文章信息
- 茶黄素类天然产物抗肿瘤机制的研究进展
- Research Progress on Anti-Tumor Mechanism of Theaflavins Natural Products
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2022, 49(8): 820-826
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2022, 49(8): 820-826
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2022.21.1292
- 收稿日期: 2021-11-09
- 修回日期: 2022-02-23
2. 730030 兰州,兰州大学第二医院萃英生物医学研究中心
2. Cuiying Biomedical Research Center, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, China
癌症是人类高致死性疾病之一,其每年发病率和死亡率居高不下。最新癌症统计报告显示,仅2020年全球就有1 930万新发及1 000万死亡病例[1]。目前癌症的治疗仍以手术为主,并结合化疗、放疗、药物靶向治疗和免疫疗法等辅助性治疗,但肿瘤复发问题使得癌症患者的五年平均生存率不到40.5%[2-3]。因此,进一步开发有效治疗癌症的新方法迫在眉睫。茶黄素是红茶发酵中形成的天然茶色素,分子质量为564.49,占红茶干重的2%~6%,是红茶质量和等级的重要决定因素[4-5]。研究发现,茶黄素是具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗病毒和抗癌作用的一类天然产物,可显著抑制癌细胞的生长、转移和侵袭等,当作为药物增敏剂与化疗药物联合应用时可显著改善肿瘤化疗耐药问题[6-9]。因此,茶黄素类天然产物近年来逐渐成为新型抗肿瘤药物研发的热点。然而茶黄素类参与的抗肿瘤生物学过程较多,作用机制较为复杂,因此本文将基于茶黄素的抗肿瘤效果对其作用机制进行分析,以明确其调控网络,为茶黄素类抗癌药物的开发提供思路。
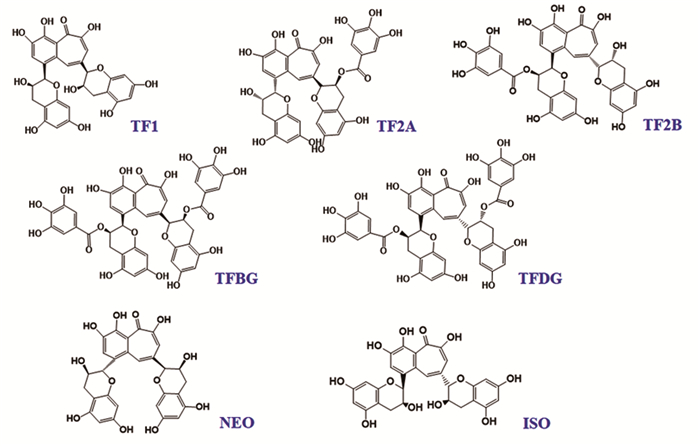
1 茶黄素类天然产物的分类及结构茶黄素类是具有苯并卓酚酮结构的天然化合物,多从红茶中提取或经茶中的多酚氧化酶或过氧化物酶与绿茶儿茶素结合生成,是红茶中发挥生物学活性的主要物质之一[6]。茶黄素类天然产物主要包括茶黄素(TF1)、茶黄素-3-没食子酸酯(TF2A)、茶黄素-3'-没食子酸酯(TF2B)、茶黄素-3, 3'-没食子酸酯(TF3, TFDG)、茶黄素-3,3'-双没食子酸(TFBG)、新茶黄素(NEO)和异茶黄素(ISO)等,见图 1[7]。茶黄素类天然产物在小肠中吸收很差,对结肠细菌的降解具有相对抵抗力,但是能通过促进双歧杆菌、副杆菌、拟杆菌、粪杆菌、抑制梭杆菌等调节肠道微生物群[10-11]。
|
| TF1: Theaflavin; TF2A: Theaflavin-3-gallate; TF2B: Theaflavin 3'-gallate; TFBG: Theaflavine-3, 3'-digallate; TFDG: Theaflavin 3, 3'-digallate; NEO: Neotheaflavin; ISO: Isotheaflavin. 图 1 茶黄素类天然产物的分子结构 Figure 1 Molecular structure of theaflavins natural products |
细胞凋亡是指细胞的程序性死亡,包括内源性凋亡和外源性凋亡[12]。内源性凋亡主要通过调控线粒体,而外源性凋亡通过形成死亡诱导信号复合物,进而激活裂解下游蛋白引起凋亡,内外源性凋亡通过相互联系,能有效扩大凋亡信号[13]。研究[14]发现TF3一方面通过增加检查点激酶2(chk2)的表达,上调Bax和下调Bcl-xL的表达,使细胞以p53不依赖的方式启动内源性凋亡,另一方面通过上调死亡受体DR5和Fas蛋白水平的方式触发外源性凋亡,最终促进肿瘤细胞凋亡。Tu等[15]研究发现,TF3对顺铂耐药细胞具有协同治疗效果。通过检测研究发现TF3主要是通过提高Bax、Bad和cleaved caspase-9蛋白水平,下调Bcl-xL的表达,经内源性途径促进细胞凋亡。并通过增加DR5、FADD和cleaved caspase-8的蛋白表达,经外源性途径促进细胞凋亡。Lahiry等[16]通过对p53突变的肿瘤细胞MDA-MB-231的研究发现,一方面茶黄素类天然产物激活jun N端激酶(JNK),引起Fas的上调和Fas-FADD的相互作用,使t-bid形成并刺激线粒体而引起凋亡;另一方面茶黄素类天然产物可抑制生长信号通路中PI3K/AKT/p-Bad的磷酸化而抑制肿瘤的生长。茶黄素通过G2/M期细胞周期停滞和诱导细胞凋亡而抑制结肠癌细胞增殖[17]。因此,茶黄素类化合物可同时促进肿瘤细胞的内源性及外源性凋亡,这种促进作用可能主要通过上调促凋亡相关蛋白和受体的表达、下调抗凋亡蛋白的表达来影响细胞凋亡信号通路的进行。
2.2 茶黄素可诱导肿瘤细胞有丝分裂阻滞此外,茶黄素亦可诱发肿瘤细胞的有丝分裂阻滞进而起到抗肿瘤的效果[18]。细胞周期是指细胞从一次有丝分裂结束至下一次有丝分裂完成的全过程。细胞周期蛋白(cyclin)和周期蛋白依赖性激酶(CDK)是启动、促进和完成细胞周期事件的关键调控分子[19]。通过流式细胞实验和蛋白印迹实验测定,TF3不仅能通过降低A2780/CP70细胞中cyclin A2、cyclin D1、cyclin E1、CDK2和CDK4蛋白的表达,导致细胞停滞在G1和S期;此外,TF3还能增加p27的表达使细胞停滞在G0和G1期。通过对顺铂耐药细胞研究时发现,TF3可显著抑制CyclinB的生成使细胞周期停滞在G2期[9, 14-15]。通过对茶黄素类研究[20]发现,TFs处理后的HeLa细胞纤维结构解聚,细胞周期阻滞在G2/M期,其IC50值为110 µg/ml。50 µg/ml TF1和20 µg/ml EGCG的组合具有较强的微管解聚作用,可有效下调PI3K/Akt信号通路的进行,诱导线粒体凋亡信号的发生,使细胞更多地停留在G2/M期[21]。TFs通过上调抑癌基因p15和p18蛋白,抑制周期蛋白D1、D3和CDK4、CDK6,使细胞周期阻滞于G0、G1期[22]。在结肠癌中,孵育过的TFDG使肿瘤细胞停滞于G2期,并通过增加p53和p21、caspase-3的表达促进肿瘤细胞的凋亡[23]。研究发现,TFBG可通过抑制SHCBP1与PLK1的结合,抑制肿瘤细胞有丝分裂,与曲妥珠单抗联用后,可显著抑制胃癌的生长[24]。因此,茶黄素类天然化合物主要通过降低细胞周期蛋白和周期蛋白依赖性激酶的表达,使细胞停滞在细胞间期,阻止细胞的大量非正常增殖。
2.3 茶黄素可作为免疫修复剂抑制肿瘤进展免疫治疗是指在通过激活或促进免疫系统改善抗肿瘤的免疫反应,进而达到治疗甚至长期缓解癌症的重要治疗方法[25]。肿瘤细胞脱落的PGE2能诱导CD4+T细胞的凋亡,而茶黄素类通过恢复CD4+T细胞的IL-2受体及Jak-3/Stat-5A信号通路,升高Bcl-2/Bax比率,提高癌症患者免疫修复力,从而避免PGE2诱导的免疫细胞凋亡[26]。
综上所述,茶黄素类化合物可通过促进肿瘤细胞的内源性及外源性凋亡促使肿瘤细胞死亡,并通过诱导肿瘤细胞阻滞于有丝分裂间期进而抑制肿瘤细胞增殖;更重要的是,茶黄素还可通过恢复CD4+T细胞活性而激活肿瘤免疫以抑制肿瘤进展。
3 茶黄素类化合物抑制肿瘤进展相关的信号通路 3.1 MAPK、PI3K/AKT及Hedgehog通路MAPK通路调节着细胞的生长、分化、应激、炎性反应等多种生理、病理效应,包括有丝分裂原ERK,应激反应性JNK和p38[27]。研究发现[28]TF2A通过MAPK中的p38、Erk和JNK途径,而TF2B主要通过MAPK中的Erk途径诱导细胞凋亡和G1期阻滞,进而抑制对顺铂耐药的卵巢癌细胞生长。Gao等[29]用免疫荧光统计分析发现,TF3通过ERK、JNK和p38通路诱导肺腺癌SPC-A-1细胞凋亡,通过ERK和JNK途径诱导食管癌Eca-109细胞凋亡,而这种凋亡作用主要激活了caspase-3和caspase-9,抗坏血酸能加强这种作用。Zhang等[30]用小鼠B16F10细胞系证明了TF1通过激活p53和JNK[31]信号转导以及抑制MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT信号转导介导抗黑色素瘤的作用。对于不同的癌细胞,茶黄素类能影响不同的MAPK路径激活下游相应蛋白,进而达到抑制肿瘤细胞增殖并增敏耐药细胞株的作用。
AKT信号通路在细胞存活和凋亡中起着至关重要的作用,正在成为癌症预防和治疗的靶向重要通路[32]。Halder等[33]研究发现,茶黄素类通过抑制Akt信号通路抑制白血病细胞生长,一方面茶黄素能抑制其下游靶标的表达如Gsk-3β、细胞周期蛋白D1和CDK2,增加叉头转录因子1(FOXO1)和p27的表达水平,另一方面茶黄素对其上游热休克蛋白(Hsp90)的抑制也减弱了Akt信号。还有研究表明茶黄素[34]能通过靶向RET致癌基因诱导甲状腺髓样癌细胞凋亡,诱导凋亡的方式主要有2种:使PI3K/Akt/Bad途径停滞,导致线粒体跨膜电位(MTP)丢失、细胞色素-c释放和caspase-3和caspase-9的激活,以及通过抑制Ras/Raf/ERK来维持p38MAPK/caspase-8/caspase-3通路。茶黄素类天然产物不仅能通过影响Akt通路上游与下游的蛋白抑制肿瘤增生,还能影响MAPK通路诱导癌细胞凋亡。
在Hedgehog(Hh)信号通路中,Hedgehog信号分子可与靶细胞膜上的两种受体Patched(Ptc)和Smoothened(Smo)结合,其中Patched是由抑癌基因编码,Smo由原癌基因编码,主要的核内转录因子之一是Gli。该通路的异常激活与肿瘤的发生发展密切相关[35]。Sur等[36-37]通过动物实验研究发现EGCG和TF1可上调Patched和下调Smo、Gli1的表达,进而减少靶基因Cyclin D1、cMyc、表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)的表达以及上调E-钙黏蛋白等。因此,茶黄素可通过抑制Hedgehog信号通路的传递进而下调下游靶基因的表达进而抑制肿瘤发生发展。
综上所述,茶黄素类天然产物不仅可以通过MAPK、AKT、Hedgehog各个通路诱导细胞凋亡,影响细胞有丝分裂使细胞停滞于各个细胞周期,还能强化通路之间的联系,增强肿瘤细胞的抑制效果。
3.2 茶黄素经NF-κB信号通路抑制肿瘤NF-κB是一种转录因子,存在于胞质中,并被IκB结合抑制。磷酸化的IκB释放激活的二聚体NF-κB,NF-κB进入细胞核并与操纵基因结合,调控肿瘤生长[38]。Adhikary等[39]研究发现茶黄素类能通过增加p53的磷酸化,抑制肿瘤的转移。通过机制研究发现,TFs类化合物会增加线粒体内活性氧(ROS),进而诱导p38MAPK介导的p53在第15位丝氨酸磷酸化,使得磷酸化的p53与IKKβ相互作用,减少IκBα的磷酸化并抑制核转录因子NF-κB入核,从而使MMP-2和MMP-9表达下降进而有效抑制癌细胞转移。此外,TFs也可通过减少IκB的磷酸化以及Akt和Cox-2的表达,抑制转录因子NF-κB入核,以浓度和时间依赖性的方式促进肿瘤凋亡和抑制肿瘤的增生[40]。综上所述,茶黄素可以通过NF-κB发挥促凋亡和抑制肿瘤细胞转移的作用。
3.3 茶黄素与免疫相关的信号通路JAK/STAT信号通路主要参与细胞增殖、分化、凋亡和免疫调节等生物学过程,现在研究主要集中于该通路在影响炎性反应和肿瘤疾病形成等方面[41]。茶黄素不仅能通过抑制NF-κB、MAPK的激活和TNF-α、IL-1、IL-6的表达起到抗炎作用[42],更重要的是通过抑制肿瘤细胞分泌免疫抑制细胞因子TGF-β和IL-10,促进免疫细胞分泌IL-2和TNF-γ[43],而增强免疫监视启动细胞免疫杀伤作用。Bhattacharyya等发现[44],茶黄素类天然产物抑制荷瘤小鼠脾淋巴细胞中p53和Bax表达,促进Bcl-2的表达,改变了Bcl-2/Bax的比值,使免疫细胞免受肿瘤细胞诱导的细胞凋亡促进了细胞的免疫修复。茶黄素类天然产物通过IL-2、IL-7受体恢复JAK-3/STAT-5A信号通路,升高Bcl-2/Bax比率,促进了T细胞的存活、增殖和分化,增强了细胞的免疫监视与杀伤作用[26, 45]。
3.4 茶黄素经Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路抑制肿瘤Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路在肿瘤的发生、发展中发挥着重要作用[46]。当Wnt与表面受体Frizzled(Fzd)结合后,活化散乱蛋白Disheveled(Dsh),阻止β-Catenin的磷酸化降解,导致大量的β-Catenin在胞质内积聚,并移向细胞核内与转录因子TCF/LEF结合,激活TCF转录活性,调节靶基因的表达[47]。Pan等[48]研究发现茶黄素TF3可通过下调β-Catenin的表达,抑制Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路,进而下调LEF-1和C-myc蛋白水平的表达,最终抑制卵巢癌细胞A2780、CP70和OVCAR3的增殖。无独有偶,Sur等[36]通过研究TF1和EGCG对N-硝基二乙胺诱导鼠舌癌和肝癌的影响时发现,TF1和EGCG均能够抑制β-Catenin的入核,减少β-Catenin mRNA的稳定性和上调拮抗sFRP1和APC的表达。由此可见,茶黄素类天然产物可通过促进β-Catenin的降解以及抑制β-Catenin的入核进而抑制肿瘤发生,此外,由于Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路与肿瘤细胞的干性有关[36],因此,茶黄素类天然产物可能通过抑制肿瘤细胞的自我更新而起到抗肿瘤的作用。
3.5 茶黄素经其他信号通路抑制肿瘤最新研究[8]表明TF3对顺铂耐药性细胞具有一定的增敏效果,TF3不仅能增加铜转运蛋白1(CTR1)的表达,增强顺铂的摄取,而且还能通过减少谷胱甘肽(GSH)的表达以减少顺铂的外排,通过细胞质中GSH与顺铂的结合可增加顺铂的入核量,更有效地损伤肿瘤细胞的DNA。Gao等[49]研究发现,低剂量的TF3可以通过影响Akt/mTOR/P70s6k/4E-BP1和Notch-1/C-myc两条信号通路,下调HIF-1α、VEGF的表达从而抑制肿瘤血管形成;而高剂量的TF3则能抑制肿瘤生长。DNA甲基转移酶(DNMT)是调控表观遗传的重要酶,茶黄素作为DNMT抑制剂,对结肠癌的生长具有显著的抑制作用[50]。
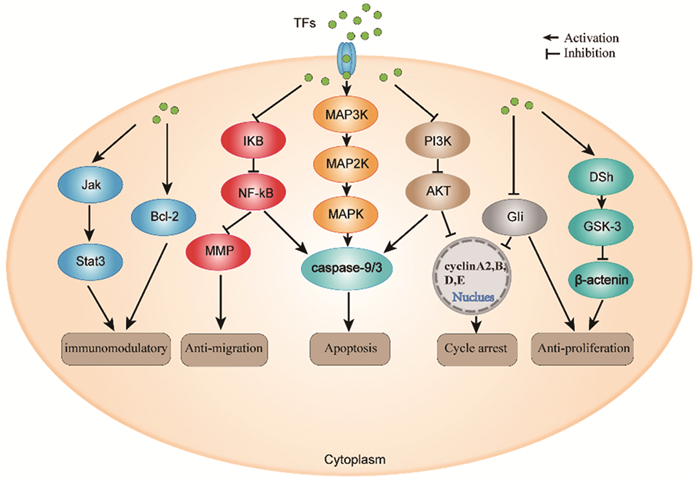
综上所述,茶黄素可能通过MAPK、PI3K/AKT及Hedgehog通路促进肿瘤细胞的凋亡和细胞周期阻滞,通过NF-κB通路抑制转移,通过JAK/STAT信号通路恢复肿瘤的免疫监视,通过Wnt/β-Catenin影响到肿瘤干性和自我更新,进而起到抑制肿瘤发生发展的作用,见表 1、图 2。
|
| 图 2 茶黄素类天然产物在信号通路中的作用 Figure 2 Role of theaflavins natural products in signal pathways |
肿瘤的发生发展是细胞内信号通路异常活化以及炎性反应、损伤等综合因素所致。本文通过综述茶黄素类天然产物在肿瘤中的抑制作用以及作用的信号通路,对茶黄素在肿瘤中的功能作用有了全面的认识。茶黄素类天然产物可作用于多个信号通路中的多个靶点,通过干扰细胞信号通路的进行,可有效抑制癌细胞增殖、促进癌细胞的凋亡、阻断细胞周期循环及恢复肿瘤免疫系统等。作为化疗、靶向治疗增敏剂,茶黄素类与药物的联合使用可显著降低药物的毒副作用,增强药物的疗效,在癌症的治疗方面具有广阔的应用前景。然而,由于茶黄素类性质不稳定、易降解的特性,目前研究还停留在细胞、动物实验阶段。如何更好地提高茶黄素类物质的稳定性、生物利用度以及开展肿瘤治疗的临床试验是目前和将来研究的重中之重。
作者贡献:
张雪:文献查阅、论文撰写
尹君丽、王稼祥:文献检索
石文贵:论文修改
焦作义:整体思路设计及论文指导
| [1] |
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. DOI:10.3322/caac.21660 |
| [2] |
Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10251): 635-648. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31288-5 |
| [3] |
Wu C, Li M, Meng H, et al. Analysis of status and countermeasures of cancer incidence and mortality in China[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2019, 62(5): 640-647. DOI:10.1007/s11427-018-9461-5 |
| [4] |
Luo T, Jiang JG. Anticancer Effects and Molecular Target of Theaflavins from Black Tea Fermentation in Vitro and in Vivo[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2021, 69(50): 15052-15065. DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.1c05313 |
| [5] |
刘昌伟, 张梓莹, 王俊懿, 等. 茶黄素生物学活性研究进展[J]. 食品科学, 2021. [网络首发] [Liu CW, Zhang ZY, Wang JY, et al. Research Progress on bioactivity of theaflavins[J]. Shi Pin Ke Xue, 2021. [Online ahead of print]]
|
| [6] |
Takemoto M, Takemoto H. Synthesis of Theaflavins and Their Functions[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(4): 918. DOI:10.3390/molecules23040918 |
| [7] |
O'Neill EJ, Termini D, Albano A, et al. Anti-Cancer Properties of Theaflavins[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(4): 987. DOI:10.3390/molecules26040987 |
| [8] |
Pan H, Kim E, Rankin GO, et al. Theaflavin-3, 3'-Digallate Enhances the Inhibitory Effect of Cisplatin by Regulating the Copper Transporter 1 and Glutathione in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(1): 117. DOI:10.3390/ijms19010117 |
| [9] |
Pan H, Li J, Rankin GO, et al. Synergistic effect of black tea polyphenol, theaflavin-3, 3'-digallate with cisplatin against cisplatin resistant human ovarian cancer cells[J]. J Funct Foods, 2018, 46: 1-11. DOI:10.1016/j.jff.2018.04.037 |
| [10] |
Liu Z, de Bruijn WJC, Bruins ME, et al. Microbial Metabolism of Theaflavin-3, 3'-digallate and Its Gut Microbiota Composition Modulatory Effects[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2021, 69(1): 232-245. DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06622 |
| [11] |
Chen T, Yang CS. Biological fates of tea polyphenols and their interactions with microbiota in the gastrointestinal tract: implications on health effects[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2020, 60(16): 2691-2709. DOI:10.1080/10408398.2019.1654430 |
| [12] |
Balaji S, Terrero D, Tiwari AK, et al. Alternative approaches to overcome chemoresistance to apoptosis in cancer[J]. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol, 2021, 126: 91-122. |
| [13] |
Carneiro BA, El-Deiry WS. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2020, 17(7): 395-417. DOI:10.1038/s41571-020-0341-y |
| [14] |
Gao Y, Yin J, Tu Y, et al. Theaflavin-3, 3'-Digallate Suppresses Human Ovarian Carcinoma OVCAR-3 Cells by Regulating the Checkpoint Kinase 2 and p27 kip1 Pathways[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(4): 673. DOI:10.3390/molecules24040673 |
| [15] |
Tu Y, Kim E, Gao Y, et al. Theaflavin-3, 3'-digallate induces apoptosis and G2 cell cycle arrest through the Akt/MDM2/p53 pathway in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer A2780/CP70 cells[J]. Int J Oncol, 2016, 48(6): 2657-2665. DOI:10.3892/ijo.2016.3472 |
| [16] |
Lahiry L, Saha B, Chakraborty J, et al. Theaflavins target Fas/caspase-8 and Akt/pBad pathways to induce apoptosis in p53-mutated human breast cancer cells[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2010, 31(2): 259-268. DOI:10.1093/carcin/bgp240 |
| [17] |
Imran A, Butt MS, Xiao H, et al. Inhibitory effect of black tea (Camellia sinensis) theaflavins and thearubigins against HCT 116 colon cancer cells and HT 460 lung cancer cells[J]. J Food Biochem, 2019, 43(5): e12822. DOI:10.1111/jfbc.12822 |
| [18] |
Xu XY, Zhao CN, Cao SY, et al. Effects and mechanisms of tea for the prevention and management of cancers: An updated review[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2020, 60(10): 1693-1705. DOI:10.1080/10408398.2019.1588223 |
| [19] |
Petroni G, Formenti SC, Chen-Kiang S, et al. Immunomodulation by anticancer cell cycle inhibitors[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2020, 20(11): 669-679. DOI:10.1038/s41577-020-0300-y |
| [20] |
Chakrabarty S, Das A, Bhattacharya A, et al. Theaflavins depolymerize microtubule network through tubulin binding and cause apoptosis of cervical carcinoma HeLa cells[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2011, 59(5): 2040-2048. DOI:10.1021/jf104231b |
| [21] |
Chakrabarty S, Nag D, Ganguli A, et al. Theaflavin and epigallocatechin-3-gallate synergistically induce apoptosis through inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling upon depolymerizing microtubules in HeLa cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(4): 5987-6003. DOI:10.1002/jcb.27886 |
| [22] |
Tan Q, Peng L, Huang Y, et al. Structure-Activity Relationship Analysis on Antioxidant and Anticancer Actions of Theaflavins on Human Colon Cancer Cells[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67(1): 159-170. DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05369 |
| [23] |
Ding Y, Chen B, Gao Z, et al. Pre-treated theaflavin-3, 3'-digallate has a higher inhibitory effect on the HCT116 cell line[J]. Food Nutr Res, 2017, 61(1): 1400340. DOI:10.1080/16546628.2017.1400340 |
| [24] |
Shi W, Zhang G, Ma Z, et al. Hyperactivation of HER2-SHCBP1-PLK1 axis promotes tumor cell mitosis and impairs trastuzumab sensitivity to gastric cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 2812. DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-23053-8 |
| [25] |
Zhang Y, Zhang Z. The history and advances in cancer immunotherapy: understanding the characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic implications[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2020, 17(8): 807-821. DOI:10.1038/s41423-020-0488-6 |
| [26] |
Chattopadhyay S, Bhattacharyya S, Saha B, et al. Tumor-shed PGE(2) impairs IL2Rgammac-signaling to inhibit CD4 T cell survival: regulation by theaflavins[J]. PLoS One, 2009, 4(10): e7382. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0007382 |
| [27] |
Lee S, Rauch J, Kolch W. Targeting MAPK Signaling in Cancer: Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Sensitivity[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(3): 1102. DOI:10.3390/ijms21031102 |
| [28] |
Pan H, Wang F, Rankin GO, et al. Inhibitory effect of black tea pigments, theaflavin-3/3'-gallate against cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells by inducing apoptosis and G1 cell cycle arrest[J]. Int J Oncol, 2017, 51(5): 1508-1520. DOI:10.3892/ijo.2017.4145 |
| [29] |
Gao Y, Li W, Jia L, et al. Enhancement of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and theaflavin-3-3'-digallate induced apoptosis by ascorbic acid in human lung adenocarcinoma SPC-A-1 cells and esophageal carcinoma Eca-109 cells via MAPK pathways[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2013, 438(2): 370-374. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.07.078 |
| [30] |
Zhang L, Meng S, Yan B, et al. Anti-Proliferative, Pro-Apoptotic, Anti-Migrative and Tumor-Inhibitory Effects and Pleiotropic Mechanism of Theaflavin on B16F10 Melanoma Cells[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2021, 14: 1291-1304. DOI:10.2147/OTT.S286350 |
| [31] |
Zhang L, Yan B, Meng S, et al. Theaflavin Induces Apoptosis of A375 Human Melanoma Cells and Inhibits Tumor Growth in Xenograft Zebrafishes Through P53- and JNK-Related Mechanism[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 1317. DOI:10.3389/fphar.2020.01317 |
| [32] |
Tewari D, Patni P, Bishayee A, et al. Natural products targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in cancer: A novel therapeutic strategy[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 80: 1-17. DOI:10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.008 |
| [33] |
Halder B, Das Gupta S, Gomes A. Black tea polyphenols induce human leukemic cell cycle arrest by inhibiting Akt signaling: possible involvement of Hsp90, Wnt/β-catenin signaling and FOXO1[J]. FEBS J, 2012, 279(16): 2876-2891. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08668.x |
| [34] |
Mazumdar M, Adhikary A, Chakraborty S, et al. Targeting RET to induce medullary thyroid cancer cell apoptosis: an antagonistic interplay between PI3K/Akt and p38MAPK/caspase-8 pathways[J]. Apoptosis, 2013, 18(5): 589-604. DOI:10.1007/s10495-013-0803-0 |
| [35] |
Doheny D, Manore SG, Wong GL, et al. Hedgehog Signaling and Truncated GLI1 in Cancer[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(9): 2114. DOI:10.3390/cells9092114 |
| [36] |
Sur S, Pal D, Mandal S, et al. Tea polyphenols epigallocatechin gallete and theaflavin restrict mouse liver carcinogenesis through modulation of self-renewal Wnt and hedgehog pathways[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2016, 27: 32-42. DOI:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.08.016 |
| [37] |
Sur S, Pal D, Roy R, et al. Tea polyphenols EGCG and TF restrict tongue and liver carcinogenesis simultaneously induced by N-nitrosodiethylamine in mice[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2016, 300: 34-46. DOI:10.1016/j.taap.2016.03.016 |
| [38] |
Khan H, Ullah H, Castilho PCMF, et al. Targeting NF-κB signaling pathway in cancer by dietary polyphenols[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2020, 60(16): 2790-2800. DOI:10.1080/10408398.2019.1661827 |
| [39] |
Adhikary A, Mohanty S, Lahiry L, et al. Theaflavins retard human breast cancer cell migration by inhibiting NF-kappaB via p53-ROS cross-talk[J]. FEBS Lett, 2010, 584(1): 7-14. DOI:10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.081 |
| [40] |
Singh M, Singh R, Bhui K, et al. Tea polyphenols induce apoptosis through mitochondrial pathway and by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB and Akt activation in human cervical cancer cells[J]. Oncol Res, 2011, 19(6): 245-257. DOI:10.3727/096504011X13021877989711 |
| [41] |
Xin P, Xu X, Deng C, et al. The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 80: 106210. DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106210 |
| [42] |
Liu W, Li J. Theaflavin-3, 3'-Digallate Attenuates Rheumatoid Inflammation in Mice Through the Nuclear Factor-κB and MAPK Pathways[J]. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz), 2019, 67(3): 153-160. DOI:10.1007/s00005-019-00536-7 |
| [43] |
Mandal D, Bhattacharyya S, Lahiry L, et al. Black tea-induced decrease in IL-10 and TGF-beta of tumor cells promotes Th1/Tc1 response in tumor bearer[J]. Nutr Cancer, 2007, 58(2): 213-221. DOI:10.1080/01635580701328503 |
| [44] |
Bhattacharyya A, Mandal D, Lahiry L, et al. Black tea protects immunocytes from tumor-induced apoptosis by changing Bcl-2/Bax ratio[J]. Cancer Lett, 2004, 209(2): 147-154. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2003.12.025 |
| [45] |
Mandal D, Lahiry L, Bhattacharyya A, et al. Tumor-induced thymic involution via inhibition of IL-7R alpha and its JAK-STAT signaling pathway: protection by black tea[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2006, 6(3): 433-444. DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2005.09.005 |
| [46] |
Zhang Y, Wang X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2020, 13(1): 165. DOI:10.1186/s13045-020-00990-3 |
| [47] |
Sferrazza G, Corti M, Brusotti G, et al. Nature-derived compounds modulating Wnt/ β -catenin pathway: a preventive and therapeutic opportunity in neoplastic diseases[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2020, 10(10): 1814-1834. DOI:10.1016/j.apsb.2019.12.019 |
| [48] |
Pan H, Kim E, Rankin GO, et al. Theaflavin-3, 3'-digallate inhibits ovarian cancer stem cells via suppressing Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway[J]. J Funct Foods, 2018, 50: 1-7. DOI:10.1016/j.jff.2018.09.021 |
| [49] |
Gao Y, Rankin GO, Tu Y, et al. Theaflavin-3, 3'-digallate decreases human ovarian carcinoma OVCAR-3 cell-induced angiogenesis via Akt and Notch-1 pathways, not via MAPK pathways[J]. Int J Oncol, 2016, 48(1): 281-292. DOI:10.3892/ijo.2015.3257 |
| [50] |
Bhattacharya R, Chatterjee R, Mandal AKA, et al. Theaflavin-Containing Black Tea Extract: A Potential DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitor in Human Colon Cancer Cells and Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma-Induced Solid Tumors in Mice[J]. Nutr Cancer, 2021, 73(11-12): 2447-2459. DOI:10.1080/01635581.2020.1828943 |
 2022, Vol. 49
2022, Vol. 49