某火电厂汽轮发电4号机组在运行过程中发生低压转子振动超标现象,经停机检查,发现低压转子汽机侧次末级叶片发生断裂,该机组为哈尔滨汽轮机厂有限责任公司生产的CZK350/324-24.2/566/ 566型超临界、一次中间再热、单轴、两缸两排气、直接空冷抽汽凝汽式供热汽轮机。断裂动叶片的材质为0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb。该合金是在Cr17型不锈钢基础上加入Cu、Nb等强化元素,并经固溶时效析出富铜相后进行强化的沉淀硬化马氏体不锈钢,简称17⁃4PH钢,该合金经1025~1055 ℃固熔处理、810~ 820 ℃退火缓冷及600~610 ℃时效热处理后,在近700 ℃仍具有优良的强度和韧性匹配性能及良好的耐蚀性和抗氧化性,因此被广泛用于制造大型汽轮机的叶片等重要部件[1-5]。为查清该机组汽轮机低压转子叶片断裂原因,对断裂的汽轮机低压转子叶片进行了综合性失效原因分析。
2 试验检测采用宏观形貌观察、断口形貌分析、化学成分分析、金相组织分析、力学性能测试等方法对断裂叶片进行分析测试,确定其断裂机理和失效原因。
2.1 宏观形貌观察对断裂的低压转子汽机侧次末级叶片进行宏观形貌分析,如图 1所示。可见叶片已断为两部分,叶顶部分承受严重异物碰撞破坏已弯曲变形,叶根部分断口未受明显破坏,对其断面宏观及微观形貌进一步分析时,发现有明显机械碰撞变形,进汽侧边缘向内发生塑性形变。

|
| 图 1 断裂叶片宏观形貌 Figure 1 Macromorphology of fractured blades |
利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对断口叶片叶根侧进行微观形貌分析,以确定其开裂模式及开裂机理。由图 2可见,叶片断口表面齐平,进汽边区域有明显的异物机械碰撞导致的塑性变形。断口上初始断裂区、裂纹扩展区等特征区域清晰可辨,开裂起源于进汽侧机械碰撞变形处边缘,并向出汽侧扩展,启裂区所占面积较小,断口的大部分为扩展区。对初始断裂区域及裂纹扩展区域进行SEM分析,可见裂纹起源区存在异物机械碰撞痕迹,裂纹扩展区存在明显疲劳辉纹与大致平行的二次裂纹[6-11],同时疲劳源区与扩展区所占断口面积较大,说明该叶片运行中承受的载荷较小、循环次数较多,具有较为典型的高周低应力疲劳断裂特征[12-22]。

|
| 图 2 断裂叶片断口宏观及微观形貌 Figure 2 Macro and micro morphology of fracture surface of the blades |
利用Axio Observer.Alm型金相显微镜对断裂的叶片取样进行显微组织检测,确定其金相组织有无异常,结果如图 3所示。由图 3可以看出,叶片金相组织为回火马氏体,组织未见粗大的淬硬马氏体及严重δ铁素体等异常组织,未见夹杂物缺陷。
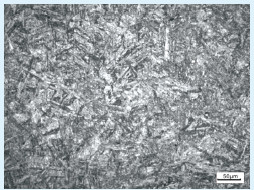
|
| 图 3 断裂叶片显微组织 Figure 3 Microstructure of fractured blade |
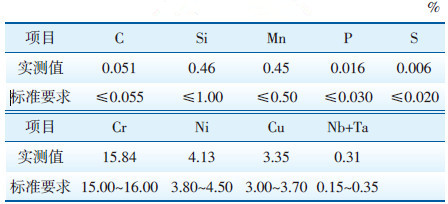
利用SPECTROMAXx型台式直读光谱仪对断裂的叶片取样进行化学成分分析,结果见表 1。由表 1可以看出,送检叶片化学成分符合GB/T 8732— 2014《汽轮机叶片用钢》标准中相关要求。
| 表 1 断裂叶片各化学成分质量分数检测结果 Table 1 Test Results of mass fractions of chemical composition |
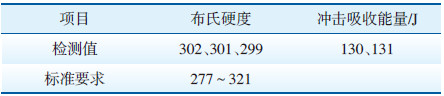
由于送检样品尺寸不足以加工拉伸试样,因此对断裂叶片取样进行硬度及冲击性能试验,利用TUKON-2500型全自动显微维氏硬度计对断裂的叶片取样进行硬度检测,结果见表 2。利用ZBC-300B型数字式冲击试验机对断裂的低压转子次末级叶片进行冲击试验,确定其韧性是否符合要求,结果见表 2。断裂叶片的硬度值满足标准要求。标准中对该材质冲击吸收能量无要求,但可见断裂叶片的常温冲击吸收能量较高(100 J),其塑韧性较好。
| 表 2 断裂叶片力学性能检测结果 Table 2 Mechanical performance test results of fractured blades |
从机组运行工况分析,机组长期在灵活性工况下运行,造成次末级部位蒸汽负荷变化频繁,汽流波动大,导致叶片发生颤振;揭缸检修时发现叶片的叶根与叶根槽装配间隙大,造成叶片晃动幅度较大,进一步加剧了叶片运行过程中的颤振。深度调峰工况下,蒸汽流量下降,导致流场不稳定,使气流从叶片表面脱落产生聚集现象,形成倒流涡流区,引发不规律的气流激振,使叶片出现动应力突增现象,严重影响叶片的安全运行。对于深度调峰机组,在由额定负荷向低负荷工况转换过程中,将不可避免地经过动应力峰值区域,叶片在该区域运行会受到严重损伤,因此机组叶片存在振动过大问题。而且在深度调峰工况下叶片长期存在鼓风现象,温度升高,导致许用应力下降,引发叶片共振,最终造成叶片损坏。
异物可能来自检修过程中掉落到缸内或管道的硬物,运行中随蒸汽进入汽轮机打击叶片形成疲劳源区。综上此次叶片断裂原因为异物打击叶片形成机械损伤并产出应力集中区,叶片在长时间运行过程中承受拉应力、弯曲应力、扭力及振动等循环交变载荷,裂纹源不断扩展最终导致叶片疲劳断裂。
4 结论及建议该汽轮机低压转子汽机侧次末级叶片断裂的主要原因为低压转子汽机侧次末级叶片受到异物机械碰撞损伤,导致叶片进汽侧受损形变并产生应力集中区域,叶片在交变载荷下在机械损伤应力集中区域萌生疲劳裂纹源,在交变应力的作用下裂纹不断扩展,最终导致叶片开裂断裂。
为防止此类叶片断裂事故发生,建议加强汽轮机运行管理,防止外来的异物随蒸汽进入汽轮机内打伤叶片,并确保汽缸内部固定零部件牢固不脱落;优化叶片结构设计,提高叶片装配质量,减少叶片振动现象[23-24];利用机组检修时间,加强汽轮机叶片无损检测工作,可利用磁粉、涡流、相控阵等无损检测方法及时发现叶片裂纹并及时消缺处理;减少机组频繁工况变化,减少交变应力对转子叶片作用。
| [1] |
张涛, 田峰, 贺飞雄, 等. 300 MW汽轮机低压转子动叶片断裂分析[J].
内蒙古电力技术, 2014, 32(5): 41-44 ZHANG Tao, TIAN Feng, HE Feixiong, et al. Failure Analysis of Low-pressure Rotor Blade of 300 MW Steam Turbine[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2014, 32(5): 41-44 (  0) 0)
|
| [2] |
薛育龙, 张文奇, 李改娣, 等. 超临界350 MW机组给水泵汽轮机第5级动叶片断裂原因调查分析[J].
汽轮机技术, 2022, 64(2): 136-140 XUE Yulong, ZHANG Wenqi, LI Gaidi, et al. Fracture Analysis on the Fifth Stage Moving Blade of Feed Water Pump Turbines of a Supercritical 350 MW Unit[J]. Turbine Technology, 2022, 64(2): 136-140 (  0) 0)
|
| [3] |
张永海, 谷伟伟, 曾立飞, 等. 某电厂给水泵汽轮机第3级动叶片断裂原因分析[J].
汽轮机技术, 2020, 62(6)455-458, 461 ZHANG Yonghai, GU Weiwei, ZENG Lifei, et al. Fracture Reason Analysis for 3th Stage Blade of the Feed Pump Steam Turbine of a Power Plant[J]. Turbine Technology, 2020, 62(6)455-458, 461 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5884.2020.06.014 (  0) 0)
|
| [4] |
张元, 方毅, 孟维歌, 等. 某电厂汽轮机叶片断裂失效分析[J].
理化检验(物理分册), 2019, 55(7): 474-477 ZHANG Yuan, FANG Yi, MENG Weige, et al. Failure Analysis on Fracture of Steam Turbine Blades in a Power Plant[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis Part A: Physical Testing, 2019, 55(7): 474-477 (  0) 0)
|
| [5] |
付星星, 张梅, 卢柳林. 汽轮机叶片断裂原因分析[J].
理化检验(物理分册), 2017, 53(11): 812-817 FU Xingxing, ZHANG Mei, LU Liulin. Analysis on Fracture Reasons of Steam Turbine Blades[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis Part A: Physical Testing, 2017, 53(11): 812-817 (  0) 0)
|
| [6] |
江国栋, 卢建湘. 火电厂汽轮机组叶片断裂分析与研究[J].
热加工工艺, 2017, 46(20): 259-261 JIANG Guodong, LU Jianxiang. Analysis and Research on Blade Fracture of Steam Turbine in a Power Plant[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2017, 46(20): 259-261 (  0) 0)
|
| [7] |
牛玉静, 冯文吉, 蒋成虎, 等. 汽轮机低压转子叶片断裂原因分析[J].
上海金属, 2017, 39(1): 65-69 NIU Yujing, FENG Wenji, JIANG Chenghu, et al. Fracture Analysis of Low-pressure Rotor for Steam Turbine[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2017, 39(1): 65-69 (  0) 0)
|
| [8] |
张元. 火电用汽轮机转子主要失效模式及裂纹检测技术分析研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学, 2019.
(  0) 0)
|
| [9] |
邓海涛, 高鹏. 一台超临界空冷600 MW汽轮机次末级叶片断裂故障诊断及原因分析[J].
汽轮机技术, 2022, 64(3)221-222, 228 DENG Haitao, GAO Peng. Fault Diagnosis and Cause Analysis of Secondary Last Stage Blade Fracture of an Air - cooled Supercritical 600 MW Steam Turbine[J]. Turbine Technology, 2022, 64(3)221-222, 228 (  0) 0)
|
| [10] |
薛永锋, 张吉荣, 常强. 国产330 MW机组中压缸次末级动叶断裂原因分析[J].
东北电力技术, 2021, 42(7)31-33, 37 XUE Yongfeng, ZHANG Jirong, CHANG Qiang. Analysis of Secondary Last Stage Rotor Blade of IP Cylinder Fracture in Domestic 330 MW Unit[J]. Northeast Electric Power Technology, 2021, 42(7)31-33, 37 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-7913.2021.07.009 (  0) 0)
|
| [11] |
郑建军, 王劭, 云峰. 风力发电机组叶片连接螺栓断裂机理及原因分析[J].
内蒙古电力技术, 2022, 40(6): 9-12 ZHENG Jianjun, WANG Shao, YUN Feng. Fracture Mechanism and Cause Analysis of Connecting Bolts for Wind Power Turbine Blades[J]. Inner Mongolia Electric Power, 2022, 40(6): 9-12 (  0) 0)
|
| [12] |
刘秀明. 大型汽轮发电机转子风扇断裂原因探析及对策[J].
东北电力技术, 2020, 41(10): 59-62 LIU Xiuming. Cause Analysis and Countermeasures of Large Turbine-Generatorn Rotor Fans Fracture[J]. Northeast Electric Power Technology, 2020, 41(10): 59-62 (  0) 0)
|
| [13] |
赵金亮, 谢小波. MAN主机涡轮增压器排气叶片损伤故障原因分析[J].
机电工程技术, 2021, 50(11): 278-281 ZHAO Jinliang, XIE Xiaobo. Analysis of Damaged Turbine Wheel Blade with Turbochager[J]. Mechanical & Electrical Engineering Technology, 2021, 50(11): 278-281 (  0) 0)
|
| [14] |
郭洪福. 背压式汽轮机调速级叶片断裂原因分析[J].
氮肥技术, 2020, 41(6)43-45, 48 GUO Hongfu. Causes analysis on fracture of backpressure steam turbine governing stage blade[J]. Danfei Jishu, 2020, 41(6)43-45, 48 (  0) 0)
|
| [15] |
孙振西, 蒋作文, 韩贯凯, 等. 烟气轮机叶片断裂原因[J].
理化检验(物理分册), 2020, 56(11)66-69, 74 SUN Zhenxi, JIANG Zuowen, HAN Guankai, et al. Cause of Fracture on Flue Gas Turbine Blade[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis Part A: Physical Testing, 2020, 56(11)66-69, 74 (  0) 0)
|
| [16] |
马劲夫. 航空发动机压气机叶片的断裂失效分析[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2021.
(  0) 0)
|
| [17] |
何风云. 发动机离心叶轮分流叶片疲劳断裂研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2017.
(  0) 0)
|
| [18] |
吴君良. 基于断裂力学的离心压缩机叶片疲劳寿命研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2014.
(  0) 0)
|
| [19] |
孙远伟. 某燃气轮机低压涡轮叶片断裂故障分析[J].
燃气轮机技术, 2021, 34(3): 57-62 SUN Yuanwei. Failure Analysis of Low Pressure Turbine Blade Fracture of a Gas Turbine[J]. Gas Turbine Technology, 2021, 34(3): 57-62 (  0) 0)
|
| [20] |
张涛, 陈志军, 王文豪, 等. 某超临界电站锅炉送风机叶片的断裂原因分析[J].
理化检验(物理分册), 2016, 52(7): 479-483 ZHANG Tao, CHEN Zhijun, WANG Wenhao, et al. Causes Analysis on Fracture of One Forced Draft Fan Blade of One Supercritical Power Station Boiler[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis Part A: Physical Testing, 2016, 52(7): 479-483 (  0) 0)
|
| [21] |
李永乐, 骆贵兵, 杨辉. 静叶可调轴流式引风机叶片断裂原因分析及对策[J].
热力发电, 2021, 50(4): 114-119 LI Yongle, LUO Guibing, YANG Hui. Cause analysis and countermeasures for blade fracture of static blade adjustable axial flow induced draft fan[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2021, 50(4): 114-119 (  0) 0)
|
| [22] |
张强, 王占文, 方旭, 等. 给水泵汽轮机动叶片断裂失效分析[J].
河北电力技术, 2022, 41(1): 88-91 ZHANG Qiang, WANG Zhanwen, FANG Xu, et al. Fracture Failure Analysis of Feed Water Pump Turbine Blade[J]. Hebei Electric Power, 2022, 41(1): 88-91 (  0) 0)
|
| [23] |
赵世伟, 胡雪梅, 李烨, 等. 轴流送风机叶片断裂事故分析及对策[J].
浙江电力, 2019, 38(5): 115-118 ZHAO Shiwei, HU Xuemei, LI Ye, et al. Analysis and Countermeasure on Blade Fracture of Axial Flow Forced Draft Fan[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2019, 38(5): 115-118 (  0) 0)
|
| [24] |
翁振宇, 关淳, 马义良, 等. 用于深度调峰机组的系列长叶片开发与应用[J].
热能动力工程, 2022, 37(2)63-69, 91 WENG Zhenyu, GUAN Chun, MA Yiliang, et al. Development and Application of Series Long Blades for Deep Peak Regulation Units[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2022, 37(2)63-69, 91 (  0) 0)
|
 2023, Vol. 41
2023, Vol. 41