Value of ultrasound combined with elastography in evaluating inflammation grading in patients with chronic liver disease at S2 stage of liver fibrosis
-
摘要:
目的 探讨超声联合弹性成像技术在慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者炎症分级中的应用价值。 方法 选择2022年1月至2024年3月在上海中医药大学附属曙光医院住院治疗并接受肝脏穿刺活检且病理结果提示慢性肝病肝纤维化分期为S2期的51例患者为研究对象,所有患者均经超声引导下肝组织穿刺活检获得病理肝纤维化分期(S1~S4)及肝脏炎症分级(G0~G4)。此外,所有患者均行超声联合弹性成像技术检查,获得剪切波速度(Vs)、声衰减系数(ATT)、肝纤维化指标(LFI)、纤维化指数(F指数)及炎症活动指数(A指数),分析超声联合弹性成像参数与病理炎症分级的相关性。 结果 根据肝脏病理炎症分级分组,G1组15例、G2组28例、G3组8例。3组间F指数、A指数、Vs、ATT差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05),其中G1组F指数、A指数、Vs均低于G3组(P= 0.007、0.006、0.040),而ATT高于G3组(P= 0.005);LFI在3组间差异无统计学意义(P= 0.373)。Vs、ATT、F指数和A指数与病理炎症分级均有相关性(r= 0.404、- 0.417、0.379、0.383,P= 0.003、0.002、0.006、0.006)。平均值图提示随着病理炎症分级的增高,患者年龄呈线性上升趋势,ATT呈线性下降趋势,A指数呈线性上升趋势。Vs与肝功能指标丙氨酸转氨酶(ALT)、天冬氨酸转氨酶(AST)、碱性磷酸酶(ALP)、γ- 谷氨酰转移酶(GGT)、总胆红素、直接胆红素(DBil)均呈正相关(均P<0.05),ATT与ALT、AST、GGT、DBil均呈负相关(均P<0.05),F指数、A指数均与ALT、AST、ALP、GGT、DBil呈正相关(均P<0.05)。 结论 超声联合弹性成像技术可用于评估慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者的炎症程度。 Abstract:Objective To explore the application value of ultrasound combined with elastography in grading inflammation in patients with chronic liver disease at S2 stage of liver fibrosis. Methods Totally 51 patients who were hospitalized at Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine from Jan. 2022 to Mar. 2024 and underwent liver biopsy with pathological results indicating a stage of S2 liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease were enrolled. All patients underwent ultrasound-guided liver biopsy to obtain the stage of pathological liver fibrosis (S1 to S4) and the grade of liver inflammation (G0 to G4). In addition, all the patients were examined by ultrasound combined with elastography; and shear wave velocity (Vs), acoustic attenuation coefficient (ATT), liver fibrosis index (LFI), fibrosis-related index (F index), and inflammatory activity index (A index) were obtained. The correlation between ultrasound combined with elastography parameters and pathological inflammation grading was analyzed. Results According to the pathological inflammation grading, there were 15 cases in group G1, 28 cases in group G2, and 8 cases in group G3. There were significant differences in F index, A index, Vs and ATT among the 3 groups (all P < 0.05). Among them, F index, A index and Vs in group G1 were significantly lower than those in group G3 (P= 0.007, 0.006, 0.040), while ATT was significantly higher than that in group G3 (P= 0.005); and there was no significant difference in LFI among the 3 groups (P= 0.373). Vs, ATT, F index and A index were correlated with pathological inflammation grade (r= 0.404, - 0.417, 0.379, 0.383; P= 0.003, 0.002, 0.006, 0.006). The mean plot showed that with the increase of pathological inflammation grade, the age of patients showed a linear upward trend, ATT showed a linear downward trend, and A index showed a linear upward trend. Vs was positively correlated with alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT), total bilirubin, and direct bilirubin (DBil) (all P < 0.05). ATT was negatively correlated with ALT, AST, GGT, and DBil (all P < 0.05); and both F index and A index were positively correlated with ALT, AST, ALP, GGT, and DBil (all P < 0.05). Conclusion Ultrasound combined with elastography can be used to evaluate the degree of inflammation in patients with chronic liver disease at S2 stage of liver fibrosis. -
Keywords:
- ultrasonography /
- elastography /
- chronic liver disease /
- liver fibrosis
-
据统计,慢性肝病和相关肝硬化每年造成约100万人死亡;慢性肝病除了增加临床负担外,还会导致严重的并发症,降低患者的生活质量,增加经济负担[1]。慢性肝病所致的肝纤维化是基于各种原因导致的肝损伤性疾病病理生理的慢性进展过程,出现并发症时不可逆转,临床诊疗的关键在于早期诊断、准确评估、动态监测[2]。目前,肝组织活检被视为评估肝纤维化及肝脏炎症的金标准,但由于其有创性、重复性差以及可能引发并发症等局限性,无法用于动态评估肝纤维化、肝脏炎症的病情变化情况及治疗效果。
本研究针对慢性肝病患者,综合弹性应变、图像纹理、组织硬度、声学衰减等超声物理因素,利用应变式实时组织弹性成像(real-time tissueelastography,RTE)和二维剪切波弹性成像(twodimensional shear wave elastography,2D-SWE)技术,分析联合弹性超声参数与慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者炎症程度的相关性,旨在为慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者的炎症程度评估提供超声诊断依据。
1 资料和方法
1.1 研究对象
选择2022年1月至2024年3月于上海中医药大学附属曙光医院住院治疗并接受肝脏穿刺活检且病理结果提示慢性肝病肝纤维化分期为S2期的患者51例。纳入标准:(1)临床确诊为慢性肝病,肝功能Child-Pugh A、B级;(2)年龄18~70岁,性别不限;(3)肝穿刺病理结果提示慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期。排除标准:(1)非慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者;(2)肝功能ChildPugh C级者;(3)存在意识障碍者;(4)合并肝性脑病、大量腹水、严重黄疸、显著肝外胆道梗阻或全肝弥漫性肝细胞肝癌等疾病者;(5)病态肥胖者;(6)心、肺、肝、肾等主要器官功能衰竭者;(7)有胆道系统感染、败血症者;(8)有不可纠正的凝血功能障碍者;(9)无法进行超声引导下穿刺者;(10)不能合作的患者。本研究通过上海中医药大学附属曙光医院医学伦理委员会审批(2022-1179-116-01),所有患者均签署了知情同意书。
1.2 仪器与方法
1.2.1 仪器
超声检查采用日立ALOKA ARIETTA850彩色多普勒超声诊断仪,凸阵探头C6-1,频率1~6 MHz,具备联合弹性成像功能。
1.2.2 研究方法及主要步骤
(1)记录患者一般资料,包括性别、身高、体重、年龄,是否合并其他疾病(高血压病、2型糖尿病、肥胖症、高脂血症等)。
(2)超声检查当日清晨采集患者血清,检测丙氨酸转氨酶(alanine transaminase,ALT)、天冬氨酸转氨酶(aspartate transaminase,AST)、γ- 谷氨酰转移酶(γ-glutamyltransferase,GGT)、碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,ALP)、总胆红素(total bilirubin,TBil)、直接胆红素(directbilirubin,DBil)、间接胆红素(indirect bilirubin,IBil)、总蛋白、白蛋白、球蛋白等。
(3)常规超声检查:通过二维超声评估肝包膜、形态、实质回声,有无回声衰减,血管走行和胆道结构,肝前腹壁厚度(mm),门静脉与脾静脉内径(mm),脾脏大小(厚×长,mm)。通过多普勒彩色超声测量门静脉与脾静脉最高流速(cm/s)。
(4)超声联合弹性成像检查:选择联合弹性成像条件,在触摸屏左侧工具栏启动CombiElasto。患者取水平仰卧位,操作者将探头置于右侧肋间朝心脏方向倾斜,垂直于肝包膜扫查。选取测量深度为1~2 cm(最深不宜超过5 cm),将取样框置于肝右叶(5、7或8段,其中以5段最佳)距离肝包膜下1~2 cm处且尽量与水平线垂直,避开肝内占位及管道结构,取样时让患者平静呼吸下屏气3~5 s,待应变曲线稳定3个周期后测量。选取波谷帧进行分析,连续测量10次,取中位数作为参考值。测量结果得到剪切波速度(shear wave velocity,Vs)、声衰减系数(attenuation coefficient,ATT)、肝纤维化指标(liver fibrosisindex,LFI)、纤维化指数(fibrosis-related index,F指数)及炎症活动指数(activity index,A指数)等指标(图 1)。质量控制要求:(1)应变曲线需稳定3个周期;(2)将方差稳定化归一化(variance stabilization normalization,VsN)≥90%判定为所测得Vs值可靠;(3)取10次测量结果的中位数作为最终测量结果,需四分位间距/ 中位数的比值≤0.3。
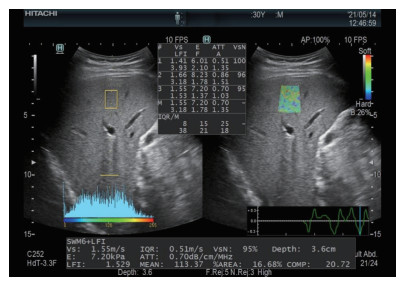 图 1 肝脏超声联合弹性成像显示肝脏弹性测量指标Fig. 1 Measurement indexes of liver elasticity by ultrasound combined with elastographyFPS: Frames per second; Vs: Shear wave velocity; E: Young’s modulus; ATT: Attenuation coefficient; VsN: Variance stabilization normalization; LFI: Liver fibrosis index; F: Fibrosis-related index; A: Activity index; IQR/M: Interquartile range/median; %AREA: Area ratio of low-strain region; COMP: Complexity.
图 1 肝脏超声联合弹性成像显示肝脏弹性测量指标Fig. 1 Measurement indexes of liver elasticity by ultrasound combined with elastographyFPS: Frames per second; Vs: Shear wave velocity; E: Young’s modulus; ATT: Attenuation coefficient; VsN: Variance stabilization normalization; LFI: Liver fibrosis index; F: Fibrosis-related index; A: Activity index; IQR/M: Interquartile range/median; %AREA: Area ratio of low-strain region; COMP: Complexity.1.2.3 肝组织标本获取与病理分期判定
所有患者均行超声引导下经皮肝右叶组织穿刺活检,选用18G活检枪采集标本长度至少20 mm。所得标本经甲醛溶液固定、石蜡包埋后切片,然后行马松三色染色、网状纤维染色及H-E染色。依据2000年修订的《病毒性肝炎防治方案》 [3]中关于肝纤维化及肝脏炎症活动的诊断标准,将肝纤维化分为5期(S0~S4):S0期为无纤维化;S1期为轻度纤维化,表现为汇管区纤维化扩大,局限窦周及小叶内纤维化;S2期为显著肝纤维化,表现为汇管区周围纤维化,纤维间隔形成,小叶结构保留;S3期为进展期肝纤维化,表现为纤维间隔伴小叶结构紊乱,无肝硬化;S4期为早期肝硬化。同时将肝脏炎症活动度分为5级(G0~G4):G0期为汇管区及周围无炎症,小叶内无炎症;G1期为汇管区炎症,小叶内变性及少数点、灶状坏死灶;G2期为汇管区轻度碎屑坏死,小叶内变性,点、灶状坏死或出现嗜酸小体;G3期为汇管区中度碎屑坏死,小叶内变性、融合坏死或见桥接坏死;G4期为汇管区重度碎屑坏死,小叶内桥接坏死范围广,累及多个小叶。
1.3 统计学处理
应用SPSS 24.0软件进行统计分析。采用Shapiro-Wilk检验对计量资料进行正态性检验,若数据符合正态分布以 x±s表示,若不符合正态分布以M(Q1,Q3)表示;计数资料用例数和百分数表示。采用Levene检验对各病理炎症分组进行方差齐性检验。对于满足正态分布且方差齐的计量资料,组间比较采用单因素方差分析,事后多重比较采用最小显著性差异法;若方差不齐,则采用Welch方差分析,事后多重比较采用GamesHowell法。对于不符合正态分布的计量资料,采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验进行组间比较,若差异有统计学意义,进一步采用Bonferroni校正的MannWhitney U检验进行两两比较。计数资料的组间比较采用χ2检验。采用Spearman秩相关分析法探究超声联合弹性成像参数与病理炎症分级的相关性。采用单因素线性相关分析法探究超声联合弹性成像参数与肝功能的关系。所有假设检验均为双侧检验,检验水准(α)为0.05。
2 结果
2.1 受试者一般情况
共纳入51例慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者,其中男32例(62.75%)、女19例(37.25%),年龄为24~70岁,平均年龄为(45.35±11.69)岁。根据病理炎症分级对患者进行分组,G1组15例,平均年龄为(36.27±7.67)岁;G2组28例,平均年龄为(47.68±11.73)岁;G3组8例,平均年龄为(54.25±6.23)岁。3组间年龄差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。在性别构成方面,G3组男性占比高于G1、G2组,差异有统计学意义(χ2= 7.886、3.956,P= 0.005、0.047)。在肝功能指标方面,ALT、AST、ALP、GGT、TBil在不同病理炎症分组间差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 不同病理炎症分级慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者的一般资料Table 1 General information of patients with chronic liver disease at liver fibrosis S2 stage stratified by pathological inflammation gradesVariable Total N= 51 G1 N= 15 G2 N= 28 G3 N= 8 Statistic P value Age/year, x±s 45.35 ± 11.69 36.27 ± 7.67 47.68 ± 11.73 54.25 ± 6.23 F = 10.09 < 0.001 Gender, n (%) χ2 = 8.10 0.017 Male 32 (62.75) 6 (40.00) 18 (64.29) 8 (100.00) Female 19 (37.25) 9 (60.00) 10 (35.71) 0 ALT/(U·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 34.00 (24.00, 90.00) 26.00 (22.00, 34.50) 45.50 (28.50, 99.00) 95.50 (28.00, 252.25) H = 6.34 0.042 AST/(U·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 33.00 (23.00, 53.50) 27.00 (20.00, 31.50) 40.00 (23.75, 90.50) 53.00 (36.50, 152.75) H = 7.83 0.020 ALP/(U·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 83.00 (73.00, 122.50) 69.00 (58.50, 81.50) 87.50 (75.75, 127.50) 151.50 (111.75, 314.75) H = 14.14 < 0.001 GGT/(U·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 37.00 (19.00, 96.00) 24.00 (15.50, 48.00) 39.00 (20.75, 96.00) 281.00 (81.50, 512.50) H = 11.73 0.003 TBil/(μmol·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 16.10 (11.40, 22.90) 15.60 (11.85, 21.60) 14.40 (10.92, 18.88) 25.40 (20.35, 32.08) H = 6.62 0.037 DBil/(μmol·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 2.90 (2.15, 5.55) 2.80 (2.25, 4.15) 2.80 (2.10, 3.83) 11.15 (6.60, 13.07) H = 5.41 0.067 IBil/(μmol·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 11.30 (8.50, 16.25) 12.80 (9.50, 17.45) 9.40 (7.97, 14.00) 14.65 (11.28, 19.62) H = 5.35 0.069 TP/(g·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 74.10 (70.45, 77.55) 74.70 (72.30, 77.70) 73.90 (70.40, 76.70) 74.95 (64.83, 77.33) H = 0.70 0.704 Albumin/(g·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 43.10 (39.35, 45.75) 45.30 (41.05, 46.70) 42.90 (40.05, 44.73) 36.30 (33.17, 42.43) H = 5.90 0.052 Globulin/(g·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 30.70 (28.45, 32.95) 30.10 (28.65, 31.40) 30.55 (27.93, 33.38) 32.60 (30.38, 35.03) H = 2.28 0.320 G1, G2 and G3 represent 1-3 grades of liver pathological inflammation, respectively. ALT: Alanine transaminase; AST: Aspartate transaminase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; GGT: γ-glutamyltransferase; TBil: Total bilirubin; DBil: Direct bilirubin; IBil: Indirect bilirubin; TP: Total protein. 2.2 各病理炎症分级患者的超声联合弹性成像参数的比较
结果如表 2所示,3组间超声联合弹性成像参数F指数、A指数、Vs、ATT差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05),LFI差异无统计学意义(P=0.373)。多重比较显示,G1组F指数(t=2.79,P=0.007)、A指数(t=2.85,P=0.006)、Vs(Z=- 2.474,P= 0.040)均低于G3组,而ATT高于G3组(Z= 3.152,P= 0.005)。
表 2 不同病理炎症分级慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者的超声联合弹性成像参数Table 2 Parameters of ultrasound combined with elastography in patients with chronic liver disease at liver fibrosis S2 stage stratified by pathological inflammation gradesVariable Total N= 51 G1 N= 15 G2 N= 28 G3 N= 8 Statistic P value F, x±s 1.58 ± 0.68 1.26 ± 0.42 1.62 ± 0.65 2.04 ± 0.91 F = 4.03 0.024 A, x±s 1.24 ± 0.33 1.08 ± 0.25 1.26 ± 0.33 1.48 ± 0.37 F = 4.14 0.022 Vs/(m·s-1), M(Q1, Q3) 1.56 (1.40, 1.92) 1.48 (1.40, 1.54) 1.71 (1.39, 1.92) 1.97 (1.79, 2.28) H = 6.31 0.043 ATT/(dB·cm-1·MHz-1), M(Q1, Q3) 0.58 (0.48, 0.65) 0.62 (0.58, 0.72) 0.56 (0.48, 0.63) 0.45 (0.44, 0.51) H = 9.94 0.007 LFI, M(Q1, Q3) 2.81 (2.26, 3.49) 2.57 (1.70, 3.10) 3.07 (2.37, 3.72) 2.89 (2.47, 3.35) H = 1.97 0.373 G1, G2 and G3 represent 1-3 grades of liver pathological inflammation, respectively. F: Fibrosis-related index; A: Activity index; Vs: Shear wave velocity; ATT: Attenuation coefficient; LFI: Liver fibrosis index. 2.3 超声联合弹性成像参数随病理炎症分级的变化
Spearman秩相关分析显示,超声联合弹性成像参数Vs、ATT、F指数和A指数与病理炎症分级均有相关性(r= 0.404、- 0.417、0.379、0.383,P= 0.003、0.002、0.006、0.006)。从平均值图(图 2)可见,随着病理炎症分级的增高,患者年龄呈线性上升趋势,ATT呈线性下降趋势,A指数呈线性上升趋势。
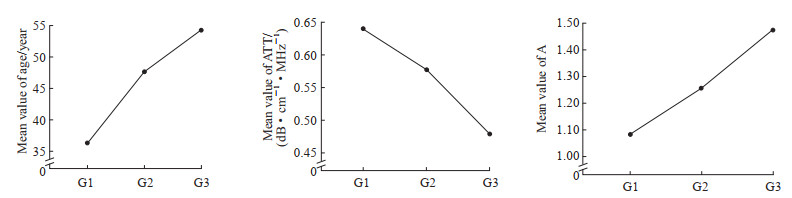 图 2 慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者年龄、ATT、A指数随病理炎症分级的平均值变化图Fig. 2 Mean plots of age, ATT, and A with pathological inflammation grades in patients with chronic liver disease at liver fibrosis S2 stageG1, G2 and G3 represent 1-3 grades of liver pathological inflammation, respectively. ATT: Attenuation coefficient; A: Activity index.
图 2 慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者年龄、ATT、A指数随病理炎症分级的平均值变化图Fig. 2 Mean plots of age, ATT, and A with pathological inflammation grades in patients with chronic liver disease at liver fibrosis S2 stageG1, G2 and G3 represent 1-3 grades of liver pathological inflammation, respectively. ATT: Attenuation coefficient; A: Activity index.2.4 超声联合弹性成像参数与肝功能指标的单因素线性相关分析
超声联合弹性成像参数Vs与肝功能指标ALT、AST、ALP、GGT、TBil、DBil均呈正相关(均P<0.05),ATT与ALT、AST、GGT、DBil均呈负相关(均P<0.05),F指数与ALT、AST、ALP、GGT、DBil均呈正相关(均P<0.05),A指数与ALT、AST、ALP、GGT、DBil均呈正相关(均P<0.05)。见表 3。
表 3 慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者超声联合弹性成像参数与肝功能指标的相关性分析Table 3 Correlation between parameters of ultrasound combined with elastography and liver function indexes in patients with chronic liver disease at liver fibrosis S2 stageIndex Vs ATT LFI F A r P value r P value r P value r P value r P value ALT 0.531 < 0.001 -0.367 0.008 0.107 0.456 0.439 0.001 0.477 < 0.001 AST 0.368 0.008 -0.388 0.005 -0.061 0.669 0.319 0.022 0.383 0.005 ALP 0.310 0.027 -0.223 0.116 -0.041 0.775 0.304 0.030 0.295 0.035 GGT 0.549 < 0.001 -0.307 0.029 -0.065 0.650 0.500 < 0.001 0.480 < 0.001 TBil 0.290 0.039 -0.257 0.069 0.064 0.654 0.267 0.058 0.267 0.058 DBil 0.330 0.018 -0.284 0.043 -0.007 0.958 0.306 0.029 0.305 0.030 Vs: Shear wave velocity; ATT: Attenuation coefficient; LFI: Liver fibrosis index; F: Fibrosis-related index; A: Activity index; ALT: Alanine transaminase; AST: Aspartate transaminase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; GGT: γ-glutamyltransferase; TBil: Total bilirubin; DBil: Direct bilirubin. 3 讨论
慢性肝病患者肝纤维化是一个较为复杂的病理过程,不同病因导致的肝细胞变性坏死、细胞外基质异常积聚、纤维瘢痕增生等均可导致肝脏正常组织结构和功能受到破坏。随着肝内微结构及血流动力学的改变,肝脏硬度会逐渐增加。当肝纤维化进一步发展,肝小叶结构紊乱及肝细胞结节样再生、假小叶形成,则会发生肝硬化。肝纤维化是慢性肝病向肝硬化发展的中间环节[4]。肝纤维化期乃至肝硬化早期在组织学上仍具有一定可逆转性,因此在恰当的时机启动抗病毒、抗纤维化治疗尤为重要。临床上慢性肝病患者肝脏病理纤维化分期≥S2期或炎症分级≥G2期是加强治疗及逆转病情的重要时期,明确患者病理分期后经治疗可延缓晚期慢性肝病相关并发症的发生。因此,对于慢性肝病患者,肝纤维化分期及炎症分级的判断对临床治疗方案的选择及评估预后具有重要意义。
近年来,多种超声弹性成像技术被广泛应用于各项肝脏相关疾病的研究中,各有优势与不足。按照世界超声联合会2015年版超声弹性成像技术临床使用指南及推荐,超声弹性成像根据手动压缩、脉冲辐射力、外部机械振动3种不同激励方式分为三大类:RTE、2D-SWE和瞬时弹性成像[5]。目前2D-SWE在肝脏炎症水平较低时,对肝纤维化的诊断效能高于RTE,但炎症严重、胆汁淤积、肝血容量增加、饮酒史等可能影响肝脏硬度的真实测值[6];而RTE的组织弥散定量检测则不受影响,只单纯反映肝纤维化进程[7]。因此,对应慢性肝病不同分期时,若单独采用RTE或2D-SWE技术则难以准确诊断并评估患者肝纤维化严重程度,联合弹性成像技术兼具RTE及2D-SWE的优势,基于弹性应变、图像纹理、组织硬度及ATT等主要物理因素定量分析肝纤维化程度、炎症活动度[8]。故本研究选择慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者作为研究对象,运用超声联合弹性成像技术评估联合弹性成像参数与慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者炎症分级的相关性。
本研究结果表明,当慢性肝病患者处于相同肝纤维化程度S2期时,随着病理炎症分级的增高,患者年龄呈线性上升趋势,ATT呈线性下降趋势,A指数呈线性上升趋势。超声联合弹性成像参数中Vs、ATT、F指数和A指数在不同病理炎症分级之间差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05),表明Vs、ATT、F指数和A指数能较好地反映慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者的肝脏炎症程度,而且A指数随着病理炎症程度加重而增加,符合慢性肝病发展的渐进性病理过程。Yada等[9]采用联合弹性成像进行肝纤维化及肝脏炎症活动度评估发现,随肝脏炎症活动度升高,A指数呈明显上升趋势,且A指数用于评估成人肝脏炎症的效能高于其他常规参数。本研究结果显示,RTE测得的LFI在不同病理炎症分级之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),表明RTE组织弥散定量检测主要受肝纤维化而不是炎症的影响[10]。
超声波在组织蛋白质中衰减最明显,特别是胶原蛋白与纤维组织、瘢痕组织衰减更明显,水分衰减最少,故在含水量多的组织中超声波衰减较低。本研究发现ATT与肝脏病理炎症分级显著相关,且随着各期病理炎症程度加重而减低,能较好地反映慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者肝脏炎症的程度。这主要是因为本研究病例选择的是慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者,其肝纤维化程度一致,ATT只反映炎症程度的影响。这可能与肝脏炎症程度增加时汇管区及周围或小叶内肝细胞损伤、炎症细胞浸润增多有关。
随着慢性肝病的不断进展,炎症介导的反应使得肝脏炎症持续加剧,肝纤维化进一步加重,胆管周围纤维化加重又使得胆汁淤积状况愈发严重,从而导致肝脏正常功能受到损害,肝功能相关指标如ALT、AST等可能升高,总蛋白、白蛋白等可能下降[4]。本研究发现A指数与ALT、AST、ALP、GGT、DBil具有相关性,分析原因可能与ALT、AST、ALP、GGT、DBil能灵敏地反映肝脏细胞的炎症程度有关。本研究存在以下局限性:(1)本研究病例数较少,后期会加大收集病例,以减少个体差异对研究结果造成的偏差。(2)超声联合弹性成像技术作为一种新的弹性成像技术,国内外相关报道少见,后期需要开展大量的研究进行补充及证实。
综上所述,超声联合弹性成像技术所测得的联合成像参数能够较准确地评估慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者的炎症程度。该技术能用于评估慢性肝病患者病情,且具有良好的可重复性,具有重要的临床应用价值,有望成为无创评估肝脏炎症程度的新方法。
-
图 1 肝脏超声联合弹性成像显示肝脏弹性测量指标
Fig. 1 Measurement indexes of liver elasticity by ultrasound combined with elastography
FPS: Frames per second; Vs: Shear wave velocity; E: Young’s modulus; ATT: Attenuation coefficient; VsN: Variance stabilization normalization; LFI: Liver fibrosis index; F: Fibrosis-related index; A: Activity index; IQR/M: Interquartile range/median; %AREA: Area ratio of low-strain region; COMP: Complexity.
图 2 慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者年龄、ATT、A指数随病理炎症分级的平均值变化图
Fig. 2 Mean plots of age, ATT, and A with pathological inflammation grades in patients with chronic liver disease at liver fibrosis S2 stage
G1, G2 and G3 represent 1-3 grades of liver pathological inflammation, respectively. ATT: Attenuation coefficient; A: Activity index.
表 1 不同病理炎症分级慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者的一般资料
Table 1 General information of patients with chronic liver disease at liver fibrosis S2 stage stratified by pathological inflammation grades
Variable Total N= 51 G1 N= 15 G2 N= 28 G3 N= 8 Statistic P value Age/year, x±s 45.35 ± 11.69 36.27 ± 7.67 47.68 ± 11.73 54.25 ± 6.23 F = 10.09 < 0.001 Gender, n (%) χ2 = 8.10 0.017 Male 32 (62.75) 6 (40.00) 18 (64.29) 8 (100.00) Female 19 (37.25) 9 (60.00) 10 (35.71) 0 ALT/(U·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 34.00 (24.00, 90.00) 26.00 (22.00, 34.50) 45.50 (28.50, 99.00) 95.50 (28.00, 252.25) H = 6.34 0.042 AST/(U·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 33.00 (23.00, 53.50) 27.00 (20.00, 31.50) 40.00 (23.75, 90.50) 53.00 (36.50, 152.75) H = 7.83 0.020 ALP/(U·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 83.00 (73.00, 122.50) 69.00 (58.50, 81.50) 87.50 (75.75, 127.50) 151.50 (111.75, 314.75) H = 14.14 < 0.001 GGT/(U·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 37.00 (19.00, 96.00) 24.00 (15.50, 48.00) 39.00 (20.75, 96.00) 281.00 (81.50, 512.50) H = 11.73 0.003 TBil/(μmol·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 16.10 (11.40, 22.90) 15.60 (11.85, 21.60) 14.40 (10.92, 18.88) 25.40 (20.35, 32.08) H = 6.62 0.037 DBil/(μmol·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 2.90 (2.15, 5.55) 2.80 (2.25, 4.15) 2.80 (2.10, 3.83) 11.15 (6.60, 13.07) H = 5.41 0.067 IBil/(μmol·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 11.30 (8.50, 16.25) 12.80 (9.50, 17.45) 9.40 (7.97, 14.00) 14.65 (11.28, 19.62) H = 5.35 0.069 TP/(g·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 74.10 (70.45, 77.55) 74.70 (72.30, 77.70) 73.90 (70.40, 76.70) 74.95 (64.83, 77.33) H = 0.70 0.704 Albumin/(g·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 43.10 (39.35, 45.75) 45.30 (41.05, 46.70) 42.90 (40.05, 44.73) 36.30 (33.17, 42.43) H = 5.90 0.052 Globulin/(g·L-1), M(Q1, Q3) 30.70 (28.45, 32.95) 30.10 (28.65, 31.40) 30.55 (27.93, 33.38) 32.60 (30.38, 35.03) H = 2.28 0.320 G1, G2 and G3 represent 1-3 grades of liver pathological inflammation, respectively. ALT: Alanine transaminase; AST: Aspartate transaminase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; GGT: γ-glutamyltransferase; TBil: Total bilirubin; DBil: Direct bilirubin; IBil: Indirect bilirubin; TP: Total protein. 表 2 不同病理炎症分级慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者的超声联合弹性成像参数
Table 2 Parameters of ultrasound combined with elastography in patients with chronic liver disease at liver fibrosis S2 stage stratified by pathological inflammation grades
Variable Total N= 51 G1 N= 15 G2 N= 28 G3 N= 8 Statistic P value F, x±s 1.58 ± 0.68 1.26 ± 0.42 1.62 ± 0.65 2.04 ± 0.91 F = 4.03 0.024 A, x±s 1.24 ± 0.33 1.08 ± 0.25 1.26 ± 0.33 1.48 ± 0.37 F = 4.14 0.022 Vs/(m·s-1), M(Q1, Q3) 1.56 (1.40, 1.92) 1.48 (1.40, 1.54) 1.71 (1.39, 1.92) 1.97 (1.79, 2.28) H = 6.31 0.043 ATT/(dB·cm-1·MHz-1), M(Q1, Q3) 0.58 (0.48, 0.65) 0.62 (0.58, 0.72) 0.56 (0.48, 0.63) 0.45 (0.44, 0.51) H = 9.94 0.007 LFI, M(Q1, Q3) 2.81 (2.26, 3.49) 2.57 (1.70, 3.10) 3.07 (2.37, 3.72) 2.89 (2.47, 3.35) H = 1.97 0.373 G1, G2 and G3 represent 1-3 grades of liver pathological inflammation, respectively. F: Fibrosis-related index; A: Activity index; Vs: Shear wave velocity; ATT: Attenuation coefficient; LFI: Liver fibrosis index. 表 3 慢性肝病肝纤维化S2期患者超声联合弹性成像参数与肝功能指标的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation between parameters of ultrasound combined with elastography and liver function indexes in patients with chronic liver disease at liver fibrosis S2 stage
Index Vs ATT LFI F A r P value r P value r P value r P value r P value ALT 0.531 < 0.001 -0.367 0.008 0.107 0.456 0.439 0.001 0.477 < 0.001 AST 0.368 0.008 -0.388 0.005 -0.061 0.669 0.319 0.022 0.383 0.005 ALP 0.310 0.027 -0.223 0.116 -0.041 0.775 0.304 0.030 0.295 0.035 GGT 0.549 < 0.001 -0.307 0.029 -0.065 0.650 0.500 < 0.001 0.480 < 0.001 TBil 0.290 0.039 -0.257 0.069 0.064 0.654 0.267 0.058 0.267 0.058 DBil 0.330 0.018 -0.284 0.043 -0.007 0.958 0.306 0.029 0.305 0.030 Vs: Shear wave velocity; ATT: Attenuation coefficient; LFI: Liver fibrosis index; F: Fibrosis-related index; A: Activity index; ALT: Alanine transaminase; AST: Aspartate transaminase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; GGT: γ-glutamyltransferase; TBil: Total bilirubin; DBil: Direct bilirubin. -
[1] YOUNOSSI Z M, WONG G, ANSTEE Q M, et al. The global burden of liver disease[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21(8): 1978-1991. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.015. [2] HERNANDEZ-GEA V, FRIEDMAN S L. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2011, 6: 425-456. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130246. [3] 中华医学会传染病与寄生虫病学分会, 肝病学分会. 病毒性肝炎防治方案[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2000, 8 (6): 324-329. [4] 陈必武. 超声联合弹性成像定量分析慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化及肝脏炎症的应用价值[D]. 右江: 右江民族医学院, 2022. [5] SHIINA T, NIGHTINGALE K R, PALMERI M L, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: Part 1: basic principles and terminology[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2015, 41(5): 1126-1147. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2015.03.009. [6] KOIZUMI Y, HIROOKA M, ABE M, et al. Comparison between real-time tissue elastography and vibrationcontrolled transient elastography for the assessment of liver fibrosis and disease progression in patients with primary biliary cholangitis[J]. Hepatol Res, 2017, 47(12): 1252-1259. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12861. [7] KENNEDY P, WAGNER M, CASTÉRA L, et al. Quantitative elastography methods in liver disease: current evidence and future directions[J]. Radiology, 2018, 286(3): 738-763. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2018170601. [8] LEE Y K, LEE D H, JOO S K, et al. Combielastography versus transient elastography for assessing the histological severity of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease[J]. Gut Liver, 2024, 18(6): 1048-1059. DOI: 10.5009/gnl240198. [9] YADA N, TAMAKI N, KOIZUMI Y, et al. Diagnosis of fibrosis and activity by a combined use of strain and shear wave imaging in patients with liver disease[J]. Dig Dis, 2017, 35(6): 515-520. DOI: 10.1159/000480140. [10] YADA N, SAKURAI T, MINAMI T, et al. Influence of liver inflammation on liver stiffness measurement in patients with autoimmune hepatitis evaluation by combinational elastography[J]. Oncology, 2017, 92(Suppl 1): 10-15. DOI: 10.1159/000451011.

 下载:
下载:
