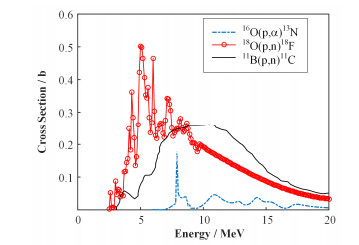
核反应堆运行过程中,由于压力容器以及一回路管道系统的机械接口、材料的应力松弛等原因,一回路高温高压,一旦泄露到一回路之外将变成气体与空气混合,因而可以通过对一回路压力边界之外空气中某些放射性核素的监测确定冷却剂在一回路的泄漏率。在反应堆一回路系统中,裂变产生的中子与冷却剂中的氢核作用产生反冲质子,反冲质子在冷却剂中通过电离、多次散射以及韧致辐射损失能量,阈能之上的反冲质子与冷却剂中的16O、18O以及11B作用产生13N、18F以及11C,反应截面如图 1所示[1-2]。三种核素均具有β+放射性,其中13N核素半衰期为9.96 min,非常适合通过符合测量来推断一回路水泄漏率,因此,开展一回路13N、18F以及11C核素的理论计算显得十分必要[3]。
|
图 1 16O(p, α)13N、18O(p, n)18F和11B(p, n)11C反应截面 Figure 1 Microscopic cross sections of 16O(p, α)13N, 18O(p, n)18F and 11B(p, n)11C reactions |
长久以来,反应堆源项计算,比如一回路16N、17N以及堆芯积存量等主要采用MCNP (Monte Carlo N Particle Transport Code)、ORIGEN等程序开展,其均不能进行反冲质子分布计算。针对一回路质子反应源项的计算,早在1980年,Dissing等[4]就采用解析方法对沸水堆13N产额进行了计算,2000年,龚学余等[5]采用ANISN程序结合重带电粒子电离公式对秦山二期反应堆一回路13N、18F以及11C核素产额进行了计算。然而,该方法无论是对反应堆几何的精确描述,还是对反冲质子物理过程的考虑,都显得不够全面充分。
GEANT4程序是欧洲核子中心开发的一款蒙特卡罗软件,其可计算反冲质子电离、多次散射以及韧致辐射等物理过程[6-7]。近年来,由于GEANT4程序可模拟的粒子种类多,粒子能量区间广,在加速器驱动次临界系统(Accelerator Driven Sub-critical System, ADS)、钍燃料循环等领域也有所应用[8-12]。
因此,本研究采用GEANT4程序,对秦山二期反应堆全堆芯进行了建模,计算了一回路水中反冲质子分布,进而计算了一回路水中13N、18F以及11C核素产额以及浓度。
1 压水堆全堆芯GEANT4描述 1.1 几何构造描述秦山二期反应堆热功率为1930 MW,堆芯体积为20.47 m3。堆芯组件121个,共分为三区,燃料富集度分别为3.1%、2.6%和1.9%。可燃毒物组件按其中可燃毒物棒数分为两种:含12根可燃毒物棒的组件和含16根可燃毒物棒的组件。
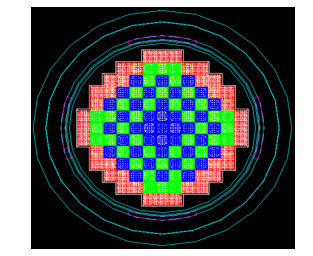
由于GEANT4程序自带的重复结构函数不能描述压水堆燃料组件,故本文在几何描述程序中编制代码,开发了压水堆组件描述程序,另外,对秦山二期反应堆从堆芯到压力容器进行了建模,如图 2所示。
|
图 2 秦山二期GEANT4全堆芯建模可视图 Figure 2 Visualization of full core modeling in GEANT4 |
中子源能谱按混合谱抽样,为55.34% 235U瓦特谱、29.64% 239Pu瓦特谱、7.98% 238U瓦特谱、7.04% 241Pu麦克斯韦谱。中子源强分布综合考虑燃料组件的轴向功率分布和径向功率分布以及每个燃料组件的v/k值。
中子分布描述采用G4-GPS (General Particle Source)来描述,由于在GPS中描述一个分布需要用一段源命令来描述,而考虑到121个组件每个组件51个轴向功率分布,共需在GPS程序中描述121×51段源,靠手工描述几乎不可能完成,故本文研究中采用C++编制程序,仅需输入中子轴向和径向源强分布即可自动生成GEANT4计算所需的GPS中子源描述。
2 G4-NONU功能实现由于该计算过程属于固定中子源的输运问题,计算过程需将裂变过程作为俘获过程处理,即输运过程中不再产生新的裂变中子,在MCNP程序中,通常采用NONU卡来实现此功能。但GEANT4程序中不具备MCNP中NONU卡相关功能的函数,故本研究中修改了GEANT4程序的裂变反应模型,将其裂变过程作俘获过程处理,即中子仅做吸收,而不产生相应的裂变中子,构造了具备有MCNP程序中NONU卡相关功能的函数G4-NONU,来实现中子输运的计算。
如图 3所示,在GEANT4程序中单纯关闭裂变反应所计算的一回路水中中子能谱与MCNP计算结果相差较大,但采用G4-NONU模型的计算结果与MCNP计算结果吻合良好,全能区总中子通量相对偏差为3.5%。

|
图 3 一回路水中中子能谱GEANT4与MCNP比较 Figure 3 Comparisons of neutron spectra in water calculated by GEANT4 and MCNP |
反冲质子在水中主要通过电离、多次散射以及韧致辐射损失能量,为了研究一回路水中反冲质子行为,本文研究计算了反冲质子能谱和经过电离、多次散射、以及韧致辐射之后反冲质子通量以及能谱。水中裂变中子产生的反冲质子,即不考虑质子电离、多次散射以及韧致辐射情况下,其通量为2.3337×1015 cm-2,考虑电离、多次散射以及韧致辐射情况下,水中质子通量为4.6857×1010 cm-2,而由于低能质子在电离、多次散射以及韧致辐射等过程中的损失,反冲质子能谱也呈现硬化,见图 4。

|
图 4 反冲质子经由电离、多次散射以及韧致辐射前后归一化能谱比较 Figure 4 Comparison of normalized energy spectrum of recoil protons before and after ionization, multiple scattering, and bremsstrahlung |
在以上研究的基础上,计算了13N、18F以及11C核素的产生率,计算依据如式(1)所示:
| $ R=\int\limits_{0}^{20\ }{N\sigma \left( E \right)\varphi \left( E \right)\text{d}E} $ | (1) |
式中:N为一回路水中16O、18O以及11B核子密度,cm-3;σ为16O(p, α)13N、18O(p, n)18F以及11B(p, n)11C反应截面,b;
| 表 1 产生率 Table 1 Production rate (cm-3·s-1) |
表 1中不确定度计算为GEANT4蒙特卡罗计算中的统计偏差,即:
| $ \overline{x}\pm \frac{2S}{\sqrt{N}} $ | (2) |
式中:S为GEANT4模拟中的标准偏差。
3.3 浓度以及活度计算不考虑活化核的吸收、净化装置的去除以及一回路水的泄漏等因素,辐照区13N、18F以及11C的浓度随时间变化满足式(3):
| $ \left\{ \begin{align} &\frac{\text{d}N\left( t \right)}{\text{d}t}=R-\lambda N\left( t \right) \\ &N\left( 0 \right)=0 \\ \end{align} \right. $ | (3) |
式中:R为核素产生率;
非辐照区域浓度随时间变化满足式(4):
| $ \left\{ \begin{align} &\frac{\text{d}N\left( t \right)}{\text{d}t}=-\lambda N\left( t \right) \\ &N\left( 0 \right)={{N}_{0}} \\ \end{align} \right. $ | (4) |
式中:
综上所述,经历过n个循环后,一回路13N、18F以及11C的浓度如式(5)所示:
| $ N\left( t \right)=\frac{R}{\lambda }\left( 1-{{\text{e}}^{-\lambda t}} \right)\frac{1-{{\text{e}}^{-\lambda nT}}}{1-{{\text{e}}^{-\lambda T}}} $ | (5) |
式中:
平衡条件下,一回路13N、18F以及11C的浓度和活度分别如式(6)所示:
| $ \begin{align} &N\left( t \right)=\frac{R}{\lambda }\left( 1-{{\text{e}}^{-\lambda t}} \right)/\left( 1-{{\text{e}}^{-\lambda T}} \right) \\ &A\left( t \right)=\lambda N\left( t \right) \\ \end{align} $ | (6) |
计算结果如表 2所示。
| 表 2 一回路13N、18F、11C的浓度和活度 Table 2 Concentration and activity of 13N, 18F and 11C of the primary circuit |
从反应率来看,三种核素13N反应率最高,主要是反应中母核核子密度起了主要影响;从表 2可见,控制棒工作状态对13N、18F以及11C活度影响不大,全提状态下较控制棒全插状态下增加4.3%、6%、5.39%,其主要原因为能引起(p, α)和(p, n)反应的主要为快中子产生的能量较高的质子。
4 结语本文工作实现了在GEANT4程序中秦山二期反应堆的几何描述以及源抽样描述,编制了C++程序实现了在GEANT4程序中自动生成GPS源。开发了G4-NONU模型实现了GEANT4程序中中子的固定源输运计算。充分考虑了压水堆一回路水中反冲质子的电离、多次散射以及韧致辐射,计算了反冲质子在水中产生的13N、18F以及11C等核素的浓度以及活度。
本工作将GEANT4程序应用于压水堆带电粒子反应产生的源项计算,建立了GEANT4程序中压水堆几何和源描述方法,可以充分考虑带电粒子的电离、多次散射以及韧致辐射等物理因素,拓展了反应堆源项计算工具。
| [1] |
Takacs S, Tarkanyi F, Hermanne A, et al. Validation and upgrading of the recommended cross section data of charged particle reactions used for production of PET radioisotopes[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B, 2003, 211(2): 169-189. DOI:10.1016/S0168-583X(03)01264-3 |
| [2] |
Hintz N M, Ramsey N F. Excitation functions to 100MeV[J]. Physical Review, 1952, 88(1): 19-27. DOI:10.1103/PhysRev.88.19 |
| [3] |
郭兰英, 赵修良, 赵立宏, 等. 测量压水堆核电站一回路水泄漏的13N监测系统[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 1998, 18(4): 282-284. GUO Lanying, ZHAO Xiuliang, ZHAO Lihong, et al. The 13N monitoring system for measuring the leakage of water in the primary coolant circuit of a PWR nuclear power station[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 1998, 18(4): 282-284. |
| [4] |
Dissing E, Svansson L. Reactor coolant pressure boundary leakage detection system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1980, 27(1): 769-775. DOI:10.1109/TNS.1980.4330925 |
| [5] |
龚学余, 郭兰英, 何宪, 等.压水反应堆一回路水中二次带电粒子核反应产物的比活度[J].原子能科学技术, 2000, 34(2):166-172. DOI:100026931(2000)0220166207. GONG Xueyu, GUO Lanying, HE Xian, et al. Specific radioactivity produced by the secondary charged particle nuclear reaction in the primary circuit water of PWR[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2000, 34(2):166-172. DOI:100026931(2000)0220166207. |
| [6] |
Agostinelli S. Geant4:a simulation toolkit[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 2003, 506(3): 250-303. DOI:10.1016/S0168-9002(03)01368-8 |
| [7] |
Allison J. Geant4 developments and applications[J]. IEEE Transaction on Nuclear Science, 2006, 53(1): 1412-1419. DOI:10.1109/TNS.2004.832314 |
| [8] |
许浒, 程翀, 刘翎箭, 等. 闪烁体耦合SIPM测量γ能谱的模拟研究[J]. 核技术, 2017, 40(1): 010401. XU Hu, CHENG Chong, LIU Lingjian, et al. Simulation study of scintillation crystal photocoupling with SiPM for gamma spectrometry[J]. Nuclear Techniques, 2017, 40(1): 010401. DOI:10.11889/j.0253-3219.2017.hjs.40.010401 |
| [9] |
Bungau G, Barlow R J. Study on neutronics design of an accelerator driven subcritical reactor[C]. Proceedings of IPAC'10, Kyoto, Japan, 2010. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/44218918_Study_on_neutronics_design_of_an_accelerator_driven_subcritical_reactor
|
| [10] |
Kolevatov X R S, Kudinovich I V, Svistunov Y A. Calculations of targets for ADS using Geant4[C]. Proceedings of LINAC08, BC, Canada, 2009. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288226108_Calculations_of_targets_for_ads_using_GEANT-4
|
| [11] |
Bungau C, Barlow R, Bungau A, et al. GEANT4 studies of the thorium fuel cycle[C]. Proceeding of 2011 Particle Accelerator Conference, New York, USA, 2011. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/265233888_GEANT4_STUDIES_OF_THE_THORIUM_FUEL_CYCLE
|
| [12] |
Russell L, Buijs A, Jonkmans G. G4-STORK:a Geant4-based Monte Carlo reactor kinetics simulation code[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2014, 71(3): 451-461. DOI:10.1016/j.anucene.2014.03.034 |
