2. 青岛海洋科学与技术国家实验室, 青岛 266237
2. Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266237, China
电测井是评价地层的重要手段, 在复杂油气识别中起着重要作用.当地层存在电性各向异性时, 相比较常规地层, 其电测井响应更为复杂(姚东华等, 2010; 洪德成和杨善德, 2011; Gao et al., 2013; Zhu et al., 2018).目前, 在各向异性地层电测井响应计算与应用研究中, 广泛采用横向各向同性(transverse isotropy, TI)模型, 指地层只存在水平与垂直电导率不同的情况, 也称单轴各向异性(Løseth and Ursin, 2007; Zhong et al., 2008; 邓少贵等, 2006).当地层发育裂缝时(Georgi et al., 2008; Tang et al., 2007), 如图 1a, 或沉积过程中横向上岩性和物性等变化时(Gao et al., 2002; Li et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2017), 如图 1b, 地层电导率沿x、y、z三个方向均不同, 即显示双轴各向异性(biaxial anisotropy)(Hou et al., 2015; Nekut, 1994; He et al., 2016).对于页岩油气、致密油气等一些复杂油气藏, 可能存在由于沉积或成岩作用引起的层理各向异性, 又存在裂缝发育引起的诱导各向异性.因此, 基于各向同性、甚至单轴各向异性介质模型的电测井理论和应用研究, 难以有效满足这类复杂油气藏的评价需要, 亟待开展基于双轴各向异性介质模型的测井响应和评价研究.

|
图 1 地层双轴各向异性成因示意图 Fig. 1 Causes of biaxial anisotropic formation |
双感应或双侧向一般只提供深、浅两种探测深度, 且只反映了地层的宏观导电特性(邓少贵等, 2018; 张庚骥, 1984; Anderson et al., 1995; Li and Wang, 2016); 阵列感应测井可以提供三种纵向分辨率、五种探测深度的电阻率信息, 但缺少分量测量, 依然难于有效识别薄互层和评价各向异性(Wang et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2007).为适应各向异性复杂油气藏勘探开发需求, 国内外石油公司陆续推出多分量感应测井仪(王磊等, 2015; Davydycheva et al., 2009), 如Schlumberger公司的Rt-Scanner和Halliburton公司的3D-Induction Xaminer等.多分量感应测井仪可同时测量9个磁场分量, 各分量对倾角、方位角、各向异性等不同地层参数有不同的敏感性, 利用反演处理可获取地层电阻率、各向异性等信息(Wang H M et al., 2006; 汪宏年等, 2008; Hong et al., 2014; Wang L et al., 2018a, b), 但其处理方法主要基于单轴各向异性介质模型.因此, 为了适应各向异性复杂油气藏评价要求, 需要基于双轴各向异性介质模型, 分析多分量感应测井的响应特征, 提升其应用效果和能力.
双轴各向异性介质的电测井响应数值模拟主要采用解析法和有限差分法.Davydycheva和Wang(2011)利用有限差分法研究了双轴各向异性介质多分量感应测井响应特征, 但有限差分算法速度慢(Chew, 1999; Anderson, 1982; 谭茂金等, 2007), 不适用于测井资料快速反演; Nekut(1994)提出了双轴各向异性介质中磁偶极子源时域解析解, 其主要考虑仪器在零源距下的时域信息; Gao等(2002)给出了双轴各向异性介质多分量感应测井频域解析解, 但未考虑仪器旋转角等问题, 而实际中测井仪器可能与地层成任意夹角放置; Yuan等(2010)使用解析法进一步考虑了任意旋转角的问题, 但对于电磁场的高维积分问题, 特别是在倾角较高时, 其积分速度和精度仍有待提高.
本文基于均匀无限厚双轴各向异性介质模型, 推导并简化多分量感应测井空间域解析式, 深入挖掘谱域电磁场的周期特性与振荡特性, 给出一种高效、精确的三重积分方法, 并对比分析不同纵横向各向异性条件多分量感应测井响应特征.
1 双轴各向异性介质多分量感应测井解析解 1.1 双轴各向异性介质多分量感应测井基本理论空间域中, 时谐源满足e-iωt时, 麦克斯韦方程组可表示为:
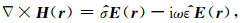
|
(1) |

|
(2) |
其中, μ0为真空磁导率; 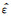

|
图 2 地层坐标系与仪器坐标系示意图 Fig. 2 Formation coordinate system and tool coordinate system |

|
(3) |
一般而言, 若不考虑线圈的尺寸及结构时, 多分量感应测井仪发射线圈可等效为磁偶极子源.对不同发射方向的磁偶极子源, 其在接收线圈处激发的电场和磁场可分别由并矢矩阵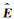
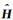

|
(4) |

|
(5) |
其中, Eij、Hij的下标i和j分别表示发射线圈和接收线圈的法向.
当仪器与地层坐标系z向的相对夹角α不为0°时, 需利用旋转矩阵R将接收线圈测量响应转换至仪器坐标系进行计算:

|
(6) |

|
(7) |
式中, T表示向量或矩阵的转置, R可表示为

|
(8) |
其中β、γ分别为方位角和旋转角, 如图 2b所示.
1.2 双轴各向异性介质多分量感应测井响应解析解
对空间域中电场E(x, y, z)、磁场H(x, y, z)和偶极子源M(x, y, z)等分别沿x、y和z进行三重傅里叶变换, 可得谱域所对应的象函数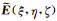


|
(9) |
将式(2)两端求旋度, 并将式(1)代入, 可得:

|
(10) |
式中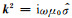

|
(11) |

|
(12) |
式(11)中, Ω为系数矩阵, 可表示为

|
(13) |
根据各方向源的不同特征, 可将式(11)展开以获得谱域中电场的解析式, 再由式(12)即可求得相应的磁场表达式.例如, 当源位于r′=(x′, y′, z′)且沿x轴方向发射时(以电场为例, 磁场不做赘述):

|
(14) |
将其整理后可得:

|
(15) |
对式(15)两端进行三重傅里叶逆变换, 即可得空间域电场的解析式:

|
(16) |
引入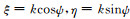

|
(17) |
由式(17)可知, 场的解析式包含三重积分.其核函数在各方向均存在振荡性, 而振荡性函数积分一直是困扰科学与工程计算的难题, 故需对其进行简化以降低积分难度.
2.1 围线积分法核函数关于无穷积分的振荡性随ζ的增大而增强, 这使得其高效、精确积分非常困难.经研究发现, 可利用围线积分法对其进行降维处理, 即将三重积分转化为两重积分.如式(17)中, 注意到:

|
(18) |
可知区间内存在±ζo和±ζe四个奇异点.由场的收敛性可知, 当z-z′>0时, 积分只在虚部大于0的极点处(表示为ζo>和ζe>)有值, 如式(19);当z-z′ < 0时, 积分只在虚部小于0的极点处(-ζo>和-ζe>)有值, 如式(20).

|
(19) |

|
(20) |
关于定积分的核函数为三角函数, 利用其周期特性将积分区间压缩以提高计算效率.以沿x方向发射的磁偶极子源为例(其余项详见附录A):

|
(21) |

|
(22) |

|
(23) |
其中:

|
(24) |

|
(25) |

|
(26) |

|
(27) |
需要注意的是, 几种特殊情况下可进一步简化积分计算.当仪器位于地层坐标系xoz平面内时, 有:

|
(28) |
同理仪器位于地层坐标系yoz平面内时:

|
(29) |
仪器轴与地层坐标系z轴平行时:

|
(30) |
经简化后, 积分区间压缩至原来的四分之一, 相应的计算量将降低至原来的四分之一.
3 核函数的快速计算与误差分析 3.1 核函数的振荡性与TI介质中场的表达式类似(Howard, 2000; Key, 2012; Johansen and Sørensen, 1979), 核函数均存在振荡性, 且其振荡性与场分量及倾角等有关.设Rx=2 Ωm, Ry=4 Ωm, Rz=8 Ωm, β=γ=0°, 以Hzz实部为例, 不同倾角下双重积分核函数在k-ψ平面上的展布如图 3.其中, 图 3a、图 3d、图 3g、图 3j横坐标表示Hzz核函数实部关于ψ的积分区间, 单位为弧度; 纵坐标表示Hzz核函数实部关于k的积分区间, 单位为1;色标表示Hzz核函数实部值, 单位为1;其余各图可依此类推.核函数沿k方向积分可得磁场与ψ的关系, 如图 3b、图 3e、图 3h和图 3k所示; 核函数沿ψ方向积分可得磁场与k的关系, 如图 3c、图 3f、图 3i和图 3l所示.可知, 当倾角增大时, 双重积分核函数沿ψ和k方向的振荡性均增强, 沿k方向的振荡区间增大.因此, 采用固定的积分区间与高斯节点时, 将难以协调计算精度与速度.

|
图 3 不同倾角下Hzz核函数实部振荡示意图 Fig. 3 Oscillation of the real part of Hzz kernel function in different dip angles |
由于不同场分量振荡性不同, 对不同核函数在不同倾角下的半无穷积分, 可截断积分区间, 在确保核函数收敛性的同时, 压缩其积分区间与节点, 以保证计算精度并提高计算效率.积分区间的自适应截断是通过预先设定一个截止因子, 当积分计算到几个点的幅值连续小于截止因子时停止积分, 当前区间即为截断区间.不同分量在不同倾角下应有不同的截止因子.例如, 在较大区间内(0~200)找到核函数最大幅值点, 取该幅值万分之一为截止因子, 再以此点为左端点通过二分法进行区间选取.图 4是Hzz分量的相位与幅度在倾角为60°时截止因子取最大幅值不同倍数的相对误差示意图.

|
图 4 Hzz分量相位与幅度在不同截止因子下的相对误差 Fig. 4 Relative errors of the phase and amplitude of Hzz by different cutoff factors |
两重积分核函数振荡性不一致, 故对其选择不同的节点数以提高计算效率.定积分可得到精确的结果, 故先计算定积分再计算半无穷积分以提高精度.如图 5是Hxx、Hxz与Hzz分量的相位与幅度在不同倾角下随ψ节点数变化的误差示意图.由图可知, 当节点增多时, 区间内节点数达到饱和, 且倾角越小时所需节点数越少; 同时, 不同场分量饱和节点数不同.

|
图 5 不同倾角下, Hxx、Hxz与Hzz分量相位与幅度随ψ节点数变化的相对误差 Fig. 5 Relative errors of the phase and amplitude of Hxx, Hxz and Hzz changing with the nodes of ψ for different dip angles |
各分量半无穷积分区间不同, 故分别选取不同的节点数.如图 6是Hxx、Hxz与Hzz分量相位与幅度在不同倾角下, 误差随积分节点数变化示意图.由图可知, 不同场分量在不同倾角下饱和节点数不同.当节点数趋于饱和时, 继续减小误差需增大积分区间并增加节点数.若精度要求不高, 区间内节点未饱和即能达到预期效果.如表 1, 表示倾角为0°、45°、85°时, 在保证不同场分量相位与幅度相对误差均小于0.1%情况下, 所需高斯节点数与相应的积分区间.

|
图 6 不同倾角下, Hxx、Hxz与Hzz分量相位与幅度随k节点数变化的相对误差 Fig. 6 Relative errors of the phase and amplitude of Hxx, Hxz and Hzz changing with the nodes of k for different dip angles |
|
|
表 1 相对误差小于0.1%时, 不同倾角下不同分量的积分区间与节点数 Table 1 The integral interval and nodes for magnetic-field components in different dip angles while relative errors within 0.1% |
显而易见, 计算耗时随倾角不同而不同.经简化表达式、优取积分区间与节点数, 在相对误差小于0.1%时, 即使倾角为85°其计算耗时仍小于0.02 s.如图 7是将模型简化后所得Hzz分量与精确解(Moran and Gianzero, 1979)之间的对比图, 其中图 7a、图 7b是各向同性(R=2 Ωm)对比图, 图 7c、图 7d为单轴各向异性(Rx=2 Ωm, Ry=8 Ωm)对比图, 结果相对误差小于10-5.

|
图 7 简化模型与精确解的对比 Fig. 7 Comparison between simplified model and exact solution |
以同轴、共面分量为实例, 针对电阻率较高与较低的地层, 深入探讨其多分量感应测井的响应特征.假定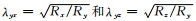

|
图 8 不同各向异性系数下, 同轴、共面分量视电阻率响应特征 (Ⅰ) Ry=2 Ωm; (Ⅱ) Ry=50 Ωm. Fig. 8 Response characteristics of coaxial and coplanar apparent resistivity with different anisotropy coefficient |
由图 8Ⅰ、Ⅱ可知, 在两种背景电阻率情况下, 其视电阻率响应特征相似:倾角为0°时, Raxx不受横向各向异性影响, Razz不受纵向各向异性影响, Rayy同时受横向、纵向各向异性影响, 且纵向各向异性影响更大.随倾角增大, 横向各向异性对Rayy的影响逐渐增大, 纵向各向异性对其影响逐渐减小, 当背景电阻率较大时, 上述现象更为明显.随倾角增大, 横向各向异性对Razz的影响逐渐减小, 对Raxx影响逐渐增大, 纵向各向异性对Razz的影响逐渐增大, 对Raxx影响逐渐减小, 这种现象与背景电阻率无关.倾角接近90°时, Raxx只受横向各向异性影响, Razz只受纵向各向异性影响, 而Rayy受横向各向异性影响更大.
综上可知, 倾角较小时, 可用Raxx、Rayy反映地层纵向各向异性信息, 用Razz表征地层横向各向异性; 倾角较大时, Raxx、Rayy反映地层横向各向异性信息, Razz表征地层纵向各向异性.
5 结论根据电磁场积分核函数周期性, 针对定积分压缩其积分区间, 可将双轴各向异性介质多分量感应测井解析解计算速度提升至少4倍; 根据电磁场积分核函数振荡特性, 针对半无穷积分自适应截取积分区间, 并根据积分区间优选节点数, 可保证计算速度的同时将误差降低至0.1%.
基于本文提供的双轴各向异性介质多分量感应解析算法, 模拟了倾斜双轴各向异性地层多分量感应测井响应, 得到了同轴、共面分量响应与纵横向各向异性系数、倾角的关系, 有助于理解复杂油气藏电磁响应特征及其各向异性评价.
附录A沿y方向发射的磁偶极子源:

|
(A1) |

|
(A2) |

|
(A3) |
沿z方向发射的磁偶极子源:

|
(A4) |

|
(A5) |

|
(A6) |
Anderson B I, Barber T D, Luling M G. 1995. The response of induction tools to dipping, anisotropic formations.//Proceedings of Society of Petrophysicists and Well-Log Analysts 36th Annual Logging Symposium. Paris: Society of Petrophysicists and Well-Log Analysts.
|
Anderson W L. 1982. Fast Hankel transforms using related and lagged convolutions. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS), 8(4): 344-368. DOI:10.1145/356012.356014 |
Chew W C. 1999. Waves and Fields in Inhomogenous Media. New York: Wiley-IEEE Press.
|
Davydycheva S, Homan D, Minerbo G. 2009. Triaxial induction tool with electrode sleeve:FD modeling in 3D geometries. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 67(1): 98-108. DOI:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2008.10.001 |
Davydycheva S, Wang T. 2011. A fast modeling method to solve Maxwell's equations in 1D layered biaxial anisotropic medium. Geophysics, 76(5): F293-F302. DOI:10.1190/geo2010-0280.1 |
Deng S G, Tong Z Q, Fan Y R. 2006. Numerical simulation of dual laterolog response in tilted anisotropic formation. Acta Petrol. Sin. (in Chinese), 27(3): 61-64. |
Deng S G, Zhang P, Wang Z K, et al. 2018. Numerical simulation of electromagnetic scattering of interface around borehole. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science) (in Chinese), 42(1): 67-72. |
Gao J, Xu C H, Xiao J Q. 2013. Forward modelling of multi-component induction logging tools in layered anisotropic dipping formations. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 10(5): 054007. DOI:10.1088/1742-2132/10/5/054007 |
Gao L, Gianzero S, Kennedy D, et al. 2002. The response of a triaxial induction sonde in a biaxial anisotropic medium. Petrophysics, 43(3): 172-184. |
Georgi D T, Schoen J H, Rabinovich M. 2008. Biaxial anisotropy: its occurrence and measurement with multicomponent induction tools.//Proceedings of SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Denver, Colorado: SPE.
|
He Z L, Huang K, Liu R C, et al. 2016. A semianalytic solution to the response of a triaxial induction logging tool in a layered biaxial anisotropic formation. Geophysics, 81(1): D71-D82. DOI:10.1190/geo2015-0105.1 |
Hong D C, Yang S D. 2011. Multi-component induction logging response in large dielectric formation. Acta Phys. Sin. (in Chinese), 60(10): 109101. DOI:10.7498/aps.60.109101 |
Hong D C, Xiao J Q, Zhang G Y, et al. 2014. Characteristics of the sum of cross-components of triaxial induction logging tool in layered anisotropic formation. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 52(6): 3107-3115. DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2013.2269714 |
Hou J S, Donderici B, Torres D, et al. 2015. Characterization of formation fractures with multicomponent induction logging based on biaxial anisotropy models: method and case studies.//Proceedings of SPWLA 56th Annual Logging Symposium. Long Beach, California: Society of Petrophysicists and Well-Log Analysts.
|
Howard A Q. 2000. Petrophysics of magnetic dipole fields in an anisotropic earth. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 48(9): 1376-1383. DOI:10.1109/8.898770 |
Johansen H K, Sørensen K. 1979. Fast Hankel transforms. Geophysical Prospecting, 27(4): 876-901. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2478.1979.tb01005.x |
Key K. 2012. Is the fast Hankel transform faster than quadrature?. Geophysics, 77(3): F21-F30. DOI:10.1190/geo2011-0237.1 |
Li H, Wang H. 2016. Investigation of eccentricity effects and depth of investigation of azimuthal resistivity LWD tools using 3D finite difference method. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 143: 211-225. DOI:10.1016/j.petrol.2016.02.032 |
Li X Y, Qin R B, Gao Y F, et al. 2017. Well logging evaluation of water-flooded layers and distribution rule of remaining oil in marine sandstone reservoirs of the M oilfield in the Pearl River Mouth basin. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 14(2): 283-291. DOI:10.1088/1742-2140/aa576b |
Løseth L O, Ursin B. 2007. Electromagnetic fields in planarly layered anisotropic media. Geophysical Journal International, 170(1): 44-80. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03390.x |
Moran J H, Gianzero S. 1979. Effects of formation anisotropy on resistivity-logging measurements. Geophysics, 44(7): 1266-1286. DOI:10.1190/1.1441006 |
Nekut A G. 1994. Anisotropy induction logging. Geophysics, 59(3): 345-350. DOI:10.1190/1.1443596 |
Tan M J, Zhang G J, Yun H Y, et al. 2007. 3-D numerical mode-matching (NMM) method for resistivity logging responses in nonsymmetric conditions. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 50(3): 939-945. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.03.037 |
Tang Y M, Wang T, Liu R. 2007. Multicomponent induction response in a biaxially anisotropic formation.//77th Ann. Internat Mtg., Soc. Expi. Geophys.. Expanded Abstracts.
|
Wang H M, Barber T, Morriss C, et al. 2006. Determining anisotropic formation resistivity at any relative dip using a multiarray triaxial induction tool.//Proceedings of Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. San Antonio: Society of Petroleum Engineers.
|
Wang H N, Tao H G, Yao J J, et al. 2008. Study on the response of a multicomponent induction logging tool in deviated and layered anisotropic formations by using numerical mode matching method. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 51(5): 1591-1599. |
Wang L, Fan Y R, Huang R, et al. 2015. Three dimensional Born geometrical factor of multi-component induction logging in anisotropic media. Acta Phys. Sin. (in Chinese), 64(23): 239301. DOI:10.7498/aps.64.239301 |
Wang L, Li H, Fan Y R, et al. 2018a. Sensitivity analysis and inversion processing of azimuthal resistivity logging-while-drilling measurements. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 15(6): 2339-2349. DOI:10.1088/1742-2140/aacbf4 |
Wang L, Fan Y R, Yuan C, et al. 2018b. Selection criteria and feasibility of the inversion model for azimuthal electromagnetic logging while drilling (LWD). Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(5): 974-982. DOI:10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30101-0 |
Yao D H, Wang H N, Yang S W, et al. 2010. Study on the responses of multi-component induction logging tool in layered orthorhombic anisotropy formations by using propagator matrix method. Chinese Journal of Geophysics (in Chinese), 53(12): 3026-3037. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.12.028 |
Yuan N, Nie X C, Liu R, et al. 2010. Simulation of full responses of a triaxial induction tool in a homogeneous biaxial anisotropic formation. Geophysics, 75(2): E101-E114. DOI:10.1190/1.3336959 |
Zhang G J. 1984. Electrolog (Ⅰ) (in Chinese). Beijing: Oil Industry Press: 118-131.
|
Zhang Z Y, Akinsanmi O, Ha K T, et al. 2007. Triaxial induction logging-an operator's perspective.//Proceedings of SPWLA 48th Annual Logging Symposium. Austin, Texas: Society of Petrophysicists and Well-Log Analysts.
|
Zhong L L, Li J, Bhardwaj A, et al. 2008. Computation of Triaxial induction logging tools in layered anisotropic dipping formations. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 46(4): 1148-1163. DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2008.915749 |
Zhou X Q, Zhang Z S, Zhang C, et al. 2017. A new lithologic classification method for tight sandstone reservoirs based on rock components and logging response characteristics. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 14(6): 1599-1607. DOI:10.1088/1742-2140/aa8eb5 |
Zhu L Q, Zhang C, Zhang C M, et al. 2018. Prediction of total organic carbon content in shale reservoir based on a new integrated hybrid neural network and conventional well logging curves. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 15(3): 1050-1061. DOI:10.1088/1742-2140/aaa7af |
邓少贵, 仝兆岐, 范宜仁. 2006. 各向异性倾斜地层双侧向测井响应数值模拟. 石油学报, 27(3): 61-64. |
邓少贵, 张盼, 王正楷, 等. 2018. 井周界面电磁散射探测数值模拟. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 42(1): 67-72. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2018.01.008 |
洪德成, 杨善德. 2011. 大介电常数地层中多分量感应测井响应研究. 物理学报, 60(10): 109101. DOI:10.7498/aps.60.109101 |
谭茂金, 张庚骥, 运华云, 等. 2007. 非轴对称条件下用三维模式匹配法计算电阻率测井响应. 地球物理学报, 50(3): 939-945. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.03.037 |
汪宏年, 陶宏根, 姚敬金, 等. 2008. 用模式匹配算法研究层状各向异性倾斜地层中多分量感应测井响应. 地球物理学报, 51(5): 1591-1599. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.05.035 |
王磊, 范宜仁, 黄瑞, 等. 2015. 各向异性介质多分量感应测井三维Born几何因子理论研究. 物理学报, 64(23): 239301. DOI:10.7498/aps.64.239301 |
姚东华, 汪宏年, 杨守文, 等. 2010. 用传播矩阵法研究层状正交各向异性地层中多分量感应测井响应. 地球物理学报, 53(12): 3026-3037. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.12.028 |
张庚骥. 1984. 电法测井. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 118-131.
|
 2020, Vol. 63
2020, Vol. 63


