扩展功能
文章信息
- 陈世悦, 毕明威, 刘惠民, 高永进, 张鹏飞
- CHEN Shi-yue, BI Ming-wei, LIU Hui-min, GAO Yong-jin, ZHANG Peng-fei
- 沙三中亚期东营三角洲—滑塌浊积体系预测模型研究
- Quantitative Prediction Model for the Dongying Delta-fluxoturbidite Depositional System in the Middle Es3 Period
- 沉积学报, 2014, 32(5): 921-929
- ACTA SEDIMENTOLOGICA SINCA, 2014, 32(5): 921-929
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2013-9-10
- 收修改稿日期:2013-12-12
2. 中国石化胜利油田分公司地质科学研究院 山东东营 257000
2. Geological Science Research Institute of China Petrochemical Shengli Oilfield Branch, Dongying, Shandong 257000
随着含油气盆地勘探程度地提高,各类隐蔽型油气藏逐渐成为主要的勘探目标。沙三段沉积时期,东营凹陷东营三角洲前缘浊积沉积形成的非构造圈闭油气资源丰富,是东营凹陷储量增长和勘探开发的重要类型[1, 2, 3, 4]。三角洲前缘滑塌浊积沉积受到构造活动、古地形特征等多种地质因素的控制[5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10],砂体横向分布较稳定,但厚度变化大,目前还没有有效手段预测滑塌浊积砂体的厚度,加强厚度预测研究十分必要。
目前对砂体厚度的预测方法可以分为两种:一是通过沉积物的供给速率、湖盆底形及构造活动等因素对滑塌浊积体进行定性的预测[11, 12, 13];二是通过对地球物理综合处理,实现砂体的识别及厚度的预测[14, 15, 16, 17],但该类方法很少考虑到前缘滑塌砂体的地质及成因特征的复杂性,加上地球物理参数的精度问题,因此很难对砂体厚度进行有效预测。笔者通过对东营凹陷沙三中亚期三角洲—滑塌浊积体系发育特征的研究,分析沉积体系内部地质关系,建立浊积砂体厚度预测模型,为定量预测三角洲前缘岩性圈闭提供一种新的思路及方法。 1 地质概况
东营凹陷是典型的中新生代断陷湖盆,形态上为北断南超、北陡南缓的箕状凹陷[18]。凹陷东接青坨子凸起,南部超覆于鲁西隆起、广饶凸起,向西以平南断层和高青断层为界、与惠民凹陷毗邻,北部以陈南断层为界、与陈家庄凸起相邻[19, 20, 21, 22];可以划分为利津洼陷、民丰洼陷、牛庄洼陷、博兴洼陷等次级洼陷[23,24]。
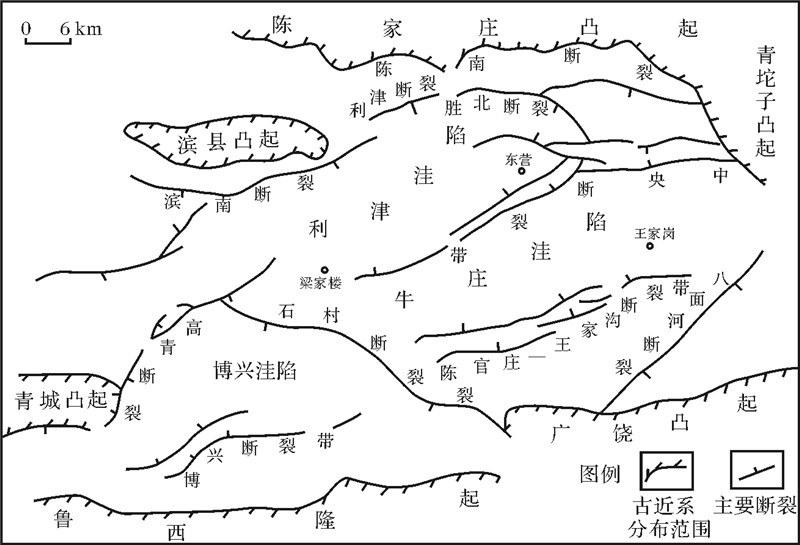
|
| 图 1 东营凹陷构造区划图(据杨伟利等,2006) Fig. 1 The tectonic division of Dongying depression (according to Yang Weili,et al.,2006) |
沙三段中亚段沉积时期,东营凹陷物源供给充足,东营三角洲沉积极其发育,自下而上可以划分为9个沉积期次(据胜利油田地质院)(图 2)。随着三角洲不断向湖盆中央进积,导致沉积物在三角洲前缘斜坡处不断堆积,在自身重力、构造运动、水动力等多种因素的影响下,尚未完全固结的沉积物发生破裂、滑动等作用沿着斜坡下滑,沉积物在斜坡坡折带能量卸载形成滑塌浊积岩沉积[25, 26, 27, 28, 29](图 3)。
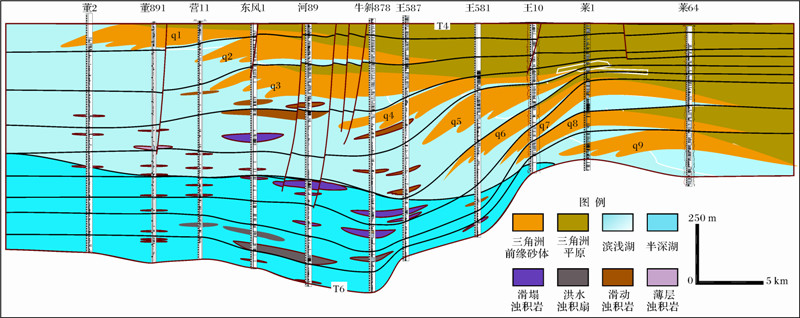
|
| 图 2 沙三中亚段东营三角洲东西向沉积相对比剖剖面 Fig. 2 The east-west correlation of sedimentary facies of Dongying Delta in the middle Es3 |
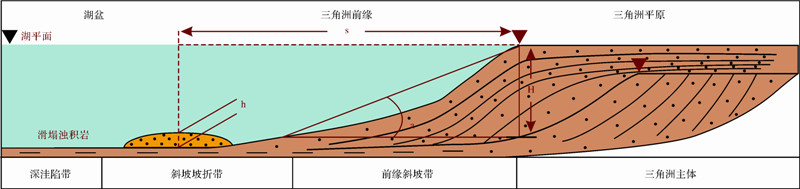
|
| 图 3 三角洲—滑塌浊积体系定量参数选定示意图 Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of quantitative parameter selected for delta-fluxoturbidite depositional system |
为了建立三角洲—滑塌浊积体系预测模型,设定了三条假设条件:①不考虑青坨子物源对东南物源和南部物源三角洲的影响;②不考虑构造活动、洼陷带可容空间大小等不可定量描述的因素的影响;③将浊积体细分为若干个独立的个体,假定每次选点都选取的是不同浊积体的最大厚度处(图 3)。通过分析认为:可以通过建立三角洲前缘滑塌浊积岩厚度h(m)与前缘地层厚度H(m)、砂岩百分含量x(%)、浊积岩滑移距离s(m)以及前缘斜坡坡角的大小a(°)的定量关系,从而建立三角洲—滑塌浊积体系的预测模型[30]。 2 东营三角洲—滑塌浊积体系预测模型研究 2.1 研究方法
本次研究以东营三角洲第四、五、六沉积期次为例,建立前缘滑塌浊积岩厚度的预测模型。对三角洲—前缘滑塌浊积体系地质模型的研究,是在单因素分析的基础上,利用灰关联分析法对前缘滑塌砂体的厚度进行定量预测。
(1) 利用控制变量的方法建立单因素关系。例如,寻找滑塌浊积体厚度h(m)与滑移距离s(m)的单因素关系,就要在前缘厚度H(m)、砂岩百分含量x(%)以及斜坡坡角a(°)为定值的情况下进行研究,消除它们对h-s关系的影响。
(2) 得到单因素关系后(如h-s、h-H、h-x、h-a等),利用灰关联分析法对前缘滑塌砂体厚度h(m)进行定量预测,建立预测模型。 2.2 灰关联分析法
灰关联分析法,即建立系统中各因素的主次关系,找出影响各项评价指标的重要因素,它包括主因素与子因素的选定、关联系数、关联度及权系数的计算等[31]。
(1) 主因素与子因素的选定
利用单因素分析的方法,确定决定浊积体厚度大小的主要参数作为主因素,其余参数作为子因素处理。
(2) 确定单项指标定量化标准
本文采用极大值标准化的方法,对数据进行标准化处理。即以单项参数除以同类参数的极大值,使参数归一在0~1之间。对于其值愈大,反映浊积体厚度越大的参数,直接除以本参数的最大值;对于其值越小,反映厚度越大的参数,用本参数的极大值减去单项参数之差再除以最大值;对于取中间值时,反映厚度越大的参数,用单项参数减去中间值并求取绝对值,再用最大绝对值减去各项参数算得的绝对值之差再除以最大绝对值[32]。
(3) 确定各项指标的权重,计算灰关联系数
定量标准化后的数据利用下列公式(公式①~④),计算出各子因素与主因素之间的灰关联系数为:
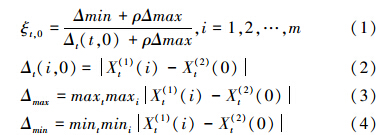
ρ∈[0.1,1]称为分辨系数,其作用在于提高灰关联系数之间的差异显著性,一般取0.5。

ri,0为子序列i与母序列0的灰关联度(公式(5)),经过归一化处理(公式(6)),所得到的结果即为各指标相对于浊积体厚度预测时的权重系数。 2.3 控制变量法建立单因素关系
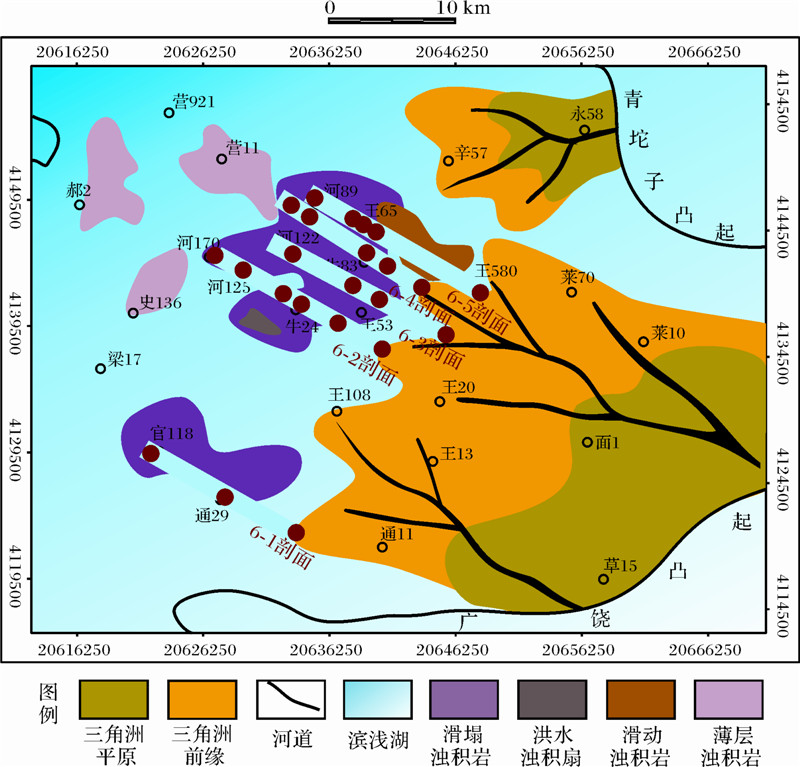
按照沙三段中亚期东营三角洲的主推进方向,选取地质剖面(以第六期次为例,如图 4所示),对三角洲及其前缘浊积体发育关系进行参数选取及定量研究(表 1)。
|
| 图 4 第六期次三角洲—滑塌浊积体系定量研究剖面位置图 Fig. 4 The quantitative research profile location of delta-fluxoturbidite depositional system in the sixth stage |
| 剖面名称 | 期次 | 前缘厚度H/m | 前缘砂岩百分含量x/% | 坡角a/° | 滑移距离s/m | 浊积体厚度h/m | 浊积体位置 |
| 6-1剖面 | 第六沉积期次 | 32 | 21.22 | 2.017 | 10 420.412 | 14 | (6-1-1) |
| 21.22 | 2.017 | 12 093.448 | 10 | (6-1-2) | |||
| 6-2剖面 | 95 | 45.16 | 1.985 | 4 232.476 | 50 | (6-2-1) | |
| 45.16 | 1.985 | 7 752.054 | 36 | (6-2-2) | |||
| 45.16 | 1.985 | 9 232.854 | 35 | (6-2-3) | |||
| 45.16 | 1.985 | 12 912.122 | 22 | (6-2-4) | |||
| 45.16 | 1.985 | 15 760.706 | 20 | (6-2-5) | |||
| 6-3剖面 | 85 | 40 | 1.837 | 4 514.339 | 45 | (6-3-1) | |
| 40 | 1.837 | 8 542.348 | 25 | (6-3-2) | |||
| 40 | 1.837 | 13 900.826 | 17 | (6-3-3) | |||
| 6-4剖面 | 140 | 66.33 | 2.261 | 3 433.239 | 45 | (6-4-1) | |
| 66.33 | 2.261 | 5 639.069 | 54 | (6-4-2) | |||
| 66.33 | 2.261 | 11 218.125 | 32 | (6-4-3) | |||
| 66.33 | 2.261 | 12827.857 | 20 | (6-4-4) | |||
| 6-5剖面 | 80 | 40.71 | 2.684 | 10 442.429 | 35 | (6-5-1) | |
| 40.71 | 2.684 | 10 795.403 | 30 | (6-5-2) | |||
| 40.71 | 2.684 | 11 887.704 | 26 | (6-5-3) | |||
| 40.71 | 2.684 | 15 305.785 | 12 | (6-5-4) | |||
| 5-1剖面 | 第五沉积期次 | 102 | 58.54 | 2.434 | 13 965.442 | 20 | (5-1-1) |
| 58.54 | 2.434 | 15 168.607 | 18 | (5-1-2) | |||
| 58.54 | 2.434 | 19 094.262 | 12 | (5-1-3) | |||
| 5-2剖面 | 112 | 61.23 | 2.62 | 8 801.325 | 37 | (5-2-1) | |
| 61.23 | 2.62 | 9 999.906 | 30 | (5-2-2) | |||
| 61.23 | 2.62 | 11 518.188 | 23 | (5-2-3) | |||
| 61.23 | 2.62 | 13 329.01 | 20 | (5-2-4) | |||
| 5-3剖面 | 110 | 59 | 2.731 | 10 064.576 | 27 | (5-3-1) | |
| 59 | 2.731 | 12 913.763 | 22 | (5-3-2) | |||
| 59 | 2.731 | 15 649.433 | 20 | (5-3-3) | |||
| 5-4剖面 | 50.3 | 2.914 | 14 141.644 | 18 | (5-4-1) | ||
| 78 | 50.3 | 2.914 | 15 854.568 | 16 | (5-4-2) | ||
| 50.3 | 2.914 | 18 419.417 | 10 | (5-4-3) | |||
| 4-1剖面 | 第四沉积期次 | 105 | 54 | 3.138 | 4 448.135 | 40 | (4-1-1) |
| 54 | 3.138 | 7 029.417 | 30 | (4-1-2) | |||
| 4-2剖面 | 138 | 83.7 | 3.235 | 5 192.124 | 41 | (4-2-1) | |
| 83.7 | 3.235 | 10 673.244 | 31 | (4-2-2) | |||
| 83.7 | 3.235 | 13 523.814 | 26 | (4-2-3) | |||
| 83.7 | 3.235 | 15 158.613 | 21 | (4-2-4) | |||
| 4-3剖面 | 112 | 65.1 | 3.235 | 7 122.876 | 36 | (4-3-1) | |
| 65.1 | 3.235 | 12 538.6 | 25 | (4-3-2) |
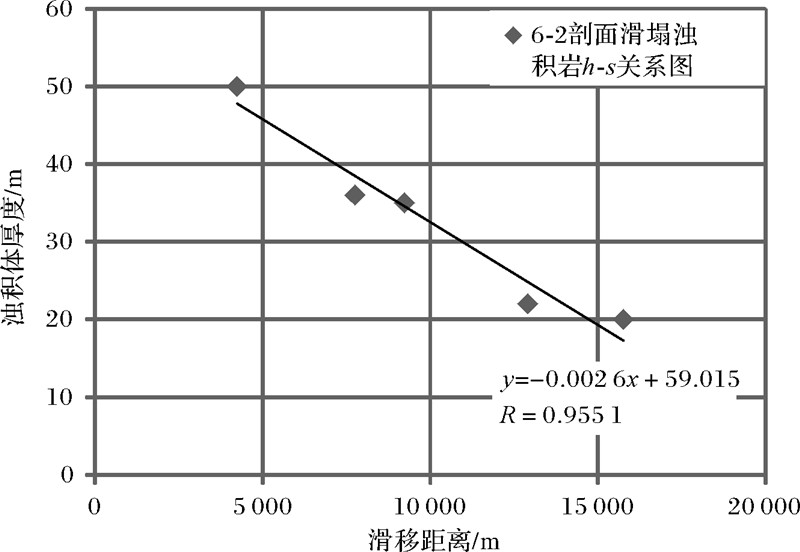
由于每条剖面三角洲前缘的H、x和a是定值,可以在单剖面的条件下,按照控制变量的方法,建立h-s的定量单因素关系。以第六期6-2剖面为例,得出该剖面的h与s的单因素关系(图 5)。
|
| 图 5 第六期次6-2剖面滑塌浊积体厚度h与滑移距离s单因素分析图 Fig. 5 The chart of single factor analysis between fluxoturbidite thickness h and turbidite slip distance s of profile 6-2 in the sixth stage |
按照同样的方法建立其他剖面的h-s关系,可以得出相同的规律,即浊积体厚度与滑移距离之间呈线性负相关关系,并且相关关系好。 2.3.2 h-H、h-x、h-a单因素关系
在三角洲前缘相同位置前缘厚度H、砂岩百分含量x以及斜坡坡角a是一一对应的,讨论h-H、h-x、h-a单因素关系时,可以将H、x、a作为一个整体来考虑,而忽略H、x、a之间的相互影响。建立h-H、h-x、h-a的单因素关系,即寻找滑移距离s相等的滑塌浊积岩进行研究。
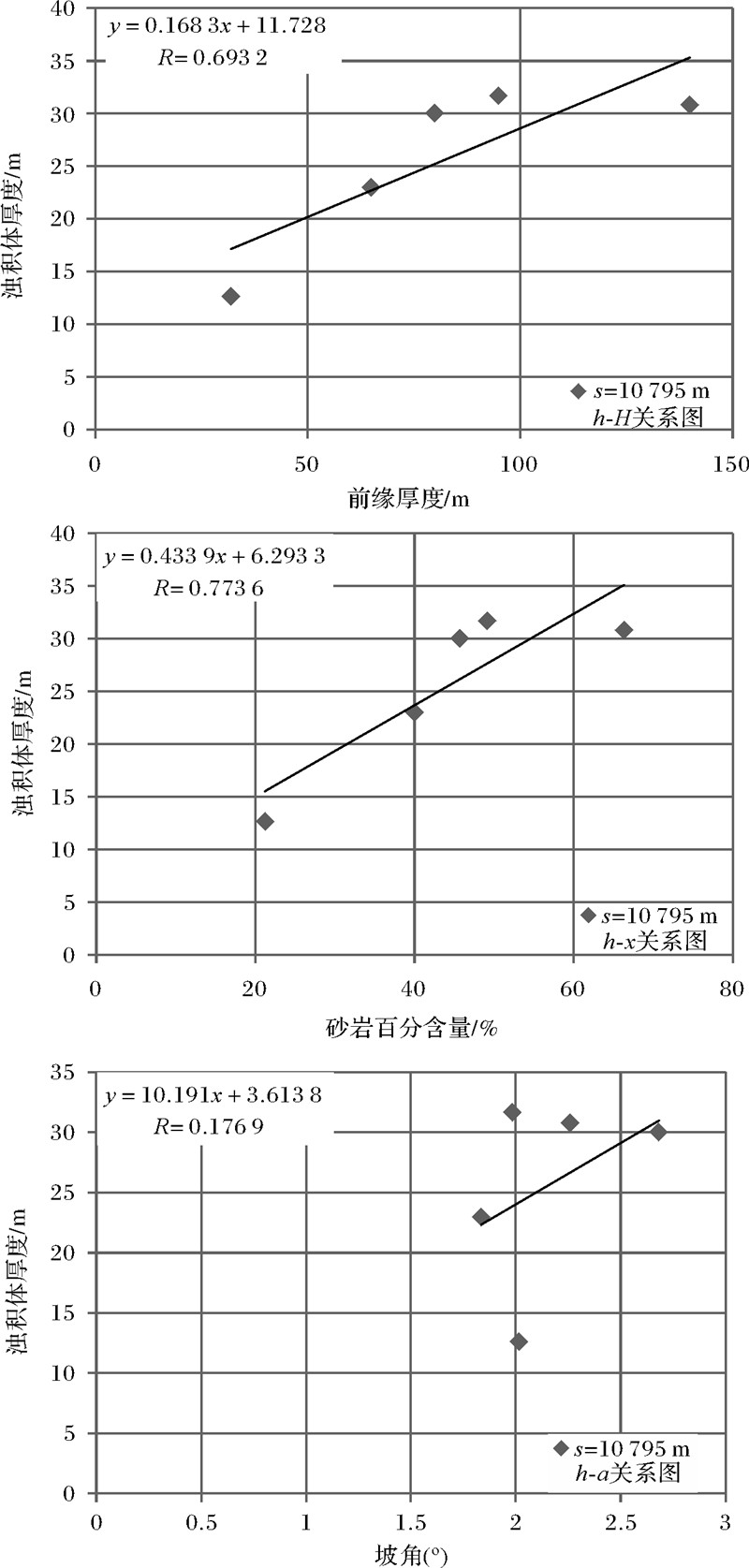
为了寻找相同滑移距离(s)下的h-H关系,根据各剖面各期次得到的h-s的线性关系式,插入一些“等距离的数据点”。例如建立s=10 795 m时滑塌浊积岩h-H、h-x、h-a的单因素关系(表 2)。
s=10 795 m等距离下h-H、h-x、h-a关系为(图 6):
h=0.168 3H+11.728,R2=0.693 2
h=0.433 9x+6.293 3,R2=0.773 6
h=10.191x+3.613 8,R2=0.176 9
| 剖面名称 | 期次 | 前缘厚度H/m | 前缘砂岩百分含量x/% | 坡角a/° | 滑移距离s/m | 浊积体厚度h/m | 浊积体位置 |
| 6-1剖面 | 第六沉积期次 | 32 | 21.22 | 2.017 | 10 795 | 12.610 | 等距离点1 |
| 6-2剖面 | 95 | 49.16 | 1.985 | 31.642 | 等距离点2 | ||
| 6-3剖面 | 65 | 40.00 | 1.837 | 22.946 | 等距离点3 | ||
| 6-4剖面 | 140 | 66.33 | 2.261 | 30.773 | 等距离点4 | ||
| 6-5剖面 | 80 | 45.71 | 2.684 | 30.000 | (6-5-2) |
|
| 图 6 s=10 795 m时第六期次滑塌浊积体厚度h与前缘 厚度H、砂岩百分含量x、斜坡坡角a单因素分析图 Fig. 6 The chart of single factor analysis between fluxoturbidite thickness h and delta front thickness H,sandstone percentage content x,slope angle a in the sixth stage |
利用同样的研究方法,对其它剖面进行h-H、h-x、h-a单因素分析。
研究发现,滑塌浊积体厚度h(m)与滑移距离s(m)呈正相关,与前缘厚度H(m)、前缘砂岩百分含量x(m)、前缘斜坡坡角a(°)呈负相关,且h(m)与s(m)相关关系最好,因此本文将滑移距离s(m)作为控制浊积体厚度h(m)的主因素,其他参数作为子因素来处理。 2.4 灰关联分析法建立浊积体预测模型
通过极大值标准化的方法,对所选的参数数据进行标准化处理(表 3)。以滑移距离s(m)做为主因素,进行灰关联分析,最终得到s(m)、x(%)、H(m)及a(°)的灰关联度分别为:1、0.628、0.623、0.563;经过归一化处理后得到各参数对应的权重系数分别为:0.355、0.221、0.223、0.201。
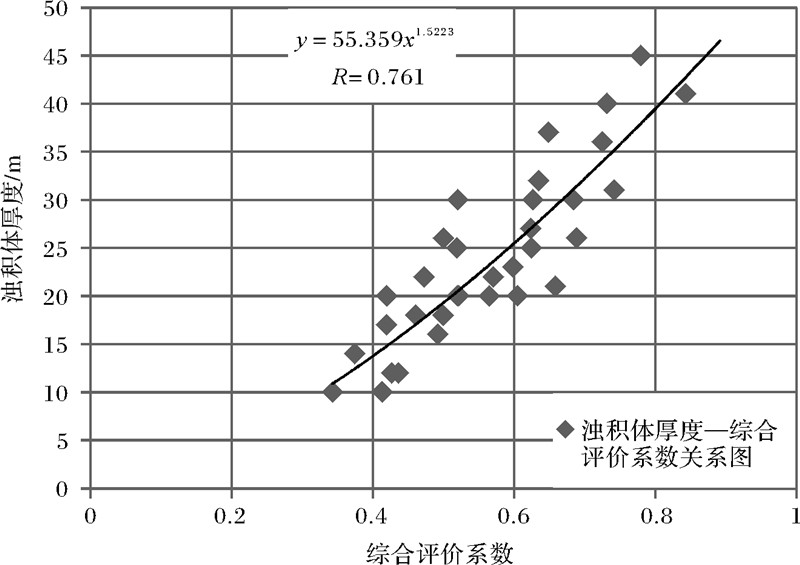
最终得到四、五、六沉积期次三角洲前缘滑塌浊积岩厚度预测模型(图 7):
h=55.359Q1.522 3,R2=0.761
Q=0.355s′+0.223x′+0.221H′+0.201a′
| 剖面名称 | 期次 | s′ | H′ | x′ | a′ | h/m | h′/m | [h-h′]/h |
| 6-1剖面 | 第六沉积期次 | 0.454 | 0.200 | 0.238 | 0.576 | 14 | 12.395 | 0.115 |
| 0.367 | 0.200 | 0.238 | 0.576 | 10 | 10.861 | 0.086 | ||
| 6-2剖面 | 0.778 | 0.594 | 0.506 | 0.566 | 50 | 27.675 | 0.447 | |
| 0.594 | 0.594 | 0.506 | 0.566 | 36 | 23.447 | 0.349 | ||
| 0.516 | 0.594 | 0.506 | 0.566 | 35 | 21.741 | 0.379 | ||
| 0.324 | 0.594 | 0.506 | 0.566 | 22 | 17.699 | 0.196 | ||
| 0.175 | 0.594 | 0.506 | 0.566 | 20 | 14.771 | 0.261 | ||
| 6-3剖面 | 0.764 | 0.531 | 0.448 | 0.524 | 45 | 25.034 | 0.444 | |
| 0.553 | 0.531 | 0.448 | 0.524 | 25 | 20.389 | 0.184 | ||
| 0.272 | 0.531 | 0.448 | 0.524 | 17 | 14.738 | 0.133 | ||
| 6-4剖面 | 0.820 | 0.875 | 0.743 | 0.645 | 45 | 37.916 | 0.157 | |
| 0.705 | 0.875 | 0.743 | 0.645 | 54 | 34.923 | 0.353 | ||
| 0.412 | 0.875 | 0.743 | 0.645 | 32 | 27.740 | 0.133 | ||
| 0.328 | 0.875 | 0.743 | 0.645 | 20 | 25.775 | 0.289 | ||
| 6-5剖面 | 0.453 | 0.500 | 0.456 | 0.766 | 35 | 20.877 | 0.404 | |
| 0.435 | 0.500 | 0.456 | 0.766 | 30 | 20.483 | 0.317 | ||
| 0.377 | 0.500 | 0.456 | 0.766 | 26 | 19.278 | 0.259 | ||
| 5-1剖面 | 第五沉积期次 | 0.269 | 0.638 | 0.656 | 0.695 | 12 | 15.676 | 0.306 |
| 0.206 | 0.638 | 0.656 | 0.695 | 20 | 20.581 | 0.029 | ||
| 0.000 | 0.638 | 0.656 | 0.695 | 18 | 19.253 | 0.070 | ||
| 5-2剖面 | 0.539 | 0.700 | 0.686 | 0.748 | 12 | 15.140 | 0.262 | |
| 0.476 | 0.700 | 0.686 | 0.748 | 37 | 28.684 | 0.225 | ||
| 0.397 | 0.700 | 0.686 | 0.748 | 30 | 27.198 | 0.093 | ||
| 0.302 | 0.700 | 0.686 | 0.748 | 23 | 25.356 | 0.102 | ||
| 5-3剖面 | 0.473 | 0.688 | 0.661 | 0.779 | 20 | 23.218 | 0.161 | |
| 0.324 | 0.688 | 0.661 | 0.779 | 27 | 26.990 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.180 | 0.688 | 0.661 | 0.779 | 22 | 23.579 | 0.072 | ||
| 5-4剖面 | 0.259 | 0.488 | 0.563 | 0.832 | 20 | 20.456 | 0.023 | |
| 0.170 | 0.488 | 0.563 | 0.832 | 16 | 18.839 | 0.177 | ||
| 0.035 | 0.488 | 0.563 | 0.832 | 18 | 17.016 | 0.055 | ||
| 4-1剖面 | 第四沉积期次 | 0.767 | 0.656 | 0.605 | 0.896 | 40 | 34.443 | 0.139 |
| 0.632 | 0.656 | 0.605 | 0.896 | 30 | 31.066 | 0.036 | ||
| 4-2剖面 | 0.728 | 0.863 | 0.937 | 0.923 | 41 | 42.736 | 0.042 | |
| 0.441 | 0.863 | 0.937 | 0.923 | 31 | 35.131 | 00.133 | ||
| 0.292 | 0.863 | 0.937 | 0.923 | 26 | 31.382 | 0.207 | ||
| 0.206 | 0.863 | 0.937 | 0.923 | 21 | 29.298 | 0.395 | ||
| 4-5剖面 | 0.627 | 0.700 | 0.729 | 0.923 | 36 | 33.959 | 0.057 | |
| 0.343 | 0.700 | 0.729 | 0.923 | 25 | 27.050 | 0.082 | ||
| 灰关联度 | 1 | 0.623 | 0.629 | 0.563 | ||||
| 权重系数 | 0.355 | 0.221 | 0.223 | 0.201 |
|
| 图 7 第四、五、六期次东营三角洲前缘滑塌浊积岩 厚度预测模型 Fig. 7 Prediction model for fluxoturbidite thickness of Dongying delta front from 4 to 6 stage |
Q为综合评价系数,s′、H′、x′、a′分别代表经过最大值标准化后的滑移距离、前缘砂体厚度、百分含量以及斜坡坡角数据。
通过对数学模型h-s′-H′-x′-a′误差验证发现,预测厚度与实测厚度之间满足:|h′-h|/h<35%,|h′-h|/h均值等于0.15预测结果较为准确。 3 预测模型的验证
利用预测模型(h=55.359Q1.522 3,Q=0.355s′+0.223x′+0.221H′+0.201a′)对第七沉积期次三角洲—滑塌浊积体系进行验证(图 8),可以发现: |h'-h|/h为0.039~0.343,|h'-h|/h均值等于0.171,滑塌浊积岩的预测厚度与实测厚度误差较小,预测模型在第七期次具有较高的预测精度(表 4)。因此,通过对东营三角洲—浊积体系建立的滑塌浊积岩预测模型,具备推广的潜力。
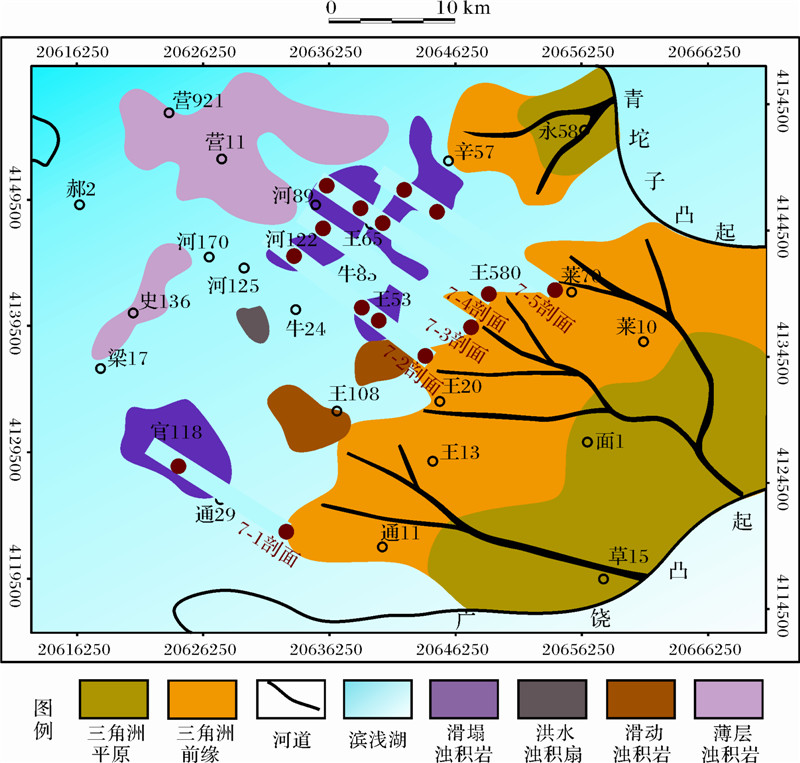
|
| 图 8 第七期次三角洲—滑塌浊积体系定量研究剖面位置图 Fig. 8 The quantitative research profile location of delta- fluxoturbidite depositional system in the seventh stage |
| 剖面名称 | 期次 | 前缘厚度H/m | 前缘砂岩百分含量x/% | 坡a° | 滑移距离s/m | 浊积体厚度h/m | 浊积体位置 | 预测厚度h′/m | (h′-h)/h |
| 7-1剖面 | 第七沉积期次 | 29.000 | 37.500 | 1.626 | 10 047.077 | 26.000 | (7-1-1) | 19.289 | 0.150 |
| 7-2剖面 | 72.000 | 48.571 | 1.715 | 4 294.390 | 47.000 | (7-2-1) | 32.167 | 0.120 | |
| 72.000 | 48.571 | 1.715 | 6 089.562 | 40.000 | (7-2-2) | 29.704 | 0.039 | ||
| 72.000 | 48.571 | 1.715 | 13 169.511 | 24.000 | (7-2-3) | 19.990 | -0.152 | ||
| 7-3剖面 | 80.000 | 39.250 | 1.620 | 13 820.341 | 17.500 | (7-3-1) | 18.673 | -0.304 | |
| 7-4剖面 | 75.000 | 38.667 | 1.676 | 8 061.429 | 35.000 | (7-4-1) | 25.602 | 0.069 | |
| 75.000 | 38.667 | 1.676 | 12 082.824 | 22.000 | (7-4-2) | 20.212 | -0.212 | ||
| 75.000 | 38.667 | 1.676 | 15 306.137 | 16.500 | (7-4-3) | 15.891 | -0.343 | ||
| 7-5剖面 | 89.000 | 48.889 | 1.731 | 11 164.220 | 32.000 | (7-5-1) | 24.156 | -0.047 | |
| 89.000 | 48.889 | 1.731 | 13 960.620 | 23.000 | (7-5-2) | 20.283 | -0.274 | ||
| |h'-h|/h均值 | 0.171 | ||||||||
本文在单因素分析的基础上,利用灰关联分析法建立三角洲—滑塌浊积体系预测模型:
(1) 滑移距离s(m)与浊积体厚度h(m)呈负相关关系,且相关关系好,作为主因素;
(2) 砂体厚度H(m)、砂岩百分含量x(%)及斜坡坡角a(°)与h(m)呈正相关关系,作为子因素;
(3) 通过计算各子因素相对于主因素的权重系数,确定灰关联系数,建立滑塌浊积岩厚度h(m)的定量预测模型:h=55.359Q1.522 3,Q=0.355s′+0.223x′+0.221H′+0.201a′(Q为综合评价系数,s′、x′、H′、a′分别表经过最大值标准化后的滑移距离、前缘砂体厚度、百分含量以及斜坡坡角数据)。
| [1] | 隋淑玲, 谭俊敏. 东营凹陷低位三角洲砂体隐蔽油气藏研究[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2004, 11(2):25-29[Sui Shuling, Tan Junmin. Study on the subtle oil gas reservoir of low stand system tract delta sandstone in Dongying sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2004, 11(2): 25-29] |
| [2] | 朱德艳. 东营凹陷古近系岩性圈闭分布及成藏条件[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2008, 15(3):32-35[Zhu Deyan. Palaeogene lithologic traps distribution and hydrocarbon accumulation conditions in Dongying depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2008, 15(3): 32-35] |
| [3] | 邱桂强, 王居峰, 张昕, 等. 东营三角洲沙河街组三段中亚段地层格架初步研究及油气勘探意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2001, 19(4):569-574[Qiu Guiqiang, Wang Jufeng, Zhang Xin, et al. Preliminary study on stratigraphic architecture of Middle-Shasan Dongying delta and its significance to hydrocarbon exploration[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(4): 569-574] |
| [4] | 王金铎, 韩文功, 于建国, 等. 东营凹陷沙三段浊积岩体系及其油气勘探意义[J]. 石油学报, 2003, 24(6):24-29[Wang Jinduo, Han Wengong, Yu Jianguo, et al. Turbidity system in the third section of Shahejie Formation of Dongying sag and its implications on petroleum prospecting[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2003, 24(6): 24-29] |
| [5] | Bai Guoping, Zhang Shanwen. Depositional patterns and Oil/Gas accumulation features of Sha-3 Member turbidites in Dongying depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Science, 2004, 1(2): 105-110 |
| [6] | Stow D A V, Mayall M. Thematic set on deepwater sedimentary systems: new models for the 21st century[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(2):125-135 |
| [7] | 高永进, 邱桂强, 陈冬霞, 等. 牛庄洼陷岩性油藏含油气性及主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(3):284-287[Gao Yongjin, Qiu Guiqiang, Chen Dongxia, et al. Oil/gas shows in lithologic reservoirs in Niuzhuang sag and their main controlling factors[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2004, 25(3): 284-287] |
| [8] | 赵密福, 信荃麟, 刘泽容. 惠民凹陷临南洼陷滑塌浊积岩分布规律及其控制因素[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2001, 8(5):14-17[Zhao Mifu, Xin Quanlin, Liu Zerong. Distribution rule and its controlling factors of slump turbidite of Linnan subsag in Huimin sag[J]. Retroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2001, 8(5): 14-17] |
| [9] | 张世懋, 丁晓琪. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组浊积岩特征及其影响因素[J]. 测井技术, 2011, 35(6):594-598[Zhang Shimao, Ding Xiaoqi. Characteristics and controlling factors of turbidites in Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2011, 35(6): 594-598] |
| [10] | 王志坤, 钟建华, 艾合买提江·阿布都热合曼, 等. 东营河125断层几何学特征及其对浊积扇和油藏的控制作用[J]. 地球学报, 2008, 29(1):95-102[Wang Zhikun, Zhong Jianhua, Ahmatjan·Abdurahman, et al. Geometric characteristics of the He-125 Fault and its control over sediment and reservoir distribution, Dongying[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2008, 29(1): 95-102] |
| [11] | 陈永红. 惠民凹陷沙三段三角洲前缘滑塌浊积体发育规律与油气聚集关系[D]. 北京:中国科学院研究生院, 2006[Chen Yonghong. The developing rule of delta-forward creeping turbidite sandbody and its oil-gas accumulation relationship of Sha 2 Member in Huimin depression[D]. Beijing: School of the Chineses Academy of Sciences, 2006] |
| [12] | 封从军, 鲍志东, 张吉辉, 等. 扶余油田中区泉四段基准面旋回划分及对单砂体的控制[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012, 42(2):62-69[Feng Congjun, Bao Zhidong, Zhang Jihui, et al. Dividing of base-level cycle and its controlling on single sandbody in the Fourth Member of Quantou Formation in Fuyu oilfield[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(2): 62-69] |
| [13] | 崔龙涛, 冯栋, 秦雁群, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地镇北地区延长组长7古地貌与砂体分布特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2013, 25(5):65-69[Cui Longtao, Feng Dong, Qin Yanqun, et al. Palaeogeomorphology reconstruction and sandbody distribution of Chang 7 reservoir in Zhenbei area, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2013, 25(5): 65-69] |
| [14] | 穆立华, 彭仕宓, 尹志军, 等. 井间砂体定量预测的泛克里格法[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2004, 31(4):73-75[Mu Lihua, Peng Shimi, Yin Zhijun, et al. Universal Kriging method for quantitative sandstone prediction between wells[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2004, 31(4): 73-75] |
| [15] | 袁书坤, 王英民, 卢双舫, 等. 陈家洼陷沙三段砂体沉积及其与油气的关系[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2008, 27(6):15-38[Yuan Shukun, Wang Yingmin, Lu Shuangfang, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and their relation to petroleum for the sandbodies in Sha No.3 Member of Chenjia sag[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2008, 27(6): 15-38] |
| [16] | Sun Luping, Zheng Xiaodong, Shou Hao, et al. Quantitative prediction of channel sandbodies based on seismic peak attributes in the frequency domain and its application[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2010, 7(1): 10-17 |
| [17] | 王家华, 夏吉庄. 三维地震约束多点建模降低井间砂体预测的不确定性[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(5):878-888[Wang Jiahua, Xia Jizhuang. Multi-point statistical modeling constrained by 3D seismic data reducing uncertainty of sandbody prediction[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(5): 878-888] |
| [18] | 潘继平, 金之钧. 中国油气资源潜力及勘探战略[J]. 石油学报, 2004, 25 (2):1-6[Pan Jiping, Jin Zhijun. Potentials of petroleum resources and exploration strategy in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2004, 25(2): 1-6] |
| [19] | 叶兴树, 王伟锋, 戴俊生, 等. 东营凹陷沙三—东营期断裂活动特征[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2006, 30(4): 7-11[Ye Xingshu, Wang Weifeng, Dai Junsheng, et al. Characteristics of fault activities of Sha-3 member and Dongying periods in Dongying depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2006, 30(4): 7-11] |
| [20] | 孔凡仙. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带砂砾岩体的勘探[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2000, 35(3):669-676[Kong Fanxian. Prospecting for sand-gravel body in northern steep slope of Dongying depression[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2000, 35(3): 669-676] |
| [21] | 武法东, 陈建渝, 刘从印, 等. 东营凹陷第三纪层序地层格架及沉积体系类型[J]. 现代地质, 1998, 12(4):559-566[Wu Fadong, Chen Jianyu, Liu Congyin, et al. Tertiary sequence stratigraphic framework and sedimentary system types in Dongying depression[J]. Geoscience, 1998, 12(4): 559-566] |
| [22] | 王志刚. 东营凹陷北部陡坡构造岩相带油气成藏模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(4):10-12[Wang Zhigang. Pooling model of steep slope structure and lithological zone in north Dongying sag[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(4): 10-12] |
| [23] | 李丕龙, 翟庆龙, 荣启宏, 等. 东营凹陷中央背斜带油气运移聚集特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2000, 27(4):64-67[Li Pilong, Zhai Qinglong, Rong Qihong, et al. Migration and accumulation of hydrocarbons in the central anticline belt of Dongying depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000, 27(4): 64-67] |
| [24] | 马丽娟, 郑和荣. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷中央隆起带构造特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2006, 28(2):103-108[Ma Lijuan, Zheng Herong. Structural characteristics of the central uplift belt of the Dongying sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2006, 28(2): 103-108] |
| [25] | Fang Yong, Deng Hongwen, Massimo Sarti, et al. Characteristics of evolution and distribution of lithologic trap in Dongying Delta, Shengli Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(5): 123-126 |
| [26] | 饶孟余, 钟建华, 王夕宾, 等. 东营凹陷东部沙三段滑塌浊积砂体沉积特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2004, 32(3):15-17[Rao Mengyu, Zhong Jianhua, Wang Xibin, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of creeping turbidite sandbody of the Member 3 of Shahejie Formation in eastern Dongying depression[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2004, 32(3): 15-17] |
| [27] | 王居峰, 贾光华, 刘军锷, 等. 史南地区沙三段浊积砂体成因模式探讨[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2003, 10(4):8-10[Wang Jufeng, Jia Guanghua, Liu June, et al. Discussion on the genesis model for turbidites of Es3 in Shinan area[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2003, 10(4): 8-10] |
| [28] | 张关龙, 陈世悦, 鄢继华, 等. 三角洲前缘滑塌浊积体形成过程模拟[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(1):50-55[Zhang Guanlong, Chen Shiyue, Yan Jihua, et al. Simulation of luxoturbidite in front of delta[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(1): 50-55] |
| [29] | 鄢继华, 陈世悦, 宋国奇, 等. 三角洲前缘滑塌浊积岩形成过程初探[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(4):573-578[Yan Jihua, Chen Shiyue, Song Guoqi, et al. Preliminary study on the formation of fluxoturbidite in front of delta[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2004, 22(4): 573-578] |
| [30] | 李宇志, 毕明威, 刘惠民, 等. 沙三中亚期东营三角洲前缘滑塌浊积岩定量预测[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(1):146-155[Li Yuzhi, Bi Mingwei, Liu Huimin, et al. Quantitative prediction of slump turbidites of the Dongying delta front in the mid Es3[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(1): 146-155] |
| [31] | 刘吉余, 彭志春, 郭晓博. 灰色关联分析法在储层评价中的应用——以大庆萨尔图油田北二区为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2005, 12(2):13-16[Liu Jiyu, Peng Zhichun, Guo Xiaobo. Application of grey relation analysis to reservoir evaluation-taking Bei 2 area, Saertu oilfield, Daqing as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2005, 12(2): 13-16] |
| [32] | 赵加凡, 陈小宏, 张勤. 灰关联分析在储层评价中的应用[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2003, 26(4):282-286[Zhao Jiafan, Chen Xiaohong, Zhang Qin. Application of grey association analysis in reservoir evaluation[J]. Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 2003, 26(4): 282-286] |
 2014, Vol. 32
2014, Vol. 32

