柴达木盆地是青藏高原内部大型中、新生代含油气盆地,盆地位于青海省西北部,略呈三角形,为中国三大内陆盆地之一.柴达木盆地是青藏高原上地势最低的断线盆地,地理环境以干旱为特征,地貌由周边向中心依次呈现高山、风蚀丘陵、戈壁、沙漠和湖沼五个环带状结构.盆地具有丰富的石油、煤、盐,以及多种金属矿藏.我国地学工作者长期在此进行基础地质地球物理研究和油气及固体矿产勘探开发研究,对柴达木盆地及整个青藏高原东部的构造演化和地质地球物理特征资源潜力有了深刻认识(曾融生等,1960; 滕吉文等,1973; 沈显杰等,1995; 赵俊猛等,2003; 易桂喜等,2010; 李永东等,2013; 王海洋等,2013;王琼等,2013;余大新等,2014).
中石化系统长期以来在此进行油气勘察工作,业已取得一批勘探成果. 柴达木盆地的诺木洪地区生物气勘探潜力大(田继先等,2010),该区地震资料品质受地表类型影响较大,该区地表主要分为三类,分别是盐沼区、戈壁、山地(图 1).图 5是盐沼区、戈壁区单炮效果对比,可以看出盐沼区单炮信噪比极低,基本上看不到目的层有效反射,整个记录都被面波、浅层折射波所覆盖,因此影响单炮质量的地表主要是盐泥结晶区域.盐泥结晶区域属于柴达木盆地海拔最低处,受沉积、蒸发等地质作用影响,地表以细土、盐、泥等结晶沉积物为主(苏明军等,2008;王西文等,2009),部分地表结晶盐泥的硬度接近岩石(图 2)(刘振敏和杨更生,1997).通过小折射、微测井记录来分析,近地表主要分为两层(图 3、4),低速层和高速层,根据常规井深设计方法,激发井深设计 在高速层顶界下某深度进行激发(李天树等,2004;张向林等,2006;王永卓等,2009),但发现激发单炮质量并不好.激发质量如图 5中盐沼区单炮,由此可见这种单炮质量是难以满足深层生物气勘探的需要,到底是什么因素使得单炮质量低,单炮质量还有没有提升的空间?针对如何提升单炮质量,我们开展了研究.
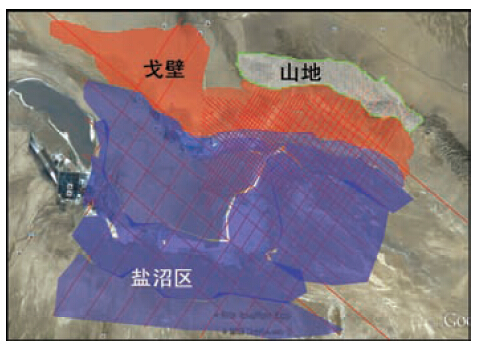 | 图 1 主要地表类型 Fig. 1 The main type of surface |
 | 图 2 结晶盐泥地表 Fig. 2 The crystallization salt mud surface |
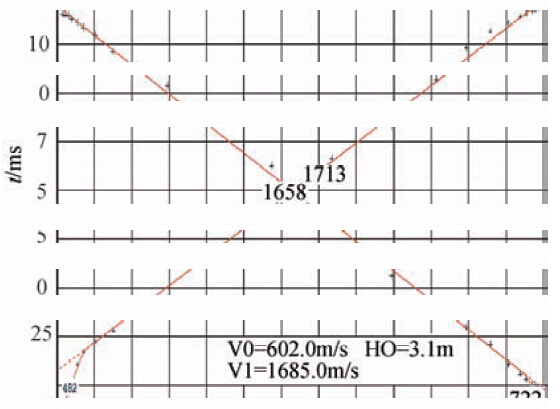 | 图 3 小折射解释结果 Fig. 3 Mini refraction interpretation results |
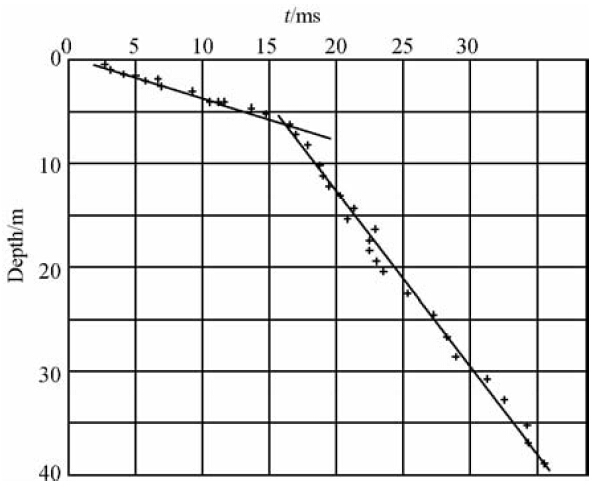 | 图 4 微测井解释结果 Fig. 4 Micro logging interpretation results |
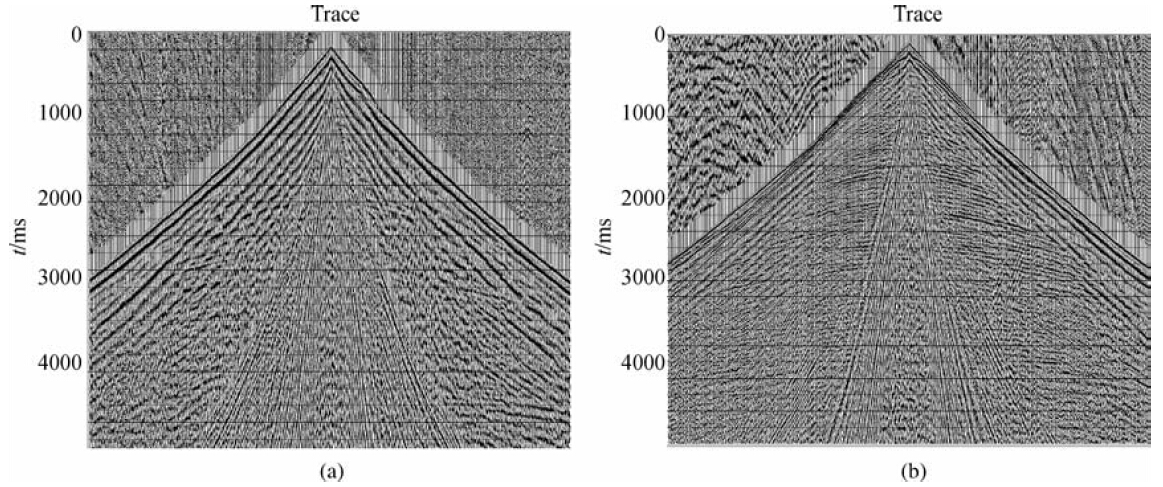 |
图 5 两种地表单炮对比 (a)盐沼区单炮;(b)戈壁区单炮. Fig. 5 Two kinds of surface single shot comparison (a)Salt marsh area single shot; (b)Gobi district single shot. |
根据对单炮中干扰波特征分析(图 6),造成信噪比低的原因主要是面波和浅层多次折射波的干扰,由以往认识知道,造成多次浅层折射是因为表层结构中含有多套强波阻抗界面(谭绍泉等,2003;李子顺,2007;王建民等,2007),使得波在其中反复振荡传播,大部分地震波能量被阻挡在这些强波阻抗界面之上(图 9a、b)(曹辉等,2012;陈国金等,2013;刘凯等,2013).既然近地表有多套强波阻抗界面,那么在微侧井记录中应该有所体现(李套山等,1997; 吕公河,2002;刘建华等,2004),或者是因为我们对微侧井记录中某些现象认识不足.基于这样的分析,我们重新审视了一下微侧井记录.对图 4中微测井记录再次进行详细的分析,可以看出,高速层顶界之下初至点并不是很平滑,在微测井和小折射记录(图 3)中都有体现,似乎在高速层顶界之下还有更加小的层,初至时间有跳跃,这就使得速度有较大差异,如果按照这些速度差异重新分层,会产生较多的薄层(图 7a),那么这种解释的薄层是不是真实的反应实际的近地表结构,我们又分析了微侧井记录的振幅特征,发现速度差异的位置,也有明显的振幅差异(图 7b),这就增强了我们对这种分层正确性的信心.那么这种分析出的近地表结构到底符不符合实际的情况,我们在生产中进行了近地表露头寻找和分析.图 8是我们在工区某位置找到的近地表岩性露头图片,从图片中可以看到,实际的近地表岩性结构和解释的结构相似,近地表为黑泥层和盐结晶层互层,这就证实了近地表结构的复杂性,存在多层.
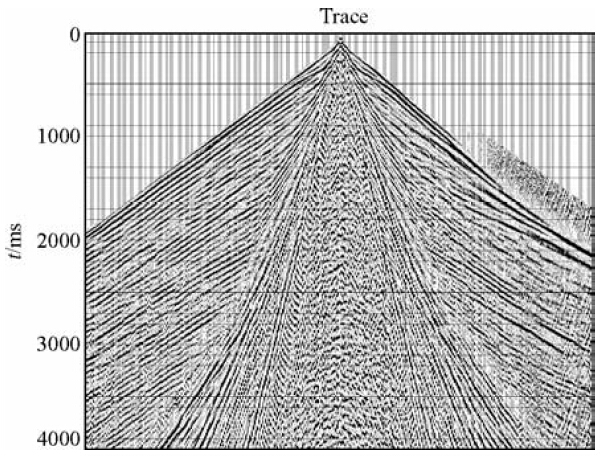 | 图 6 含多次浅层折射波单炮 Fig. 6 Containing multiple shallow refraction wave single shot |
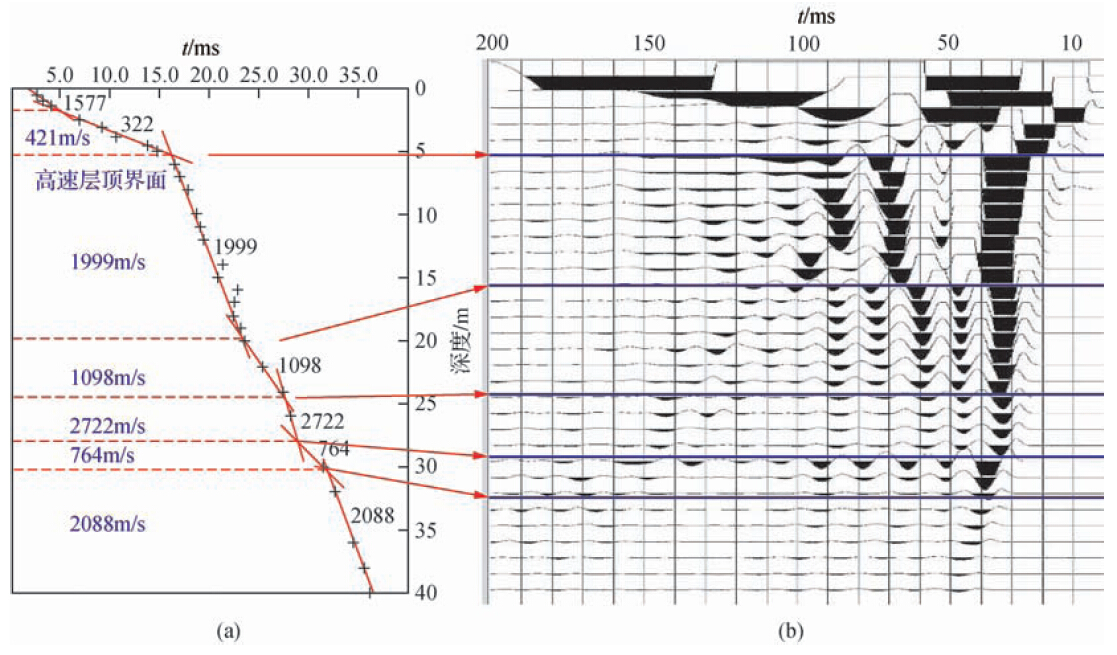 |
图 7 微测井记录解释及对应微测井记录 (a)微测井记录解释;(b)微测井记录. Fig. 7 Micro logging interpretation and the corresponding micro logging (a)Micro logging interpretation;(b)Micro logging. |
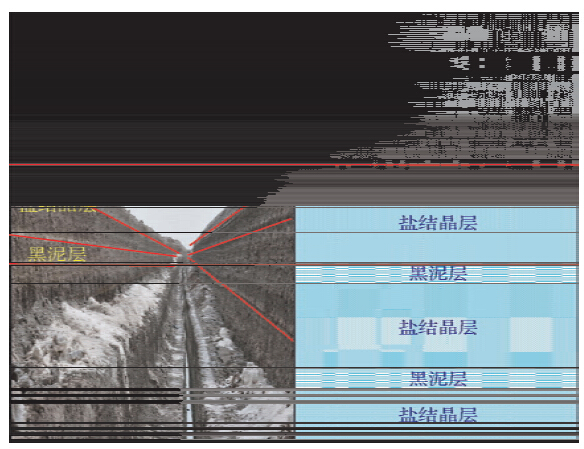 | 图 8 近地表岩性地表露头及近地表岩性结构示意图 Fig. 8 The near surface rock outcrops and near surface lithology structure schematic diagram |
那么这种近地表结构是不是影响单炮质量的因素,我们通过根据解释结果建立实际的近地表结构模型进行正演模拟,通过正演模拟寻找问题的答案.图 9a、b是建立的地质模型及正演模拟单炮,由于盐结晶层中存在许多小孔洞,所以在模型中进行了体现,模型参数从上到下各层速度420 m/s,1900 m/s,1098 m/s,2722 m/s,764 m/s,2088 m/s,3100m/s,3500m/s,各层底界深度分别为8 m,15.3 m,20.5 m,24.5 m,34.5 m,40 m,300 m.空洞参数:10 m×5 m,350 m/s.
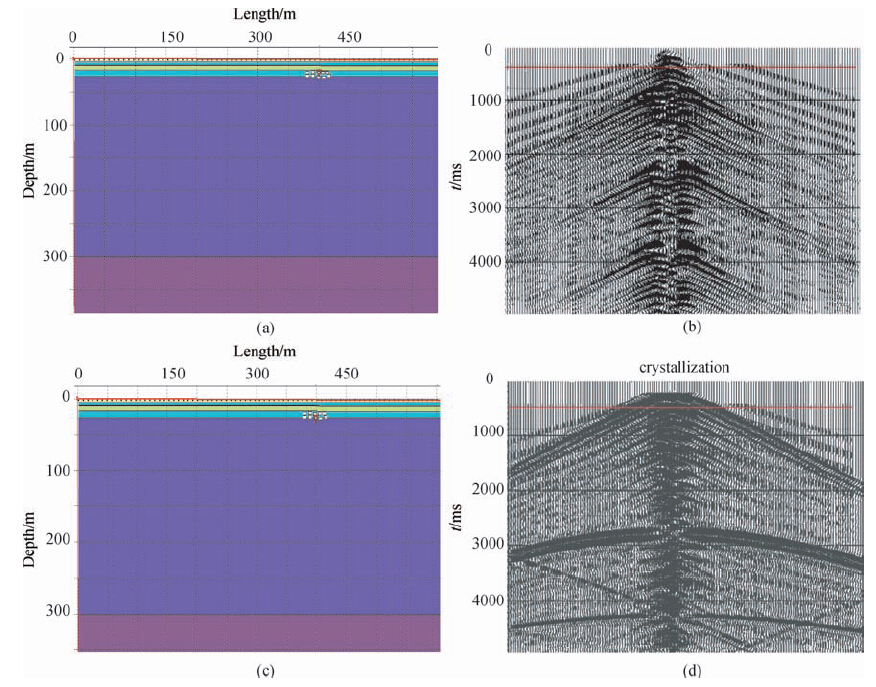 |
图 9 不同激发深度模拟结果 (a)盐泥结晶互层中激发;(b)盐泥结晶互层中模拟单炮; (c)盐泥结晶互层下激发;(d)盐泥结晶互层下模拟单炮. Fig. 9 The simulation results of different excitation depth (a)Salt mud interbed in crystallization of excitation; (b)Salt mud interbed in simulation of single shot crystallization; (d)Salt mud interbed excitation crystallization; (d)Salt mud interbed simulation under the single shot crystallization. |
从模拟记录中可以看出,在盐结晶互层中激发,由于盐结晶层对地震波的屏蔽作用(王建民等,2002;张付生,2004;曹国滨等,2007;高峻,2009;王海等,2009),使得折射波较多,能量强,掩盖了地下有效波,当激发点为与盐结晶互层之下时,浅层折射能量弱,地下有效波能量较强.从这里可以看出,激发应该选择在盐结晶互层之下激发,能够得好资料.
根据这一分析结论,进行了实际单炮采集试验.图 10是在高速层顶界下,盐结晶互层中激发以及盐结晶互层之下激发单炮效果对比,图 10a是具体每一炮激发点位位置,其中5号点位是位于盐结晶互层之下激发的.从图中可以看出1号点位单炮浅层折射较为严重,随着深度的增加,浅层折射影响逐渐减弱(刘组沅,1983;刘艾奇和皇甫煊,2004;李振春和王清振,2007;宫同举等,2009),4号、5号点位单炮质量较好.因此这就验证了模拟的分析结果的正确性,因此,对于该地区盐沼区的激发点位应该选择在盐结晶互层之下激发,能够得到较好的单炮效果.最终获得盐泥结晶区剖面效果较好,深层目的层信噪比、分辨率较高,满足生物气勘探需求.
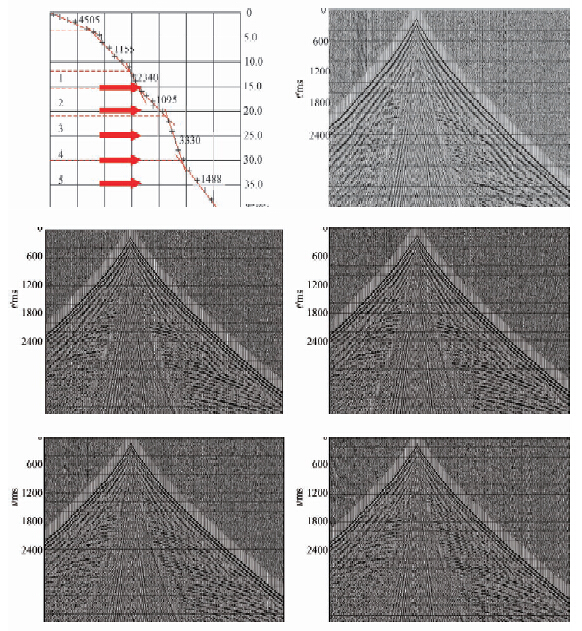 |
图 10 同深度点位激发单炮 (a)激发位置点位;(b)1号点位激发单炮;(c)2号点位激发单炮;(d)3号点位激发单炮; (e)4号点位激发单炮;(f)5号点位激发单炮. Fig. 10 Different depth point excitation of single shot (a)Excitation position point;(b)1 point excitation of single shot; (c)2 point excitation of single shot; (d)3 point excitation of single shot; (e)4 point excitation of single shot;(f)5 point excitation of single shot. |
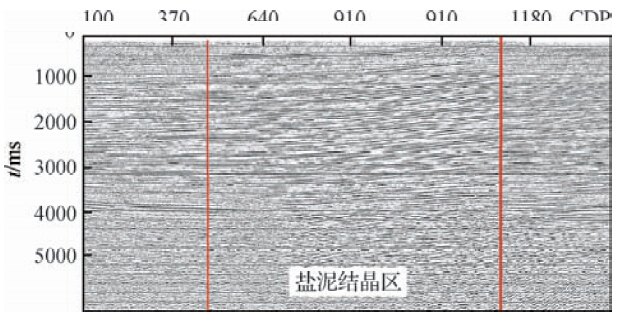 | 图 11 盐泥结晶区剖面效果 Fig. 11 Salt mud crystal section effect |
柴达木盆地诺木洪地区影响单炮质量的是盐沼区的近地表激发条件,盐泥互层形成多套近地表地层,严重影响地震波能量的传播,形成强烈的浅层折射,通过分析研究在盐结晶互层之下激发,避开盐泥互层的强屏蔽作用,使得地震波能够更多的传入地下,同时在微测井记录、小折射记录解释中,当出现初至不平滑时,通过多种分析方法分析是不是由于地质因素引起的,避免由以往解释经验的套用所导致的某些地质因素的遗漏.
致 谢 感谢中石化地球物理公司胜利分公司研究所及西部公司参与木洪地区施工技术人员给予的帮助及支持.
| [1] | Cao G B, Li Y W, Cui R G. 2007. Reserch on multiwave acquisition method and the application results in Ken71 area [J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 22(5): 1510-1516. |
| [2] | Cao H, Chen G J, Wu Y S, et al. 2012. The virtual source method in seismic technology[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 27(3): 1078-1085. |
| [3] | Chen G J, Cao H, Wu Y S, et al. 2013. The virtual source method of seismic technology and numerical model tests [J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 28(5): 2725-2733. |
| [4] | Gao C J, Sun C Y, Peng H C, et al. 2009. Serveral contrast extracted quality factor [J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 32(4): 296-300. |
| [5] | Gao Y B, Zhang Y. 2006. On optimization of explosion parameters[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 21(3): 938-943. |
| [6] | Li T S, Gao H Q, Liu Z X, et al. 1997. Ghost reflection information collection and its forming mechanism and frequency response[J]. Petrophysics (in Chinese), 36(4): 38-44. |
| [7] | Li T S, Chen B D, Su D R. 2004. Application of twin-well microlog in near surface investigation [J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petrole (in Chinese), 43(5): 471-474. |
| [8] | Li Y D, Zhang Y, Xiong X, et al. 2013. Lithospheric effective elastic thickness and its anisotropy in the northeast Qinghai-Tibet plateau.Chinese Journal Geophysics,56(4): 1132-1145,doi: 10.6038/cjg20130409. |
| [9] | Li Z C, Wang Q Z. 2007. A review of research on mechanism of seismic attenuation and energy compensation [J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 22(4): 1147-1152. |
| [10] | Li Z S. 2007. Seismic wave attenuation regulation and buildup [J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 22(5): 1545-1551. |
| [11] | Liu J H, Xu Y, Hao T Y. 2004. Study on the physical mechanism of the seismic wave attenuation [J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 19(1): 1-7. |
| [12] | Liu K, Tong S Y, Liu H S, et al. 2013. The complex near surface areas of high resolution seismic excitation parameters optimization[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 28(6): 3040-3048. |
| [13] | Liu Y Q, Huang F X. 2004. The optimization technology of depth selection [J]. Geophysics (in Chinese), 43(6): 605-607. |
| [14] | Liu Z M, Wang G S. 1997. Types of salt crusting in Chaerhan salt lake and its genetic environment [J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals (in Chinese), 19(2): 105-108. |
| [15] | Liu Z Y. 1983. The experimental study of seismic wave attenuation in rock [J]. Earthquake Science Research (in Chinese), 6(1): 34-40. |
| [16] | Lv G H. 2002. Determination of seismic ghost reflection interface and its application[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting (in Chinese), 37(3): 295-299. |
| [17] | Qiu N S, Kang Y S, Fan H H, et al. 1999. Pressure and reservoir distribution in tertiary, western qaidam basin.Chinese J.Geophys. (in Chinese), 42(6): 826-833. |
| [18] | Shen X J, Wang J A, Zhang J M, et al.1995.Network basin simulation and oil-gas prospect prediction of the caidam basin. Chinese J.Geophys. (in Chinese),38(1): 83-92. |
| [19] | Su M J, Wang X W, He H H, et al. 2008. The lithologic and stratigraphic gas reservoirs in the north slope of the Sanhu area, Qaidam basin: a study on their genetic conditions and characterization techniques[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 23(4): 1190-1198. |
| [20] | Tan S Q, Xu J X, Zhang Q H, et al. 2003. The effect of ghost reflect and lithology on the choice of stimulated well depth [J]. Oil and Gas Geophysics (in Chinese), 1(3): 11-14. |
| [21] | Tian J X, Sun P, Zhang L, et al. 2010. Seismic property technique to predict quaternary biogas pool in Qaidam basin [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience (in Chinese), 21(2): 305-309. |
| [22] | Teng J W, Kan J C, Liu T H, et al. 1973. Refracted and reflected waves from the crystalline basement in the eastern part of Chaidam Basin.Chinese J.Geophys. (in Chinese),1973,16(1): 62-70. |
| [23] | Zeng R S, Kan R J, He C D, et al. 1960. A study of the crystalline basement in chai-da-mu basin by low frequency refraction seismic method.Chinese J.Geophys. (in Chinese),9(2): 155-168. |
| [24] | Wang H, Zhao H X, Jin Z G. 2009. Optimization of excitation parameters of high resolution seismic exploration [J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting (in Chinese), 44(3): 261-264. |
| [25] | Wang H Y, Thomas H, Chen Y S, et al. 2013.Pn wave tomography of eastern Tibetan plateau.Chinese Journal Geophysics, 56(2): 472-480,doi: 0.6038/cjg20130211. |
| [26] | Wang J M, Liu C, Yang B J, et al. 2002. The application of ground penetrating rader for seiemic exploration in Bayanchagan area[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 17(4): 745-752. |
| [27] | Wang J M, Chen S M, Su M X, et al. 2007. A study of near surface high-frequency compensation technology in 3-D seismic exploration[J]. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese), 50(6): 1837-1843. |
| [28] | Wang X W, Chen Z Y, Su M J, et al. 2009. Key techniques of predicting gas reservoirs in the San Hu area of the Qaidam basin and their applications[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 24(3): 921-935. |
| [29] | Wang Q, Gao Y, Shi Y T,et al. 2013.Seismic anisotropy in the uppermost mantle beneath the northeastern margin of Qinghai-Tibet plateau: evidence from shear wave splitting of SKS, PKS and SKKS.Chinese Journal Geophysics, 56(3): 892-905,doi: 10.6038/cjg20130318. |
| [30] | Wang Y Z, Du G F, Fu C K, et al. 2009a. Effect of stimulating effect on seismic ghost reflection interface and its application[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 24(4): 1454-1460. |
| [31] | Wang Y Z, Du G F, Fu C K, et al. 2009b. Influence of ghost reflection interface on seismic shooting effect and its application[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 24(4): 1454-1460. |
| [32] | Yi G X, Yao H J, Zhu J S,et al. 2010. Lithospheric deformation of continental China from Rayleigh wave azimuthal anisotropy.Chinese J.Geophys. (in Chinese), 53(2): 256-268,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.02.004. |
| [33] | Yu D X, Li Y H, Wu Q J,et al.2014.S-wave velocity structure of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau from joint inversion of Rayleigh wave phase and group velocities.Chinese Journal Geophysics,57(3): 800-811,doi: 10.6038/cjg20140310. |
| [34] | Zhang H S, Teng J W, Tiao X B, et al. 2013. Lithospheric thickness and upper mantle anisotropy beneath the northeastern Tibetan Plateau.Chinese Journal Geophysics,56(2): 459-471,doi: 10.6038/cjg20130210. |
| [35] | Zhao J M. 2003.Q Value structure of the upper crust along the profile from baicheng to da qaidam.Chinese J.Geophys. (in Chinese), 46(4): 503-509. |
| [36] | Zhang X L, Tao G, Liu X R. 2006. Progress in oil geophysical exploration[J]. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese), 21(1): 143-151. |
| [37] | 曹国滨, 李云伟, 崔汝国.2007.垦71地区多波采集方法及应用效果[J].地球物理学进展, 22(5): 1510-1516. |
| [38] | 曹辉, 陈国金, 吴永栓,等.2012.虚源法地震技术综述[J].地球物理学进展, 27(3): 1078-1085. |
| [39] | 陈国金, 曹辉, 吴永栓,等.2013.虚源法地震技术及数值模型试验[J].地球物理学进展, 28(5): 2725-2733. |
| [40] | 宫同举, 孙成禹, 彭洪超,等.2009.2009年8月10日几种提取品质因子方法的对比[J].勘探地球物理进展, 32(4): 296-300. |
| [41] | 高银波, 张研.2006.关于井炮激发参数优化设计的思考[J].地球物理学进展, 21(3): 938-943. |
| [42] | 李套山, 高宏强, 刘振夏,等.1997.虚反射信息的采集及其形成机制、频率响应的理论探讨[J].石油物探, 36(4): 38-44. |
| [43] | 李天树, 陈宝德, 苏德仁.2004.双井微测井技术在表层结构调查中的应用[J].石油物探, 43(5): 471-474. |
| [44] | 李振春, 王清振.2007.地震波衰减机理及能量补偿研究综述[J].地球物理学进展, 22(4): 1147-1152. |
| [45] | 李子顺.2007.地震波衰减规律及其恢复方法[J].地球物理学进展, 22(5): 1545-1551. |
| [46] | 李永东, 郑勇, 熊熊, 等.2013.青藏高原东北部岩石圈有效弹性厚度及其各向异性. 地球物理学报, 56(4): 1132-1145,doi: 10.6038/cjg20130409. |
| [47] | 刘建华, 胥颐, 郝天珧.2004.地震波衰减的物理机制研究[J].地球物理学进展, 19(1): 1-7. |
| [48] | 刘凯, 童思友, 刘怀山,等.2013.复杂近地表区高分辨率地震勘探激发参数优选[J].地球物理学进展, 28(6): 3040-3048. |
| [49] | 刘艾奇, 皇甫煊.2004.激发井深选择的优化技术[J].石油物探, 43(6): 605-607. |
| [50] | 刘振敏, 杨更生.1997.察尔汗盐湖盐壳类型及形成条件[J].化工矿产地质, 19(2): 105-108. |
| [51] | 刘组沅.1983.岩石中地震波衰减的实验研究[J].地震科学研究, 6(1): 34-40. |
| [52] | 吕公河.2002.地震勘探虚反射界面的测定及其利用[J].石油地球物理勘探, 37(3): 295-299. |
| [53] | 邱楠生, 康永尚, 樊洪海, 等.1999.柴达木盆地西部地区第三系温度压力和油气分布相互关系探讨. 地球物理学报, 42(6): 826-833. |
| [54] | 沈显杰, 汪缉安, 张菊明, 等.1995.用网络式盆地模拟结果预测柴达木盆地的油气远景. 地球物理学报, 38(1): 83-92. |
| [55] | 苏明军, 王西文, 何亨华,等.2008.柴达木盆地三湖地区北斜坡岩性地层气藏形成的地质条件与预测技术研究[J].地球物理学进展, 23(4): 1190-1198. |
| [56] | 谭绍泉, 徐锦玺, 张庆淮,等.2003.虚反射和岩性对激发井深选择的影响[J].油气地球物理, 1(3): 11-14. |
| [57] | 滕吉文, 阚荣举, 刘道洪, 等.1973.柴达木东盆地的基岩首波和反射波. 地球物理学报, 16(1): 62-70. |
| [58] | 田继先, 孙平, 张林,等.2010.利用地震属性预测柴达木盆地三湖地区第四系生物气藏[J].天然气地球科学, 21(2): 305-309. |
| [59] | 王海, 赵会欣, 晋志刚.2009.高分辨率地震勘探激发参数的优选[J].石油地球物理勘探, 44(3): 261-264. |
| [60] | 王海洋, Thomas HEARN, 陈永顺, 等.2013.青藏高原东部的Pn波层析成像研究. 地球物理学报, 56(2): 472-480,doi: 10.6038/cjg20130211. |
| [61] | 王建民, 刘财, 杨宝俊,等.2002.地质雷达技术在巴彦查干地区地震勘探中的应用[J].地球物理学进展, 17(4): 745-752. |
| [62] | 王建民, 陈树民, 苏茂鑫,等.2007.近地表高频补偿技术在三维地震勘探中的应用研究[J].地球物理学报, 50(6): 1837-1843. |
| [63] | 王琼, 高原, 石玉涛, 等.2010.青藏高原东北缘上地幔地震各向异性:来自SKS、PKS和SKKS震相分裂的证据. 地球物理学报, 2013,56(3): 892-905,doi: 10.6038/cjg20130318. |
| [64] | 王西文, 陈志勇, 苏明军,等.2009.柴达木盆地三湖地区天然气地震预测关键技术及应用[J].地球物理学进展, 24(3): 921-935. |
| [65] | 王永卓, 杜桂锋, 傅朝奎,等.2009a.虚反射界面对地震激发效果的影响及其应用[J].地球物理学进展, 24(4): 1454-1460. |
| [66] | 王永卓, 杜桂锋, 傅朝奎,等.2009b.2虚反射界面对地震激发效果的影响及其应用[J].地球物理学进展, 24(4): 1454-1460. |
| [67] | 易桂喜,姚华建,朱介寿,等.2010.用Rayleigh面波方位各向异性研究中国大陆岩石圈形变特征. 地球物理学报, 53(2): 56-268,doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.02.004. |
| [68] | 余大新, 李永华, 吴庆举,等.2014.利用Rayleigh波相速度和群速度联合反演青藏高原东北缘S波速度结构. 地球物理学报,57(3): 800-811,doi: 10.6038/cjg20140310. |
| [69] | 曾融生, 阚荣举, 何传大, 等.1960.柴达木盆地低频地震探测结晶基底的工作方法. 地球物理学报,9(2): 155-168. |
| [70] | 张洪双, 滕吉文, 田小波, 等.2013.青藏高原东北缘岩石圈厚度与上地幔各向异性. 地球物理学报, 56(2): 459-471,doi: 10.6038/cjg20130210. |
| [71] | 张向林, 陶果, 刘新茹.2006.油气地球物理勘探技术进展[J].地球物理学进展, 21(1): 143-151. |
| [72] | 赵俊猛.拜城—大柴旦剖面的上地壳Q值结构. 2003.地球物理学报, 46(4): 503-509. |
 2014, Vol. 29
2014, Vol. 29

