磁法勘探是利用地球磁性的物理特性找矿的重要方法.因地球本身具有磁场,以往主要利用磁法来寻找地下容易被磁化的铁磁性的矿床,随着勘探仪器精度的提高,地面高精度磁法勘查的技术逐渐成熟,现代地质勘查中主要利用地面高精度磁法测量来进行地质构造带及各类磁性矿床的勘查工作(孙中任等,2004,2007,2011;吴小平等,2010a,b;谢俊举等,2012;谢汝宽等,2013; 石磊等,2014).
一般在地质预查与普查阶段,大都以地质填图、水系沉积物测量、槽探等方法为主,如有必要,可以开展一些物探的剖面测量的辅助性工作.其中地面高精度磁法的剖面测量就是一种方便、快捷的实用方法(于长春等,2007;熊盛青,2009;杨春燕,2010;吴小平等,2010a,b;谢俊举等,2012;谢汝宽等,2013).
地球物理勘探中的剖面测量一般都采用直线剖面,有时根据实际需要,也会采用一些折线剖面测量工作,但实际解释工作还是采用分段直线剖面解译.而野外实际环境非常复杂多变,有时会遇到直线剖面上的一段距离区间非人力可以到达,这会给剖面测量工作带来麻烦,往往就无法获取剖面解译资料(于长春等,2007;熊盛青,2009;吴小平等,2010a,b;杨春燕,2010;谢俊举等,2012).
等值投影方法是利用等值线的数值相等的这一特性,将等值结果值投影到推测等值点位,而未进行数据实测的点位上,便于剖面数据解译的一种数据等值处理方法.它能极大的减少野外工作量,并能高效的解决因野外实际地形条件影响实际观测的问题.
1等值与等值投影自然世界中有很多种等值现象.比如地面高程相等的等高线、温度相等的等温线、树木截面的年轮线、各类物探测量数据的等值线等.为了研究的方便,我们在实际工作中,常常将等值的点连接成线或连接成面,这样就出现了等值线或者等值面(李树文等,2000;谢汝宽等,2013;曾小牛等,2014).
现实世界主要是立体的三维世界,但科学研究或是实际应用中往往在二维平面来解决问题,因此,要将立体三维等值线进行投影转换后开展研究.投影转换往往因投影的目标不同会有不同的图形形态.图 1所示为地表等高线在水平面上的投影.从图中可以看到:地形等高线是互不相交的环形.图 2所示是地形等高线在垂直剖面上的投影.从图中可以看到:地形等高线是互相平行的直线段.

|
图 1 地形等高线在水平地面上的投影 Fig. 1 Projection of topographic contour on the ground section |

|
图 2 地形等高线在垂直剖面上的投影 Fig. 2 Projection of topographic contour on the vertical section |
图 3所示为树木的年轮线在树木的横断面的投影.从图中可以看到:树木的年轮线是一族互不相交的同心圆.图 4所示的小板凳上面的木板上的图案为树木纵剖面上的年轮线投影.我们可以看到:树木年轮线却是相互平行的平行线.

|
图 3 树的年轮在树木横断面上的投影 Fig. 3 Projection of tree’s lags on the cross section of the tree |

|
图 4 树的年轮在树木纵剖面上的投影 Fig. 4 Projection of tree’s lags on the profile section of the tree |
以上投影目标均是平面,其实很多种情况还可以将等值投影到曲面上.但投影到曲面的等值线或等值面不便于科学研究,只是更具艺术效果和文化气息.
由此可见,等值线的投影结果不但与具体等值线的形态有关,还与最终投影目标体的位置与形态有关.
2 二维磁性地质体地表磁异常在横剖面上的投影图 5所示为二维磁性地质体在地表的磁异常等值线.从图中可以看到,二维磁性地质体在地表的等值线是一族平行线,其走向与磁性地质体的走向一致.
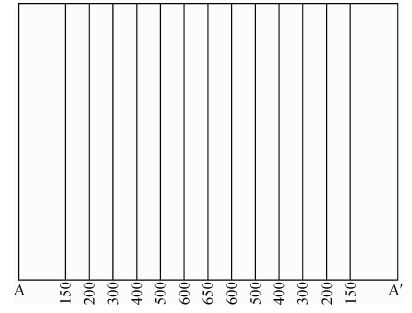
|
图 5 二维磁性地质体在地表的等值线 Fig. 5 The contours of 2D magnetic body on the ground surface |
图 6所示是跨越二维磁性体表面的任意一条剖面AB,从图中看到,AB剖面并不是直线剖面(实际工作中因地形地貌原因可能无法获得直线剖面).我们将AB剖面人为拉直制成剖面曲线;同时将AB剖面上的所有点向AA’剖面投影,除去重复点位后制成剖面图如图 7所示.从图 7可以看到:AA’剖面是所有贯穿二维磁性体的最短剖面,任意的AB剖面将会使磁性体的剖面异常形体扭曲并将异常拉宽.

|
图 6 穿越磁性体地表的任意测量剖面AB Fig. 6 An arbitrarily survey section across 2D magnetic body |
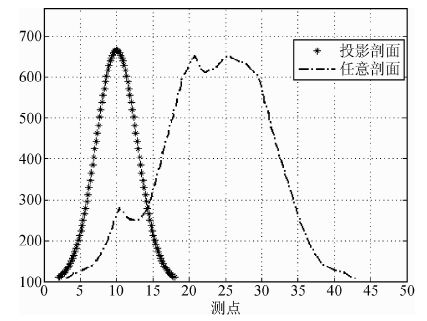
|
图 7 任意剖面测量结果及其在垂直磁性体横剖面上的磁异常投影 Fig. 7 The curves of arbitrarily survey section and its projection |
图 8所示是二维磁性地质体横切剖面AA’的标准磁异常曲线.将该曲线与图 7中投影剖面比较,可以看到:投影剖面与标准剖面曲线形态一致,这样很好的说明了等值投影剖面曲线可以替代标准横切剖面.

|
图 8 二维磁性体横剖面标准磁异常曲线 Fig. 8 The st and ard cross section curve of 2D magnetic body |
在马来西亚彭亨(Pahang)州而连突(Jerantut)县某地,村民在山中伐木砍柴时发现了磁铁矿石,经地质工作人员多次现场踏勘,发现该地系花岗闪长岩和泥质板岩的接触带位置产有磁铁矿,但由于该地山高林密,系原始野生森林,林中除了小型野猪和猴子等小型动物外,还有大象和孟加拉虎的生活痕迹,给地质工作的开展增加困难.为了查明磁铁矿带的产状及延伸情况,决定在该地进行地面高精度剖面测量,由于山中只有一条山民打柴的小路勉强可以盘旋而上,于是决定磁法剖面测量沿着山间小路进行(如图 9所示).图 10所示为将实测剖面展开所得的剖面曲线.从图 9的点位图可知,实测剖面在测区范围内实际是进行了迂回,将该剖面上的两个峰值点进行连接(如图 9),可以基本确定磁性体的大致走向为北西-南东,走向160°,这与地质人员现场踏勘的接触带走向基本吻合一致.因此,这次剖面测量是很成功的.

|
图 9 马来西亚某地面高精度磁法剖面测量点位图 Fig. 9 The layout figure of magnetic survey points for some place of Malaysia |
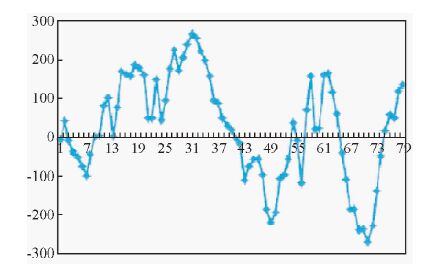
|
图 10 马来西亚某地面高精度磁法剖面测量的异常剖面图 Fig. 10 The profile section magnetic survey curve of some place of Malaysia |
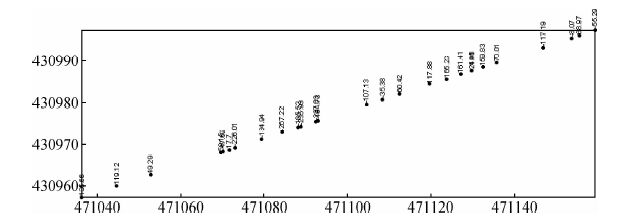
为了更好的解析此次高磁剖面测量的结果,采用等值投影的方法,将实测剖面投影到垂直接触带走向的剖面方向上.从实测剖面分析,最终将1-52测点投影到1号剖面(图 11),53-79测点投影到2号剖面(图 12).
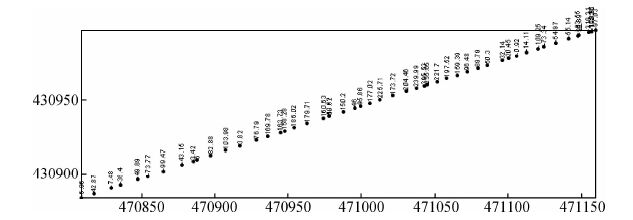
|
图 11 等值投影剖面点位图 1 Fig. 11 The layout points of projection 1 |
|
图 12 等值投影剖面点位图 2 Fig. 12 The layout points of projection 2 |
整理好等值投影剖面的点位顺序及投影点的实测磁场值,根据等值投影原则,可以制作出磁性体横断面的磁异常剖面曲线(图 13、图 14).综合两条剖面磁异常曲线,可知磁性体是向南西方向倾斜的2层磁性异常叠加.且随着走向南东方向,互层的磁性体的间距逐渐加大.利用特征点法和切线法初步可以估计磁性体的顶部埋深约60~100 m.后来在22号测点位置(470966,430976)布置钻孔,向北东70°方向,倾角70°打钻,分别在80 m和120 m附近见到视厚度为8.8 m和20 m的磁铁矿矿体.

|
图 13 等值投影1号剖面磁异常曲线图 Fig. 13 The section curve of projection 1 |

|
图 14 等值投影2号剖面磁异常曲线图 Fig. 14 The section curve of projection 2 |
在野外受地形地貌条件限制的地区,假定磁性体呈二维形态展布时,在选区评价(预查)或者普查阶段,如果要进行地面高精度磁法剖面测量工作,可以根据实际情况,只要贯穿二维磁性体异常范围区间,进行任意剖面测量,然后对测量结果进行等值投影换算,这样可以获得二维磁性体的剖面等效曲线.这样既能快速高效的完成相应的勘探工作,又可以解决那些人力所不能及的地方的测点的测量工作.
致 谢 感谢审稿专家提出的宝贵修改意见和编辑部的大力支持!
| [1] | Bertin J, Loeb J. 1980. Experimental and Theoretical Aspects of Induced Polarization (in Chinese)[M]. Chen Ling Trans. Beijing: Geology Press. |
| [2] | BIAN Gang, XIA Wei, JIN Shao-Hua, et al. 2015. Datum reduction with the least squares fitting method in correction of multi-station geomagnetic diurnal variations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 58(4): 1284-1289, doi: 10.6038/cjg20150416. |
| [3] | CHEN La-chun, TAO De-yi, GAO Bao-long, et al. 2009. The application of Time-domain induced polarization method in Siding Lead-Zinc mine in Guangxi province[J]. Geology and Exploration (in Chinese), 45(3): 280-286. |
| [4] | DUAN Chun-jie, AI Jing-xu, YE Zeng-lu. 2013. The Application of wavelet transform coherency algorithm in seismic data interpretation[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 28(1): 434-438, doi: 10.6038/pg20130149. |
| [5] | GUO Hua, WU Cheng-ping. 2014. The relation between aeromagnetic gradient data and geologic anomaly[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 29(4): 1650-1656, doi: 10.6038/pg20140421. |
| [6] | Guo Z H, Guan Z N, Xiong S Q. 2004. Cuboid ΔT and its gradient forward theoretical expressions without analytic odd points[J]. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese), 47(6): 1131-1138. |
| [7] | HE Ji-shan. 2006. Dual-Frequency Induced Polarization (in Chinese)[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press. |
| [8] | HOU Zun-Ze, YANG Wen-Cai, WANG Yun, et al. 2015. The production and application of irrational scale wavelet details for gravity field[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 58(3): 1035-1041, doi: 10.6038/cjg20150328. |
| [9] | Huang H P. 2008. Airborne geophysical data leveling based on line-to-line correlations[J]. Geophysics, 73(3): F83-F89. |
| [10] | LI Qin, LI Qing-chun, Jing Yue-hong. 2014. The varying inclination method for magnetic reduction to the pole[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 29(4): 1497-1502, doi: 10.6038/pg20140403. |
| [11] | LI Shu-wen, HAO Xu, JIN Kan-kun, et al. 2000. Morphological interpretation of induced polarization anomalies and its application[J]. Geology and Prospecting (in Chinese), 36(1): 48-50. |
| [12] | LI Su-yi, LIN Jun, YANG Gui-hong, et al. 2013. Ground-Airborne electromagnetic signals de-noising using a combined wavelet transform algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 56(9): 3145-3152, doi: 10.6038/cjg20130927. |
| [13] | LI Yong, LIN Pin-rong, XIAO Yuan, et al. 2011. Induced Polarization effect on frequency-domain electromagnetic sounding with electric dipole source[J]. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese), 54(7): 1935-1944, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.07.028. |
| [14] | LIU Jian-xin, LIU Chun-ming, TONG Tie-gang, et al. 2004. The application of the dual frequency induced polarization method in a copper and polymetallic ore deposit in Tibet[J]. Geology and Prospecting (in Chinese), 40(2): 59-61. |
| [15] | LIU Jian-xin, HU Hou-ji, LIU Chun-ming, et al. 2006. Application of synthetical geophysical method on exploration of deep-seated resources[J]. Geology and Prospecting (in Chinese), 42(4): 71-74. |
| [16] | LIU Jian-xin, LI Jie, YANG Jun. 2010. The application of modified Wavelet frequency division restructuring to petrol seismic survey data processing[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 25(6): 2009-2014, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.06.016. |
| [17] | Luo Y, Wang P, Duan S L, et al. 2012. Leveling total field aeromagnetic data with measured vertical gradient[J]. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese), 55(11): 3854-3861, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.033. |
| [18] | Mauring E, Kihle O. 2006. Leveling aerogeophysical data using a moving differential median filter[J]. Geophysics, 71(1): L5-L11, doi: 10.11090/1.2163912. |
| [19] | REN Jin-feng, LIAO Yuan-tao, SUN Ming, et al. 2013. A method for quantitative division of sequence stratigraphy withhigh-resolution based on wavelet transform and its application[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 28(5): 2651-2658, doi: 10.6038/pg20130546. |
| [20] | SHI Lei, MENG Xiao-hong, GUO Liang-hui, et al. 2014. A simple algorithm for estimating the magnetization direction of magnetic bodies under the influence of remanent magnetization[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 29(4): 1748-1751, doi: 10.6038/pg20140434. |
| [21] | SUN Zhong-ren, ZHAO Xue-juan, ZHEN Fan-yu. 2007. The importance of anomaly separation in the mapping of ground high-precision magnetic survey[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration (in Chinese), 31(9): 43-46, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8918.2007.z1.011. |
| [22] | SUN Zhong-ren, Zhao Xue-juan, Wang Li-na. 2011. Discussion of current methods of the normal magnetic field for data processing of ground magnetic surveys[J]. Geology and Exploration (in Chinese), 47(4): 679-685. |
| [23] | WANG Chang-yong, YAN Hong, YAN Yong-bang. 2009. The application of the dual frequency induced polarization method in Chuduoqu area of Tibet[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration (in Chinese), 33(5): 541-544. |
| [24] | WANG Jing-qiang, GUO Chang-sheng, FU Yong-tao. 2013. The application of Wavelet Transform in Marine Sediments acoustic velocity in-situ measurement[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 28(6): 3317-3323, doi: 10.6038/pg20130662. |
| [25] | WANG Wei-nan, YU Qin-fan, TONG Mao-song, et al. 2011. Electrode configuration design of induced polarization potential decay spectrum logging[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 26(1): 371-375, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2011.01.045. |
| [26] | Wang Y G, Zhang F X, Liu C, et al. 2013. Edge detection in potential fields using optimal auto-ratio of vertical gradient[J]. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese), 56(7): 2463-2472, doi: 10.6038/cjg20130732. |
| [27] | WU Bin, CAO Shu-xiang, ZHANG Chun, et al. 2010. The application of Induced Polarization method on the exploration of underground water in Red Beds, central Sichuan[J]. Journal of Sichuan Geology (in Chinese), 30(1): 111-114. |
| [28] | Wu X P, He J S, Liu J X. 2006. The effect of the electromagnetic wave’s impedance transform to the results of the ground probing radar[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 21(1): 251-255. |
| [29] | Wu X P, Liu J X, Duan W H. 2010a. A utilitarian method for the explanation of time domain electromagnetic sounding[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 25(3): 898-903, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.03.024. |
| [30] | Wu X P, Liu J X, Duan W H, et al. 2010b. The effect of topography aberration on the pseudo-section of the dipole-dipole array resistivity sounding[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 25(2): 635-641, doi: 10.3966/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.02.037. |
| [31] | XIE Jun-ju, WEN Zeng-ping, LI Xiao-jun, et al. 2012. Analysis of velocity pulses for near-fault strong motions from the Wenchuan earthquake based on wavelet method[J]. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese), 55(6): 1963-1972, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.06.017. |
| [32] | XIE Ru-Kuan, WANG Ping, GUO Hua, et al. 2013. Aeromagnetic total field gridding enhancement with horizontal gradient[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 56(2): 660-666, doi: 10.6038/cjg20130230. |
| [33] | Xiong S Q. 2009a. The strategic consideration of the development of china’s airborne geophysical technology[J]. Geology in China (in Chinese), 36(6): 1366-1374. |
| [34] | XIONG Sheng-Qing. 2009b. The present situation and development of airborne gravity and magnetic survey techniques in China[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 24(1): 113-117. |
| [35] | YANG Chun-yan. 2010. Application of Induced Polarization method in prospecting groundwater resources[J]. Journal of Qujing Normal University (in Chinese), 29(3): 53-55. |
| [36] | YU Chang-Chun, FAN Zheng-Guo, WANG Nai-Dong, et al. 2007. High-resolution aeromagnetic exploration methods and their application in daye iron mines[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 22(3): 979-983, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.03.048. |
| [37] | YU Ji-yu, LIU Fu-chen, HUANG Huai-feng. 2009. The processing measure for normal field noise of Induced Polarization water prospecting[J]. Yellow River (in Chinese), 31(4): 57. |
| [38] | ZENG Xiao-Niu, LIU Dai-Zhi, LI Xi-Hai, et al. 2014. An improved iterative Wiener filter for downward continuation of potential fields[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 57(6): 1958-1967, doi: 10.6038/cjg20140626. |
| [39] | ZENG Xiao-Niu, LI Xi-Hai, JIA Wei-Min, et al. 2015. A new regularization method for calculating the vertical derivatives of the potential field[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 58(4): 1400-1410, doi: 10.6038/cjg20150426. |
| [40] | ZHANG Quan. 2010. The application of locating concealed copper-molybdenum mine field by Dual Frequency Induced Polarization method at Wangjiadian Area[J]. Gansu Metallurgy (in Chinese), 32(6): 75-79, 92. |
| [41] | Zhang F X, Zhang F Q, Liu C, et al. 2007. A technique for elaborate explanation of faulted structures: three directional small subdomain filtering[J]. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese), 50(5): 1543-1550, doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.05.031. |
| [42] | ZHANG Ying, PAN Bao-zhi, HE Sheng-lin, et al. 2012. Identification of the features of wavelet analysis based reservoir fluid[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 27(6): 2554-2560, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.06.032. |
| [43] | ZHAO Ju-lin, XUE Bin-yi, FENG Jun, et al. 2009. The apparent resistivity parameters in direct current IP method and the secondary electric field sampling[J]. Geophysical and Geochamical Exploration (in Chinese), 33(1): 46-48. |
| [44] | ZHONG Jia, ZOU Zi-ming. 2014. The algorithm of density visualization of magnetic flux lines based on geo-magnetic dipole field[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 29(6): 2614-2619, doi: 10.6038/pg20140622. |
| [45] | 边刚, 夏伟, 金绍华,等. 2015. 利用最小二乘拟合法进行多站地磁日变基值归算[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(4): 1284-1289, doi: 10.6038/cjg20150416. |
| [46] | 陈腊春, 陶德益, 高宝龙,等. 2009. 激电测深法在广西融安县泗顶铅锌矿接替资源勘查中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 45(3): 280-286. |
| [47] | 段春节, 艾敬旭, 叶增炉. 2013. 基于小波变换的相干技术在断层解释中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 28(1): 434-438, doi: 10.6038/pg20130149. |
| [48] | 郭华, 吴成平. 2014. 航磁梯度数据与地质异常反映之间的关系[J]. 地球物理学进展, 29(4): 1650-1656, doi: 10.6038/pg20140421. |
| [49] | 郭志宏, 管志宁, 熊盛青. 2004. 长方体ΔT场及其梯度场无解析奇点理论表达式[J]. 地球物理学报, 47(6): 1131-1138. |
| [50] | 何继善. 2006. 双频激电法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社. |
| [51] | 侯遵泽, 杨文采, 王允,等. 2015. 重力场实数尺度小波分解及其应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(3): 1035-1041, doi: 10.6038/cjg20150328. |
| [52] | J 伯廷, J 洛布. 1980. 激发极化的实验和理论[M]. 陈玲译. 北京: 地质出版社. |
| [53] | 李荡. 2012. 基于ARM的高精度双频激电仪接收机的设计[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学. |
| [54] | 李勤, 李庆春, 景月红. 2014. 变倾角磁异常化极方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 29(4): 1497-1502, doi: 10.6038/pg20140403. |
| [55] | 李树文, 郝旭, 金瞰昆,等. 2000. 激电异常的形态解释方法及其应用研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 36(1): 48-50. |
| [56] | 李肃义, 林君, 阳贵红,等. 2013. 电性源时域地空电磁数据小波去噪方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(9): 3145-3152, doi: 10.6038/cjg20130927. |
| [57] | 李勇, 林品荣, 肖原,等. 2011. 电偶源频率电磁测深激发极化效应研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(7): 1935-1944, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.07.028. |
| [58] | 刘达龙. 2011. 双频激电法在浙江省常山县苦麻岭地区钨、锡、钼多金属萤石矿勘查中的应用研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学. |
| [59] | 柳建新, 刘春明, 佟铁钢,等. 2004. 双频激电法在西藏某铜多金属矿带的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 40(2): 59-61. |
| [60] | 柳建新, 胡厚继, 刘春明,等. 2006. 综合物探方法在深部接替资源勘探中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 42(4): 71-74. |
| [61] | 柳建新, 李杰, 杨俊. 2010. 改进的小波分频重构算法在石油地震勘探中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 25(6): 2009-2014, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.06.016. |
| [62] | 骆遥, 王平, 段树岭,等. 2012. 航磁垂直梯度调整ΔT水平方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(11): 3854-3861, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.033. |
| [63] | 任金锋, 廖远涛, 孙鸣,等. 2013. 基于小波变换的高精度层序地层定量划分研究及其应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 28(5): 2651-2658, doi: 10.6038/pg20130546. |
| [64] | 石磊, 孟小红, 郭良辉,等. 2014. 剩磁影响下磁性体磁化方向估计的一种简单算法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 29(4): 1748-1751, doi: 10.6038/pg20140434. |
| [65] | 孙中任, 赵雪娟, 黄永卫. 2004. 浅谈常规数据处理在地面高精度磁测工作中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 40(S1): 250-256. |
| [66] | 孙中任, 赵雪娟, 甄凡玉. 2007. 地面高精度磁测成图工作中异常分离的重要性[J]. 物探与化探, 31(9): 43-46, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8918.2007.z1.011. |
| [67] | 孙中任, 赵雪娟, 王丽娜. 2011. 地面磁测数据正常场改正现行方法探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, 47(7): 679-685. |
| [68] | 王昌勇, 严鸿, 严永帮,等. 2009. 双频激电法在西藏楚多曲地区的应用效果[J]. 物探与化探, 33(5): 541-544. |
| [69] | 王景强, 郭常升, 付永涛. 2013. 小波分析在海底沉积物声速原位测量中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 28(6): 3317-3323, doi: 10.6038/pg20130662. |
| [70] | 王伟男, 余钦范, 童茂松,等. 2011. 激发极化电位衰减谱测井电极系设计[J]. 地球物理学进展, 26(1): 371-375, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2011.01.045. |
| [71] | 王彦国, 张凤旭, 刘财,等. 2013. 位场垂向梯度最佳自比值的边界检测技术[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(7): 2463-2472, doi: 10.6038/cjg20130732. |
| [72] | 武斌, 曹蜀湘, 张淳,等. 2010. 激发极化法在四川红层地区水资源勘察中的应用[J]. 四川地质学报, 30(1): 111-114. |
| [73] | 吴小平, 何继善, 柳建新. 2006. 电磁波的阻抗变换作用对地质雷达探测效果的影响[J]. 地球物理学进展, 21(1): 251-255. |
| [74] | 吴小平, 柳建新, 段无悔. 2010a. 一种实用的时间域电磁测深解释方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 25(3):898-903, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.03.024. |
| [75] | 吴小平, 柳建新, 段无悔,等. 2010b. 地形畸变对偶极-偶极电阻率测深拟断面图的影响[J]. 地球物理学进展, 25(2): 635-641, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.02.037. |
| [76] | 谢俊举, 温增平, 李小军,等. 2012. 基于小波方法分析汶川地震近断层地震动的速度脉冲特性[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(6): 1963-1972, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.06.017. |
| [77] | 谢汝宽, 王平, 郭华,等. 2013. 考虑航磁水平梯度变化的ΔT网格化方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(2): 660-666, doi: 10.6038/cjg20130230. |
| [78] | 熊盛青. 2009a. 发展中国航空物探技术有关问题的思考[J]. 中国地质, 36(6): 1366-1374. |
| [79] | 熊盛青. 2009b. 我国航空重磁勘探技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 地球物理学进展, 24(1): 113-117. |
| [80] | 杨春燕. 2010. 激发极化法在地下水资源勘探中的应用[J]. 曲靖师范学院学报, 29(3): 53-55. |
| [81] | 于长春, 范正国, 王乃东,等. 2007. 高分辨率航磁方法及在大冶铁矿区的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 22(3): 979-983, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.03.048. |
| [82] | 于纪玉, 刘福臣, 黄怀峰. 2009. 激发极化法找水野外常见干扰及处理措施[J]. 人民黄河, 31(4): 57. |
| [83] | 曾小牛, 刘代志, 李夕海,等. 2014. 位场向下延拓的改进迭代维纳滤波法[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(6): 1958-1967, doi: 10.6038/cjg20140626. |
| [84] | 曾小牛, 李夕海, 贾维敏,等. 2015. 位场各阶垂向导数换算的新正则化方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(4): 1400-1410, doi: 10.6038/cjg20150426. |
| [85] | 张权. 2010. 双频激电法在王家店探测隐伏铜钼矿的应用[J]. 甘肃冶金, 32(6): 75-79, 92. |
| [86] | 张凤旭, 张凤琴, 刘财,等. 2007. 断裂构造精细解释技术——三方向小子域滤波[J]. 地球物理学报, 50(5): 1543-1550, doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.05.031. |
| [87] | 张莹, 潘保芝, 何胜林,等. 2012. 基于小波分析的储层流体性质识别[J]. 地球物理学进展, 27(6): 2554-2560, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.06.032. |
| [88] | 赵聚林, 薛斌义, 冯军,等. 2009. 直流激发极化法中的视电阻率参数及二次场采样[J]. 物探与化探, 33(1): 46-48. |
| [89] | 钟佳, 邹自明. 2014. 地磁偶极子场磁力线疏密可视化算法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 29(6): 2614-2619, doi: 10.6038/pg20140622. |
 2015, Vol. 30
2015, Vol. 30

