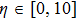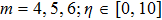† Corresponding author. E-mail:
In this paper, the entropy generation of a flow through a movable plate with variable temperature is studied. Suitable similarity variables are applied to transform the local entropy generation rate to entropy generation number. A modified differential transform method (DTM) with shooting method is used to obtain the similarity solution of the entropy generation. The effects of different parameters (Prandtl number, variable wall temperature) on the irreversibility (such as 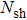

The issue of the boundary layer flow through a moving plate is increasingly attracting the attention of scholars and researchers because of its importance for many practical applications. Hence, many studied topics have been disclosed in recent decades.[1–8] One of the topics is concerned with the numerical solutions. For example, Yang and Zhang et al.[9] used the finite difference method to detect bifurcations and chaos of a nonlinear forced vibration of the system. Anuar and Yacob et al.[10] studied thermal field of flow through a moving plate with the effect of thermal radiation. Numerical solutions are obtained by Runge–Kutta–Fehlberg method with shooting technique. In the study of Ali and Nazar et al.,[11] the shooting method is applied to obtain the problem of flow through a movable plate with a magnetic field near the stagnation point. Sharma and Bhargava et al.[12] considered the issue of free convection in a micro-polar fluid with viscous dissipation. Moreover, its numerical solution can be obtained by the meshless-Galerkin method. In order to study axially moving two-dimensional materials, Hatami and Azhari et al. proposed[13] that a p-version finite element can be used to obtain the numerical results. However, as mentioned above, it can be seen that those numerical solutions do not have the characteristics of differentiation and integration because the numerical data is discrete. Hence, in order to resolve the issue, Puhov in 1976[14] proposed the method of modified differential transform method (DTM) with shooting method to study this kind of problem. Because DTM is an extension of the Taylor series method, a numerical method can be used to obtain analytic solutions for ordinary differential equations (ODEs) problems,[15–20] partial differential equations (PDEs) problems,[21–24] differential-algebraic equations (DAEs) problems,[25–28] differential difference equations (DDEs) problems,[29–32] linear integro-differential equation problems[33–39] and eigenvalue problems.[40–44] Hence, in view of the above, a modified differential transform method (MDTM) will be used to obtain the numerical results for entropy generation in Flow through a movable plate with variable temperature in the x axis. Another important issue studied in this paper is irreversibility analysis, which is one of the energy conservation methods,[45–50] because irreversibility often arises in energy transfer processes.[51–52] Consequently, in order to study the irreversibility of a thermal system, many scholars have studied irreversibility due to heat convection. Such as, Bejan[53–54] proposed the expression for the entropy generation rate, whose goal is to study entropy generation in a heat Transfer process. Since then, many researchers have studied the effect of various conditions on Irreversibility of flow field. Such as Rashidi and Mohammadi et al. presented the irreversibility analysis for a permeable surface with a variable heat source.[55] Guillermo Ibanez[56] presented entropy generation analysis for a channel with permeable plates and analyzed irreversibility due to the effect of hydrodynamic slip and convective boundary. Adnan Saeed Butt and Asif Ali[57] examined entropy generation due to the effect of thermal radiation in a moving plate. Hedayati and Malvandi et al.[58] presented the entropy generation minimization (EGM) for heat transfer on a moving wedge. Yazdi and Hashimc et al.[59] proposed the second law analysis for Power-Law Fluid on Micro-patterned movable surface. For other interesting studies in solving heat transfer problem, Yang proposed integral transform so as to solve the heat transfer problems. The results indicated that the method is powerful for finding analytical solution for heat transfer equation, such as steady heat transfer equation[60–61] and heat diffusion equation.[62] However, unlike the above mentioned topics, this present work will investigate the effect of variable wall temperature in a moving plate on entropy generation.
Consider that the plate is movable with velocity. Moreover, the temperature of the plate along the axis direction is variable. Hence, the governing equations for boundary layer flow are in the following

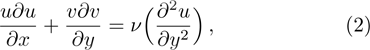
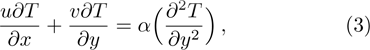

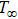
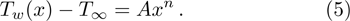
The dimensionless parameters are proposed as the same method[5] in the following
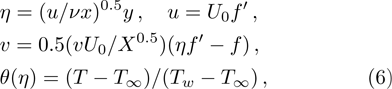
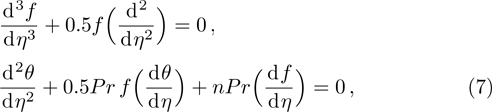
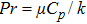
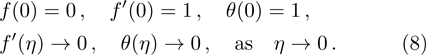
Because the boundary conditions are 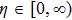
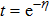
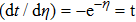
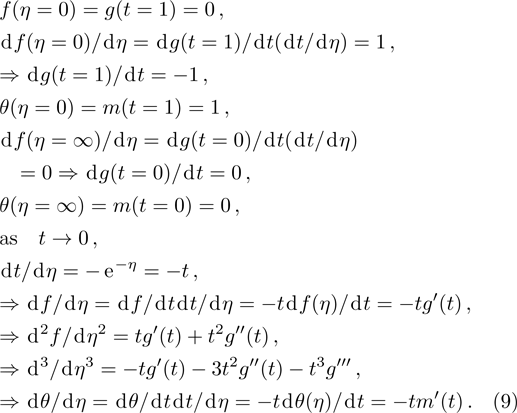
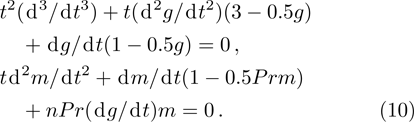
For Eq. (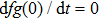
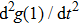
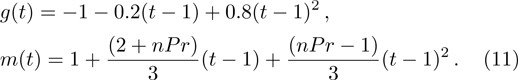
The issue of irreversibility is important because energy conservation cannot be ignored in many practical applications. Hence, in order to study irreversibility of a thermal system, the local entropy generation rate for a flow through a moving plate with variable temperature is defined as
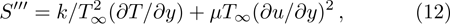
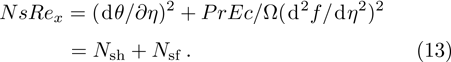
Following Bejan.[28,38–39] who proposed that the ratio of the local entropy generation rate to the characteristic entropy generation rate is equal to the entropy generation number. Therefore, from Eq. (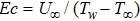
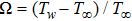
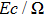

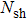
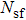
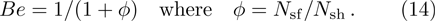
Now, consider a brief description of standard DTM. Let v(t) be an analytic function in a domain D. Here t = a represents any point in D. Then, Taylor series expansion for the function of v(t) is defined as
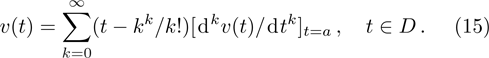
It is worth mentioning that the function of v(t) can be a Maclaurin series when a = 0
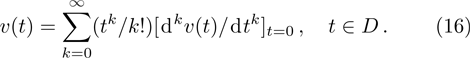
The differential transformed function v(t) is expressed as
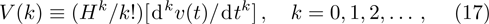
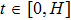
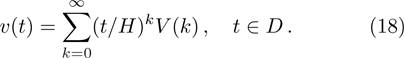
In practical applications, because the differential transformation method is derived from the Taylor series expansion, it is found that the number of arguments required to restore the unknown function precisely can be reduced by specifying an appropriate value of the constant H. In other words, the function v(t) can be obtained in terms of a finite series as follows:
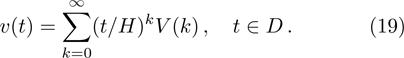
Next, we state some important properties of the Taylor differential transformation derived using the above expressions, which are needed in the sequel. The operation properties of differential transformation. If the transformed functions for both U(k) and V(k) are derived from u(x) and v(x), respectively, then the fundamental mathematical operations of differential transformation are listed as follows. (The other proofs can be seen in references.)
(i) If 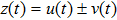
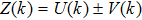
(ii) If 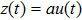
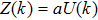
(iii) If 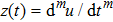
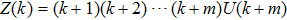
(iv) If 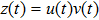
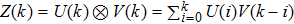
(v) If 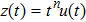
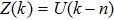
We only give the proof of (v), the proof of the others can be seen in references. For simplicity, Considering H = 1,
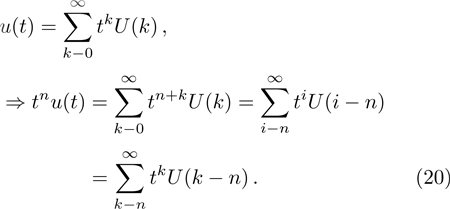
Now, back to our model (
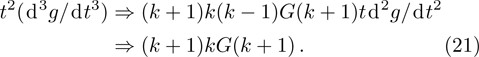
So we have
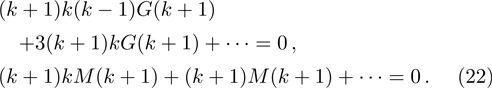
After solving G(k), then we can have M(k) after substituting it into the second equation of Eq. (
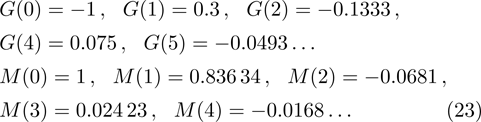
The algorithms are coded in the computer algebra package-Mathematica. The environment variable Digits controlling the number of significant digits is set to 32 in all the calculations done in this paper. Case 1. Consider the case, as shown in Tables
| Table 1
The present method f′, f′, f″ for case 1, iterations m = 6. . |
| Table 2
The present method θ, θ′, θ″ for case 1, iterations m = 6. . |
| Table 3
The absolutely maximum error for Table |
| Table 4
The present method θ, θ′, θ″ for case 2, iterations m=6. . |
| Table 5
The absolutely maximum error for table |
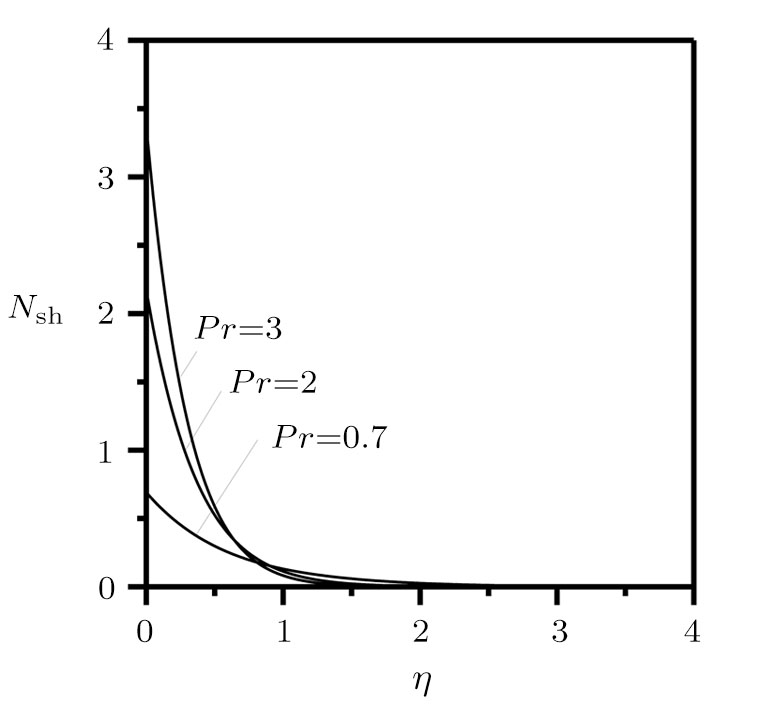
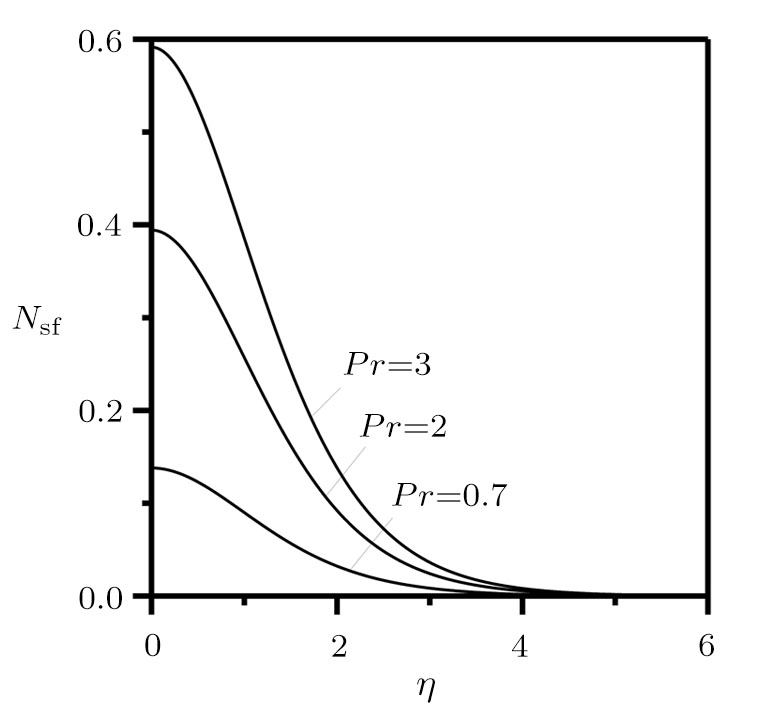
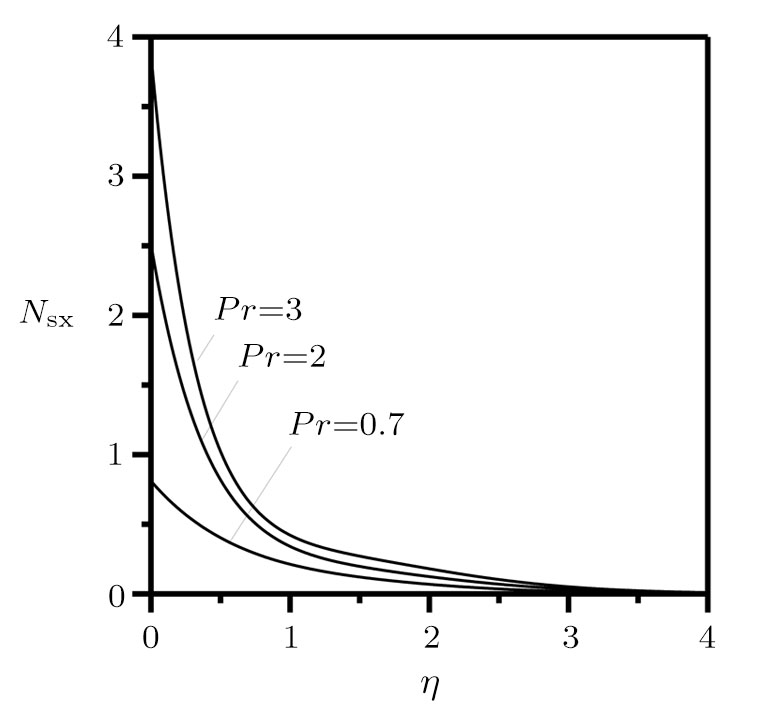
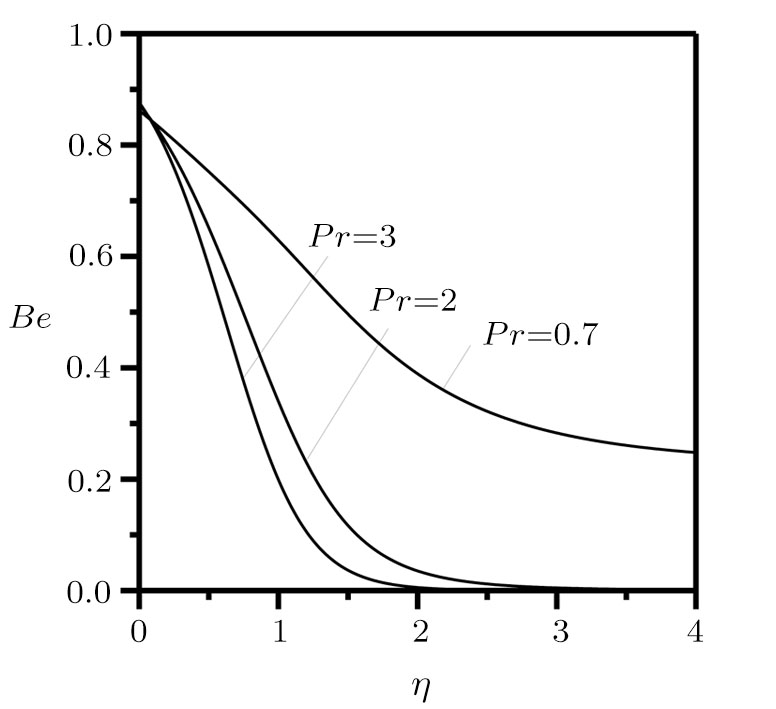
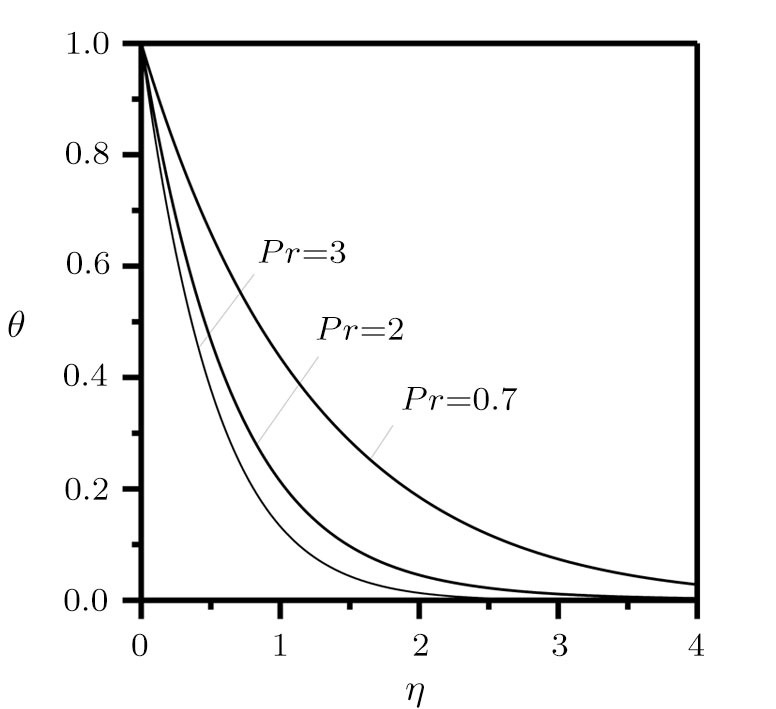
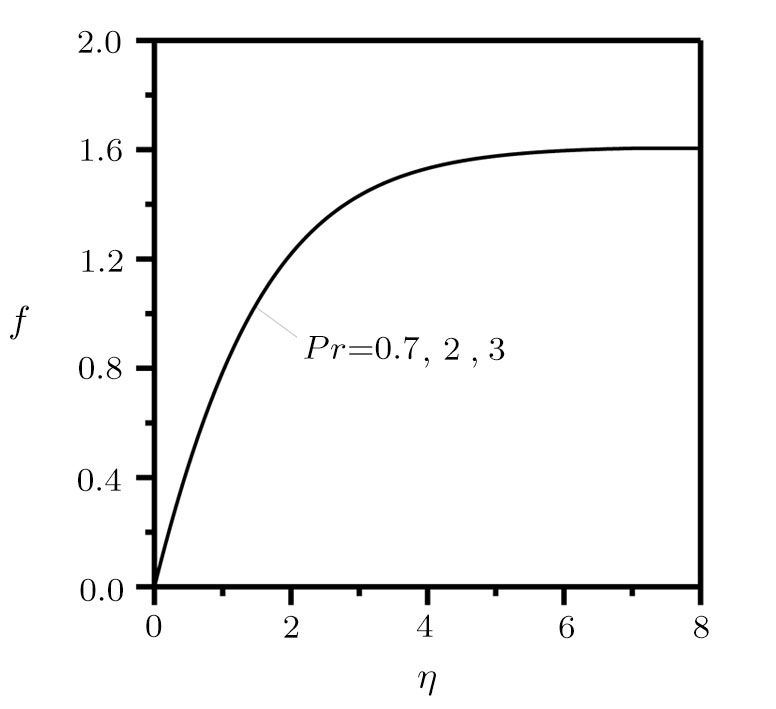
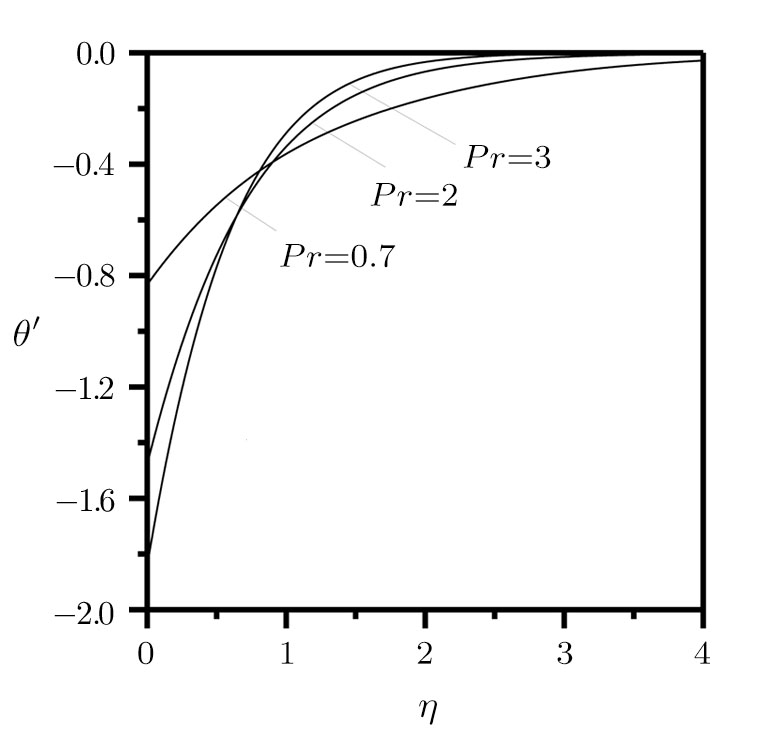
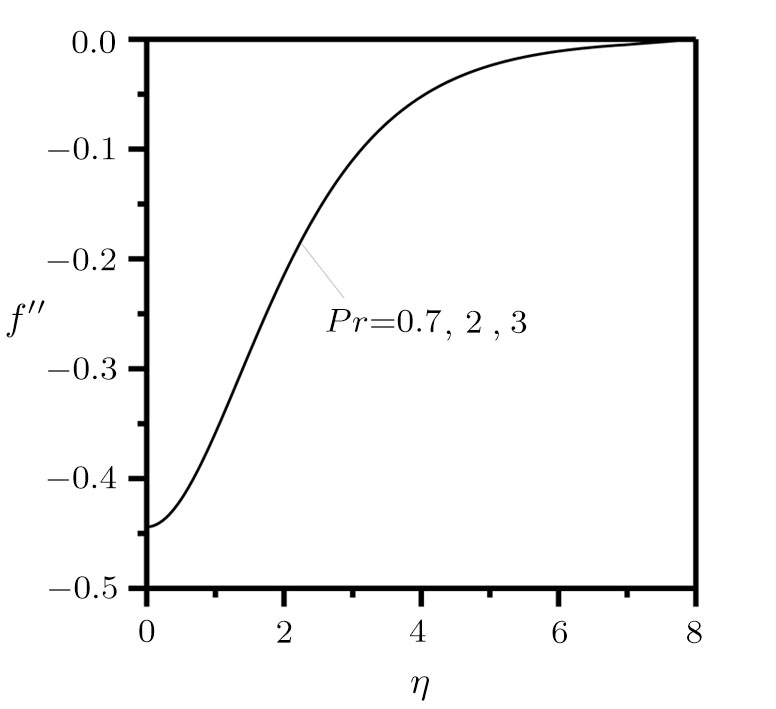
The irreversibility analysis is presented for variable temperature in a moving plate. Similarity solutions, such as velocity-gradient, temperature-gradient, heat transfer irreversibility 
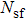
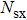
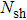
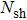
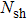
In Fig. 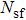
So, from Eq. (
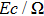
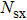
However, their irreversibility is dominated by friction when η reaches infinity. Finally, it is concluded that there is a boundary layer flow through a movable plate with variable temperature in x axis, its temperature profile and stream function is presented in Figs. 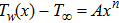
A practical thermal system is irreversible, hence the issues of energy conservation have attracted much attention in recent years. In this paper, therefore, the irreversibility for boundary layer flow through a moving plate with variable temperature will be analyzed because of their importance in many practical applications. In order to obtain the similarity solution of boundary layer flow, modified ADM with shooting method will be used to obtain similarity solution for boundary layer. For example, velocity-gradient, temperature-gradient, heat transfer irreversibility 
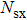
(i) The study of entropy generation is important because energy conservation can not be ignored in many practical applications.
(ii) In order to study Irreversibility of a moving plate with various temperature, suitable similarity variables are used to transform the local entropy generation rate to entropy generation number.
(iii) A modified differential transform method (DTM) with shooting method is used to obtain the similarity solution of the entropy generation, the proposed numerical method, their accuracy of analytic solution is very high.
(iv) The similarity solution profiles 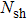
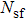
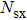
(v) It is worth mentioning that the temperature profile will decrease as a result of the increasing of Prandtl number. Meanwhile, the 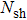
| [1] | |
| [2] | |
| [3] | |
| [4] | |
| [5] | |
| [6] | |
| [7] | |
| [8] | |
| [9] | |
| [10] | |
| [11] | |
| [12] | |
| [13] | |
| [14] | |
| [15] | |
| [16] | |
| [17] | |
| [18] | |
| [19] | |
| [20] | |
| [21] | |
| [22] | |
| [23] | |
| [24] | |
| [25] | |
| [26] | |
| [27] | |
| [28] | |
| [29] | |
| [30] | |
| [31] | |
| [32] | |
| [33] | |
| [34] | |
| [35] | |
| [36] | |
| [37] | |
| [38] | |
| [39] | |
| [40] | |
| [41] | |
| [42] | |
| [43] | |
| [44] | |
| [45] | |
| [46] | |
| [47] | |
| [48] | |
| [49] | |
| [50] | |
| [51] | |
| [52] | |
| [53] | |
| [54] | |
| [55] | |
| [56] | |
| [57] | |
| [58] | |
| [59] | |
| [60] | |
| [61] | |
| [62] |