文章信息
- Sacituzumab Govitecan治疗晚期HER2阴性乳腺癌的疗效及安全性Meta分析
- Efficacy and Safety of Sacituzumab Govitecan on Advanced HER2-negative Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2022, 49(4): 328-334
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2022, 49(4): 328-334
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2022.21.0757
- 收稿日期: 2021-06-30
- 修回日期: 2021-12-09
乳腺癌是全球女性最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,目前乳腺癌的5年生存率已高达90%,但转移性乳腺癌仍然无法治愈。其中晚期三阴性乳腺癌(triple-negative breast cancer, TNBC)与HR(hormone receptor)阳性/人表皮生长因子受体-2(human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, HER2)阴性乳腺癌的5年生存率均低于30%[1-2],多线治疗后其对化疗反应低,无进展生存期短,缺乏有效的药物[3]。Sacituzumab govitecan是一种由SN-38(伊立替康的活性代谢产物)与靶向滋养层抗原-2(Trop-2)的人源化单克隆抗体偶联组成的抗体-药物偶联物(antibody-drug conjugate, ADC)药物[4],动物实验证明,Sacituzumab govitecan在肿瘤中对SN-38的传递作用是伊立替康的300多倍[5],研究表明,其在转移性三阴性乳腺癌、结直肠癌等难治性实体瘤中表现出良好的效果[6]。该药正在国内三阴性乳腺癌上市的临床试验中,也在HR+/HER2-晚期乳腺癌(NCT03901339)[7]的Ⅲ期临床试验中。本文通过对3篇相关文献进行二次综合分析,评估Sacituzumab govitecan对晚期HER2阴性乳腺癌的疗效及安全性。
1 资料与方法 1.1 纳入与排除标准纳入标准:(1)研究类型:纳入已经完成并且发表的有关Sacituzumab govitecan对晚期乳腺癌治疗的临床试验。语言限定为:中文、英文;(2)人群:年龄≥18岁的晚期乳腺癌患者;(3)干预:试验组为单药Sacituzumab govitecan,是否设置对照组不限;若设置对照组,干预措施不限;(4)结局指标:总有效率(overall response rate, ORR)、临床获益率(clinical benefit rate, CBR)、中位无进展生存期(median progression-free survival, mPFS)、中位总生存期(median overall survival, mOS)、中位反应持续时间(median duration of response, mDOR)及其不良反应。
排除标准:(1)非乳腺癌患者或者未接受Sacituzumab govitecan治疗;(2)个案、综述、报告、会议摘要等文献;(3)文献中的试验设计为细胞实验或动物实验;(4)重复发表或实验数据不全。
1.2 检索策略计算机检索Embase、Web of Science、PubMed数据库中已发布的Sacituzumab govitecan试验。通过计算机检测及手工检索,使用Google学术、百度文库等网站查找相关文献及全文。研究者手工提取数据。检索时限:数据库建库至2021年5月1日。通过主题词和自由词形结合的方式检索。检索词:breast cancer、breast neoplasms、Sacituzumab govitecan、IMMU-132和Trodelvy。
1.3 文献筛选由两位研究员独立阅读、筛选文献,自制表格提取资料,并交叉核对,如遇分歧,可通过协商或听取第三方研究员意见。
1.4 文献资料提取及质量评价所提取资料包括文献标题、第一作者姓名、发表时间、参与者数量、入组患者年龄、病理组织类型、分组、治疗线数目、试验组与对照组治疗方案、疗效指标(ORR、CBR、mPFS、mOS、mDOR)及安全性指标(不良事件的类型、级别及例数)。如遇分歧,可通过协商或听取第三方研究员意见。
因本研究进行Meta分析的3篇研究,其中2篇为非随机对照研究,缺乏对照组,故采用部分MINORS[8]评价工具行文献质量评估。评价指标共12条,每条分为0~2分,0分表示未报道,1分表示有报道但信息不充分,2分表示有报道且信息充分。评价指标具体为:研究目的是否明确、纳入患者的连贯性、预期数据的收集、终点指标是否能恰当地反映研究目的、终点指标评价客观、随访时间是否充分、失访率低于5%、是否估算了样本量、对照组的选择是否恰当、对照组是否同步、组间基线是否可比以及统计分析是否恰当。其中随访时间≥3月被认为随访充分。
1.5 统计学方法采用单个率的Meta分析进行各研究间发生率的合并计算。在Stata软件中r为事件发生率(如ORR、CBR、不良事件发生率等指标),n为样本量,在command窗口输入命令,计算各样本率的标准误(ser为率的标准误):generate ser=sqtr(r*(1-r)/n),进行Meta分析。采用风险比(HR)及95%CI做为合并的生存资料(mPFS、mOS、mDOR)的效率量,采用比值比(OR)及95%CI作为合并的事件发生率(如ORR、CBR、不良事件发生率等指标)的效应量。应用I2检验对各研究结果进行异质性检验,若P≥0.1,I2≤50%,说明各研究间异质性较小,采用固定效应模型进行Meta分析。若P < 0.1,I2 > 50%,说明各研究间异质性较大,采用随机效应模型减少异质性对结果的影响。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。统计检验均采用双侧检验。
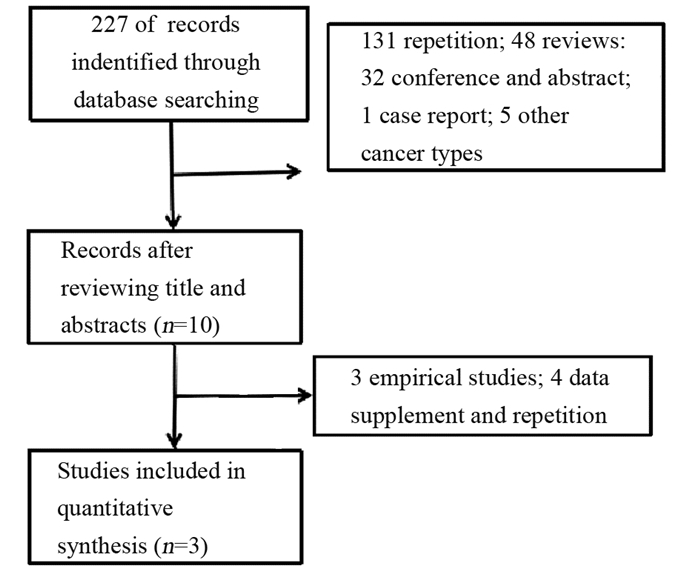
2 结果 2.1 检索过程文件检索结果初检出227篇。采用EndNote软件剔除重复文献,通过阅读摘要和全文排除不符合的文献,最终检索到随机对照试验1篇,队列研究2篇。文献筛选流程及结果见图 1。
|
| 图 1 文献筛选流程图 Figure 1 Flow diagram of literature search and selection |
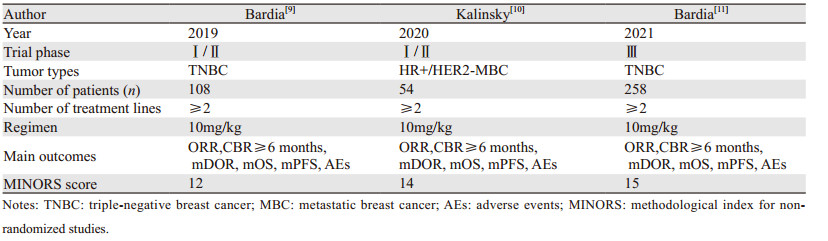
本研究纳入文献共3篇,发表于2019至2021年间,共420例HER2阴性晚期乳腺癌患者纳入分析,接收的药物剂量均为10 mg/kg,纳入研究的基本特征见表 1。
3篇文献均符合要求,总样本量为420例。其中经Sacituzumab govitecan治疗后的有效例数为143例(P=0.874, I2=0),各研究中无明显异质性,采用固定效应模型,所有文献加权合并后得到缓解率为34.0%,95%CI: 29.4%~38.6%,见图 2A。获得CBR的例数为217例(P=0.994, I2=0),各研究中无明显异质性,采用固定效应模型,所有文献加权合并后CBR为45.0%,95%CI: 40.2%~49.8%,见图 2B。纳入研究的乳腺癌患者对Sacituzumab govitecan治疗的mDOR、mPFS和mOS均无异质性(P=0.498, I2=0; P=0.996, I2=0; P=0.696, I2=0),均可采用固定效应模型进行定量合成,结果分别为:HRmDOR=7.394, 95%CI: 6.231~8.773; HRmPFS=5.589, 95%CI: 4.953~6.308; HRmOS=12.59, 95%CI: 11.58~13.68,见图 2C~E。

|
| A: ORR; B: CRB; C: mDOR; D: mPFS; E: mOS. 图 2 Sacituzumab govitecan对乳腺癌患者疗效的Meta分析 Figure 2 Meta-analysis of effect of Sacituzumab govitecan on patients with breast cancer |
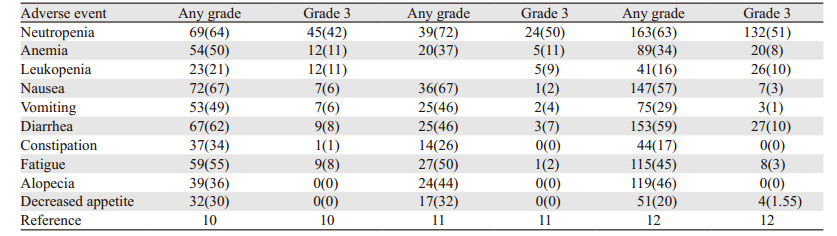
从中性粒细胞减少、贫血、白细胞减少、恶心、呕吐、腹泻、便秘、乏力、脱发、食欲下降等10个方面分析接受Sacituzumab govitecan治疗患者的不良反应发生率,结果见表 2。
|
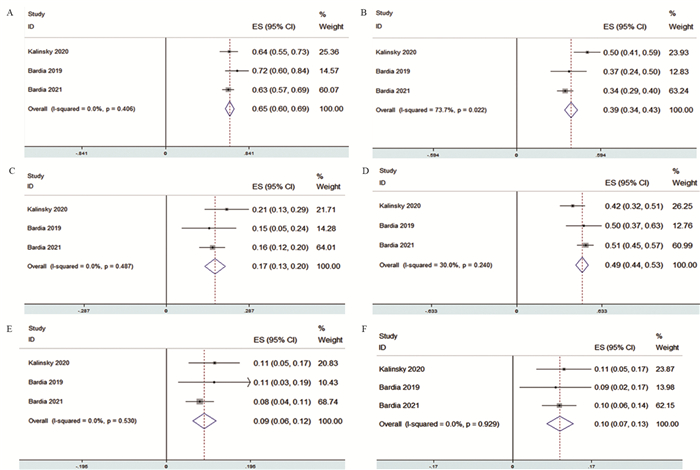
为评估Sacituzumab govitecan的安全性,本研究分析了三种最常见的血液学毒性,包括贫血、白细胞减少及中性粒细胞减少。接受Sacituzumab govitecan治疗患者的全级血液学毒性中,发生中性粒细胞减少的风险最高,发生率为65%(OR=0.65, 95%CI: 0.60~0.69)、贫血的发生率为39%(OR=0.39,95%CI: 0.34~0.43)、白细胞减少的发生率为17%(OR=0.17, 95%CI: 0.13~0.20),见图 3A~C。而三级以上的血液学毒性中,出现中性粒细胞减少的风险最高,其发生率为49%(OR=0.49, 95%CI: 0.44~0.53),贫血的发生率为9%(OR=0.09, 95%CI: 0.06~0.12),白细胞减少的发生率为10%(OR=0.10, 95%CI: 0.07~0.13),见图 3D~F。
|
| A: the incidence of neutropenia; B: the incidence of anemia; C: the incidence of leukopenia; D: the incidence of high-grade neutropenia; E: the incidence of high-grade anemia; F: the incidence of high-grade leukopenia. 图 3 Sacituzumab govitecan对乳腺癌患者血液学毒性的Meta分析 Figure 3 Meta analysis of haematological adverse events of Sacituzumab govitecan on patients with breast cancer |
接受Sacituzumab govitecan治疗患者的全级消化道反应中发生恶心的风险最高,其发生率为61%(OR=0.61, 95%CI: 0.56~0.66),呕吐的发生率为36%(OR=0.36, 95%CI: 0.31~0.40),腹泻的发生率为58%(OR=0.58, 95%CI: 0.54~0.63),便秘的发生率为21%(OR=0.21, 95%CI: 0.17~0.25),见图 4A~D。三级以上的消化道反应中,发生腹泻的风险最高,其发生率为9%(OR=0.09, 95%CI: 0.07~0.12),恶心的发生率为3%(OR=0.03, 95%CI: 0.01~0.05),呕吐的发生率为2%(OR=0.02, 95%CI: 0.00~0.03),见图 4E~G。在Bardia等[9, 11]的研究中,三级以上便秘的发生率为0。

|
| A: the incidence of nausea; B: the incidence of vomiting; C: the incidence of diarrhea; D: the incidence of constipation; E: the incidence of high-grade nausea; F: the incidence of high-grade vomiting; G: the incidence of high-grade diarrhea. 图 4 Sacituzumab govitecan对乳腺癌患者消化道反应的Meta分析 Figure 4 Meta analysis of gastrointestinal adverse events of Sacituzumab govitecan on patients with breast cancer |
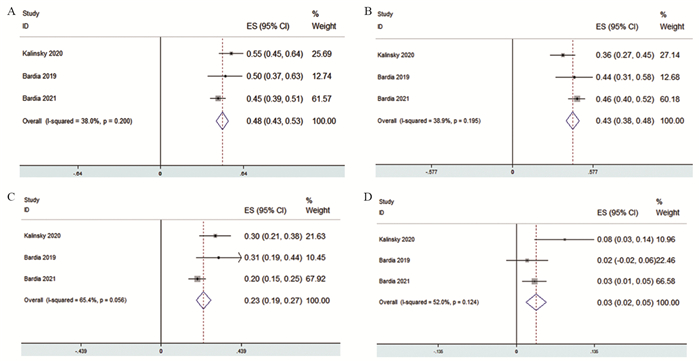
接受Sacituzumab govitecan治疗的患者最常见的不良反应为乏力,其发生率为48%(OR=0.48, 95%CI: 0.43~0.53),脱发的发生率为43%(OR=0.43, 95%CI: 0.38~0.43),食欲下降的发生率为23%(OR=0.23, 95%CI: 0.19~0.27),见图 5A~C。其中乏力出现三级以上不良反应率最高的发生率为3%(OR=0.03, 95%CI: 0.02~0.05),三级以上食欲减退的发生率均为0,见图 5D。Bardia[9]和Kalinsky[10]研究中脱发的发生率为0。
|
| A: the incidence of fatigue; B: the incidence of alopecia; C: the incidence of decreased appetite; D: the incidence of high-grade fatigue. 图 5 Sacituzumab govitecan对乳腺癌患者的其他毒性分析 Figure 5 Other adverse events of Sacituzumab govitecan on patients with breast cancer |
HR阳性乳腺癌是全球乳腺癌中最常见的亚型,预后相对较好,但仍有30%~40%患者出现内分泌耐药。研究表明,HR阳性/HER2阴性乳腺癌二线化疗的PFS为4.0~6.3月,三线化疗的PFS为2.4~5.5月[12]。HER2阳性乳腺癌曾一度以进展快、预后差著称,随着抗HER2靶向药物的革新和诊疗策略的发展,为HER2阳性乳腺癌患者带来了极大的生存获益。目前尚未发现Trop-2在HER2阳性乳腺癌中高表达,无Sacituzumab govitecan针对HER2阳性乳腺癌疗效的数据。三阴性乳腺癌由于侵袭性高、转移性强,缺乏有效的治疗靶点,对化疗反应率低,敏感度低。过去20年研究表明,常规化疗并不能使一线化疗后进展的三阴性乳腺癌患者生存获益[13]。靶向滋养层抗原-2(Trop-2)在结直肠癌、HR阳性乳腺癌等多种上皮细胞肿瘤中高表达,其表达强度与肿瘤的侵袭生长、不良预后相关[14]。Trop-2在90%以上的三阴性乳腺癌中高表达,被认为是探索三阴性乳腺癌抗肿瘤治疗中的重要靶点[15]。
Sacituzumab govitecan基于其对二线以上三阴性乳腺癌的客观缓解率达33.0%,中位缓解持续时间达7.7月,获得了FDA的加速获批,并写入中国抗癌协会晚期乳腺癌诊疗规范的用药推荐[16]。迄今入组患者例数最多的ASCENT[17]研究显示,Sacituzumab govitecan单药对比单药化疗(艾日布林、长春瑞滨、吉西他滨或卡培他滨)治疗TNBC晚期乳腺癌患者ORR更高(35% vs. 5%),mPFS(6.5 vs. 1.7月)、mOS(12.1 vs. 6.7月)显著获益。本研究结果与ASCENT研究相关数据一致,在无进展生存和总生存方面显现了突出的优势。对既往接受过多线治疗TNBC或HR阳性/HER2阴性的乳腺癌患者,Sacituzumab govitecan可带来显著临床获益,或可填补在三阴性乳腺癌进展后尚无标准治疗方案的空白。
安全性方面,通过具体事件的分析可知,Sacituzumab govitecan最常见的不良反应包括白细胞减低、中性粒细胞减少、贫血、恶心、呕吐、腹泻、食欲减退、乏力等。在Trodeloy的说明书中警示了本品可能引起严重的中性粒细胞减少和腹泻。本研究结果显示:中性粒细胞减少的任何级别不良反应的发生率和≥3级不良反应发生率分别为65%和49%,腹泻的任何级别不良反应的发生率和≥3级不良反应发生率分别为59%和9%。多数老年TNBC患者体能状态差,合并症多,承受力差,常常因不能耐受药物的不良反应而停药。ASCENT研究显示,接受Sacituzumab govitecan治疗的患者发生3级以上的主要不良反应为中性粒细胞减少和腹泻等,这些反应大部分可以在辅助用药、护理措施的支持下得到控制,其因AE导致的停药率约为5%,未观察到该药所致的相关死亡事件,说明Sacituzumab govitecan总体安全可控。ASCENT老年TNBC患者的亚组分析显示[17],治疗年龄 > 65岁的患者与 < 65岁患者的安全性相似,两组因AE导致的停药率均为2%左右,可作为已往治疗受限的老年TNBC患者治疗的新选择,但是当确定或疑似发生严重不良反应后应及时停药。SN-38作为Sacituzumab govitecan的偶联物,主要经UGT1A1代谢而失活。在编码UGT1A1基因突变的人群中更易出现SN-38的蓄积,这与SN-38的不良反应密切相关。Bardia等[18]研究对其3级以上不良事件的发生率进行分析,结果显示UGT1A1*28突变纯合子发生严重腹泻的比例与对照组无明显差异,而发生严重中性粒细胞减少的频率更高。
此研究存在一定局限性:(1)目前报道的关于Sacituzumab govitecan在乳腺癌中治疗的临床试验数量较少,且多数为单臂试验,证据质量相对不足。目前关于该研究的临床试验正在不断进行中,需要更多随机对照研究,以进一步评估Sacituzumab govitecan的疗效及安全性;(2)虽然Shen等[19]研究对三阴性乳腺癌Trop-2的表达水平进行分组,发现Trop-2中高表达组患者的生存获益高。但是目前各临床试验中对于Trop2表达高低的判定方法并不统一。受试验数据可用性等限制,疗效方面本文未对乳腺癌患者Trop-2的表达水平与疗效的相关性进行分析。
Sacituzumab govitecan治疗晚期乳腺癌的疗效良好,不良反应发生率较高,在积极有效的安全管控下,大部分患者可耐受。考虑本研究的局限性,期待更多临床研究进一步证实Sacituzumab govitecan的疗效以及合适的不良反应管理方法以指导临床应用。
作者贡献:
张倩:文献检索、筛选,数据分析和文章撰写
李娜:文献检索、筛选和文章撰写
杨华:研究设计、文章修改
| [1] |
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. DOI:10.3322/caac.21660 |
| [2] |
Harb WA. Management of patients with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer with visceral disease: challenges and treatment options[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2015, 7: 37-46. |
| [3] |
BrufskyA, Valero V, Tiangco B, et al. Second-line bevacizumab-containing therapy in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: subgroup analysis of the RIBBON-2trial[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2012, 133(3): 1067-1075. DOI:10.1007/s10549-012-2008-6 |
| [4] |
Goldenberg DM, Sharkey RM. Sacituzumab govitecan, a novel, third-generation, antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) for cancer therapy[J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2020, 20(8): 871-885. DOI:10.1080/14712598.2020.1757067 |
| [5] |
Sharkey RM, Govindan SV, Cardillo TM, et al. Selective and Concentrated Accretion of SN-38 with a CEACAM5-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC), Labetuzumab Govitecan (IMMU-130)[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2018, 17(1): 196-203. DOI:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0442 |
| [6] |
Starodub AN, Ocean AJ, Shah MA, et al. First-in-Human Trial of a Novel Anti-Trop-2 Antibody-SN-38 Conjugate, Sacituzumab Govitecan, for the Treatment of Diverse Metastatic Solid Tumors[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2015, 21(17): 3870-3878. DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-3321 |
| [7] |
Rugo HS, Bardia A, Tolaney SM, et al. TROPiCS-02: A Phase Ⅲ study investigating Sacituzumab govitecan in the treatment of HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer[J]. Future Oncol, 2020, 16(12): 705-715. DOI:10.2217/fon-2020-0163 |
| [8] |
Dent O. Methodological index for non-randomized studies[J]. ANZJ Surg, 2003, 73(9): 675-676. DOI:10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02762.x |
| [9] |
Bardia A, Mayer IA, Vahdat LT, et al. Sacituzumab Govitecan-hziy in Refractory Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380(8): 741-751. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa1814213 |
| [10] |
Kalinsky K, Diamond JR, Vahdat LT, et al. Sacituzumab govitecan in previously treated hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer: final results from a phase Ⅰ/Ⅱ, single-arm, basket trial[J]. Ann Oncol, 2020, 31(12): 1709-1718. DOI:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.09.004 |
| [11] |
Bardia A, Hurvitz SA, Tolaney SM, et al. Sacituzumab Govitecan in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(16): 1529-1541. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa2028485 |
| [12] |
Park IH, Lee KS, Ro J. Effects of second and subsequent lines of chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer[J]. Clin Breast Cancer, 2015, 15(1): e55-e62. DOI:10.1016/j.clbc.2014.09.001 |
| [13] |
Zeichner SB, Terawaki H, Gogineni K. A review of systemic treatment in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer (Auckl), 2016, 10: 25-36. |
| [14] |
Shvartsur A, Bonavida B. Trop2 and its overexpression in cancers: regulation and clinical/therapeutic implications[J]. Genes Cancer, 2015, 6(3-4): 84-105. |
| [15] |
Vidula N, Yau C, Rugo HS. Trop2 gene expression (Trop2e) in primary breast cancer (BC): Correlations with clinical and tumor characteristics[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2017, 35(15_suppl): 1075. DOI:10.1200/JCO.2017.35.15_suppl.1075 |
| [16] |
国家肿瘤质控中心乳腺癌专家委员会, 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌专业委员会, 中国抗癌协会肿瘤药物临床研究专业委员会. 中国晚期乳腺癌规范诊疗指南(2020版)[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2020, 42(10): 781-797. [National Cancer Quality Control Center Breast Cancer Expert Committee, China Cancer Association Breast Cancer Specialized Committee, China Cancer Association Clinical Research of Cancer Medicine Specialized Committee. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment of advanced breast cancer in China (2020 Edition)[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2020, 42(10): 781-797. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200817-00747] |
| [17] |
Kalinsky K, Oliveira M, Traina TA, et al. Outcomes in patients (pts) aged≥65 years in the phase 3 ASCENT study of sacituzumab govitecan (SG) in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2021, 39(15 suppl): 1011. |
| [18] |
Bardia A, Messersmith WA, Kio EA, et al. Sacituzumab govitecan, a Trop-2-directed antibody-drug conjugate, for patients with epithelial cancer: final safety and efficacy results from the phase Ⅰ/Ⅱ IMMU-132-01 basket trial[J]. Ann Oncol, 2021, 32(6): 746-756. DOI:10.1016/j.annonc.2021.03.005 |
| [19] |
Shen M, Liu S, Stoyanova T. The role of Trop2 in prostate cancer: an oncogene, biomarker, and therapeutic target[J]. Am J Clin Exp Urol, 2021, 9(1): 73-87. |
 2022, Vol. 49
2022, Vol. 49