文章信息
- miR-524-5p调控HEG1表达对食管癌细胞上皮间质转化的影响
- Effect of miR-524-5p on Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition in Esophageal Cancer Cells by Regulating HEG1 Expression
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2023, 50(11): 1059-1065
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2023, 50(11): 1059-1065
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2023.23.0426
- 收稿日期: 2023-04-23
- 修回日期: 2023-08-29
2. 100050 北京,北京友谊医院肝移植中心
2. Liver Transplant Center, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100050, China
食管癌(esophageal cancer, EC)是临床上常见的迁移、侵袭能力很强的癌症之一[1],致病因素包括吸烟、饮酒、社会地位低下、生存环境不佳、微量元素缺乏等[2]。食管癌术后预后较差,化疗是治疗食管癌的主要手段,但长期使用化疗药物会产生耐药性,导致治疗效果不佳。目前,靶向疗法在食管癌的临床治疗中已发挥了重要作用[3]。研究发现miRNA及其靶基因在食管癌中与免疫浸润、肿瘤微环境、癌症干性特性和上皮间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition, EMT)呈现不同程度的相关性[4]。研究表明多种miRNA通过调控其靶基因影响食管癌细胞的迁移、侵袭能力,如miR-493过表达靶向Wnt5a/PD-L1[5]、miR-2053过表达靶向KIF3C[6]等均可抑制食管癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭,起抑癌作用。Starbase数据库预测显示miR-524-5p与具有EGF样结构域的心脏发育蛋白1(heart development protein with EGF-like domains 1, HEG1)有结合位点。已知HEG1在肝癌细胞中表达上调,并且可以促进肝癌细胞侵袭转移和EMT进程[7-8]。本研究拟探讨miR-524-5p是否通过调节HEG1影响食管癌细胞的增殖、EMT和侵袭转移并对此进行研究。
1 材料与方法 1.1 细胞人食管癌细胞TE-1购自上海泽叶生物科技有限公司;人食管癌细胞KYSE30、KYSE150购自上海烜雅生物科技有限公司;人食管癌细胞NEC由上海生化细胞所提供;人正常食管上皮细胞HEEC购自上海研域生物科技有限公司。
1.2 试剂与仪器RPMI 1640培养基购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;miR-524-5p过表达(miR-524-5p mimic)或阴性对照(miR-524-5p NC)序列购自上海吉玛制药公司;胎牛血清(FBS)、LipofectamineTM2000转染试剂购自赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;CCK-8试剂盒购自上海宏叶生物科技有限公司;双荧光素酶试剂盒购自上海通蔚实业有限公司;一抗MMP2、MMP9、E-cadherin、Vimentin、N-cadherin、Snail和二抗均购自艾博抗(上海)贸易有限公司;HEG1抗体购自美国Invitrogen公司。仪器:CO2恒温培养箱购自德国艾本德公司;荧光倒置显微镜购自徕卡显微系统上海贸易有限公司;PCR仪购自赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司。
1.3 方法 1.3.1 细胞培养将1.1中四种人食管癌细胞和人正常食管上皮细胞用RPMI1640培养基(含有10%FBS,青霉素100 u/ml,链霉素100 μg/ml),在5%CO2、37℃培养箱中培养,每2天更换一次培养基,传代培养至对数期用于后续实验。调整培养的5种细胞浓度至每升1×107个,于6孔板每孔接入1 ml上述浓度细胞,培养24 h。
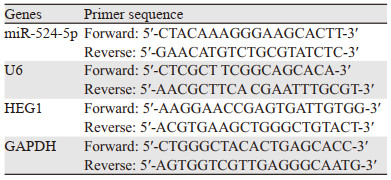
1.3.2 RT-qPCR检测miR-524-5p及HEG1 mRNA表达收集1.3.1中培养的细胞,加入TRIzol溶液提取总RNA,按照反转录试剂盒进行PCR扩增,引物由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司提供,扩增条件为:95℃ 60 s, 95℃ 10 s, 60 ℃ 30 s,共40个循环。miR-524-5p以U6为内参,HEG1以GAPDH为内参。引物设计见表 1。
利用GEPIA数据库查询HEG1在食管癌肿瘤组织和正常食管组织中的表达水平。
1.3.4 细胞转染与分组KYSE30细胞以2×105个/孔的密度接种6孔板中,37℃恒温CO2培养箱培养过夜后,采用LipofectamineTM2000试剂转染核酸序列,实验分为四组:转染miR-524-5p mimic(miR-524-5p mimic组)、miR-524-5p NC(miR-524-5p NC组)、共转染miR-524-5p NC和pcDNA3.1(miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1组)和共转染miR-524-5p NC和pcDNA3.1-HEG1(miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1-HEG1组),另设置未经转染的细胞为正常对照组(Control组)。转染后细胞培养6 h,弃掉培养基,更换为1.3.1中使用的培养基继续培养72 h,收集细胞用于后续实验。
1.3.5 细胞增殖能力检测使用CCK-8试剂盒检测KYSE30细胞增殖能力,细胞按照1.3.4中的方法转染后,继续培养72 h,分别于24、48和72 h三个时间段加入CCK-8溶液,培养2 h后,用酶标仪在450 nm下读取吸光度值。
1.3.6 KYSE30细胞克隆形成实验按照1.3.4的方法转染细胞后,培养24 h后收集KYSE30细胞,重新在培养皿中按照1×103个/皿接种KYSE30细胞,继续培养2周后,弃培养液,PBS冲洗,加入固定液固定15 min,弃去固定液,结晶紫染色,显微镜观察并计数克隆细胞数目。
1.3.7 Western blot检测蛋白表达将细胞按照1.3.4的方式培养24 h后,收集细胞,裂解后提取总蛋白,测定蛋白浓度。随后进行电泳、转膜及5%脱脂牛奶室温封闭等操作,封闭2 h后加入一抗MMP2、MMP9、E-cadherin、Vimentin、N-cadherin、Snail、HEG1(1:1 000)培养过夜,PBS清洗后加入二抗(1:2 000)培养2 h,GAPDH(1: 1 000)为内参,加入ECL显影,Image J软件分析条带灰度值,计算蛋白表达量。
1.3.8 KYSE30细胞迁移能力检测细胞划痕实验:将细胞按照1.3.4的方法培养至对数期后,用无菌10 μl移液枪枪头尖在6孔板底部垂直划线,PBS冲洗后加入无血清的RPMI1640培养基,培养24 h,分别在培养的0和24 h时用显微镜观察并拍照,计算划痕愈合率。
1.3.9 KYSE30细胞侵袭能力检测Transwell实验:将基质胶用不含血清的RPMI 1640培养基稀释8倍后,每个小室加入50 μl,置于CO2恒温培养箱(37℃)培养30 min,将按照1.3.4的方法转染细胞,消化重悬后,在小室的上室中接入200 μl浓度为1×105/ml的细胞悬液,下室为600 μl含血清的RPMI1640培养基,培养24 h后,加入固定液固定,结晶紫染色,擦去上室细胞,倒置显微镜拍照并计数。
1.3.10 双荧光素酶报告基因检测利用Starbase数据库(https://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/)预测miR-524-5p与HEG1的结合位点,构建野生型(WT)和突变型(MUT)HEG1质粒,利用LipofectamineTM2000试剂将miR-524-5p mimic或NC和HEG1野生或突变质粒共转染KYSE30细胞,并且转染海肾质粒为内参,转染48 h后用双荧光素酶报告基因试剂盒检测荧光素酶活性。
1.4 统计学方法采用SPSS26.0和GraphPad Prism 9软件进行数据分析。所有数据均表示为平均值±标准差(x±s),多组比较采用单因素方差分析,两两组间比较采用SNK-q检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
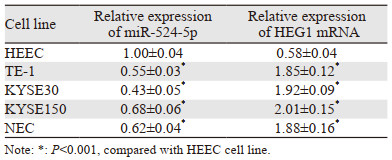
2 结果 2.1 miR-524-5p和HEG1在人食管癌细胞和正常食管上皮细胞中的表达miR-524-5p在食管癌细胞TE-1、KYSE30、KYSE150、NEC中的表达均显著降低,HEG1 mRNA相对表达量在各细胞系中均显著上调(均P=0.000),见表 2。说明在食管癌细胞中miR-524-5p为低表达,HEG1高表达。本实验选择miR-524-5p表达量最低的KYSE30细胞作为后续实验细胞。
|
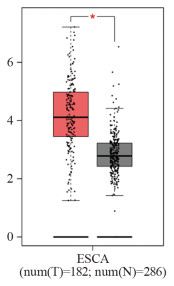
在GEPIA数据库中,HEG1在食管癌组织中表达显著高于正常食管组织(P < 0.05),见图 1。
|
| ESCA: esophageal carcinoma. 图 1 HEG1在食管癌组织和正常食管组织中的表达 Figure 1 Expression of HEG1 in esophageal cancer tissues and normal esophageal tissues |
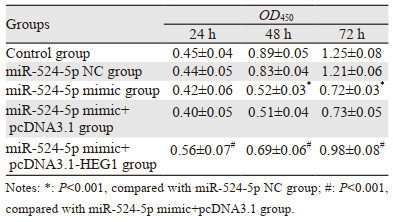
在24、48、72h时,miR-524-5p NC组和Control组的KYSE30细胞增殖能力比较,差异均无统计学意义(均P > 0.05),在24 h时,与miR-524-5p NC组比较,miR-524-5p mimic组KYSE30细胞增殖能力差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),与mimic+pcDNA3.1组比较,miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1-HEG1组KYSE30细胞增殖能力明显增强(P=0.000);在48 h和72 h时,与miR-524-5p NC组比较,miR-524-5p mimic组KYSE30细胞增殖能力明显降低(均P=0.000),与miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1组比较,miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1-HEG1组KYSE30细胞增殖能力明显增强(均P=0.000),见表 3。
|
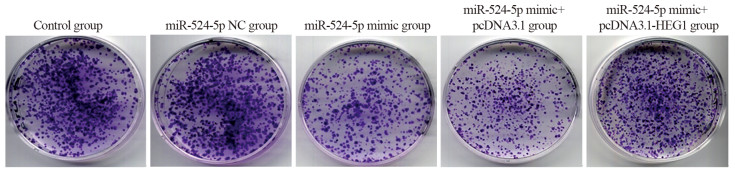
miR-524-5p NC组(385.13±17.12)和Control组细胞克隆形成数(387.88±16.04)比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);与miR-524-5p NC组比较,miR-524-5p mimic组的KYSE30细胞克隆形成数(143.22±10.85)明显降低(P=0.000),与miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1组(152.25±11.34)比较,miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1-HEG1组KYSE30细胞克隆形成数(293.10±13.74)明显上升(P=0.000),见图 2。
|
| 图 2 各转染组KYSE30细胞平板克隆形成情况 Figure 2 Plate clone formation of KYSE30 cells in each transfection group |
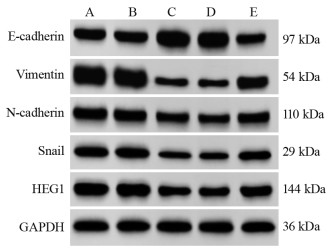
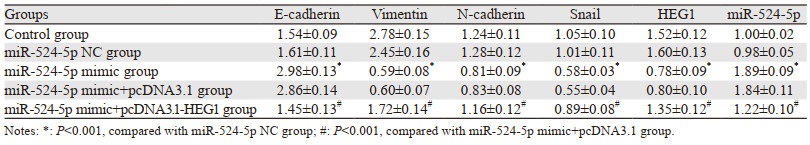
miR-524-5p NC组和Control组上皮标志蛋白E-cadherin、间质标志蛋白Vimentin、N-cadherin、Snail以及HEG1蛋白、miR-524-5p表达量比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);与miR-524-5p NC组比较,miR-524-5p mimic组上皮标志蛋白E-cadherin、miR-524-5p表达明显上调,间质标志蛋白Vimentin、N-cadherin、Snail及HEG1蛋白表达明显下调(均P=0.000),与miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1组比较,miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1-HEG1组上皮标志蛋白E-cadherin、miR-524-5p表达明显下调,间质标志蛋白Vimentin、N-cadherin、Snail及HEG1蛋白表达明显上调(均P=0.000),见图 3、表 4。
|
| A: Control group; B: miR-524-5p NC group; C: miR-524-5p mimic group; D: miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1 group; E: miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1-HEG1 group. 图 3 不同转染组中EMT相关蛋白和HEG1蛋白表达量 Figure 3 EMT-related protein and HEG1 protein expression in different transfection groups |
|
miR-524-5p NC组细胞划痕愈合率((42.59±2.33)%)和Control组((43.28±3.51)%)比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);与miR-524-5p NC组比较,miR-524-5p mimic组KYSE30细胞划痕愈合率((21.68±1.65)%)明显降低(P=0.000);与miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1组((22.15±1.44)%)比较,miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1-HEG1组KYSE30细胞划痕愈合率((34.25±1.65)%)明显升高(P=0.000),见图 4。
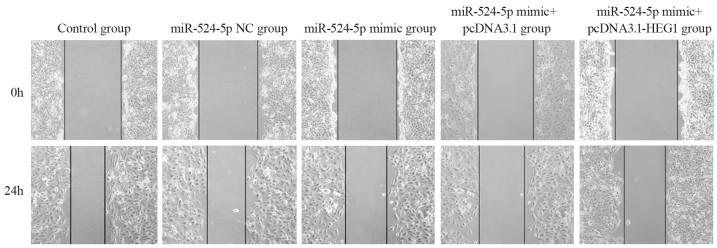
|
| 图 4 划痕实验检测各组KYSE30细胞迁移能力 Figure 4 Scratch assay of the migration ability of KYSE30 cells in each group |
miR-524-5p NC组(212.48±9.12)和Control组细胞侵袭数目(208.26±7.48)比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);与miR-524-5p NC组比较,miR-524-5p mimic组KYSE30细胞侵袭数目(89.35±6.95)明显降低(P=0.000),与miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1组(91.02±7.05)比较,miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1-HEG1组KYSE30细胞侵袭数目(149.75±8.47)明显升高(P=0.000),见图 5。
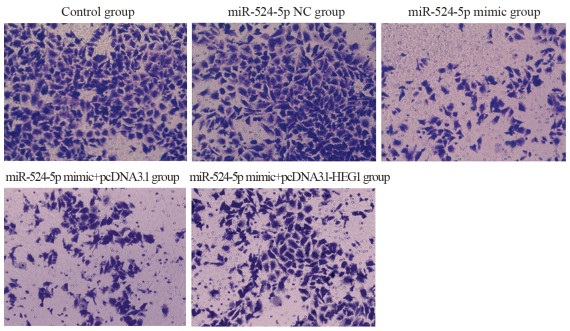
|
| 图 5 Transwell实验检测KYSE30细胞侵袭能力 Figure 5 Invasion ability of KYSE30 cells detected by Transwell assay |
miR-524-5p NC组和Control组细胞MMP2、MMP9蛋白表达比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);与miR-524-5p NC组比较,miR-524-5p mimic组KYSE30细胞侵袭迁移相关蛋白MMP2、MMP9表达明显降低(均P=0.000),与miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1组比较,miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1-HEG1组KYSE30细胞侵袭迁移相关蛋白MMP2、MMP9表达明显升高(均P=0.000),见图 6、表 5。
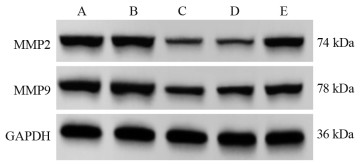
|
| A: Control group; B: miR-524-5p NC group; C: miR-524-5p mimic group; D: miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1 group; E: miR-524-5p mimic+pcDNA3.1-HEG1 group 图 6 侵袭迁移相关蛋白表达量 Figure 6 Expression of invasive- and migration-related proteins |
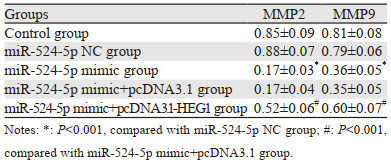
|
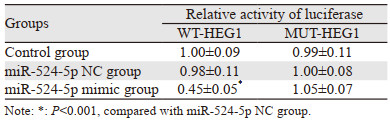
miR-524-5p可以靶向结合HEG1的3′UTR区域,见图 7。双荧光素酶报告基因实验结果,miR-524-5p mimic组与WT-HEG1共转染组细胞荧光素酶活性显著低于miR-524-5p NC组与WT-HEG1共转染组(P=0.000),miR-524-5p mimic组与MUT-HEG1共转染组的细胞荧光素酶活性与miR-524-5p NC组与MUT-HEG1共转染组差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),Control组、miR-524-5p NC组之间与WT-HEG1共转染和与MUT-HEG1共转染差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表 6。说明miR-524-5p可与HEG1的3′UTR区结合。

|
| 图 7 miR-524-5p与HEG1 3′UTR结合位点 Figure 7 Binding site of miR-524-5p to HEG1 3 UTR |
食管癌是致命性的恶性肿瘤之一,已发现多种miRNA可以通过靶向不同靶标来调节食管癌进展,如miR-33a-5p靶向DKK1抑制食管癌进展[9];miR-375通过阻断ERBB2/VEGFA通路抑制食管癌发展[10]等。miR-524-5p已被发现对多种肿瘤细胞的耐药性、迁移侵袭、EMT进展有抑制作用[11-13]。但尚未见miR-524-5p对食管癌细胞调节作用的相关性研究报道。本研究中首先通过miR-524-5p在食管癌四种不同细胞系和正常食管上皮细胞中的表达,确定了其在食管癌细胞中呈低表达。随后设置miR-524-5p过表达组探讨miR-524-5p对食管癌细胞增殖、迁移侵袭和EMT进程的影响。结果显示通过过表达miR-524-5p可以显著降低食管癌细胞的增殖能力和克隆形成,与以往研究的上调miR-524-5p可抑制胃癌细胞增殖具有一致性[14],证明了过表达miR-524-5p可抑制食管癌细胞的增殖。
完整的EMT癌细胞状态主要集中在复发癌组织中[15]。EMT是癌细胞侵袭和转移的根源,其发生过程主要表现为上皮标志蛋白E-cadherin下调,间质标志蛋白N-cadherin、Vimentin、Snail等上调[16-17]。EMT与恶性肿瘤的迁移、侵袭、化学耐药性相关[18]。因此,抑制癌细胞的EMT进程对于预防恶性肿瘤复发具有重大意义。miRNA可抑制恶性肿瘤的EMT进程,如miR-451抑制胶质瘤细胞的EMT和转移[19];miRNA-10a-5p抑制肝癌细胞的转移[20]。本研究结果显示,过表达miR-524-5p明显提升了KYSE30细胞的上皮标志蛋白E-cadherin表达水平,下调了间质标志蛋白N-cadherin、Vimentin、Snail的表达水平,表明过表达miR-524-5p抑制了KYSE30细胞EMT进程。癌细胞转移扩散是癌症患者死亡的主要原因,miR-524-5p过表达已被证明可以抑制乳腺癌细胞的侵袭和迁移[13]。MMP2、MMP9是与癌细胞侵袭和迁移密切相关的蛋白,抑制其表达可有效抑制癌细胞的转移扩散进程[21]。本研究划痕实验和Transwell实验结果均显示过表达miR-524-5p后,KYSE30细胞侵袭迁移能力减弱,且MMP2、MMP9蛋白表达下调,说明miR-524-5p过表达可抑制KYSE30细胞的侵袭迁移。
HEG1是一种新型黏蛋白样膜蛋白,与血管生成、胚胎发育及细胞-细胞连接密切相关,在促进肿瘤进展中发挥着重要作用。已有报道显示,HEG1在恶性间皮瘤[22]、肝细胞癌[7]、肺腺癌[23]中高表达,可作为肿瘤的诊断和治疗靶点。本研究通过GEPIA数据库对HEG1在EC中的表达进行分析发现HEG1在食管癌肿瘤组织中表达水平显著高于正常组织;进一步分析显示,HEG1在四种不同食管癌细胞系中的表达均高于正常食管上皮细胞,提示HEG1可能在食管癌中充当促癌基因。使用Stabase数据库对miR-524-5p的潜在靶基因进行预测,发现HEG1与miR-524-5p存在互补的结合位点,可能为miR-524-5p的下游靶基因。双荧光素酶报告基因检测证实,miR-524-5p可与HEG1的3′UTR区结合;qRT-PCR和Western blot结果显示,过表达miR-524-5p可下调HEG1表达,表明miR-524-5p可负向调控HEG1表达。因此本研究推测,HEG1可能为miR-524-5p调节KYSE30细胞恶性生物学行为的重要靶蛋白。为了验证此推测,本研究在过表达miR-524-5p的基础上采用质粒转染上调HEG1表达,结果显示上调HEG1表达可明显减弱过表达miR-524-5p对KYSE30细胞恶性生物学行为的抑制作用,提示过表达miR-524-5p可能通过下调HEG1抑制KYSE30细胞的增殖、EMT进程和侵袭迁移。
综上所述,miR-524-5p在食管癌细胞和组织中低表达,过表达miR-524-5p可以负向调节HEG1在食管癌细胞系KYSE30细胞中的表达,减轻KYSE30细胞的增殖、EMT进程和侵袭迁移能力。然而本研究仅开展了细胞实验,随后将在动物实验中进行验证,以期明确miR-524-5p在食管癌进展中的作用。
利益冲突声明:
所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
作者贡献:
王娅菲:实验操作、数据整理及文章撰写
耿天祥、陈林林:实验操作、数据整理及分析
李治国:数据分析
李世朋:实验设计及文稿审校
| [1] |
Watanabe M, Otake R, Kozuki R, et al. Recent progress in multidisciplinary treatment for patients with esophageal cancer[J]. Surg Today, 2020, 50(1): 12-20. DOI:10.1007/s00595-019-01878-7 |
| [2] |
Uhlenhopp DJ, Then EO, Sunkara T, et al. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: update in global trends, etiology and risk factors[J]. Clin J Gastroenterol, 2020, 13(6): 1010-1021. DOI:10.1007/s12328-020-01237-x |
| [3] |
Yang YM, Hong P, Xu WW, et al. Advances in targeted therapy for esophageal cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020, 5(1): 229. DOI:10.1038/s41392-020-00323-3 |
| [4] |
Zhao Y, Xu L, Wang X, et al. A novel prognostic mRNA/miRNA signature for esophageal cancer and its immune landscape in cancer progression[J]. Mol Oncol, 2021, 15(4): 1088-1109. DOI:10.1002/1878-0261.12902 |
| [5] |
Bian W, Li Y, Zhu H, et al. miR-493 by regulating of c-Jun targets Wnt5a/PD-L1-inducing esophageal cancer cell development[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2021, 12(10): 1579-1588. DOI:10.1111/1759-7714.13950 |
| [6] |
Yao W, Jia X, Xu L, et al. MicroRNA-2053 involves in the progression of esophageal cancer by targeting KIF3C[J]. Cell Cycle, 2021, 20(12): 1163-1172. DOI:10.1080/15384101.2021.1929675 |
| [7] |
Zhao YR, Wang JL, Xu C, et al. HEG1 indicates poor prognosis and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma invasion, metastasis, and EMT by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2019, 133(14): 1645-1662. DOI:10.1042/CS20190225 |
| [8] |
Dewdney B, Hebbard L. A novel function for HEG1 in promoting metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2019, 133(19): 2019-2022. DOI:10.1042/CS20190704 |
| [9] |
Song Q, Liu H, Li C, et al. miR-33a-5p inhibits the progression of esophageal cancer through the DKK1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2021, 13(16): 20481-20494. |
| [10] |
Ren S, Tan X, Fu MZ, et al. Downregulation of miR-375 contributes to ERBB2-mediated VEGFA overexpression in esophageal cancer[J]. J Cancer, 2021, 12(23): 7138-7146. DOI:10.7150/jca.63836 |
| [11] |
Nguyen MT, Lin CH, Liu SM, et al. miR-524-5p reduces the progression of the BRAF inhibitor-resistant melanoma[J]. Neoplasia, 2020, 22(12): 789-799. DOI:10.1016/j.neo.2020.10.009 |
| [12] |
Li X, Li Z, Zhu Y, et al. miR-524-5p inhibits angiogenesis through targeting WNK1 in colon cancer cells[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2020, 318(4): G827-G839. DOI:10.1152/ajpgi.00369.2019 |
| [13] |
Jin T, Zhang Y, Zhang T. miR-524-5p Suppresses Migration, Invasion, and EMT Progression in Breast Cancer Cells Through Targeting FSTL1[J]. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2020, 35(10): 789-801. |
| [14] |
Zhu CY, Meng FQ, Liu J. MicroRNA-524-5p suppresses cell proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis in gastric cancer by regulating CASP3[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23(18): 7968-7977. |
| [15] |
Lüönd F, Sugiyama N, Bill R, et al. Distinct contributions of partial and full EMT to breast cancer malignancy[J]. Dev Cell, 2021, 56(23): 3203-3221. e11. DOI:10.1016/j.devcel.2021.11.006 |
| [16] |
Na TY, Schecterson L, Mendonsa AM, et al. The functional activity of E-cadherin controls tumor cell metastasis at multiple steps[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2020, 117(11): 5931-5937. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1918167117 |
| [17] |
Chen P, Li X, Zhang R, et al. Combinative treatment of β-elemene and cetuximab is sensitive to KRAS mutant colorectal cancer cells by inducing ferroptosis and inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transformation[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(11): 5107-5119. DOI:10.7150/thno.44705 |
| [18] |
Pan G, Liu Y, Shang L, et al. EMT-associated microRNAs and their roles in cancer stemness and drug resistance[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2021, 41(3): 199-217. DOI:10.1002/cac2.12138 |
| [19] |
Nan Y, Guo L, Lu Y, et al. miR-451 suppresses EMT and metastasis in glioma cells[J]. Cell Cycle, 2021, 20(13): 1270-1278. DOI:10.1080/15384101.2021.1933303 |
| [20] |
Shen D, Zhao HY, Gu AD, et al. miRNA-10a-5p inhibits cell metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting SKA1[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2021, 37(9): 784-794. DOI:10.1002/kjm2.12392 |
| [21] |
Wang J, Cai H, Liu Q, et al. Cinobufacini Inhibits Colon Cancer Invasion and Metastasis via Suppressing Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway and EMT[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2020, 48(3): 703-718. DOI:10.1142/S0192415X20500354 |
| [22] |
Naso JR, Tsuji S, Churg A. HEG1 is a highly specific and sensitive marker of epithelioid malignant mesothelioma[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2020, 44(8): 1143-1148. DOI:10.1097/PAS.0000000000001469 |
| [23] |
Zou X, Zhang Y, Wang N, et al. HEG1 as a novel potential biomarker for the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Med, 2023, 12(3): 3288-3298. DOI:10.1002/cam4.5081 |
 2023, Vol. 50
2023, Vol. 50