;含 0.1% 乙酸的乙腈提取时,回收率较乙腈提 取时稳定,相对标准偏差较小,故最终选择含 0.1% 乙酸的乙腈作为提取剂。
|
图 3 不同提取溶剂对噻霉酮的提取效率 Fig. 3 Extraction efficiencies of benziothiazolinone with different solvents |
以番茄为分析样品,当添加 100 μg/kg 的噻霉 酮,且吸附剂用量均为 50 mg 时,比较 PSA、 C18、PCX、PEP、NH2、酸性氧化铝和石墨化炭 黑 (GCB) 7 种吸附剂对样品的净化效果。结果发 现:以 PCX、PSA、GCB、NH2 和酸性氧化铝为 净化剂时,噻霉酮的回收率均达不到检测要求; 以 C18 和 PEP 为净化剂时,噻霉酮的回收率均可 满足检测要求。研究比较了未净化和以C 1 8 、 PEP及 C18 和 PEP 共同净化时噻霉酮的基质效 应,分别为 0.295、0.365、0.505 和 0.565。可见: 以 PEP 和 C18为混合吸附剂时净化,效果更好,故本研究最终选择 C18 和 PEP 共同净化样品。
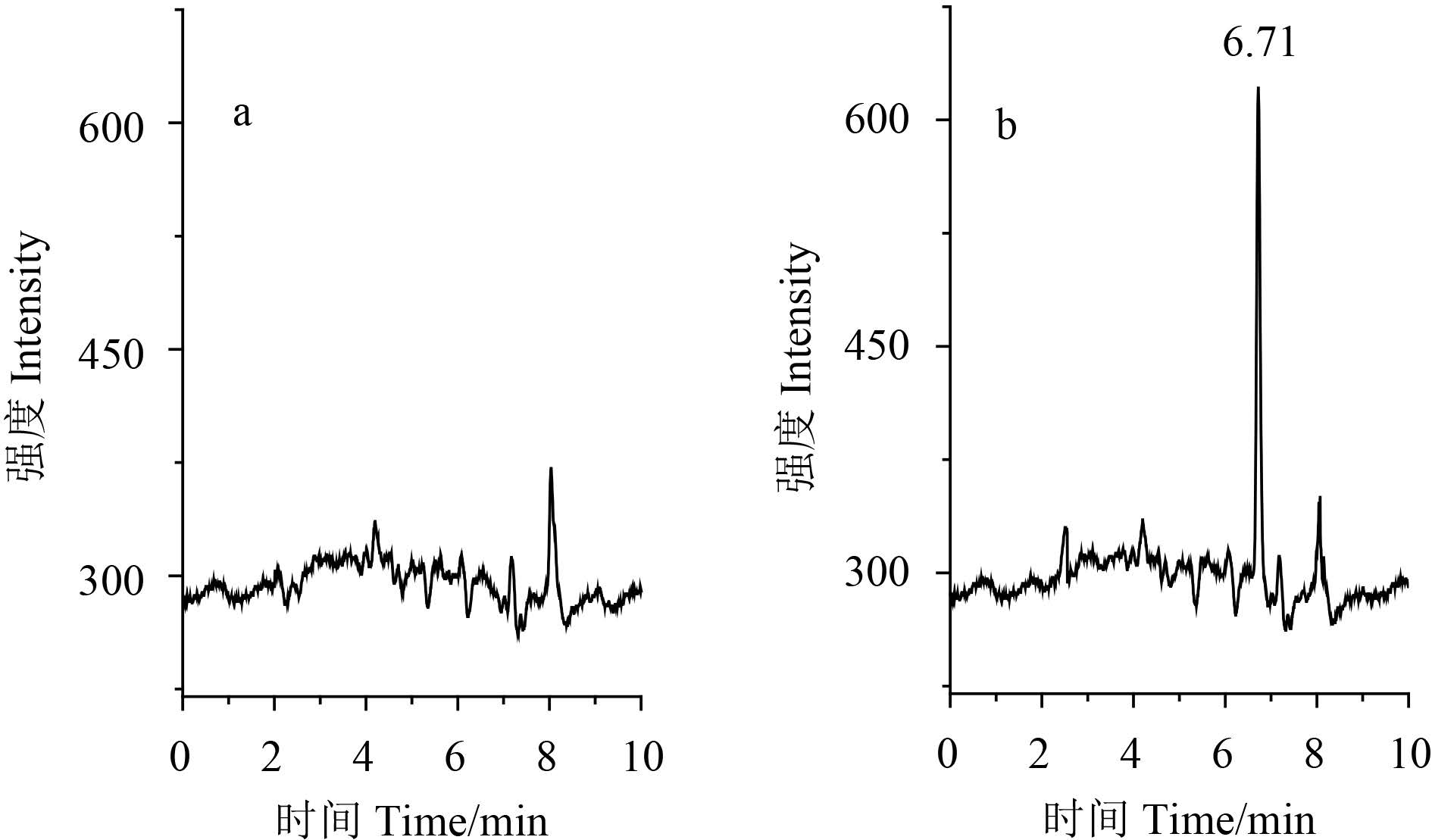
进一步比较 C18 和 PEP 的用量均为 20、50、 75、100、125、150、175 和 200 mg 时的回收率和 基质效应。结果表明:两者用量均为 50~200 mg 时,回收率和基质效应无明显差别;两者用量均 为 20 mg 时,提取液颜色相对较深,样品基质效 应相对较大。故最终选择 C18 和 PEP 各 50 mg 净 化样品。经前处理净化的空白番茄和空白番茄添 加标准品色谱见图 4。
|
图 4 番茄空白样品 (a) 和添加 10 μg/kg 噻霉酮 (b) 色谱图 Fig. 4 Chromatograms of blank tomato (a) and blank tomato spiked 10 μg/kg benziothiazolinone (b) |
本研究尝试在上清提取液中加入 100 mg 硫酸 镁,以达到吸附提取液中水分或盐析的效果。结 果发现:加入硫酸镁后,噻霉酮的回收率低于30%,表明硫酸镁对噻霉酮有一定的吸附作用,故未使用硫酸镁。
同时本研究对前处理方法的兼容性进行了考 察。以番茄为分析样品,在样品中添加吡虫啉、 啶虫脒、哒螨灵、多菌灵、抗蚜威、灭多威、残 杀威、克百威、甲萘威、仲丁威、嘧啶磷、三唑 磷、二嗪磷、甲基嘧啶磷、百治磷、杀扑磷、治 螟磷、氧乐果、甲胺磷、敌百虫、马拉硫磷、喹 硫磷、久效磷、速灭磷、伐灭磷、倍硫磷、辛硫 磷、吡呀酮、噻虫嗪、噻虫啉、烯啶虫胺、恶霜 灵、戊唑醇、二甲戊灵、苯霜灵、甲霜灵和噻霉 酮 37 种常用农药的混合标准溶液,每种农药的添 加水平为 1.0 mg/kg;按照 1.2 节的条件进行前处 理,参照文献[18]的条件测定。结果表明:嘧啶 磷、哒螨灵和噻虫啉的回收率分别为 65%、60% 和 62%;其余 34 种农药的回收率均在 80% 以 上。表明该前处理方法的通用性较强。
2.3 方法的线性范围和检出限结果 (表 1) 表明:不同样品基质对噻霉酮均 有抑制效应。采用基质匹配标准曲线可有效消除 样品基质效应。在 10~500 ng/mL 范围内,噻霉 酮的峰面积 (y) 与其质量浓度 (x) 间呈良好的线性 关系,决定系数 (R2) 均大于 0.996。通过在基质空 白提取液中添加标准溶液的方式,确定噻霉酮在 黄瓜、葡萄、葡萄干、番茄酱、番茄和苹果中的 检出限 (LOD) (以 S/N ≥ 3 计) 均为 3.0 μg/kg,定 量限 (LOQ)( 以 S/N ≥ 10 计) 均为 10 μg/kg。
|
|
表 1 噻霉酮的基质效应、线性关系、检出限和定量限 Table 1 Matrix effects, linear relationships, LODs and LOQs of benziothiazolinone |
从表 2 可知:在 10、20 和 100 μg/kg 3 个添 加水平下,噻霉酮的平均回收率在 80%~98%,相对标准偏差在 2.4%~13% (n = 6),表明该方法的准确度高,通用性好。
|
|
表 2 不同基质中噻霉酮的添加平均回收率和相对标准偏差 (n = 6) Table 2 Recoveries and relative standard deviations (RSD) of benziothiazolinone in different matrix (n = 6) |
利用本方法对市售的黄瓜、葡萄、葡萄干、 番茄酱、番茄和苹果约 50 余份样品进行噻霉酮残 留的检测。结果均未检测出目标分析物。
3 结论本研究以含 0.1% 乙酸的乙腈为提取剂,经 QuEChERS 方法净化,通过色谱和质谱条件的优 化,建立了果蔬及其制品中噻霉酮残留的检测方 法。该方法操作简单、快速、灵敏度高、实用性 强,适用于果蔬及其制品中噻霉酮残留快速确证 检测。
| [1] | 王晓敏, 刘清国, 龚德勇. 新农药噻霉酮对芒果炭疽病的防治效果[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2013, 41(1):90-92. WANG X M, LIU Q G, GONG D Y. Control effect of benziothiazolinone on mango anthracnose[J]. Guizhou Agric Sci, 2013, 41(1):90-92. |
| [2] | 赵子丹, 葛谦, 牛艳, 等. 小麦及土壤中噻霉酮残留量的高效液相色谱分析方法[J]. 农药, 2015, 54(7):518-519. ZHAO Z D, GE Q, NIU Y, et al. Determination of benziothiazolinone residues in wheat and soil by HPLC[J]. Agrochemicals, 2015, 54(7):518-519. |
| [3] | 于福利, 刘伟, 雷琪. 噻霉酮在黄瓜和土壤中的残留分析方法[J]. 农药, 2009, 48(2):130-131. YU F L, LIU W, LEI Q. Residue analysis of benziothiazolinone in cucumber and soil[J]. Agrochemicals, 2009, 48(2):130-131. |
| [4] | 龙胜基, 陈钟, 李雄. 3% 噻霉酮水分散粒剂在烟草和土壤中的残留检测方法[J]. 生物技术世界, 2013(5):56. LONG S J, CHE Z, LI X. Residual detection method for 3% of the water dispersible granules in tobacco and soil[J]. Biotech World, 2013(5):56. |
| [5] | 食品中农药残留最大限量:GB 2763-2014[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2014. Maximum residue limits for pesticides in food:GB 2763-2014[S]. Beijing:Standard Press of China, 2014. |
| [6] | 钱程, 吴琼, 吕岱竹, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定豇豆中溴氰虫酰胺等5种农药残留[J]. 农药学学报, 2014, 16(5):594-599. QIAN C, WU Q, LV D Z, et al. Using ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to analyze 5 pesticide residues in cowpea[J]. Chin J Pestic Sci, 2014, 16(5):594-599. |
| [7] | 江泽军, 张鹏, 李永飞, 等. 分散固相萃取-高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定水稻和土壤中的福美双与甲霜灵残留[J]. 农药学学报, 2015, 17(3):313-320. JIANG Z J, ZHANG P, LI Y F, et al. Simultaneous determination of thiram and metalaxyl residues in rice and soil by dispersive solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chin J Pestic Sci, 2015, 17(3):313-320. |
| [8] | DE OLIVEIRA SILVA R, DE CASTRO R C, MILHOME M A L, et al. Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of twenty multi-class pesticide residues in cashew[J]. LWT-Food Sci Technol, 2014, 59(1):21-25. |
| [9] | ANDRADE G, MONTEIRO S H, FRANCISCO J G, et al. Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry and dynamic multiple reaction monitoring method for determining multiple pesticide residues in tomato[J]. Food Chem, 2015, 175:57-65. |
| [10] | WALORCZYK S, DROŻDŻYŃSKI D, KIERZEK R. Determination of pesticide residues in samples of green minor crops by gas chromatography and ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta, 2015, 132:197-204. |
| [11] | 吴岩, 姜冰, 徐义刚, 等. QuEChERS-液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定果蔬中16种农药残留[J]. 色谱, 2015, 33(3):228-234. WU Y, JIANG B, XU Y G, et al. Determination of 16 pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables by QuECHERS-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chin J Chromatogr, 2015, 33(3):228-234. |
| [12] | 李蓉, 储大可, 张朋杰, 等. QuEChERS/HPLC-MS/MS法测定黄瓜、菜心、葡萄、香蕉中127种农药残留[J]. 分析测试学报, 2015, 34(5):502-511. LI R, CHU D K, ZHANG P J, et al. Determination of 127 pesticide residues in cucumber, flowering cabbage, grape and banana by QuECHERS method coupled with high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry[J]. J Instrum Anal, 2015, 34(5):502-511. |
| [13] | BIZIUK M, STOCKA J. Multiresidue methods for determination of currently used pesticides in fruits and vegetables using QuEChERS technique[J]. Int J Environ Sci Dev, 2015, 6(1):18-22. |
| [14] | CHOI S, KIM S, SHIN J Y, et al. Development and verification for analysis of pesticides in eggs and egg products using QuEChERS and LC-MS/MS[J]. Food Chem, 2015, 173:1236-1242. |
| [15] | HU M F, LIU X G, DONG F S, et al. Determination of ametoctradin residue in fruits and vegetables by modified quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe method using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chem, 2015, 175:395-400. |
| [16] | BRESIN B, PIOL M, FABBRO D, et al. Analysis of organo-chlorine pesticides residue in raw coffee with a modified "quick easy cheap effective rugged and safe" extraction/clean up procedure for reducing the impact of caffeine on the gas chromatography-mass spectrometry measurement[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2015, 1376:167-171. |
| [17] | 黄何何, 张缙, 徐敦明, 等. QuEChERS-高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定水果中21种植物生长调节剂的残留量[J]. 色谱, 2014, 32(7):707-716. HUANG H H, ZHANG J, XU D M, et al. Determination of 21 plant growth regulator residues in fruits by QuEChERS-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chin J Chromatogr, 2014, 32(7):707-716. |
| [18] | 粟有志, 李芳, 李艳美, 等. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定葡萄干中105种农药残留[J]. 分析试验室, 2015, 34(4):433-441. SU Y Z, LI F, LI Y M, et al. Determination of 105 pesticide residues in raisin by solid-phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chin J Anal Lab, 2015, 34(4):433-441. |
 2016, Vol. 18
2016, Vol. 18


