文章信息
- 付言峰, 李兰, 周艳红, 李碧侠, 方晓敏, 王学敏, 任守文. 2015.
- FU Yanfeng, LI Lan, ZHOU Yanhong, LI Bixia, FANG Xiaomin, WANG Xuemin, REN Shouwen. 2015.
- 瘦素受体对苏钟猪脂肪沉积调控的影响
- Role of leptin receptor in the regulation of fat deposition in Suzhong pigs
- 南京农业大学学报, 38(6): 986-992
- Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 38(6): 986-992.
- http://dx.doi.org/10.7685/j.issn.1000-2030.2015.06.017
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2015-01-05
2. 中国农业大学动物医学院, 北京 100193;
3. 国家兽用生物制品工程技术研究中心, 江苏 南京 210014;
4. 南京农业大学动物科技学院, 江苏 南京 210095
2. College of Veterinary Medicine, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193, China;
3. National Research Center of Veterinary Biologicals Engineering and Technology, Nanjing 210014, China;
4. College of Animal Science and Technology, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing 210095, China
随着生活水平的不断提高,人们对猪肉品质的要求也越来越高[1, 2]。脂肪沉积是影响猪肉品质和营养价值的一个关键因素[3],因为脂肪沉积可以影响很多重要的肉质性状,如背膘厚、肌内脂肪含量、瘦肉率等[4, 5]。另外,猪作为一个良好的动物模型,在研究人类肥胖候选基因的研究中发挥重要的作用[6]。因此,开展猪的脂肪沉积机制研究具有重大意义。
随着定位克隆、物理作图和候选基因等分子生物学技术的发展,研究人员已成功发现许多影响猪脂肪性状的主效基因,如过氧化物酶体增殖物活化受体基因(PPARs)[7]、肥胖易感基因(FTO)[5, 6, 7, 8]、脂蛋白脂肪酶基因(LPL)[9]等。瘦素受体(LEPR)是一种跨膜受体,属于Ⅰ类细胞因子受体家族,由细胞外的配体结合区、跨膜区及胞内区3部分组成[10, 11]。瘦素受体与瘦素(LEP)相互结合发挥着广泛作用,如机体体质量平衡控制[12, 13]。
在小鼠上,前人研究发现LEPR mRNA在越来越多的组织上有表达,包括心、肝、肾、肺、小肠、卵巢和脂肪组织等[14]。在猪上,LEPR mRNA在脂肪组织、脑、肌肉、脂肪、肝、下丘脑、垂体[11, 15, 16, 17]和繁殖组织(子宫内膜、卵巢)[17]上均有表达。但是,关于中国高脂肪含量猪和低脂肪含量猪LEPR的表达差异及表达量、编码序列单核苷酸多态(cSNP)与肉质性状关联分析的报道还很少。
苏钟猪是以太湖猪为亲本培育的优质瘦肉型猪,肌间和肌内脂肪丰富,本试验通过实时荧光定量PCR方法、免疫印迹和直接测序等技术,从mRNA表达、蛋白表达、cSNP挖掘和性状关联等方面分析了LEPR对脂肪沉积的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验动物
在江苏洪泽鑫象公司,用背膘仪活体测定背膘厚度大小选取了10头6月龄、(95±3)kg体质量的半同胞健康苏钟猪(高脂猪和低脂猪各半),这些猪均在同一天被电击昏后屠宰,之后参照屠宰程序[18, 19]采集猪的心、肝、肾、眼肌(背最长肌)和背膘等组织样,迅速置于液氮冷冻保存。同时,测定了这些试验猪的脂肪沉积相关性状,包括背最长肌横切面积(求积仪,Haguang)、瘦肉率(SFK,Denmark)、背膘厚(游标卡尺,MNT)等,并根据背膘厚度和试验猪左半边胴体的前躯、中躯和后躯脂肪质量进一步确定了高脂猪和低脂猪(表 1)。另外本实验室保存有51头苏钟猪肌肉样或血样,并有这些猪的耳号、出生日期和背最长肌性状(横切面积、pH值、肉色、大理石花纹评分和系水力)等记录,笔者采用高盐法[20]提取这些猪组织样中的基因组,进行LEPR基因的cSNP研究。
| 试验动物分组 Group of animal | 瘦肉率/% Lean meat rate | 眼肌面积/cm2 Longissimus dorsi muscle area |
| 大理石 花纹评分 Marbling score |
| 低脂猪Low-fat pigs | 56.62±1.35a | 61.86±2.46a | 3.9±0.53a | 2.4±0.46 | 2.1±0.48a | 4.71±1.12 |
| 高脂猪High-fat pigs | 49.42±2.39b | 48.52±3.57b | 5.2±1.21b | 2.7±0.56 | 3.2±0.80b | 4.72±1.33 |
| 注:同列不同的小写字母上标代表显著性差异(P<0.05)。Values with different superscripts are significant difference within column(P<0.05). |
猪LEPR基因的cDNA(GenBank:NM_001024587)全长4 050 bp,其编码序列为第16~3 513 bp。LEPR_1引物用于RT-qPCR,LEPR_2引物用于LEPR第18外显子(2 726~3 464 bp)的cSNPs检测。所有引物序列均用Oligo 6.0软件设计,由上海英潍捷基(Invitrogen)生物公司合成(表 2)。
| 引物 Primers | 引物对序列 Primer pairs sequences(5′→3′) | 退火温度/℃ Annealing temperature | 产物长度/bp Product size | 用途 Usage |
| LEPR_1 | CCGCTGCCTCCATCCAGTGTG/TCTGGCACCGGGAGACTGGT | 60 | 197 | RT-qPCR |
| LEPR_2 | CAGTGACATTTGGCCCTCTT/CCATTATCTTCTGAGTCTGAG | 60 | 759 | PCR-sequencing |
| GAPDH | GGTGAAGGTCGGAGTGAACG/TGGGTGGAATCATACTGGAACA | 60 | 150 | RT-qPCR |
利用Trizol(Invitrogen,USA)/氯仿方法[5, 21]从猪组织样中提取总RNA,以上述提取的总RNA为模板,利用First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit试剂盒进行反转录,合成cDNA第一链(Fermentas,Lithuania),25 μL反应体系,试验步骤参考说明书进行。
利用实时荧光定量PCR仪(ABI Stepone plus,USA)进行PCR扩增。反应体系如下:2×real-time PCR Master Mix(SYBR Green)10 μL,上下游引物(10 μmmol · L-1)各1 μL,模板(cDNA稀释10倍)1 μL,Taq DNA Polymerase 0.3 μL,加DEPC水到20 μL(ABI,USA)。反应条件如下:95 ℃ 2 min热启动HotStar Taq酶活性;94 ℃ 10 s,60 ℃ 40 s,共40循环;45~95 ℃,读板时按0.1 ℃ · s-1进行熔解曲线分析。内参基因为GAPDH。
1.4 Western blot检测蛋白表达
组织样用蛋白裂解液裂解[5, 22],提取出的总蛋白用BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(Invitrogen,USA)检测。Western blot过程参照Patel等[23]和付言峰等[24]的方法,一抗用小鼠抗人LEPR抗体(mAb,sc-8391,Santa Cruz,USA),二抗用辣根过氧化物酶标记山羊抗小鼠抗体(A0216,Beyotime,中国)。利用灰度分析软件(Gel-Pro32)分析电泳条带灰度比值(以GAPDH为内参)。
1.5 直接测序法检测cSNPs
首先进行LEPR基因目的片段(cDNA第2 726~3 464 bp,位于CDS区)的PCR扩增。反应体系(15 μL):7 μL Premix Taq(TaKaRa,China),6 μL ddH2O,0.5 μL各种引物(10 pmol · L-1)和1 μL DNA。反应条件:94 ℃ 5 min;94 ℃ 30 s,60 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 60 s,共30循环;72 ℃ 7 min。利用ABI 3730XL DNA测序仪(Applied Biosystems,USA)对上述PCR产物进行直接测序,每个样品测序2次,即正向和反向各测1次。测序序列和NCBI序列通过DNAMAN 5.2进行比对,最终得到LEPR的cSNPs。
1.6 数据处理与统计
实时荧光定量PCR的数据利用2-ΔΔCT法[25, 26]分析,得到LEPR mRNA的相对表达量。用SAS 8.2统计软件包的GLM程序进行LEPR mRNA、蛋白表达量、cSNP与脂肪沉积性状之间的关联分析。结果均以最小二乘均值±标准误(LS means±SE)表示。
2 结果与分析
2.1 LEPR mRNA表达对脂肪沉积的影响
组织样中提取的总RNA利用分光光度计测定出的A260/A280结果大都处于1.8~2.1的区间,总RNA含量为1.60~2.22 μg · μL-1,说明提取的RNA质量较高,可以进行后续的RT-qPCR试验。
RT-qPCR结果表明:LEPR mRNA在猪心、肝、肾、眼肌(背最长肌)和背膘中均有表达,且不同组织样中的表达量差异显著(P<0.05)。其中背膘的表达量最高,且显著高于其他组织(P<0.05),其次为背最长肌的表达量,且高脂猪的表达量显著高于低脂猪(P<0.05)(图 1)。由于高脂猪的眼肌(背最长肌)面积和瘦肉率显著低于低脂猪(表 1),即高脂猪的脂肪沉积量显著高于低脂猪,结合文献报道[12, 13],笔者推测猪脂肪沉积增加,引起LEPR mRNA表达量升高,促进脂肪分解,控制猪只体质量的平衡。
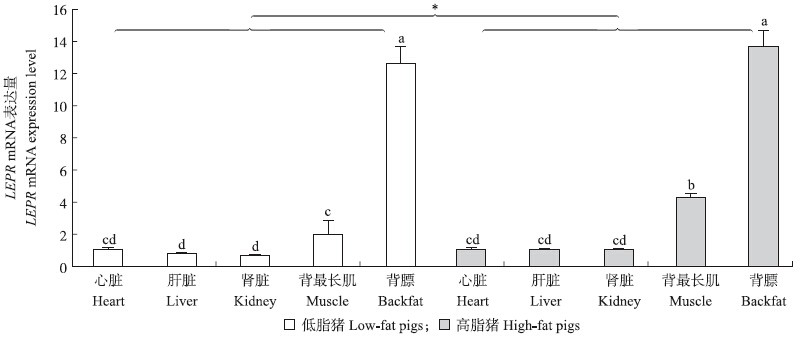 |
图 1 苏钟猪不同组织样的LEPR mRNA表达量(GAPDH为内参基因)Fig. 1 The mRNA expression level of LEPR in different tissues of Suzhong pigs(GAPDH was used as an internal gene)柱形图上不同的小写字母或“*”表示在0.05水平差异显著。 The“muscle”was abbreviation of“longissimus dorsi muscle”. Values with different low case letters or“*”show significant difference at 0.05 level. The same as follows. |
Western blot结果表明:猪LEPR蛋白(NCBI Protein:NP_001019758)在苏钟猪的心脏、肝脏、肾脏、背最长肌和背膘组织中均有表达,且不同组织间表达量差异显著(P<0.05),其中背膘中的表达量最高,显著高于其他组织样,其次为背最长肌,而肾脏中的LEPR蛋白表达量最低(图 2)。
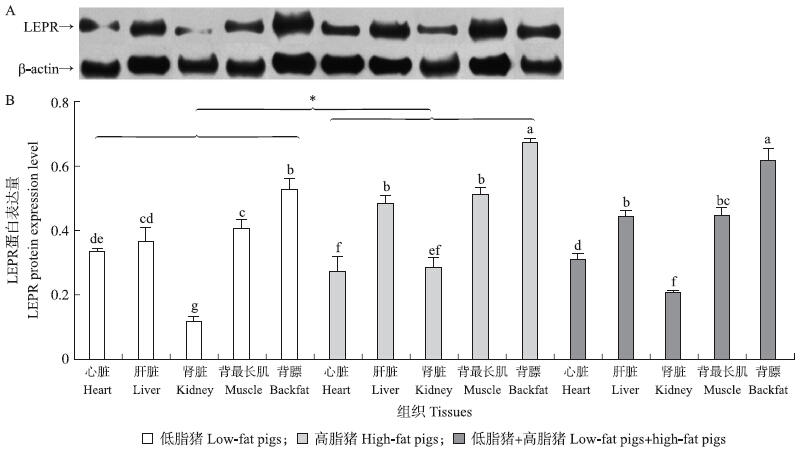 | 图 2 LEPR在苏钟猪不同组织样中蛋白表达量的Western blot分析结果(β-actin为内参)Fig. 2 Western blot results of LEPR protein expression in different tissues of Suzhong pigs(β-actin was used as an internal protein)A:电泳条带Western blot bands;B:LabImage分析得到的电泳条带灰度值比值Gray value of scanned western blot lane images by LabImage software |
笔者对LEPR基因cDNA序列第2 726~3 464 bp(位于CDS区,覆盖了第18外显子92.65%的序列)进行了直接测序扫描,结果发现3个cSNPs,即c.2856 C>T,c.2935 C>T和c.3155 C>T。3个位点的突变均为C→T的突变。这3个cSNPs中,只有c.2856 C>T位点有3种基因型,呈现多态性,分别为CC、CT和TT基因型(图 3)。
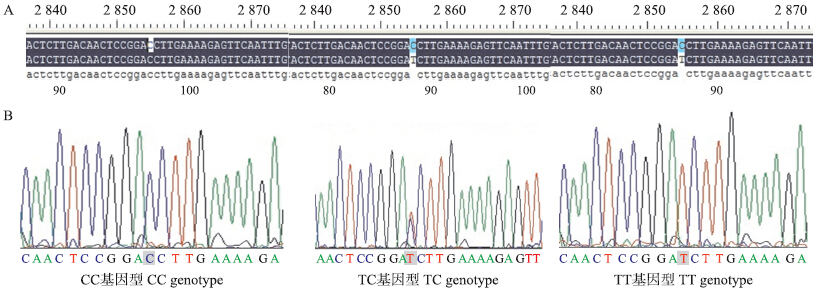 | 图 3 LEPR基因部分编码序列的测序结果Fig. 3 The PCR-sequencing results for the LEPR partial CDS sequenceA:测序序列与NCBI序列比较结果Comparison results of sequencing results and NCBI results;B:测序峰值及基因分型图Peak value figure using sequencing and genetype |
LEPR的cSNPs(c.2856 C>T)基因型与脂肪沉积相关肉质性状的关联分析结果表明:对于背最长肌面积/体质量、瘦肉率、pH值和肉色评分,CC基因型显著大于TT基因型(P<0.05);相反,对于肉色L*值、肉色a*值和大理石花纹评分,CC基因型显著小于TT基因型(P<0.05)。
考虑到背最长肌面积/体质量、瘦肉率和肉色a*值,低脂猪极显著大于高脂猪(P<0.01)。笔者推测,TT基因型猪关联的肉质性状中,背最长肌肉色更亮、大理石花纹更丰富、瘦肉率和眼肌面积更低,与高脂 猪的肉质性状结果类似,即TT基因型更有利于猪的脂肪沉积,T等位基因是脂肪沉积有利等位基因(表 3)。
| 肉质性状 Meat quality traits |
| 加性效应 Additive effect | 显性效应 Dominant effect |
| 背最长肌面积/体质量Longissimus dorsi muscle area/Body weight | 0.66±0.03A | 0.54±0.01B | 0.47±0.02C | 0.10±0.02** | -0.03±0.02 |
| 瘦肉率Lean meant rate | 54.68±3.29Aa | 52.90±1.24Aab | 49.03±2.11Ab | 2.82±1.98 | 1.04±2.29 |
| pH值pH value | 6.12±0.12Aa | 5.85±0.05ABb | 5.7±0.08Bb | 0.21±0.07** | -0.06±0.08 |
| 肉色L*值(亮度)Luminosity(L*)value | 39.12±2.4Aa | 40.63±0.9Aab | 45.36±1.54Ab | -3.13±1.45* | -1.60±1.67 |
| 肉色a*值(品红色→绿色)a* value(range from magenta to green) | 4.67±1.11Aa | 5.88±0.42Aab | 6.74±0.71Ab | -1.03±0.67 | 0.18±0.77 |
| 肉色b*值(黄色→蓝色)b* value(range from yellow to blue) | 2.80±0.69 | 3.16±0.26 | 4.07±0.44 | -0.64±0.41 | -0.27±0.48 |
| 肉色评分Meat color score | 4.44±0.17Aa | 3.35±0.06Bb | 3.19±0.11Bb | 0.62±0.10** | -0.46±0.12** |
| 大理石花纹评分Marbling score | 4.73±0.54ABa | 3.35±0.07Aa | 6.30±0.35Bb | -0.79±0.32* | -0.70±0.38 |
| 系水力Water holding capacity | 10.85±3.33 | 11.06±1.25 | 14.90±2.14 | -2.03±2.01 | -1.82±2.32 |
| 注: 1)肉色L*、a*、b*是肉色测定仪的直接测定结果,L*:0~100,a*:127~-128,b*:127~-128。2)肉色评分:1~6,大理石花纹评分:1~10,二者均使用美国农业部肉色比色板测定。3)同行不同大小写字母分别表示差异极显著(P<0.01)和差异显著(P<0.05)。 Notes: 1)Luminosity(L*),a* and b* was three parameters of meat color measured using chroma meter cr400,Japan. Among these parameters,values of L* ranged from 0 to 100,values of a* ranged from 127 to -128 and values of b* ranged from 127 to -128. 2)Values of meat color score ranged from 1 to 6(color range from white to red),and values of marbling score ranged from 1 to 10,both of them were measured using American shade guide. 3)Values with different superscripts capital letter and small letter in the same line show significant difference at 0.01 and 0.05 levels. |
脂肪沉积可以影响猪的肉质性状,如背膘厚、背最长肌面积和肌内脂肪含量等[3, 5],这些肉质性状又进一步影响猪肉的品质,如适口性、香气、嫩度等,直接决定了猪肉的品质和价格,所以猪育种工作者对其越来越重视[24]。关于影响脂肪沉积的基因有肥胖易感基因(FTO)[5]、氟烷基因(halothane)[27]、激酶插入域受体(Kinase insert domain receptor,KDR)基因[28]等。而本文的瘦素受体(LEPR)基因与瘦素(leptin)相互结合后,在体质量平衡、脂肪沉积过程中发挥着重要的作用[12, 13]。关于其在中国本地猪种不同脂肪含量猪中的研究还鲜有报道,所以本试验开展了LEPR的mRNA和蛋白表达及cSNPs对猪脂肪沉积的影响研究。
RT-qPCR结果表明:LEPR mRNA在苏钟猪的心、肝、肾、背最长肌和背膘5种组织中均有表达,且背膘中的表达量显著高于其他组织,这与前人报道的LEPR在其他品种猪的表达结果一致[29]。苏钟猪高脂猪的脂肪沉积高于低脂猪,且高脂猪LEPR mRNA表达量显著高于低脂猪,说明脂肪沉积越高,LEPR mRNA表达量越高。推测原因可能是脂肪沉积增加引起LEPR表达量增加,从而促进脂肪分解,控制猪只体质量平衡[12, 13]。有研究对波兰5个品种猪分别添加能量饲料后,LEPR在各品种猪肌肉组织的表达量均随着年龄增长而显著升高[30]。
Western blot结果表明:LEPR蛋白在苏钟猪的心、肝、肾、背最长肌和背膘中均有表达,其中背膘中的表达量最高,且高脂猪的蛋白表达量显著高于低脂猪(P<0.05),这与LEPR mRNA表达趋势相同。高脂猪比低脂猪的脂肪含量高、瘦肉率低,而LEPR mRNA和蛋白的表达量都更高,前人对LEPR配体leptin也有类似的研究结果,其发现瘦肉率高的猪leptin mRNA表达量更低,说明瘦肉率与leptin的表达量也成反比[31]。另有报道,LEPR在高肌内脂肪含量猪背最长肌的表达量显著高于低肌内脂肪含量猪[32]。
PCR-sequencing和关联分析结果表明,LEPR部分编码序列中检测到3个cSNPs多态位点,其中c.2856 C>T多态位点对瘦肉率、肉色、大理石花纹评分等肉质性状影响显著,T等位基因为脂肪沉积的有利等位基因。这个SNP突变不直接引起氨基酸的改变,但其可以通过与其他SNP的连锁不平衡间接引起氨基酸的改变[20, 33]。有研究表明,LEPR多态性显著关联着杜洛克×长白×大白三元杂交猪的脂肪含量、脂肪分布和脂肪组成[34],LEPR多态性显著关联韩国本地猪×大白二元杂交猪的系水力、肌内脂肪、胆固醇和风味评分[32]。
综上所述,LEPR mRNA和蛋白在苏钟猪的背膘和背最长肌中均有高表达量,且高脂猪的LEPR表达量显著高于低脂猪,可能是脂肪沉积的增加引起LEPR的表达量增加,从而使LEPR更好得发挥其“促进脂肪分解,控制猪只体质量平衡”的作用;LPER多态位点c.2856 C>T中T为脂肪沉积的有利等位基因。上述结果表明LEPR基因对猪的脂肪沉积有一定影响,可以作为苏钟猪肉质改良育种中重要的候选基因。
| [1] | van Wijk H,Arts D,Matthews J,et al. Genetic parameters for carcass composition and pork quality estimated in a commercial production chain[J]. J Anim Sci,2005,83(2):324-333 |
| [2] | van Wijk H,Dibbits B,Baron E,et al. Identification of quantitative trait loci for carcass composition and pork quality traits in a commercial finishing cross[J]. J Anim Sci,2006,84(4):789-799 |
| [3] | Wood J,Enser M,Fisher A,et al. Fat deposition,fatty acid composition and meat quality:a review[J]. Meat Science,2008,78(4):343-358 |
| [4] | Hausman G,Poulos S. Recruitment and differentiation of intramuscular preadipocytes in stromal-vascular cell cultures derived from neonatal pig semitendinosus muscles[J]. J Anim Sci,2004,82(2):429-437 |
| [5] | Fu Y,Li L,Ren S. Effect of FTO expression and polymorphism on fat deposition in Suzhong pigs[J]. Asian Austral J Anim,2013,26(10):1365-1373 |
| [6] | Madsen M B,Birck M M,Fredholm M,et al. Expression studies of the obesity candidate gene FTO in pig[J]. Anim Biotechnol,2009,21(1):51-63 |
| [7] | Mandard S,Müller M,Kersten S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor a target genes[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci,2004,61(4):393-416 |
| [8] | Frayling T M,Timpson N J,Weedon M N,et al. A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity[J]. Science,2007,316(5826):889-894 |
| [9] | Shen Y,Lookene A,Zhang L,et al. Site-directed mutagenesis of apolipoprotein CII to probe the role of its secondary structure for activation of lipoprotein lipase[J]. J Biol Chem,2010,285(10):7484-7492 |
| [10] | Ruiz-Cortés Z T,Men T,Palin M F,et al. Porcine leptin receptor:molecular structure and expression in the ovary[J]. Mol Reprod Dev,2000,56(4):465-474 |
| [11] | Richards M P,Poch S M. Molecular cloning and expression of the turkey leptin receptor gene[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B:Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,2003,136(4):833-847 |
| [12] | Israel D,Chua S,Jr. Leptin receptor modulation of adiposity and fertility[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab,2010,21(1):10-16 |
| [13] | Suzukawa M,Nagase H,Ogahara I,et al. Leptin enhances survival and induces migration,degranulation,and cytokine synthesis of human basophils[J]. The Journal of Immunology,2011,186(9):5254-5260 |
| [14] | Margetic S,Gazzola C,Pegg G,et al. Leptin:a review of its peripheral actions and interactions[J]. Int J Obes,2002,26(11):1407-1433 |
| [15] | Smolinska N,Przala J,Kaminski T,et al. Leptin gene expression in the hypothalamus and pituitary of pregnant pigs[J]. Neuro Endocrinol Lett,2004,25(3):191-195 |
| [16] | Siawrys G,Przala J,Kaminski T,et al. Long form leptin receptor mRNA expression in the hypothalamus and pituitary during early pregnancy in the pig[J]. Neuroendocrinology Letters,2005,26(4):305-310 |
| [17] | Bogacka I,Przala J,Siawrys G,et al. The expression of short form of leptin receptor gene during early pregnancy in the pig examined by quantitative real time RT-PCR[J]. Journal of Physiol Pharmacol,2006,57(3):479-489 |
| [18] | Lord E,Murphy B,Desmarais J,et al. Modulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ and γ transcripts in swine endometrial tissue during early gestation[J]. Reproduction,2006,131(5):929-942 |
| [19] | Fu Y,Fu J,Ren Q,et al. Expression of Eph A molecules during swine embryo implantation[J]. Molecular Biology Reports,2012,39(3):2179-2185 |
| [20] | Fu Y,Fu J,Wang A. Association of EphA4 polymorphism with swine reproductive traits and mRNA expression of EphA4 during embryo implantation[J]. Mol Biol Rep,2012,39:2689-2696 |
| [21] | Sambrook J,Russell D W. Molecular Cloning:A Laboratory Manual[M]. New York:Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press,2001 |
| [22] | 付言峰,周艳红,王爱国,等. 梅山猪胚胎附植期EphB2的组织表达及RNA-seq分析[J]. 遗传,2014,36(12):1243-1248 [Fu Y F,Zhou Y H,Wang A G,et al. Tissue expression of EphB2 and RNA-seq analysis during embryo implantation in Meishan pigs[J]. Hereclitas,2014,36(12):1243-1248(in Chinese with English abstract)] |
| [23] | Patel K,Makarenkova H,Jung H.The role of long range,local and direct signalling molecules during chick feather bud development involving the BMPs,follistatin and the Eph receptor tyrosine kinase Eph-A4[J]. Mechanisms of Development,1999,86(1/2):51-62 |
| [24] | 付言峰,方晓敏,李碧侠,等. 瘦素受体表达量在苏钟猪脂肪沉积调控中的作用[J]. 中国兽医学报,2012,32(9):1266-1271 Fu Y F,Fang X M,Li B X,et al. Function of leptin receptor expression in the regulation of fat deposition in Suzhong pigs[J]. Chin J Vet Sci,2012,32(9):1266-1271(in Chinese with English abstract)] |
| [25] | Schmittgen T,Livak K. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method[J]. Nature Protocols,2008,3(6):1101-1108 |
| [26] | Fu Y,Fu J,Yang L,et al. Expression of Eph-Ephrin a molecules in endometrium during swine embryo implantation examined using real-time RT-PCR[J]. Agricultural Sciences in China,2011,10(9):1445-1451 |
| [27] | Alves L R,Antunes R C,Andrade R B,et al. Effect of the halothane genotype on intramuscular fat deposition in swine[J]. Genetmol Res,2014,13(1):363-370 |
| [28] | Fu Y,Sun W,Xu C,et al. Genetic variants in KDR transcriptional regulatory region affect promoter activity and intramuscular fat deposition in Erhualian pigs[J]. Anim Genet,2014,45(3):373-380 |
| [29] | Tyra M,Ropka-Molik K,Terman A,et al. Association between subcutaneous and intramuscular fat content in porcine ham and loin depending on age,breed and FABP3 and LEPR genes transcript abundance[J]. Mol Biol Rep,2013,40(3):2301-2308 |
| [30] | Tyra M,Ropka-Molik K,Eckert R,et al. H-FABP and LEPR gene expression profile in skeletal muscles and liver during ontogenesis in various breeds of pigs[J]. Domest Anim Endocrinol,2011,40(3):147-154 |
| [31] | Piórkowska K,Oczkowicz M,Różycki M,et al. Novel porcine housekeeping genes for real-time RT-PCR experiments normalization in adipose tissue:assessment of leptin mRNA quantity in different pig breeds[J]. Meat Science,2011,87(3):191-195 |
| [32] | Li X,Kim S W,Choi J S,et al. Investigation of porcine FABP3 and LEPR gene polymorphisms and mRNA expression for variation in intramuscular fat content[J]. Mol Biol Rep,2010,37(8):3931-3939 |
| [33] | Niu B,Ye L,Li F,et al. Identification of polymorphism and association analysis with reproductive traits in the porcine RNF4 gene[J]. Animal Reproduction Science,2009,110(3/4):283-292 |
| [34] | Galve A,Burgos C,Silió L,et al. The effects of leptin receptor(LEPR)and melanocortin-4 receptor(MC4R)polymorphisms on fat content,fat distribution and fat composition in a Duroc×Landrace/Large White cross[J]. Livestock Science,2012,145(3):145-152 |
 2015, Vol. 38
2015, Vol. 38


