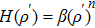|
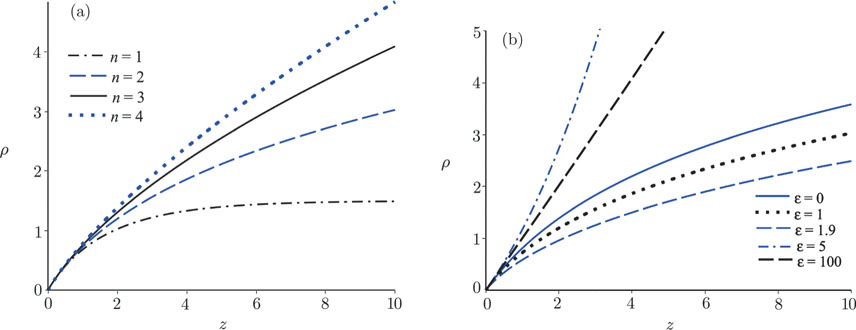
Plot of the numerical solutions to (45) given 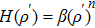 for various values of the power-law parameter n. The other parameters are fixed as b = c = 1 and β = 1, while boundary conditions are taken as ρ(0) = 0, ρ′(0) = 1. In (a) we fix ϵ = 1 and plot the solutions for various n. As n increases, the solutions uniformly increase in magnitude. In (b) we fix n = 2 and plot the solutions for various ϵ. For 0 < ϵ < 2, the solutions uniformly decrease in magnitude as ϵ increases. At ϵ = 2, the problem becomes singular, and for ϵ > 2 we then obtain a new type of solution branch. The curve starts out steep, and gradually decreases in slope as ϵ increases toward infinity. for various values of the power-law parameter n. The other parameters are fixed as b = c = 1 and β = 1, while boundary conditions are taken as ρ(0) = 0, ρ′(0) = 1. In (a) we fix ϵ = 1 and plot the solutions for various n. As n increases, the solutions uniformly increase in magnitude. In (b) we fix n = 2 and plot the solutions for various ϵ. For 0 < ϵ < 2, the solutions uniformly decrease in magnitude as ϵ increases. At ϵ = 2, the problem becomes singular, and for ϵ > 2 we then obtain a new type of solution branch. The curve starts out steep, and gradually decreases in slope as ϵ increases toward infinity.
|